Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers Set 2 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Paper Set 2 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Explain the significance of the Stock Exchange.
Answer:
The stock exchange is a market for the purchase and sale of second-hand securities. It is the central place where industrial and financial securities are brought and sold. It is the place where a buyer of security can find a seller or a seller can find a buyer.
Significance of Stock Exchange:
The utility of the stock exchange can be explained with the help of three heads. That is to the investor, to the company, and the society.
(i) From the Point of View of Investors:
- The liquidity of the investment is increased. Thus, it provides an investment incentive.
- The listed securities become good collateral securities for loans.
- The stock exchange protects the interests of investors through strict enforcement of rules.
- It reflects the correct information on the prices of securities. This enables an investor to know the present worth of his investment.
- It promotes the habit of saving among the public by providing a ready market for investment.
- The risk of an investor is greatly reduced when he purchases a listed security.
(ii) From the Point of View of the Company:
- A listed company generally enjoys a better reputation and credit.
- The market for the listed securities has widened.
- The bargaining power of the listed companies rises in the event of a merger or amalgamation.
- The stock exchange provides an opportunity for companies to raise capital by the sale of shares. So, the rapid progress of companies is largely facilitated by stock exchanges.
- The listing facilities provided by the stock exchange make the securities attractive.
- The listing of securities gives the impression that the company is sound.
- A well-organized stock exchange minimizes price fluctuations and maintains the steadiness of the prices of securities.
(iii) From the Point of View of the Society:
- Stock exchange promotes the habit of saving and facilitates capital formation. This capital flows into industry and thus facilitates economic growth.
- It assists the superior companies in raising further capital. It places a premium on efficiency.
- The government has to undertake projects of national importance and social value.
- For this, it requires huge funds. The stock exchange provides the necessary instrument for raising these funds.
- The stock exchange acts as a mirror of society’s economy.
- It directs the flow of investment towards stable and increasing yields.
- It provides a medium for evaluating the real worth of different securities.
![]()
Question 2.
What is e-banking? Explain the various types of e-banking.
Answer:
The concept of E-banking enables a customer to transact with his/her bank from anywhere such as from home, office, or from any place and time that would be convenient to him/her. We may transact beyond the bank’s working hours. E-banking is a system of banking that is carried out with the use of electronic tools and facilitated through electronic delivery channels. Most of banks offer E-banking through ATMs (Automatic Teller Machines), telephonic transactions, etc. Electronic banking provides efficient services at low costs and without any geographical barriers.
Types or kinds of services under E-banking:
- Automatic Teller Machine (ATM)
- Anywhere Banking
1. Automatic Teller Machine (ATM):
ATM is one of the methods of electronic fund transfer. It has removed the time limitations of customer services. ATM is an unattended or unmanned device usually located on or off the bank premises. The operation mechanism begins when the card is inserted into the ATM, the terminal reads and transmits the tape data to the processor, which activates the account. It works for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (24 × 7). ATMs were used only for withdrawal, electronic transfer of funds, etc. But now they are used for recharging cell phones, bill payments, etc.
2. Anywhere Banking:
With the introduction of ATMs and telebanking, financial details can be accessed from anywhere. A customer can operate his account from any branch of his bank situated in India. This is also known as “Core Banking”. The various services provided under Anywhere banking are as follows:
- Tele Banking
- Internet Banking (I-Banking)
(A) Tele Banking:
It refers to banking on the telephone. The customer can dial the branch’s designated telephone number which is connected to the computer. The customer can enquire about his balance, previous transactions, or fund transfers between the accounts. The customer has to choice and facility of calling the bank at any time and it is more beneficial to the majority of customers.
(B) Internet Banking (I-Banking):
Internet banking is one of the popular modes of E-banking. It has made banking not only personalized but also customized. It enables to obtain general purpose formation by a customer through banks “websites, electronic fund transfers (EFT), Electronic payments such as E-cheque, and card-based payments (credit cards, debit cards, and smart cards) these are called Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS). The RTGS provides continuous processing and enables the settlement of fund transfers.
