TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 8 Biology Solutions TS 8th Class Biology Project Work FA 1 2 3 4 English Medium.
TS 8th Class Biology Project Work FA1, FA2, FA3, FA4 English Medium
Project – 1. Cell – The Basic Unit Of Life
Title of The Project : Diversity in cells.
Introduction :
Before the first microscope was invented around 350 years ago 1 people were not aware of the living world that was not visible to the naked eye. Thereafter many scientists were observing and describing unknown world with the help of microscope. In 1665 Robert I looke, a British scientist, observed thin slices of cork (soft bark from Oak tree) under a simple magnifying device.
He observed that the cork resembled the structure of a honey comb consisting of mans empty spaces or empty box like structures. He thought the cork wax made up of very small cavities. Robert Hooke called these cavities as cell. Cell is a Latin word for a little room. In 1831 Robert Brown discovered the nucleus of cell. After several observations it was confirmed that the cell is the structural and functional unit of living body. There are millions of living organism in nature. The have different shapes, sizes and vary in the number of cells they contahi. This project is determined to know the diversity in cells of living organism.
![]()
Objectives:
- Observing different cells.
- Identifying the diversity in the cells.
Project Method:
This project has been conducted on practical method.
Required Apparatus:
Micro-scope, slides, permanent slides of different cells, pencil, note book etc.,
Procedure Of The Project:
Observing the transverse section of stem of Tridax/ Spinach. The stem of the tridax (Gaddichamanthi) is collected. It is cleaned and cut into a piece of about 2cm in length. Ven’ thin section is taken with the help of blade. It is kept on the slide and observed under
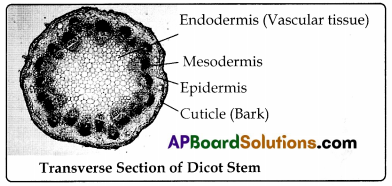
Observing Permanent Slide Of Tridax:
Permanent slides are observed under microscope and drawn the observed picture.
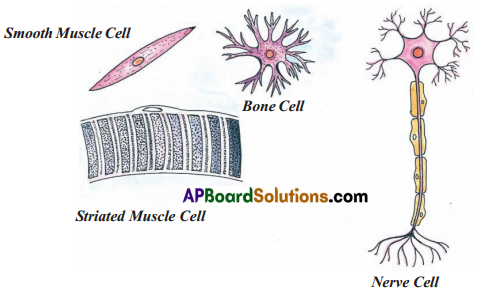
- Muscle cell : The cell is pointed on both the points possessing centrally nucleus.
- Bone cell : Rounded structure having small branches. Centrally nucleus is present.
- Nerve cell : Elongated cell. It consists of three parts called axon, dendrites and cell body, central nucleus is present.
- Red blood cells : Biconcave in shape and red in colour. Nucleus is absent.
- Chlamydornonas : Unicellular organism. Egg shaped structure chloroplasts and nucleus are present.
- Amoeba: It is unicellular organism. it is irregular in shape, body has pseudopodia.
Result:
Shape of the organism depends on type of tissues and their cells.
All the observed cells are not similar in shape. There is diversity in shape, structure and in case of presence or absence of nuclei. Naturally cell is very minute structures we can see them only under microscope. The Egg of Ostrich is very large. It is the biggest cell.
![]()
Conclusion:
Cells are in various shapes based on the organs, functions and structures. Even plants have meristematic tissue, cambial tissue such as xylem and phloem, cuticular cells, outer and inner layered cells, spongy tissues etc…
We cannot imagine the organ and organism without cell a true.
This project helps us to know the diversity among different cells of the organism.
Project 2. Story Of Micro Organisms (1)
Title Of The Project : Observing micro organisms
Introduction :
The organism which are not seen with unaided eyes are called microorganisms. Microbiology as a science was born in 1674 when Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek observed a drop of lake water through a glass lens that he had carefully found. Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek built a single lens powerful microscope. which could magnify the object 3(X) times. Ile observed small moving organisms in 1678.
He called them “animalcules.’ which were later called “bacteria”. This helped further discoveries of other microorganisms. Microorganisms are classified as Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa, Algae, Virus and certain micro arthropods. These are seen only under microscope. Microorganisms are found in water, air and the soil. The aim of the project is to know the characterestic features of these organisms.
Objectives:
- To know the various types of micro organisms.
- To know different methods of observing micro organisms.
To observe different micro organisms.
Conducting The Project: This project is done in two ways
- Collecting and observing micro organisms from different habitats.
- Observing the permanent slides of different micro organisms.
Procedure – 1:
Water from near h- ponds has collected. The surface of the water has precipitated with greenish residue. 1 -2 drops of collected pond water were poured on the slide and observed under microscope. Various microbial structures were observed in the collected pond water. They are in different shapes and structures. Some were moving and some were non-motile. Rough sketches of observed organisms were drawn on the paper. All the sketches have been compared with the pictures of permanent slides.
Result:
Water micro organisms are various types. They are in different shapes and structures such as round, thread like, fibrous, spiral, bell-shaped, oval etc.,
The following micro organisms were observed in the permanent slides which were seen in the collected pond water.
Procedure -II:
Pieces of prolong air exposed bread was collected. One of the tiny pieces was observed under microscope. Rough sketch of the observed piece was drawn.
![]()
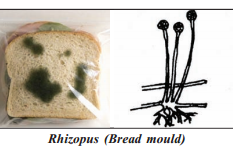
Observing Permanent Slide Of Fungi:
Laboratory permanent slide of Rhiiopus was observed under microscope. Collected bread mould and the picture of slide were compared both of them were almost similar in structures.
Procedure – III:
One or two drops of butter milk were taken on the slide. The slide was heated slightly for 3-4 seconds. It was stained with crystal violet and the slide was left undisturbed for 30 to 60 seconds. Then the slide was washed gently with water. Later the stained part was observed under micro scope. Rough sketch was drawn.
Observing The Permanent Slide Of Lactobacillus Bacterium:
The permanent slide of lactobacillus was observed picture of slide and drawn sketch were compared each other. It is as follows.
