Collaborative study sessions centered around TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2017 can enhance peer learning.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2017
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Discuss the different types of partners.
Answer:
There are different types of partners in a partnership firm. They are :
1) Active Partner: An active partner is one who takes active part in the day-to-day working of the business. He may act in various capacities as manager, advisor or organisor. He is also known as working partner or managing partner.
2) Sleeping Partner: A sleeping partner or dormant partner is one who contribute capital, share profits and losses but does not take part in the working of the concern. He is not known to the public. So, he is also called as secret partner.
3) Nominal Partner : A nominal partner is who lends his to the firm. He does neither contribute any capital nor does he shares profits of the business. They do not participate in the management of the business. But they are liable to third parties for all acts of the firm.
4) Partners in Profits : He is a partner who shares in the profits of the firm but not losses. But he is liable to third parties like any other partner. He is not allowed to take part in the man-agement of the business.
5) Partner by Estoppel: When a person is not a partner, but posses himself as partner either by words or in writing or by his acts, he is called partner by estoppel. He neither contributes the capital nor participate in profits and losses. But he is liable to any creditor like any other partner.
6) Partner by Holding out: If a person is considered by out-sider as partner in the firm and he does not disclaim it, he is called partner by holding out. He neither contributes the capital to the firm nor participate in profits and losses! But he is liable to third parties for the debts of the firm.
7) Limited Partner : The liability of limited partners is lim-ited to the extent of their capital contribution. This type of part-ners found in limited partnership.
8) General Partners : The partners having unlimited liability are called general partners.
9) Minor Partner : A minor is a person who has not yet attained the age of majority i.e., 18 years. According to Indian contract Act, a minor cannot enter into a contract. A minor may be admitted to the benefits of existing partnership with the consent of all partners. The minor is not personally liable “for liabilities of the firm.
Question 2.
What is a Joint Stock Company ? What are the features of it?
Answer:
“A company is an association of many persons who contrib-ute money or money’s worth to a common stock and employ it in some trade or business and share the profits or loss arising there from”.
– L.J. Lindley
A Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association of individuals for profit having a capital divided into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition of membership”.
From the above definitions the features of Joint Stock Company is as given below.
Features :
1) Association of persons : A company is an association of persons join hands with a common motive earning profits through business.
2) Separate legal entity: The company is created by law. It has a separate legal entity apart from its members. Eventhough it is invisible and intangible having no body or soul, it can act just like any other human being. It can enter into contracts purchase and sell goods, conduct lawful business in its own name. It can sue and can be sued in a court of law.
3) Perpetual existence : The company has a permanent ex-istence. The shareholders may come or may go but the company will go on forever. The continuity of the company is not affected by death, lunacy or insolvency of shareholders.
4) Common seal: A company being an artificial person cannot put its signature. The law requires every company to have a seal and get its name engraved on it. The seal of the company is affixed on all important documents and contracts as signature.
5) Limited liability : The liability of its shareholders is lim-ited to the value of shares they have purchased.
6) Transferability of shares : The shareholders of the public company are free to transfer their shares. They do not need the consent of other shareholders.
7) Separation of Ownership and Management: The share-holders are the owners of the company. But they are too many. They are widely scattered and cannot take part in the day-to-day affairs of the company. The management is entrusted to Board of Directors who are elected by the shareholders. So, the ownership is separated from management.
8) Membership : To form a Joint Stock Company minimum of 2 members in the case of private company and 7 members in the case of public company. The maximum is 50 members in the case of private company and unlimited in public companies.
9) Formation: The Company comes into existence only when it is registered under the Indian Companies Act, 1956.
10) Submitting annual statements: A Joint Stock Company is required to file annual statements with the Registrar of companies at the end of the financial year. These statements are available for inspection in the office of the Registrar.
![]()
Question 3.
What is business finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organizations.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called Business Finance. R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
B.O. Wheeler defined business finance as follows: “Finance is that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of a business enterprise.”
