Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2018 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2018 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Note: Answer ANY TWO out of the following five questions.
Question 1.
Define Banking. Explain the functions of the Banking.
Answer:
Meaning: A bank is an institution that deals with money and credit. It accepts deposits from the public, makes the funds available to those who need them and helps in sending money from one place to another.
Definition: According to the Indian Banking Regulation Act 1949, banking means “the accepting for lending or investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawable by cheque, draft or otherwise”.
Functions of Bank:
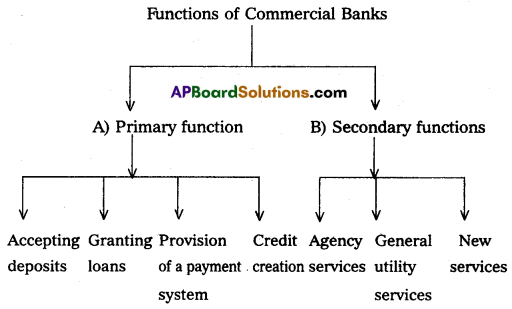
(A) Primary Functions:
1. Accepting Deposits:
Banks accept the various types of deposits, such as:
- Fixed deposit account: Money in those accounts is deposited for a fixed period and cannot be withdrawn before the expiry of that period. So fixed deposits are also called “Time deposits” or “Term deposits”. The rate of interest on this account is higher than other types of deposits.
- Current deposit account: Money from these accounts can be withdrawn many times. So current deposits are also called “Demand deposits”. Normally no interest is paid on that account. Their accounts are maintained by traders and businessmen who make several payments every day.
- Savings Deposit Account: Those accounts aim to encourage small savings of the public. Certain limits are imposed on several withdrawals and the amount to be withdrawn.
- Recurring Deposit Account: Money in these accounts is deposited in monthly installments for a period to encourage regular savings by the fixed-income group. It is repaid to depositors along with interest on maturity which is nearly the same as interest on fixed deposits.
2. Granting of Loans:
Various types of loans granted by banks are given below:
- Money at call and short notice: These loans are interbank loans where banks with surplus lend to the needy bank and repay at very short notice, say one day to fourteen days.
- Cash credit: Cash credit is a short-period loan granted to a customer for one year or less. He may withdraw the amount as per his needs. Interest is charged only on the amount utilized.
- Overdraft: The bank provides an overdraft facility to its customers through which they are allowed to withdraw more than their deposits. Interest is charged on bank overdraft amount.
- Loans: Loans are given for a fixed period at an agreed rate of interest. It is made normally against security.
- Discounting of bill of exchange: If the holder of the bill needs the money before maturity, then he can discount the bill at the bank. The bank can get its payment from the debtor on maturity.
3. Provision of a Payment System:
Banks create a very useful medium of exchange in the form of cheques. Through a cheque, the depositor directs the bankers to make payment to the payee.
4. Credit Creation:
Credit creation is the natural outcome of the process of advancing loans as adopted by the bank. Banks can create credit many times more than deposits.
(B) Secondary Functions of Services:
(i) Agency Services:
- Banks help their customers in transferring money from one place to another through cheques.
- Banks collect and pay various credit instruments like cheques, bills, promissory notes, etc.
- Banks undertake to purchase and sale of shares, bonds, and debentures on behalf of their customers.
- Banks preserve the will of their customers and execute after death.
(ii) General Utility Services:
- Letters of credit are issued to their customers for their creditworthiness.
- Banks issue transfer cheques to help to travel without fear.
- Banks provide safety deposit lockers.
- Acceptance or collecting foreign bills of exchange.
(iii) New Services:
- Free checkbook.
- Anywhere banking.
- Free Internet banking.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the objectives and functions of SEBI.
Answer:
Introduction:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was established by the Government of India in April 1988 to promote healthy growth of the securities market and for investor protection. It was to function under the administrative control of the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India. It got statutory status in January 1992.
Objectives of SEBI:
- To regulate stock exchanges and the securities industry to promote their orderly functioning.
- To protect the rights and interests of investors and to guide and educate them.
- To prevent trading malpractices in the securities industry.
- To regulate and develop a code of conduct and fair practices by intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers, etc. to make them competitive and professional.
Functions of SEBI:
SEBI assigned regulatory, development, and protective functions to control and regulate the capital market.
