Regularly solving AP 10th Class Maths Model Papers Set 7 contributes to the development of problem-solving skills.
AP SSC Maths Model Paper Set 7 with Solutions
Instructions :
- In the duration of 3 hours 15 minutes, 15 minutes of time is allotted to read the question paper.
- All answers shall be written in the answer booklet only.
- Question paper consists of 4 Sections and 33 questions.
- Internal choice is available in section – IV only.
- Answers shall be written neatly and legibly.
Section – I
(12 × 1 = 12M)
Note:
- Answer all the questions in one word or phrase.
- Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 1.
What does the shaded region show?
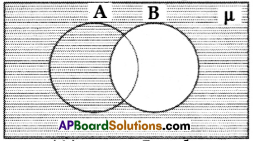
Solution:
µ – B
Question 2.
Statement (A) : Let age of Mary and his daughter be ‘x’ and ‘y’ years and Mary told her daughter “Seven years ago I was seven times as old as you were” then linear equation form is x – 7y + 42 = 0.
Statement (B): The solutions of 2x – y = 5 and 3x + 2y = 11 is x = 3 and y = -1.
Which of the above statements are true?
i) Both A and B are true
ii) A is true, B is false
iii) A is false, B is true
iv) Both A and B are false
Solution:
(ii) A is true, B is false
![]()
Question 3.
If the less than type Ogive and more than type Ogive intersect each other at (42, 18), then the median of the given data is
A) 60
B) 42
C) 18
D) 26
Solution:
B) 42
Question 4.
Find the number of zeros of the polynomial from the adjacent graph.
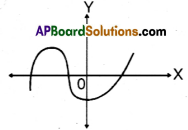
Solution:
Three zeroes.
Question 5.
Find the LCM and HCF of 12 and 18 by the prime factorization method.
Solution:
We have 12 = 2 × 2 × 3 = 22 × 31
18 = 2 × 3 × 3 = 21 × 32
HCF (12, 18) = 21 × 31 = 6
LCM (12, 18) = 22 × 32 = 36
Question 6.
If n(A) = 8, n(B) = 3, n(A∩B) = 2 then find n(A∪B).
Solution:
n (A) = 8, n (B) = 3, n (A∩B) = 2,
n (A ∪ B) = ?
n(A∪B) = n (A) + n (B) – n(A∩B) = 8 + 3 – 2
= 9
Question 7.
Evaluate \(\frac{\tan 36^{\circ}}{\cot 54^{\circ}}\).
Solution:
We have tan(90° – θ) = cotθ
tan 36° ⇒ tan (90° – 54°) = cot 54°
⇒ \(\frac{\tan 36^{\circ}}{\cot 54^{\circ}}\) = \(\frac{\cot 54^{\circ}}{\cot 54^{\circ}}\) = 1
Question 8.
Find the distance between (0, 0) and (a sinθ, a cosθ)
Solution:
Distance = \(\sqrt{a^2 \sin ^2 \theta+a^2 \cos ^2 \theta}\) = \(\sqrt{a^2 \times 1}\) = a
Question 9.
If the length of a shadow of a pole is equal to the length of the pole then find the angle of elevation.
Solution:
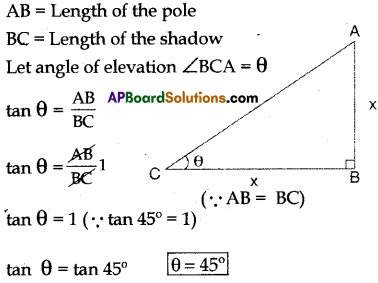
Question 10.
Which of the following situations have equally likely events ?
i) Getting 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 when a dice is rolled
ii) Winning or loosing a game
iii) Head or tail when a coin is tossed
A) i or ii
B) ii and iii
C) i and iii
D) i and ii and iii
Solution:
D) i and ii and iii
![]()
Question 11.
Write the equation with roots \(\frac{1}{\alpha}\) and \(\frac{1}{\beta}\) ?
Solution:
cx2 + bx + a = 0
Question 12.
If the ratio of the corresponding altitudes of two similar triangles is \(\sqrt{3}\) : 2 then what is the ratio of their areas ?
