Collaborative study sessions centered around TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2015 can enhance peer learning.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2015
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define Partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations.
Answer:
Partnership is defined by section 4 of Indian Partnership Act of 1932 “as the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them act for all”.
Merits:
- Easy formation: It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal, documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsory.
- Large resources : The resources of more than one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute,to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial power: We can pool capital, organising ability, managerial capacity, technical skill etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making: The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility: The partnership is flexible in nature at any time the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations after taking necessary consent of all the partners.
- Sharing risks: The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach : The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation : All partners actively participate in the business as per their specialisation and knowledge.
Limitations:
- Unlimited liability : The unlimited liability is fundamental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability : The partnership concern suffers from uncertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- limited resources: There is limitation in raising additional capital for expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners.
- Non-transferability of share: No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust: The mutual distrust among partners is the main cause for dissolution of partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions: Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
Question 2.
What is Memorandum of Association ? Explain its clauses.
Answer:
The Memorandum of Association is the most important document of the company. It is to be filed with the Registrar for obtaining the certificate of incorporation. It is the charter of the company. It forms the foundation on which the super structure of the company is based. It establishes the relationship between the company and the outside world. The contents of the Memorandum cannot be altered at the option of directors or even the shareholders. It is to be altered only with the central governments approved and court approval in many cases.
The Memorandum has tajbe divided into paragraphs, consecutively numbered and has to be printed. It should be signed by seven members in the case of public company and by two members in the case of Private company.
Memorandum of Association contains the following clauses.
1) Name clause: In this clause, the name of the company should be stated. The company is free to adopt any name it likes. But it should not resemble the name of another registered company. It should not any words pertaining to Government or local government, such as royal, crown, state etc. The name of the company must end with the word ‘Limited’ if it is a public company or with the words ‘Private Limited’ if it is a private company.
2) Situation clause : The place and the state in which the registered office is to be situated must be mentioned in this clause.
3) Objects clause: This is the most important Clause of the Memo-randum. This gives out the various objects for which the company is formed. The objects of the company must be legal and be very clearly defined. A company has power to carry on only those types of business which are included in the objects clause. Any action beyond the express powers of the company is ultravirus i.e., beyond the scope of the memorandum. Therefore, it should be carefully drafted.
4) Liability clause: This clause clearly states that the liability of members is limited to the extent of the face value of the shares purchased by them.
5) Capital clause : The amount of capital required by the company is stated in this clause. This is called authorised or nominal or registered capital. This capital is divided into small units called as shares. The company must mention the number and kinds of shares and the value of each share.
6) Association and subscription clause : This clause contains the names of the persons who signed in the memorandum. The memorandum must be signed by atleast seven persons in case of public company and atleast two persons in the case of private company. Each subscriber must take atleast one share in the company. The subscribers declare that they agree to incorporate the company and agree to take the shares stated against their name. The signatures of the subscribers are attested by atleast one witness each. The addresses and occupations of subscribers and the witnesses are also given.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Business Finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organizations.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called business finance.
R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
Need and signifiance of business finance:
- To commence a new business : Money is needed to start a new business and to procure fixed assets like land and buildings etc., working capital is required to meet the day-to-day expenses and holding current assets like cash, stock-in-trade etc.
- To expand the business: Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
- To develop and market new products: Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products.
- To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
- To take over another business: In other to overcome competition an enterprise may decide to take over another business.
- To move to new premises : Sometimes a business may be forced to shift the business in another place.
- Day-to-day running ; A business needs money to meet the day-to-day requirements like wages, taxes etc.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
What is meant by Industry ? Explain various types of industries with suitable examples.
Answer:
Industry is concerned with the making or manufacturing of goods. It is that part of the production which is involved in changing the form of goods at any stage from raw material to the finished product.
E.g. : Weaving woollen yarn, into cloth. Thus industry imparts form utility in goods.
The goods may be consumer goods or producer goods. Consumer goods are the goods, which are used finally by consumers. E.g: Food grains, textiles, cosmetics. Producer goods are the goods used . by the manufacturers for producing some other goods. E.g: Machinery, tools equipment etc.
Classification or types of industries : The industries may be classified as follows.
1) Primary industry : Primary industry is concerned with pro-duction of goods with the help of nature. It is nature-oriented industry, which requires very little human effort. E.g: Agriculture, Farming, Fishing, Horticulture etc.
2) Genetic industry : Genetic industry is related to the reproducing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale. E.g : Nurseries, cattle breeding poultry, fish hatcheries etc.
