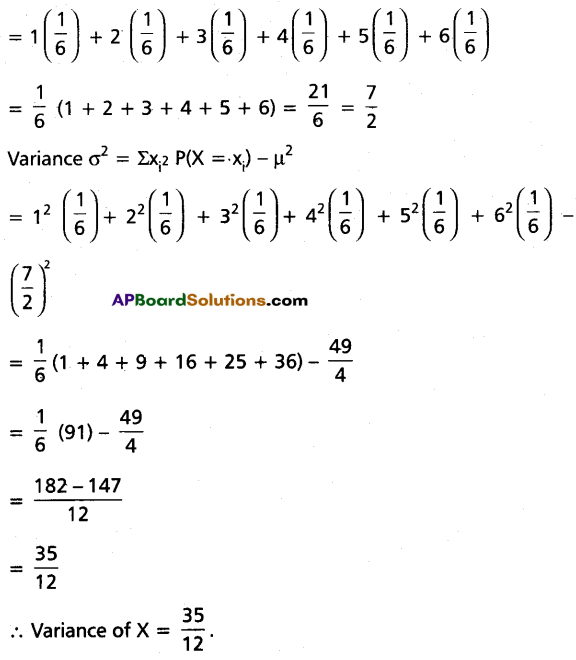Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Question Paper March 2019 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Question Paper March 2019
Time: 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 75
Note: This question paper consists of three Sections A, B, and C.
Section – A
(10 × 2 = 20 Marks)
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions.
- Answer all the questions.
- Each question carries two marks.
Question 1.
If z = (cos θ, sin θ), then find (z – \(\frac{1}{z}\)).
Solution:
Given z = (cos θ, sin θ)
⇒ z = cos θ + i sin θ
\(\frac{1}{z}=\frac{1}{(\cos \theta+i \sin \theta)}\) = cos θ – i sin θ
z – \(\frac{1}{z}\) = (cos θ + i sin θ) – (cos θ – i sin θ)
= cos θ + i sin θ – cos θ + i sin θ
= 2i sin θ
∴ z – \(\frac{1}{z}\) = 2i sin θ
Question 2.
If z = x + iy, and |z| = 1, then find the locus of z.
Solution:
Given z = x + iy
Also |z| = 1
⇒ \(\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\) = 1
⇒ x2 + y2 = 1
∴ The locus of z is x2 + y2 = 1.
![]()
Question 3.
If 1, w, w2 are the cube roots of unity, then find the value of (1 – w + w2)3.
Solution:
Since 1, w, and w2 are the cube roots of unity.
∴ 1 + w + w2 = 0 and w3 = 1
(1 – w + w2)3 = (-w – w)3
= (-2w)3
= -8w3
= -8(1)
= -8
∴ (1 – w + w2)3 = -8
Question 4.
Find the set of solutions of x2 + x – 12 ≤ 0 by the algebraic method.
Solution:
Given x2 + x – 12 ≤ 0
⇒ x2 + 4x – 3x – 12 ≤ 0
⇒ x(x + 4) – 3(x + 4) ≤ 0
⇒ (x + 4) (x – 3) ≤ 0
⇒ x ∈ [-4, 3]
∴ The set of solutions of x2 + x – 12 ≤ 0 is [-4, 3].
Question 5.
If α, β, γ are the roots of 4x3 – 6x2 + 7x + 3 = 0, then find the value of αβ + βγ + γα.
Solution:
Given 4x3 – 6x2 + 7x + 3 = 0 ………..(1)
Since α, β, γ are the roots of (1)
∴ αβ + βγ + γα = s2 = \(\frac{7}{4}\)
Question 6.
Find the number of ways of preparing a chain With 6 different coloured beads.
Solution:
The number of ways of preparing a chain with 6 different coloured beads = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (n – 1)!
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (6 – 1)!
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5)!
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (120)
= 60
Question 7.
If nC4 = 210, then find n.
Solution:
Given nC4 = 210
⇒ \(\frac{n(n-1)(n-2)(n-3)}{4 !}\) = 5 × 6 × 7
⇒ n(n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3) = 24 × 5 × 6 × 7
⇒ n(n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3) = 7 × 8 × 9 × 10
⇒ n(n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3) = 10 × 9 × 8 × 7
⇒ n = 10
![]()
Question 8.
