These TS 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 10th Lesson Some Natural Phenomena will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 10th Lesson Some Natural Phenomena
Question 1.
You might have seen that when you take off woolen or polyester clothes, especially in dry season the hair on your skin stands on end. Why does hair get attracted towards clothes?
Answer:
- While moving the clothes, friction is produced between our hod and the clothes.
- Due to this friction, opposite electric charges develop on our hair and the clothes.
- Unlike charges attract each other. So the hair gets attracted towards the clothes.
Question 2.
Why is the plastic scale not able to attract pieces of paper before it gets rubbed by dry hair?
Answer:
Because it is not charged, the plastic scale is not able to attract pieces of paper before it get rubbed by hair.
Question 3.
Lightning Safety.
Which is the safe place during thunderstorm? Why?
Answer:
- A house or a building of low height
- If we are travelling in a bus or in a car we are safe inside provided that doors and windows are closed.
- If we are in a forest it is a good idea during the thunderstorm to take shelter under shorter trees.
Question 4.
What is meant by earthing? How is It useful to us?
Answer:
The process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing.
Earthing is provided in buildings to protect us from electrical shocks due to any leakage of electrical current.
Question 5.
Some mythical/folk stories told that the earth is balanced on the horn of a bull and when the bull shifts it to the other horn, an earthquake takes place. How could it be true?
Answer:
- No. In ancient times, people did not know the true cause of earthquakes. Their ideas were, therefore, expressed in mythical / folk stories. Similar myths were prevalent in other parts of the world.
- Now we know that the tremors are caused due to the disturbance at deep down inside portion of uppermost layer of the earth. This uppermost layer of the earth is called, crust.
Question 6.
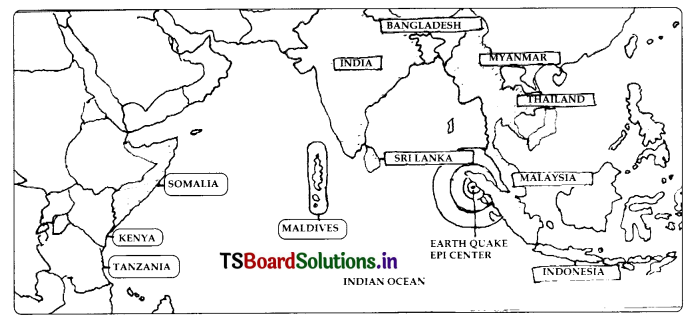
Countries damaged by the Tsunami in Indian Ocean.
Answer:
Question 7.
What could cause a disturbance inside the earth?
Answer:
- The outermost layer of the earth (called, crust) is not a single piece. It is fragmented.
- Each fragment of earth is called a plate.
- The plates will be moving continuously.
- When these plates brush past one another, or a plate goes under another plate due to collision, they cause disturbance in the earth’s crust.
- This disturbance under deep earth, shows up as an earthquake on the surface of the earth.
Question 8.
Can we predict when and where the next earthquake takes place?
Answer:
- Although we know for sure what causes an earthquake, it is not yet possible to predict when and where the next earthquake might occur.
- Tremors on the earth can also be caused when a volcano erupts. or a meteor hits the earth or an underground nuclear explosion is carried.
Question 9.
How do we know the occurrence of an earthquake?
Answer:
To know the occurrence or the time of occurrence of an earthquake, seismologists use a device, called, seismoscope.
Question 10.
How do we measure the Intensity of the earthquake?
Answer:
- The intensity of an earthquake is expressed in terms of a magnitude on Richter scale.
- Richter scale is not a linear scale. It is a logarithmic scale.
- For example, the earthquake of magnitude 6 on Richter scale has thousand times more destructive energy than an earthquake of magnitude 4 on the same scale (and not simply, one and a half times the destructive energy of an earthquake of magnitude 4)
Question 11.
A part from the Richter scale, Is there any other method of measuring the intensity of an earthquake?
Answer:
- On Richter scale, the power of an earthquake is expressed in terms of magnitude. It measures the ground motion at a given point.
- There is another method of measuring the intensity of an earthquake, using
the Moment magnitude scale.
Question 12.
How does is a ‘Moment magnitude scale’, used to measure the intensity of an earthquake? Explain.
Answer:
- The intensity of an earthquake can be measured using the Moment magnitude scale.
