Collaborative study sessions centered around TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2017 can enhance peer learning.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2017
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations.
Answer:
Partnership is defined by section 4 of Indian Partnership Act of 1932 “as the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them act for all”.
Merits:
- Easy formation: It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsory.
- Large resources : The resources of more than one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial Capacity: They pool capital, organising ability, managerial capacity etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making: The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility: The partnership is flexible in nature and at any time after mutual consent, the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations.
- Sharing risks: The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach : The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation : All partners actively participate in the business as per their specialisation and knowledge.
Limitations:
- Unlimited liability : The unlimited liability is the fundamental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability : The partnership firm suffers from uncertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- Limited resources: There is limitation in raising additional capital for expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners.
- Non-transferability of share : No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust: The mutual distrust among partners is the main cause for the dissolution of the partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions: Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
Question 2.
What is a Joint Stock Company ? What are the features of it ?
Answer:
“A Company is an association of persons who contribute money or money’s worth to a common stock and employ it in some trade or business and share the profits or losses arising there from”.
– L.J. Lindley
A Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association of individuals for profit having a capital divided into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition of membership”.
From the above definitions, the features of Joint Stock Company is as given below.
Features:
- Association of persons : A company is an association of persons join hands with a common motive earning profits through business.
- Separate legal entity : The company is created by law. It has a separate legal entity apart from its members. Eventhough it is invisible and intangible having no body or soul, it can act just like any other human being. It can enter into contracts, purchase and sell goods, conduct lawful business in its own name. It can sue and can be sued in a court of law.
- Perpetual existence: The company has a perpetual exist-ence. The shareholders may come or may go but the company will go on forever. The continuity of the company is not affected by death, lunacy or insolvency of shareholders.
- Common seal: A company being an artificial person can-not put its signature. The law requires every company to have a seal and get its name engraved on it. The seal of the company is affixed on all important documents and contracts signature.
- Limited liability : The liability of shareholders is limited to the value of the shares they have purchased.
- Transferability of shares : The shareholders of the public company is free to transfer their shares. They do not need the consent of other shareholders.
- Separation of Ownership and Management: The share-holders are the owners of the company. But they are too many. They are widely scattered and cannot take part in the day-to-day affairs of the company. The management is entrusted to Board of Directors who are elected by the shareholders. So, the ownership is separated from management.
- Membership : To form a Joint Stock Company minimum two members are required in the case of private company and seven members in the case of public company. The maximum membership is fifty in private companies and unlimited in public companies.
- Formation: The Company comes into existence only when it is registered under the Indian Companies Act, 1956.
- Submitting annual statements: A Joint Stock Company is required to file annual statements with the Registrar of companies at the end of the financial year. These statements are available for inspection in the office of the Registrar.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Business Finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organisation.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called business finance.
R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
Need and significance of business finance :
- To commence a new business : Money is needed to start a new business and to procure fixed assets like land and buildings etc., working capital is required to meet the day-to-day expenses and holding current assets like cash, stock-in-trade etc.
- To expand the business: Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
- To develop and market new products: Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products.
- To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
- To take over another business : In order to overcome competition an enterprise may decide to take over another business.
- To more to new premises : Sometimes a business may be forced to shift the business in another place.
- Day-to-day running : A business needs money to meet the day-to-day requirements like wages, taxes etc.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each :
Question 4.
Define Trade’ and explain the various types of aids to trade.
Answer:
All the human activities engaged in buying and selling of goods and services comes under trade. Therefore trade includes sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services with the intention of making profit. The object of trade is to make goods available to those who need them and willing to pay for them. Trade is the final stage of business activities and involves transfer of ownership.
Aids to trade : Trade or exchange of goods and services involves several difficulties which can be removed by aids to trade. Aids to trade refer to those activities which directly or indirectly facilitate smooth exchange of goods and services.
Aids to trade includes transport, warehousing, banking, insurance, advertising and communication.
1) Transport: All the goods are not consumed at the same place where they are produced. Goods are to be moved from the places of production to the places where they are demanded. The activity concerned with the movement of goods is called transpor-tation. It can be done by rail, road, water and air.