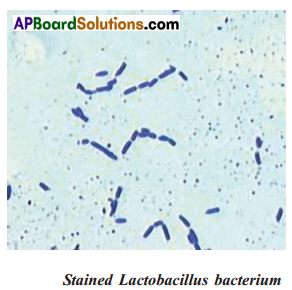
Procedure – IV:
Has’ was soaked in the pond water. It had been prepared as hay decoction. It was stored for 3 – 4 days. Liter a drop of sample was taken on the slide and observed under microscope. Rough sketches were drawn based on the observation.
Observing Permanent Slide Of Protozoans:
Slides of Amoeba and Paramoecium were observed. The pictures drawn after observing hay decoction and the pictures of slides were compared each other. They were as given below.
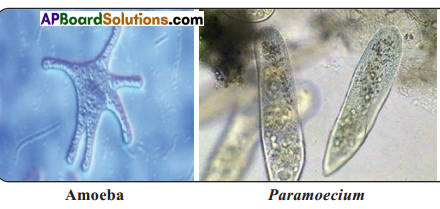
Procedure – IV:
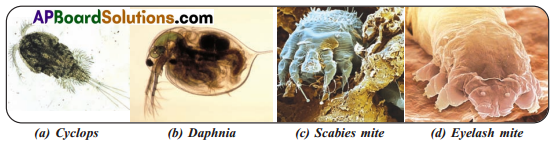
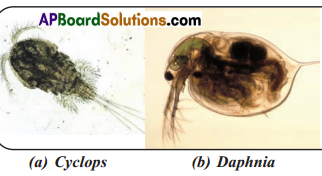
Soil was collected from the field. Some water was added and stirred the mixture. The sample was allowed to settle down the particles. One drop of sample was taken on the slide and observed under microscope. A Rough sketches were drawn. The sketch was compared with the pictures of micro Arthropods given in the lesson. The given diagrams are Cyclops, Daphnia, Scabies mite, Eyelash mite etc., But Cyclops and Daphnia were observed in 11w collected soil sample.
Conclusion:
Micro organisms play greater role in the nature. Some are harmful and some are very important. Viruses are the smallest microbes that cause various diseases.
Project 3. Story Of Micro Organisms (2)
Title Of The Project : Micro organisms in soil fertility
Introduction:
About 78% of air around us is nitrogen gas. Plants need it mainly for synthesizing proteins. But they cannot make it from the atmosphere directly. Micro organisms like Rhizohiurn, nostoc, anahena, azotobacter etc., help to provide nitrogen to the plants by fixing them from atmosphere to form certain compounds. Micro organisms present in the soil, air and water act upon wastes around us and decomposes them, They are converted into simple substances. Thus microorganisms help us in cleaning the environment.
![]()
Objectives:
- Observing the micro organisms that rises the soil fertility
- Observing root nodules of leguminaceac plants
- Understa tiding how corn post is synthesized.
Conducting The Project:
Roots having root nodules of Ieguminaceae plants were collected. Sorne prominent nodules were crushed on a slide,
A drop of water was poured on the crushed sample and observed under micro scope.
Rhizobium bacteria were seen in the sample of root nodules.
Maintaining Compost Pit: (Observing Importance Of Organic Matter)
Two pits were dug up in the corner on the school garden. Half of them were filled with loose soil. Some biological wastes such as fallen leaves, vegetable wastes, waste papers etc., were put in one of the pits. The second pit was filled with plastic vastes, polythenc bags and with some empty glass bottles. Both the pits were covered with loose soil. Sufficient water was sprinkled on pits. This was done for 3-4 weeks. Later the upper soil was removed and observed the changes.
Observation And Reasons:
Pit – 1: The pit with biological wastes developed decayed and decomposed mater. All the wastes were converted into organic compost.
Reason : The useful soil micro organisms converted the biological wastes into decomposing material.
Pit – 2: No change was occured in the pit containing plastic wastes. All the plastic wastes were remain unchanged.
Reason : Soil microbes have no influence on the harmful plastics
![]()
Conclusion:
Some micro organisms are very useful in our daily life. Micro organisms not only in converting the soil as fertile material, hut also play a key role in formation of many daily nutritious products. For example in making of curd and in preparation of idly, dosa, bread and cake. Some microorganisms are also used in preparation of medicines required to cure different diseases.
Project- 4. Story Of Micro Organisms – 2
Title Of The Project : Harmful micro organisms
Introduction:
Micro organisms are present everywhere. They are to be found in air, water, soil, within bodies of animals and plants and over the surfaces as well. Some micro organisms are harmful to us. They cause diseases in crop plants, livestock and in human beings. Micro organisms which cause diseases are called as pathogens.
Micro biology was developed by the greater contributions of eminent scientists Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Louis Pasteur etc. Some insects and animals carry diseases causing micro organisms. They are called as Vectors. This project reveals the diseases caused by harmful microbes in plants and animals.
Objectives:
- To know about disease causing micro organisms.
- Observing plant diseases and their symptoms.
- Observing the diseases that are caused in plants and animals.
Conducting The Project:
Members in the group had noted down the classification of micro organisms. They are as follows – Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Protozoans and Xematodes Survey was conducted on plant diseases that affect in the local area.
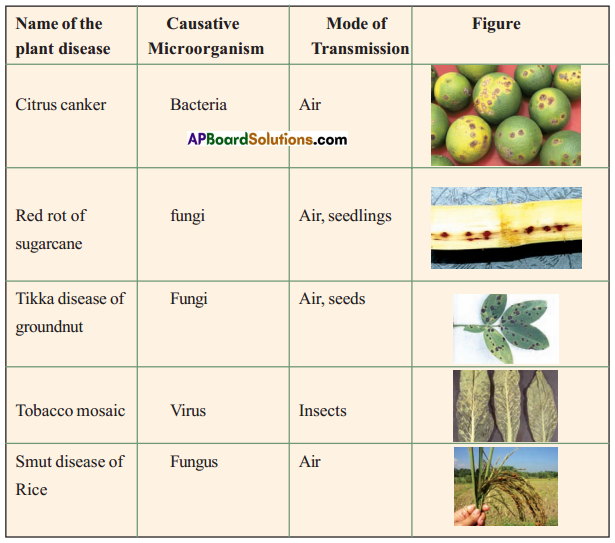
Again our group visited nearby veterinary hospital. Information was collected on various animal diseases. They are Anthrax, foot and mouth disease, mouth ulceration, viral diseases. Septisemta, fowl pox in poultry, bird flue, coccidiasis, gill decaying disease in prawn, Rabies in dog etc.