Need for business finance :
1. To start a new business : Money is needed to start a business and to procure fixed assets like buildings, plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures etc., working capital is required for holding current assets such as stock of materials, transportation expenses etc. The amount of finance to be procured depends on the type of business, nature of business and usage of technology.
2. To expand the business : Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
3. To develop and market new products : Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products. Invention and innovation of products should be given much priority to sustain in the market. Marketing research needs more funds.
4. To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
5. To take over another business : Business needs money to overcome competition or to get strengthened. An enterprise may decide to take over another business.
6. To move to new premises: A business unit may be forced to shift the business to new premises according to directions of the government. In such case, finance is needed for expenses like transport, packaging, installation of machinery etc.
7. Pay for the day-to-day running of the business : A busi-ness enterprise needs money to meet the day – to – day expenses like wages, taxes advertisement, rent etc. It also needs to meet liabilities like repayment of loan, installments, creditors etc.
Section – B
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each:
Question 4.
Define business. What are its characteristics ? Give any four characteristics.
Answer:
In the words of L.H.Haney “Business may be defined as hu-man activities directed towards providing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods”. According to Wheeler “Business is an institution organised and opei ated to provide goods and services to the society under the incentive of private gain”. Spriegal considers all activities concerned with production and sale of goods are business activities.
An analysis of the above definitions brings out the following characteristics of business.
1) Economic activities : All those activities relating to the production and distribution of goods and services are called eco-nomic activities. Business is carried on with a profit motive. Any activity undertaken without economic considerations will not be part of business.
2) Deals with goods and services : Eyery business concern produces or purchases goods and services with a view to selling them for profit. Goods may be consumer goods or producer goods. Consumer goods like coffee, bread or shoes are meant for direct use by the consumers. Producer goods are used for the production of consumer or capital goods like raw materials, machinery etc. Services like transport, warehousing etc., may be considered as intangible and invisible goods.
3) Exchange of goods and services : A business must in-volve exchange of goods and services with a profit motive. Pro-duction or purchasing of goods and services for personal consumption do not constitute business. Th’e purchase of goods should be to sell them again. If a person cooks his food at home, it is not business,.but if the same person cooks at a restaurant it is business because he exchanges his services for money.
4) Continuity of transactions : In business only those trans-actions are included which have regularity and continuity. An iso-lated, transaction will not be called business, even if the person earns profit from the deal. A person builds a house for himself but later on sells it for a profit, it is not business. On the other hand, if a house building society builds houses and sells them, this will be called business.
5) Profit motive : The profit motive is an important element of business. Profits are essential for the survival as well as the growth. Profit must, however, be earned through legal and fair means. Business should never exploit society to make money.
6) Risk and uncertainly: The business involves a large ele-ment of risk and uncertainity. The factors on which business de-pends are never certain, so the business opportunities will also be uncertain. There may be shift in demand, strike by employees, floods, war, fall in prices etc. A business man can reduce risks through correct forecasting and insurance. But all risks cannot be eliminated.
7) Creation of utility: Business creates various types of utilities in goods so that consumers may use them. The utility may be form utility, place utility and time utility. When raw materials are converted into finished goods it creates form utility. When the goods are transported from the places of production to the ultimate consumers, it creates place utility. The process of storing goods when they are not required and supplying them at a time when they are needed is called creation of time utility.
8) Art as well as science : Business is an art because it re-quires personal skills and experience. It is also a science because it is based on certain principles and laws.
Question 5.
Briefly explain the different types of cooperative societies.
Answer:
According to the needs of people different types of co-op-erative societies are started in India. They are :
1) Consumers Co-operative Society : These are started to help lower and middle class people. These societies protect weaker sections from the clutches of profit hungry businessmen. These societies make bulk purchases directly from producers and sells these goods to members on retail basis. The commission and profit of the middlemen are eliminated. The members contribute capital and membership is open to all irrespective of caste, creed, colour etc.
