TS SCERT 7th Class Science Guide Telangana 16th Lesson Forest: Our Life Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 7th Class Science 16th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Forest: Our Life
Question 1.
How can you say forest is a habitat for people?
Answer:
- A forest is a community of trees, shrubs, herbs and other plants and organisms that cover a large area using carbondioxide, water, soil nutrients etc.
- Forests take up a large amount of carbondioxide and some other harmful particles and gases and keep the air clean.
- Forests serve as lungs of our earth.
- Forests are renewable natural resources, which play an important role in the maintenance of ecological balance.
- They are important source of timber, fuel, wood, cane, resins, lac, oils, fruits, nuts, fire wood, fodder for animals, honey etc.,
- By knowing all the above valuable information, forests are called as habitats for people.
- We obtain medicinal products from the forest.
![]()
Question 2.
What variations do we see in forest types ?
Answer:
There are 7 types of forests based on the climatic conditions.
- Tropical evergreen forests.
- Moist deciduous forests (Equatorial forests)
- Dry deciduous forests.
- Alpine forests (Forests of cold areas)
- Tidal forests.
- Thorn forests.
- Mangroves.
Question 3.
How do we depend on forests?
Answer:
We depend on forests for the following needs.
- Forests prevent floods and soil erosion.
- People living in forests depend on its products for their livelihood.
- Forests help in maintaining the ratio of oxygen and carbondioxide in air.
- They are good habitats for many plants, animals and human beings.
- Various things and material such as timber, fuel wood, cane, resins, lac, oils, fruits, nuts, firewood, fodder for animals, honey etc., are obtained from the forests.
- We depend on forests for obtaining valuable medicinal drugs to cure dreadful diseases.
Question 4.
How can you say forests are lungs of our earth?
Answer:
Forests take up a large amount of carbondioxide and other gases and keep the air clean. They serve as lungs of our earth. They give us oxygen for breathing.
![]()
Question 5.
List the things that we use in our daily life which are made from wood.
Answer:
The things that we use in our daily life which are made from wood are.
- Wooden chair
- Door
- Window
- Bench
- Table
- Bamboo
Question 6.
What is deforestation? How can it be stopped?
Answer:
Excessive cutting down of trees in and around forests is called Deforestation.
Conservation of forests:
- Efforts should be made along with forest officials to save forests by planting more plants.
- We should see to conserve soil moisture by making bunds along edges of plantation areas, digging trenches etc.,
- We should decrease cutting trees for harvesting crops. Inspite of that efforts should be made to improve the ‘yielding’ within the available land area.
- Making a plan of growing trees in areas allotted near villages or towns is essential.
- We should maintain social forestry, that is people’s own efforts to revive forests, which are well known as ‘Karthik Vanam’.
Question 7.
This is not a forest product. (Conceptual Understanding)
A) Soapnut
B) Plywood
C) Matchstick
D) Kerosene
Answer:
D) Kerosene
Question 8.
If you want to develop social forestry in your village, which type of plants would you like to grow ? Why?
Answer:
If I want to develop social forestry in my village, I would like to grow the following plants. Neem, Tamarind, Amla, Soapnuts, Casuarina (sarividi) Eucalyptus, Coconut, Mango, Sapota etc. By growing the above mentioned plants, we have the following advantages.
- Economically profitable as “Social forestry”.
- Plant products like fruits, seeds, wood, fuel wood are available.
- Soil erosion will be prevented and retain the fertile soil.
- Keep our surroundings always cool and clean.
- Those plants give us plenty of oxygen and they remove the carbondioxide from atmosphere.
![]()
Question 9.
Collect the pictures of forest products and stick them in your scrap book.
Answer:
Aim : To collect the pictures of forest products to make a scrap book.
Procedure: I collected old news magazines referred for forest products. The following pictures are collected.
Question 10.
Write a note on livelihood of forest tribes of our State.
Answer:
- In various forest areas of Andhra Pradesh, we find some people still living there and making their home. These people are called “Forest tribes”.
- Forests are the sources of livelihood for all tribes.
- For example, ‘Chenchus’ (adivasis) never harm the forests. ‘Koyas’ also make efforts to conserve forests arid depend on them.
- They collect various food products like soapnuts, honey, tamarind, bamboo etc., and sell them in the “santha” (a weekend market) and purchase material like clothes etc.
- These tribes collect medicinal plants from the forest for which they are well known throughout the State.
Question 11.
Collect some songs / stories / poems about conservation of trees.
Answer:
Save a Tree. Save other Lives Tool
There is a school in a village. The school has no boundary wall. The Headmaster arranged for the construction of a boundary wall with the help of higher authorities. They were measuring the boundaries. There was a mango tree in the school. The tree was on the boundary line. A person staying next to the school argued that the tree belonged to him. The children studying in the school had been playing, reading, having lunch etc., for years under the tree.

The children came to know that the person sold the tree. It was going to be cut very soon. They tried to convince that person not to remove the tree, but he adamantly denied the children’s request. Neelima who was studying class VII was worried about it. She thought throughout the night and got an idea.
The next morning she told the idea to her friends. They collected money from their savings. All the children visited all the families and collected some more money. They went to that person and gave him all the money they collected. Seeing the concern of the children, the person agreed that the tree would not be cut.
![]()
Question 12.
