These TS 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 6th Lesson Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 6th Lesson Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces
Question 1.
When does a concave mirror form virtual image?
Answer:
A concave mirror forms virtual image when the object is placed between pole and focal point.
Question 2.
What is the location of the object for a concave mirror to obtain the image at the same point?
Answer:
The image and the object will coincide if the object is placed at the centre of curvature.
Question 3.
What are the values of radius of curvature and focal length of a plane mirror?
Answer:
Both the radius of curvature and focal length of a plane mirror are infinitely.
Question 4.
Define focal point of a spherical mirror.
Answer:
Focal point is that common point on the principal axis at which the reflected rays converge if the corresponding incident rays are parallel to principal axis.
Question 5.
What is the relation between radius of curvature and focal length of a concave mirror?
Answer:
The focal point is the midpoint of center curvature and pole. So, local length is half of radius of curvature.
∴ f = \(\frac{F}{2}\)
Question 6.
How do you find magnification produced by a spherical mirror?
Answer:
There are two ways of finding the magnification:
- The ratio of size of the image to size of the object (m =\(\frac{h_i}{h_o}\))
- The ratio of image distance to object distance (m = \( \frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}\).
Question 7.
What does the sign of magnification indicate?
Answer:
+ve magnification: flw image ¡s erect, virtual.
-ve magnification: The image is inverted, real.
Question 8.
What happens to image when an object is moved towards a concave mirror from infinity?
Answer:
The image moves away from mirror starting from focal point to infinity.
Question 9.
Where should an object be placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror so that a magnified and virtual Image of the object is formed?
Answer:
Object must be placed between the pole and focus of the concave mirror.
Question 10.
The focal length of convex mirror is 50cm. What is the radius of curvature?
Answer:
Focal length (f) = 50cm. (1M) (AS2)
The relation between R and f is given by R = 2f
R = 2 x 50=100cm
∴ Radius of curvature is 100 cm.
Question 11.
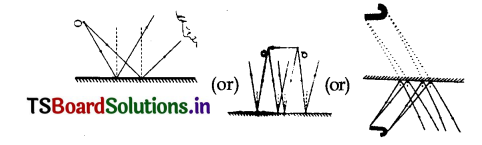
Copy the figure in your answer book and show the direction of light after reflection.
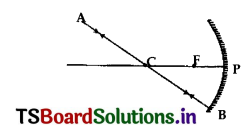
Answer:
Here the incident ray passes through ‘C’ hence after reflection, it retraces the same path.
AB = incident ray of light
BA = reflected ray of light
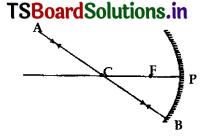
Question 12.
A man standing in front of a mirror finds his image having a very large head and legs of normal size. What type of mirrors are used In designing such a mirror?
Answer:
The upper part of such a mirror is concave mirror and lower part is a plane mirror.
Question 13.
Write the properties of image formed by plane mirror.
Answer:
The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, erect (upright) laterally inverted has same size as that of the object, and is formed distance as that of the object Iron, the mirror.
Question 14.
Write the properties of image formed by convex mirror.
Answer:
The image formed by a convex mirror is virtual, erect (upright), diminished, and is formed closer to the mirror than the object.
Question 15.
Write the magnification values for given positions of object for a concave mirror and explain.
a) Object is kept at Focus.
b) Object is kept In between Focus and Pole.
Answer:
a) Magnification m > -1
-ve sign indicates real, inverted m > — 1 indicates size of image is greater than the size of object.
b) Magnification m> + 1
+ ve sign indicates virtual, erect and m > 1 indicates enlarged behind the mirror. As u increases y decreases.
Question 16.
The focal length of concave mirror is f. Is there any change in focal length when it is completely immersed In water? If not why?
Answer:
As there Is no change in medium then there is no change in focal length. The incident angle ∠i and reflected angle ∠r are same, as both rays are travelling in same medium i.e., water.