2) Producers Co-operative Society: Small producers find it difficult to collect various factors of production they also face marketing problem. The production of goods is undertaken by members in their houses or at common place. They are paid wages for their services. They are supplied raw material and equipment by the society. The output is collected and sold by the society. The profits are distributed among members after retaining some profit in the general pool. Ex. : Appco, Co-Optex, Emniganur weavers co-operative society.
3) Marketing Co-operative Society : These societies are established by producers for selling their products at remunerative prices. These societies pool production from different members and undertake to sell these products by eliminating middlemen. The goods are sold when the! market is favourable. The societies provide some advance money to the members for helping them in meeting their urgent needs. The sale proceeds are shared among members according to their contributions. These societies provide services like grading, warehousing, insurance, finance etc.
4) Co-operative Credit Society : The people with moderate means are formed with the object of extending short term credit to their members. They also develop thrift among the members. The funds are contributed by the members. These societies are divided into rural credit co-operative societies and urban credit co-operative societies.
5) Co-operative Housing Society : The low and middle income group of people are not able to construct their own house for want of money. Co-operative society arrange loans for their members from financial institutions and government agencies against security of the houses. These societies helps the members to become owners of house over a period of time. Ex. : Housing Board Colonies.
6) Co-operative Farming Societies : These societies are basically agricultural co-operatives. These are formed by the small land owners. They pool their resources to achieve the benefits of large scale farming and maximising agricultural product. They solve the problems of finance, irrigation seeds, fertilizers etc.
Question 6.
What are the different types of promoters ?
Answer:
The following are different types of promoters.
- Professional promoters : The professional promoters are specialised persons or agencies and promotion is their whole time occupation.
- Accidental promoters: Accidental promoters are not spe-cialists in company formation. They promote their own firms as promoters.
- Occassional promoters : These promoters take interest in floating some companies. They are not in promotion work on regular basis, but takeup promotion of some company and then go to their earlier profession. Ex : Engineers, lawyers etc.
- Financial promoters : Financial promoters float new en-terprises during favourable conditions in the securities market.
- Technical promoters : Technical promoters promote new enterprise on the basis of their specialised knowledge and training in technical fields.
- Institutional promoters : IDBL, NIDC and other specialised institutions provide technical, managerial and financial assistance in the promotion of a company.
Question 7.
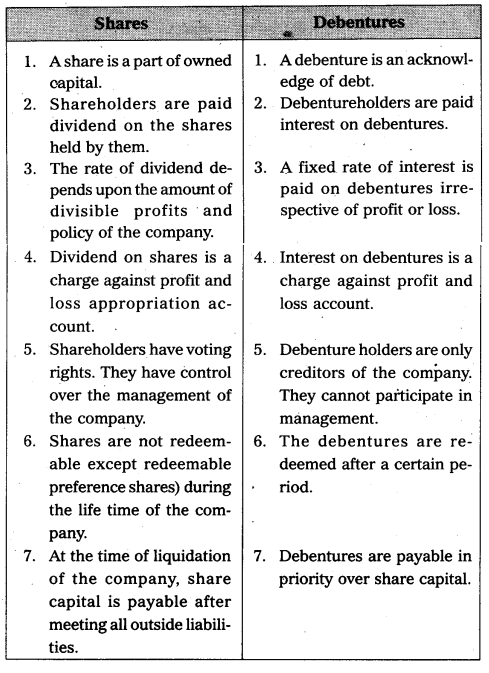
Differentiate between a share and a debenture.
Answer:
Question 8.
Explain the disadvantages of equity shares.
Answer:
Disadvantages:
- If only equity shares are issued, the company cannot take the advantage of trading in equity.
- There is danger of over capitalisation in case of excess issue of the shares.
- These shareholders can put obsticks is management.
- In case of higher profits, increase in the value of shares may lead to speculation in the market.
![]()
Question 9.
State any four merits of MNC’s to host country.
Answer:
Merits of MNCs to host countries :
- Provide Capital: MNCs bring in much needed capital for the development of industries. These corporations make direct foreign investment and speed up the process of economic development.
- Transfer of Technology : Developing countries are tech-nically backward. They lack resources to carry research and de-velopment. MNCs serve as a vehicles for the transfer of advanced technology to these countries.