We can see animals not only in the forests but also in the zoo. Write some similarities and differences between the conditions in which animals are found in the zoo and the forest.
Answer:
| Forest animals | Zoo animals |
| 1) They live in natural habitat. | 1) They live in artificial or man made atmosphere. |
| 2) They depend on food products available in the forest. | 2) These are also to be fed with the food on which they used to depend when they were in forests. |
| 3) Animals move freely in the forest. | 3) Animals have restrictions to move. (kept in the bones or cages) |
| 4) They follow natural feeding habits. | 4) Food is supplied to the animals by the zoo’s staff. |
| 5) Sometimes, animals may be attacked by poachers. | 5) Animals are protected by security of government department. |
| 6) Living processes depend on the forest habitat. | 6) Living processes depend on the habitat that is arranged artificially. |
Question 13.
Chanta said Torest is a good habitat. How can you support her?
Answer:
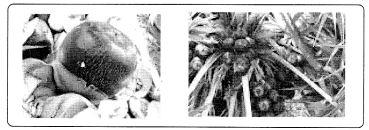
- I can support Chantas opinion. Forest is a good habitat.
- Because habitat is the natural living place of an organism or a group of organisms.
- We can notice several different types of organisms in the forest.
- There are different types of plants ranging from small grass to tall trees and several different types of animals – ranging from small insects and worms to large animals
- All these organisms are living in the forest habitat and sharing the resources. For example, plants are food for some of the insects and also for deer, rabbit, birds, goat, sheep etc., are food for tiger, lion, wolf.
- In other words, organisms living in a forest habitat do not live by themselves. Hence, I strongly say that the forest is the good habitat.
![]()
Question 14.
How do we depend on forests?
Answer:
We depend on forests for the following needs.
- Forests prevent floods and soil erosion.
- People living in forests depend on its products for their livelihood.
- Forests help in maintaining the ratio of oxygen and carbondioxide in air.
- They are good habitats for many plants, animals and human beings.
- Various things and material such as timber, fuel wood, cane, resins, lac, oils, fruits, nuts, firewood, fodder for animals, honey etc., are obtained from the forests.
- We depend on forests for obtaining valuable medicinal drugs to cure dreadful diseases.
Question 15.
Draw or collect pictures of forests. Discuss with your friends. Write about fate of forests in your State and what steps would you take to conserve them.
Answer:
Pictures : Students’ Activity.
Fate of Forests: In the forests of Andhra Pradesh, we can see different types of trees and animals. They are nature’s boon to us. Recent surveys reveal us depletion of forest range area is alarming in our state. Now-a-days, thermal, nuclear power plants, mining industries led by multinational companies are a major threat to forests throughout the state.
How do we conserve the forests from destructing?
- There is a way to safeguard forests by making the people in the neighbourhood partners in the joint forest management.
- If we take due care of plants growing around us, we may not be adding a forest but adding to greenery around us which is essential for our own existence.
- Efforts have been made by communities along with government officials to grow trees in allotted places as social forestry.
- People should work together to protect the nearby forests and to share forest produce. These groups are for the protection of forests and are called ‘Vana Samrakshana Samithis’.
- Growing trees along with agriculture in the farm is called “Agro – forestry”. It is to be implemented. By implementing the above activities, we can conserve our forests.
Question 16.
Find out about state of forests in India and write a brief report on it,
Answer:
- The term ‘wild life’ refers to animals and plants living under natural conditions. Generally it is called ‘forest’.
Unfortunately, either unknowingly or knowingly, people destroyed the forests in India in the past several years. - To avoid this, the Government of India realised the importance of forests and initiated several programmes to preserve wild life in the country and the wild life act was passed in 1972.
- Several forests have been declared as reserve forests and protected. National parks, where wild life is protected, have been created.
- Thus, there are 66 national parks in the country. Collection, marketing and selling of forest products by private parties is banned and is taken up by the government.
- In addition, projects have taken up to protect and increase the number of endangered species (animals or plants which are about to disappear).
- All these efforts have been fairly successful in restoring the wild life in the country.
![]()
Question 17.
Plant a tree on your birthday or during any celebration in the family.
Answer:
(Note : This is to be done by the students on their special occasions.)
TS 7th Class Science 16th Lesson Notes Forest: Our Life
- Orchard : The flowering plants.
- Plantation : The process of planting plants.
- Timber : The part of the plant useful for furniture.
- Fire wood : The part of the plant useful for cooking food.
- Soil erosion : Removal of top most soil.
- Bunds : The edge of the canals and tanks.
- Deforestation : Destruction of forests is called deforestation.
- Tribe : The people who live in forests.
- With the advance of civilization through ages, most parts of forests are reduced now,
- Forest is a place where there are many different trees. It is a home for wild animals.
- We should not cut the trees to build factories, buildings etc., or to grow crops, orchards etc.
- We obtain various things and material from the forest.
- A forest is a good habitat for many plants and animals.
- Forests help in binding of soil and protecting it from erosion.
- People living in forests depend on its products for their livelihood.
- Social forestry could help overcome deforestation. Forests are lungs of our earth.
- Destroying forests poses threat to life of animals and plants living there as well our own survival.
- Government officials grow trees in areas alloted near villages / towns as social forestry.
- People s own efforts to revive forests, which are well known as “Karthik Vanani “.