(A) Regulatory Functions:
- Registration of brokers, sub-brokers, and other players in the market.
- Registration of collective investment schemes and mutual funds.
- Regulation of stock brokers, portfolio exchanges, merchant bankers in stock exchanges, and any other securities market.
- Regulation of takeover bids by companies.
- Calling for information by undertaking inspections, conducting inquiries, and audits of stock exchanges and intermediaries.
- Levying fee or other charges for carrying out the purpose of the act.
- Performing and exercising such powers under the Securities Contracts Regulation Act 1956, as may be delegated by the Government of India.
(B) Development Functions:
- Training for intermediaries of the securities market.
- Conducting research and publishing information useful to all market participants.
- Undertaking measures to develop the capital markets by adopting a flexible approach.
(C) Protective Functions:
- Prohibition of fraudulent and unfair trade practices like making misleading statements, manipulations, price rigging, etc.
- Controlling insider trading and imposing penalties for such practices.
Question 3.
Explain the redressal mechanism available to consumers under the Consumer Protection Act, of 1986.
Answer:
Consumer Protection refers to the measures adopted the protect consumers from unethical malpractices by businesses and to provide them with speedy redressal of their grievances. The judicial mechanism set up under the Consumer Protection Act 1986, consists of consumer courts (forums) at the district, state, and national levels. These are known as district forums, the State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (State Commission), and the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (National Commission).
1. District Forum:
District forum is established by the State Government in each district.
- Composition: The district forum consists of a Chairman and two other members, one of them shall be a woman candidate. They are headed by the person of the rank of a District Judge.
- Jurisdiction: A written complaint can be filed before the District Consumer Forum, where the value of goods or services and the compensation claimed does not exceed ₹ 20 lakhs.
- Appeal: If a consumer is not satisfied by the decision of the District Forum, he can challenge the same before the State Commission, within 30 days of the order.
2. State Commission:
State commission is established by the state governments in their respective states.
- Composition: It consists of a president and two members, one of them shall be a woman. It is headed by a person of the level of High Court Judge.
- Jurisdiction: A written complaint can be filed before the State Commission where the value of goods or services and the compensation claimed exceeds ₹ 20 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 1 crore.
- Appeal: In case the aggrieved party is not satisfied with the order of the state commission he can appeal to the National Commission within 30 days of passing of the order.
3. National Commission:
It was constituted in 1988 by the central government. It is the highest authority to settle consumer disputes at the national level.
- Composition: It consists of a president and not less than four members, one of them shall be a woman. It is headed by a sitting or retired Judge of the Supreme Court.
- Jurisdiction: All the complaints about those goods and services and compensation value of more than ₹ 1 crore can be filed directly before the National Commission.
- Appeal: An appeal can be filed against the order of the National Commission to the Supreme Court within 30 days from the date of the order passed.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Note: Answer any four questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Explain any five characteristics of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
Entrepreneurs tend to have specific characteristics that distinguish them from other people. The following are some characteristics that every successful entrepreneur must possess.
1. Innovation:
Innovation is an important characteristic of an entrepreneur in modern business. Innovation may take the form of the introduction of a new method or introducing improvements in the existing method. Innovation helps in increasing production and reducing the cost of production.
2. Risk-taking:
The entrepreneur has to pay for all factors of production in advance. There is a chance that he may be rewarded with a handsome profit or he may suffer a heavy loss. Therefore, the risk-bearing is the final responsibility of an entrepreneur.
3. Organisation of Production:
He makes arrangements for land, labor, capital, raw materials, etc, required for setting up a production process. He assesses the viability of having different production processes and selects one that is most suitable.
4. Decision Making:
Every activity of the business requires decision-making. An entrepreneur has to make decisions about the establishment of the business its management and the coordination of various resources.
5. Leadership:
An entrepreneur has to be a leader because he is such a person who organizes, directs, commands, and controls the functioning of the organization. His personality will influence the working of his subordinates because he is taken as a role model. He motivates them to achieve goals quickly and efficiently.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the types of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
Based on American Agriculture, Danhof classified entrepreneurs into four categories. They are
- Innovating entrepreneurs
- Initiative entrepreneurs
- Fabian entrepreneurs
- Drone entrepreneurs
1. Innovating Entrepreneurs:
Innovating entrepreneurs introduce new products; new methods of production, discover new markets, and reorganize the enterprise. Such entrepreneurs can work only when a certain level of development is already achieved, and people look forward to change and improvement.