- Generate Employment: It creates large scale employment opportunities in host countries. They offer excellent pay scales and career opportunities to managers technical and clerical staff.
- Foreign Exchange : MNCs help the host countries to increase their exports. They reduce their dependence on imports. MNCs enable host countries to improve their balance of payments position.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each :
Question 10.
Define entrepot-trade.
Answer:
When goods are imported from one country and the same are exported to another country, such trade is called entrepot trade. E.g.: India importing wheat from U.S. and exporting the same to Srilanka.
Question 11.
What is sole proprietorship ?
Answer:
Sole trade is the oldest and most commonly used form of business organisation. It is also known as sole proprietorship, in-dividual partnership single entrepreneurship. In sole trade concern a single individual introduces his own capital, skill and intel-ligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is the easiest to form and is also the simplest in organisation. All that is required is that the indi-vidual concerned should decide to carry on particular business and find the necessary capital. For this purpose, he may depend mostly on his own savings or he may borrow part or whole from his friends or relatives. He can start business in his own or may obtain the assistance of his family members or paid employees.
A sole trader is a person who sets up the business with his own resources, manages the business himself by employing per-sons for his help and alone bears all gains and risks of the business.
Question 12.
Define ‘Kartha’.
Answer:
The senior most male member of the family is Kartha. All the affairs of the Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Kartha or Manager. The liability of the Kartha is unlimited. He acts on behalf of the other members of the family. He is not accountable to anyone. He is the great master of the grandshow.
Question 13.
Define minimum subscription.
Answer:
The minimum amount of capital to be collected by the com-pany before the allotment of shares is known as minimum sub-scription. A public company cannot commence business unless the minimum subscription has been subscribed. It is fixed by taking into account the following requirements.
- Amount required for the purchase of property.
- Amount need for payment of preliminary expenses.
- Amount required for working capital.
- Amount need for any expenditure in the formation of the company.
Question 14.
Define fixed capital.
Answer:
The capital which is used to acquire fixed assets such as land and buildings, plant and machinery etc., is called fixed capital. Capital used by the business organisations to asset the long term requirements is called fixed capital or block capital. The amount of fixed capital required by the business concern epends on the size and nature of business.
Question 15.
What is meant by preferential share ?
Answer:
As the name suggests, these shares have certain preferences as compared to equity shareholders. There is a preference for payment of dividend and also repayment of capital at the time of liquidation when the company has distributable profits, the dividend is first paid to preference shares. In the event of liquidation, after the payment of outside creditors, preference share capital is returned. Because of these preferences they are called as preference shares. These shares do not carry any voting rights. Hence they cannot participate in the management.
Question 16.
Define manufacturing enterprises.
Answer:
Manufacturing Enterprise :

Question 17.
What is e-trade ?
Answer:
E-trading is also known as “Online trading” or E-broking. It is used for buying and selling stocks in stock exchanges.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
Answer the following question :
Question 18.
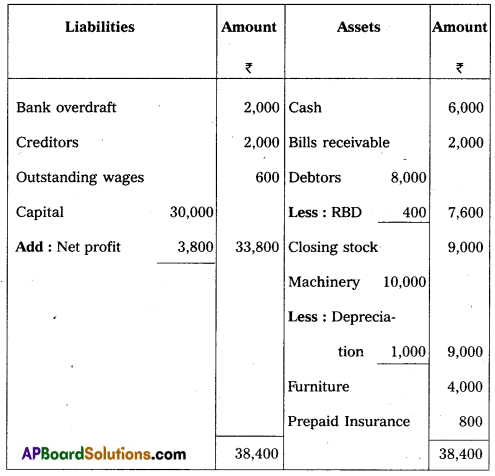
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Final accounts of Sathwika Traders as on 31.12.2012.