![]()
Diseases Caused In Man:
Many micro organisms cause various diseases in human beings. We can obtain knowledge on pathology. The given tabulated information gives some brief idea on diseases in man.
Some Common Diseases Caused By Micro Organisms In Human
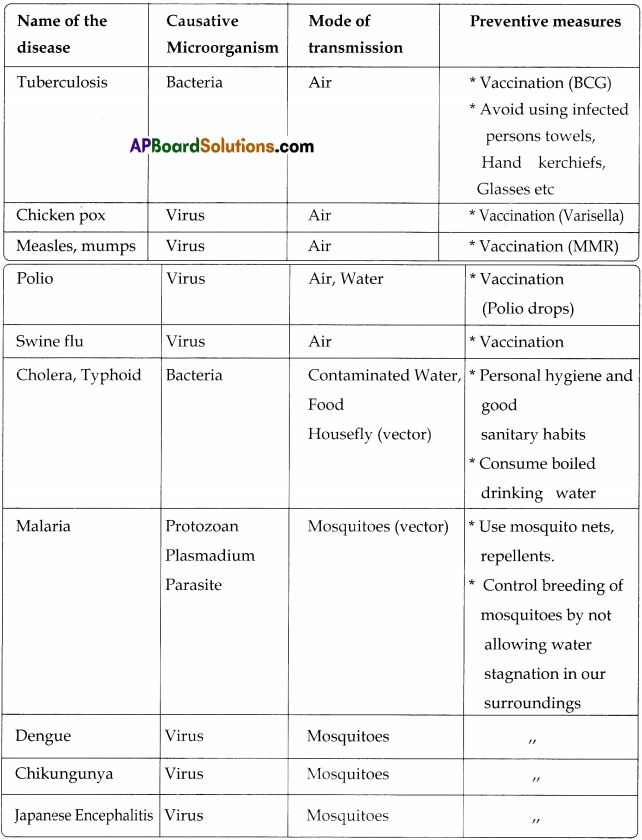
Conclusion:
Treatment is available for almost all diseases. But first and forermost prevention is better than cure. Everyone should he hygienic and maintain perfect healthy tips. All the surroundings should always be clean and tidy. As we aware of that some micro organisms are harmful, there are many more microbes which help human beings in many ways.
Project – 5. Story Of Micro Organisms-2
Title Of The Project: The Vaccine – That Sustains Life.
Introduction:
The proverb tells us that “Prevention is better than cure.” When we are affected with any disease we consult doctor and we use medicine or tablets prescribed by doctor. Taking medicine gives temporary relief from the disease. But the disease may affect once again to our body predominantly vaccination keeps us away from the diseases. We may have heard that children below 5 years must take polio drops – our national objective is to make polio free society.
Dr. Jonas Salk discovered vaccine for polio in 1952. He wanted to distribute it freely to everyone. So he never patented his polio vaccine. Dr. Albert Sabin discovered oral polio vaccine in 1957.
Administering vaccines for permanent immunity is called vaccination. The weakened disease causing micro organisms which are injected into our bodies are called as vaccines. Polio vaccine is given in the form of oral drops which prevents polio in children. While many other vaccines are injected to prevent diseases like smallpox, chickenpox, hepatitis, tuberculosis etc.
![]()
Objectives:
- To know the invention of vaccine.
- Tabulating the information on different types of vaccines and vaccination.
- To know about uses of vaccines.
Content Analysis:
Acquiring immunity to a disease by a vaccination was discovered by a British doctor called Edward Jenner in the year 17%. The decision of Dr. Edward Jenner to step up his medical practice in country yard i.e., in a village, which helped mankind save from extinction from diseases with discovery of vaccines. He keenly observed that the milkmaid who developed cowpox, a less serious disease, did not develop the deadly smallpox.
He thought they are developing immunity which is preventing small pox, a very dangerous disease wiping out millions of people in those days. In 1796, Jenner took the fluid from a cowpox postule on a dairymaids hand and inoculated a 8 years old boy with his parents permission. Six weeks later, he exposed the boy to smallpox and the boy did not develop any symptoms of smallpox. This invention of small pox vaccine saved millions of people from deadly disease. This showed the way for the discovery of number of vaccines which prevent us from harmful diseases.
The following tabulated information was collected from nearby primary health centre.
Disease —- Vaccine
- Cholera — Cholera Vaccine
- Diphteria — DPT
- Hepatitis – A — Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis – B — Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis-E — Hepatitis E
- Epiglottis — HIB
- Cervical Cancer — HPV
- Polio Mylities — Polio Vaccine
- Rota — Roto virus vaccine
- Rubella — MMR, MMRV
- Tetanus — DPT
- Tuberculosis — BCG
At present vaccines are available for various diseases – cholera, typhoid, diptheria, whoophing cough, polio, tuberculosis etc., moreover, scientists had taken a valuable step towards invention of many dreadful diseases such as malaria, ebola, zika, HIV AIDS etc. Trials on the prevention is almost at advanced and success stage.
Conclusion:
Vaccines if taken once, the immunity of an individual persists for life time. While in some cases the immunity will last only for limited amount of time. Present world of medicine created numerous vaccines on a large scale from micro organisms to protect human and other animals from several diseases.
Reproduction In Animals
Title Of The Project:
Project – 6. Reproduction by single parent of animals.
Abstract:
In some animals the formation of gametes does not take place. Still they produce offsprings like themselves. Various modes of asexual reproductions exist in the nature which have been explained in this project. Asexual reproduction in the animal organisms and higher animals is a vital biological process.
Illustrations were given in our report. Some organisms that undergo asexual reproduction depend on aclimatised condition (favourable or unfavourable condition). Collected data says how reproduction rejuvenates lost population.
![]()
Objectives:
- To know about importance of reproduction.
- To observe asexual reproduction in some organisms.
- To know about different modes of asexual reproduction in some animals and animal organisms.
