These AP 10th Class Biology Important Questions and Answers 1st Lesson Nutrition will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Important Questions and Answers Nutrition
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Nutrition 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define photosynthesis. (OR) What is photosynthesis?
Answer:
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants containing the green pigment called chlorophyll which build up complex organic molecules from relatively simple inorganic ones using sun light as an energy source.
Question 2.
What is the balanced equation to show the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Question 3.
Bhumika told that “If there were no green plants, all life on the earth would come to an end” Comment.
Answer:
All the living organisms on the earth depends on the plants either directly or indirectly for the food and oxygen.
Question 4.
Which disease occurs in child when there is an immediate second pregnancy or repeated child births in a mother?
Answer:
Marasmus
Question 5.
Give two examples for nutritional deficiency diseases.
Answer:
Nutritional deficiency diseases: Kwashiorkor, Marasmus, Beri-Beri, Glossitis, Pellagra, Anemia, Scurvy, Rickets, etc.
Question 6.
Your neighbour’s children appear with swollen legs, hands and other body parts. They have dry skin and frequently suffering from Diarrhoea. What are the reasons for it ? What suggestions do you give to their parent ?
Answer:
The children appear with swollen legs, hands and other body parts. They have dry skin and suffering from diarrhoea.
The reason for it is malnutrition and they are suffering from Kwashiorkor and Marasmus diseases.
They are advised to take proteins and calorie rich foods like liver, meat, eggs, milk, fruits, cereals and leafy vegetables.
![]()
Question 7.
What suggestions do you give to your friend suffering from constipation?
Answer:
Constipation can often be avoided by
a) having plenty of roughages in our daily diet. Ex : Leafy vegetables, beans, cabbage, etc.
b) drink plenty of water daily.
c) avoid junk food,
d) swallow the food only after its thorough mastication.
Question 8.
Which organelle of the leaf absorbs energy from the sunlight for photosynthesis ?
Answer:
Chloroplast.
Question 9.
Which gas is evolved in the diagram experiment? How can this gas be tested for confirmation?

Answer:
i) Oxygen gas is evolved in this experiment.
ii) If the burning splinter is kept near the mouth of the test tube, it burns brightly.
Question 10.
Classify the following vitamins into water soluble and fat soluble
i) Riboflavin ii) Retinol iii) Tocoferol iv) Thiamin
Answer:
Water soluble vitamins : Riboflavin (B2), Thiamin (B1)
Fat soluble vitamins : Retinol (A), Tocoferol (E)
![]()
Question 11.
Prepare your own tabular column to get information about food deficiency diseases from a doctor.
Answer:
| S.No. | Name of the disease | Symptoms | Deficiency due to which nutrient |
| 1. | Kwashiorkor | Hands and legs swollen, fluffy face, loose motions. | Protein deficiency |
| 2. | Marasmus | Lean, weak, swollen joints, no development in muscles, loose motions. | Both proteins and calories deficiency. |
Question 12.
Why is KGH used in Mohl’s half leaf experiment? (OR)
Why do we use KOH solution in Mohl’s half-leaf experiment?
Answer:
1) We conducted Mohl’s half leaf experiment to prove CO2 is essential for photosynthesis.
2) So KOH is used in this experiment to absorb the CO2 present inside the bottle.
Question 13.
What questions will you ask a doctor to know about malnutrition ?
Answer:
- What is malnutrition?
- What are the causes for malnutrition?
- What are the different types in malnutrition?
- How can we overcome the malnutrition?
- What are the reasons for malnutrition in our country?
![]()
Question 14.
Name the vitamin which is synthesized by the bacteria present in the human intestine.
Answer:
B12 (Cyanocobalamine) is the vitamin which is synthesized by the bacteria present in the human intestine.
Question 15.
Which digestive juice doesn’t contain enzymes ?
Answer:
Bile juice which is produced by liver doesn’t contain enzymes. But it converts fats into small globules. This process is called emulsification.
Question 16.
One student takes high calorie food. Another student takes less calorie food. But both are affected with diseases. Name the diseases by which they are affected.
Answer:
Student takes high calorie food affected by – Obesity.
Student takes less calorie food affected with – Marasmus.
Question 17.
Mention the two chemicals which you have used in an experiment to test the presence of starch in the leaf.
Answer:
The chemicals used in an experiment to test the presence of starch in the leaf are
- Methylated spirit
- Iodine solution.
Question 18.
18. Write two slogans for campaign on Mal-nutrition.
Answer:
- Be cool and say no to fast food.
- Be smart – Eat smart
- Eat healthy – Look healthy – Feel healthy
![]()
Question 19.
Identify the two parts A and B indicated in the given figure.
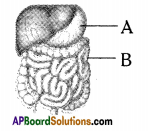
Answer:
A – Stomach
B – Large intestine
Question 20.
Doctors advise not to eat food items at the time of fever. What are the reasons for this ?
Answer:
- At the time of fever body temparature is high.
- At that time digestive enzymes do not properly work to digest food.
- That’s why doctors advise not to eat food items at the time of fever.
Question 21.
If we chew the grains like wheat, jowar, rice we feel sweet. Why?
Answer:
- The grains like wheat, jowar, rice contain carbohydrates.
- Ptyalin acts on them and coverts them into sugars. So we feel sweet.
Question 22.
What teeth you use when you eat peas and banana? Why?
Answer:
- Premolars and molars are used when we eat peas and banana.
- Their function is to chew and grind the seed and food material.
Question 23.
What is autotrophic nutrition?
Answer:
It is a type of nutrition in which an organism makes its own food from the simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide and water using light as source of energy.
Question 24.
What is nutrition ?
Answer:
Nutrition: Nutrition is the process of intake or procurement of nutrients.
Question 25.
What are the main modes of nutrition ?
Answer:
Autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition are the main modes of nutrition.
Question 26.
What are different types of heterotrophic nutrition ?
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types. They are:
- Saprophytic nutrition
- Parasitic nutrition and
- Holozoic nutrition.
Question 27.
What are the symptoms of disease pellagra?
Answer:
Dermatitis, diarrhoea, loss of memory and scaly skin are the symptoms of disease pellagra.
![]()
Question 28.
Which vitamin deficiency causes Rickets ? What are its symptoms?
Answer:
Vitamin D Calciferol deficiency results in Rickets. The symptoms shown are improper formation of bones, knocknees, swollen wrists, delayed dentition, weak bones, etc.
Question 29.
For proper vision which vitamin is required? What is its chemical name?
Answer:
Vitamin A is required for proper vision. The chemical name of vitamin ‘A’ is Retinol.
Question 30.
What are the complex molecules produced by plants from simple Inorganic substances?
Answer:
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are produced from simple inorganic substances like water and CO2.
Question 31.
What are the essential factors required for photosynthesis?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and sunlight are the essential factors required for photosynthesis.
Question 32.
What is the equation for photosynthesis proposed by C.B.Van Neil in the year 1931?
Answer:
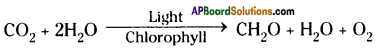
Question 33.
In which form are carbohydrates stored in plants?
Answer:
Carbohydrates are stored in plants in the form of starch.
Question 34.
What is the reagent that is used to test the presence of starch in leaves?
Answer:
The reagent that is used to test the presence of starch in leaves is Iodine solution. The colour of the leaf will turn to blue-black in colour.
Question 35.
Who found that water was essential for the increase of plant mass?
Answer:
Von Helmont found that water was essential for increase of plant mass in the year 1648.
Question 36.
Who performed series of experiments in 1770 to reveal the role of air in growth of green plants?
Answer:
Joseph Priestly performed series of experiments in 1770 to reveal the role of air in growth of green plants.
![]()
Question 37.
What is the role of potassium hydroxide solution kept inside the glass bottle in the Mohl’s half leaf experiment?
Answer:
Potassium hydroxide solution kept inside the glass bottle in the Mohl’s half leaf experiment absorbs the carbon dioxide present inside the bottle.