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS):
Real-time refers to the process of instructions that are executed immediately after they are received. Gross Settlement means settlement of funds transfer and thus payments are considered final and irrevocable.
Electronic Clearance Service (ECS):
This scheme provides an alternative method of effecting bulk payment transactions periodically.
National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT):
NEFT means allowing individuals and firms to transfer their funds from one bank to another bank. There is no ceiling on the minimum or maximum funds according to RBI.
Question 3.
What is planning? Do you think planning can work in a changing environment?
Answer:
Planning is deciding in advance what to do and how to do it. It is one of the basic managerial functions. Before doing something, the manager must formulate an idea of how to work on a particular task. Thus planning is closely connected with creativity and innovation. But the manager would first have to set objectives, only then will a manager know where he has to go. Planning seeks to bridge the gap between where we are and where we want to go. It requires deciding since it involves choosing from an alternative course of action.
Planning involves setting objectives and developing appropriate courses of action to achieve these objectives. Objectives provide direction for all managerial decisions and actions. All members need to work towards achieving organizational goals. These goals set the targets which need to be achieved. This plan should be forecasting the future course of events. There are many steps in planning.
- Determination of objectives for the whole organization.
- Laying down policies to be followed.
- Laying down the standards of performance.
- Preparation of budgets for the whole organization.
Planning can work in a changing environment explained below.
1. Focus on Objectives:
Planning determines the objectives of the enterprise and also various departments. Besides it devises the ways for achieving the objectives, good plan is required. Planning compels managers to consider the future and makes them recognize the need for revising and extending plans in light of the dynamic business environment.
2. Economical Operation:
The working of the enterprise will be systematic and purposeful. Under planning there will be jointly directed effort instead of uncoordinated decisions made based on facts. The resources are utilized in the best possible way.
3. Reduces Uncertainty and Change:
An enterprise works in a dynamic world. The future is uncertain. Changes take place in the business environment, economic policies, and supply of resources. There may be changes in technology. Planning can work in a changing environment.
4. Facilitates Control:
Planning helps the managers to exercise proper and effective control over their subordinates. In a planned organization, the work to be done is determined in advance. This enables the management to check on the performance of subordinates.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
What are the differences between the primary market and the secondary market?
Answer:
| Concept | Primary Market | Secondary Market |
| 1. Nature | It is concerned with the issue of new shares. | It is concerned with the marketing of existing shares. |
| 2. Sale of Securities | It enables the company to sell securities to the investors directly or through intermediaries. | It helps the holders of securities to exchange their securities. |
| 3. Capital Formation | It is directly connected with the promotion of capital formation. | It is indirectly connected with the promotion of capital formation. |
| 4. Securities Dealing | It deals with the buying of securities. | It enables both buying and selling of securities. |
| 5. Value of Securities | It enables the management of the company to decide the value of the securities. | It enables the demand and supply to determine the price of securities. |
| 6. Location | It has no fixed geographical location. | It is located at specific places. |
Question 5.
Explain any five principles of Insurance.
Answer:
It is the provision that a prudent man makes against untoward happenings which may occur by chance and carried out through the transfer of risks of many individuals to one person or a group of persons.
1. Utmost Good Faith:
The contracts of insurance are included in the category of contracts. Those contracts require absolute and utmost faith on the part of the parties concerned.
2. Insurable Interest:
No person can enter into a valid contract of insurance unless he has an insurable interest in the object. Essentially speaking, insurable interest is like financial interest in a life or things.
3. Indemnity:
All contracts of insurance, except for life insurance contracts, are contracts of indemnity. The principle of indemnity does not apply to life and other kinds of personal insurance. In such cases, the loss caused by the death of a person cannot be calculated in terms of money, nor is money any compensation for the loss of life.
4. Subrogation:
According to the insurer steps into the shoes of the insured and becomes entitled to all rights of the insured regarding the subject matter of insurance after the claim of the insured has been fully settled.