Solution:
\((\sqrt{3})^2\) : (2)2 = 3 : 4
Section – II
(8 × 2 = 16 M)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 13.
Find the value of log5\(\sqrt{625}\).
Solution:
log5 \(\sqrt{625}\) = log5 25
= log552
= 2log55
= 2 × 1 = 2
Question 14.
Is it right to say that sin (A + B) = sin A + sin B ? Justify your answer.
Solution:
No, sin (A + B) ≠ sin A + sin B.
For example, take A = 30°, B = 60°
sin (30° + 60°) = sin 90° = 1
sin 30° + sin 60°
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\)
Thus, sin (30° + 60°) ≠ sin 30° + sin 60°.
Question 15.
Find the value of’ k’ for which the pair of equations 2x – ky + 3 = 0, 4x + 6y – 5 = 0 represent parallel lines.
Solution:
Given pair of equations
2x – ky + 3 = 0 and 4x + 6y – 5 = 0
a1 = 2; b1 = -k ; c1 = 3 ;
a2 = 4 ; b2 = 6 ; c2 = -5
Given the pair of lines are parallel
∴ \(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) = \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) ≠ \(\)
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) = \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) ⇒ \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{-\mathrm{k}}{6}\)
⇒ -4k = 2 × 6 ⇒ -4k = 12 ⇒ k = \(\frac{12}{-4}\) = -3
Question 16.
Find the 20th term from the end of the AP : 3, 8, 13,…., 253.
Solution:
Given AP : 3, 8, 13, …., 253
Required 20th term from the end of this AP. is
∴ a = 253 ; d = -5
a20 = a + (20 – 1)d
= 253 + 19(-5)
= 253 – 95
= 158
∴ The 20th term from the end of this AP is 158.
Question 17.
A wire attached to vertical pole of height 18 m is 24 m long and has a stake attached to the other end. How far from the base of the pole should the stake be driven so that the wire will be taut?
Solution:
Height of the pole (BC) = 18 m
Length of the wire (AC) = 24m
Distance between the pole and stake = AB.
From the figure,
∆ABC is a right triangle
∴ By Baudhayan theorem (Pythagoras theorem)
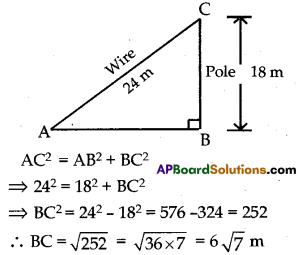
Hence the stake should be driven 6\(\sqrt{7}\) m far from the base of the pole so that the wire will be taut.
Question 18.
A box contains 3 blue and 4 red balls. What is the probability that the ball taken out randomly will be red ?
Solution:
Total number of balls = 3 + 4 = 7
Total number of possible outcomes = 7
Favourable outcomes that the ball be a red ball = 4
Probability for the ball drawn to be the red = \(\frac{4}{7}\)
Question 19.
Check whether x2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2)2 a quadratic equation.
Solution:
No, LHS x2 + 3x + 1
RHS : (x – 2)2 = x2 – 4x + 4
Therefore
x2 + 3x + 1 = x2 – 4x + 4
x2 + 3x + 1 – x2 + 4x – 4 = 0
7x – 3 = 0
It is not in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Therefore the given equation is not a quadratic equation.
Question 20.
Find the length of AB from adjacent figure.
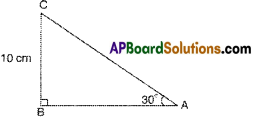
Solution:
∠ABC = 90°, ∠BAC = 30°
tan 30° = \(\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{AB}}\) AB = 10\(\sqrt{3}\) m
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{10}{\mathrm{AB}}\) Length of side AB = 10\(\sqrt{3}\) m
Section – III
(8 × 4 = 32 M)
Note:
- Answer all the questions,
- Each question carries 4 marks.
Question 21.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 – x – 30 and verify the relation between the zeroes and its co – efficients.