Question 38.
Who found that gas bubbles liberated from hydrilla plant contain the gas oxygen?
Answer:
Jan Ingenhousz in 1779 found that the gas bubbles liberated from hydrilla plant contain the gas oxygen.
Question 39.
Who coined the term chlorophyll for the extract of green coloured substance from the leaf?
Answer:
Pelletier and Caventou in the year 1817 coined the term chlorophyll for the extract of green coloured substance from the leaf.
Question 40.
Chloroplast is formed by how many membranes?
Answer:
Chloroplast is formed by 3 membranes.
Question 41.
What is grana?
Answer:
Grana : The stacked sac like structures formed by the third layer of chloroplasts is called grana.
Question 42.
What is the function of stroma?
Answer:
It is believed to be responsible for enzymatic reactions leading to the synthesis of glucose, which inturn join together to form starch.
Question 43.
What is stroma?
Answer:
Stroma : The fluid filled portion of chloroplast is called as stroma.
Question 44.
What are the two major phases found in photosynthesis?
Answer:
The two major phases found in photosynthesis are:
Question 45.
Why is light reaction phase called photochemical phase?
Answer:
A series of chemical reactions occur in a very quick succession initiated by light and therefore the phase is technically called the photochemical phase.
Question 46.
Where does the light reaction take place?
Answer:
The light reaction takes place in chlorophyll containing thylakoids called grana of Chloroplasts.
Question 47.
What are the end products of light reaction?
Answer:
The end products of light reaction are O2, ATP and NADPH.
Question 48.
What are called the assimilatory powers?
Answer:
ATP and NADPH formed at the end of the light reaction are called assimilatory powers.
![]()
Question 49.
What are dark reactions?
Answer:
Dark reactions: The reactions that occur in both presence or absence of light are called dark reactions. The occurance of dark reaction is independent of light.
Question 50.
Who observed dark reactions?
Answer:
- The entire series of reactions involved in the conversion of CO2 to glucose were identified by Melvin Calvin.
- The dark reactions are also called as Calvin Cycle.
Question 51.
What is Calvin cycle?
Answer:
Calvin cycle: The cycle of reactions in fixation of carbon dioxide to glucose is called Calvin cycle.
Question 52.
How is glucose produced during dark reaction?
Answer:
In the dark reaction, the hydrogen of the NADPH is used to combine with CO2 by utilizing ATP energy and ultimately produce glucose.
Question 53.
Write some of the events that occur in the chloroplasts during photosynthesis.
Answer:
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
- Splitting of water molecule.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
Question 54.
What is photolysis of water? Which gas is released?
Answer:
Photolysis of water:
- Photolysis of water Splitting of water molecule by light activated chlorophyll molecule is known as photolysis of water.
- Oxygen is released during (photosynthesis) photolysis of water.
Question 55.
In which cells of the leaves photosynthesis takes place?
Answer:
The mesophyll cells of leaf containing palisade and spongy tissue photosynthesis takesplace.
Question 56.
What is the ultimate source of energy?
Answer:
The ultimate source of energy is the Sun.
![]()
Question 57.
What are guard cells?
Answer:
Guard cells: The two kidney shaped cells which surrounds the stoma are called guard cells.
Question 58.
How does CO2 enter into leaf?
Answer:
CO2 present in the atmosphere enters through stomata into the cells of leaf by diffusion.
Question 59.
What is the first stable product formed in dark reaction or photosynthesis?
Answer:
Phosphoglyceric acid or PGA is the first stable product formed in dark reaction or photosynthesis.
Question 60.
Why ATP and NADPH are required in photosynthesis?
Answer:
ATP and NADPH are required for the utilization of carbon dioxide and formation of glucose during photosynthesis.
Question 61.
Why chloroplasts are green in colour?
Answer:
Chloroplasts are green in colour due to the presence of a green colouring pigment called chlorophyll.
Question 62.
What are the examples for parasitic organisms?
Answer:
The examples for parasitic organisms are cuscuta (plant), lice, leeches and tapeworms (animals).
Question 63.
How does amoeba take food into the body?
Answer:
Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger like extensions called pseudopia of the cell surface.
![]()
Question 64.
How does paramoecium take food?
Answer:
Food is moved to the cytosome by the movement of cilia which covers the entire surface of the cell where the food is ingested.
Question 65.
What is ingestion?
Answer:
Ingestion : The process of taking food into the body is called ingestion.
Question 66.
Name the three pairs of salivary glands. What is the enzyme secreted by them?
Answer:
- The three pairs of salivary glands in mouth are :
i) Parotid glands
ii) Submandibular glands and
iii) Sublingual glands. - The enzyme secreted by salivary glands is amylase (ptyalin).
Question 67.
What is the role of amylase in digestion of food?
Answer:
Amylase helps in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates to simple ones.
Question 68.
What is digestion?
Answer:
Digestion : The process of breaking down of complex food substances into simple substances so that they can be used by the body with the help of enzyme is called digestion.
Question 69.
How does the food from oesophagus move into the stomach?
Answer:
Food passes through oesophagus by wave like movements called peristaltic movements and reaches the stomach.
![]()
Question 70.
What is chyme?
Answer:
Chyme : Chyme is a soft slimy substance of food in which some proteins and carbohydrates have broken down.
Question 71.
What is the function of sphincter muscle present at the exit of stomach?
Answer:
- The sphincter muscle is responsible for regulating the openings of the stomach into small intestine.
- So that only small quantities of the food material may be passed into the small intestine from the stomach at a time.
Question 72.
What does the gastric juice contain?
Answer:
The gastric juice secreted by the walls of stomach contains Hydrochloric acid, protein digesting enzyme, pepsin and mucus.
Question 73.
What makes the internal condition of the intestine gradually to a basic or alkaline one?
Answer:
Liver and pancreatic juice make the internal condition of the intestine gradually to a basic or alkaline one.
Question 74.
What is emulsification?
Answer:
Emulsification : Fats are digested by converting them into small globule like forms by the help of bile juice secreted from liver. This process is known as emulsification.
Question 75.
For what intestinal juice secreted by small intestine is responsible?
Answer:
The enzymes present in intestinal juice finally convert the protein to amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 76.
What are the enzymes that act on proteins?
Answer:
Pepsin and Trypsin are the enzymes that act on proteins. Both these enzymes convert proteins to peptones.
Question 77.
What is absorption?
Answer:
Absorption : Transport of the products of digestion from the walls of the intestine into blood is called absorption.
Question 78.
What is defecation?
Answer:
Defecation: The passage of undigested material from the body by the way of anus is called defecation.
Question 79.
What are roughages in the food?
Answer:
Roughages are the fibres of either carbohydrates or fats which help in constipation.
Question 80.
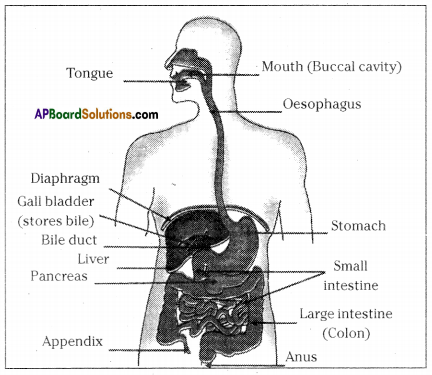
What are the parts of human digestive system?
Answer:
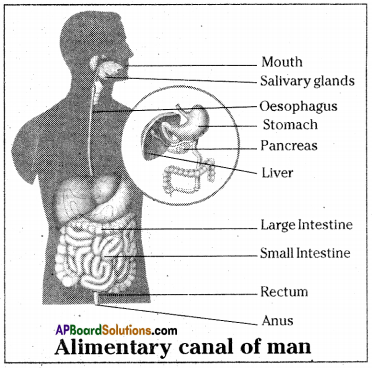
Mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus.
![]()
Question 81.
What is a balanced diet?
Answer:
Balanced diet: Diet containing nutrients in required amounts is known as balanced diet.