∴ Focal length is independent of medium.
Question 17.
Along with your mother, you went to a shop. There you are observing a shining new steel curved spoon Then by observing your face in spoon, what questions you are getting in your mind?
Answer:
- Can a spoon acts like a mirror?
- If it acts like a minor is it plane mirror (or) spherical mirror?
- Is image of face inside and outside of spoon same?
- Does size of face change by bringing face close and far to spoon?
- Is the face erect or invert?

Question 18.
Why does a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror after reflection is reflected back along the same path?
Answer:
A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror falls perpendicular to the surface of the mirror that means ∠i = 0. According to the law of reflection ∠i = ∠r = 0. Therefore, the ray is reflected along the same path.
Question 19.
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What Is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer:
A concave mirror produces an erect image if the object is placed between the pole and the focus of the concave mirror. Thus, object may be placed at any position whose distance is less than 15cm from the concave mirror. The image is virtual and erect. The image is larger than the object.
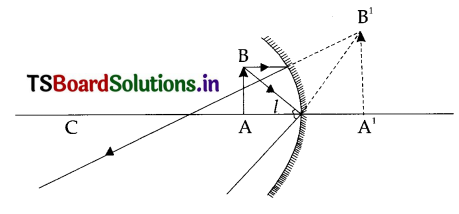
Question 20.
How do you prove that the light rays from far sources are parallel?
Answer:
- Stick two parts on thermocouple block.
- These are parallel to each other.
- When the source is near we see the shadows of the pins diverged.
- As the source is away from the pins the angle of divergence gets reduced.
- If the source is far we will get parallel shadows.
- That means to get parallel beam of light source must be far.

Question 21.
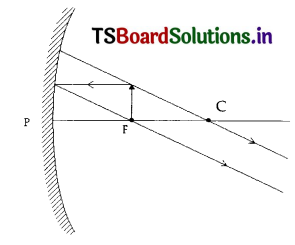
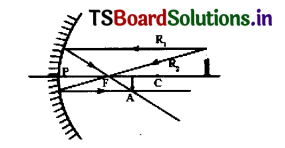
In the given ray diagram mention the pole of mirror (P), focus (F), centre of curvature(C), position of Image (I).
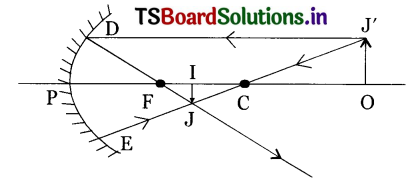
Answer:
Here object is placed beyond ‘C’ of a concave mirror so image is formed in between
Fand C.
OJ’ – object, Ij – image position between F and C.
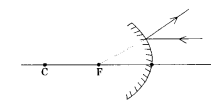
Question 22.
What represents this ray diagram?
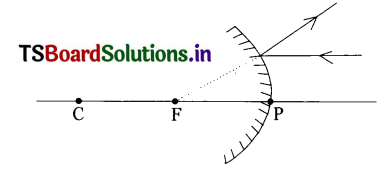
Answer:
- The given mirror is convex mirror.
- The incident ray is parallel light ray.
- F is the virtual focus i.e., image is virtual.
- Virtual image cannot be caught on screen.
So a convex mirror always forms a virtual image as the reflected rays are divergent.
Question 23.
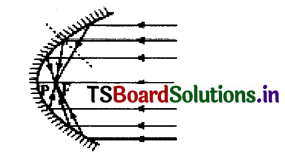
a) What Is the mirror used in car headlight?
b) Where are the bulbs kept In car?
c) In the car headlights the light from bulb fall on mirror and reflects. Draw the ray diagram indicating It.
Answer:
a) Concave mirror of parabolic shape are used.
b) The bulb is kept at the focus of mirror.
c)
Question 24.