2) Warehousing : Goods are produced in anticipation of demand. There is time gap between production and consumption. Hence, it became necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. Agricultural products like wheat and rice are seasonal in nature but they are consumed throughout the year. On the other hand, goods such as umbrellas and woollen cloths are produced throughout the year but they are demanded only during particular season. Therefore, these goods need to be stored in warehouses till they are demanded. Warehousing creates time utility.
3) Insurance : Business is subject to risks and uncertainities. Risks may be due to theft, fire, accident or any other natural ca-lamity. Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Insurance compa-nies who act as risk bearers covers risks.
4) Banking: Producers and traders require money for carrying on production and trade. Banks are the institutions which supply funds for industries and trade. They pool savings from the public and make them available to industries. So, banking is an important function of commerce.
5) Advertising: Exchange of goods is possible when the con-sumers have the knowledge about the existence of the product. Through advertisement, producers communicate all information about the goods to prospective consumers. It creates a strong desire to buy the product. Advertising is done through T.V, radio, newspapers, magazines, hoarding, wall posters etc.
6) Communication : Communication means exchange of information from one person to another. It is necessary to finalise and settle terms such as price, discount, facility of credit etc. Modem means of communication like telephone, telex, e-mail, teleconference etc., play an important role in establishing contact between businessmen, producers and consumers.
Question 5.
What is Joint Hindu Family business and discuss its main features ?
Answer:
This form of organisation is prevalent in India only and that to among Hindus. It does not have any seperate and distinct legal existance from that of its members. No outsider can be admitted into this form of business and the membership can be acquired by birth. The business of Joint Hindu Family is controlled under the Hindu law.
All the affairs of the Joint Hindu family are controlled and managed by the senior male member of the family known as Karta or Manager. The other members are co-parceners. He works in consultation with other members of the family and act on behalf of them. He is not accountable to any one. He has a final say on all the matters. The liability of the Karta is unlimited but the liability of the other members is limited to their share in the business.
Joint Hindu family business is governed by two laws – Dayabhaga and Mitakshara.
Mitakshara: It is applicable to whole of India except Assam and Bengal. According to this law, three successive generations in the male line (son, grand son, great grand son) inherit the ancestral property by birth.
Dayabhaga: It is applicable in Assam and Bengal. According to this, the male heirs become members only on the death of the father.
Features or characteristics of Joint Hindu Family Business :
- Formation : The Joint Hindu Family Business is created by the operation of Hindu law. There must be atleast two members in the family having some ancestral property. It is not created by an agreement but by operation of law.
- Membership : There are two types of members in a Joint Hindu Family Business viz. The Karta who is the male head of the family and the co-parceners who are the male members of the family.
- Liability: The liability of Karta is unlimited whereas the liabilities of co-parceners are limited to their interest in the Joint Hindu Family Business.
- Management: The right of management is vested with Karta. Other co-parceners have no right to participate in the management and even cannot inspect the books of accounts.
- Profit sharing : All co-parceners have equal share in the profits of the business.
- Continuity: Death of any co-parcener does not effect the continuity of business. Even on the death of Karta, it continues to exist as the eldest of co-parceners takes position of Karta.
- Legal status: A Joint Hindu Family Business do not enjoy a separate legal status. It is not separable from the members who constituted it.
Question 6.
Explain the functions of promoters.
Answer:
A promoter conceives an idea for setting up a particular business at a given place and performs various formalities required for starting a company. A promoter may be an individual, a firm, association of persons or a company. Promoter takes lead for bringing money, men, machinery and material together for establishing an enterprise.
Promoter performs the following functions.
- A promoter conceives an idea for the setting up of a business.
- He makes preliminary investigations and ensures about the future prospects of the business.
- He brings together various persons who agree to associate with him and share the business responsibilities.
- He prepares various documents and gets the company incorporated.
- He raises the required finances and gets the company going.
Question 7.
Differentiate between a share and a debenture.
Answer:
| Shares | Debentures |
| 1. A share is a part of owned capital. | 1. A debenture is an acknowledgement of debt. |
| 2. Shareholders are paid dividend on the shares held by them. | 2. Debentureholders are paid interest on debentures. |
| 3. The rate of dividend depends upon the amount of divisible profits and policy of the company. | 3. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures irrespective of profit or loss. |
| 4. Shares are not redeemable except redeemable preference shares during the life time of the company. | 4. The debentures are redeemed after a certain period. |
| 5. At the time of liquidation of the company, share capital is payable after meeting all outside liabilities. | 5. Debentures are payable in priority over share capital. |
Question 8.