Question 82.
What are the nutrients present in balanced diet?
Answer:
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and mineral salts are the nutrients present in balanced diet.
Question 83.
What is malnutrition?
Answer:
Malnutrition : Eating of food that does not have one or more than one nutrients in required amount is known as malnutrition.
Question 84.
What are different types of malnutrition?
Answer:
Malnutrition is of three types. They are:
- Calorie malnutrition
- Protein malnutrition and
- Protein calorie malnutrition.
Question 85.
What are the two sources of vitamins to our body?
Answer:
The two sources of vitamins to our body are one is diet and the other is bacteria present in the intestine synthesise enzymes and supply them to the body.
Question 86.
Vitamins are classified into how many groups?
Answer:
Vitamins are classified into two groups. They are fat soluble (eg : A, D, E and K) and water soluble (eg : B complex, Vitamin C).
Question 87.
What is the chemical name of vitamin B12?
Answer:
The chemical name of vitamin B12 is Cyanocobalamine.
Question 88.
Which vitamin deficiency causes sterility in males?
Answer:
Vitamin E. i.e., tocopherol deficiency causes sterility in males.
Question 89.
What is the name of vitamin ‘C’? Deficiency of vitamin ‘C’ causes which disease?
Answer:
The chemical name of vitamin ‘C’ is Ascorbic acid. Its deficiency results in Scurvy disease.
Question 90.
What are saprophytes?
Answer:
Saprophytes: Saprophytes are the organisms which obtain their food from dead plants, dead and decaying animal bodies and other organic matter. Eg: Fungi, many bacteria.
![]()
Question 91.
What is peristaltic movement?
Answer:
Peristaltic movement: The muscles present in the wall of oesophagus rhythmically contracts and relaxes. This produces an wave like movement known as a peristaltic movement.
Question 92.
Name the intestinal enzymes present in small intestine and what are their functions.
Answer:
Peptidases and sucrases are the enzymes present in the intestinal juice. Peptidases converts peptides to amino acids. Sucrase converts sucrose (cane sugar) into glucose.
Question 93.
Name the parts of small intestine.
Answer:
The anterior part of small intestine is called the duodenum, the middle part is the jejunum and the posterior part is called the ileum.
Question 94.
What is the enzyme present only in children?
Answer:
Renin is the enzyme present only in children. It helps in curdling of milk.
Question 95.
How many types of teeth are present in our mouth?
Answer:
Four types of teeth are present in our mouth. They are incisors, canine, premolars and molars.
Question 96.
What is the use of tongue?
Answer:
Tongue is useful for mixing and pushing the food in between teeth and helps to push into oesophagus.
Question 97.
What was the opinion of C.B. Van Neil on the equation for photosynthesis?
Answer:
For each molecule of carbohydrate formed, one molecule of water and one molecule of oxygen is also produced.
![]()
Question 98.
“Plants are capable of surviving under a range of situations.” How do you support this statement?
Answer:
- Plants are capable of surviving under a range of situations.
- They survive from very hot, dry and brightly lighted conditions to wet, humid and dimly lighted ones.
- The requirement of light and other factors varies from one plant to other.
Question 99.
From where do we get energy to do work?
Answer:
We get energy to do work from the food we eat.
Question 100.
What did Priestly hypothesize on the experiment he conducted on the role of air in the growth of plants?
Answer:
Priestly hypothesized that plants restore to the air whatever breathing animals and burning candles remove.
Question 101.
How does gaseous exchange occur in plants?
Answer:
Gaseous exchange occurs in plants through the stomata present in leaves and also through the lenticels present on stems.
Question 102.
How do the aquatic plants acquire CO2 to manufacture food?
Answer:
Aquatic plants utilizes or absorbs the carbon dioxide dissolved in water in the form of bicarbonates to manufacture food.
Question 103.
In the experiment to prove that starch is produced during photosynthesis. Why do we boil the leaf in alcohol?
Answer:
We boil the leaf in alcohol to remove all the chlorophyll present in the leaf. The leaf turns to white in colour.
Question 104.
In the experiment to show that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis, why do we immerse leaf in boiling water?
Answer:
- Immersing leaf in boiling water will breakdown the cell membranes of leaf cells.
- It makes the leaf more permeable to iodine solution, so that it can reach the starch present inside the leaf cells.
Question 105.
Why do we have to destarch the leaf before conducting experiment on photosynthesis?
Answer:
This is because if starch is present it will interfere with the result of the experiment.
Question 106.
Why is a water bath used for heating alcohol in which leaf is kept inside the beaker for testing the presence of starch?
Answer:
A water bath is used here for heating alcohol because alcohol is a highly inflammable liquid. So if alcohol is heated directly over a flame, then it will catch fire at once.
Question 107.
What are the reasons for vomiting?
Answer:
Causes for vomiting :
- Overeating especially when the food contain a high proportion of fat.
- When we eat something very indigestible or poisonous.
![]()
Question 108.
Why do we feel bilious or liverish?
Answer:
We feel bilious or liverish because of having eaten rich meals for several days.
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Nutrition 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Vitamin A, D, E and K are fat soluble vitamins. Write the deficiency diseases and resources of these vitamins in a tabular form.
Answer:
| Vitamin – A | Night blindness, myopia, dry eyes, scaly skin | Leafy vegetables, Carrot, Tomato, Pumpkin, Fish, Egg, Liver, Cod liver oil, Shark liver oil, Milk. |
| Vitamin – D | Rickets | Liver, Egg, Butter, Morning sun rays. |
| Vitamin – E | Fertility disorders | Fruits, Vegetables, Sprouts, Meat, Egg, Sunflower oil. |
| Vitamin – K | Blood clotting do not occur | Green leafy vegetables, Milk |
Question 2.
A doctor visited your school to check up the health of school children. What kind of questions do you ask to know about the pancreas?
Answer:
- Where is pancreas located?
- Why pancreas is called as mixed gland?
- What are the hormones released by the pancreas?
- What are the enzymes released by the pancreas?
- What are the disorders occur if pancreas does not work properly?
- What is the role of pancreas in digestion?
Question 3.
Look at the following equation and answer the questions:
Fats + Bile → Fat globules
a) What is the name of that reaction?
b) Which gland plays major role in this reaction?
Answer:
a) The name of the reaction is Emulsification.
b) The gland LIVER plays major role in this reaction.
Question 4.
We know that food is the main source to maintain biological processes in a perfect manner. Our diet should be a balanced one which contains proper amount of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, mineral salts and fats. Two third of world population is affected by food related diseases. Some of them are suffering by consuming high calorific food. Most of them are facing various diseases due to lack of balanced diet. Eating of food that does not have one or more than one nutrients in required amount is known as malnutrition. Poor health, will full starvation, lack of awareness of nutritional habits, socio-economic factors are all the reasons of malnutrition.
i) Define Balanced diet.
ii) What is malnutrition and what could be the possible reasons for it?
Answer:
i) The food containing proper amount of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, mineral salts and fats is known as “balanced diet”.
ii) Eating of food that does not have one or more than one nutrients in required amounts is known as “malnutrition”.
Poor health, starvation, lack of awareness of nutritional habits, socio-economic factors are all reasons for malnutrition.
![]()
Question 5.
What questions do you ask your teacher to know about the obesity and its consequences?
Answer:
- What are the reasons for Obesity?
- How to reduce the body weight?
- What are the consequences of obesity?
- What type of food you suggest to people suffering from obesity?
Question 6.
Prepare four questions for the Gastro-enterologist to know the problems that occur in the digestive system.
Answer:
- Why do the people suffer from indigestion problems?
- Why do we get vomitings?
- Why do we get belching?
- Why do we get ulcers in stomach?
- What is acidity?
Question 7.
Balance the following equation. Write what you have received through this equation.
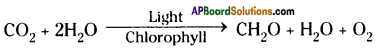
Answer:
![]()
- This equation represents the process of photosynthesis. For the photosynthesis to occur, four factors are required. They are carbon dioxide, water, light and chlorophyll.
