These AP 10th Class Biology Important Questions and Answers 6th Lesson Reproduction will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Reproduction
10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Reproduction 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What questions you ask the doctor, who visited your school on World AIDS day?
Answer:
- How does AIDS disease occurs?
- How does the AIDS transmit?
- What are the symptoms of AIDS?
- What are the precautions to be taken to prevent AIDS?
![]()
Question 2.
What is colostrum?
Answer:
The first secretion from the Mammary glands, after giving birth, rich in antibodies.
During the end of pregnancy, a watery yellowish lymph like fluid accumulates in mammary glands. It is known as colostrum.
Question 3.
Name the types of asexual reproduction in the following organisms:
a) Paramoecium b) Yeast
Answer:
a) Paramoecium : Paramoecium reproduces by splitting into two. (Transverse binary fission)
b) Yeast: Yeast reproduces by Budding.
Question 4.
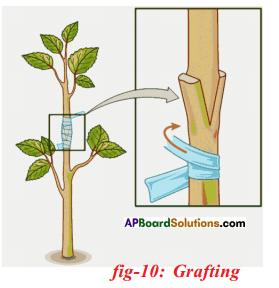
What are the advantages of grafting method in plants.
Answer:
- Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters.
- It can be used to produce varieties in seedless fruits.
Question 5.
What measures can be taken to avoid sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
- Avoid sex with unknown or multiple partners.
- Sex with life partners only.
- Follow ethical and healthy life practices because contraceptives always cannot prevent STD’s.
- In case of any doubt, consult a qualified doctor for early detection if diagonised with disease take complete treatment.
![]()
Question 6.
What is parthenogenesis?
Answer:
The process of developing zygote from female gametes without fertilization is known as parthenogenesis.
Question 7.
In flowering plants, I am formed as the result of double fertilization. The cotyledons digest and absorb me. Who am I?
Answer:
Endosperm.
Question 8.
In what way does mitotic division help the living organism?
Answer:
- growth
- cell repair
- healing wounds.
Question 9.
Give any two suggestions to create awareness to stop female foeticide.
Answer:
- Preparing relevant slogans
- Organising rallies
- Awareness campaign by using electronic and print media
Question 10.
Write two precautions you take, while observing Rhizopus in the laboratory.
Answer:
- Don’t touch the experimental bread with hand.
- If you touch the bread, thoroughly wash your hands.
- Leave the bread in the open air for about an hour.
- Avoid opening of the plastic bag as much as you can.
- Sprinkle water over bread.
- Place the bag in a dark and warm place.
![]()
Question 11.
Mention two materials you have used to observe Rhizopus on bread mould.
Answer:
Bread mould sample, plain glass slide, cover slip, water, disposable gloves.
Question 12.
What type of reproduction occurs in paramoecium during favourable conditions?
Answer:
During favourable conditions paramoecium reproduce asexually by fission.
Question 13.
What type of reproduction occurs in paramoecium during unfavourable conditions?
Answer:
During unfavourable conditions paramoecium reproduce sexually by conjugation.
Question 14.
Which bacteria is responsible for formation of curd from milk?
Answer:
Lactobacillus bacteria is responsible for formation of curd from milk.
Question 15.
What is asexual reproduction?
Answer:
The reproduction in which a single parent is involved, without formation of gametes is known as asexual reproduction.
Question 16.
What is fission?
Answer:
Splitting of organisms into two or more offsprings in a symmetrical manner is known as fission. Ex: Paramoecium and bacteria.
![]()
Question 17.
How budding occurs in yeast?
Answer:
- A bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at specific site.
- These buds develop when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals.
Question 18.
Which animals reproduce through fragmentation?
Answer:
Fragmentation is a common mode of reproduction in Algae, Fungi and many land plants.
Question 19.
What is Regeneration?
Answer:
- Many fully differentiated organisms have the ability to give rise to new individual organism from their body parts.
- If the individual is some how cut or broken up into many pieces, many of these pieces grow into separate individuals. Ex: Hydra and planaria.
Question 20.
In which plant, small plants grow at the edge of leaves?
Answer:
In Bryophyllum, small plants grow at the edge of leaves.
Question 21.
By means of which plants propagate vegetatively through stem?
Answer:
Plants propagate vegetatively through stem by means of stolons, bulbs, corms, tuber etc.
![]()
Question 22.
Through which the Vallisneria, Strawberry propagate vegetatively?
Answer:
Vallisneria, Strawberry propagate vegetatively through stolons.
Question 23.
Which plants produce the new plants through roots?
Answer:
New plants are produced from the roots of Dahlia, radish, carrot etc.
Question 24.
What are the artificial propagation methods in plants?
Answer:
Cutting, Layering and Grafting are the artificial propagation methods in plants.
Question 25.
Which method is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters?
Answer:
Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters.
Question 26.
Which method will you adopt to get two desirable characters from two different plants in a single plant?
Answer:
I will adopt grafting method to get two desirable characters from two different plants in a single plant.
Question 27.
Which fungus is commonly called as bread mould?
Answer:
Rhizopus is commonly called bread mould.
![]()
Question 28.
How bread mould appears when you observe it under microspore?
Answer:
The common bread mould consists of fine thread like projections called hyphae and thin knob like structures called Sporangia.
Question 29.
In which plants leaf is known as Sporophyll? Why?
Answer:
In fern plants leaf is known as Sporophyll. Because on the lower surface of the leaf sporangia are present.
Question 30.
What is fertilisation?
Answer:
Union of male and female gametes is known as fertilisation.
Question 31.
What is external fertilisation?
Answer:
If the fertilisation occurs outside the body of the organism then it is known as external fertilisation. Eg : Frog and fish.
Question 32.
What is internal fertilisation?
Answer:
If the fertilisation occurs inside the body of the female organism then it is known as internal fertilisation. Eg : Terrestrial animals (Reptiles, Aves, Mammals).
![]()
Question 33.
What are the parts present in male reproductive system of man?
Answer:
A pair of testis, Accessory glands and System of ducts.
Question 34.
The male reproductive organ testis produces?
Answer:
Testis produces male reproductive cells or spermatozoa.
Question 35.
Sperms are temporarily stored in which part of duct system?
Answer:
Sperms are temporarily stored in epididymis of duct system.
Question 36.
What are the accessory glands present in male reproductive system?
Answer:
The accessory glands present in male reproductive system are one prostrate gland . and two cow cowper glands.
Question 37.
The fluid secreted by accessory glands is
Answer:
The fluid secreted by the accessory glands is semen.
Question 38.
What is the function of semen?
Answer:
Semen provide nutrients for sperm to keep alive and helps as a medium for the movement of sperms.
Question 39.
Which hormone regulates the development of the male reproductive organs?
Answer:
The hormone testosterone regulates the development of the male reproductive organs.
![]()
Question 40.
How are the secondary sexual characters are controlled in males?
Answer:
Secondary sexual characters in males are controlled by the male sex hormone testosterone.
Question 41.
Men produce sperm from the age of about?
Answer:
Men produce sperm from the age of about 13 or 14 years and can go on doing so most their lives.
Question 42.
Which are capable of changing the sex of the organism in which they grow like wasp?
Answer:
Some bacteria and other micro-organisms have been found capable of changing the sex of the organism of wasp in which they live.
Question 43.
The female gamete ovum is produced by
Answer:
The female gamete ovum is produced by graffian follicles of Ovary.
Question 44.
What is ovulation?
Answer:
The release of ovum from graffian follicle is known as ovulation.
Question 45.
Fertilisation of ovum occurs in which part of female reproductive system?
Answer:
Fertilisation of ovum occurs in fallopian tube or oviduct of female reproductive system.
![]()
Question 46.
What is placenta?
Answer:
Placenta is the nourishment tissue formed by the outer membrane of the embryo called chorion and the part of the uterine tissue.
Question 47.
When do placenta is formed during the development of embryo?
Answer:
Placenta is formed at around 12 weeks of pregnancy or during the embryonic development.
Question 48.
What keeps embryo moist and protects it from minor mechanical injury?
Answer:
The embryo develop in amniotic fluid filled cavity which keeps it moist and protects it from minor mechanical injury.
Question 49.
Which membrane forms umbilical cord?
Answer:
Allantois membrane which originates from the digestive canal of the embryo forms the major part of tube like structure called umbilical cord.
![]()
Question 50.
What is foetus?
Answer:
From the third month of pregnancy the embryo is called foetus.
Question 51.
What is gestation period?
Answer:
Total time required for the development of embryo and foetus is called gestation period.
Question 52.
What is the gestation period in human beings?
Answer:
The gestation period in human beings is 9 months or 280 days.
Question 53.
Collect the information about gestation periods in different animals.
Answer:
Gestation period in different animals:
| Animal | Gestation period |
| Cat and dog | 63 days |
| Horse | 330 days |
| Cow | 280 days |
| Rat and mouse | 20-22 days |
Question 54.
What is after birth?
Answer:
The muscular contractions of the uterus continue until they push out the tissues of the placenta, which are commonly called the ‘after birth’.
![]()
Question 55.
What are labour pains?
Answer:
The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscle layers of the uterus is known as labour pains.
Question 56.
What is colostrum?