TRIAL BALANCE
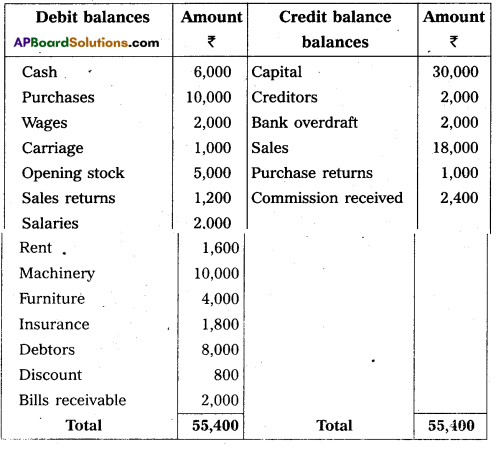
Adjustments :
i) Closing stock ₹ 9,000.
ii) Outstanding wages ₹ 600.
iii) Prepaid insurance ₹ 800.
iv) Depreciation on machinery 10%.
v) Provision for bad debts on debtors 5%.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss a/c of Sathwika Traders for the year ending on 31.12.2012.
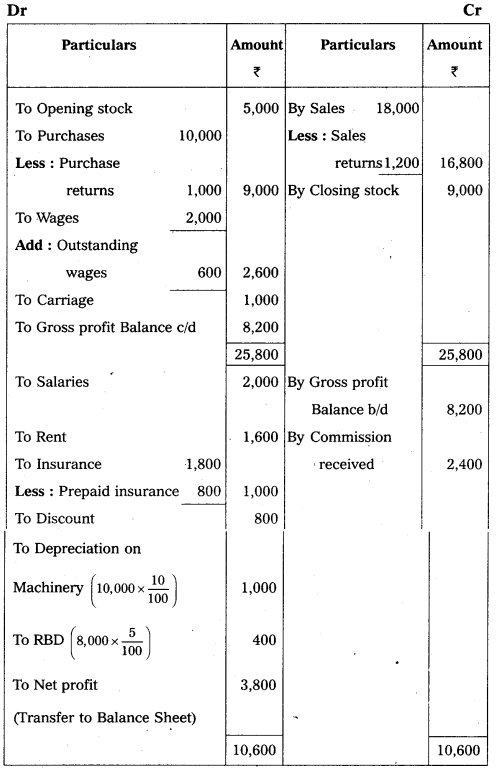
Balance Sheet of Sathwika Traders as on 31.12.2012
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions :
Question 19.
Prepare a three-column cashbook from the following par-ticulars :
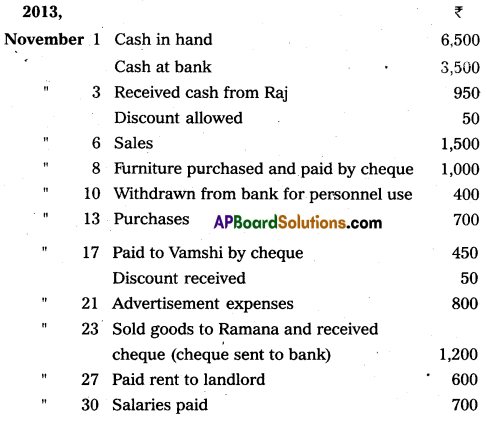
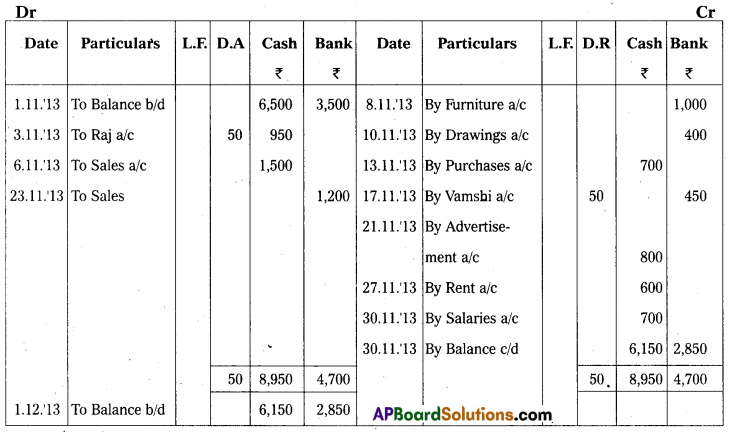
Answer:
Three Column Cash Book
Question 20.
