Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2019 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2019 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Note: Answer any TWO of the following questions not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is a Stock Exchange? Explain its functions.
Answer:
Introduction:
Stock exchange is an organized secondary market, where investors buy and sell the listed securities.
Definition:
“Stock exchange is an association, organization or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, established to assist, regulate and controlling business in buying, selling and dealing in securities”. – The Securities Contracts Act 1956
“Security exchanges are marketplaces where securities that have been listed thereon may be bought and sold either for investment or speculation”. – “Pyle”
Functions of Stock Exchange:
- Provides infrastructure for trading: In the stock exchange, instantaneously trading gets executed. It draws investment by providing a ready and continuous market for securities.
- Provides information regarding prices: It gives sensible information through reliable sources and publishers to investors (bout the prices of securities. The proposed investor knows the notation and the investor knows the price of his holdings.
- Protects investor’s wealth: It protects the interests and wealth of investors through the enforcement of its rules and regulations.
- Clearing House: Without a clearing house one will find a lot of trades mismatched. It acts on behalf of both buyer and seller and helps in the trading of securities.
- Provides liquidity: The holder of securities can easily encash the securities by selling them to the buyer whenever he wants.
- Helps to raise new capital: The requirement of additional capital of an existing company can be raised by issuing the rights shares, through the stock exchange.
- Acts as a Barometer: An efficient stock exchange acts as a Barometer of business conditions in the country.
- Increases credit worthiness of company: A company that got its shares to be listed in the stock exchange enjoys a good reputation.
- Minimizes the dangers of speculation: Following the rules and regulations of the Acts, it minimizes the dangers of speculative dealings and price manipulations.
- Facilitates speculation: Stock exchange facilitates speculation thereby businessmen can speculate and earn profits from fluctuations in security prices.
Question 2.
Define banking and explain the functions of banking.
Answer:
Bank is derived from the French word “Banco” which means a Bench, It is believed that the early bankers, the Jews of Lombardy transacted their business on benches in the marketplace.
Definition: “Banking is defined as accepting for lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order or otherwise”. – Banking Regulation Act 1949 – Section 5 (1) (b)
Functions of Banks:
The core functions of a bank are
- Acceptance of money deposits from the public.
- Lending (or) making advances to the public.
- Undertaking Agency Services.
- Rendering General Utility Services.
1. Acceptance of Deposits:
Banks accept money from the public in various forms which constitute borrowings by banks. The deposits are one of the main sources of funds for the banks.
2. Lending (or) making advances to the public:
Banks lending the deposit amounts. It is a profit motive. The bank will not lend the whole of the deposits it keeps a certain amount to meet contingencies and the remaining portion is lent to the business community at a higher rate of interest. The difference between the rate of interest allowed and deposits and the rate charged on the loans is called as ‘spread’, it is the main source of income for a bank. An advance is a credit facility provided by a bank to its customers. It is generated for shorter periods. Further, the purpose behind granting an advance is to meet the day-to-day requirements of a business.
3. Agency Functions or Services:
Banks perform these functions for their customers. These are
- To collect or pay bills, cheques, interest, dividends, rent, etc., on behalf of customers.
- For rendering these services, banks collect charges from their customers.
- To act as executor, trustee, and attorney on the customer’s will.
- To work as a correspondent, agent, or representative of their clients.
4. General Utility Services:
These services are provided to the general public. These are
- A letter of credit may be issued by the bank at the request of the importer to the exporter.
- Bank drafts and traveler’s cheques are issued to provide facilities for fund transfer from one part of the country to another part.
- Acceptance or collection of foreign bills of exchange.
- Banks arrange safe deposit lockers for the safe custody of customers’ securities, valuables, and jewelry.
- Other general public utility services.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the contribution of Henry Fayol in the field of management?
Answer:
Henry Fayol (1841 – 1925):
Henry Fayol was a French mining engineer who later turned into a leading industrialist and a successful manager. His lifelong experience, in the field of managing, was produced in the form of a monograph titled”. ‘Administration industrielle-et-generale’ in 1916 in the French language. This monograph was reprinted in French several times but was never translated into English until – 1929. Fayol’s contribution to the science of management may be summarised as follows:
- Classification of industrial activities.