- 6 molecules of carbon dioxide and 12 molecules of water in the presence of sun light and chlorophyll forms 1 molecule of glucose, 6 molecules of water and 6 molecules of oxygen.
Question 8.
Pregnant ladies are advised to eat leafy vegetables and take folic acid pills. Why?
Answer:
- Folic acid is the part of the B – a complex family of vitamins.
- Dark green leafy vegetables are a good source of folic acid.
- Folic acid is often prescribed for pregnant women because it is essential for the normal development of the brain and spinal cord of the foetus.
- It also help in protection against birth defects.
- It also required for the synthesis of nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
Hence pregnant ladies are advised to eat leafy vegetables and take folic acid pills.
Question 9.
You want to know about intestinal juice from your nearby doctor. Which questions do you ask him?
Answer:
- Which part of the small intestine secrete intestinal juice?
- Intestinal juice contains which enzymes?
- Intestinal juice converts peptids into?
- Sucrose present in intestinal juice converts sucrose to?
- Digestion of which nutrient resumes in small intestine?
- Which digestive juice involved in the complete digestion of food?
Question 10.
Photosynthesis process provides food for all organisms. It mainly takes place by two phases. Light reaction is first phase.
H2O → H + OH
Above equation in light reaction shows what?
Answer:
- The first phase of photosynthesis is light reaction. It occurs in grana of the chloroplast.
- During this phase light-activated chlorophyll molecule splits water molecule into Hydrogen (H+) and Hydroxyl ions (OH–)
- This reaction is known as photolysis of water which means splitting by light (photo means light, lysis means breaking). This was discovered by Hill. Hence it is also called Hill’s reaction.
![]()
Question 11.
Write names of the given sentences.
i) Organelle in which photosynthesis occurs.
Answer:
Chloroplast
ii) Life process in which complex food is converted into simple substances.
Answer:
Digestive system
iii) The part after large intestine in digestive tract.
Answer:
Anus
iv) Deficiency of Vitamin “K” causing disease.
Answer:
Delay in blood clotting.
Question 12.
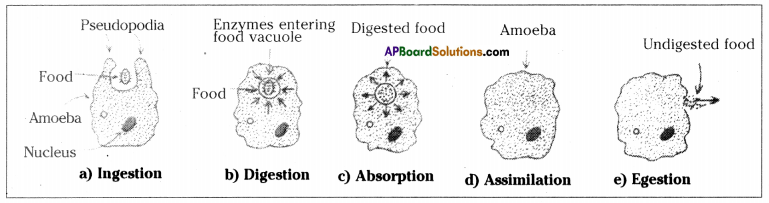
Write about the nutrition in Amoeba. (OR)
Observe the below given organism and write its name. How nutrition occurs in this organism ?
Answer:
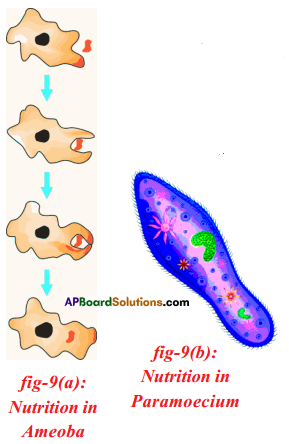
- The mode of nutrition in Amoeba is holozoic nutrition.
- Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger like extensions called pseudopodia.
- These pseudopodia fuse over the food particle forming food vacuole.
- Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simple ones which then diffuse into the cytoplasm.
- The remaining undigested material is moved to the surface of the cell and thrown out.
Question 13.
Write a short note on heterotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
- Heterotrophic nutrition is that mode of nutrition in which an organism cannot make its own food from simple inorganic materials like CO2 and water and depends on other organisms for food.
- Examples are all animals, most bacteria and fungi.
- Heterotrophs depend on others for their food requirement.
![]()
Question 14.
How is a more serious form of indigestion caused?
Answer:
- A more serious form of indigestion is caused by stomach and duodenal ulcers.
- These conditions occur more often in people who may be described as hurried or worried.
- The ulcers occur more often in busy people who get into the habit of hurrying over meals and rushing from one activity to another without sufficient rest.
Question 15.
What is parasitic nutrition? Write briefly about it.
Answer:
- Parasitic nutrition is that nutrition in which an organism derives its food from the body of another living organism without killing it.
- The organism which obtains the food is called a parasite and the organism from whose body food is obtained is called the host.
- A parasite usually harms the host.
- The host may be a plant or an animal.
- Parasitic mode of nutrition is seen in several fungi, bacteria, a few plants like cuscuta and animals like plasmodium.
Question 16.
Write about holozoic mode of nutrition.
(OR)
What is holozoic nutrition?
Answer:
- Holozoic nutrition means feeding on solid food.
- Holozoic nutrition is that nutrition in which an organism takes the complex organic food materials into its body by the process of ingestion.
- The ingested food is digested and then absorbed into the body cells of the organism.
- The undigested and unabsorbed part of the food is thrown out of the body of the
organism by the process of ingestion. - The human beings and most of the animals have a holozoic mode of nutritions.
Question 17.
Briefly explain about saprophytic nutrition.
(OR)
What are saprophytes? How does nutrition occur in them?
Answer:
- Saprophytic nutrition is that nutrition in which an organism obtain its food from dead and decaying plant and animal bodies.
- Organisms having saprophytic mode of nutrition are called saprophytes.
- Fungi and bacteria are saprophytes.
- The saprophytes breakdown the complex organic molecules present in dead and decaying matter and convert them into simple substances outside their body.
- These simple substances are then absorbed by saprophytes as their food.
Question 18.
What is malnutrition? What are the reasons for it? What are the different types of malnutrition?
Answer:
- Eating of food that does not have one or more than one nutrients in required amount is known as malnutrition.
- Reasons for malnutrition: Poor health, will-full starvation, lack of awareness of nutritional habits, socio economic factors are all the reasons for malnutrition.
- Different types of Malnutrition:
- Calorie malnutrition,
- Protein malnutrition and
- Protein calorie malnutrition.
Question 19.
Write a short note on obesity. (OR)
What are the ill effects of obesity?
Answer:
- Obesity is due to over eating and excess of energy intake.
- It is a big health hazard. Obese children when grow, they will be target of many diseases.
- Obesity children usually suffer from diabetes, cardiovascular, renal, gall bladder problems.
- Eating junk foods and other food habits lead to obesity.
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Nutrition 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions by observing the diagram showing the experiment:
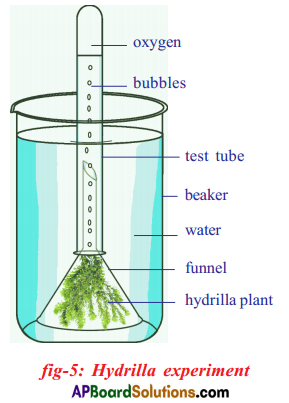 a) What will you prove by this experiment?
a) What will you prove by this experiment?
Answer:
By this experiment we will going to prove oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
b) What apparatus do you use in this experiment?
Answer:
- Beaker
- Test-tube
- Funnel
- Hydrilla Plant
- Burning splinter.
c) What would be the results if the experiment is done in shadow?
Answer:
If we conduct this experiment in shadow no change in the water level of the Test-tube. No photosynthesis occur. No air bubbles are form.
d) What will you do to obtain result from the experiment?
Answer:
If the burning splinter is kept near the mouth of test tube, burns brightly.
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following questions by observing the diagram showing the experiment.
 a) What will you prove by this experiment?
a) What will you prove by this experiment?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is necessary for the photosynthesis.
b) What apparatus do you use in this experiment?
Answer:
Wide mouthed bottle, split cork, KOH solution, Iodine, Potted plant.
c) Why do we use KOH solution in this experiment?
Answer:
KOH is used for the absorption of CO2 in the bottle.
d) Why did we study two leaves in this experiment?