3) Extractive industry : It is engaged in reusing some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industries comes in raw farm and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products. E.g : Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil industry, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
4) Construction industry : The industry is engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabrication of products. These industries are engaged in the construction of buildings, roads, dams, bridges and canals.
5) Manufacturing industry: This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human uses. E.g: Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cotton textile industry, Iron and steel industry, Fertiliser industry etc.
6) Service industry : In modern times, service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation and therefore it is named as service industry. These are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. E.g: Banking, transport, insurance etc.
Question 5.
Discuss the differences between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.
Answer:

Question 6.
Briefly explain the different types of Co-operative societies.
Answer:
According to the needs of people different types of co-operative societies are started in India. They are:
1) Consumers Co-operative Society: These are started to help lower and middle class people. These societies protect weaker sections from the clutches of profit hungry businessmen. These societies make bulk purchases directly from producers and sells these goods to members on retail basis. The commission and profit of the middlemen are eliminated. The members contribute capital and membership is open to all irrespective of caste, creed, colour etc.
2) Producers Cooperative Society: Small producers find it difficult to collect various factors of production they also face marketing problem. The production of goods is undertaken by members in their houses or at common place. They are paid wages for their services. They are supplied raw material and equipment by the society. The output is collected and sold by the society. The profits are distributed among members after retaining some profit in the general pool. Ex.: Appco, Co-Optex, Emniganur weavers co-operative society.
3) Marketing Co-operative Society : These societies are established by producers for selling their products at remunerative prices. These societies pool production from different members and undertake to sell these products by eliminating middlemen. The goods are sold when the market is favourable. The societies provide some advance money to the members for helping them in meeting their urgent needs. The sale proceeds are shared among members according to their contributions. These societies provide services like grading, warehousing, insurance, finance etc.
4) Co-operative Credit Society : The people with moderate means are formed with the object of extending short term credit to their members. They also develop thrift among the members. The funds are contributed by the members. These societies are divided into rural credit co-operative societies and urban credit co-operative societies.
5) Cooperative Housing Society: The low and middle income group of people are not able to construct their own house for want of money. Co-operative society arrange loans for their members from financial institutions and government agencies against security of the houses. These societies helps the members to become owners of house over a period of time. Ex.: Housing Board Colonies.
6) Co-operative Farming Societies: These societies are basically agricultural co-operatives. These are formed by the small land owners. They pool their resources to achieve the benefits of large scale farming and maximising agricultural product. They solve the problems of finance, irrigation seeds, fertilizers etc.
Question 7.
State any four merits of MNC of Home Country.
Answer:
Merits of MNCs to home country:
- Availability of resources : The country can obtain raw materials, land and labour at comparatively low cost.
- Develop exports: They can export commodities and finished products for assembling or for distribution in foreign markets. Thereby market in widened.
- Generate income: They can earn huge income from dividends, licencing fees, royalty and management contracts. They can acquire technical and managerial expertise, of foreign countries.
- Provides employment : They can increase job and career opportunities at home and abroad in connection with overseas operations.
Question 8.
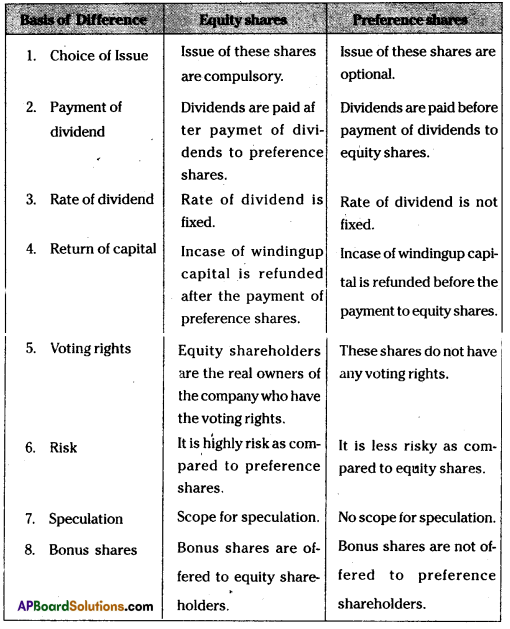
Differentiate between the Equity Shares and Preferential Shares.
Answer:
The following are the differences between equity shares and preference shares.
Question 9.
What are the sources of short term finance ?