Answer:
Colostrum: During the end of pregnancy a watery yellowish lymph like fluid accumulates in the mammary glands. It is known as colostrum.
Question 57.
What is the importance of feeding colostrum to new born baby?
Answer:
It is very important to feed colostrum to the new born baby because it helps in developing the immune system of the child.
Question 58.
What is the need of sexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction help organisms to develop characters that would be help them to adapt better to their surroundings.
Question 59.
In which mountain regions can Sal trees grow?
Answer:
Sal trees grow in the Himalayan mountains.
![]()
Question 60.
What are the different parts of a flower?
Answer:
Sepals, petals, stamens and carpels are the different parts of a flower.
Question 61.
What are stamens and carpels?
Answer:
The reproductive parts of a flower which possess the sex cells or germ cells are called stamens and carpels.
Question 62.
What are unisexual flowers? Give examples.
Answer:
Flowers having either stamens or carpels are called unisexual flowers.
Eg: Bottlegourd, papaya.
Question 63.
What are Bisexual flowers? Give some examples.
Answer:
Flowers having both the stamen and carpel are called bisexual flowers. Eg: Datura.
Question 64.
What are the three parts of carpel or gynoecium?
Answer:
The three parts of carpel or gynoecium are ovary, style and stigma.
![]()
Question 65.
What is self pollination?
Answer:
Plants having flowers. Where reproductive cells of stamen of the flower fertilise the female reproductive cells of the carpel of the same flower is called self pollination.
Eg: Plants of pea family.
Question 66.
How cross fertilisation occurs?
Answer:
If the male cells of flower of a plant fertilise the female cells of flowers on the same or different plants of the same species, the type of pollination is called cross pollination.
Question 67.
What did Darwin showed regarding fertilization of plants?
Answer:
Darwin in 1876 showed that plants when isolated had the greatest tendency to self fertilize while when surrounded by varieties of the same flower, they readily cross fertilize.
Question 68.
Which cells are composed the embryosac of ovule?
Answer:
The embryosac of ovule composed of gametophyte cells.
Question 69.
How many cells and nuclei does an embryosac consisting in majority of flowering plants?
Answer:
The majority of flowering plants have an embryosac consisting of seven cells and eight nuclei.
Question 70.
What is double fertilisation?
Answer:
Double fertilisation: Union of one male nucleus with an egg and the second male nucleus with the fusion nucleus is called double fertilisation.
Question 71.
What is germination?
Answer:
The seed produced after fertilisation contains the future plant or embryo that develops into a seedling under appropriate conditions. This process is called germination.
Question 72.
Who gave the phrase “omnis cellula de cellula”? What does it mean?
Answer:
The ‘phrase omnis cellula de cellula’ means cells arise from pre-existing cells. It was given by Rudolph Virchow who discovered cell division.
![]()
Question 73.
Who stated that the animals can reproduce through binary fission of cells?
Answer:
In 1852 Robert Remak of Germany stated that animals can reproduce through binary fission of cells.
Question 74.
Who discovered the process of mitosis?
Answer:
Mitosis was discovered by Walther Flemming in 1879.
Question 75.
What is the most important discovery of Walther Flemming regarding chromosomes?
Answer:
Walther Flemming’s most important discovery was chromosomes appear double in nature.
Question 76.
Who proposed that chromosomes carried a different set of heritable elements?
Answer:
Wilhelm Roux proposed that chromosomes carried a different set of heritable elements.
Question 77.
What are the hypothesis made by August Weiseman on chromosomes?
Answer:
- In successive generations, individuals of the same species have the same number of chromosomes.
- In successive cell division the number of chromosomes always remain constant.
![]()
Question 78.
Who confirmed the scheme of mitotic division?
Answer:
The scheme of mitotic division was confirmed in 1904 by Theodor Boveri.
Question 79.
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
Answer:
The structure of (DNA) deoxy ribonucleic acid was discovered in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick.
Question 80.
The cells in which organ do not divide?
Answer:
Cells present in organs such as heart and brain of an individual never divide.
Question 81.
What is time required for completion of mitosis?
Answer:
The process of mitosis is completed in 40 to 60 minutes.
Question 82.
What is interphase?
Answer:
The period between two cell divisions is called interphase.
![]()
Question 83.
Into how many phases the interphase can be divided?
Answer:
Interphase can be divided into three phases. They are G1 phase, S phase and G2 phase.
Question 84.
What is G1 phase of interphase?
Answer:
G1 phase is the linking period between the completion of mitosis and the begining of DNA replication (Gap 1 phase).
Question 85.
What is S phase of interphase?
Answer:
S phase is the period of DNA synthesis leading to duplication of chromosomes.
Question 86.
What is G2 phase of interphase?
Answer:
G2 phase is the time between the end of DNA replication and the beginning of mitosis (Gap 2 phase).
Question 87.
Who conducted some experiments using the cell fusion technique on phases of interphase?
Answer:
Potu Narasimha Rao and Johnson conducted some experiments using the cell fusion technique to understand the functional relationship between the phases of interphase.
![]()
Question 88.
What is cytokinesis?
Answer:
Division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis.
Question 89.
What are the different stages present in mitosis?
Answer:
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase are the different stages present in mitosis.
Question 90.
In which phase of the mitosis chromosomes split lengthwise to form chromatids?
Answer:
In prophase of the mitosis chromosomes split lengthwise to form chromatids.
Question 91.
During which phase of mitosis chromatids are pulled towards poles?
Answer:
During anaphase of mitosis chromatids are pulled towards poles.
Question 92.
How many haploid daughter cells are formed after meiosis?
Answer:
Four haploid daughter cells are formed after meiosis.
Question 93.
What are the diseases that can be sexually transmitted?
Answer:
Sexually transmitted diseases include bacterial infections such as Gonorrhoea and Syphilis and Viral infections such as AIDS.
![]()
Question 94.
In what way the sexually transmitted diseases spread from person to person?
Answer:
Sexually transmitted diseases spread by unsafe sexual contacts, using infected devices, infected blood transfusion, from an infected mother to child.
Question 95.
Which state has the highest number of HIV patients in the country?
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh and Telangana has the highest number of HIV patients in the country.
Question 96.
Which factors are contributing to the spread of HIV in Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
Illiteracy, poor health, unemployment, migration, non-traditional sex practise, unethical contacts and trafficking are some of the factors contributing to the spread of HIV in Andhra Pradesh.
Question 97.
Expand “ASHA”.
Answer:
Accredited Social Health Activist.
Question 98.
What is Red ribbon express?
Answer:
Red Ribbon express is an AIDS/HIV awareness campaign train by the Indian Railways. The motto of the Red ribbon express is “Embarking on the Journey of Life”.
Question 99.
What is contraception?
Answer:
The prevention of pregnancy in women by preventing fertilisation is called contraception.
![]()
Question 100.
Which device not only prevents fertilisation but also transmitting some sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
Condoms and diaphragm (cap) prevents fertilisation and also useful to not transmitting some sexually transmitted diseases like gonorrhoea, syphilis, AIDS.
Question 101.
What are spermicides?
Answer:
Spermicides are the pills used for killing sperms.
Question 102.
What are the surgical methods to birth control in males and females?
Answer:
Vasectomy for males and Tubectomy for female are the surgical birth control methods in human beings.
Question 103.
What is Vasectomy?
Answer:
In males, a small portion of vas deferens is removed by surgical operation ami both ends are tied properly. This method is called vasectomy.
Question 104.
What is Tubectomy?
Answer:
In females, a small portion of oviducts (fallopian tube) is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are tied. This prevents the ovum from entering into the oviducts. This method is called Tubectomy.
![]()
Question 105.
What is the marriage age for girls in India?
Answer:
The marriage age for girls in India is 18 years.
Question 106.
What is foeticide?
Answer:
Foeticide is the act of destruction or aborting a foetus because it is female.
10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Reproduction 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the questions you asked the doctor who visited your school to know “the ways of transmission of HIV”?
Answer:
I shall ask the following questions to the doctor.
- What are the ways of transmission of HIV?
- How can we prevent the spread of HIV?
- What precautions should we take while doing transfusion of blood:
- How does HIV transmit from mother to baby?
- Why should we use disposable syrenges?
Question 2.
The chromosomal number is reduced to half in the daughter cells produced by meiosis. What happens if the number is not reduced to half in daughter cells?
(OR)
In Meiosis, the chromosome number in the daughter cells are reduced to half that of their parent cells. Guess, what would happen, if the reduction of chromosome number is not done.
Answer:
- If the reduction of chromosomes number is not done, the chromosomal number is doubled in the offsprings.
- The change in chromosomal number leads to development of abnormal characters in the individual.
- The offspring differs from parental generation.
- Abnormal characters will be formed in new generation, which are not useful for the existence of individual.
![]()
Question 3.
What questions do you ask a doctor to know about different birth control methods?
Answer:
- What is family planning?
- What is meant by contraception?
- How many types of contraceptive methods are there?
- What are the contraceptive devices used for female?
- What are the contraceptive devices used for male?
- What is tubectomy?
- What is vasectomy?
- What are surgical methods of birth controls?
Question 4.