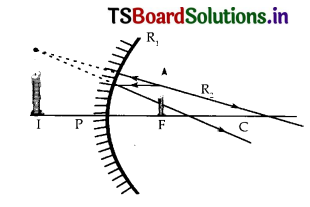
The light ray incident on concave mirror as shown in figure. The light ray reflects. Then answer the following questions:
i) How the light ray reflects when a parallel beam of light incident on it?
ii) The light ray which passes through the focus incident on mirror then how it reflects?
iii) Depending on the answers of the above questions draw the reflected ray which incident on point P.
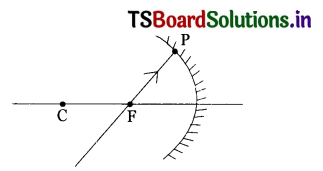
Answer:
i) The light ray passes through focus.
ii) The light ray reflects parallel to the principal axis.
iii)
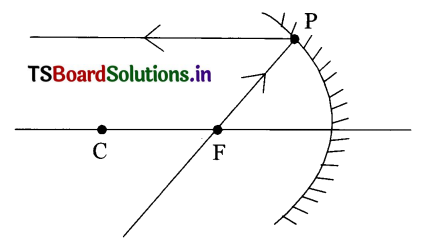
In the given diagram incident ray passes through focus, hence after reflection, it is parallel to principal axis.
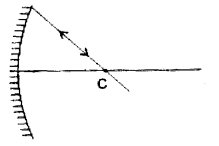
Question 25.
A ray of light 1M is incident on a mirror as shown in the figure. The angle of incidence for this ray is the angle between It and the line joining two other points in the figure. Name this two points.
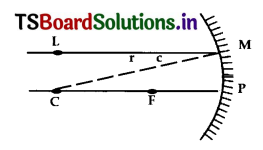
Answer:
The angle of incidence for a ray falling on a spherical mirror is the angle between the incident ray and the normal to the point of incidence. A line joining the centre of curvature and the point of incidence is normal to the point of incidence. Thus, the given two points are C and M as shown in figure.
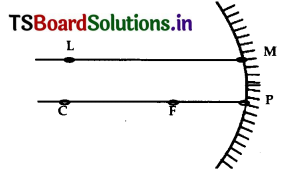
Question 26.
Draw the diagram that explains the formation of an image by a plane mirror.
Answer:
Question 27.
Name the type of mirror used in a solar furnace. How Is high temperature achieved by this device?
Answer:
Concave mirror is used in solar furnace. The sun rays are focused at a point by the concave mirror. The concentrated beam of sunlight at a point increases the temperature at that point.
Question 28.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged image of an object placed at 10 cm infront of It. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Answer:
The image formed infront of the concave mirror is real. So magnification M is negative.
m= – 3; u = -10 cm
m = \(\frac{-\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}\)
-3 = \(\frac{-\mathrm{v}}{-10} \)
By mirror formula \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{v} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{-10}+\frac{1}{-30} \Rightarrow \frac{-3-1}{30} \Rightarrow \frac{-4}{30}\)
f = \(\frac{-30}{4}\) = -7.5 cm
Radius of curvature R = 2f = 2 x (-7.5)
R =-15 cm
Question 29.
An object is kept at a distance of 20 cm infront a concave mirror. The focal length of mirror Is 30 cm. Then:
a) What is image distance?
b) What Is the magnification in this case?
Answer:
a) The object is kept within the focal of mirror. So image is virtual, erect, magnified.
Object distance(u) =-20cm
Image distance (v) = ?
Focal length (f) = 30 cm
Mirror formula
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}-\frac{1}{30}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}-\frac{1}{20} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{30}=\frac{30-20}{30 \times 20}=\frac{10}{600}\)
v = \(\frac{600}{10}\) = +60 cm
b) Magnification(m) = \(\frac{-v}{u}=-\frac{-60}{-20}\) = +3 cm
‘+‘ indicates image is virtual erect.
Question 30.
An object is kept at a distance of 5 cm infront of convex mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 1o cm. Then
a) What is the Image distance (v)?
b) Magnification in this case is how much?