Solution:
Given polynomial is x2 – x = 30
To find zeroes x2 – x – 30 = 0 say
⇒ x2 – 6x + 5x – 30 = 0
⇒ (x – 6) (x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = 6 or x = – 5
Sum of the zeroes
= 6 + (- 5) = 1
= \(\frac{-(-1)}{1}\) \(=\frac{-(\text { Coefficient of } x)}{\text { Coefficient of } x^2}\)
Product of the zeroes
= 6 (- 5) = – 30
= \(\frac{-30}{1}\) \(=\frac{- \text { Constant term }}{\text { Coefficient of } x^2}\)
![]()
Question 22.
Evaluate : (1 + tanθ + secθ) (1 + cotθ – cosecθ)
Solution:
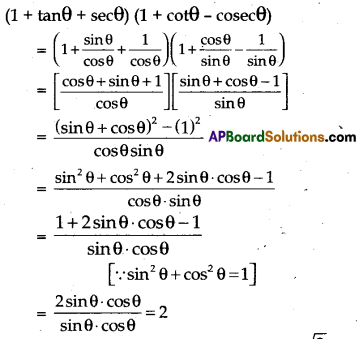
Question 23.
Show that 3\(\sqrt{2}\) is irrational.
Solution:
Let us assume, the contrary, that 3\(\sqrt{2}\) is rational.
i.e., we can find co-primes a and b (b ≠ 0) such that 3\(\sqrt{2}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{b}}\).
Rearranging, we get \(\sqrt{2}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{3 \mathrm{~b}}\)
Since 3, a and b are integers, \(\frac{a}{3 b}\) is rational, and so \(\sqrt{2}\) is irrational.
But this contradicts the fact that \(\sqrt{2}\) is irrational. So, we conclude that 3\(\sqrt{2}\) is irrational.
Question 24.
Find the roots of 5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0 by the method of completing the square.
Solution:
5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0
Given 5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0
5x2 – 7x = 6
(Dividing both sides by 5)
\(\frac{5 x^2}{5}\) – \(\frac{7 x}{5}\) = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
x2 – \(\frac{7 x}{5}\) = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
x2 – 2.x.\(\frac{7}{10}\) = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
(Adding \(\left(\frac{7}{10}\right)^2\) both sides)
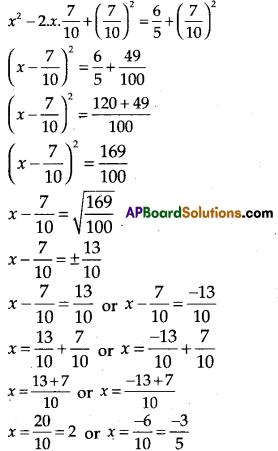
Therefore the roots of the given equation are 2 and \(\frac{-3}{5}\).
Question 25.
If the distance between two points (x, 1) and (-1, 5) is ‘5’ find the value of ‘x’.
Solution:
Distance between two points
= \(\sqrt{\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2+\left(y_1-y_2\right)^2}\)
Distance between
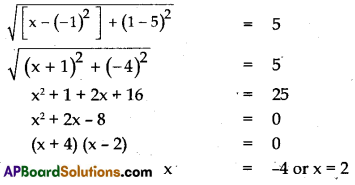
Question 26.
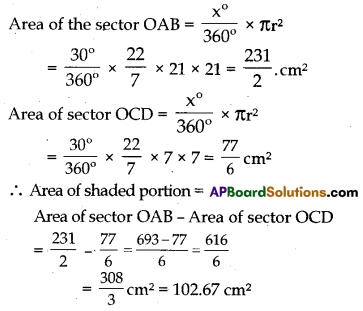
AB and CD are respectively area of two concentric circles of radii 21 cm and 7 cm. with centre O (See
figure). If ∠AOB = 30°, find the area of the shaded region. (use π = \(\frac{22}{7}\))
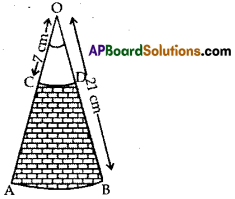
Solution:
Question 27.
Diagonals AC and BD of a trapezium ABCD with AB||DC intersect each other at the point ‘O’ using the criterion of similarity for two triangles, show that \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OC}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{OB}}{\mathrm{OD}}\).