5. Contribution:
In such cases, the companies concerned will follow the principle of contribution. Each company will contribute that proportion of the loss that the policy issued bears to the total amount for which insurance has been effected with all the companies.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the need for entrepreneurship?
Answer:
They are following the need for entrepreneurship.
1. Formation of Capital:
Entrepreneurs’ efforts to mobilize the capital result in motivating the investors to divert their idle savings in industrial securities. Investment of public money in the industrial sector helps the country to use such resources for productive purposes.
2. Balanced Regional Development:
Entrepreneurs in the public and private sectors help to remove regional disparities by setting up industries in backward areas.
3. Generates Employment:
Entrepreneurs help in generating employment directly and indirectly. They do not depend on government jobs and private jobs.
4. Improvement of Per Capita Income:
This will increase the national income and wealth of a nation. The increase in national income is an indication of an increase in the per capita income of the country.
5. Improvement of Standard of Living:
Small-scale industries set up by entrepreneurs help to avoid scarcity of goods and improve the standard of living for consumers.
6. National Self-Reliance:
Entrepreneurs are very much required for national self-reliance.
7. Planning Production:
Entrepreneurs are considered economic agents since they unite all means of production.
8. Backward and Forward Linkages:
Always the entrepreneur initiates change and tries to maximize his profits by innovations. Setting up of an enterprise by the changing technology.
9. Dispersal of Economic Power:
The modern world is dominated by economic power. Economic power is the natural outcome of industrial.
Question 7.
Explain the objectives of EDP (Entrepreneurial Development Programme).
Answer:
The main objectives of an EDP (Entrepreneurial Development Programme) are as follows.
- To identify and train potential entrepreneurs.
- To impart basic managerial understanding.
- To select the right project and product.
- To provide post-training assistance.
- To formulate an effective and profitable project.
- To make him learn compliance with the law.
- To develop a broad vision of the business.
- To make him subscribe to industrial democracy.
- To develop a passion for integrity and honesty.
- To enable him to communicate clearly and effectively.
Question 8.
What are the advantages of SEZ (Special Economic Zones)?
Answer:
The following are the major benefits of SEZs.
- Employment generation: SEZs are viewed as highly effective tools for job creation.
- Economic development: SEZs are viewed as the engines for economic development.
- Growth of labor-intensive manufacturing industry: The establishment of SEZs would lead to feist growth of labor-intensive manufacturing and service industries in the country.
- Balanced regional development: SEZs are beautifully crafted initiatives for achieving balanced regional development.
- Capacity building: SEZs are important for stronger capacity building.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain any five principles of Management.
Answer:
‘Henry Fayol’ has been rightly called the “Father of administrative management” for his practical approach to management theory. He has identified 14 fundamental principles of management. Those are:
- Division of labor and specialization
- Parity of authority and responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of command
- Unity of direction
- Subordination of individual to general interest
- Remuneration of personnel
- Centralization
- Scalar chain
- Order
- Equity
- Stability of tenure of personnel
- Initiative
- Esperit-de-corps
1. Division of Labour and Specialisation:
Division of labor leads to specialization which increases the efficiency of individual employees. Division of labor is a famous principle of economics. Fayol applied this principle to management. He recommended work of all kinds must be subdivided and allocated to several persons. Subdivision makes each task simpler and results in greater efficiency.
2. Parity of Authority and Responsibility:
According to Fayol, authority and responsibility must flow in the same direction. Responsibility is the natural outcome of authority. A proper balance between authority and responsibility helps to prevent the misuse of authority and promotes a fair fixation of responsibility.
3. Discipline:
Discipline means the observation of certain rules and regulations. People in the organization should be bound to accept certain codes of conduct. The three basic requisites of discipline are disciplined supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreement on goals, and judicious application of penalties.
4. Unity of Command:
The principle states that a subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to one and only one superior. No employee, therefore, should receive instructions from more than one person. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict.
5. Unity of Direction:
Unity of direction is essential for achieving unity in action, in the pursuit of common goals by a group of persons. For this Fayol advocates ‘one head and one plan’. Unity of direction (one head, one plan) is not the same as unity of command (one employee receives orders from one superior).