- It measures the amount of displacement that occurred along a fault zone.
- The Moment magnitude measures energy released by the earthquake more accurately than the Richter scale. It measures the 517k of large earthquakes, more reliably.
Question 13.
How to protect from earthquakes?
Answer:
- The buildings in these zones should be designed so that they can withstand major tremors.
- The Central Building Research Institute, Roorkee, has developed know-how to make quake-proof houses.
- In highly seismic areas, the use of mud or timber is better than the heavy construction material. Keep roofs as light as possible. In case the structure falls, the damage will not be heavy.
- It is better if the cupboards and shelves are fixed to the walls, so that they do not fall easily.
- Be careful where you hang wall clocks, photo frames, water heaters, etc.. so that in the event of an earthquake, they do not fall on people
- Since some buildings may catch fire due to an earthquake, it is necessary that all buildings, especially tall buildings, have fire fighting equipment in working order.
Question 14.
Do you know the places in combined And bra Pradesh where earthquakes occurred and their intensities?
Answer:
According to ‘Seismic hazard map’, combined Andhra Pradesh lies in zones II and III. Many earthquakes occurred in combined Andhra Pradesh also just like in many other states. A few of them are mentioned here alone with their intensities.

Due to the Tsunami that occurred in Suma there Andaman, many people died in A.P also.
Question 15.
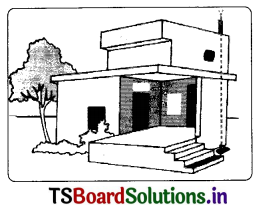
What are lightning conductors? How they are useful?
Answer:
Lightning Conductor is a device used to protect buildings from the effect of lightning. A
metallic rod, taller than the building, is installed in the walls of the building during its construction.
One end of the rod is kept out in the air and the other end is buried deep in the ground. The rod provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground. The projected end of the metal rod is at a height more than the height of the building. Hence it receives the charge first during the lightning because it is close to the cloud than the building.
As it is a good conductor of electricity, it allows all the charge to flow through it thereby causing no damage to the building.
Question 16.
Draw a Typical seismograph record. (or) Draw the picture of a seismograph.
Answer:
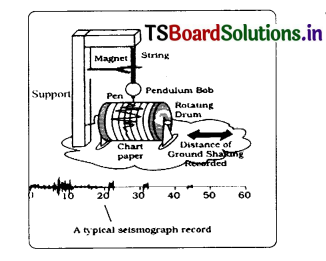
Question 17.
When a plastic comb is rubbed with dry hair, It acquires a small charge. Which type of charge is It?
Answer:
Static electric charge.
Question 18.
Two inflated balloons are separately rubbed with woolen clothes. Do these balloons attract or repel each other?
Answer:
Repel.
Question 19.
What happens, before a charged body attracts an uncharged body?
Answer:
Induction.
Question 20.
Which is the surest test to know, whether a body is charged, or not?
Answer:
Repulsion.
Question 21.
What Is the device used to test whether an object is carrying static charge, or not?
Answer:
Ehxtroscope.
Question 22.
What is the magnitude of destructive earthquakes, on Richter scale?
Answer:
Higher than 7.
Question 23.
What type of waves are recorded by a seismograph?
Answer:
Seismic waves.
Question 24.
During lightning and thunderstorm, which is a safe place?
Answer:
A house or building with low height.
Question 25.
Can we keep electrical lights on, during a lightning?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 26.
Generally, which follows a thunderstorm?
Answer:
Lightning and cyclone.
Question 27.
What is the range on Richter scale?
Answer:
0 to 10 (zero to ten).
Question 28.
Which type of scale is, Richter scale?
Answer:
Logarithmic scale.
Question 29.
Where do the earth tremors occur?
Answer:
Earth trust (deep inside).
Question 30.
What are those places called, where the earthquakes are more likely to occur?
Answer:
Seismic zones.
Question 31.
Name one natural disastrous phenomenon, that could not be predicted or eliminated.
Answer:
Earthquake (also, an eruption of a Volcano).
Question 32.
Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Answer:
- When we touch a charged object, it loses charge to the earth through our body.
- Thus, charge is trartsíerred from the object to the earth. This process is called, earthing.
Question 33.
Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake Is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph? Is it likely to cause much damage?