Introduction:
Reproduction is one of the most important and fundamental properties of living organisms by which every kind of living organisms multiples to form new individuals of its own kiniL in this process, one generation of living organisms gives rise to the next generation. This process is not essential to the life of any individual but is a functional essential for the life of the species. Reproduction done by single parent is known as asexual reproduction.
Required Apparatus:
Laboratory slides of animal organisms such as Planaria, Turbellaria, bacteria, record book, drawing pencil etc.,
Project Implementation:
Some multicellular animals such as Hydra reproduce by budding. Animal organisms like amóeba, paramoecium undergo binary or multiple fissions that give rise to daughter individuals.
Procedure I:
Laboratory slide of planaria was observed under compound microscope. A rough sketch was drawn in the record note book.
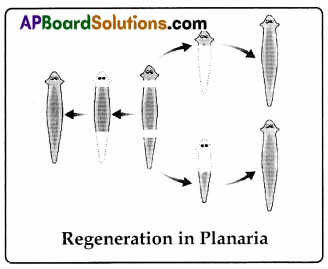
Mode of asexual reproduction occurs in the life cycle of planaria is ‘Regeneration’.
Regeneration:
Fully differentiated organisms have the ability to give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts. That is, the individual is somehow cut or broken up into many pieces, many of these pieces grow into seperate individuals. In planaria when the body parts cut into pieces, each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells.
These cells proliferate and make large numbers of cells, from this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues. These changes take place in an organised sequence referred to as development. However, regeneration is not the same as reproduction, since most organisms would not normally depend on being cut up to be able to reproduce.
Observing Slide Of Turbellaria:
The slide of Turhellaria was observed under microscope. A rough sketch was drawn in the record hook. Turhellaria performs a vital mode of asexual reproduction by mean of fragmentation.
Fragmentation:
The organism breaks up into two or more pieces or fragments upon maturation these fragments grow into new individuals.
Observing The Slide Of Bacteria:
Laboratory slide of bacteria that shows asexual reproduction was observed under micro-scope. Relevant sketch was drawn in the note book. A minute dot-like structures were seen in the slide. Naturally bacteria perform asexual reproduction by means of spore formation.

Spore Formation:
Some bacteria form spores, each which is a resting stage in which the cell protected by a thick wall that protects the cell from unfavorable conditions, such as high temperatures, drought, high acidity and alkalinity. On return of favourable conditions, the thick wall breaks open and the organisms reproduces and grows in the usual fashion.
![]()
Result Of The Project:
Collecting data on certain modes of asexual reproduction in animals proliferate their population then man’s modes of asexual reproduction even in plant kingdom. It is called vegetative reproduction. The project made us understanding how animal organisms perform asexual reproduction other than budding and Fission
Conclusion:
The continuity of life has been possible from the time of its origin, millions of years ago upto the present day, only due to phenomenon of reproduction. In fact, perpetuation of self and of the species is one of the most remarkable features of living organisms.
Project – 7. Biodiversity And Its Conservation
Title Of the Project:
Various National parks and Bird sanctuaries in India.
Abstract:
Measures of saving flora and fauna so that they are not lost from the earth surface are carried out through conscious steps of conservation. In our country, we have forest area that has been demarcated as national sanctuaries, reserved forests and parks to conserve different types of flora and fauna. All the valuable data has been documented in this
project. The map gives us idea on geographical location of sanctuaries and parks.
Introduction:
A national park is a large area hitched to conserve the wild life, particularly the wild animal species in their natural habitat. No human activity is allowed in any form. Even grazing of domestic animal is prohibited. A sanctuary is a place where conservation of species takes place with an objective of allowing human activity in a limited way without effecting the habitat.
National Parks:
National parks in India are IUCN category protected areas. India’s first National park was established in 1936 as Hailey National park, at present called as Jim corbett National park, Uttarakhand. By 1970, India only had five national parks. In 1972, India enacted the wild life protection Act and project Tiger to safeguard the habitats of conservation reliant species plans are underway to establish many more national parks in India. All of India’s national parks are listed below alongside their home state or territory, area and the data that they were established.
Here are some of the National parks listed below.
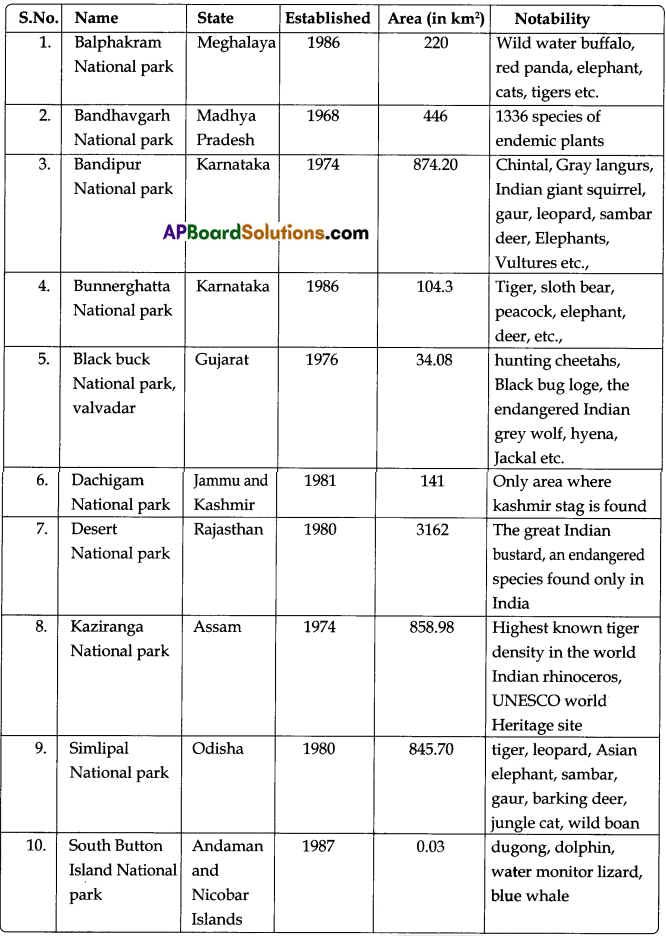
Some of the Famous Birds Sanctuaries in India:
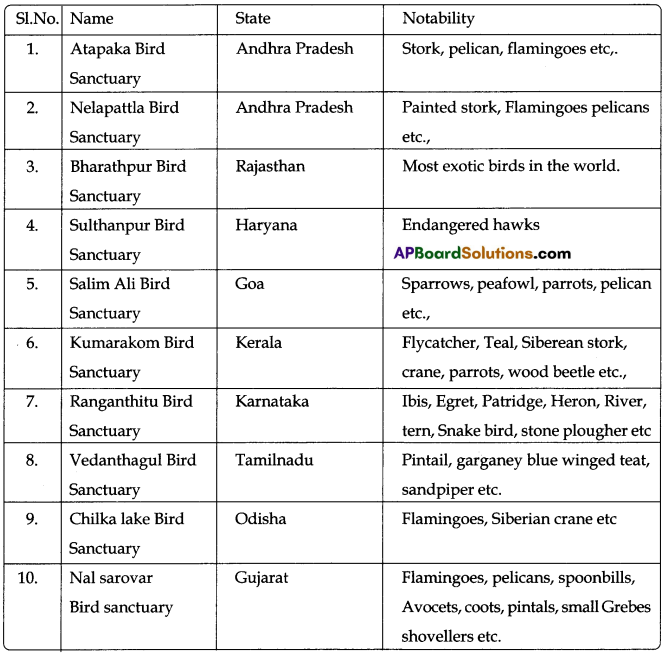
Conclusion:
Unfortunately, either knowingly or unknowingly,man has destroyed the wild life in the past several years. Fotunately, man has realised this mistake before it was too late. As a results, several measure were introduced to preserve wild life. Government of india has taken initiative to conserve wildlife by making National parks and sanctuaries to conserve forest, flora and fauna from being destroyed.