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
SEBI
Answer:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) helps to overcome undesirable practices in the stock exchange. It is the controller of capital issues. It was established in the year 1988 (1-4-1988). Its headquarters is located in Mumbai.
Question 11.
Internet Banking.
Answer:
Internet banking is one of the popular modes of E-banking. It has made banking not only personalized but also customized. It enables to obtaining general-purpose information from a customer through bank websites, and Electronic Fund Transfers (EFT) through passwords. Electronic payment can be effected through electronic means. Such as E-cheques, card-based payments, and electronic fund transfers.
Question 12.
Balanced Regional Development.
Answer:
Entrepreneurs in the public and private sectors help to remove regional disparities by setting up industries in the backward areas. The government gives various concessions and subsidies to the entrepreneurs.
Question 13.
Project Report.
Answer:
It is the document prepared by the entrepreneur where he has to put his ideas and other information in black and white.
Question 14.
Street Stalls
Answer:
Street Stalls: Street traders display their products on pavements and street corners of different localities in urban areas.
![]()
Question 15.
Second-hand goods shop.
Answer:
Second-hand goods shops: Second-hand goods shops deal in used articles or second-hand goods such as old furniture and old books. In these shops the goods price is low.
Question 16.
Letter of Credit.
Answer:
It is a letter that is obtained by an exporter to satisfy himself about the creditworthiness of an importer.
Question 17.
Scientific Management.
Answer:
It was introduced by F.W. Taylor scientific management is the art of knowing exactly what you want your men to do and then seeing that they do it in the best and cheapest way.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
Question 18.
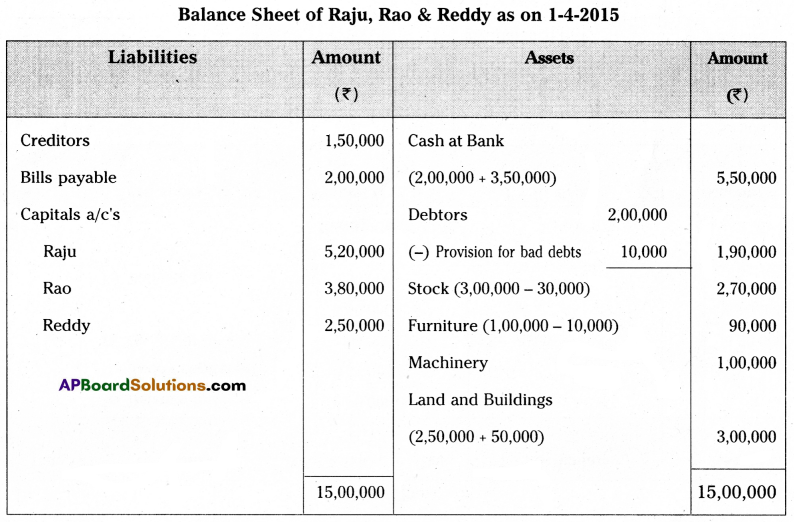
Raju and Rao are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their balance sheet as of 31, March 2005 was as under.