Define Multi-National Corporations and explain any four features of MNCs.
Answer:
A Multi National Corporation may be defined as a company that operates in several countries. Such a company has factories, branches or offices in more than one country. The operations of multinational company extend beyond the country in which it is incorporated. Its head quarters are located in one country (Home country). It carries on business in other countries. (Hot countries)
Definition :
According to international Labour Organisation’s report, multi-national corporation refers to an enterprise whose managerial head quarters are located in one country, while it carries out operations in number of other countries as well.
According to Prof. Vernon it is defined as a cluster of operations of diverse nationality joined together by common management strategy”.
Features of MNC:
- Global Operations : Multi-National Corporations carry production and marketing operations in different countries of the world. They possess all the infrastructural facilities in all the countries of their operations.
- Giant Size : The assets and sales of MNC are quite large. The sales turnover of some MNCs extend the gross national product of several developing countries.
- Centralised Control : It has its head office in home country. It exercises control over all branches and subsidiaries.
- Dominant Position and Status : They occupy a dominant position in the market due to their giant size. They also takeover the firms to acquire huge economic power.
- Internationalised Research and Development: These are intended to capture the quality and serve according to the requirements of the host nation.
- Sophisticated Technology : MNC has advanced techno-logy so as to provide world class products and services. It employs capital intensive technology in manufacturing, marketing and other areas of business.
- Professional Management: A MNC employs professional managers to integrate and manage world wide operations.
![]()
Question 9.
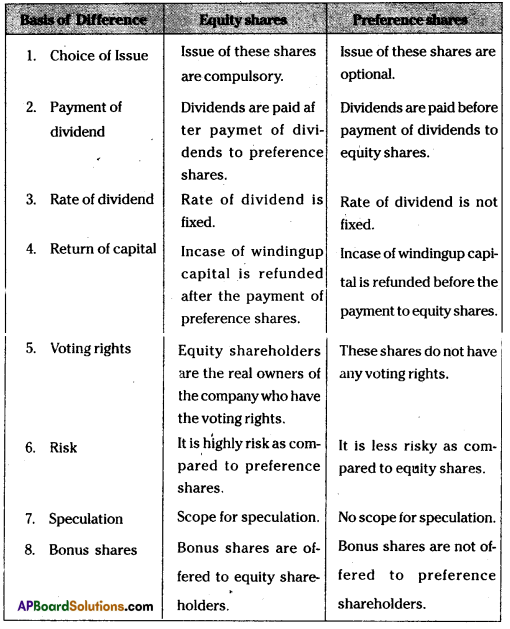
Write the differences between the equality shares and preference shares.
Answer:
The following are the differences between equity shares and preference shares.
Section – C
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each:
Question 10.
What is profession ?
Answer:
Profession is an occupation involving the provision of personal services of a specialised and expert nature. The service is based on professional education, knowledge, training etc. The specified service is provided for a professional fees charged from the clients. For example, a doctor helps his patients though his expert knowledge of science of medicine and charges a fee for the service.
Question 11.
Define sole proprietorship.
Answer:
Sole trade is the odest and most commonly used form of business organisation. It is also known as sole proprietorship, individual partnership, single entrepreneurship. In sole trade concern a single individual introduces his own capital, skill and intelligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is the easiest to form and is also the simplest in organisation.
All that is required is that the individual concerned should decide to carry on particular business and find the necessary capital. For this purpose, he may depend mostly on this own savings or he may borrow part or shile from his friends or relatives. He can start business in his own house or on rented premises. He may run the business on his own or may obtain the assistance of his family members or paid employees.
A sole trader is a person who sets up the business with his own resources, manages the business himself by employing persons for his help and alone bears all gains and risks of the business.
Question 12.
What do you mean by co-operative society ?
Answer:
Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interests. It works on the principle of self help and mutual help. The motto of cooperative society is “Each for all and all for each”. People come forward as a group, pool their individual resources, utilise them in the best possible manner and derive some common benefits out of it.
Question 13.
Define ‘Memorandum of Association’.
Answer:
The Memorandum of Association is the constitution of the company. It is the charter of the company. It provides the foundation on which the company structure is built. It defines the scope of companies activities as well as relation with the outside world. The purpose of memorandum, is to enable the shareholders, creditors and those who deal with the company to know the permitted range of activities of the company.
