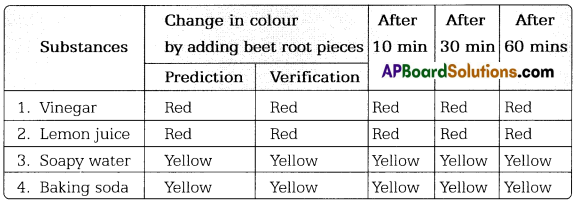
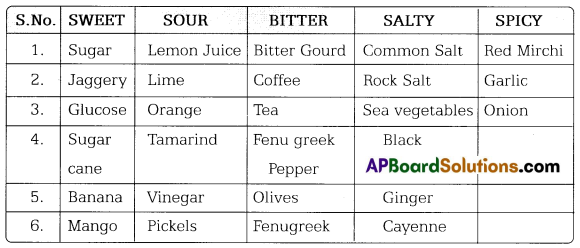
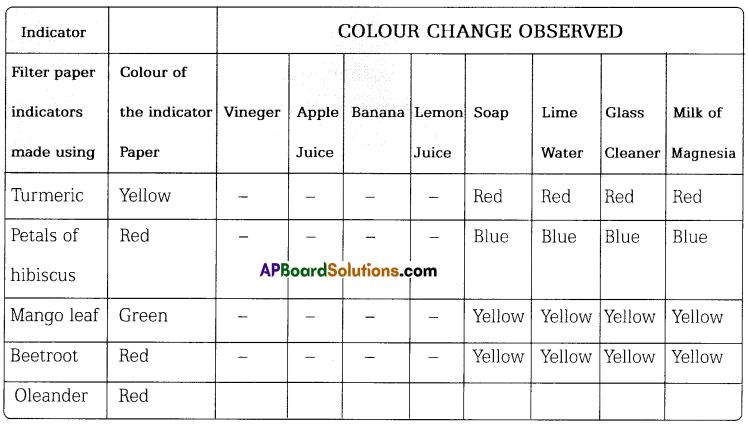
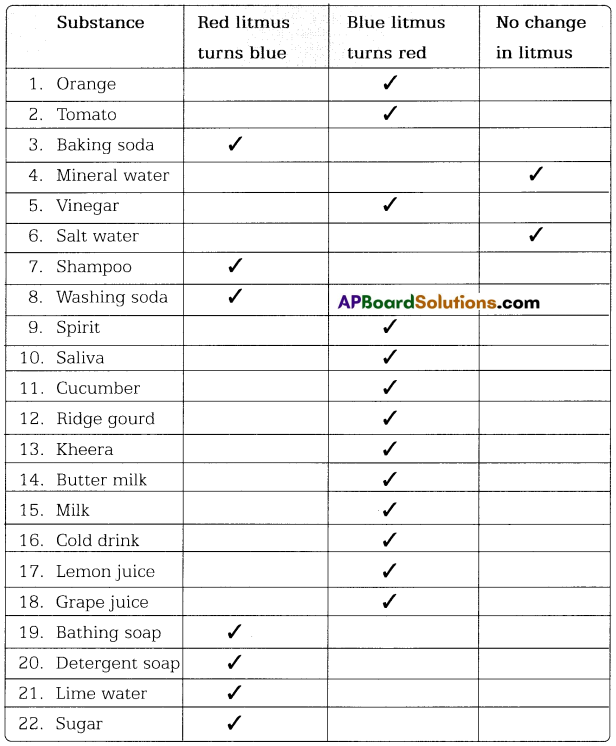
TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 7 Science Solutions 3rd Lesson Silk-Wool Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 7th Class Science 3rd Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Silk-Wool
Question 1.
In sericulture industry do which stages of silkworm weavers buy? Why do they do so?
Answer:
Weavers buy cocoons kept in sealed bags, at the cocoon market.
The weavers obtain fibre from cocoon.
![]()
Question 2.
Which place in our state is called silk city’?
Answer:
Pochampally in Andhra Pradesh is called ‘silk city’.
Question 3.