Answer:
We should test two leaves of which one must be having the availability of CO2 and other must not be having the availability of CO2 to prove that CO2 is essential for photosynthesis.
Question 3.
Describe an experiment conducted by Joseph Priestley which revealed the essential role of air in the growth of green plants.
(OR)
What is the role of air in the growth of green plants?
(OR)
Write the experiment of bell jar and pudina plant, performed by Priestley to prove that air plays key role in Photosynthesis.
Answer:

- Joseph Priestley in 1770 performed a series of experiments that revealed the essential role of air in the growth of green plants.
- Priestley discovered oxygen in 1774.
- Priestley observed that a candle burning in a closed space, a bell jar, soon gets extinguished.
- Similarly, a mouse would soon suffocate in a closed space of the bell jar.
- He concluded that a burning candle or an animal, both somehow, damage air.
- But when he placed a mint plant in the same bell jars, he found that the mouse stayed alive and the candle when lighted from outside continued burning in the presence of the mint plant.
- Priestly hypothesized as plants restore to the air whatever breathing animals and burning candles remove.
![]()
Question 4.
B1, B2, B3, A, C, D, E, K are the symbols of vitamins. Classify these vitamins based on solubility and diseases due to vitamins deficiency.
| S.No. | Water soluble | Disease due to deficiency | Fat soluble | Disease due to deficiency |
Answer:
| S.No. | Water soluble | Disease due to deficiency | Fat soluble | Disease due to deficiency |
| 1. | B1 | Beri – Beri | A | Eye, skin diseases |
| 2. | B2 | Glossitis | D | Rickets |
| 3. | B3 | Pellagra | E | Fertility disorders |
| 4. | C | Scurvy | K | Delay in blood clotting |
Question 5.
During Photosynthesis, several events occurs in the chloroplast. Explain the light dependent reactions.
(OR)
Write the mechanism of light dependent reactions in Photosynthesis.
Answer:
Light reaction takes place in grana thylakoids of chloroplast.
The following events occurs in the light dependent reaction.
1. Step -1: The chlorophyll on exposure to light energy becomes activated by absorbing photons of light energy.
2. Step – II: The activated energy is used in splitting the water molecule into hydrogen (H+) and hydroxyl ion (OH–). This reaction is known as photolysis or Hill’s reaction.
H2O → H + OH
3. Step – III : Water (H2O) and oxygen (O2) are produced by the OH– ions through a series of reaction.
4. Step – IV: H+ ions are involved in the synthesis of ATP and NADPH which are the end products of light reaction. These are called assimilatory powers.
Question 6.
You might have conducted and experiment in your school laboratory to prove that CO2 is essential for Photosynthesis. Raju, who is in 9th class, wanted to perform the same experiment. He had some doubts regarding this experiment. Clarify them.
i) Prior to the experiment, the potted plant was kept in a dark room for a week. Why?
Answer:
To destarch the plant.
ii) KOH pellets were kept in the glass jar. Why?
Answer:
To absorb CO2
iii) Write the apparatus used to perform this experiment.
Answer:
Potted plant, wide mouthed transparent bottle, splitted cork.
iv) What will be the result, if the same experiment is conducted in dark?
Answer:
Photosynthesis does not take place.
Question 7.
Write the differences between light and dark reactions of photosynthesis.
Answer:
| Light reaction | Dark reaction |
| 1. It occurs in the grana of the chloroplast. | 1. Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. |
| 2. It occurs only in the presence of light. | 2. It occurs in the presence or absence of light. |
| 3. Light reaction absorbs oxygen and light energy. | 3. Dark reaction absorbs only CO2. |
| 4. End products are O2, ATP and NADPH. | 4. End product is Glucose. |
| 5. Photolysis of water occurs. | 5. Carbon fixation occurs. |
| g. First stage of photosynthesis. | 6. Second stage of photosynthesis. |
Question 8.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of internal structure of leaf. Which mesophyll cells of the leaf consist of chloroplast?
Answer:
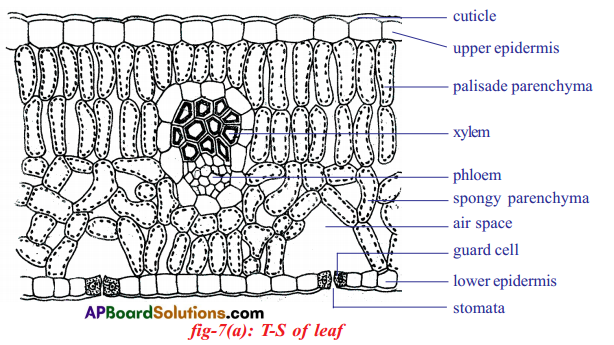 Palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma consist of chloroplast.
Palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma consist of chloroplast.
![]()
Question 9.
Keep a plant for a week in the dark. Then insert one leaf of this plant into a transparent bottle containing potassium hydroxide solution. Keep the plant in sunlight. Test the leaf in the bottle and any other leaf of the plant with Iodine, after a few hours.
 i) What is the aim of this experiment?
i) What is the aim of this experiment?
ii) What will be observed in the leaf kept in the bottle and a leaf from the plant?
iii) Why was the plant kept in the dark first and then in the sunlight?
Answer:
i) To prove that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis.
ii) The leaf part kept in the bottle does not show colour change in iodine test, whereas the leaf exposed to air turns bluish-black in the iodine test.
iii) To remove starch from leaves (destarching).
Question 10.
Analyse the following information and answer the questions.
| Vitamins | Resources | Deficiency symptoms |
| Thiamine | Cereals, oil seeds, vegetables, milk, meat, fish, eggs | Vomitings, fits, loss of appetite, difficulty in breathing, paralysis. |
| Ascorbic acid | Green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, sprouts, carrot | Delay in healing of wounds, fractures of bones. |
| Retinol | Leafy vegetables, carrot, tomato, pumpkin, papaya, mango, meat, fish, egg, liver, milk, cod liver oil, Shark liver oil. | Night blindness, xeropthalmia, cornea failure, scaly skin. |
| Calciferol | Liver, egg, cod liver oil, Shark liver oil | Improper formation of bones, knock-knees, swollen wrists, delayed dentition, weak bones. |
| Tocoferol | Fruits, vegetables, sprouts, sunflower oil | Sterility in male, abortions in female. |
| Phylloquinone | Green leafy vegetables, milk, meat, eggs | Delay in blood clotting, over-bleeding. |
i) Which vitamins deficiency causes diseases related to bones?
Answer:
Calciferol – Vitamin – D, deficiency causes diseases related to bones,
ii) Which vitamins we get by eating fruits?
Answer:
Retinol – Vitamin – A, and Tocoferol – Vitamin – E we get them by eating fruits,
iii) Which vitamin deficiency causes Paralysis? To prevent iii), what type of food we have to eat?
Answer:
Paralysis is caused by the Vitamin (B}) Thiamine deficiency.
To prevent this disease, we have to eat cereals, oil seeds, vegetables, milk, meat, fish and eggs.
iv) To avoid vitamin deficiency diseases, what type of food we have to eat?
Answer:
To avoid vitamin deficiency diseases, we have to take proper diet.
Our diet should be a balanced one which contains proper amount of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, mineral salts and fats.
![]()
Question 11.
What are fat soluble vitamins? Explain the deficiency diseases due to deficiency of fat soluble vitamins and their symptoms.
Answer:
Fat soluble vitamins :
| Name of the vitamin | Name of the diseases | Symptoms |
| Vitamin – A (Retinol) | Night blindness, xerophthalmia | Cornea failure, unable to see during night, scaly skin |
| Vitamin – D (Calciferol) | Rickets | Improper formation of bones, knock- knees, swollen wrists, delayed in dentition, weak bones |
| Vitamin – E (Tocoferol) | Sterility | Sterility in males, abortions in females |
| Vitamin – K (Phylloquinone) | Over-bleeding | Delay in blood clotting |
Question 12.