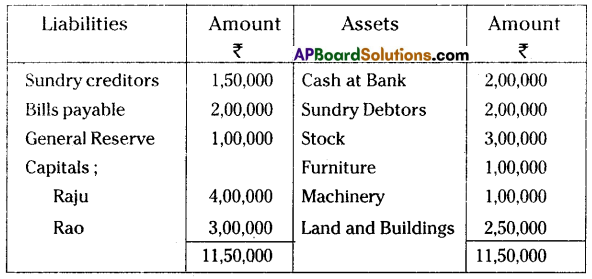
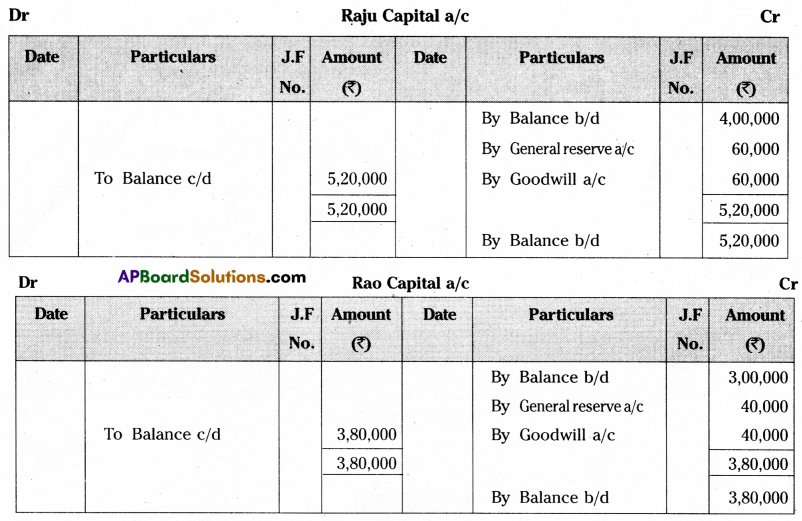
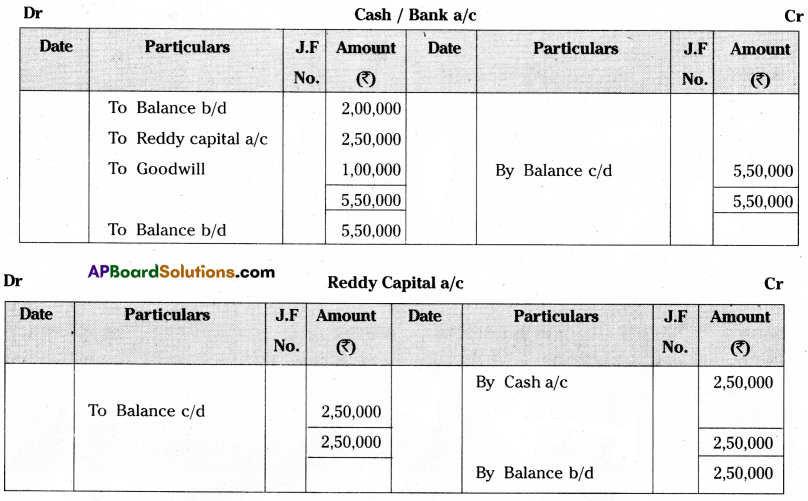
They decided to admit Mr. Reddy into partnership by giving him 1/4th share in future profits of the firm under the following conditions:
(a) Reddy is to bring ₹ 2,50,000 as capital and ₹ 1,00,000 as goodwill in cash.
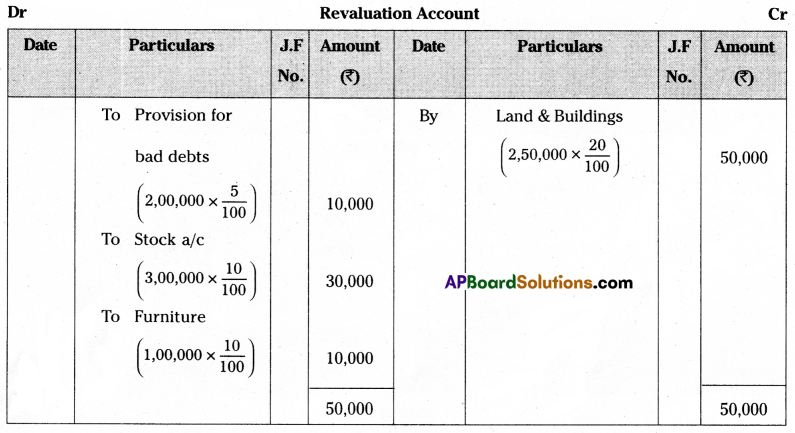
(b) Stock and furniture to be depreciated by 10%.
(c) Make a provision of 5% on sundry debtors.
(d) Land & Buildings are to be appreciated by 20%.