Answer:
The following are the sources of short-term finance :
1. Bank credit : Commercial banks extend the short term financial assistance to business in the form of loans, cash credits, overdrafts and discount of bills. Bank loans are provided for a specific short period. Such advance is credited to loan account and the borrower has to pay interest on the entire amount of loan sanctioned. Bank grants cash credits upto a specific limit. The firm can withdraw any amount within that limit. Interest is charged on the actual amount withdrawn. In overdraft, the customer can overdraw his current account. The arrangement is for short period only. Commercial banks finance the business houses by discounting the bills of exchange and promissory notes.
2. Trade credit: Just as firm grants credit to customers, so it often gets credit from suppliers. It is known as trade credit. It does not make available of funds in cash but it facilitates the purchase of goods without immediate payment of cash.
3. Installment credit: Business firms get credit from equipment suppliers. The suppliers may allow the purchase of equipment with payments extended over a period of 12 months or more. Some portion of the cost price is paid on delivery and the balance is paid in number of installments. The supplier changes interest on the unpaid balance.
4. Customers advance: Many times, the manufacturer of goods insist on advance by customers incase of big order. The customers advance represent a part of the price of the product which will be delivered at a later date.
5. Commercial paper : Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for shorter period, varying from 90 days to 365 days. It is issued by one firm to another firm. The amount raised by C.P. is large. As the debt is totally unsecured, firms having good credit rating can issue commercial paper.
Section – D
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What is Profession ?
Answer:
Profession is an occupation involving the provision of personal service of a specialised and expert nature. The service is based on professional education, knowledge, training etc. The specfied service is provided for a professional fees charged from the clients. For example; a doctor helps his patients through his expert knowledge of science of medicine and charges a fee for the service.
![]()
Question 11.
Trade
Answer:
All the human activities engaged in buying and selling of goods and services comes under trade. Therefore trade includes sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services with the intention of making profit. The object of trade is to make goods available to those who need them and willing to pay for them. Trade is the final stage of business activities and involves transfer of ownership.
Aids to trade : Trade or exchange of goods involves several difficulties which can be removed by aids to trade. Aids to trade refer to those activities which, directly or indirectly facilitate smooth exchange of goods and services.
Aids to trade includes transport, warehousing, banking, insurance, advertising and communication.
Question 12.
Karta
Answer:
The senior most male member of the family is Karta. All the affairs of the Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Karta or Manager. The liability of the Karta is unlimited. He acts on behalf of the other members of the family. He is not accountable to anyone. He is the great master of the grandshow.
Question 13.
Active partner
Answer:
An active partner is one who takes active part in the day-to-day working of the business. He may act in various capacities as manager advisor or organisor. He is also known as working partner or managing partner.
Question 14.
Retained earnings
Answer:
Ploughing back of profits or retained earnings refers to the process of reinvestment of the earnings year of after. In this technique all the profits are not distributed to shareholders. A part of the profits is retained in the business as a reserve. These reserves are used to finance long-term and short-term needs of the company. It is also known as self financing or internal financing.
Question 15.
Business Finance
Answer:
Business finance is viewed as the activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting. The financial needs and overall objectives of the business enterprise. So,
business finance is the process of acquiring and utilising funds by the business. A business concern needs money to get started, to operate and to expand.
Question 16.
E – Banking
Answer:
Electronic banking is one of the most successful online business. E-banking allows customers to access their accounts and execute orders through use of website.online banking allows the customers to get their money from an Automatic teller machines instead of walking upto the cash desk in the bank. The customers can view their accounts, transfer funds and can pay bills. Ex : internet banking.
Question 17.
Define Service Enterprises.
Answer:
Service Enterprises : These enterprises involve in providing or rendering service. Service sector may be defined interms investment made in equipment.
- A Micro enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment does not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs.
- A Small Enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 10 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 2 crores.
- A Medium Enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 2 crores but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
Part – II (Marks 50)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question :
Question 18.
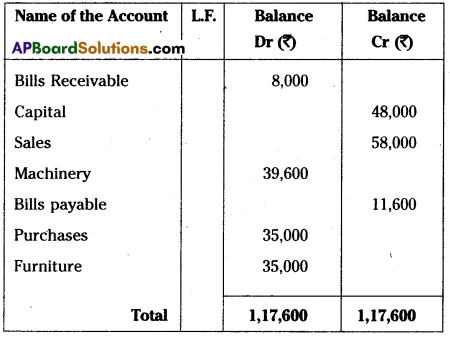
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Krishna Trader’s Final Accounts for the year ended 31-03-2014.