Apparao and Ramulamma are a newly married illiterate couple. They don’t want children for few years. Suggest some birth control methods for them.
(OR)
Mention any four birth control methods.
Answer:
a) condoms
b) diaphragm (Cap)
c) pills
d) copper – T
e) loop
Question 5.
Why is it important for gametes to have half the number of chromosomes?
Answer:
- If gametes have 2 sets of chromosomes, the number of chromosomes will be 4 sets in zygote after fertilization because of this the chromosomal number will be doubled in each generation. This results in abnormalities in off-spring.
- Hence, to maintain a constant number of chromosomes, garnets should have half set of chromosomes.
![]()
Question 6.
Identify the flower parts a, b, c, d and write their main function.
 Answer:
Answer:
a) Ovary: Female reproductive organ in flower. It produces female gametes called ovules.
b) Style: Ovary has a pipe like structure called style. It allows the pollen tube to enter the ovary for fertilization.
c) Stamen: These are male parts called androecium. It has two parts. They are filament and Anther.
d) Anther : Produces male gametes called pollen grain.
Question 7.
Draw and label the diagram of human sperm cell.
Answer:
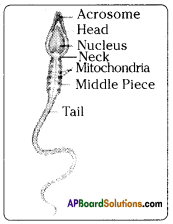
Question 8.
How can we get the desired useful triats with the help of two selected triats by using grafting method?
Answer:
- Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant.
- One which is attached to soil is called stock and the cut stem of another plant without roots is called scion.
- Both stock and scion are tied with the help of a twine thread and covered by a polythene cover.
- Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters.
- This technique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of plants with various flowers and fruits. Ex: Mango, citrus, apple, rose.
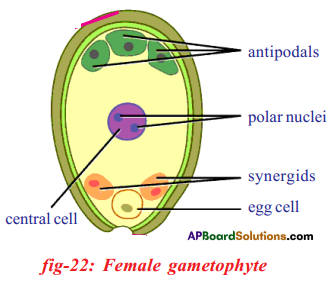
Question 9.
Draw the labelled diagram of Embryo-sac A.
Answer:
![]()
Question 10.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
i) Which phases take same time duration?
Answer:
G1 phase and S phase.
ii) In which phase, DMA synthesis takes place?
Answer:
S Phase.
Question 11.
Write the process involved in seedless fruit development with two suitable examples.
Answer:
In some plants ovary directly develops into fruit without the process of fertilization, this phenomenon is called as parthenocarypy.
Ex: Grapes, water melon.
Question 12.
What precautions will you take to keep away from diseases like AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
- Avoid sex with unknown partners or multiple partners.
- Use condom every time.
- Use disposable syringes and needles.
- Transfusion of safe blood to the patients.
- HIV mother can have child with doctor’s advice only.
Question 13.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
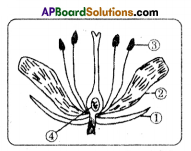 i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
Answer:
Male reproductive parts – anther / pollen grain / stamen
Female reproductive parts – ovary / ovule / style / stigma.
ii) Write the names of (1) and (2) in the diagram.
Answer:
- Sepal or calyx
- Petal or corolla
Question 14.
When does Parthenogenesis occur? Write names of two animals in which parthenogenesis takes place.
Answer:
a) Parthenogenesis is a process of reproduction where there is a shift from sexual to asexual mode of reproduction.
b) In this process generally the female garnets develops into zygote without fertilization.
c) This strange kind of reproduction occur in bees, ants and wasps.
d) The parthenocarpic zygote develop into male (Monoploid) while the fertilized one developed into female (Diploid)
![]()
Question 15.
Draw the figure of metaphase in mitosis, and write about it.
Answer:
- Chromosomes move to spindle equator, centromeres attached to spindle fibres.

- Centromeres split, separating the chromatids.
Question 16.
Prepare 4 questions on meiosis, to conduct a Quiz programme.
Answer:
- Where does meiosis occur in?
- How many daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis?
- In which phase of meiosis karyokinesis takes place?
- Name the scientist who discovered meiosis for the first time.
Question 17.
Write slogans on ‘Child marriages – a social evil’.
Answer:
- Child marriage, a loosing game.
- She is a child herself, why burden her with another child?
- My childhood, my right.
- A child should call ‘mother’ but a child should not be called mother.
- Good marriages take place slowly. Go slow with children’s marriage.
- Say no to child marriage.
Question 18.
Write 5 slogans on the prevention of HIV/AIDS.
Answer:
- Open your eyes before AIDS closes them.
- Hate the disease but not the diseased.
- Spread the knowledge not the virus.
- Wear protection to prevent infection.
- AIDS brings pain! Girls please obstain.
Question 19.
What is fission? Give examples.
Answer:
- Fission is a method of asexual reproduction in which a single-celled organism splits into two or more offsprings.
- This splitting usually occurs in a symmetrical manner.
- When an organism is split into two offsprings it is called binary fission.
- When an organism is split into more offsprings, it is called multiple fission.
- This is often the only mode of reproduction for single celled organisms.
Ex : Paramoecium and bacteria.
![]()
Question 20.
Write a short notes on fragmentation.
Answer:
- Fragmentation is a reproductive method in multicellular organisms with relatively simple body organisation.
- Some can grow from a separate piece of parent organism. This can be from any part of the body.
- This happens only in the simplest such as some flat-worms, moulds, lichens, spirogyra, etc.
- Fragmentation is a common mode of reproduction in algae, fungi and many land plants.
Question 21.
What do you know about parthenogenesis? Explain with examples.
Answer:
- Parthenogenesis is an asexual reproduction in which unfertilized eggs develop into offsprings.
- In this process generally egg develops into new individual without meiosis and fertilization. So the offsprings are diploid.
- In some species of animals reproduction occurs only through parthenogenesis. There are no males known in these species. Ex: Rotifers.
- In another type of parthenogenesis meiosis does occur and the egg can develop whether fertilized or not.
- The monoploid offsprings develop into males and diploid into females.
Ex: Bees, Ants and Wasps. - Nowadays we are able to develop seed less fruits like watermelon, grapes, pomegranate etc.
Question 22.
Describe the vegetative propagation through the stem with examples.
Answer:
- Production of new plants from the vegetative parts such as stem, root, leaves of the existing plant is called vegetative propagation.
- Aerial weak stems like runners and stolons, when they touch the ground, give off adventitious roots.
- When the connection with the parent plant is broken, the portion with the newly struck roots develops into an independent plant.
- Some examples for propagation by stem are from stolons, bulbs, corms and tubers as follows.
a) Stolons – Vallisneria, Strawberry
b) Bulbs – Alliumcepa or onion
c) Corms – Colacasia
d) Tuber – Potato
![]()
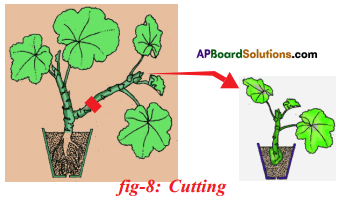
Question 23.
Write short note on artificial propagation method cutting.
Answer:
- Cutting is an artificial method of vegetative propagation in which new plants are developed from the cut portion of existing plant.
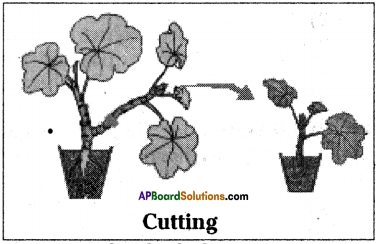
- Some plants grow individually when a piece of the parent plant having bud is cut from the existing plant.
- The lower part of this cutting is buried in moist soil.
- After few days the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant.
Ex: Rose, Hibiscus.
Question 24.
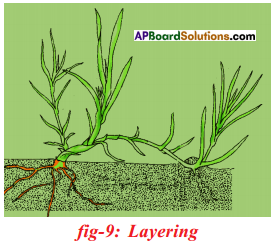
What is layering? Explain briefly about it.
Answer:
- Stems that form roots while still attached to the parent plants are called layers. Propagating the plants in this method is layering.
- A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and a part of it is covered with moist soil leaving the tip of the branch exposed above the ground.
- After sometime, new roots develop from the part of the branch hurried in the soil.
- The branch is then cut off from the parent plant, later it develops roots and grows to become a new plant. Ex: Nerium.
Question 25.
Write a short note on Grafting.
Answer:
- Grafting is a method of artificial vegetative propagation in which two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant.
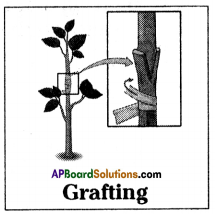
- One which is attached to soil is called stock and the cut stem of another plant without roots is called scion.
- Both stock and scion are tied with help of a twine thread and covered by a polythene cover.
- After few days both will unite by forming new tissue and grow as a single one.
- Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable characters.
- Plants in which grafting is done more in mango, apple, citrus, plants.
![]()
Question 26.
What are the advantages of grafting?
Answer:
- Grafting enables us to combine the most desirable characteristics of the two plants (scion and stock) in its flower and fruits.
- By grafting method, a very young scion can be made to flower and produce fruits quite fast when it is grafted to the stock.
- Grafting can be used to produce varieties of seedless fruits.
Question 27.