Prepare necessary ledger accounts and show the new balance sheet.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
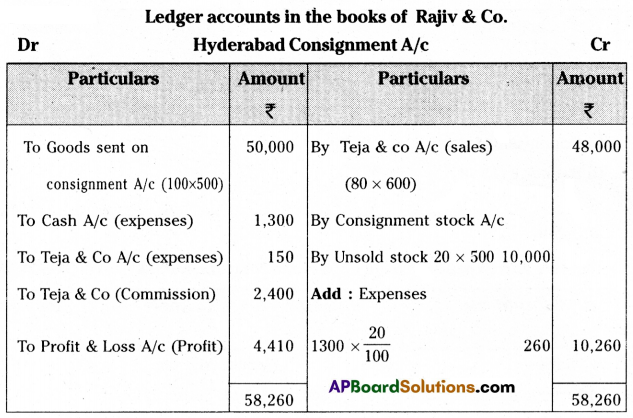
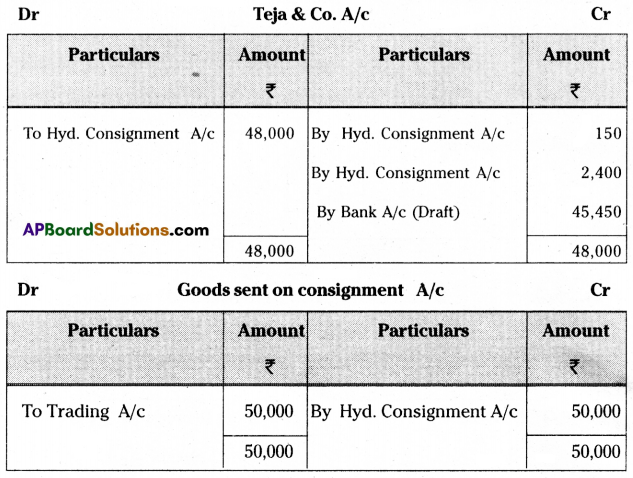
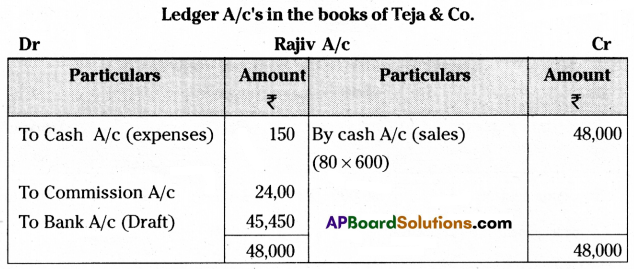
Rajiv & Co. of Chennai consigned 100 Radios to Teja & Co. of Hyderabad. The cost of each radio was ₹ 500. Rajiv & Co. paid insurance ₹ 500, and freight ₹ 800. Account sales were received from Teja & Co. Showing the sale of 80 Radios at ₹ 600 each. The following expenses were deducted by them.
Selling expenses ₹ 150
Commission ₹ 2,400
Rajiv & Co. received a bank draft for the balance due. Prepare important ledger accounts in the books of Rajiv & Co. and Teja & Co.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
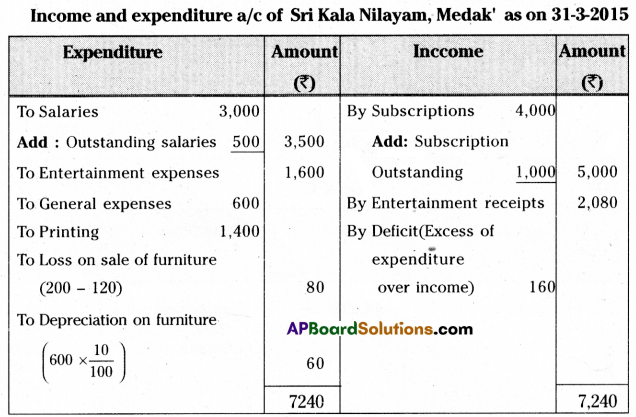
From the following receipts and payments account of Sri Kala Nilayam, Medak for the year ended 31-03-2015, prepare income and expenditure account.