- Classification of managerial functions.
- Universal principles of management.
- Significance of management function.
- Managerial qualities and training.
- Macro approach to management.
- The human aspect of management.
Henry Fayol has been rightly called “The father of management”. He has identified 14 principles of management those are division of labor, authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of command; unity of direction; subordination; remuneration; centralization, scalar chain, order, equity, stability of tenure; initiative; esprit-de-corps, etc.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the Primary Market and the Secondary Market.
Answer:
| Concept | Primary Market | Secondary Market |
| 1. Nature | It is concerned with the issue of new shares. | It is concerned with the marketing of existing shares. |
| 2. Sale of Securities | It enables the company to sell securities to the investors directly or through intermediaries. | It helps the holders of securities to exchange their securities. |
| 3. Capital Formation | It is directly connected with the promotion of capital formation. | It is indirectly connected with the promotion of capital formation. |
| 4. Securities Dealing | It deals with the buying of securities. | It enables both buying and selling of securities. |
| 5. Value of Securities | It enables the management of the company to decide the value of the securities. | It enables the demand and supply to determine the price of securities. |
| 6. Location | It has no fixed geographical location. | It is located at specific places. |
Question 5.
Write any three merits and two demerits of Road Transport.
Answer:
Merits:
- Cheapness: All forms of animal – driven, man – driven and motor-driven transport are cheaper compared to the other forms.
- Safety: Damage due to the handling of goods is lesser in the form of transport.
- Flexibility: This advantage could be claimed only by road transport. It may go the place of loading and delivery of goods at the place of use.
Demerits:
- Irregular operation: Most of the transporting systems operating on roads are not coordinated.
- Limited carrying capacity: Limited load-carrying capacity is one of the drawbacks of road transport.
- Slow speed: Speed is an essential element in marketing but it is not possible in road transport.
- Rates: The rate structure is often oscillating in character.
Question 6.
What are the characteristics of Entrepreneurs?
Answer:
Characteristics:
- Innovation: Innovation means “doing new things or doing things that are already being done in a new way”. Entrepreneurs deal with the changes. He does not continue with the old ideas.
- Risk-taking: Any new business poses a risk for entrepreneurs. They may succeed or fail. Entrepreneur takes risks.
- Self-confidence: They have the confidence that they can change the existing position.
- Hard work: Entrepreneurs are hard workers. Few people in our society work harder than entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs do not depend on others.
- Goal setting: Entrepreneurs get happiness by setting and striving for goals. They may not always achieve those goals.
- Accountability: Entrepreneurs take success or failure in their stride. They were responsible and Accountable for results.
- Leadership: Leadership represents an abstract quality of a man. The entrepreneur has to be a leader because he is such a person, who organizes, directs, commands, and controls the functions of the organization.
- Managerial skills: Entrepreneurs require managerial skills to achieve the goals of their enterprises.
Question 7.
Explain the special provisions enacted by the Telangana State for MSMEs.
Answer:
The special provisions for the micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are as follows:
- An adequate number of smaller plots in industrial parks for SMEs and developed sheds.
- Special funds for addressing incipient sickness.
- Special fund for IP registration assistance.
- Special fund for anti-pirating assistance.
- Special fund for technology transfer and modernization of the MSME sector.
- Reimbursement of land conversion charges for units in own land.
- Marketing assistance to participate in national.
- Consultant panel to respond to MSME entrepreneur needs.
- Separate state-level bankers committee for industries.
Question 8.
List out the advantages of SEZs.
Answer:
Advantages of SEZs:
- Employment generation: SEZs are viewed as highly effective tools for job creation.
- Economic development: SEZs are viewed as the engines for economic development.
- Growth of labor-intensive manufacturing industry: The establishment of SEZs would lead to fast growth of labor-intensive manufacturing and service industries in the country.