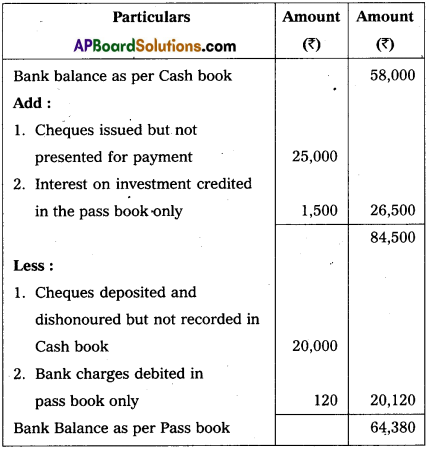
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement of Padma Traders and find the balance as per the passbook as on 31.12.2014.
i) Cashbook balance as on 31.12.2014 is ₹ 58,000.
ii) Cheques amounting to ₹ 25,000 issued on 25.12.2014 were presented for payment on 5.1.2015.
iii) A cheque for ₹ 20,000 deposited on 21.12.2014 was returned dishonoured on 8.1.2015.
iv) Interest on investment ₹ 1,500 was collected and credited by bank but no entry is in the cashbook.
v) Bank charges debited in passbook only is ₹ 120.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Padma Traders as on 31.12.2014.
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions :
Question 21.
Explain the advantages of double entry system.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of Double entry system of book-keeping.
- The system maintains a complete record of all the busi-ness transactions, as it records both the aspects of the transaction.
- It provides a check on the arithematical accuracy of ac-counts with the help of trial balance.
- Errors and frauds can be deducted under this system. So, it reduces the chance of committing errors and frauds.
- It reveals the result of the operations i.e., profit or loss, by preparing profit and loss a/c.
- The financial position of the business can be ascertained through the preparation of balance sheet.
- It is a scientific system and permits the accounts to be kept in detailed form and provides sufficient information for the purpose of control.
- The results of .one year can be compared with the results of previous year and reasons for the changes are known.
- It provides accounting information readily to management for making decisions.
Question 22.
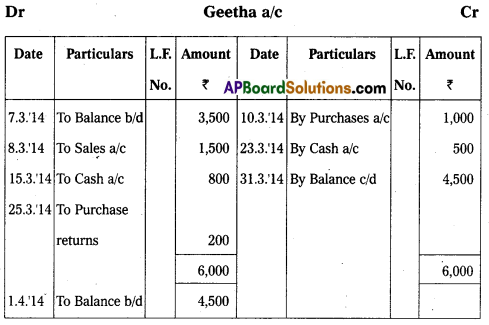
Prepare Geetha account from the following particulars :

Answer:
Question 23.
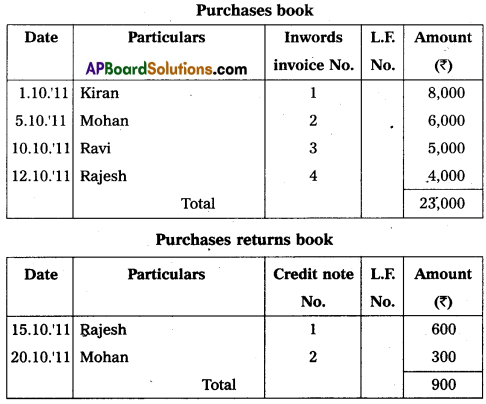
Enter the following transactions in the proper subsidiary books.

Answer:
Question 24.
Explain the various types of errors.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors.
1) Error of principle: Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors: When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is caused clerical errors. They are given divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of Omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of Commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors: These errors arise when one error is compensated by other error or errors.
![]()
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any Five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is book-keeping ?