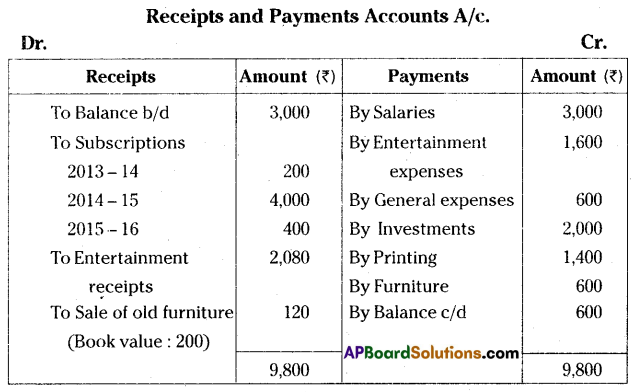
Additional Information:
1. Outstanding Salaries ₹ 500.
2. Subscriptions outstanding for 2014-15 ₹ 1,000.
3. Depreciate furniture by 10%.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
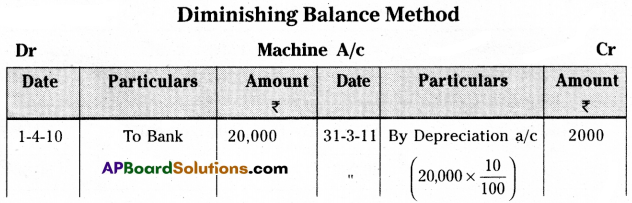
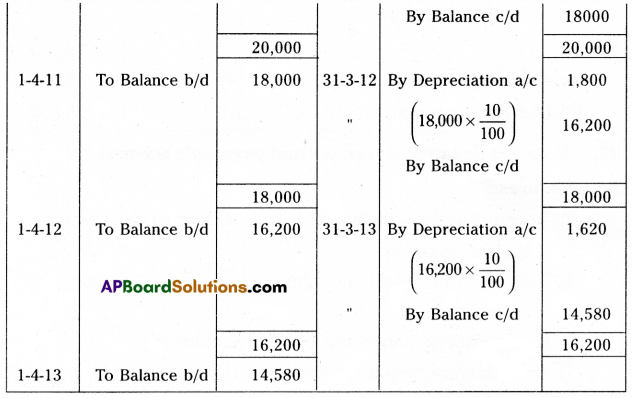
Madhu and Co. purchased a machine on 1st April 2010 for ₹ 20,000. Depreciation is charged at 10% under the diminishing balance method. Prepare machine a/c upto 31st March 2012.
Answer:
Question 22.
Mohan Commenced his business with a capital of ₹ 35,000 on 1st April 2008. His position as of 31st March 2009 was as follows.
Sundry creditors – ₹ 12,000
Bills payable – ₹ 9,000
Bills receivable – ₹ 22,000
Debtors – ₹ 38,000
Cash at Bank – ₹ 4,000
Furniture – ₹ 21,000
Machinery – ₹ 26,000
Stock – ₹ 10,500
On July 1st he sold his motorbike for ₹ 20,000 and invested the same in his business and also he withdrew ₹ 2,000 per month. Prepare a statement of affairs and also find out the profit earned by him.
Answer:
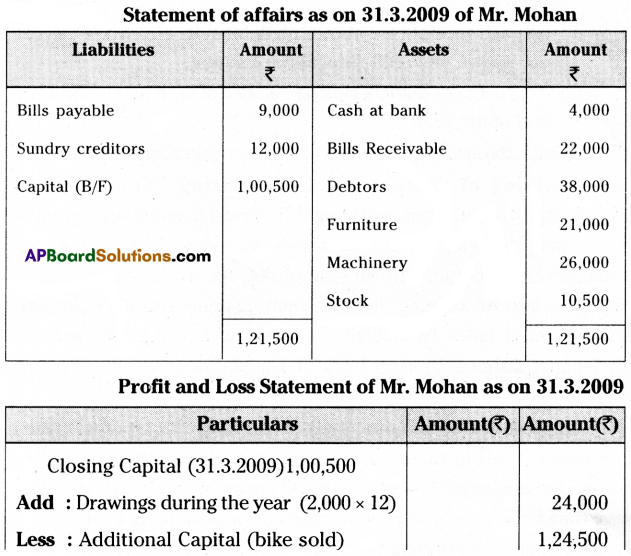

Question 23.