Solution:
Given: ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC intersect at ‘O’
To prove: \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OC}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{OB}}{\mathrm{OD}}\)
proof: In ∆OAB and ∆OCD,
∠OAB = ∠OCD [Alternate interior angles]
∠OBA = ∠ODC [alternate interior angles]
∴ By AA criterion of similarity of triangles,
∆OAB ~ ∆OCD
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OC}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{OB}}{\mathrm{OD}}\)
[ratios of corresponding sides]
Hence proved.
![]()
Question 28.
A sum of ₹ 700 is to be used to give seven cash prizes to students of a school for their overall academic performance. If each prize is ₹ 20 less than its preceding prize, find the value of each of the prizes.
Solution:
Let cost of the first prize be ₹ x
∴ a = x ; d = -20
n = 7; S7 = 700
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\)[2a + (n – 1)d]
S7 = 700
\(\frac{7}{2}\)[2x + (7 – 1)(-20)] = 700
2x + 6(-20) = 700 × \(\frac{2}{7}\)
2x – 120 = 200
2x = 200 + 120
2x = 320 ⇒ ∴ x = \(\frac{320}{2}\) = 160
Cost of first prize = ₹ 160.
∴ The value of each of the 7 prizes
(in rupees) = 160, 140, 120, 100, 80, 60, 40
Section – IV
(5 × 8 = 40 M)
Note:
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries 8 marks.
- Each question has internal choice.
Question 29.
A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder with two hemispheres stuck to each of its ends. The length of the capsule is 14 mm. and the width is 5 mm. Find its surface area.
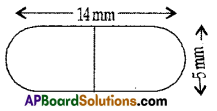
(OR)
A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm. subtends a right angle at the centre. Find the area of the corresponding: (use π = 3.14).
i) Minor segment
ii) Major segment
Solution:
Length of the cylinder = AB
= 14 mm – 2 × 2.5 mm
= 14 mm – 5 mm = 9 mm
Curved surface area of cylinder = 2π rh
= 2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 2.5 × 9 mm2
= 141.43 mm2
Curved surface area of hemisphere
= 2πr2
= 2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 2.5 × 2.5 mm2
= 39.29 mm2
∴ Total surface area of the capsule
= CSA of cylinder + 2 × CSA of hemisphere
= 141.43 + 2 × 39.29
= 141.43 + 78.58
= 220.01 mm2
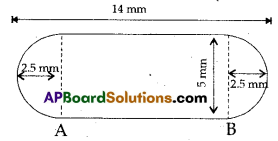
(Or)
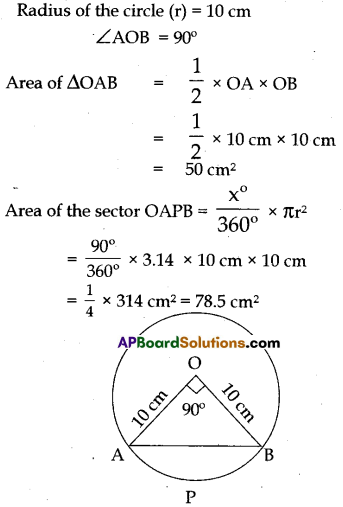
i) Area of the minor segment = Area of the sector OAPB – Area of ∆OAB
= 78.5 cm2 – 50 cm2
= 28.5 cm2
ii) Area of the circle = πr2
= 3.14 × 10 cm × 10 cm
= 314 cm2
∴ Area of the major segment = Area of the circle – Area of minor segment
= 314 cm2 – 28.5 cm2
= 285.5 cm2
Question 30.
The median of the following data is 525. Find the values of x and y, if the total frequency is 100. Here, CI stands for class interval and Fr for frequency.
| CI | Fr |
| 0-100 | 2 |
| 100 – 200 | 5 |
| 200 – 300 | X |
| 300 – 400 | 12 |
| 400 – 500 | 17 |
| 500 – 600 | 20 |
| 600-700 | y |
| 700 – 800 | 9 |
| 800 – 900 | 7 |
| 900 -1000 | 4 |
(Or)
Show that the points A (7, 3), B (6, 1), C (8, 2) and D (9, 4) taken in that order are vertices of a parallelogram.