- Balanced regional development: SEZs are beautifully crafted initiatives for achieving balanced regional development.
- Capacity Building: SEZs are important for stronger capacity building.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the steps in the process of organizing?
Answer:
The process of organizing are following steps.
- Identification and division of work: The first step in the process of organizing involves identifying and dividing the work that has to be done by previously determined plans. The burden of work can be shared among the employees.
- Departmentalization: Once work has been divided into small and manageable activities then those activities which are similar are grouped. Such sets facilitate specialization. This grouping process is called departmentalization.
- Assignment of duties: It is necessary to define the work of different job positions and accordingly allocate work to various employees. Jobs are then allocated to the members of each department by their skills and competencies.
- Establishing reporting relationships: Merely allocating work is not enough. Each individual should also know whom he has to take orders and to whom he is accountable. The establishment of such clear relationships helps to create a hierarchical structure and helps in coordination among various departments.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any FIVE of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Explain the meaning of control.
Answer:
Control means the power to influence or direct people’s behavior or the course of events. Control means seeing that everything is taking place in conformity with the established rules and expressed commands. In other words, control means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans.
Question 11.
What is a Bill of Lading?
Answer:
It is an official receipt of the shipping company acknowledging the receipt of goods on board.
Question 12.
Define Wholesale Trade.
Answer:
Wholesale Trade involves purchasing goods in large quantities from producers or manufacturers and selling in smaller lots to retailers for resale to ultimate consumers. The trader involved in wholesale Trade is called a wholesaler.
Question 13.
What is an Exchange Rate?
Answer:
The rate at which the currency of one country is exchanged for the currency of another country is known as the “Exchange Rate”. In other words, the exchange rate is the value of one currency for conversion to another.
Question 14.
What is meant by Project Report?
Answer:
It is the document prepared by the entrepreneur where he has to put his ideas and other information in black and white. Project Report is a written document of what an entrepreneur proposes to take up and his course of action to establish his enterprise.
Question 15.
Define Adoptive Entrepreneur.
Answer:
An adoptive entrepreneur is one who instead of innovating new things, he just adopts the successful innovations innovated by others. Adoptive Entrepreneurs are also called “Imitative entrepreneurs”.
Question 16.
Explain Mobile Banking.
Answer:
The delivery of Banking services to a customer through a mobile phone is called “Mobile Banking”. This service is provided free of cost to all customers of the bank, irrespective of their mobile service network provider and the make of the handset owned by the customer. Customers to know their account balance and debit, credit transactions of the account, etc., through alerts.
Question 17.
What do you mean by Bull?
Answer:
A Bull or Tejawalla is an operator who expects a rise in the prices of securities in the future. In anticipation of a price rise, he makes purchases of shares and debentures to sell at a higher price in the future such a speculator is called a “Bull” because of the resemblance of his behavior with the bull. A bull tends to throw his victims up in the air, in similarly a bull speculator tries to raise the prices of securities by placing big purchase orders.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
Question 18.