How is tissue culture more beneficial than other traditional methods for the artificial propagation of plants? (OR)
What is tissue culture? What are its uses?
Answer:
- The traditional methods for the artificial propagation of plants are being replaced by the modern methods of artificial propagation of plants involving tissue culture, as it is more beneficial than the traditional methods.
- In tissue culture, a few plant cells or plant tissue are placed in a growth medium with plant hormones in it and it grows into new plants.
- Thousands of plants can be grown in very short interval of time.
- There will be no climatic impact on the propagation, so multiplication can be done throughout the year.
- It is possible to obtain plants that are free from pathogens.
Question 28.
How does the Rhizopus propagate?
Answer:
- Rhizopus propagates by means of spores.
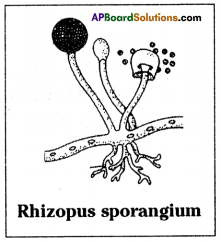
- The Rhizopus parent plant produces hundreds of microscopic reproductive units called spores.
- When the spore case of the plant bursts, the spores spread into air.
- These air borne spores fall on food or soil, under favourable conditions like damp and warm conditions, they germinate and produce new plants.
![]()
Question 29.
Write a short note on spore formation. (OR)
How spores are produced in sporangia of fungi?
Answer:
- Spore formation is a method of asexual reproduction which occurs through microscopic reproductive units called spores.
- Most of the fungi like rhizopus, mucor etc., bacteria and non-flowering plants such as ferns and mosses reproduce by the method of spore formation.
- In fungi like rhizopus spores are produced in some specialised structures called sporangia which bursts and spreads the spores into air. These spores when fall on food or soil under favourable conditions germinate and produce new plants.
- In non-flowering plants like fern, the leaves called sporophyll bears clusters of sporangia on their lower side. These sporangia produce the spores which produce the new plant when it falls on ground under favourable conditions.
Question 30.
How is external fertilisation different from internal fertilisation? (OR)
What are the differences between external and internal fertilisation?
Answer:
- Fertilisation that takes place outside the body of mother is called external fertilisation. This is most common in animals like fishes and amphibians. As the chance of fertilisation is controlled by nature it becomes necessary to give rise to vast number of eggs and sperms by these animals.
- Fertilisation that takes place inside the body of mother is called internal fertilisation. This is common in most of the land animals. As the chance of fertilisation is not controlled by the nature, these animals generally produce less number of eggs.
Question 31.
Write a short note on ovulation. (OR)
What is ovulation? How it occurs?
Answer:
- Release of the egg or ovum is called ovulation.
- The ova develop in tiny cellular structures in ovary called follicles, which at first look like cellular bubbles.
- As a follicle grows, it develops a cavity filled with fluid.
- Each follicle contains a single ovum.
- When an ovum is mature, the follicle ruptures at the surface of the ovary and the tiny ovum is flushed out.
- This release of ovum is called ovulation.
![]()
Question 32.
How does the uterus get adapted to receive the embryo?
Answer:
- The uterus at the time of fertilization is beautifully adapted to receive the developing embryo, providing it with food and disposing of its wastes.
- A few days prior to this time, the uterus was small, its tissues were thin, and its supply of blood vessels was poor.
- When the fertilized egg or zygote is about to enter the uterus become much larger, its inner wall becomes thick, soft and moist with fluid, its blood supply is greatly increased and waiting for an embryonic occupant.
Question 33.
What is colostrum? What is its importance?
Answer:
- During the end of pregnancy, a watery lymph like fluid accumulates in the mammary glands.
- This is called colostrum.
- For the first few days after the baby is born, the mammary glands secrete only colostrum.
- It is very important to feed the new born baby with colostrum because it helps in developing the immune system of the child.
Question 34.
What is the importance of mitosis in human beings?
Answer:
- Mitosis is the cell division that transforms a human fertilized egg into a baby in nine months and into an adult in the next 20 years.
- The bone marrow cells actively divide by mitosis to produce red blood cells.
- Mitosis helps in replacing the worn out cells in the skin.
- Mitotic divisions in the cells surrounding the wound helps in cease the wound and healing.
Question 35.
Collect the information about the significance of the experiments done by Dr Potu Narasimha Rao and Johnson.
Answer:
- Nearly 4 decades back Dr.P.N. Rao and Johnson did some elegant experiments using the cell fusion technique to understand the functional relationship between the phases of cell cycle.
- These experiments have, for the first time provided evidence that the progression of cells through the cell cycle is sequential and unidirectional and are controlled by a series of chemical signals that can diffuse freely between nucleus and cytoplasm.
- These experiments revealed for the first time the structure of interphase chromosomes that are not ordinarily visible under the microscope.
- These experiments are considered to be a ‘milestone’ in the cell cycle studies.
![]()
Question 36.
Ramu said that it is very essential to create more awareness in Andhra Pradesh on the risk of HIV infection and AIDS. Do you support him? If so, how can you support his statement?
Answer:
Yes, what Ramu said is right. I support his statement with the following reasons.
- Andhra Pradesh has the highest number of HIV patients in the country.
- According to official statistics, the state had 5 lakh of the 24 lakh HIV positive patients
in the country during 2011-12. - While one in every 300 adults is suffering from HIV elsewhere, in Andhra Pradesh one in every 100 adults is a HIV patient, that is almost one per cent.
- The prevalence of HIV is 1.07 per cent among males and 0.73 among females in the state, which again is higher than in other states.
Question 37.
Briefly explain about the contraception and contraceptive methods.
Answer:
The prevention of pregnancy in the woman by preventing fertilisation is called contraception. Any device or chemical which prevents pregnancy in a woman is called a contraceptive. Contraceptive methods are of various types and used by any of the partners as preferable. Some of the contraceptive methods are:
- Use of physical devices such as condoms and diaphragm (cap).
- Use of hormonal pills which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into oviduct.
These pills can be induced either orally or inserting into female reproductive organ vagina. - Use of spermicides that kills the sperms.
- Use of intra-uterine device called copper – T, loop, etc.
- Use of surgical methods such as vasectomy for male and tubectomy for female.
![]()
Question 38.
Classify the given organisms basing on the type of reproduction.
Man, Flatworm, Mould, Dog, Bacteria, Frog, Fern, Datura, Hen, Yeast.
Answer:
| Sexually reproducing organisms | Asexually reproducing organisms |
| Man | Flat worm |
| Dog | Mould |
| Frog | Bacteria |
| Datura | Fern |
| Hen | Yeast |
Question 39.
What will happen if the amnion is ruptured before the foetus is developed completely?
Answer:
- Amnion is the embryonic membrane that grows around the embryo itself.
- The cavity within the amnion is filled with a fluid called amniotic fluid, which keeps the growing embryo moist and protects it from minor mechanical injury.
- If the amnion ruptures by accident before the foetus developed completely, the amniotic fluid is released out through vagina.
- As there is no protective fluid around the foetus, it starts getting damaged.
- So if possible delivery must done immediately by surgerical method, otherwise abortion must be done.
- If baby dies inside the uterus which leads to infections in uterus causing problems
to mother that leads to death.
Question 40.
How will you appreciate the contribution of August Weiseman to the cell biology?
Answer:
- Science is not advanced only by the collection of data. Someone must think about and interpret the data. August Weiseman belongs to this category who think and interpret the data.
- Even though his poor eyesight not allowed him to use a microscope to study cells, he made great contribution to the cell biology making use of his thinking capacity and interpretation skills.
- He hypothesised that
a) In successive generations, individuals of the same species have the same number of chromosomes.
b) In successive cell division, the number of chromosomes remains constant. - His hypothesis proved right in case of mitosis.
- We should take such a great person who overcame his defect with his will as our role model.
![]()
Question 41.
How will you appreciate the contribution of Dr. P.N. Rao to the ceil biology?
Answer:
- Dr. Potu Narasimha Rao, a renowned scholar and eminent cytologist came from a poor family in Muppalla village of Guntur district.
- He did his research work on the cytogenetics of tobacco plant and cancer cells in culture medium.
- He conducted research in cell kinematics and triggering factor of cell division i.e., mitosis.
- He observed the interphase and its three phases.
- To understand the functional relationship between these phases he did elegant experiments on cell fusion technique along with his research associate Dr.Johnson.
- His researches revealed that the cell cycle is sequential, unidirectional and controlled by a series of chemical signals.
- His experiments are considered to be a milestone in the cell cycle.
- He is an exemplary person who proved that poverty is not a barrier to the talent and wisdom.
Question 42.
Write briefly about natural vegetative propagation in plants.
Answer:
- In natural vegetative propagation new plants are produced from stem, root, leaves of old plants without the help of any reproductive organs.
- In bryophyllum small plants grow at the edge of leaves.
- Aerial weak stems like runners stolons, when they touch the ground give it adventitious roots.
- When the connection with the parent plant is broken the stem portion with the adventitious roots develops into an independent plant.
- Some examples for propagation by stem are from stolons, bulbs, corms, tuber etc.
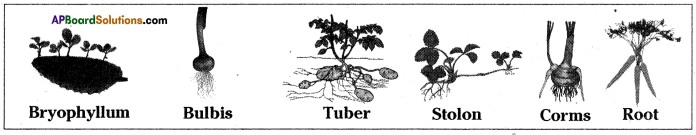
- Stolons – Vallisneria, strawberry.