Answer:
- The power of an earthquake is measured on Richter scale. It is not a linear scale. It is a logarithmic scale.
- Yes, it would be recorded by a seismograph.
- But it is not likely to cause much damage.
Question 34.
Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Answer:
- A house or a building of a low height is a safe place.
- If you are travelling in a bus or in a car, close the doors and windows. Then you are safe inside that vehicle.
- If you are in a forest, take shelter under short trees. Then you are safe.
Question 35.
Does your habitation lie in a earthquake-prone area? Explain.
Answer:
Yes.
- I live in Warangal district, Telangana.
- According to seismic hazard map. Telangana lies in seismic zones II and III.
- Warangal district lies in zone li
Question 36.
Which place in Andhra Pradesh experiences earthquakes most of the times?
Answer:
In Andhra Pradesh, Ongole and its nearby places experienced earthquakes most of the times. The intensity of these earthquakes lie between 5 and 7 on Richter scale.
Question 37.
When does a piece of matter have a “charge?”
Answer:
- When matter gains electric charges or loses them, it acquires a charge.
- Transfer of electric charges is likely to take place between two materials when they are rubbed together.
- Thus matter gets charged when electric charges are transferred from one body to another.
- The process by which a body gets charged is called electrification’.
Question 38.
What happens if two objects having same charge are brought close to each other? What happens if two objects having different charges are brought close? Can you give an example for this?
Answer:
- When two objects carrying the same type of charge are brought closer to each other, they repel each other (Like charges repel each other),
- When two objects carrying opposite charges are brought closer to each other, they attract each other. (Unlike charges attract each other).
Examples:
- When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth, glass rod gets +vely charged, and the silk cloth, – rely charged.
- When a plastic straw is rubbed with a polythene sheet, polythene sheet gets + vely charged, and the plastic straw. – vely charged.
- Bring the glass rod (+vely charged) near the piece of the polythene sheet (- vely charged). They repel each other (two +ve charges repel each other)
- Bring the glass rod (+ vely charged) near the plastic straw (-rely charged). They attract each other opposite charges attract each other.)
Question 39.
Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
Answer:
The instrument used to detect the presence of charge on – a body is called, an ‘electroscope’.

Construction of an ‘electroscope’ :
- An empty jam bottle is taken
- A piece of cardboard is taken and used to cover the bottle (lid). Electroscope
- A hole is pierced at the center el the cardboard lid.
- A metal paper clip is taken and opened as appears in the diagram.
- Two strips of aluminum foil about 4 cm 1 cm each are cut, They are hung from the paper clip.
- The paper clip with the aluminum foils is inserted into the cardboard lid so that the clip is perpendicular to the cardboard,
- The bottle is now closed with this lid. The electroscope is now ready.
Question 40.
Prepare a model of seismograph.
Answer:
Cotistriiction Instruction:
A) Cut a cardboard Lox with the front opening, 4 holes, and a paper slot. Slide Dowell into snug hole.
B) Make a snug pen-diameter hole in the bottom of a cup or can. Insert pen from inside until it is good and stuck. This may require taping it inside and out.
C) Tie a string tight around the pen, or duct tape it. (You might want to do this before putting the pen in the can.) Fill the can with pennies.
D) Hang the cup inside the box so that the pen just touches the bottom lightly (with the cap off; replace cap when not in use!). You may need to reinforce the box top so it doesn’t sag.
Attach string to the sides of the can with tape to restrict lengthwise motion. Here we are trying to just get the back-and-forth movement (see arrow), not set off a circular pendulum motion. Put paper roll on dowell in box; feed paper end out the slot. Make sure that the uncapped pen is touching the paper.
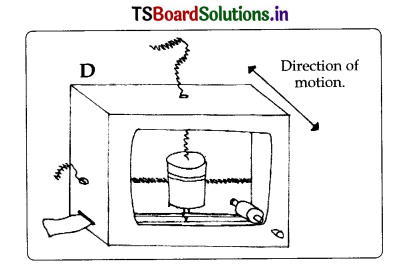
Materials :
- Rigid cardboard box, ~14”
- Can or cup, 12 oz.
- String, three -18-inch pieces
- Roll of adding machine paper
- Pennies, cup full
- Felt-tip pen
- Tape
- Dowell must fit paper, roll
Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
The scientist who first introduced the concept of two different kinds of charges is ( )
A) Sir Isaac Newton
B) Gilbert
C) Benjamin Franklin
D) Robert Boyle
Answer:
C) Benjamin Franklin
Question 2.