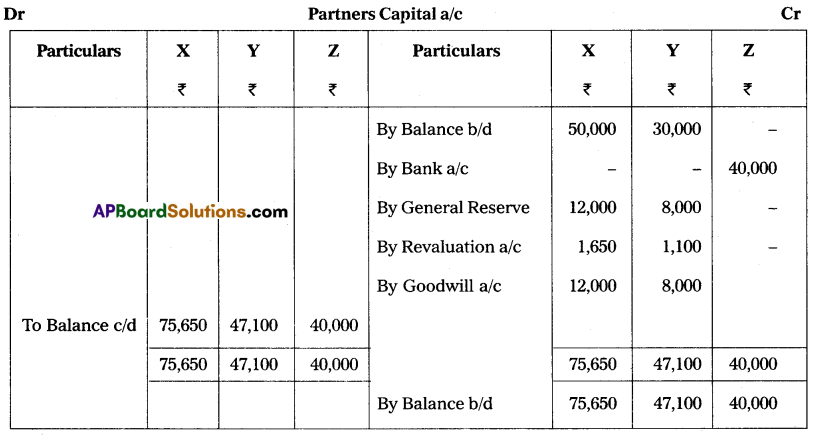
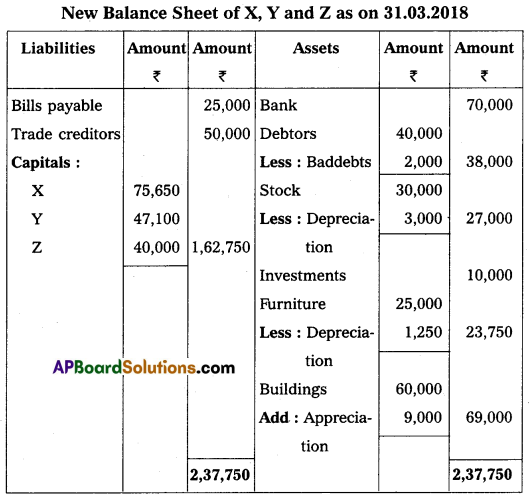
The following was the balance sheet of X and Y, who were sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their balance sheet as of 31st March 2018 was as under:
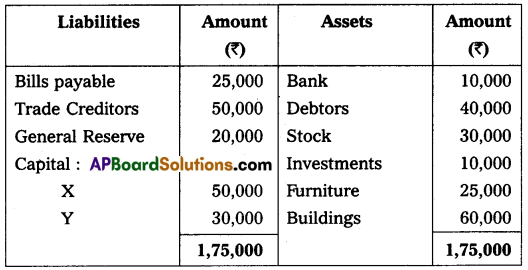
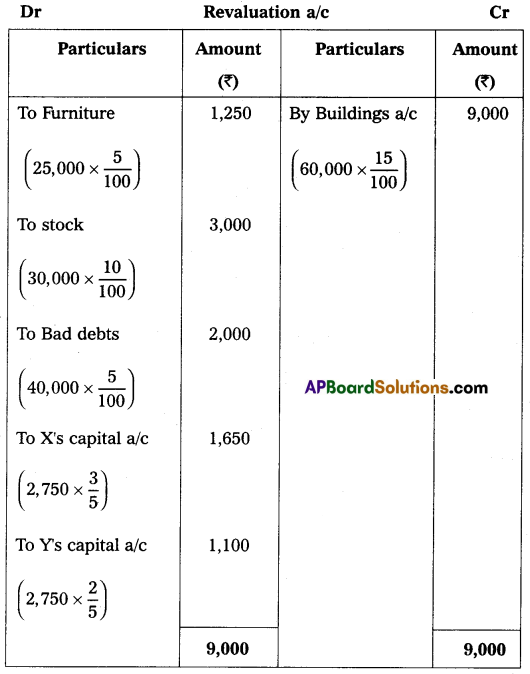
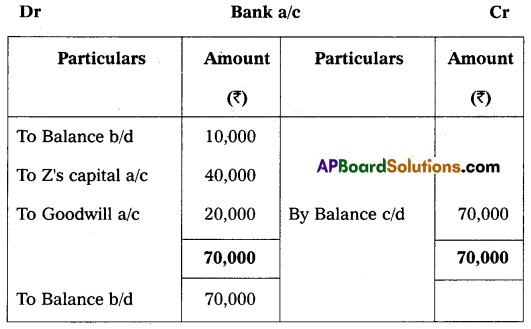
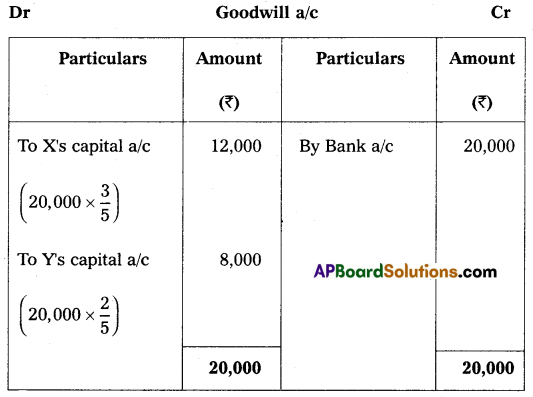
On 1st April 2018, they agreed to admit Mr. Z as a new partner for \(\frac{1}{5}\)th share in profits on the following terms:
1. Z should bring ₹ 40,000 for capital and ₹ 20,000 goodwill in cash.
2. Depreciate furniture by 5% and stock by 10%.
3. Appreciate building value for 15%.
4. Provide for bad debts at 5% on debtors.
Pass necessary Ledger Accounts and Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Note: Answer any ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
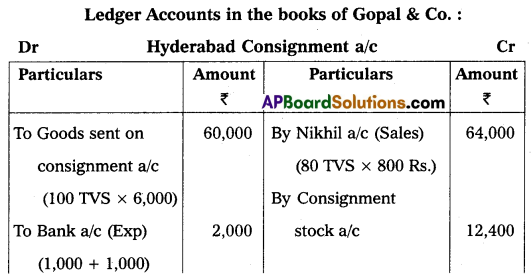
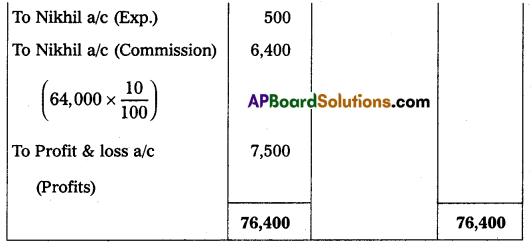
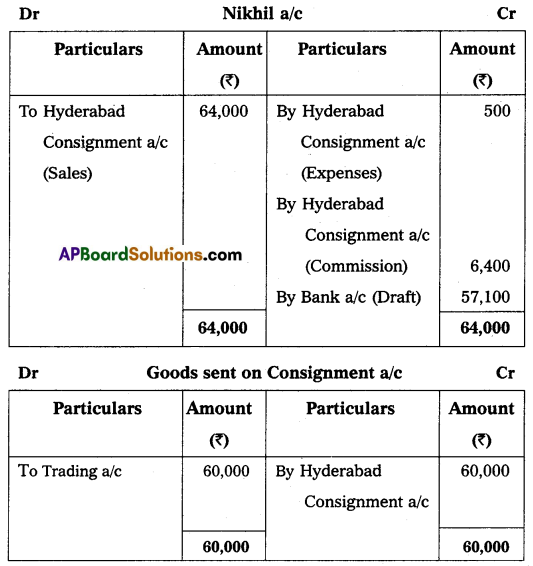
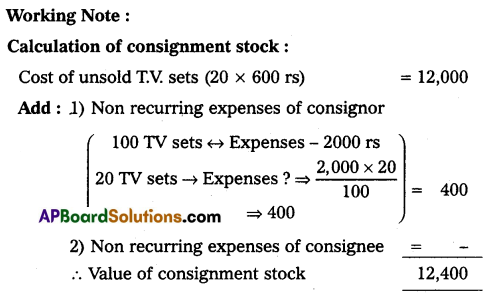
Gopal & Co. of Mumbai consigned 100 T.V. sets to Nikhil of Hyderabad. The cost of each T.V. was ₹ 600. Gopal paid insurance ₹ 1,000, and freight ₹ 1,000. Account sales were received from Nikhil showing the sale of 80 TV sets at ₹ 800 each. The following expenses were deducted by Nikhil:
Selling Expenses ₹ 500
Commission 10% on sales
Gopal received a bank draft for the balance due and prepared important Ledger Accounts in the books of Gopal.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
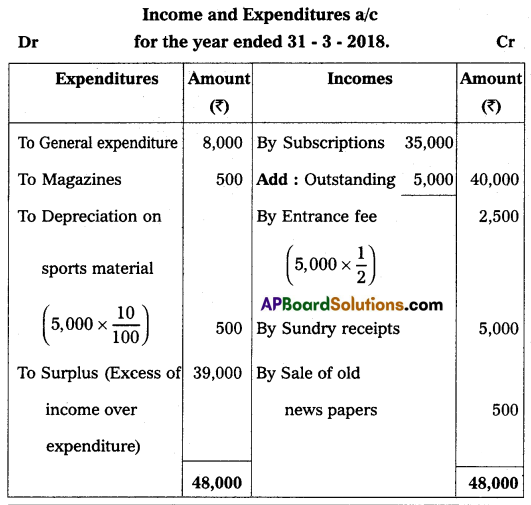
From the following Receipts and Payments Account, prepare the Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31.3.2018:
Receipts and Payments Account for the year ended 31.03.2018.