Read the table and answer the following questions.
| Sl. No. | Vitamin | Resources | Deficiency disease | Symptoms |
| 1. | Cyanoco- balamine | Synthesised by bacteria present in the intestine. | Pernicious anaemia | Lean and weak, less appetite. |
| 2. | Ascorbic acid | Green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, sprouts | Scurvy | Delay in healing of wounds, fractures of bones. |
| 3. | Retinol | Leafy vegetables, carrot, tomato, pumpkin, papaya, mango, meat, fish, egg, liver, milk, Cod and Shark liver oil | Eye and skin diseases | Night Blindness, Xeropthalmia, Cornea failure, Scaly skin. |
| 4. | Tocoferol | Fruits, vegetables, sprouts, sunflower oil | Fertility disorders | Sterility in males, abortions in females. |
| 5. | Phylloquinone | Green leafy vegetables, meat, egg and milk | Problems related to blood clotting | Delay in blood clotting, over bleeding. |
i) Name the anti-sterility vitamin from the above table.
Answer:
Tocoferol (Vitamin E) is the anti – sterility vitamin.
ii) WTiich vitamin deficiency that causes the gums bleeding?
Answer:
Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) deficiency causes the gums bleeding.
iii) Name the fat soluble vitamins from the above.
Answer:
Retinol (Vitamin A), Tocoferol (Vitamin E), Phylloquinone (Vitamin K) are fat soluble vitamins.
iv) Name the symptoms that appear due to deficiency of vitamin K.
Answer:
Delay in blood clotting, over bleeding are the symptoms appear due to deficiency of vitamin K.
Question 13.
Mention different modes of nutrition. Explain the mode of nutrition in Cuscuta.
Answer:
There are different modes of nutrition
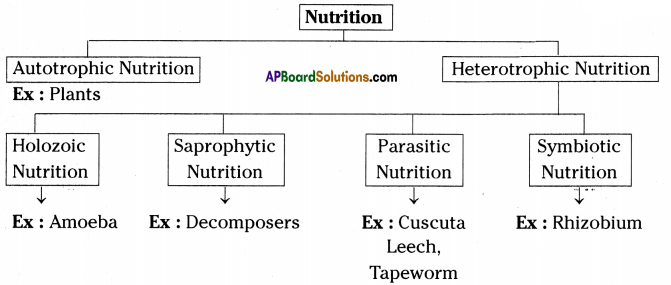 Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta :
Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta :
- Cuscuta plant is the best example for parasitic nutrition.
- It contains no chlorophyll and has root like structures called haustoria.
- With the help of haustoria, cuscuta absorbs nutrients from it’s host plant.
- As cuscuta grows on the host plants, its roots gradually degenerated and it establishes firmly on the host plant.
- Meanwhile, the root rots away after stem contact has been made with a host plant.
- As dodder grows, it sends out new haustoria and establishes itself very firmly on the host plant.
- After growing in a few spirals around one host shoot, the dodder finds its way to another.
- It continues to twine and branch until it resembles a fine densley tangled web of thin stems enveloping the host plant.
Question 14.
Is the malnutrition reason for diseases? Why? Write any of such disease and its characters.
Answer:
- Yes, malnutrition is the reason for occurrance of diseases.
- Malnutrition is eating of food that does not have one or more than one nutrients in required amount.
- This results in scarcity of nutrients for the proper growth and health of the individual.
- Kwashiorkor disease occurs in children due to the deficiency of proteins in the diet.
- Characteristic features of kwashiorkor disease :
- Body parts becomes swollen due to accumulation of water in the intercellular spaces.
- Very poor muscle development, swollen legs, fluffy face, difficult to eat, diarrhoea, dry skin are the symptoms of Kwashiorkor disease.
- The child becomes lethargic and shows little interest in its surroundings or in playing and learning.
![]()
Question 15.
Which issues do you take into consideration to tell that plants play a key role in animals nutrition?
Answer:
- Plants play a very important role in nutrition of animals. Actually plants are the producers whereas animals are dependent on plants for their nutrition.
- Many plants or plants parts are eaten as food. There are around 2000 plant species which are cultivated for food. Nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals are available from these plants.
- Seeds of plants are good sources of food for animals including humans because they contain many healthful fats.
- Infact majority of the food consumed by human beings are seed based food. Edible seeds include cereals like wheat, rice, maize etc. and legumes like pea, groundnut and nuts.
- Oil seeds are often pressed to produce rich oils like sunflower, groundnut, sesame etc.
- Seeds are typically high in unsaturated fats and considered as a health food.
- Fruits are the ripened ovaries of plants including the seeds within. Many plants and animals have coevolved such that the fruits of the former are an attractive food source to the later.
- Vegetables are a second type of plant matter that is commonly eaten as food.
- Hence all the nutrients required by animals are available to the animals from plants. Hence plants are playing an important role in nutrition of animals including human beings.
Question 16.
Give examples for the vitamin deficiency diseases.
Answer:
| S. No. | Vitamin | Deficiency diseases |
| 1. | Thiamine (B1) | Beri beri |
| 2. | Riboflavin (B2) | Glossitis |
| 3. | Niacin (B3) | Pellagra |
| 4. | Pyridoxine (B6 | Anaemia |
| 5. | Cyanocobalamine (B12) | Pernicious anaemia |
| 6. | Folic acid (B9) | Anaemia |
| 7. | Pantothenic acid | Burning feet |
| 8. | Biotin | Nerves disorders |
| 9. | Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) | Scurvy |
| 10. | Retinol (Vitamin A) | Night blindness, Xerophthalmia, Rupture of cornea, Scaly skin |
| 11. | Calciferol (Vitamin D) | Rickets, fragile bones |
| 12. | Tocoferol (Vitamin E) | Fertility disorders, Sterility in males, Abortions in females |
| 13. | Phylloquinone (Vitamin K) | Blood clotting |
Question 17.
We know that by taking different types of food materials we will get vitamins. For this what changes shall we take in our food habits?
Answer:
- Eating of rice polished only for one time gives us vitamin thiamine in abundant amount.
- We should eat balanced food containing nutrients in equal quantities.
- Fresh leafy vegetables are rich source of vitamins Riboflavin, Folic acid and Vitamin ‘C’. So our diet should contain these leafy vegetables.
- Sufficient amount of non-vegetarian foods like meat, poultry, fish, kidney and liver should present in our food.
- Eating fresh fruits also add number of vitamins to our body.
- Whole cereals like wheat, rice provide number of vitamins to our body. So we shall eat required quantities of cereals in our food.
![]()
Question 18.
Describe what disaster occurs on earth, if photosynthesis life process stops.
Answer:
- Plants are the universal food providers. If they stop photosynthesis all the animals would die due to starvation.
- Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis. It is essential for survival of all living beings. If photosynthesis does not take place, there would be no oxygen on the earth and no chance of survival of life on this planet.
- plants utilise CO2 for photosynthesis. If it does not occur, CO2 utilisation is stopped and hence increase in the levels of CO2 This leads to global warming.
Question 19.
Describe the experiment conducted by Jan Baptist Von Helmont and discuss his results in the growth of plant body mass.
(OR)
How is water required for the growth of plant body mass?
Answer:
- In the year 1648 a Belgian scientist Jan Baptist Von Helmont conducted an experiment that continued for five years.
- He took a small willow tree and planted it in a large pot of soil.
- Before he did the experiment he carefully measured the mass of the dry soil and mass of the tree.
- He covered the soil with a lid so that nothing could fall on to the surface of the soil and add to its mass.
- There were holes in the lid so that the tree could grow out of the soil and so that air and water could reach the roots.
- Von Helmont left the tree for five years giving it only rain water to drink.
- At the end of five years he measured the mass of the tree and the mass of the dry soil for a second time.
- The results of this experiment are shown below.