Find the number of terms in the expansion of (2x + 3y + z)7.
Solution:
The number of terms in the expansion of (2x + 3y + z)7 = \(\frac{(7+1)(7+2)}{2}\)
= \(\frac{8.9}{2}\)
= 36
Question 9.
Find the variance of the following data:
5, 12, 3, 18, 6, 8, 2, 10
Solution:
Given ungrouped data 5, 12, 3, 18, 6, 8, 2, 10
mean x =\(\bar{x}=\frac{5+12+3+18+6+8+2+10}{8}\)
= \(\frac{64}{8}\)
= 8
variance σ2 = \(\frac{1}{8}\) [(5 – 8)2 + (12 – 8)2 + (3 – 8)2 + (18 – 8)2 + (6 – 8)2 + (8 – 8)2 + (2 – 8)2 + (10 – 8)2]
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) [9 + 16 + 25 + 100 + 4 + 0 + 36 + 4]
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) (194)
= 24.25
Question 10.
The mean and variance of a binomial distribution are 4 and 3 respectively. Fix the distribution and find P(x ≥ 1).
Solution:
Let x follow a binomial distribution with parameters n and p.
Given mean = np = 4 ……….(1)
variance = npq = 3
\(\frac{n p q}{n p}=\frac{3}{4}\)
⇒ q = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
p = 1 – q
= 1 – \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
From(1)
n(\(\frac{1}{4}\)) = 4
⇒ n = 16
P(x ≥ 1) = 1 – P(x = 0)
= 1 – \({ }^{16} \mathrm{C}_0\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)^0\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^{16-0}\)
= 1 – \(\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^{16}\)
Section – B
(5 × 4 = 20 Marks)
II. Short Answer Type Questions.
- Answer any five questions.
- Each question carries four marks.
Question 11.
If x + iy = \(\frac{1}{1+\cos \theta+i \sin \theta}\), then show that 4x2 – 1 = 0.
Solution:
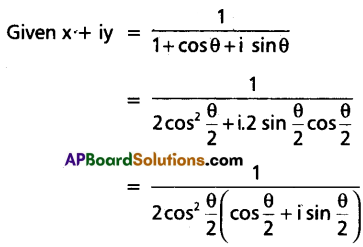
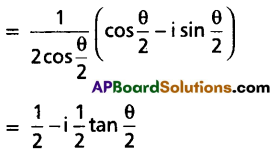
Now, equating real points on both sides, we have x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
⇒ x2 = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
⇒ 4x2 = 1
⇒ 4x2 – 1 = 0
Question 12.
If c2 ≠ ab and the roots of the equation (c2 – ab)x2 – 2(a2 – bc)x + (b2 – ac) = 0 are equal, then show that a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc or a = 0.
Solution:
Given (c2 – ab) x2 – 2 (a2 – bc) x + (b2 – ac) = 0 ……..(1)
since (1) has equal roots
∴ 4(a2 – bc)2 – 4(c2 – ab) (b2 – ac) = 0
⇒ (a2 – bc)2 – (c2 – ab) (b2 – ac) = 0
⇒ a4 – 2a2bc + b2c2 – (b2c2 – ac3 – ab3 + a2bc) = 0
⇒ a4 – 2a2bc + b2c2 – b2c2 + ac3 + ab3 – a2bc = 0
⇒ a4 + ab3 + ac3 – 3a2bc = 0
⇒ a(a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc) = 0
⇒ -a = 0 (or) a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc = 0
⇒ a = 0 (or) a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc
![]()
Question 13.
If the letters of the word MASTER are permuted in all possible ways and the words thus formed are arranged in the dictionary order, then find the rank of the word MASTER.
Solution:
The alphabetical order of the letters of the word REMAST is A, E, M, R, S, T
The no. of words beginning with A is 5! = 120
The no. of words begin with E is 5! = 120
The no. of words begin with MAE is 3! = 6
The no. of words begin with MAR is 3! = 6
The no. of words begin with MASE is 2! = 2
The no. of words begin with MASR is 2! = 2
The next word is MASTER = 1
∴ Rank of the word MASTER = 120 + 120 + 6 + 6 + 2 + 2 + 1 = 257
Question 14.