Question 14.
What is working capital ?
Answer:
The capital required by business enterprise to run its day- to-day operations such as purchase of raw materials, payment of wages and holding current assets like stock of raw materials, bills receivable is called working capital. The amount of working capital required varies from business to business. Generally trading concerns require more working capital as compared to manufacturing concerns.
Question 15.
What is meant by retained earnings ?
Answer:
Retained earnings or ploughing back of profits refers to the process of reinvestment of the earning of the year after year. In this technique all the profits are not distributed to shareholders. A part of the profit is retained in the business as a reserve which are used for financing long term and short term needs of the company.
Question 16.
Define Micro Enterprise.
Answer:
In case of manufacturing enterprises, a micro enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in plant and machinery does not exceed ₹ 25 lakhs. In case of service enterprises, a Micro Enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment does not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs.
Question 17.
What do you mean by ‘e-business’ ?
Answer:
The term E-business was first used in IBM in 1997. It defined E-business as ” The transformation of key business processes through the use of internet technology”. E-business is defined “as the application of information and communication technologies which support all the activities of the business with customers”.
Part – II
(Marks – 50)
Section – D
Answer the following question :
Question 18.
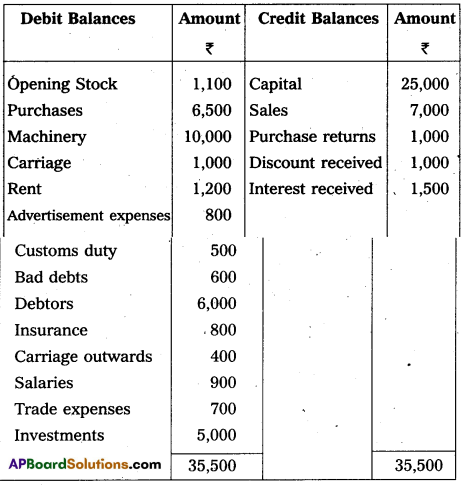
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Final Accounts of Vikram as on 31-03-2015 :
Trial Balance
Adjustments:
(1) Closing stock – ₹ 6,000.
(2) Prepaid Insurance – ₹ 200.
(3) Outstanding Salaries – ₹ 600.
(4) Accrued Interest – ₹ 500.
Answer:
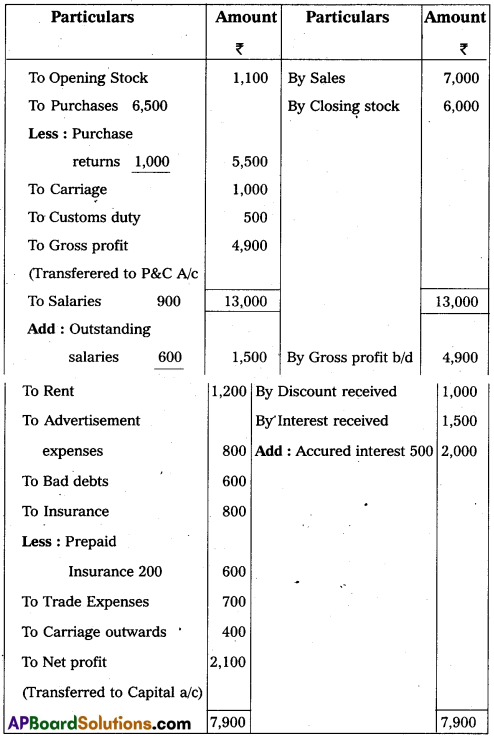
Trading Profit and Loss A/c of Vikram as on 31-3-2015
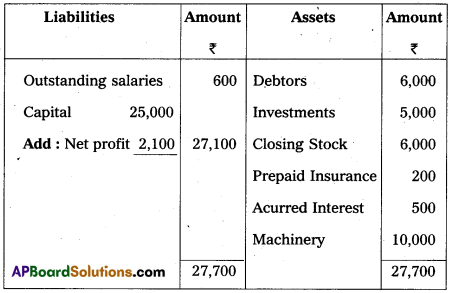
Balance sheet of Vikram as on 31-3-2015
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following question :
Question 19.