Bulbs – Onion (Alliumcepa)
Corms – Colacasia
Tuber – Potato
![]()
Question 43.
What are sexually transmitted diseases and mention the ways to prevent them?
Answer:
- A disease which can be transmitted through sexual contact is called sexually transmitted disease or STD.
- These include bacterial infections such as gonorrhoea, syphilis, Herpis and viral infections such as herpes and AIDS.
- Lack of hygiene is usually a major factor in providing conditions for spread of STDs.
- But unprotected sex with multiple and unknown partners is the highest reason for the spread of STDs.
- Some of the ways to prevent STD are as follows.
a) Being faithful to one’s life partner.
b) Avoid sexual contact with unknown person.
c) Using condom during sexual intercourse.
d) Maintaining personal hygiene.
Question 44.
Why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individual through regeneration ?
Answer:
- Many organisms have the ability to give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts.
- Regeneration happens through mitosis and a particular type of tissue can give rise to its own kind only.
- In complex organisms, different tissues and organs have altogether different structures.
- Regenerating a different kind of tissue from another kind is not possible.
- Hence complex organisms are not able to give rise to new individuals through regeneration.
Question 45.
How an organism will be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Answer:
- Reproduction through spores gives several advantages to an organism like they are produced in very large numbers and it helps in propagation of species.
- Spores can remain dormant till favourable conditions become available.
- Spores help an organism to overcome unfavourable conditions.
- Spores can be spread through water, air or animals and thus is good for the spread of an organism to more places.
![]()
Question 46.
What is the role of the placenta in embryo development?
Answer:
- Placenta is a tissue formed by the cells from the embryo and the mother.
- It is formed around 12 weeks of pregnancy and becomes an important structure for nourishment of the embryo.
- Placenta is a disc which is embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue.
- On the other side mother’s blood spaces are present.
- This provides a large surface area for diffusion of glucose, oxygen and other nutrients from the mother of the embryo.
Question 47.
Why do we practise vegetative propagation for growing some types of plants?
(OR)
Why vegetative propagation is adopted over other types of propagation?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practised in some plants because
- It is the only method of reproduction in seed less plants.
- We get more number of matured plants in a very short time.
- Thousands of plants can be grown in very short time.
- This method can help the breeder in preserving the characters he need.
- It is very easy and economical method for the multiplication of ornamental plants.
Question 48.
What is Mitosis? Which type of cells it occurs in organisms? Write about the different stages of it.
Answer:
- Mitosis is a method of cell division, in which the nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei.
- Each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
- Mitosis takes place in all body cells which retains same number of chromosomes.
- Different stages of mitosis:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
10th Class Biology 6th Lesson Reproduction 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Explain the changes involved in the formation of seed from Ovule.
(OR)
Pollen grain reached the stigma of a flower. Explain the changes that occurs up to the formation of seeds in a sequence.
Answer:
Process of double fertilization:
- At the time of fertilization there will be a total of 7 cells arranged in three groups in a mature embryo sac.
- They are one egg (female garnet) two synergids, one central cell (secondary or polar nucleus) and three antipodals.
- While all the cells are in haploid (n) condition only the polar nucleus is diploid (2n). This is due to the fusion of two nuclei.
- The synergids are also known as helper cells.
- Fertilization is the process of fusion of male and female gametes. For the fusion pollen grains have to reach the surface of the stigma. This is called pollination.
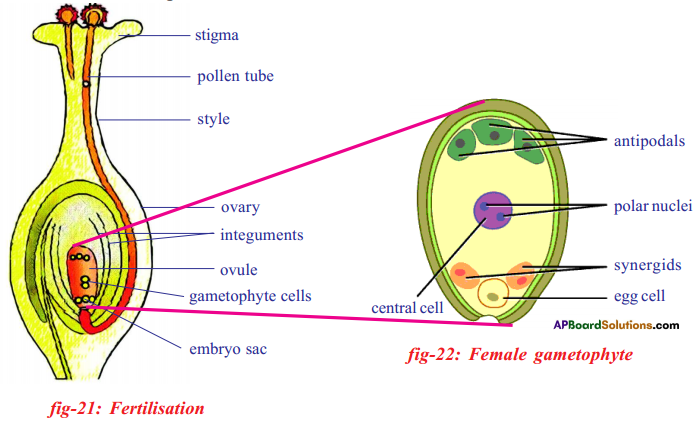
- Pollen grain received by the stigma, germinate and give rise to pollen tubes. The pollen tube has two male nuclei.
- Usually the pollen tube enters the ovule through microphyle and discharges the two male gametes into the embryo sac.
- One male nucleus (garnet) approaches the egg and fuses with it to form diploid (2n) zygote this is called first fertilization.
- The other male nucleus reaches the secondary nucleus (2n) (polar nucleus) and fuses with it to form endosperm nucleus which will be triploid. This is second fertilization. Thus double fertilization occurs in embryosac.
Changes after double fertilization: - After double fertilization, the ovule increases in size rapidly as a result of formation of endosperm tissue by mitosis and the development of new embryo.
- The embryo consists of cotyledons an epicotyl and a hypocotyl. The cotyledons become greatly enlarged because of stored food for the seedling.
- The zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and is converted into a seed. The ovary grows to form a fruit.
![]()
Question 2.
Observe the given diagram and answer the following questions.
 i) What are the four main parts of a flower?
i) What are the four main parts of a flower?
Answer:
Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium are the main parts of a flower.
ii) Which parts of the flower produces gametes?
Answer:
Androecium and gynoecium produces gametes.
iii) Which parts of the flower help in pollination?
Answer:
Petals or corolla help flower in pollination.
iv) Which part protect the flower during its bud stage?
Answer:
Sepals or calyx protect flower in bud stage.
v) Which part of the flower will turn into a fruit in the future?
Answer:
Ovary of the flower will change into fruit.
Question 3.
Organisms reproduce asexually in many ways. Some of the organisms are given below. Fill the below table based on the collected information about the organism and mode of asexual reproduction in it.
a) Onion b) Spirogyra c) Strawberry d) Ginger e) Honey-bee f) Paramoecium g) Planaria h) Yeast
| Name of the organism | Mode of Asexual reproduction |
Answer:
| Name of the organism | Mode of Asexual reproduction |
| a) Onion | Bulb |
| b) Spirogyra | Fragmentation |
| c) Strawberry | Stolons |
| d) Ginger | Rhizome |
| e) Honey – bee | Parthenogenesis |
| f) Paramoecium | Binary fission |
| g) Planaria | Regeneration |
| h) Yeast | Budding |
![]()
Question 4.
i) Draw a neat labelled diagram of L.S. of flower.
ii) What are the sexual parts in the flower ?
Answer:
i)
 ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
B. Gynoecium or Pistil
Question 5.
Read carefully and answer the following questions.
According to Weismann prediction, every organism undergoes two kinds of cell divisions. In Mitosis, there is no change in chromosomal number (2n) and in Meiosis, chromosomal number is reduced to half (n).
i) What does ‘n’ and ‘2n’ indicate?
Answer:
‘n’ indicates haploid state. ‘2n’ indicates diploid state.
ii) In which cells, Meiosis takes place?
Answer:
Meiosis occurs in sex cells during the formation of gametes.
iii) What happens, if chromosomal number is not reduced in Meiosis?
Answer:
The chromosomal number not constant in successive generations.
iv) Which type of cell division occurs in the skin cells?
Answer:
Mitosis
![]()
Question 6.
Observe the diagram and answer the following.
i) Which part produce the female gamete?
Answer:
Ovary
ii) Where does the fertilization takes place in female reproductive system?
Answer:
Fallopian tube
iii) Where does the embryo develops until it is ready to born?
Answer:
Uterus
iv) In some cases doctor’s cut and tie the cut ends of the fallopian tubes. What is the name of surgery?
Answer:
Tubectomy
Question 7.
Briefly explain the stages of cell cycle.
Answer:
The process of cell division is called “mitosis”. The period between two cell divisions is called “Interphase”.
This is actually the period when the genetic material makes it’s copy so that it is equally distributed to the daughter cells during mitosis. Interphase can be devided into three phases.
G1 Phase: This is the linking period between the completion of mitosis and the beginning of DNA replication (GAP-1 Phase). The cell size increase during this period.
S Phase: This is the period of DNA synthesis (Synthesis phase) leading duplication of chromosomes.
G2 Phase: This is the time between the end of DNA replication and the beginning of mitosis. Cell organells devide and prepare chromosome for mitosis.
![]()
Question 8.
i) Draw a labelled diagram of the human male reproductive system.
ii) What is the function of testosterone?
Answer:
i) Male reproductive system:
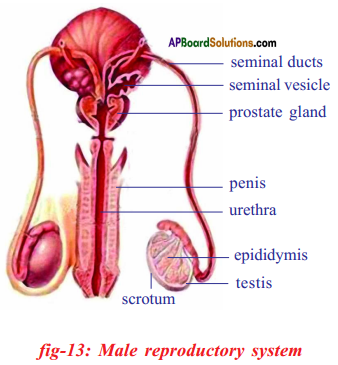 ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.
ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.
Question 9.
Describe the life cycle of a flowering plant with a help of neat labelled diagrams. (OR) Draw the life cycle of a flowering plant.
Answer:
- Adult plant produces flowers:
When the plant matures and is ready to reproduce, it develops flowers. Flowers are special structures involved in sexual reproduction, which includes pollination and fertilisation.
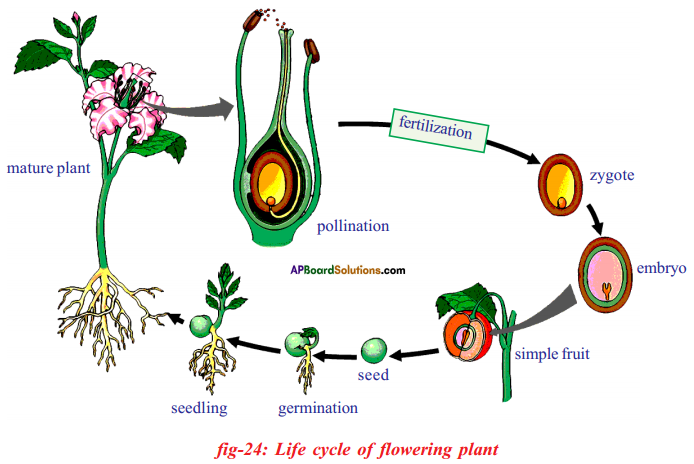
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination.
- Fertilisation:
i) After pollen grains falls on the stigma fertilization occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grains joins with the female gametes present in the ovule.
ii) In the ovary the male nucleus of pollen combines with the nucleus of female gamete or egg present to form zygote. - Formation of fruit and seed: After fertilisation, a combined cell i.e. zygote grows into an embryo within a seed formed by the ovule.
- Each seed contains a tiny plant called an embryo which has root, stem and leaf parts ready to grow into a new plant when conditions are favourable.
- Another part of the flower (the ovary) grows to form fruit, which protects the seeds and helps them spread away from the parent plant to continue the cycle.
![]()
Question 10.
Analyze the following information and answer the following questions.
| S.No. | Name of the plant | Method of propagation |
| 1. | Mango | Grafting |
| 2. | Rose, Hibiscus | Cutting |
| 3. | Jasmine | Layering |
| 4. | Bryophyllum | Small plants grow on edges of leaves |
| 5. | Colacasia | Cor ms |
| 6. | Onions | Bulbs |
i) What do you call the given reproduction methods?
Answer:
Given reproduction methods are called ‘vegetative propagation’.
ii) What is the major difference between sexual reproduction and vegetative reproduction in plants?
Answer:
In sexual reproduction gametes form zygote. Plant parts like root, stem and leaf are used in vegetative reproduction. It is one of asexual method.
iii) Potato plants do not produce seeds. How can you propagate this plant?
Answer:
Potato plants propagates through the ‘eyes’.
iv) What are the advantages of propagating plants with the above given methods?
Answer:
In vegetative propagation
- More plants are produced in less time
- Characters are not changed.
- It would be possible to develop new varieties with useful characters.
Question 11.
Explain the methods of artificial propagation in various plants.
Answer:
Artificial propagation:
- Cutting: Some plants can grow individually when a piece of the parent plant having bud is cut off from the existing plant. The lower part of this cutting is buried in moist soil.
After few days the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant after developing roots. E.g. Rose, Hibiscus. - Layering: A branch of the plant with atleast one node is bent towards the ground and part of it is covered with moist soil. After a few days new roots develop from the part of the branch buried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant.
E.g: Nerium, Jasmine
- Grafting: Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. This technique is very useful in propagating improved varieties of various flowers and fruits. Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable character. E.g: Mango, citrus, apple, rose.
![]()
Question 12.
Observe the following figures and find the stages of cell division and explain.
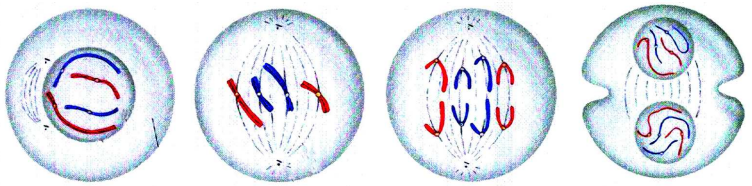 Answer:
Answer:
In the mitotic cell division, the division of nucleus (karyokinesis) followed by the division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis). Finally brings about the formation of two daughter cells. There are four stages in mitosis division.
They are
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
| 1) Prophase | 1) Chromosomes condense and get coiled. They become visible even in light microscope. Nucleoli become smaller. 2) Chromosomes split lengthwise to form chromatids, connected by centromeres. 3) Nuclear membrane disappears. 4) Centrosome, containing rod-like centrioles, divide and form ends of spindle |
| 2) Metaphase | 1) Centrosomes move to spindle equator, spindle fibres attached to centromeres. |
| 3) Anaphase | 1) Centromeres split, separating the chromatids. 2) Spindle fibres attached to centromeres contract, pulling chromatids towards poles. |
| 4) Telophase | 1) Chromatids elongate, replication at this stage to become chromosomes and become invisible. 2) Nuclear membrane form round daughter nuclei. 3) Cell membranes pinches into form daughter cells (animals) or new cell wall material becomes laid down across spindle equator (plants) 4) Nucleus divides into two and division of cytoplasm starts. Two cells are form. |
Question 13.
Mention the stages of Mitosis with the help of diagrams. Explain the changes that takes place in Prophase.
Answer:
Mitosis is a method of cell division, in which the nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus. Mitosis takes place in all body cells which retains same number of chromosomes.
Different stages of mitosis:
1) Prophase 2) Metaphase 3) Anaphase 4) Telophase
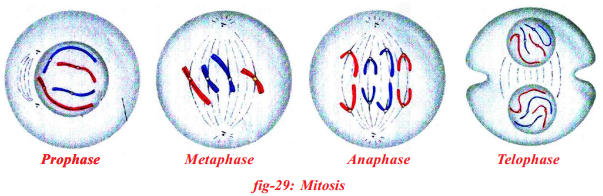
1) Prophase
- In this phase chromosomes condense and get coiled.
- They become visible even in light microscope.
- Nucleoli becomes smaller.
- Chromosome split lengthwise to form chromatids, connected by centromeres.
- Nuclear membrane breaks down.
- Centrosome containing rod like centrioles, divide and form ends of spindle.
![]()
Question 14.
Describe the process of double fertilization in plants. Explain the uses of endosperm that is formed.
Answer:
Double fertilization:
- In flowering plant germinated pollen grain forms pollen tube.
- The end of the pollen tube ruptures and two male garnets are released in the Embryosac.
- Out of two male garnets one male garnet fuses with female garnet which is called fertilization.
- Another male garnet fuses with the secondary nucleus and forms endosperm.
- So in flowering plant fertilization occures twice hence it is called double fertilization.
Uses of Endosperm:
- Cotyledons develops by utilizing endosperm.
- The Cotyledons utilizes the stored food in the endosperm.
- Some of the plants utilizes the endosperm completely and changes in to seed.
- Because of the stored food the size of the cotyledons increases.
Question 15.
Explain any two natural and two artificial vegetative propagation methods to produce more number of plants in less time period with examples.
Answer:
Natural propagation:
i) Leaves – Small plant grow at the edge of the leaves. Ex: Bryophyllum
ii) Stems:
a) Stolon – Ex: Jasmine, strawberry b) Bulbs – Ex: Onion
c) Corns – Ex: Colocasia d) Rhizome – Ex: Ginger e) Tuber – Ex: Potato
iii) Root – Ex: Roots of murayya, guava
Artificial propagation:
Cutting: Some plants can grow individual when a piece of parent plant having bud is cut off from the existing plants. Ex: Rose, Hibiscus.
Layering: A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and a part of it is covered with moist soil leaving the tip of the branch exposed above the ground. Ex: Nerium, Jasmine.
Grafting: Two plants are joint together in such a way that stems join and grow as a single plant one which is attached to soil is called stock and stem of another plant without roots is called scion. Both stock and scion are tied with a twine thread and cover by a polythene cover. Ex: Mango, citrus, apple, rose.
![]()
Question 16.
Read the following table and answer the following questions.
| SI. No. | Structure | Location |
| 1. | Tricuspid valve | Right auriculo-ventricular aperture |
| 2. | Guard cells | Epidermis of leaves |
| 3. | Glomerulus | Nephron |
| 4. | Alveoli | Lungs |
| 5. | Acrosome | Above the head of a sperm. |
i) Name the structure concerned to the heart.
Answer:
Tricuspid valve
ii) What is the function of acrosome?
Answer:
It helps the sperm in penetrating into ovum.
iii) Name the structures which are helpful for gaseous exchange.
Answer:
Alveoli and guard cells
iv) Name the part performing Excretion.
Answer:
Glomerulus
Question 17.
a) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of Human female reproductive system.
b) What happens when the Fallopian tubes are closed?
