Solving AP 10th Class Physical Science Model Papers Set 7 regularly is an effective strategy for time management during exams.
AP SSC Physical Science Model Paper Set 7 with Solutions
Time: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 50
Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 4 sections and 17 questions.
- Internal choice is available only for Q.No.12 in section III and all the questions in section IV.
- In 2 hours, 15 minutes is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the answer booklet only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
Section-I
(8 × 1 = 8 Marks)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
| Case | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 30°C | 50°C | -273K | 27°C |
| B | 30K | 30°C | 0°C | 300K |
In which case A and B are in thermal equilibrium?
Answer:
Case – 4
Question 2.
The net angle of deviation produced by the glass slab is _________
Answer:
Zero
Question 3.
‘The physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their electronic configurations’. Which law does the above statement represent?
Answer:
Modern Periodic Law
![]()
Question 4.
Choose the suitable answers for Section B with Section A.
| Section-A | Section-B |
| 1. The values of the principal quantum number | (P) 0 to n – 1 |
| 2. The values of magnetic quantum number | (Q) 1, 2, 3,….. |
| (R) +1/2, -1/2 | |
| (S) -l to +l |
Answer:
1 – Q; 2 – S
Question 5.
Which electric device converts electric energy into mechanical energy?
Answer:
Electric Motor
Question 6.
With the information given, answer the question.
Alkane participates in substitution reactions.
CH4 + Cl2 → X + HCl
In which presence, the above reaction takes place?
Answer:
In the presence of sunlight
Question 7.
On some bottles in the laboratory, we observe the label shown in the diagram. What does that bottle contain?

Answer:
Concentrated Acid (or) Concentrated Base
Question 8.
What do you conclude from the given diagram?

Answer:
The focal length depends on the surrounding medium.
Section-II
(3 × 2 = 6 Marks)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 9.
Write any two questions about the ‘Formation of Mirages’.
Answer:
- How do the mirages form?
- What is the science behind the formation of mirages’?
- In what situations do mirages form?
![]()
Question 10.
Pose any two questions to understand the difference between valency and valency electrons.
Answer:
- What is valency?
- How many valency electrons are there in a chlorine atom?
Question 11.
Give the names of the functional groups.
- -COOR
- -OH
Answer:
- Ester
- Alcohol
Section-III
(3 × 4 = 12 Marks)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 12.
Draw any one of the following diagrams.
(A) An eye specialist suggested a +2D lens to the person with a defect in vision. What kind of defect in vision does he have? Draw the diagrams to show the defect of vision and its correction with a suitable lens.
(B) Draw a neat diagram showing how the acid solution in water conducts electricity.
Answer:
(A) Eye specialist suggested a +2D lens, which is a convex lens. Convex lens is used to correct hypermetropia. So the person has hypermetropia.
Defect of Vision:
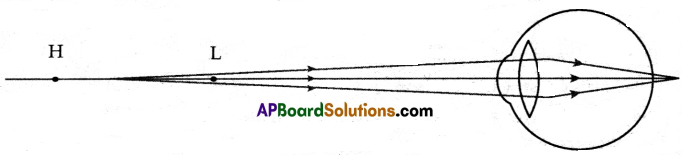
Correction:

(B)
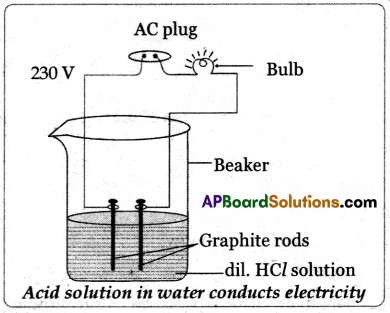
Question 13.
The arrangement of electrons in different shells of atoms of 18th group elements is given in the table.
| Element | Z | Electronic Configuration | |||
| K | L | M | N | ||
| Helium (He) | 2 | 2 | |||
| Neon (Ne) | 10 | 2 | 8 | ||
| Argon (Ar) | 18 | 2 | 8 | 8 | |
| Krypton (Kr) | 36 | 2 | 8 | 18 | 8 |
Answer the following:
(i) What is the general electronic configuration of the above elements except He?
(ii) What is the valency of Argon?
(iii) Write the Lewis dot structure of Neon.