Mass (Kg) At start After five years Change in mass (Kg) Tree 2.27 76.74 74.47 Drv soil 90.72 90.66 0.06 - This experiment changed the belief of hundreds of years. This is because Von Helmont arrived at a result that
a) The substances needed for the growth of a plant do not come from the soil only.
b) The plant grow because of the water it gets.
Question 20.
Write an account on the mechanism of dark reaction.
(OR)
Write an account on carbon fixation.
(OR)
Briefly explain the Melvin Calvin cycle.
Answer:
- The reactions of photosynthesis which do not require light energy are called dark reactions. These reactions occur both in presence and absence of light.
- Dark reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast and these were discovered by American scientist Melvin Calvin.
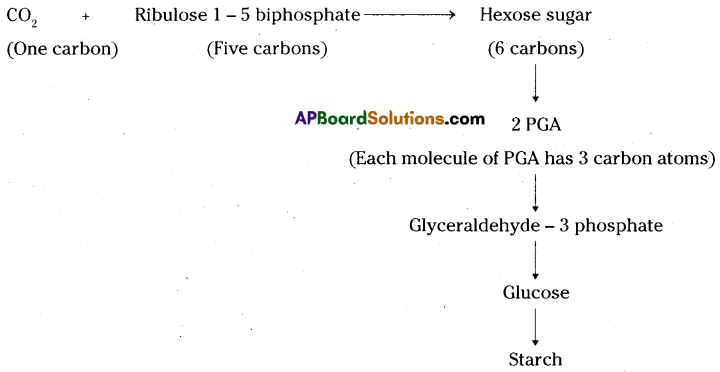
- In the first reaction carbon dioxide is accepted by Ribulose 1 – 5 biphosphate, a five carbon sugar to form hexose sugar.
- It is an unstable compound so it breaks down into two molecules of three carbon compounds called phospho glyceric acid (PGA).
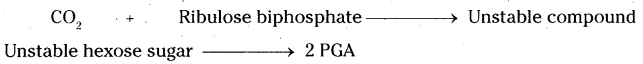
- Phospho glyceric acid undergoes a series of reactions and is converted to glyceral- dehyde – 3 phosphate. NADPH and ATP produced in light reactions are used up at this stage.
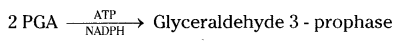
- Two molecules of glyceraldehyde – 3 phosphate combine together to form glucose molecule.
- In the end glucose is converted into starch.
Summary reaction :
![]()
Question 21.
Describe the buccal cavity of human beings.
(OR)
How is food masticated in buccal cavity?
Answer:
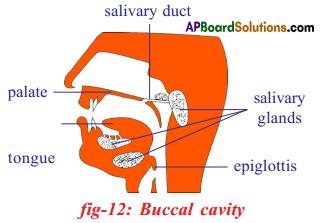
- The cavity or space in the mouth is called oral cavity or buccal cavity.
- Teeth, tongue and openings of three salivary glands are present in buccal cavity
- Incisors, canines, premolars and molars are the different types of teeth present in the mouth.
- Tongue is muscular and pushes the food on to the teeth during mastication. It also helps in swallowing the food into oesophagus.
- Three pairs of salivary glands present in the buccal cavity are parotid, sub-lingual and sub-maxillary glands.
- Parotid glands are present near the ears. The other two pairs of glands open below the tongue through ducts.
Question 22.
What is indigestion? How can we avoid indigestion?
Answer:
Indigestion: Indigestion is a general term when there is difficulty in digesting food. Healthy people can usually avoid problems related to indigestion by:
- Having simple, well balanced meals.
- Eating them in a leisurely manner. ,
- Thoroughly masticating the food.
- Avoiding taking violent excercises soon after eating food.
- Drinking plenty of water and having regular bowel movements.
Question 23.
What are vitamins? Why they are called essential nutrients? What is their role in the human body?
Answer:
- Vitamins are organic substances.
- They are micro – nutrients required in small quantities.
- Actually vitamins are not synthesised in the body and therefore they are essential nutrients.
- Though our body cannot synthesis vitamins we do not generally suffer from vitamin deficiency disease.
- This is because of two sources of vitamins for our body. Diet is the primary source.
- In addition, bacteria present in the intestine synthesis vitamins and supply them to us
- By themselves vitamins cannot generate any energy or carryout any chemical reaction.
- In the body vitamins combine with some of the enzymes and make the enzymes active.
- In the absence of vitamins, enzymes become inactive and cannot catalyse the reactions.
- Vitamins are normally present in all types of natural foods – milk, meat, fruits and vegetables.
- Vitamins are of two types:
- Water soluble vitamins eg: B complex and Vitamin C and
- Fat soluble vitamins eg: A, D, E and K.
![]()
Question 24.
Give an account of water soluble vitamins, their occurrence, deficiency diseases and symptoms.
Answer:
Vitamins, available sources and deficiency diseases:
| Vitamin | Resources | Deficiency diseases | Symptoms |
| B complex Vitamins: 1) Thiamine (B1) |
Cereals, oil seeds, vegetables, milk, meat, fish, eggs. | Beri Beri | Vomitings, fits, loss of appetite, difficulty in breathing, paralvsis. |
| 2) Riboflavin (B2) | Milk, eggs, liver, kidney, green leafy vegetables. | Glossitis | Mouth cracks at corners, red and sore tongue, photophobia, scaly skin. |
| 3) Niacin (B3) | Kidney, liver, meat, egg, fish, oil seeds. | Pellagra | Dermatitis, diarrhoea, loss of memory scalv skin. |
| 4) Pyridoxine (B6) | Cereals, oil seeds, vegetables, milk, meat, fish, eggs, liver. | Anaemia | Hyper irritability, nausea, vomiting, fits. |
| 5) Cyano cobalamine (B12) | Synthesised by bacteria present in the intestine. | Pernicious anaemia | Lean and weak, less appetite. |
| 6) Folic acid | Liver, meat, eggs, milk, fruits, cereals, leafy vegetables. | Anaemia | Diarrhoea, loss of leucocytes, problems related to mucus in the intestines. |
| 7) Pantothenic acid | Sweet potatoes, ground nuts, vegetables, liver, kidney, egg. | Burning feet | Walking problems, sprain. |
| 8) Biotin | Pulses, nuts, vegetables, liver, milk, kidney. | Nerves disorders | Fatigue, mental depression, muscle pains. |
| 9) Vitamin ‘C’ (Ascorbic acid) | Green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, sprouts. | Scurvy | Delay in healing of wounds, fractures of bones. |
Question 25.
 a) What apparatus do you use during the conduction of the experiment?
a) What apparatus do you use during the conduction of the experiment?
b) Before conducting the experiment, why do you keep the potted plant in dark place for a week?
c) What test do you conduct to know the formation of carbohydrates in leaves?
d) During the test, which part of the leaf turns into blue and which part doesn’t? Why?
Answer:
a) Potted plant, Light screen, Iodine solution, Petridish, Black paper.
b) To destarch the leaves.
c) Iodine Test
d) The part of the leaf exposed to light turn into blue. Unexposed part does not turn into blue.
Reason: Photosynthesis occurs only in the presence of sunlight. The unexposed part does not receive the sunlight.
![]()
Question 26.
Draw the diagram of equipment arrangement in Hydrilla experiment. You did to prove that oxygen releases in photosynthesis. Write the reasons why test tube is placed upside down on funnel.
Answer:
 Reasons for placing the test tube upside down on funnel:
Reasons for placing the test tube upside down on funnel:
- To count the number of bubbles coming out of the hydrilla twigs per minute during photosynthesis.
- To collect sufficient amount of oxygen at the end of the test tube so that it can be tested with glowing splinter.
- Amount of oxygen produced in the test tube can be measured by the displacement of water within the test tube.
Question 27.
Describe the internal structure of the leaf.
(OR)
How is the internal structure of leaf modified to prepare starch through the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
- A transverse section of a typical leaf shows that it is covered on both sides by epidermis. Epidermal layers are covered on both sides by cuticle.