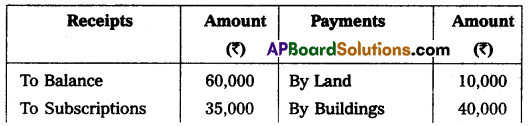
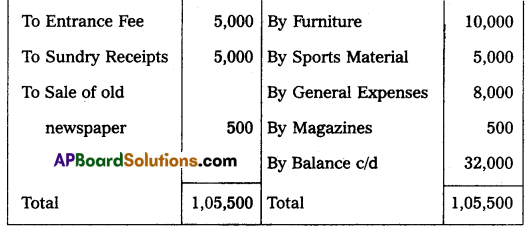
Additional Information:
1. Capitalize 50% of entrance fee.
2. Subscriptions still outstanding amount to ₹ 5,000.
3. Depreciate sports material by 10%.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Note: Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Distinguish between Receipts & Payments and Income & Expenditure Accounts.
Answer:
| Basis of Difference | Receipts and Payments A/c | Income and Expenditure A/c |
| 1. Type of Account | It is a real account. | It is a nominal account. |
| 2. Debit and Credit Side | Receipts are shown on the debit side and payments are on the credit side. | Income is shown on the credit side and expenditure on the debit side. |
| 3. Basic Structure | It is a summary of cash and bank transactions. | It is a summary of income earned and expenditures incurred during the year. |
| 4. Opening & Closing Balance | Opening balance and closing balance represent cash in hand or cash at the bank. | There is no opening balance closing balance shows either a surplus or deficit. |
| 5. Contents | Both revenue and capital items are considered. | Only revenue items are considered. |
| 6. Adjustments | No adjustments are required. | All adjustments relating to current-year income and expenditure are taken into consideration. |
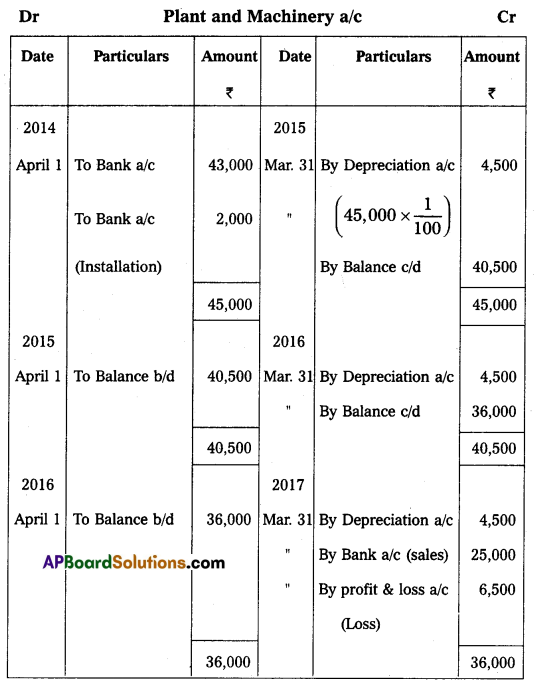
Question 22.
Raju bought a Plant and Machinery on 1st April 2014 for ₹ 43,000 and paid ₹ 2,000 for its installation. Depreciation is to be allowed at 10% under the straight-line method. On 31st March 2017, the plant was sold for ₹ 25,000. Assuming that the accounts are closed at the end of the financial year. Prepare Plant & Machinery Account.