(iv) Why do the above elements not take part in bond formation?
Answer:
(i) ns2 np6
(ii) Zero
(iii) ![]()
(iv) They are stable as they have 8 electrons (Except Helium) in their outermost orbit.
![]()
Question 14.
How do you appreciate the role of the higher specific heat of the water in stabilizing atmospheric temperature during winter and summer seasons?
Answer:
- The sun sends a lot of heat energy to the earth daily.
- If there is no water on Earth, all this heat is received by the atmosphere of Earth.
- Due to this, the temperature of the earth increases.
- But it is not happening.
- Here we have to appreciate the role of water present enormously on earth in oceans.
- All the heat energy sent by the sun is received by water (storehouse).
- The specific heat of water is high.
- Instead of the atmosphere, the water receives this heat.
- In this manner, the atmospheric temperature is stabilized.
Section-IV
(3 × 8 = 24 Marks)
Notes:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 8 marks.
- Each question has an internal choice.
Question 15.
(A) What are the postulates of valence bond theory?
(OR)
(B) Distinguish between esterification and saponification reactions of organic compounds.
Answer:
(A) Postulates of VBT:
- A covalent bond is formed between two atoms when they approach each other having unpaired opposite electron spins in their valence orbitals.
- The greater the overlapping of the orbitals, the stronger will be the bond. This gives the directional character to the bond.
- Electrons remain in their atomic orbitals only but the electrons pair in the overlapping orbitals are shared by both the atoms involved in the overlapping.
- The direct overlapping of atomic orbitals results sigma bond, and lateral overlaps result in a pi bond.
- Without the formation of a sigma bond, the pi bond does not exist. It means the sigma bond is independent and the pi-bond is dependent.
(OR)
| Esterification | Saponification |
| 1. The formation of the ester is known as the esterification reaction. | 1. The formation of soap is known as the saponification reaction. |
| 2. Alcohol reacts with carboxylic acids to produce esters. | 2. Higher fatty acids react with bases to form soaps. |
| 3. Water is a byproduct of esterification reaction. Eg: Ethyl Acetate (CH3COOC2H5) |
3. Glycerol is the byproduct of the saponification reaction. Eg: Sodium Sterate (C17H35COONa) |
4.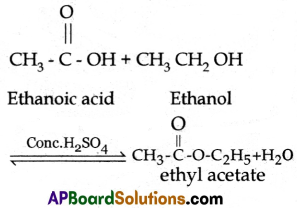 |
4.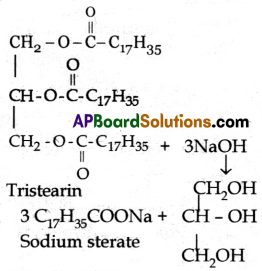 |
| 5. This reaction is an example of a dehydration reaction. | 5. This reaction is an example of hydrolysis. |
| 6. This reaction is slow and reversible. | 6. This reaction is irreversible. |
| 7. This process is used for the preparation of different esters. | 7. This is used for the preparation of soaps. |
Question 16.
(A) Write short notes on the froth floatation process.
(OR)
(B) Explain Kirchhoff’s laws with examples.
Answer:
(A) Froth Floatation Process:
(i) This method is mainly useful for sulfide ores which have no wetting property whereas the impurities get wetted.
(ii) The ore with impurities is finely powdered and kept in water, containing pine oil taken in a floatation cell.
(iii) Air under pressure is blown to produce froth in water.
(iv) Froth so produced, takes the ore particles to the surface, whereas impurities settle at the bottom.
(v) Froth is separated and washed to get ore particles.
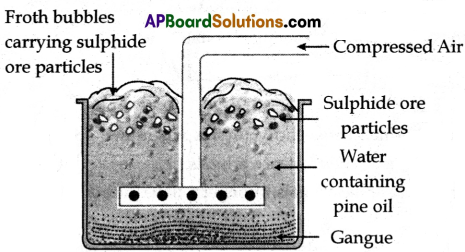
Froth floatation process for the concentration of sulphide ores.
(OR)
(B) (i) The rules that apply to any DC circuit containing batteries and resistors connected in any way are called Kirchhoff’s laws.