Answer:
a) Object distance(u)=-5cm
Image distance (v) = ?
Focal length (f) = + 10cm,
Mirror equation is \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}\)
\(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{5} \)
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{5} \)
v = \(\frac{10 \times 5}{15}=\frac{10}{3} \) = 3.33 cm
b) Magnification (m)
= \(-\frac{\mathrm{v}}{4}=-\left(\frac{\frac{10}{3}}{-5}\right)=+\frac{10}{15}=\frac{2}{3}\) = 0.66
Image is virtual, erect, diminished.
Question 31.
You, with your friends visited a science center where so many mirrors are kept on the table. How you will distinguish mirrors without touching them? What questions are on the basis of which you can identify mirrors?
Answer:
You can distinguish between these mirrors just by looking into them that is, by bringing your face close to each other turn by turn. All of them will produce an image of our face but of different types.
i) Can all mirrors produce same image?
ii) Can all mirrors prodUce real image?
iii) Can all mirrors produce magnified image?
iv) How you will identify the nature of mirrors by touching them? A plane mirror will produce an image of the same size. A concave mirror will produce magnified image and your face will look much bigger. A convex mirror will produce a diminished image and your face will look much smaller.
Question 32.
Describe a setup showing how you heat a utensil by using solar energy and mirrors.
Answer:
Making of a solar cooker:-
- Make a wooden/iron frame in the shape of TV dish.
- Cut acrylic mirror sheets into 8 or 12 pieces in the shape of isosceles triangles with a height equal to the radius of your dish antenna.
- Stick the triangle mirrors to the dish. Arrange it so that concave part faces sun.
- Find its focal point and place a vessel at that point. It will get heated.
- In this way we will prepare a solar cooker.
Question 33.
Sukumar saw his face in car rearview mirror. He observed that his Image is smaller than the original.
a) What type of mirror it is?
b) What is the nature of image?
c) Draw the ray diagram for It.
Answer:
a) The mirror is convex mirror which is also called as Rear view mirror.
b) The nature of image is erect, irt, smaller than size of object.
c)
Question 34.
Lavanya is playing with plane mirror, she has seen her image in It.
a) What is the the reason for forming that image?
b) She kept the mirror in the Sun, when she touched it later, she felt that It is hot. What could be reason for that?
c) She stood away from the mirror which is exposed to sunlight and observed that the mirror is shining. What could be the reason for it?
Answer:
a) When Lavanya looked into the mirror, some rays from her eyes reach the mirror and got reflected. The reflected rays seemed to be coming from a particular points. These points forms the image of her face.
b) Atoms or molecules of the mIrror which are exposed to light absorb light energy and converts it into heat energy . So the mirror would heat up.
c) When the mirror exposed to light under the Sun, seems to be shining because when light falls on the mirror a part of the light energy is reflected in different directions called ‘Scattering of light’. This scattering of light appears to be shining.
Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
If an object is placed at C’ on the principal axis in front of a concave mirror, the position of the image is …………………… . ( )
A) at infinity
B) between F and C
C) at C
D) beyond C
Answer:
C) at C
Question 2.
Magnification m = ( )
A) v/u
B) u/v
C) h0/hi
D) hi/ho
Answer:
A) v/u
Question 3.
A ray which seems to be travelling through the focus of a convex mirror passes ……………………… after reflection. ( )
A) parallel to the axis
B) along the same path in opposite direction
C) through F
D) through C
Answer:
A) parallel to the axis
Question 4.
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence ……………… . ( )
A) Always
B) Sometimes
C) Under special conditions
D) Never
Answer:
A) Always
Question 5.
The image of an object formed by a plane mirror is
A) virtual
B) real
C) diminished
D) upside-down
Answer:
A) virtual
Question 6.
In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at …………… . ( )
A) a flat surface
B) a bent-in surface
C) a bulging-out surface
D) an uneven surface
Answer:
C) a bulging-out surface
Question 7.