![]()
Conclusion:
Unfortunately, either knowingly or unknowingly,man has destroyed the wild life in the past several years. Fotunately, man has realised this mistake before it was too late. As a results,several measure were introduced to preserve wild life. Government of india has taken initiative to conserve wildlife by making National parks and sanctuaries to conserve forest, flora and fauna from being destroyed.
References:
- A text book Biology class -IX APSOERT Old Edition.
- A text of Biology class – VIII- AP.SCERT – New Edition.
- Web portal walk through India.com.
Project – 8 Biodiversity And Its Conservation
Title Of The Project : The ways human activities disturb biodiversity
Abstract:
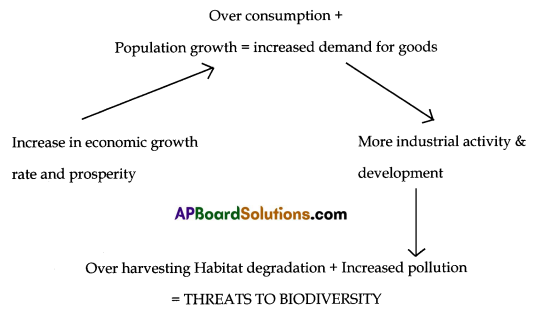
Human population growth is a major factor affecting the environment. Almost the environmental problems we face today can be traced back to the increase in population in the world. This project explains briefly about the impact of human activities on wonderful biodiversity. The effects of over population and over consumption are not only felt locally or nationally. Pollution generated in one area can affect the air, water, vegetation or animals in another.
Introduction:
The variety and variability seen in plants and animals is called Biodiversity. We know that many habitats exist in nature, which are quite different from each other. There are diverse forms in nature. There are different ways of nature that allow the diverse forms to take their places and roles in nature.
Diversity is not only seen in wild plants and animals. There is a great diversity in food crops. Nearly 50,000 varieties of rice plants were grown in India but now we use just about a dozen of them. Nearly five thousand plant species were used as staple food by humans., but now less than twenty species feed the majority of the world’s population.
Objectives:
- To know human activities impact biodiversity.
- To analyse the measures to protect biodiversity some human activities that lead to
destruction of biodiversity.
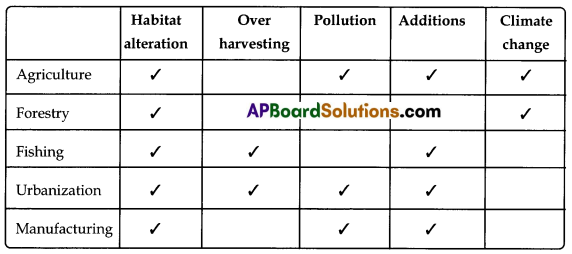
I. Indiscriminate Agricultural & Domestic Activities:
Man has destroyed the wild life in the past several years. Hunting of animals either for food or for pleasure, cutting off trees and clearing of forests (deforestation) for fuel, for starting new human settlements, to increase the area of agricultural land for the construction of dams and reservoirs has resulted in large scale destruction of forests.
As a result, several, animals and plant species have permanently disappeared from the face of earth, even before man realises their importance.
![]()
II. Industrialisation:
Industrialisation and pollution destroy enormous flora and fauna. The effects of over population and over consumption are felt throughout the world. The effect of global CO2 changes, loss of biodiversity and marine pollution do not respect political boundaries and ultimately affect everyone in the world. The relationship between human activity and biodiversity impact.
III. Introducing New Species:
Man has introduced new species of animals and plants in areas where they were originally absent. This resulted in an increase in the competition for food and space between existing and newly introduced species. The newly introduced species also introduced new types of parasites and diseases resulting in mass disappearance of native species.
IV. Over Exploitation:
Humans have historically exploited plant and animal species in order to maximize short-term profit, at the expense of sustainability of the species or population. Over exploitation of wild animals and plants for products of economic importance (such as ivory, skins) and for food also resulted in the disappearance of many creatures.
Tabulated details of Human activities and their impacts on biodiversity
Content Analysis:
The existence of biodiversity in nature teaches us that every plant and animal whether useful or not has right to exist on earth. Almost all human activities destroy the beauty of nature still man is not trying to introspect his deeds. He wants to dominant by implementing dreadful indiscriminate activities. He discards the ideal thoughts towards
conservation of nature.
Every organism is a part of our ecosystem. Loss of any organism endermic or otherwise effects the food chain and food web of the ecosystem, which has impact on the survival of other organisms.