Trial Balance
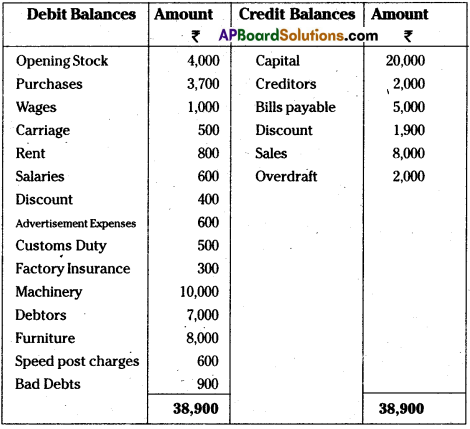
Adjustments:
i) Value of Closing Stock ₹ 4,500
ii) Prepaid wages ₹ 200
iii) Outstanding rent ₹ 200
iv) Depreciation on machinery 10%,
Depreciation on furniture 5%
Answer:
Trading Account for the ended 31-03-2014
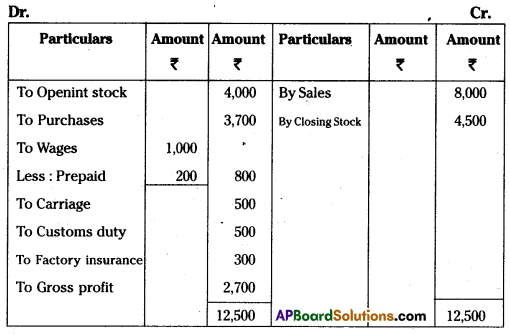
Profit & Loss A/c for the year ended 31-03-2014
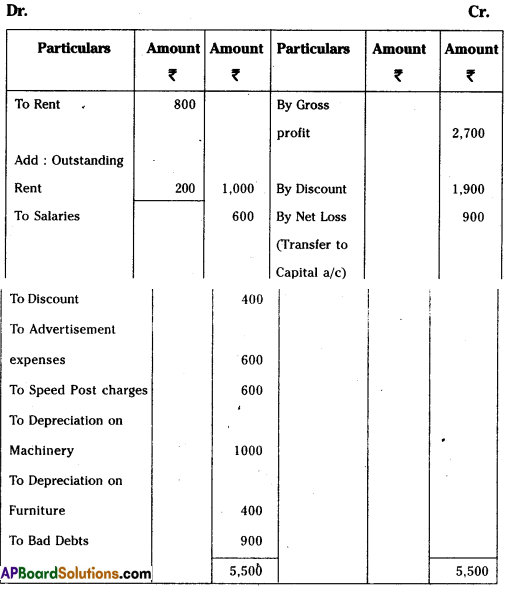
Balance Sheet as on 31-03-2014
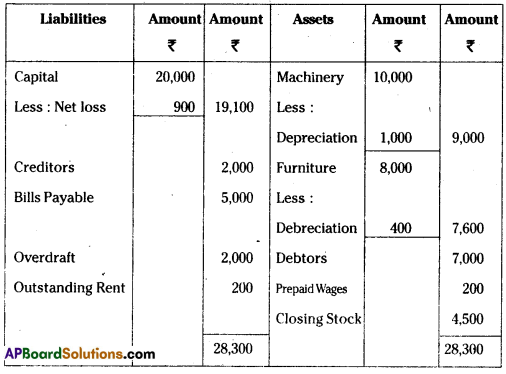
Section – F (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions :
Question 19.