Some bodies can be charged by ( )
A) rubbing
B) induction
C) electric contact
D) any of them
Answer:
B) induction
Question 3.
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, both the materials acquire charge. Conventionally, the charge on the gla rod is taken as …………………….. charge and that on the silk cloth as …………………….. charge. ( )
A) -ve, ve
B) +ve, -ve
C) +ve, +ve
D) -ve, ve
Answer:
B) +ve, -ve
Question 4.
Tremors are caused in this part of the earth ( )
A) crust
B) mantle
C) outer core
D) inner core
Answer:
A) crust
Question 5.
“Seismograph” is related to ( )
A) a volcano
B) an earthquake
C) Forest fires
D) sunspot
Answer:
B) an earthquake
Question 6.
Richter scale is a ( )
A) linear scale
B) logarithmic scale
C) conventional measure
D) none
Answer:
B) logarithmic scale
Question 7.
The nature of force operating between two charged bodies is ( )
A) frictional
B) electromagnetic
C) electrostatic
D) gravitational
Answer:
C) electrostatic
Question 8.
Unit of electric charge is ( )
A) volt
B) coulomb
C) watt
D) ampere
Answer:
B) coulomb
Question 9.
When two bodies are rubbed together ( )
A) charges are created in both the bodies.
B) charges are transferred from one body to the other.
C) the bodies acquire similar charges
D) the bodies acquire unequal quantities of dissimilar charges.
Answer:
B) charges are transferred from one body to the other.
Question 10.
A lightning conductor installed in a building ( )
A) does not allow the lightning to fall on the building
B) provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground
C) stops the lightning from reaching the building
D) directs the lightning to strike on some far-off place, away from that building.
Answer:
B) provides easy route for the transfer of electric charge to the ground
Question 11.
Lightning rods are made of ( )
A) plastic
B) bakelite
C) copper
D) iron
Answer:
C) copper
Question 12.
An effective early-warning system for a cyclone is ( )
A) satellite
B) airship
C) radar
D) submarine
Answer:
A) satellite
Question 13.
A typhoon essentially is ( )
A) a tropical storm
B) an earthquake
C) a tidal wave
D) a volcano
Answer:
A) a tropical storm
Question 14.
Which one of the following event can lead to an earthquake? ( )
A) volcanic eruption
B) underground nuclear bomb explosion
C) meteor hitting the earth
D) any of them
Answer:
D) any of them
Question 15.
An electrostatic charge ( )
A) resides only on the surface of the body
B) charges the entire body.
C) is generated in a body. due to friction.
D) is always positive in nature.
Answer:
C) is generated in a body. due to friction.
Question 16.
Which of the following gets charged, during rubbing? ( )
A) amber
B) ebonite
C) plastic
D) all of them
Answer:
D) all of them
Question 17.
During rubbing of two bodies with one another, there is transfer of ……….. from one body, to the other. ( )
A) electrons
B) protons
C) neutrons
D) mass
Answer:
A) electrons
Question 18.
When you are in an open space, the safest way to protect yourself from lightning is ( )
A) to use an umbrella to cover yourself
B) to take shelter under a tall tree
C) to squat low on the ground
D) to run away from the place of lightning
Answer:
C) to squat low on the ground
Question 19.
Crust of earth is fragmented into plates. The boundaries of the earth plates are called ( )
A) Seismic zones
B) Fault zones
C) A or B
D) Borders
Answer:
B) Fault zones
Question 20.
A Richter scale is not a linear scale. It ranges from ( )
A) 0 to 9
B) o to 1.0
C) 1 to infinity
D) 1 to 100
Answer:
A) 0 to 9
Question 21.
Which of the following countries in the world is most prone to earthquakes? ( )
A) China
B) Japan
C) India
D) Russia
Answer:
B) Japan
Question 22.
In India, the state most prone to earthquakes is ( )
A) Chattisgarh
B) Chennai
C) Gujarat
D) Kerala
Answer:
C) Gujarat
Question 23.
The terms, ‘discharge’ and ‘earthing’ are related to this phenomenon ( )
A) volcano
B) earthquake
C) lightning
D) explosion
Answer:
A) volcano