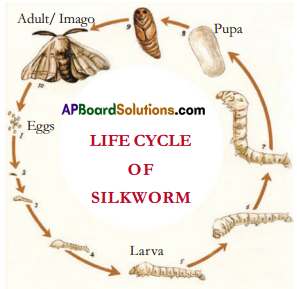
Prepare a chart showing life cycle of silkworm and display that in the classroom.
Answer:
Question 4.
Why are cocoons stiffled?
Answer:
The cocoons have to be stiffled to kill the larva inside as otherwise, it will cut its way out after growing into a moth and spoil the cocoon.
![]()
Question 5.
What will happen if cocoon is not boiled?
Answer:
The phenomena of extracting silk from cocoon by killing the matured caterpillar or pupa in boiling water is called stiffling. If cocoons are not boiled, matured caterpillar inside the cocoon develops into moth and emerges out by destroying the entire cocoon. As a result all the silk in the cocoon is spoiled and finally it will not be useful for reeling. Therefore, cocoons are to be boiled by the process of stiffling.
Question 6.
What are the differences between fleece of Angora goat and camel?
Answer:
Angora goat lives in Kashmir. It has soft hair. Camel lives in Rajasthan. It has a rough and coarse hair.
Question 7.
Make a flow chart showing various stages of production of woollen fabric.
Answer:
Flow chart of different stages of making of woollen cloth.
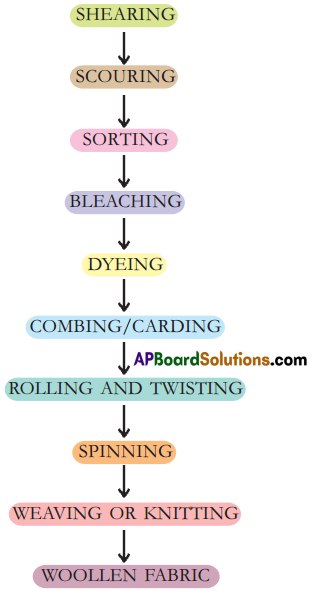
Question 8.
In what way is knitting different from weaving ?
Answer:
1. For knitting woollen fabrics, needles are required. But all types of yarn whether wool or silk or cotton are woovon on handloorns and powerlooms.
2. Wool can be knit easily because it has a natura! bend or crimp on it.
![]()
Process of weaving on a handloom:
- Woollen threads are stretched from the top of the loom to the bottom.
- These are called warp threads.The threads that go side to side are called weft threads.
- A shuttle – like big needle takes the weft threads over and under the warp threads.
- One more important part of the loom is the harness.
- The harness lifts every other warp thread so that the weft threads go over one and under the next. Thus, a fabric is woven.
Question 9.
Prepare a scrap book with pictures ot clitterent wool yielding animals.
Answer:
Wool yielding animals:
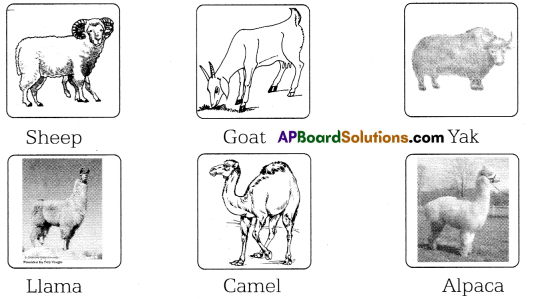
Question 10.
Fill up the blank and give your reasons for the statement fabric protects us from cold.
Answer:
Woollen
Reason : Wool is a poor conductor of heat. Air trapped in between the woollen fibres and our body prevents the flow of heat from our body to our surroundings. So, we feel hot and protected from cold. Woollen cloth also helps to put out fire, by breaking contact between the fire and the air. If you are going to visit Dal lake at Kashmir which type of clothes would
Question 11.
If you are going to visit Dal lake at Kashmir which type of clothes would you like to keep in your luggage ? Why?
Answer:
- Kashmir is a very cold place. Sometimes, the temperature falls to below 0°C.
- So, we have to protect our body from severe cold waves.
- For this, we have to wear woollen clothes to warm up our body.
- So, we have to carry woollen clothes like sweaters, mufflers, hats, long coats etc., along with us, in our trip to Kashmir.
![]()
Question 12.
Do you find any similarities between silk and wool weaving ? What are they?