Answer:
a) Female reproductive system
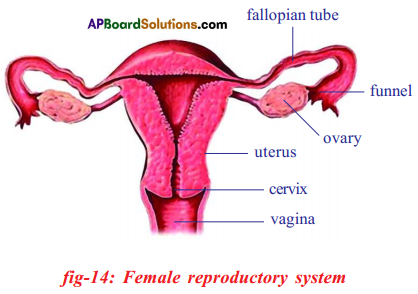 b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.
b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.
![]()
Question 18.
Observe the following table.
| Reproduction system | Organisms |
| Fission | Paramoecium, Bacteria |
| Budding | Yeast, Hydra |
| Fragmentation | Flatworms, Spirogyra |
| Rhizome | Ginger, Turmeric |
| Cutting | Rose, Hibiscus |
| Grafting | Citrus, Apple |
On the basis of information given in the table write- the answers to the following questions.
i) Write the names of two organisms that show Asexual reproduction.
Answer:
Yeast, Hydra, Bacteria, Paramoecium (any two you may write)
ii) Write two artificial vegetative propagation methods mentioned in the table.
Answer:
Cutting, Grafting
iii) Write the names of two plants, which undergo natural vegetative propagation mentioned in the table.
Answer:
Ginger, Turmeric
iv) In fission, how many organisms can we get from one organism?
Answer:
Two
Question 19.
Among the following organisms can we see asexual reproduction? Write about the method of asexual reproduction in any of the two organisms.
Answer:
а) Paramoecium b) Yeast c) Spirogyra d) Amoeba e) Planaria
Yes, we can see asexual reproduction in all the following organisms.
Method of asexual reproduction – Organism
Binary fission – Paramoecium, amoeba
Budding – Yeast
Fragmentation – Spirogyra
Regeneration – Planaria
1) Binary fission in Paramoecium: A single cell divides into two equal daughter cells. First the cytoplasm divides into two parts followed by nuclear division.
2) Asexual reproduction in Yeast: Budding is the common method of asexual reproduction in yeast. In this method, yeast cell wall at a particular region becomes soft and bulges into an outgrowth called bud. Cytoplasm enters into this bulge and then nucleus divides mitotically into two nuclei, one moves into the bud. Finally bud is detached from the parent cell and grows into an independent yeast cell.
![]()
Question 20.
See the adjacent picture. Which type of pollination will occur in this ? Why do you think so?
 Answer:
Answer:
- Self-pollination occurs if stamens and carpels matures at the same time.
- If they mature at different times, cross pollination occurs.
- Cross pollination occurs in this plant.
- For cross pollination the pollen grains are carried from other plants belonging to the same species.
- The mechanism of dispersal of pollen grains from one plant to other plant is facilitated mostly by wind and insects.
- Cross pollination is believed to be advantageous for the plant.
- The seeds produced by the flower will contain another source of genetic material
- Which may contain genes which are advantageous to the survival of the seedlings.
Question 21.
What are the consequences if meiosis do not happen in the body cells of the organism?
Answer:
- Each organism has a fixed number of chromosomes.
- This number has to be maintained in its offspring.
- Any sudden change in the number of chromosomes will be harmful to the offspring. Assume parent has 10 chromosomes.
- In the absence of meiosis during sexual reproduction gametes will also have the same number of chromosomes as parent i.e., 10 chromosomes.
- Union of female and male gametes occur forming zygote during sexual reproduction. The number of chromosomes doubled in zygote will have 10+10 chromosomes.
- In the next generation, the offspring will have forty chromosomes. If this continues cells in the offsprings will have thousands of chromosomes within few generation.
- This results in formation of abnormalities in each generation. Hence by way of meiotic division, the chromosome number is maintained constant from generation to generation.
![]()
Question 22.
Describe different artificial vegetative methods to produce large scale production of plants.
Answer:
- Different artificial vegetative propagation methods are cutting, layering, grafting and tissue culture methods.
- Cutting: Some plants grow individually when a piece of parent plant having bud is cut from the existing plant. After burying in the soil the cut parts having buds grow as an individual plant after developing roots. E.g. Rose.
- Layering: A branch of the plant with at least one node is bent towards the ground and part of it is covered with moist soil. After sometime, new roots develop from the part of the branch hurried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant. E.g: Nerium.
- Grafting: Two plants are joined together in such a way that two stems join and grow as a single plant. This technique is very useful in propagating improved vari¬eties of various flower and fruits. Grafting is used to obtain a plant with desirable character. E.g: Mango, citrus, apple, rose.
- Tissue culture: In this method, few plant cells or plant tissues are placed in a growth medium with plant hormones in it and it grows into new plants. Thousands of plants can be grown in very short interval of time.
Question 23.
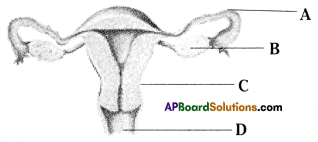
i) Labelled parts of A, B, C, D above drawn Human female reproductive system.
ii) In which part fertilization takes place?
iii) Which part is in connection with implantation?
iv) What is ovulation?
Answer:
i) A: Fallopian tube
B: Ovary
C: Uterus
D: Vagina
ii) Fertilization takes place in fallopian tube.
iii) Uterus
iv) Release of ovum from graffian follicle of ovary is known as ovulation.
![]()
Question 24.
Write some programmes conducted by you to bring awareness in the people about health and hygeine and family planning?
Answer:
- Organising Health camps on World Health day to people of the village.
- Conducting immunisation programs for every three months.
- Supplying tablets on the deworming day.
- Organising seminars by expert doctors on individual health and cleanliness programs.
- Propagating small family norms conducting camps for family planning operations.
- Educating the masses through pamplets on the needs of taking balanced diet.
- Need of using toilets and washing hands and legs before and after meals.
- Educating the people by conducting adult education centres. This is basically required for enlightening the people on health aspects.
Question 25.
Government made an act on determining sex through ultrasound scanning and telling it as crime. What do you do to tell this to others?
Answer:
- I will educate people knowing the sex of foetus inside mother’s womb is a severe crime as per the act made by government.
- The purpose of ultrasound tests are to know the growing condition of the foetus and also to see whether it is suffering with severe ailments.
- By knowing the sex of the foetus, if it is female people are ready for aborting it.
- This leads to reduction in male female ratio in the country.
- Children either male or female are equal to parents.
- We should see proper development of girl child after her birth.
Question 26.
Write about the embryonic membranes that nourish, protect and support to the embryo?
Answer:
- The growing embryo form two membranes – Chorion and Amnion.
- Chorion establishes connection with the walls of the uterus and helps in the supply of nutrients to the embryo and in the removal of wastes from the embryo.
- Amnion forms a sac like structure around the embryo and amniotic fluid is present between layers of Amnion.
- Amnion and Amniotic fluid give protection to the embryo against mechanical shocks.
- Placenta is a tissue formed around 12 weeks of pregnancy by the cells from the embryo and mother.
- Embryo receives all the required nutrients and oxygen for its metabolism from the mother through the blood vessels present in the placenta.
- Another membrane called allantois, which originates from the digestive canal of the embryo forms the major part of a tube like structure called umbilical cord.
- Umbilical cord contains very important blood vessels that connect the embryo with the placenta.
![]()
Question 27.
Write brief history of cell division.
Answer:
- In 1852 a German scientist, Robert Remak published his observations on cell division and stated that the binary fission of cells was the means of reproduction of animal cells.
- This view was widely publicized by Rudolf Virchow who gave the phrase “Omnis cellulade cellula” means all cells arising from pre existing cells.
- In 1879 Walther Flemming reported that there were string like structures in the nucleus which split longitudinally during cell division. He named the process as mitosis means fine threads as the dividing structures resembled threads.
- Wilhelm Roux proposed that each chromosome carried a different set of heritable elements and suggested that the longitudinal splitting observed by Flemming ensured the equal division of these elements.
- Combined with the rediscovery of Gregor Mendel’s 1866 paper on heritable elements in peas, these results highlighted the central role of the chromosomes in carrying heritable material or genetic material.
- The scheme of mitotic division was confirmed in 1904 by Theodor Boveri.
- The chemical nature of the genetic material was determined in a series of experiments over the next fifty years.
- The structure of DNA – the constituent of the genetic material was determined in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick.
Question 28.
Explain briefly about child birth. (OR) How child birth occurs after gestation period?
Answer:
- Total time required for the embryonic and foetal development is about 9 months or 280 days.
- After this time, foetus is expelled from the uterus by the mother. This is child birth.
- Child birth is a complicated process and involves the participation of child and mother.
- The foetal hormones produced inside, stimulate the contraction of the muscles present in the walls of uterus.
- These contractions called labour pains help in the expulsion of the foetus from the uterus.
- During this process the amnion ruptures, placenta is separated from the walls of J the uterus.
- At child birth the head usually comes out first.
- The foetus is still attached to the mother’s uterus through the umbilical cord, which is later separated by the doctors.
Question 29.