The focal length of a spherical mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm is ( )
A) 10 cm
B) 15 cm
C) 20 cm
D) 30 cm
Answer:
B) 15 cm
Question 8.
The real image is formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when the object is …………………… . ( )
A) at a distance equal to radius of curvature.
B) at a distance less than the focal length.
C) between focus and centre of curvature.
D) at a distance greater than radius of curvature.
Answer:
C) between focus and centre of curvature.
Question 9.
The image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect and magnified. The position of object is ………………… . ( )
A) at focus
B) between focus and centre of curvature
C) at pole
D) between pole and focus
Answer:
D) between pole and focus
Question 10.
Magnification produced by a convex mirror is always ……………. . ( )
A) more than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) more or less than
Answer:
B) less than
Question 11.
In order to obtain a magnification of ‘- 2’ with a concave mirror, the object should be placed ( )
A) between pole and focus
B) between focus and centre of curvature
C) at the centre of curvature
D) beyond the centre of curvature
Answer:
B) between focus and centre of curvature
Question 12.
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is ( )
A) Convex mirror
B) Plane mirror
C) Concave mirror
D) Both convex and concave mirrors
Answer:
C) Concave mirror
Question 13.
The image formed by a plane mirror is ………………….. . ( )
A) virtual image
B) behind the mirror
C) same size of the object
D) all
Answer:
A) virtual image
Question 14.
The minimum distance of an object from concave mirror for which the mirror forms real image is ……………… . ( )
(Let ‘f’ be the focal length of concave mirror)
A) f
B) 2f
C) 4f
D) zero
Answer:
D) zero
Question 15.
The properties of image when a real object is kept in between focus and centre of curvature of a concave mirror. ( )
A) Size of image is greater than size of object
B) Image is inverted
C) Image is real
D) All the above
Answer:
C) Image is real
Question 16.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object? ( )
A) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
B) Beyond the centre of curvature.
C) At the centre of curvature.
D) Between the principle focus and the centre of curvature.
Answer:
A) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Question 17.
Focal length of plane minor is …………………… . ( )
A) zero
B) infinity
C) negative
D) positive
Answer:
B) infinity
Question 18.
All the distances in case of spherical mirror are measured in relation to: ( )
A) the focus of the mirror
B) the image to the object
C) object to image
D) the pole of the mirror
Answer:
D) the pole of the mirror
Question 19.
The radius of curvature and focal length of a concave mirror are ( )
A) zero
B) negative
C) positive
D) infinity
Answer:
B) negative
Question 20.
A mirror forms a virtual image of a real object ( )
A) It must be a concave mirror.
B) It must be a plane mirror.
C) It must be a convex mirror.
D) It may be any of the mirrors mentioned above.
Answer:
A) It must be a concave mirror.
Question 21.
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If ¡t is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will ( )
A) retraces its path
B) pass through the pole
C) pass through the centre of curvature
D) pass through the focus
Answer:
D) pass through the focus
Question 22.
If an incident ray passes through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror, the reflected ray will ………………… . ( )
A) pass through the focus
B) retrace its path
C) pass through the pole
D) be parallel to the principal axis
Answer:
B) retrace its path
Question 23.
A real, inverted and equal in size Image is formed by: ( )
A) A plane mirror
B) A convex mirror
C) A concave mirror
D) A spherical mirror
Answer:
C) A concave mirror
Question 24.
In case of concave mirror, the minimum distance between a real object and its real image is : ( )
A) f
B) 2f
C) 4f
D) zero
Answer:
D) zero
Question 25.
We get a diminished image with a concave mirror when the object is placed
A) at F
B) between the pole and F
C) at C
D) beyond C
Answer:
D) beyond C
Question 26.
We get a virtual image in a concave mirror when the object is placed …………….. . ( )
A) at F
B) between the pole and F
C) at C
D) beyond C
Answer:
B) between the pole and F
Question 27.