2. Initiative Entrepreneurs:
These entrepreneurs adopt the methods arid techniques already successfully executed by innovating entrepreneurs. Initiative entrepreneurs do not innovate the changes themselves, they only initiate techniques and technology innovated by others, so they are also called “Adaptive entrepreneurs”. This type of entrepreneur is found in underdeveloped countries.
3. Fabian Entrepreneurs:
These entrepreneurs neither fall in the innovative entrepreneur’s category nor the adaptive entrepreneur’s category. These are great caution and skepticism in experimenting with any changes in their enterprises. They follow in the footsteps of their successors. They are no risk-takers.
4. Dron Entrepreneurs:
These are characterized by a refusal to adopt opportunities to make changes in production formulae. Such entrepreneurs may even suffer from losses but they are not ready to make changes in their existing production method. They may close down their business but they don’t adapt to changes.
Question 6.
What is SEZ? Explain their objectives.
Answer:
Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic laws that are more liberal than a country’s economic laws. The main aim of the SEZ is to attract larger foreign investments. It is intended to make SEZ engines for economic growth. The SEZ Act was passed by parliament in May 2005.
Objectives:
- Generation of additional economic activity.
- Promotion of exports of goods and services.
- Promotion of investment from domestic and foreign sources.
- Creation of employment opportunities.
- Development of infrastructure facilities.
- To exempt import duties and service tax.
Question 7.
What is Trade? Various types of Home Trade.
Answer:
Trade:
Trade means the buying and selling of goods or services between two persons two business organizations or two countries. It involves the exchange of goods from the producer to the customer. Trade is broadly classified into two types, they are home trade and international trade.
Types of Home Trade:
A trade that takes place with the country is known as “Home Trade”. It is also called as “Domestic Trade” or “Internal Trade”. Home trade is divided into two types. They are
- Wholesale trade
- Retail trade
1. Wholesale trade:
Wholesale trade means buying and selling goods in large quantities or bulk. The traders who are engaged in wholesale trade are called wholesalers. A wholesaler buys goods in bulk quantity from the manufacturers and sells them in small lots to retailers or industrial users.
2. Retail trade:
Retail trade means buying goods from wholesalers and selling in very small quantities to ultimate consumers. The trader who engages in retail trade is called a retailer. He is the last link in the chain of distribution of goods.
Question 8.
What are the advantages of Life Insurance Policies?
Answer:
Life insurance policies are introduced for the protection of life against uncertainty. Some of the advantages of life insurance policies are given below:
- Encourages savings habit: Life insurance policies encourage the saving habit of the people, by taking premiums at regular intervals.
- Policy can be assigned or mortgaged: A life insurance policy can be used to assign or mortgage to avail housing loans or other loans from insurance companies or other financial institutions.
- Tax benefits: The Ministry of Finance extends income tax benefits on the amount of premium paid by the insured.
- Protection to family members: Life insurance provides economic protection to family members of the insured in case of his untimely death.
- Best source of investment: Life insurance is considered the best source of investment since it ensures better returns on investment.
![]()
Question 9.
The distinction between primary and secondary markets.
Answer:
| Primary Market (New Issue Market) |
Secondary Market (Stock Exchange Market) |
| 1. There is the sale of securities to investors by new companies or new issues by existing companies. | 1. There is the trading of existing shares only. |
| 2. Securities are sold by the company to the investors directly or through an intermediary. | 2. Ownership of existing securities is exchanged between investors. The company is not involved at all. |
| 3. In the primary market the flow of funds is from savers to investors, i.e., the primary market directly promotes capital formation. | 3. The secondary market enhances the liquidity of shares, i.e., indirectly promotes capital formation. |
| 4. In this market only the buying of securities takes place but securities cannot be sold here. | 4. Both buying and selling of securities can take place on the stock market. |
| 5. Prices of securities are determined and decided by the management of the company. | 5. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of the securities. |
| 6. In the primary market there is no fixed geographical location. | 6. Secondary markets are located at specified places for trading activities. |
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any five questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Explain any two functions of the entrepreneur.