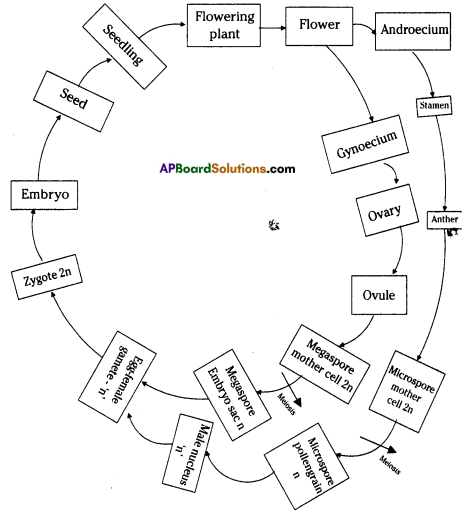
Draw the life history of flowering plant in the form of block diagram.
Answer:
Life history of a flowering plant:
![]()
Question 30.
In a flower self fertilization takes place. Write the process, the flower organs which involve in self fertilization.
Answer:
- Fusion of male and female gametes produced by the same individual is called self fertilization.
- Self ferlization occurs in bisexual flowering plants.
- The flower organs which involve in self fertilization are stamens (androecium) and carpels (Gynoecium).
- Majority of flowering plants have an embryo sac consisting of seven cells and eight nuclei.
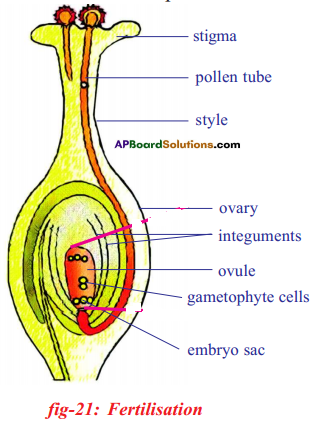
- The pollen grains produced by anther of stamen are transferred to the stigma of the same flower by wind or insects.
- The stigma of the carpel secretes a sticky substance which promotes the growth of pollen grains.
- Under favourable conditions pollen grains germinate on the stigma and give rise to pollen tubes.
Only one pollen tube finally reaches the embryo sac. - This pollen tube will have two male nuclei, which migrate to the tip of the pollen tube at the time of fertilization. Usually the pollen tube enters the ovule through micropyle and discharges the two male gametes into its embryo-sac.
- One male nucleus (gamete) approaches the egg and fuses with it to form a diploid zygote. This is first fertilization.
- The other male nucleus reaches the secondary nucleus (2n) and fuses with it to form the endosperm nucleus which will be triploid. This is second fertilization in the embryo sac.
- Thus double fertilization occurs in embryo sac which is unique in flowering plants.
![]()
Question 31.
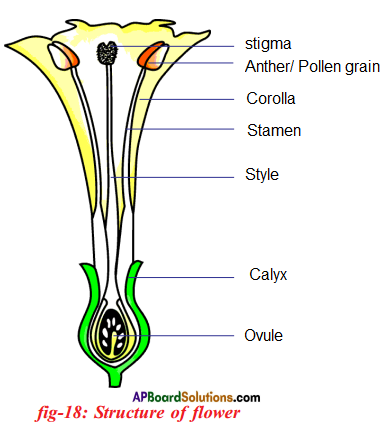
Describe the structure of flower with a neatly labelled diagram.
Answer:
- A typical flower consists of an outer whorl of green sepals (calyx) which protects the parts with in.
- The second whorl has petals (corolla) which are usually brightly coloured. They sometimes emit fragrance also.
- Petals are soft and are useful to attract insects to facilitate cross pollination.

- The third whorl of the flower consists of stamens (Androecium) which are the male reproductive organs.
- Each stamen is made up of a filament and an anther.
- Each anther usually has two anther lobes. The anther produces pollen grains (microspores).
- The inner most fourth whorl is gynoecium or pistil. It consists of ovary, style and stigma.
- Ovary occupies central portion on the thalamus. A swollen ovary is present on the thalamus.
- Inside the ovary future seeds, known as ovules are present.
- Ovary has a pipe like extension called style. The tip of the style ends in stigma. The stigma receive the pollen grains.
Question 32.
Write a brief note on male reproductive system of human beings.
Answer:
- The male reproductive system of human beings consists of a pair of testis, accessory glands and a system of ducts.
- Testis are male reproductive organs and produces spermotozoa or sperms and also secretes male sex hormone Testosterone.

- Inside each testis several lobules are present. Each lobule has several tubules called seminiferous tubules.
- Germinal epithelial cells in the seminiferous tubules undergo meiotic division to produce sperms.
- The accessory glands include one prostrate gland and two cowper glands. Secretion of these glands produce semen.
- The duct system consists of vasa efferentia.
They collect spermatozoa from seminiferous tubules. - Vasefferentia continue as epididymis where sperms are stored temporarily.
- From epididymis sperms moved into tubule called vas deference and then into urethra.
![]()
Question 33.
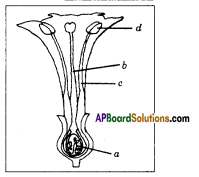
Describe the female reproductive system in human beings.
Answer:
- A pair of ovaries, oviducts, uterus and vagina are the parts present in female reproductive system.
- Ovaries are present just below the Kidneys in the abdominal cavity.
- Each ovary has several sac like structures called ovarian follicles or Graffian follicles.

- Every time only one follicle matures and release one ovum into the body cavity.
- Ovaries secrete two female sex hormones called oestrogen and progesterone which control the development of female reproductive organs, ovulation and menstruation.
- Just above the ovaries are the tubes called oviducts or fallopian tubes where fertilisation takes place.
- The two oviducts connect to a bag like organ called uterus at their other ends.
- The uterus is connected through a narrow opening called cervix to another tube called vagina which opens to the outside of the body.
- Vagina is a tubular structure and is also called birth canal because it is through this passage that the baby is born after the completion of development inside the uterus of the mother.
Question 34.
Describe briefly about the reduction division or meiosis.
(OR)
Why meiosis is also known as reduction division? Comment on it.
Answer:
- Meiosis occurs only during the formation of gametes in sexual reproduction.
- During meiosis only one set of chromosomes are passed on to the daughter cells. Hence daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes of the mother cells.
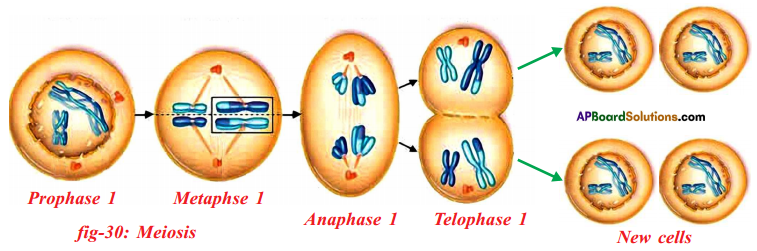
- In meiosis karyokinesis and cytokinesis occur two times.
- During first phase of meiosis the parent cell divides twice, though the chromosomes divide only once.
- The second phase meiosis is similar to normal mitosis, but chromosomes do not duplicate more over the chromosome number distributed equally to each cells.
- Thus the four daughter cells have just half the number of chromosomes of the parent cells.
- These are haploid (containing only one set of chromosomes).
- Thus meiotic division is also called reduction division.
![]()
Question 35.
Describe the developmental stages of human embryo after fertilization with the help of neatly labelled diagrams.
Answer:
- During fertilization, chromosomes of the ovum and the chromosomes of the sperm make up into pairs and the resulting cell is called zygote.
- Fertilization takes place in the oviduct or fallopian tube.
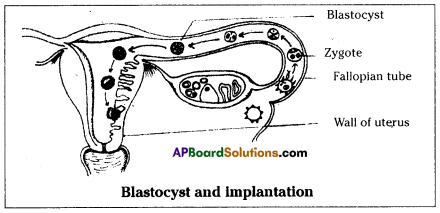
- The zygote which is diploid travels down the fallopian tube. As it moves it undergoes several mitotic divisions forming the embryonic stage called blastocyst.
- Blastocyst moves towards the wall of the uterus and finally gets attached and embedded in the wall of the uterus. This is called implantation.
- The growing embryo forms two membranes Chorion and Amnion.
- Chorion establishes connection with the walls of the uterus and helps in the supply of nutrients to the embryo and removal of wastes from the embryo.
- Amnion forms a sac like structure around the embryo. The space between the amnion and embryo is filled with a fluid called amniotic fluid.
- Amnion and amniotic fluid give protection to the embryo against minor mechanical injury.
- Placenta is a tissue formed by the cells from the embryo and the mother. It is formed around 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta nourishes the growing embryo.
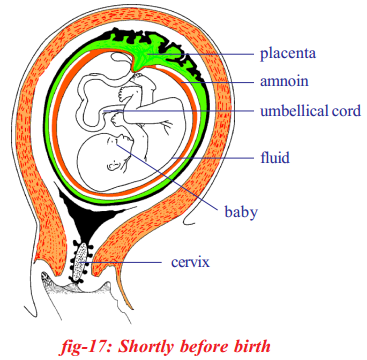
- A tough cord called umbilical cord is also formed by the embryo which is connected to the walls of the uterus through the placenta.
- From 3 months of pregnancy, the embryo is called foetus.
- Pregnancy lasts on an average 9 months or 280 days. This period is called gestation period.
- After this time foetus is expelled from the uterus by the mother – this is child birth.
- This process is complicated and involves the participation of foetus and mother.
![]()