Write the features of receipts and payments account.
Answer:
- Receipts and payment accounts are similar to cash books.
- It is a real account.
- This account reveals opening and closing balances of cash and bank.
- It is maintained and the cash basis of accounting.
- Credit transactions are not recorded in receipts and payment accounts.
- All cash receipts are shown on the debit side, and all cash payments are shown on the credit side of the account.
- This account depicts the closing balance of cash and bank at the end of the year.
Question 24.
What is the meaning and importance of computerized accounting?
Answer:
Meaning of Computerised Accounting:
Computerized accounting is nothing but replacing the manual accounting system of maintaining the books of accounts with the use of relevant software packages for accounting on a computer. As its name suggests, “Computerised Accounting” is an accounting done with the support of a computer. It tends to involve dedicated accounting software and digital spreadsheets to keep track of a business or client’s financial transactions.
Importance of Computerised Accounting:
Computers play a predominant role in an accounting system. Computerized accounting systems are important to business by all means. The use of computers saves time for business and all financial information for the business is integrated and well organized. Accounting is a financial method used by businesses to collect, organize, process, and summarise data for reports and statements. Computer and business software allow more efficient processing and organization of data.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
Define the term Depreciation.
Answer:
The diminution in the financial value of a fixed asset owing to wear and tear, effluxion of time, obsolescence, or similar causes.
Question 26.
Features of Single Entry.
Answer:
- This system generally maintains personal accounts of debtors and creditors only.
- It does not consider real and nominal accounts.
Question 27.
Overriding Commission.
Answer:
It is an extra commission granted when the consignor wants his agent to put in extra hard work to increase sales, especially in the case of new products. It is calculated on total sales.
Question 28.
Not-for-profit organisations (Non trading).
Answer:
The organizations, whose main object is not to earn profit but to render service to their members are called not-for-profit organizations.
Question 29.
A and B are partners sharing profits and losses equally. They decided to admit Krishna for 1/5th share of profit in the business. Calculate the new profit-sharing ratio of A, B & C.
Answer:
The Old Ratio of A and B is 1 : 1
Krishna Share (given) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Remaining Share = 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
New Ratio of ‘A’ = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{4}{10}\)
New Ratio of ‘B’ = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{4}{10}\)
New Ratio of ‘C’ = \(\frac{1}{5} \times \frac{2}{2}=\frac{2}{10}\)
∴ New Ratio of A, B and Krishna = \(\frac{4}{10}: \frac{4}{10}: \frac{2}{10}\) = 4 : 4 : 2 = 2 : 2 : 1.
![]()
Question 30.
What is the Gaining Ratio?
Answer:
On the retirement of a partner from the partnership business, the remaining or continuing partners stand to gain. Because the share of profit enjoyed by retiring partners hereafter will be enjoyed by continuing partners. Therefore the continuing partners will benefit. The benefit or gain may not be equal. Therefore it is necessary to calculate the ratio in which the continuing partners gain on retirement of a partner.
∴ Ratio of Gaining = New Ratio – Old Ratio
Question 31.
Computerized accounting is more useful than manual accounting comments.
Answer:
Computerized accounting is more useful than manual accounting because it has unique features. They are
- Fast, powerful, and simple
- Accuracy and Error-free
- Improved user-free experience
- Improved business performance
- Rapid decision making
Question 32.
Wings
Answer:
Wings: Wings accounting NXT is the next-generation accounting and inventions software giving total control over finance and inventory of business concerns all the time. Wings have a simple interface. Right-click menus give the user easy access to common commands.