![]()
Conclusion:
If we want to protect the diversity first we must be a part of conservation and then make others aware of it. Otherwise today we see extinction of some species tomorrow it could be our species. Nature is for humans need, not for his greed. We usually think of how to utilize nature for our own benefits.
Human being is a part of the nature. He is not the whole. If we protect the nature it protects us. This earth belongs to all animals and plants and every organism have equal right to live. Human beings must be sensitised in this aspect to protect biodiversity.
References:
- Contents extracted from research details given by Quebec biodiversity – Canada.
- A text of Biology class -IX – AP. SCERT Old Edition.
- A text of Biology class – VIII – AP. SCERT New Edition.
Project 9. Title Of The Project: Adaptations in an Ecosystems
Introduction:
Organisms influence the habitat and environment to fulfill his needs. Though they show some changes they sustain the favourable conditions for their survival. The number of organisms decrease which are eaten by other dominated animals. For example birds control insect population by consuming them.
As a result the ecosystem of birds remain constant. Likewise all the organisms show permanent adaptations according to the changes occur in the habitat. Living beings cannot survive themselves. They only can live in the habitat which
provides food and facilities. They create favourable habitat due to inter relationship between biotic and abiotic factors. This project reveals how animals adapt the environmental condition to live within the available habitat.
Objectives:
- Understanding different ecosystems
- Observing different adaptations
Implementing Project:
Group work was accomplished on visiting near by pond to observe aquatic plants.
Aquatic Plants :
Aquatic plants are the plants that are fully merged, sub merged, free floating in the water environment.
Eg: Ulphia, lechornia, Lemna, Pistia, Trampa, Nilambo, Nymphia, Marsella, Hydrilla, Vallisnaria, Cyprus etc.,
![]()
Adaptations In Aquatic Plants:
Some structural modifications of an organism have an ability to adapt living conditions in the water.
Modification In Roots:
Roots are absent in free floating plants or vegetatively less developed. Roots if present, possess root caps, root hairs balancing structures.
Modifications In Stem:
Stem is slender, elongated, spongy type in lufly merged aquatic plants. Plants like Nymphia and Nilambo have tubers stem.
Modifications In Leaves:
Leaves are small and thin in hydrilla plant. Ribbon type leaves are present in vallisnaria. The slit like structures are present in the leaves of utricularia. In Nilambo the upper surface of leaf is exposed to air and the lower surface contacts with water.
Desert Plants:
The plants that grow in drought hit or water scarce are called desert plants or xerophytes. Some plants show xerophytic features even in polar regions. These are classified as seasonal xerophytes, succulent xerophytes, and less succulent xerophytes.
Seasonal Xerophytes:
These plants complete their life cycle in 3-8 weeks. These plants live in less rain fall areas. Roots cannot penetrate deeper layers. These plants complete their life cycle before exhausting water from the humus. Eg: Euphorbia, Cassia, Echinops
![]()
Succulent Xerophytes:
These plants live in sandy areas in the beach and deserts. Plants tend to have narrow and small leaves or no leaves at all. This reduces the rate of transpiration and plants can conserve water. Plants have succulent stems and store water in their stems. Eg : Kittanara, cactus, opuritia, kalabanda.
Less Succulent Perinnials:
Vital adaptation to withstand, water scarcity conditions present inside and outside of the plants. Eg : Alfalfa, calotrophis, casuarina.
Content Analysis:
Plants in desert areas show several structural and physiological adaptations to in the water scarcity conditions. Plants tend to reduce their growth in unfavourable season. Usually they shed leaves and produce seeds during this period.
Conclusion:
The Boabab tree is swollen. It stores water in its trunk and survives the scorching heat of dry seasons. Now a days many xerophytes are grown as ornamental plants in pots at homes. Some plants as a whole seem to be flowers. Some with thorns. Some have flowers with bright colour petals. Now a days these kind of plants are used as gifts for Birthday’s and other occasions also.
References:
- A text book of Biology class -IX – AP.SCERT Old edition
- A text book of Biology class -IX – AP.SOERT New edition.
Project – 10. Production And Management Of Food From Plants
Title Of The Project : Modern tools in Agriculture
Introduction:
To get a better yield from the crop, a farmer has to plan and organise a number of activities even before raising a crop. Not all the soils are suitable to grow several crops. Then the field should ploughed. This facilitates uniform distribution of water and fertilizers.
Several operations such as ploughing the soil, sowing the seed, transplantation and removal of weeds and adaptation of fertilizers are to he carried out by the farmer. Some of the agricultural operations may be carried out manually and others with special instruments or implements. This project lead us to study the different tools used by the farmer in practicing agricultural methods to rise the crop.
Objectives:
- To know the importance of modern tools in agriculture.
- Understanding usage of agritools.
Project Implementation:
Ploughing the soil in the crop field : Ploughing the soil is the first and foremost agricultural operation. Plough is a popular implement in agriculture. In olden days T shaped plough was used. But farmers would take long time to finish ploughing. Now a days tractors are used for ploughing.

Iron ploughs cut 3 to 5 furrows at a time in the soil. The depth of the furrows can be altered depending on the soil type and other field condition. There is economy in ploughing the field with such new implementations. Soil is ploughed straight with uniform depth and width.
![]()
Soil Iron Leveller:
The modern iron leveller consists of a flat blade with vertical handles connected to the tractor. By levelling the soil water and nutrients can he reached to every part of the land.

Sowing Seeds With Seed Drilling:
Modern seed drill is an instrument used to sow seeds in the soil. There is a funnel like device on the top of the seed harrow. Farmers pour the seeds in the vessel connected to funnel. Drill is attached to the tractor. Tractor goes slowly in the field while dropping the seeds. It also covers the sown seeds with soil immediately with the help of a blade attached to it. It is time saving and the easiest way of sowing the seeds.

Modern Paddy Planter:
It is useful for farmers those who cultivate paddy in large areas. It is easy to maintain proper distance sowing the seedlings. It is time saving and money saving process.

Modern Techniques In Irrigation:
Sprinkler : It is used for conserving water in Agriculture in the areas where water is scarcely available, these sprinklers are handy to use. It provides uniform watering all over the field. It is beneficial in the way that every drop of water reaches to every plant in a field.