Answer:
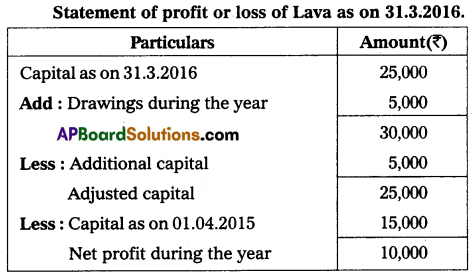
Question 23.
Calculate the Profit/Loss earned by Lava who keeps his books under a single-entry system.
Capital as on 01.04.2015 – ₹ 15,000
Fresh capital introduced – ₹ 5,000
Drawings during the year – ₹ 5,000
Capital as on 31.03.2016 – ₹ 25,000
Answer:
Question 24.
Mention any three advantages and two disadvantages of Computerised Accounting.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Automation: Since all the calculations are handled by the software, computerized accounting eliminates many of the routines.
- Accuracy: This accounting system is designed to be accurate to the minute detail.
- Speed: Using accounting software, the entire process of preparing an account becomes faster.
- Reliability: Because of the accurate calculations, the financial statements prepared by computers are highly reliable.
Disadvantages:
- If the user enters incorrect information, all automatic calculations will be incorrect.
- It is harder to locate and correct errors until the user learns the particular characteristics of the program.
- It requires special programs and qualified staff for operations.
- Computerized accounting needs regular backup.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is Obsolescence?
Answer:
Diminution (reduction) in the value of fixed assets due to new inventions, new improvements, changes in fashions, and changes in customers’ tastes and preferences.
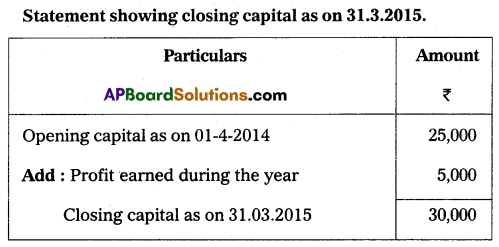
Question 26.
Calculate closing capital as of 31.03.2015:
Opening capital as of 01.04.2014 is ₹ 25,000.
Profit earned during the year is ₹ 5,000.
Answer:
Question 27.
What is the Delcredere Commission?
Answer:
Remuneration or additional commission paid to the consignee for taking the responsibility of collecting the amount on credit sales made by him.
Question 28.
Explain specific donations.
Answer:
A donation received by the organization for a specific purpose is called a “Specific Donation”. Specific donations are also called “Special Donations”. For example: Donation for Building.
Question 29.
A and B are partners sharing profits and losses equally. They decided to admit C for \(\frac{1}{5}\)th share of profit in the business. Calculate the new profit-sharing ratio of A, B, and C.
Answer:
The Old Ratio of A & B is 1 : 1
Give \(\frac{1}{5}\)th share to ‘C’
Total Profits Assumed ‘1’
Remaining Share = 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
A’s new ratio = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{5}\)
B’s new ratio = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{5}\)
C’s Share = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
∴ The new ratio of A, B, and C is = 2 : 2 : 1
Question 30.
What is Goodwill?
Answer:
Goodwill is the reputation or good name associated with the name of the firm. Goodwill is an intangible asset. Firms that have goodwill will enjoy continuous patronage of customers.
![]()
Question 31.
Define Spreadsheets.
Answer:
A spreadsheet is an interactive computer application program. It helps the organization with the analysis and storage of data in tabular form. It is a table of values arranged in rows and columns. Each value can have a pre-defined relationship to the other values.
Question 32.
Explain Word Tally.
Answer:
Tally is a versatile and massive software package. Tally’s software business was set up in 1986 by S.S. Goenkar, who was the founder of the Company Peutronics Private Limited, Bangalore. Tally is user-friendly software used to solve all the complicated accounting structures. Tally maintains ledger-wise balance and displays net debit or credit balance for a ledger. Using a reverse journal to make transient journal vouchers to get intermediate profit and loss accounts and balance sheets.