Solution:
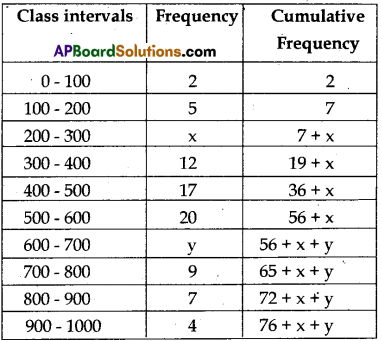
Given that, the total frequency, n = 100
U.C. ⇒ 2 + 5 + x + 12 + 17 + 20 + y + 9 + 7 + 4 = 100 ⇒ x + y = 100 – 76 = 24 → (1)
\(\frac{n}{2}\) = 50; Median 525 which is in the class 500 – 600.
So, l = 500, f = 20,
cf = 2 + 5 + x + 12 + 17 = x + 36, h = 100
So,
525 = l + \(\frac{\left(\frac{n}{2}-c f\right)}{f}\) × h ⇒ 525 = 500 + \(\left[\frac{50-(x+36)}{20}\right]\) × 100
⇒ 525 = 500 + 5 (-x + 14)
⇒ 5(-x + 14)25 ⇒ -x + 14 = 5
⇒ x = 9 → (2)
Put(2) in (1), 9 + y = 24 ⇒ y = 15
So, required values are x =9 and y = 15
(Or)
Let the points A (7, 3), B (6, 1), C (8, 2) and D (9, 4) are vertices of a parallelogram.
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
So the midpoints of the diagonals AC and DB should be equal.
Now, we find the mid points of AC and DB by using \(\left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)\) formula.
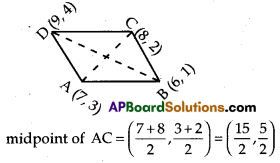
midpoint of DB = \(\left(\frac{9+6}{2}, \frac{4+1}{2}\right)\) = \(\left(\frac{15}{2}, \frac{5}{2}\right)\)
Hence, midpoint of AC midpoint of DB.
Therefore, the points A, B, C, D are vertices of a parallelogram
![]()
Question 31.
Which of the following experiments have equally likely outcomes? Explain.
i) A driver attempts to start a car. The car starts or does not start.
ii) A player attempts to shoot a basketball. She/ he shoots or misses the shot.
iii) A trial is made to answer a true-false question. The answer is right or wrong.
iv) A baby is born. It is a boy or a girl.
(OR)
Prove that (sinA + cosecA)2 + (cosA + secA)2 = 7 + tan2A + cot2A
Solution:
i) A car fails to start in rare cases. So, it doesn’t have equally likely outcomes.
ii) As, we don’t have any assurance that he shoots the shot, he may or may not shool So, it have equally likely outcomes.
iii) The answer may be right or wrong with equal chances. So, they are equally likely outcomes.
iv) A baby born may be a boy or a girl with equal chances. So, they are equally likely outcomes.
(Or)
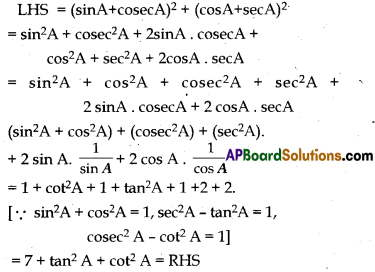
Question 32.
A wire of length 18 m had been tied with electric pole at an angle of elevation 30° with the ground. As it is covering a long distance, it was cut and tied at an angle of elevation 60° with the ground. How much length of the wire was cut ?
(OR)
Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of the triangle whose vertices are (0, -1), (2, 1) and (0, 3). Find the ratio of this area to the area of the given triangle.
Solution:
Actual length of wire PB = 18 m, length of wire used = BQ, height of pole = AB.