Drip irrigation : This method is employed in water scarcity areas. As the water reaches the plants drop by drop this is called drip irrigation. A long tube followed by small tubes attached to a motor. Holes are made in the tubes. So that water come out from the holes. The holes are arranged in such a way that it provide water extractly at the place where plant roots could receive water

Modern Weed Harrow:
This is attached to the tractor. It saves time to remove the weeds.

Modern Harvester:
Now a days it is a common practice to harvest the crop with the help of harvester. This machine can cut the crop and seperate the pure grains from unwanted material.

Conclusion:
Timely work is to be done to have better harvest. Farmers have to get innovative tools to improve the yield within the available agricultural land area.
![]()
Project – 11. Production And Management Of Food From Animals
Title Of The Project: Tvpesofchickenofpoultrv
Introduction:
Commercial establishments that supply meat giving birds such as layers, broilers and even birds are called hatchery. Production and rearing of hens on a large scale is called poultry. We know that farmers rear cocks and hens in villages. Most of these are Natukollu. This project helps us to know about different types of meat giving hens.
Objectives:
- To understand poultry for hens.
- To know about types of birds of poultry.
Project Implementation:
We get 74% chicken and 64% of eggs onI’ from poultry. Poultry has emerged as one of the major industries in last two decades. India achieved 4th position in the world by producing 41 .06 million eggs per annum. Genenally poultry farms are of two types. One is for production of eggs and other for meat. Broilers are commonly used variety in poultry. They are reared for meat.
Broilers:
New Hampshire, white, plymouth, Rhode island red, white leg horn, Anoka are the foreign varieties of meat giving species. Broilers are the young chicken of about S – 10 weeks of age. They are raised specially for meat production. BroiLers are grown to a weight of ‘eight 2 kg in 10 weeks on about 3kg of feed with an efficient feed conversion and mass production with a minimum amount of labour. Some of the desired features of the birds to he used for broiler production are fast growth, high feed efficiency, early feathering, good body structure and low mortality.

Layers:
These birds start laying eggs from the six month onwards. One day old chicks are brought from the hatchery. Then the3’ are placed in the brooders. Temperature is maintained in the brooders. The 20th week old chick are called growers. Electric lights proper mesh and sterilized conditions are necessary for layers. Most of the eggs are hatched during January to April. Hence egg prices are high. Layers are valuable as both egg and meat. Hatchability of eggs is generally influenced by 37- 38°C temperature.
![]()
Emu Culture:
Emu is the flight less bird from Australia. It is the second largest bird in the world after Ostrich. This amaging bird weights nearly 50 kg and run at 40 mph. Emu farming is also a commercial practice like hen. Recently farmers, started Emu farming. Meat, chicks, skin, leather, oil, feathers, eggs are the main products in F.mu culture.
Content Analysis:
The major products of poultry industry are eggs and chicken. The success of poultry industry is linked to the strategies of marketing of eggs and chicken. Balanced feed with proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals, vitamins and water in sufficient quantity is very important to the stock for a successful poultry farm.
Conclusion:
All the efforts are made in growing the birds for egg and meat production will go waste if proper management strategy is not followed for rearing layers and broilers poultry chicken suffer from bacterial, fungal and viral diseases. So a ranges of antibiotics are used for treatment of poultry diseases.
Project – 12. Not For Drinking Not For Breathing
Title Of The Projects: Pollution in the nearby river (or lake)
Introduction:
Adding any substance to water results in the change of physical and chemical characteristics of water, which inturn interferes with its use for human utility. Turbiolity, toxicity and heat loading are the three chief aspects of water pollution. Most of the Indian rivers are polluted heavily. This project has been documented on river krishna. The second largest water body in Andhra Pradesh.
Objectives:
- To know the reasons for water pollution.
- To understand the ill effects of water pollution.
- To get idea on remedial steps to reduce water pollution.
Project Implementation:
It is important to know the sources of water pollution in the river. Effects are very drastic due to various dreadful sources.
Sources Of Water Pollution:
i. Sewage and other oxygen demanding wastes : Sewage is defined as water-borne wastes from houses, animal and food processing plants etc., It is the largest pollutant of water.
Effects of sewage on water : The dissolved O2, in the water is 6- 7 mg/litre or 6-7 ppm. When the Dissolved oxygen (DO) is reduced to 4-5 ppm, fishes, especially juveniles die. Biological Oxygen Demand in (BOD) O2 consumed by aerobic bacteria for the decomposition of organic matters in the water. A high BOD indicates that the level of dissolved oxygen are falling with its potentially dangerous, effects on the river organisms.
ii. Industrialisation : Untreated industrial effluents released into water bodies pollute the river. In organic and organic pollutants like oils, greases, plastics, metallic wastes, toxins etc. They are non – degradable Acid wastes also enter river water and course pollution.
![]()
Effects : All the organic wastes depletes O2 level, Inorganic wastes render the water unfit for drinking.
iii. Agriculture related pollutants : Chemical pesticides disturb carnivores in the river. These toxins affect the reproductive system of aquatic birds and fish. Modern agricultural practices require fertilizers. These fertilizers are leached by the rain water into the river and disturb the ecosystem.
Effects : Due to concentration of nitrogen containing compounds water becomes unfit for drinking.
iv. Thermal pollutants : Pollutants are released from nearby thermal power plant damage the river water.
Effects : Thermal pollution effects the spawning and hatching of aquatic animal. Warm water holds less oxygen affects the aquatic life.
v. Aqua-culture pollution : Aquaculture in the recent times also became one of the sources of water pollution. The eutrophicated aquaculture pond water is released into the creek an effluent water polluting the river in some regions.
Measures To Prevent Water Pollution:
The simple solution to water pollution is dilution of the pollutants to the maximum possible lower levels. Mud – ball technique is used to minimise the synthetic fertilizer pollution. Installing cooling tower prevents thermal pollution. Water hyalinth, Ipomea etc., can purify water polluted by biological and chemical wastes. Industrial effluents should be treated by trickling filter method and activated sludge processes to remove the impurities.