(i) These laws are two types:
- Junction law
- Loop law
(a) Junction Law: At any junction point in a circuit where the current can divide, the sum of the currents into the junction must be equal to the sum of the currents leaving the junction.
Example:
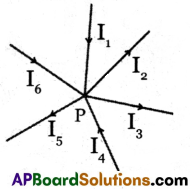
- In the above figure ‘P’ is called a junction, where three or more conducting wires meet.
- At any junction point in a circuit where the current can divide, the sum of the currents into the junction must be equal to the sum of the currents leaving the junction.
- This means that there is no accumulation of electric charges at any junction in a circuit. We have, I1 + I4 + I6 = I5 + I2 + I3
(b) Loop Law: The algebraic sum of the increases and decreases in potential difference across various components of the circuit in a closed circuit loop must be zero.
Example:
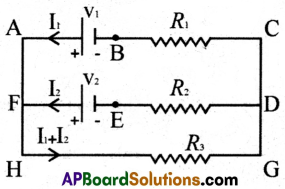
I – From the ABCDEFA loop
Potential difference at batteries = -V1 + V2
Potential difference at resistance = +I1R1 – I2R2
The resultant Potential difference in the loop is -V1 + V2 + I1R1 – I2R2 = 0
II – From the AFEDCBA loop
Potential difference at batteries = -V2 + V1
Potential difference at resistance = +I2R2 – I1R1
The resultant Potential difference in the loop is -V2 + V1 + I2R2 – I1R1 = 0
III – From the FEDGHF loop
Potential difference at batteries = -V2
Potential difference at resistances = +I2R2 + (I1 + I2) × R3
The resultant Potential difference in the loop is -V2 + I2R2 + (I1 + I2) × R3 = 0
![]()
Question 17.
(A) Explain Faraday’s law of induction with the help of an activity.
(OR)
(B) Write an activity to show that the focal length of a lens depends on its surrounding medium.
Answer:
(A) Apparatus: Galvanometer, Coil, Bar magnet.
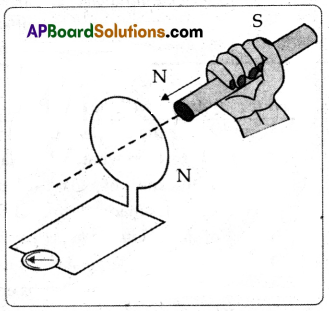
Procedure:
- Connect the terminals of a coil to a sensitive galvanometer as shown in the figure.
- Normally, we would not expect any needle deflection in the galvanometer because there is no EMF in the circuit.
- Now, if we push a bar magnet towards the coil, with its north pole facing the coil, the needle in the galvanometer deflects, showing that a current has been set up in the coil, the galvanometer does not deflect if the magnet is at rest.
- If the magnet is moved away from the coil, the needle in the galvanometer again deflects, but in the opposite direction, which means that a current is set up in the coil in the opposite direction.
- If we use the end of the south pole of a magnet instead of the north pole, the result i.e., the deflections in the galvanometer are exactly opposite to the previous one.
- This activity proves that the changes in magnetic flux linked with a closed coil, produce current.
Conclusion:
From this Faraday’s law of induction can be stated as “Whenever there is a continuous change of magnetic flux linked with a closed coil, a current is generated in the coil. This induced emf is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux passing through it.”
(OR)
(B) Aim: To verify experimentally that the focal length of a lens depends on its surrounding medium.
Apparatus: Convex lens of known focal length, circular lens holder, tall cylindrical glass tumbler, black stone, water.
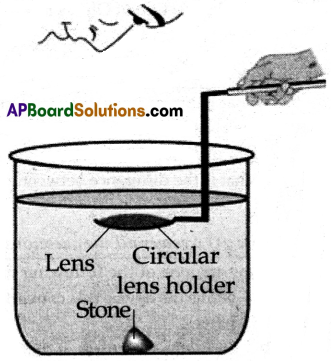
Procedure:
- Take a cylindrical glass tumbler whose height is much greater than the focal length of the lens and fill it with water, such that the height of the water level from the top of the stone is greater than the focal length of the lens.
- Keep a black stone at the bottom of the vessel.
- Now dip the lens into the water using a circular lens holder such that it is at a distance that is less than or equal to the focal length of the lens in the air.