Prove that \(\frac{4 n C_{2 n}}{2 n C_n}=\frac{1 \cdot 3 \cdot 5 \ldots(4 n-1)}{\{1 \cdot 3 \cdot 5 \ldots(2 n-1)\}^2}\)
Solution:
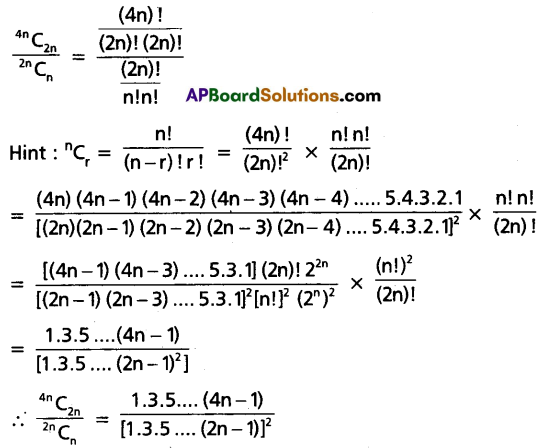
Question 15.
Resolve \(\frac{x^3}{(x-a)(x-b)(x-c)}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
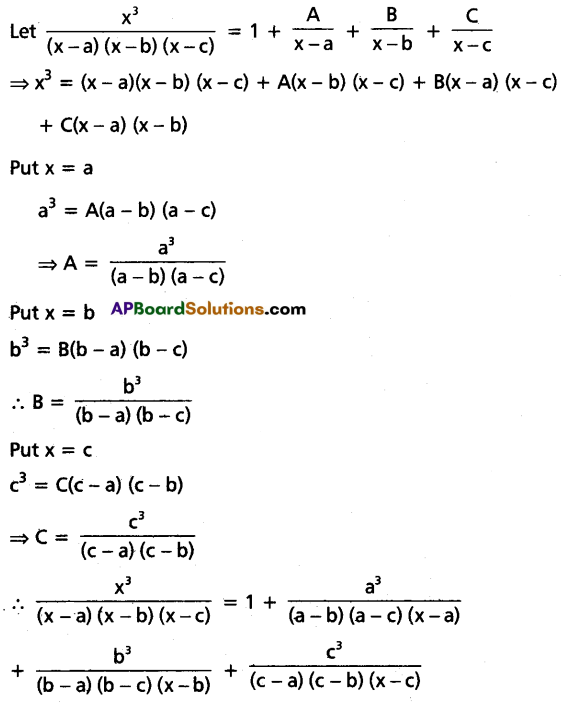
Question 16.
The probability for a contractor to get a road contract is \(\frac{2}{3}\) and to get a building contract is \(\frac{5}{9}\). The probability to get atleast one contract is \(\frac{4}{5}\). Find the probability that he gets both contracts.
Solution:
Let A be the event of getting a road contract and B be the event of getting a building contract.
∴ P(A) = \(\frac{2}{3}\), P(B) = \(\frac{5}{9}\) and P(A ∪ B) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
By addition theorem on probability, we have
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
⇒ P(A ∩ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∪ B)
= \(\frac{2}{3}+\frac{5}{9}-\frac{4}{5}\)
= \(\frac{30+25-36}{45}\)
= \(\frac{19}{45}\)
∴ The probability to get both the contracts = \(\frac{19}{45}\)
Question 17.
A speaks truth in 75% of the cases and B in 80% of cases. What is the probability that their statements about an incident do not match?
Solution:
Let E1 and E2 be the events that A and B respectively speak the truth about an incident.
∴ P(E1) = \(\frac{75}{100}=\frac{3}{4}\)
⇒ P(\(E_1^c\)) = 1 – \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
∴ P(E2) = \(\frac{80}{100}=\frac{4}{5}\)
⇒ P(\(E_2^c\)) = 1 – \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
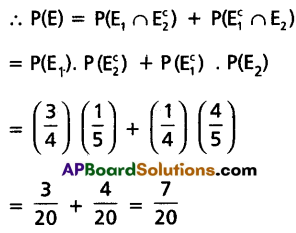
If E is the event that their statements do not match about the incident, then this happens in two mutually exclusive ways.