Conclusion:
Natural resources are the divine gifts for us by nature. We can use these resources in a meaningful way which will help us. If we destroy these resources human life become an unsolvable puzzle. We should keep these resources clean and healthy, not only for us but also for future generations.
Project – 13. Why Do We Fill Ill?
Title Of The Project: Transmission of Diseases
Introduction:
A person said to be healthy when all the body functions are carried out normally.
Disease is a condition in which normal body functions are disturbed either temporarily or permanently. There are several stages from the time the diseases-causing organism enters our body and the person becomes sick. This is called process of disease. Transmission of disease is one of the stages. In this project the detail account on transmission of diseases are given.
Objectives:
- To know the various modes of transmission of diseases.
- To understand the remedial steps to terminate the disease.
Transmission Of Disease:
There are several methods by which a disease-causing organism can be transferred from the reservoir to the host organism.
![]()
Direct Contact:
Disease-causing organism may be transferred immediately from reservoir or camer to a healthy person by direct physical contact. Carrier is not required for this type of transfer of disease-causing organisms. This type of transfer is seen in diseases where the disease-causing organism can not live for a longer time out side the body of human host.
Diseases like skin and eye infections are transferred by direct physical contact. Soil also has several disease-causing organisms and direct contact of wounded portion with soil will also lead to infections. Tetanus causing bacteria are commonly transferred from soil into the body in this fashion. In this disease, muscles remain in a permanent state of contraction. This may lead to the death of the person. It is advisable to take anti-tetanus injection when injured.
Droplet Infection:
Droplets of saliva are sprayed out when we cough, sneeze, or spit. These salivary droplets from sick persons contain the disease-causing organisms. These salivary droplets act as a source of infection for others. Diseases like mumps, influenza, measles, chicken pox, common cold, whooping cough and tuberculosis are transmitted in this manner.The above two are direct transmission methods for the disease-causing organisms from the reservoir to the host. There are indirect methods of transfer of the disease-causing organisms from the reservoir to the host.
Vehicle Borne Transmission:
In this mode of transmission; the disease -causing organisms is transmitted through another living animal which is called as VECTOR. In several cases, the, vectors are insects and rats or mice. The most common insect vectors are flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches, lice, bugs, ticks and mites. The common vertebrate vectors are rats, mice and bats. Diseases such as plague, malaria are transmitted in this manner.
Carriers play a very important role in the transmission of a disease. As mentioned above, the carrier appears normal but is infected with a disease-causing organism. Therefore, it is very difficult to identify the carrier organisms from the rest of the normal, uninfected organisms around us. In several cases, elimination of the carrier organisms can control diseases. For example, reducing or even eliminating the mosquito population can control malaria.
![]()
Air Borne Transmission:
Air acts as a carrier or vehicle for transferring some of the disease-causing organisms. Air may have the organism or the spores or cysts of the organism. These may be released when a sick person coughs, spits, sneezes or blows his nose. These get dried in course of time and release the organisms into air or into soil. When wind blows, these organisms are carried along with dust and infect another person. Diseases such as tuberculosis, influenza, chicken pox, measles, pneumonia are transferred in this manner.
Unhygienic Habits:
Eating food without washing hands, eating food or drinking water from unhygienic sources also causes the transfer of disease – causing organisms. In the last two years, a disease called MAD – COW DISEASE has spread in cattle of Briton due to the contamination of cattle feed with the disease – causing organisms.
B. Incubation Period:
This is the second stage in the process of disease. This is the time between the entry of the disease-causing organism into the body and the appearance of the sickness. During infection, only few disease-causing organisms will be able to enter the body of the host. This small number of disease-causing organisms is not sufficient to cause any disease disturb the health of the host. They select a suitable tissue in the body of the host and settle down in the tissue. This will give protection to the disease.-causing organism from the defence system of the host. They get their energy requirements from the host tissue and they use some of the biochemical reactions of the host. They divide and multiply very rapidly and increase in numbers.
For each disease, the incubation period is highly specific. However, different diseases have different incubation periods. The incubation period may be from few days to few years. For diseases like CHICKEN POX, MEASLES and MUMPS, the incubation period ranges from 10 days to 3 weeks. For diseases like HEPATITIS, RABIES, LEPROSY, the incubation period ranges from weeks to years. For example, incubation period for AFRICAN -SLEEPING SICKNIESS is 20 to 30 years. As no sickness is seen during the incubation period, this disease can not be detected for a period of 20 – 30 years after infection.
C. Manifestation:
This is the third stage in the process of disease. This stage comes after the incubation period of the disease.
We have learnt that the disease-causing organism multiplies in numbers during the incubation period. When a large number of these organisms are produced in the host tissue, any one of the following events occur —
- They destroy the tissues of the host and are released into the blood. This causes extensive damage to the host tissue.
- They may block passages in the tissue and interfere with the free flow of substances in the tissue. Several parasitic worms block the passage of food in the intestines.
- They may release a toxic substance. This substance may kill the host cells or interfere with the normal functioning of the host cells.
Damage to the host tissues, blocking of the passages or interfering with the normal functions of the host causes sickness in the host. Some characteristic signs or indications of disturbed functions in the body that appear during sickness can help us to identify the sickness. Such signs or indications are called Symptoms.
Each disease produces a specific type of symptoms. Some of the symptoms are visible to the naked eye. Some of the symptoms can only be felt by a sick person but can not be seen by others. Some symptoms can be detected with specific instruments or tests. Doctors identify the disease by the symptoms. The appearance of the symptoms is called manifestation of disease.
![]()
D. Termination:
This is the last stage in the process of disease. In this stage, the disease process is halted either temporarily or permanently. This may occur naturally or with the help o drugs that kill the disease-causing organisms. There are three methods by which a disease can be terminated —
- The immune system of the patient fights and kills the disease-causing organism. As the number of the disease-causing organisms decreases, the symptoms also disappear and the intensity of the sickness is reduced.
- Using medicines prescribed by doctors reduces the number of the disease causing organisms.
- On the extreme side, the patient dies due to sickness that naturally results in the termination of the disease.
Conclusion:
Prevention is better than cure. Every individual should have an idea on hygienic and healthy habits. No one should pollute the atmosphere in their surrounding areas.