From the figure, In ∆ APB, we have ∠A = 90°, ∠P = 30°
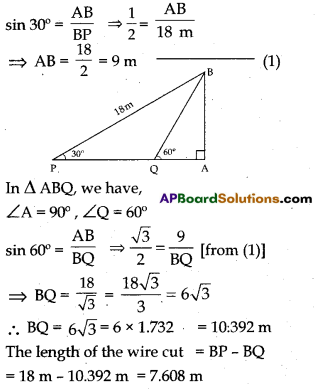
(Or)
The vertices of ∆ABC are A (0, -1), B (2, 1), C (0, 3)
Here, x1 = 0, y1 = -1, x2 = 2, y2 = 1, x3 = 0, y3 = 3
Area of ∆ABC
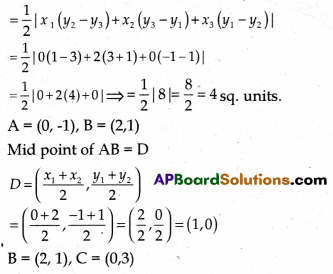
Mid point of BC = E
E = \(\left(\frac{2+0}{2}, \frac{1+3}{2}\right)\) = \(\left(\frac{2}{2}, \frac{4}{2}\right)\) = (1, 2)
C = (3, 0), A = (0, -1)
Vertices of ∆DEF = D(1, 0), E (1, 2), F(0, 1)
Here x1 = 1, y1 = 0, x2 = 1, y2 = 2, x3 = 0, y3 = 1
Area of ∆DEF
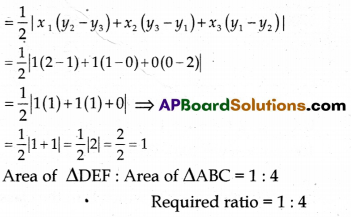
Question 33.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial p(x) = x2 + x – 20 using graph.
(OR)
Construct a triangle of sides 4 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm. Then, construct a triangle similar to it, whose sides are \(\frac{2}{3}\) of the corresponding sides of the first triangle.
Solution:
Let y = x2 + x – 20
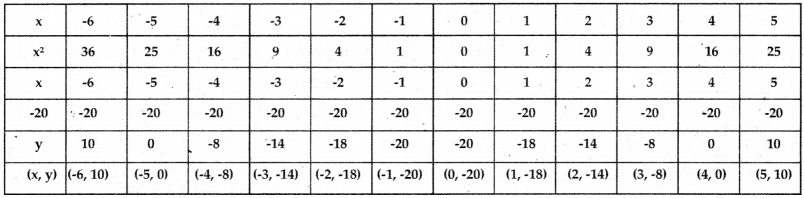
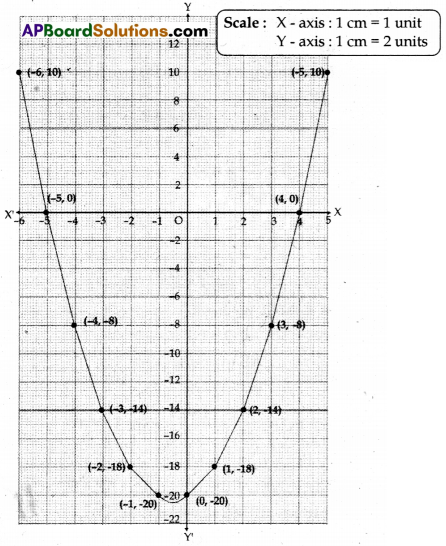
(Or)
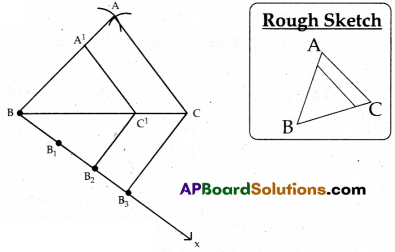
Steps of construction:
- Construct a triangle ABC with sides 4cm, 5 cm and 6cm.
- Draw a ray BX, making an acute angle with BC on the side opposite to vertex A.
- Locate 3 points B1, B2, B3 on BX so that BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3.
- Join B3C and draw a line from B2 to C1 which is parallel to B3C and it is intersecting BC at C1.
- Draw a line through C1 parallel to AC to intersect AB at A1. So, ∆A1BC1 is the required triangle.