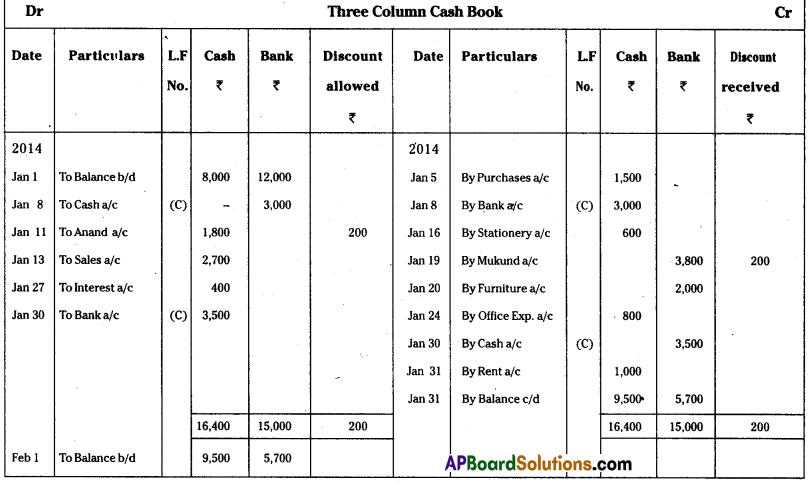
Prepare Cash, Bank and Discount Columns Cash Book from the following :
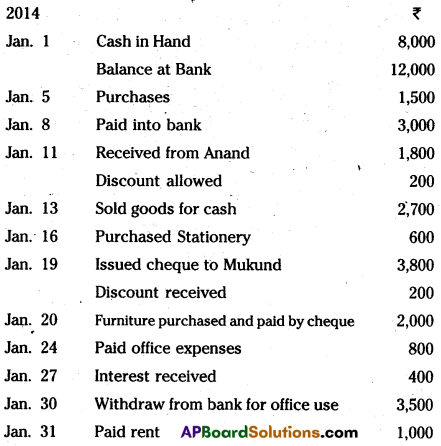
Answer:
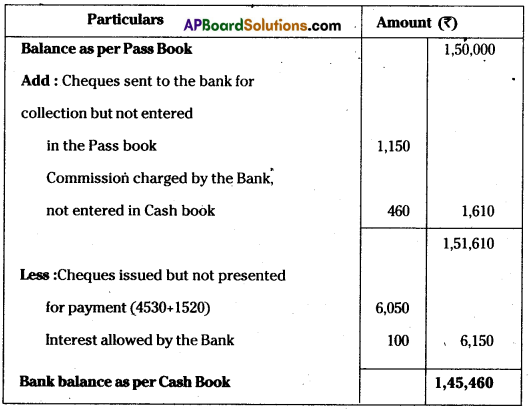
Question 20.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement of New India Stores on 30th June 2013 from the following particulars :
a) Balance as per Pass Book ₹ 1,50,000.
b) Two cheques for ₹ 4,530 and ₹ 1,520 issued on 25th June were presented for payment at the bank in July.
c) A cheque for ₹ 1,150 sent to the bank for collection was not entered in the Pass book till 30th June.
d) The bank allowed ₹ 100 as interest and charged ₹ 460 as bank Commission but both of them were not entered in the cash book.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of New Indian Stores As on June 30th, 2013
Section – F (2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions :
Question 21.
Explain different types of accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
Answer:
The accounts are broadly divided into two types.
1) Personal Accounts
2) Impersonal accounts.
1) Personal Accounts : These accounts which relate to the persons, group of persons or institutions are called personal accounts. Ex.: Rama’s a/c, Andhra Bank a/c., LIC a/c, Infosys Ltd. The rule in personal accounts is “Debit the receiver and credit the giver”. According to this, benefit receivers account is debited and benefit givers account is credited.
2) Impersonal Accounts : Impersonal accounts are those accounts which are not personal accounts. They are again divided into
i) Real Accounts
ii) Nominal Accounts,
i) Real Accounts: These accounts related to the, assets and properties of the business firm. Ex.: Building, machinery, stock, goodwill etc.
The rule in real accounts is “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”. When an asset is received the asset account is debited -and when the asset goes out of the business, the asset is credited,
ii) Nominal Accounts : These accounts relate to expenses, incomes or gains or losses. Ex. : Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Commission received a/c etc.
The rule in nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains”.
![]()
Question 22.
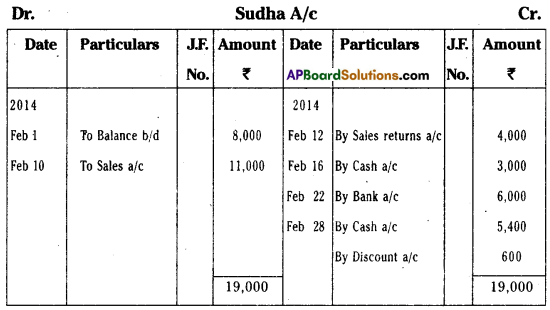
Prepare Sudha account from the following :

Answer:
Question 23.