- Lower epidermis is interrupted by a large number of openings called stomata. The central opening is called stoma.

- Each stoma is surrounded by two kidney shaped cells called Guard cells.
- Stomata regulate the exchange of gases and loss of water vapour from the leaves.
- Mesophyll is the tissue present between two epidermal layers. Upper mesophyll tissue is called palisade parenchyma and lower tissue is known as spongy parenchyma.
- The cells in the palisade parenchyma are long elongated arranged in rows.
- The cells in the spongy parenchyma are irregularly arranged cells with large inter cellular spaces.
- More number of chloroplasts are present in palisade parenchyma than the spongy parenchyma.
- In the midrib and veins vascular bundles are present with phloem located towards the lower side and xylem towards the upper side.
Question 28.
Write about the parasitic nutrition in cuscuta plant.
Answer:
- Dodder (genus cuscuta) is a leafless, twining, parasitic plant belongs to family convolvulaceae.
- The dodder contains no chlorophyll and instead absorbs food through haustoria.

- The dodder’s seed germinates, forming an anchoring root, and then sends up a slender stem that grows in a spiral fashion until it reaches a host plant.
- It then twines around the stem of the host plant and throws out haustoria, which penetrate it.
- Water is drawn through the haustoria from the host plant’s stem and xylem, and nutrients are drawn from its phloem.
- Meanwhile, the root rots away after stem contact has been made with a host plant.
- As the dodder grows, it sends out new haustoria and establishes itself very firmly on the host plant.
- After growing in a few spirals around one host shoot, the dodder finds its way to another and it continues to twine and branch until it resembles a fine densley tangled web of thin stems enveloping the host plant.
![]()
Question 29.
Describe the digestion of food materials in alimentary canal with the help of a diagram.
(OR)
How is the food digested in your body?
Answer:
- The alimentary canal is basically a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus.
- Food is masticated by our teeth in the mouth and mixed with saliva to make it slippery and wet.
- Saliva which contains amylase helps in the breakdown of carbohydrates into simple ones.
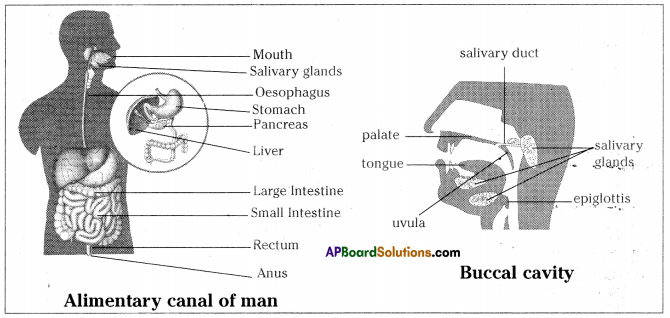
- The soft food mixed with saliva passes through oesophagus or food pipe by wave like movements called peristaltic movements to the stomach.
- The gastric glands in the stomach secrete gastric juice that contains hydrochloric acid, protein digesting enzyme pepsin and mucus.
- Partially digested food chyme is released in small amounts by sphincter muscles reach small intestine.
- Bile juice secreted by liver and pancreatic juice secreted by the pancreas release into the duodenum of small intestine.
- Emulsification of fats is done by bile juice. Pancreatic juice contains enzyme trypsin for carrying on the process of digestion of proteins and lipase for fats.
- Complete digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins takes place in the small intestine by intestinal juice.
- Finger-like projections present in the walls of small intestine are called villi. They absorb the digested food into the blood.
- Rest of the food is sent into the large intestine where most of the water present in it is absorbed from the food.
- This material is then expelled through the anus which is the last part of the alimentary canal.
Question 30.
Draw a flow chart of human digestive system.
Answer:
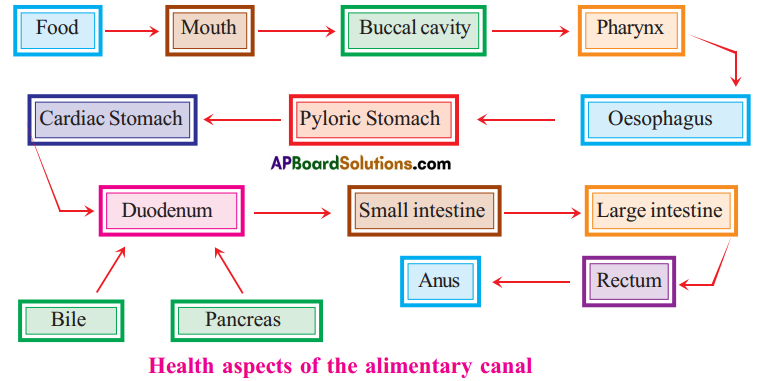
![]()
Question 31.
Write briefly about nutrition in paramoecium. (OR)
Explain the nutrition process in paramoecium with the help of diagrams.
Answer:
Paramoecium :
- Paramoecium is a unicellular aquatic organism.
- The paramoecium has thin, hair like cilia all over its body.
- The cilia move back and forth rapidly in water.
- When the cilia is present around, the mouth region of paramoecium move, back and forth. They sweep the food particles present in water into the mouth of paramoecium.
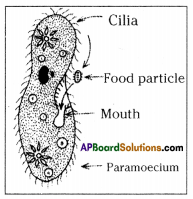
- This is the first step in the nutrition of paramoecium which is called ingestion and is followed by digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
Question 32.
Describe the digestion of food in the stomach. (OR)
How is the food digested in your stomach ?
Answer:
- The stomach is a large organ which expands when food enters it.
- The muscular walls of the stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
- The gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach secrete gastric juice which contains hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus.
- The hydrochloric acid facilitates the action of the enzyme pepsin and also kills the germs present in the food.
- The enzyme pepsin digests proteins and mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of the acid under normal conditions.
![]()
Question 33.
Describe the digestion of food in the small intestine. (OR)
What are the changes that you see during the digestion of food in small intenstine?
(OR)
Small intestine is a long coiled tube. How the food is digested in small intestine of human being?
Answer:
- The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal.
- It is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
- It receives the secretion of liver and pancreas for this purpose.
- These juices make the internal condition of the intestine gradually to a basic or alkaline one.
- Bile juice secreted by liver breaks down fats into small globules like forms. This process is called emulsification.
- Pancreatic juice contains enzymes like trypsin for carrying on the process of digestion of proteins and lipase for fats.
- Walls of the small intestine secrete intestinal juice. This is also known as succus entericus.
- The intestinal juice consists of enzymes like enterokinase, peptidase, lipase, sucrase, nucleotidase, nucleosidase etc.
- Enzymes present in the intestine completely digest the partially digested food.
- Following digestive processes take place in the intestine.
a) Peptidases convert peptides into amino adds.
b) Intestinal lipase completely digest fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
c) Enzymes sucrase, maltase, lactase hydrolyse sucrose, maltose and lactose respectively converting them into glucose.
d) Nucleotidase and nucleosidase complete the digestion of nucleic acids. - The end products of digestion are absorbed in the intestine.
Question 34.
What are the health aspects of the alimentary canal?
Answer:
- The human alimentary canal usually functions remarkably well considering how badly we treat it on occasions.
- Vomiting is the body’s method of ridding itself unwanted or harmful substances from the stomach.
- There are many causes of vomiting, but one of the most common is over eating, especially when the food contains a high proportion of fat.
- The liver is unable to cope with the excessive fat and we get a feeling of nausea and sometime headache.
- Indigestion is a general term used when there is difficulty in digesting food.
- A more serious form of indigestion is caused by stomach and duodenal ulcers. These conditions occur more often in people who may be described as hurried or worried.
- Those who are able to relax, who are not continually tensed up, and who live at a slower pace, seldom get ulcers.
- For good health it is necessary to empty the bowels regularly.
- If the food residues remain in the colon for too long, the bacteria present have more time to produce harmful substances which may be absorbed by the blood.
- Constipation can often be avoided by having plenty of roughage in the diet.