Answer:
All types of yarn whether silk or wool (or cotton) are woven in the same manner.
Process of weaving on a handloom:
- The threads (silk or wool) are stretched from the top of the loom to the bottom.
- These are called warp threads. The threads that go side to side are called weft threads.
- A shuttle – like big needle takes the weft threads over and under the warp threads.
- One more important part of the loom is the harness.
- The harness lifts every other warp thread so that the weft threads go over one and under the next. Thus a fabric is woven.
Question 13.
Write 5 differences between wool and silk manufacturing.
Answer:
- Fibres of silk and wool are obtained from animals.
- They are ‘natural fibres.’
But they differ in their manufacturing from ‘fibre to fabric’.
They are as follows.
| Wool manufacturing | Silk manufacturing |
| 1. Wool is obtained from animals like sheep, goat, yak, llama, camel, alpaca etc. | 1. Silk moth is like a butterfly. Its eggs are called ‘seeds’. |
| 2. This wool is cleaned (scouring). | 2. The eggs are hatched. They turn into very small worms (caterpillars). |
| 3. Then ‘Wool Classing’ is done to get quality wool. | 3. These silk worms build cocoons around them. |
| 4. This wool is now bleached and dyed | 4. Cocoons are stiffled. |
| 5. The coloured wool fibres are then combed (carding wool). | 5. Silk fibre is obtained from these cocoons (reeling process). |
| 6. Then the wool is spinned into long threads. | 6. This silk fibre is woven into silk fabrics. |
Question 14.
Observe designs on silk sarees, trace them in your notebook and make your own designs.
Answer:
Students Activity.
![]()
Question 15.
In East India, silk is called pat. You may collect different pieces of silk fabric from a cloth store and write the names of the type of fabric and make a chart.
Answer:
Students Activity.
TS 7th Class Science 3rd Lesson Notes Silk-Wool
- Animal Fibres : Silk and wool fibres are obtained from animals like silk worms and sheep, goat, camel, yak etc., Animal fibres are natural fibres.
- Silkworm : Silkworm is an insect which is used in rearing of silk.
- Cocoon : A silky closed nest like structure made by the larva of silk moth is called cocoon.
- Mulberry : If the silk worms are fed Mulberry leaves, we get Mulberry silk.
- Sericulture : Rearing of silk worms and obtaining silk from them is called sericulture.
- Bombyx Mori : A type of an insect from which silk is obtained.
- Reeling : Separation of silk fibre from cocoon is called ‘reeling’.
- Fleece : The hair of animals is called wool (or) fleece or fur. This contains proteins.
- Shearing : Removing fleece from sheep, using razors is called, ‘shearing’.
- Scouring : Clearing of fleece with a stream of water is called scouring.
- Knitting : Woollen fabrics arc knitted, using a long needle and long threads of wool yarn. It is called, knitting.
- Bleaching : The process of cleaning the fibres before dying with colours.
- Weaving : Knitting is otherwise known as weaving.
- Dyeing : Dipping of fibres in the colours.
- Warp : Woollen threads are stretched from the top of loom to the bottom.
- Weft : The threads which go side to side.
- All clothes are made up of fibres. These are obtained from natural and , man-made sources.
- Natural sources of fibres are cotton, fufe, gongoora, coconut, silk and wool. Viese are obtained from plants and animals.
- Plant fibre is a carbohydrate while animal fibre is a protein.
- Egg, larva, pupa, adult moth are the stages in the life cycle of silk worm.
- In sen culture industry, eggs of silk moths are called ‘seeds. Silk moth is like a butterfly.
- The centres, where silk moths are sold, are called ‘Grinages’.
- The silk fibre is made up of two types of proteins, sirisine and fibroin ‘and is very strong.
- Pochumpally silk and Dharmavaram silk are famous types of silk produced by Andhra Pradesh.
- Pochampalli silk is also called ‘Tie and Die or ‘jamdani silk.
- Wool is obt ained from the hair of animals like sheep, goat, yak, lama, camel, alpaca etc.
- Angora goat or the Merino sheep have soft hair.
- During spring season, fleece of sheep is removed.
- Fleece is separated after ‘wool classing’ or ‘sorting’. Fleece is the soft mass of wool.