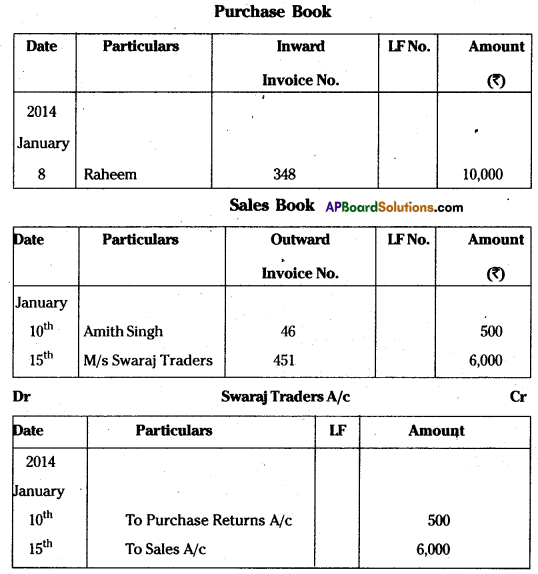
Enter the following transactions in proper subsidiary books :
Jan. 8th Purchase of goods from Raheem ₹ 10,000 as per Invoice No.348.
Jan. 10th Returned goods to Amith Singh ₹ 500 as per Debit Note No. 46.
Jan 15th Sold goods to M/s. Swaraj Traders ₹ 6,000 as per Invoice No. 451.
Answer:
Question 24.
What are the various types of errors ? Explain.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors.
1) Error of principle: Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors: When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is caused clerical errors. They are given divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of Omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of Commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors: These errors arise when one error is compensated by other error or errors.
Section – C (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions :
Question 25.
Define Accounting.
Answer:
The American Institute of Public Accountants defined accounting as “the art of recording, classifying and summerising in significant manner and interms of money transactions and events which are in part, atleast of financial character and interpreting the results thereof”.
Question 26.
Double Entry Book Keeping System.
Answer:
According to J.R. Batliboi “Every business transaction has a two-fold effect and that it affects two accounts in opposite directions and if a complete record were to be made of each such transaction, it would be necessary to debit one account and credit another account. This recording of the two fold effect of every transaction has given rise to the term Double entry system of book-keeping is that “for every debit there must be corresponding value of credit”.
Question 27.
What is Ledger ?
Answer:
Ledger is a book which facilitates recording of all type of transactions related to personal, real and nominal accounts separately. According to Cropper “The book which contains a classified and permanent record of all the transactions of a business is called ledger”.
![]()
Question 28.
Credit Note
Answer:
It is a note (document)prepared and sent to the customer to inform that his account is credited with the amount of the goods returned by him. It is a common practice to make it in red ink.
Question 29.
Contra Entry
Answer:
Contra means the other side, if the double entry of a transaction is complete in the cash book it self such entry is called contra entry. Contra entry arise when the cash and bank accounts are simultaneously involved in a transaction. It happens when either cash or cheques are deposited in the bank or cash is withdrawn from it for office use. In both the cases entries are to made in cash and bank columns.
Question 30.
Journalize the following in the books of Mr. Jayanth :

Answer:
Question 31.
Rama & Co. started business on 1st Jan. 2014 with Assets: Cash – ₹ 12,000, Stock – ₹ 8,000, Furniture – ₹ 20,000, Machinery – ₹ 10,000 and Creditors – ₹ 3,000 and Bank Overdraft – ₹ 2,000. Pass opening entry.
Answer:
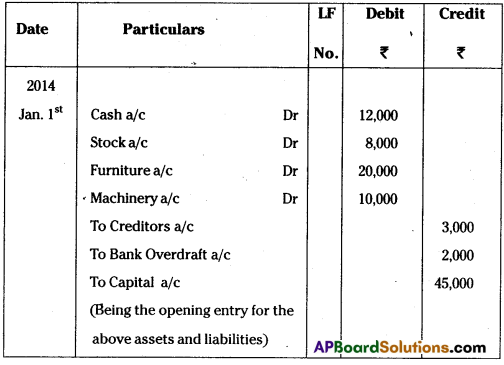
In the above entry, it is debited the four assets with their values and credited the liabilities with their values. The difference between the assets total and liabilities total is credited to Capital A/c. i.e (12,000 + 8,000 + 20,000 + 10,000 = 50,000) – (3,000,+ 2,000 = 5,000) = ₹ 45,000
Question 32.
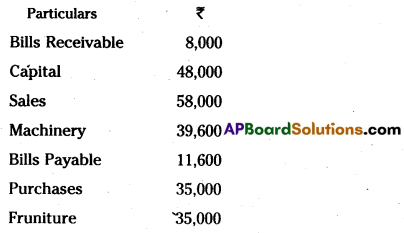
Prepare Tried Balance of Rohit.
Answer:
Trial Balance of Rohit