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror making an angle of 900 with the mirror surface. The angle of reflection for this ray of light will be …………. . ( )
A) 45°
B) 90°
C) o°
D) 60°
Answer:
C) o°
Question 28.
The angle of incidence between the plane of a mirror and light ray is 45°. The angle of reflection is ……………………. . ( )
A) 30°
B) 45°
C)60°
D) 90°
Answer:
B) 45°
Question 29.
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a local length of -15cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be …………………… . ( )
A) both are convex
B) both are concave
C) the mirror is convex but the lens is concave.
D) the mirror is concave and the lens is convex.
Answer:
A) both are convex
Question 30.
A student obtained a blurred image of an object on a screen by using a concave mirror. In order to obtain a sharp image on the screen, he will have to shift the mirror: ()
A) To a position very lar away from the screen
B) Either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object.
C) Towards the screen
D) Away from the screen
Answer:
B) Either towards or away from the screen depending upon the position of the object.
Question 31.
The image of a distant object is obtained on a screen by using a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror can be determined by measuring the distance between ( )
A) The object and the screen
B) The object and the mirror
C) The mirror and the screen as well as that between the object and the screen
D) The mirror and the screen
Answer:
D) The mirror and the screen
Question 32.
If the object is placed at focus of a concave mirror, the image is formed at ( )
A) focus
B) infinity
C) between F and O
D) centre of curvature
Answer:
B) infinity
Question 33.
An object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between its image and the pole is: ( )
A) between f and 2f
B) equal to 2f
C) equal to f
D) greater than 2f
Answer:
B) equal to 2f
Question 34.
To get an Image larger than the object, one can use ( )
A) A concave mirror but not a convex mirror.
B) A convex mirror but not a concave mirror.
C) A plane mirror.
D) Either a convex mirror or a concave mirror.
Answer:
A) A concave mirror but not a convex mirror.
Question 35.
A concave mirror focal length f’ produces an image n’ times the size of the object. If the image is real then the d distance of the object from the mirror is:
A) \(\frac{(n+1) f}{n} \)
B) (n + 1) f
C) (n-1)f
(D) \(\frac{(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{f}}{\mathrm{n}}\)
Answer:
B) (n + 1) f
Question 36.
A teacher hold a pencil close loa spherical mirror and asked four students W, X, Y and Z to predict the nature of the mirror with the help of the image formed In the mirror. The image was erect and enlarged. The four students identified It as follows:
W – Convex in nature
X – Concave in nature
Y- Plane mirror
Z – Plano cancave mirror
The correct statement was given by ………………….. . ( )
A) W
B) X
C) Y
D) Z
Answer:
B) X
Question 37.
This figure shows that ( )
1) mirror is convex
2) mirror is concave
3) it forms virhial image
4) it forms real image
A) 1 & 2 correct
B) 1 & 3 correct
C) 2 & 3 correct
D) 2& 4 correct
Answer:
B) 1 & 3 correct
Question 38.
The angle of reflection in the given figure is …………………… . ( )
A) 90°
B) 60
C) 0°
D)30°
Answer:
Question 39.
………………………… Mirrors are used in solar cookers. ( )
A) Convex
B) Plane
C) Parabolic
D) Spherical
Answer:
D) Spherical
Question 40.
No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be ……………………. . ( )
A) convex only
B) either plane or convex
C) concave only
D) plane only
Answer:
B) either plane or convex
Question 41.
A concave mirror is made by cutting a portion of a hollow glass sphere of radius 24cm. Find the focal length of the mirror. ( )
A) 12 cm
B) 18 cm
C) 24 cm
D) 6 cm
Answer:
A) 12 cm
Question 42.
Looking into a mirror one finds his image long and thin; the mirror is ………………. . ( )
A) parabolic
B) concave
C) convex
D) cylindrical
Answer:
D) cylindrical
Question 43.
The mirror used by E.N.T. specialists is ( )
A) Plane
B) Concave
C) Convex
D) None of these
Answer:
B) Concave