(i) A speaks the truth and B tells a lie.
(ii) A tells a lie and B speaks the truth.
Section – C
(5 × 7 = 35 Marks)
III. Long Answer Type Questions.
- Answer any five questions.
- Each question carries seven marks.
Question 18.
If n is an integer and Z = cis θ, (θ ≠ (2n + 1)\(\frac{\pi}{2}\)) then show that
\(\frac{z^{2 n}-1}{z^{2 n}+1}\) = i tan nθ.
Solution:
Given z = cos θ + i sin θ
z2n = (cos θ + i sin θ)2n = cos 2nθ + i sin 2nθ
z2n – 1 = cos 2nθ + i sin 2nθ – 1
= 1 – 2 sin2nθ + i . 2 sin nθ cos nθ
= -2 sin2nθ + 2i sin nθ cos nθ
= 2i2 sin2nθ + 2i sin nθ cos nθ
= 2i sin nθ (i sin nθ + cos nθ)
= 2i sin nθ (cos nθ + i sin nθ)
z2n + 1 = cos 2nθ + i sin 2nθ + 1
= 2 cos2nθ – 1 + i 2 sin nθ cos nθ + 1
= 2 cos2nθ + i 2 sin nθ cos nθ
= 2 cos nθ (cos nθ + i sin nθ)
∴ \(\frac{z^{2 n}-1}{z^{2 n}+1}=\frac{2 i \sin n \theta(\cos n \theta+i \sin n \theta)}{2 \cos n \theta(\cos n \theta+i \sin n \theta)}\)
= \(\frac{\mathrm{i} \sin n \theta}{\cos n \theta}\)
= i tan nθ
∴ \(\frac{z^{2 n}-1}{z^{2 n}+1}\) = i tan nθ
![]()
Question 19.
Solve the equation x4 + x3 – 16x2 – 4x + 48 = 0, given that the product of two of the roots is 6.
Solution:
Let α, β, γ, δ be the roots of x4 + x3 – 16x2 – 4x + 48 = 0
such that αβ = 6
s1 = α + β + γ + δ = -1 …….(1)
s2 = αβ + αγ + αδ + βγ + βδ + γδ = -16 …….(2)
s3 = αβγ + βγδ + αγδ + βγδ = 4 …….(3)
s4 = αβγδ = 48
⇒ 6γδ = 48
⇒ γδ = 8
From (3),
⇒ 6γ + 6δ + 8α + 8β = 4
⇒ 6(α + β + γ + δ) + 2α + 2β = 4
⇒ 6(-1) + 2α + 2β = 4
⇒ 2α + 2β = 10
⇒ α + β = 5
From(1),
⇒ 5 + γ + δ = -1
⇒ γ + δ = -6
α + β = 5, αβ = 6
⇒ α = 2, β = 3
γ + δ = -6, γδ = 8
⇒ γ = -2, δ = -4
∴ The roots are 2, 3, -2, -4.
Question 20.
If 36, 84, and 126 are three successive binomial coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)n, then find n.
Solution:
Let nCr-1, nCr, and nCr+1 be three successive binomial coefficients in the expansion of (1 + x)n.
nCr-1 = 36 …….(1)
nCr = 84 …….(2)
nCr+1 = 126 …….(3)

⇒ 9r + 15 = 14r
⇒ 5r = 15
⇒ r = 3
From (4), \(\frac{n-3+1}{3}=\frac{7}{3}\)
⇒ 3n – 6 = 21
⇒ 3n = 27
⇒ n = 9
Question 21.
If x = \(\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1.3}{5.10}+\frac{1.3 .5}{5 \cdot 10.15}\) + …….∞, then find 3x2 + 6x.