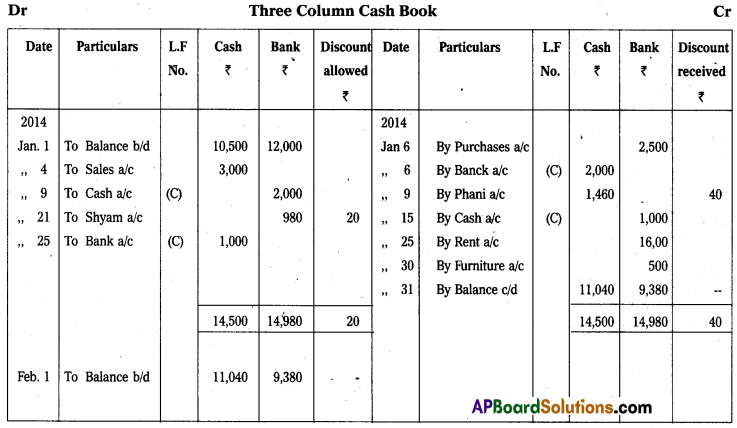
Prepare three column Cash Book from the following information :

Answer:
Question 20.
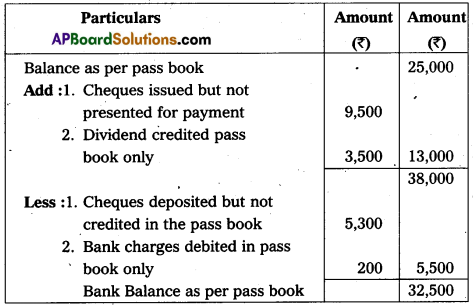
From the following information, prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement of Manisha & Co. as on 31st December, 2013 :
(a) Bank balance as per Cash Book ₹ 25,000.
(b) Cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 9,500.
(c) Cheques deposited into Bank but not credited upto December 31, 2013 – ₹ 5,300.
(d) Bank credited ₹ 3,500 for receiving dividend through Electronic Clearing System.
(e) Bank charges debited by Bank ₹ 200.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Manisha & Co as on 31.12.2013
Section – F
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain the different types of Accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
Answer:
Accounts are broadly divided into three types.
- Personal Accounts : These accounts relate to persons or firms. Ex.: Rama’s a/c, Gopal’s a/c, Andhra Bank a/c. The rule in personal accounts is “Debit the receiver and credit the giver”.
- Real Accounts : These accounts relate to assets and properties. Ex.: Cash a/c, Stock a/c, Buildings a/c.
The rule in real accounts is “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”. - Nominal Accounts : These accounts relate to expenses losses, incomes and gains. Ex. : Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Interest received a/c. The rule in nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains”.
![]()
Question 22.
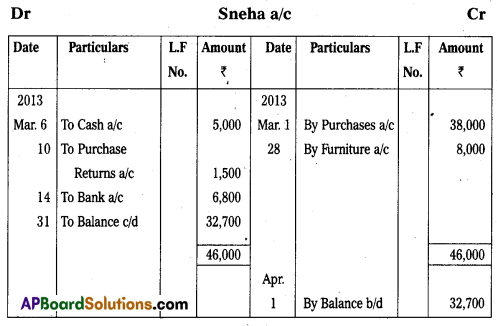
Prepare ‘Sneha’ account from the following :

Answer:
Question 23.
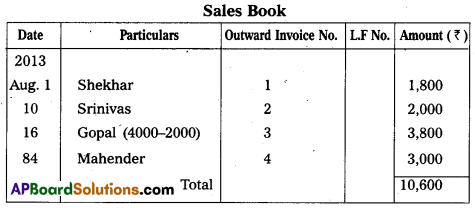
Prepare Sales Book from the following particulars :

Answer:
Question 24.
What are the various types of Errors ? Explain.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors
1) Error of principle: Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors : When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is called clerical errors. They are again divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors: These errors arise when one error is compensated by other error or errors.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions :
Question 25.
What is Book-Keeping ?
Answer:
Book-keeping is the art of recording business transactions in regular and systematic manner. According to Carter “Book-keeping is the science and art of correctly recording books of accounts all those business transactions that result in transfer of money or money’s worth.
Question 26.
Explain Business Entity concept of Accounting.