Answer:
Book-keping is the art of recording business transactions in v regular and systematic manner. According to carter “Book-keeping is the science and art of correctly recording books of accounts all those business transactions that result in transfer of money or money’s worth.
Question 26.
Explain convention of conservatism.
Answer:
According to this convention, the principle of anticipate no profit but provide for all possible losses should be applied. The principle of conservatism requires that in the situation of uncertainity of doubt, the business transactions should be recorded in such a manner that the profits and assets are not overstated and the losses and Liabilities are not understated.
Question 27.
What is posting ?
Answer:
Posting is the process of entering in the ledger the entries given in the journal. Posting into the ledger is done periodi-cally, may be weekly or fortnightly as per the convenience of the business.
Question 28.
What is meant by favourable balance ?
Answer:
When the cash book shows, the debit balance and the pass book shows credit balance, it is called favourable balance. Favourable indicate that the businessman has got money in his account with the bank.
Question 29.
What is meant by cash discount ?
Answer:
If a debtor clears his debt before or on the date specified, he may receive some rebate in the form of cash from the creditor. This is treated as cash discount received by the debtor. In the same way, the rebate given by the creditor is treated as discount allowed. The discount column is maintained on both sides of the cash book.
Question 30.
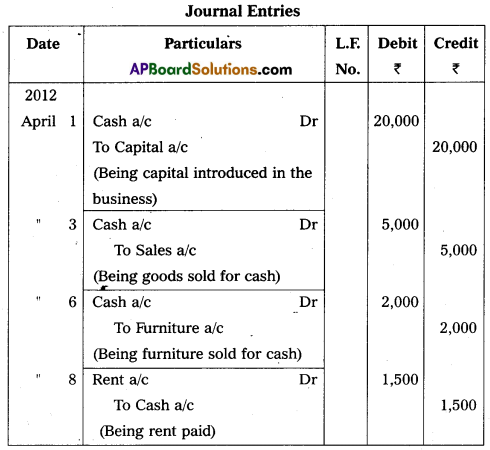
Journalize the following transactions.

Answer:
Question 31.
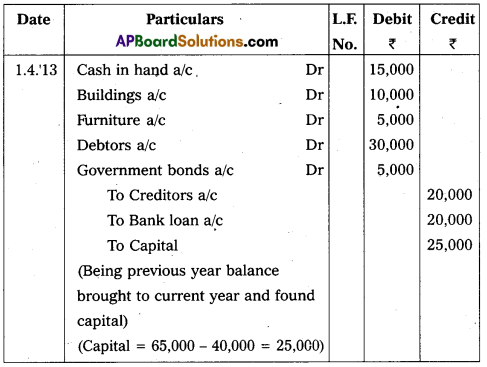
Write the opening entry as on 1.4.2013 from the following :
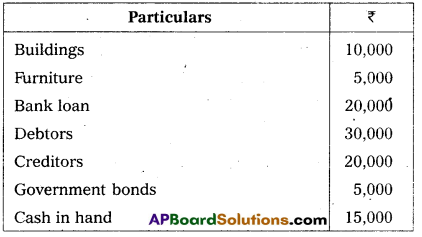
Answer:
Opening entry as on 01.04.2013
Question 32.
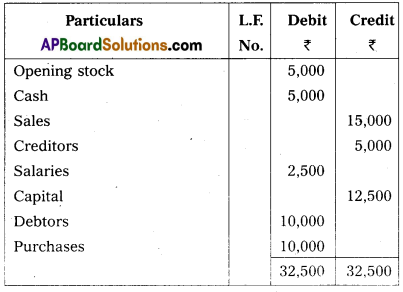
Prepare a Trial Balance of Ramu from the following as on 31.12.2012.
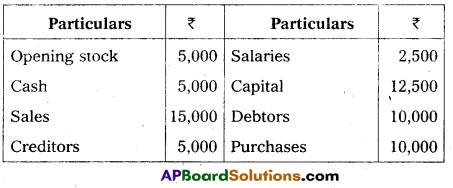
Answer:
Trial Balance of Ramu as on 31.12.12