Solution:
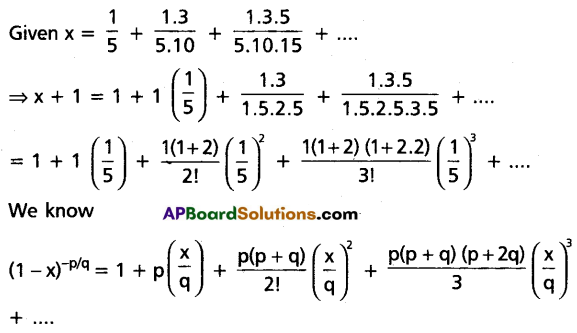
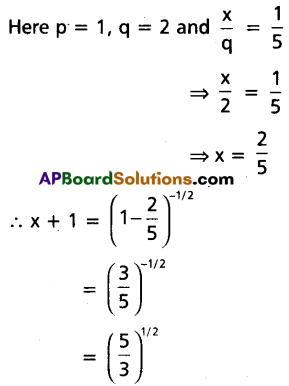
⇒ (x + 1)2 = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
⇒ x2 + 2x + 1 = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
⇒ 3x2 + 6x + 3 = 5
⇒ 3x2 + 6x = 2
Question 22.
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the following data:
| xi | 2 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 35 |
| fi | 6 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 8 | 2 |
Solution:
We can form the following table for the given data.
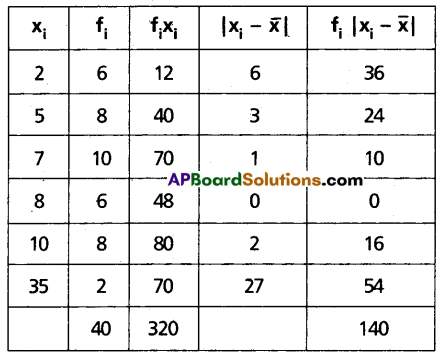
Here N = 40 = Σfi
Σfixi = 320
Mean \(\frac{1}{N} \Sigma f_i x_i=\frac{320}{40}\) = 8
From table, \(\Sigma f_i\left|x_i-\bar{x}\right|\) = 140
Mean deviation about mean = \(\frac{1}{N} \Sigma f_i\left|x_i-\bar{x}\right|\)
= \(\frac{1}{40}\) (140)
= 3.5
![]()
Question 23.
Three boxes numbered I, II, and III contain the balls as follows:
| White | Black | Red | |
| I | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| II | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| III | 4 | 5 | 3 |
One box is randomly selected and a ball is drawn from it. If the ball is red, then find the probability that it is from Box II.
Solution:
Let B1, B2, and B3 be the events of selecting I, II, and III boxes respectively.
∴ P(B1) = P(B2) = P(B3) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
P\left(\frac{R}{B_1}\right) = Probability of selecting a red ball shown the first box = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
P\left(\frac{R}{B_2}\right) = Probability of selecting a red ball from the second box = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
P\left(\frac{R}{B_3}\right) = Probability of selecting a red ball from the third box = \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Assuming that the ball is red, the probability it is from box II.
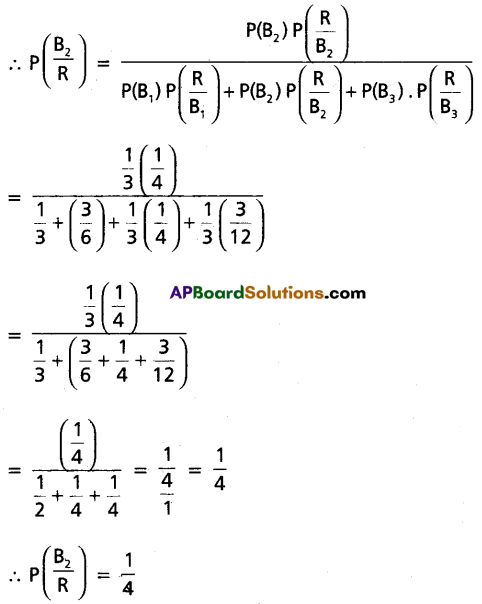
Question 24.
A cubical die is thrown. Find the mean and variance of X, giving the number on the face that shows up.
Solution:
Let S be the sample space and X be the number on the face that shows up when a cubical die is thrown.

Mean µ = 1 P(X = 1) + 2 P(X = 2) + 3 P(X = 3) + 4 P(X = 4) + 5 P(X = 5) + 6 P(X = 6)