Answer:
Business is treated as separate from the proprietor. All the transactions are recorded in the books of business but not in the books of proprietor. The proprietor is also treated as creditor of the business when he contributes capital he is treated as a person who has invested amount in business. So, capital appears on the liabilities side in the Balance Sheet.
Question 27.
Pass Journal Entries in the books of Sirini:

Answer:
Journal Entries in the books of Sirini.
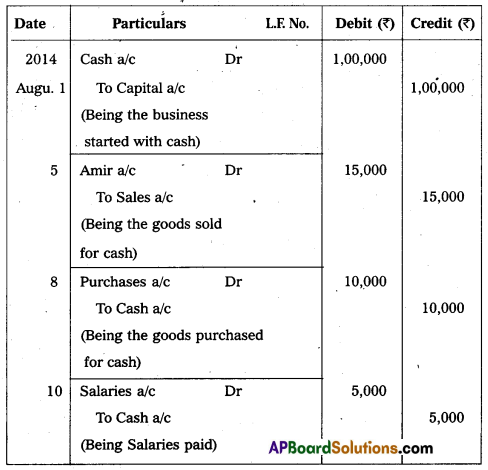
Question 28.
What do you know about ’Contra Entry’ ?
Answer:
Contra means the other side. If the double entry of a transaction is complete in the cash book itself such entry is called contra entry. Contra entry arises when cash and bank accounts are simultaneously involved in a transaction. It happens when either cash or cheqeus are deposited in the bank and cash is withdrawn for office use. In both the cases entries are made in cash and bank columns.
Question 29.
Write opening Journal Entry form the following as on 1st April,
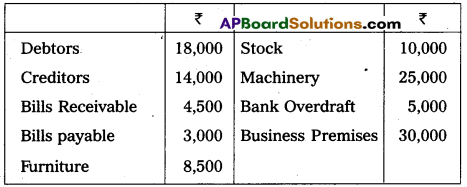
Answer:
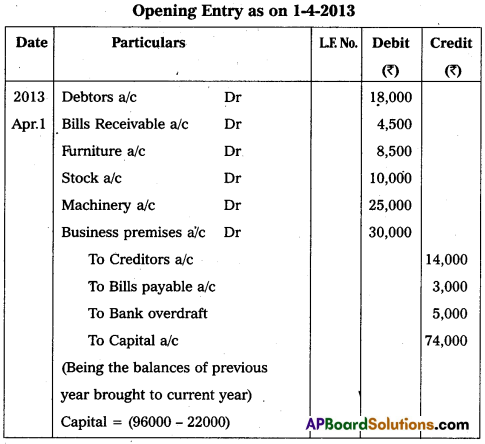
Opening Entry as on 1-4-2013
Question 30.
What is meant by Bank Reconciliation Statement ?
Answer:
The statement prepared for reconciling the balance of cash book and pass book is known as Bank Reconciliation Statement. Kohler explains it as “A statement displaying the items of difference between the balance of an account reported by a bank and the account appearing on the books of bank customer”. Bank Reconciliation Statement may be defined as “a statement prepared with uncommon adjustments of cash book and pass book to find out the reasons of difference in the balance as shown by traders cash book and bankers pass book”.
![]()
Question 31.
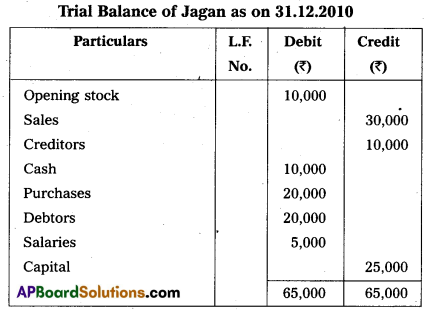
Prepare Trial Balance of Jagan from the following balances as on 31-12-2010.
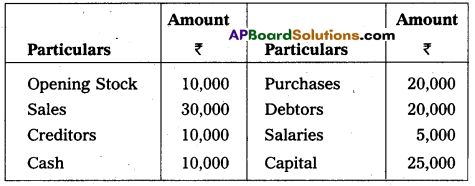
Answer:
Question 32.
Suspense Account.
Answer:
Suspense account is an imaginary account, opened and used as a temporary measure to make the two side of the trial balance agree. As and when the errors which causes the disagreement in trial balance is detected, rectification entries should be passed through suspense account. Detection and rectification of all the errors will result in automatic closure of suspense account.