Answer:
1. Formation of New Producing Organisation:
It is the function of an entrepreneur, to arrange land, labor, capital, raw materials, etc., required for setting up a production process. According to J.B.Say, the function of a producer/entrepreneur is to rationally combine the forces of production into a new producing organization.
2. Decision Making:
An entrepreneur as a decision maker takes various decisions regarding the following:
- Ascertaining the objective of the enterprise
- Sources of finance
- Product mix
- Pricing policies
- Promotion strategies etc.
Question 11.
Explain the meaning of entrepreneur.
Answer:
- The word entrepreneur is derived from the French verb “Entrepredre” which means “To undertake”. An entrepreneur may be referred to such a single person or a group who promotes a new enterprise by collecting various factors of production and bearing the risks.
- The American Heritage Dictionary defines an entrepreneur as “a person who organizes, operates, and assumes the risk for a business venture”.
Question 12.
Wholesaler.
Answer:
Wholesale trade means buying and selling goods in large quantities or bulk. The trader who engages in wholesale trade is called a wholesaler. He buys goods in bulk from producers and sells them in small lots to retailers or industrial users.
Question 13.
Double Insurance.
Answer:
When more than one insurance policy is taken on the same subject, it is called “Double Insurance”. In life insurance, any number of policies can be taken by the insured upon his life, he can claim the amount an all these policies. But this is not in the case of fire and marine insurance. If he takes two or more policies for the same property, he is entitled to the compensation of the actual loss only.
Question 14.
Bonded Warehouses.
Answer:
Bonded warehouses are licensed by the government to accept imported goods before payment of tax and customs duty. Importers are not permitted to remove goods from the docks or the airport till customs duty is paid.
Question 15.
SENSEX.
Answer:
SENSEX is the benchmark index of the BSE. The BSE – SENSEX (Sensitive Index) is also called the “BSE – 30”. SENSEX is an important indicator of the Indian Stock Market. It was launched in 1986 with 30 of the most actively traded stocks in the market which represent 13 sectors of the economy. The index with the base year of 1978-79, the value of the base year was 100.
Question 16.
Financial market.
Answer:
A financial market is a place where buyers and sellers participate in the trade of financial assets such as equities, bonds, currencies, and derivatives. Financial markets mobile savings and make them available for productive investment.
![]()
Question 17.
What is meant by consumer protection?
Answer:
Consumer Protection means safeguarding the interests and rights of consumers. In other words, it refers to the measures adopted to protect consumers from the redressal of their grievances.
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
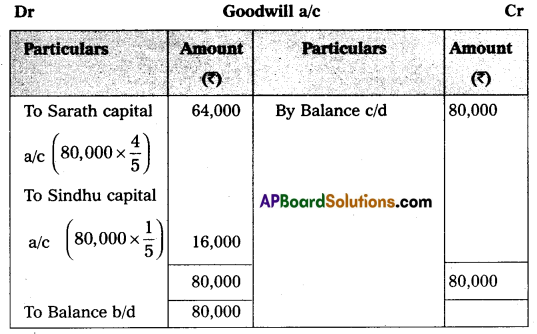
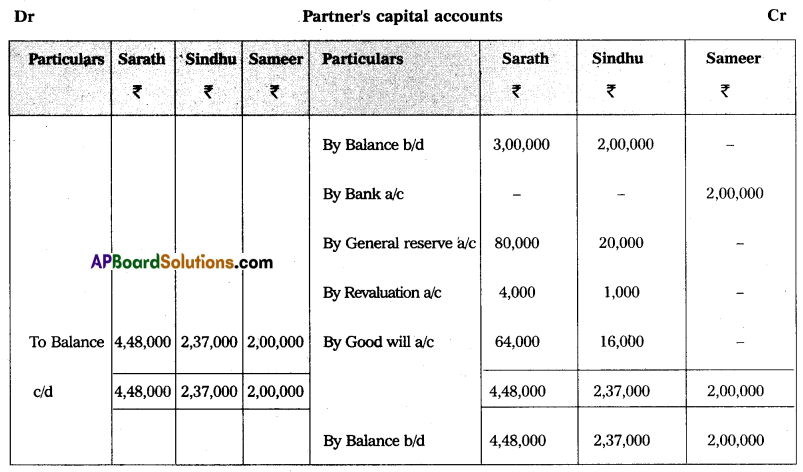
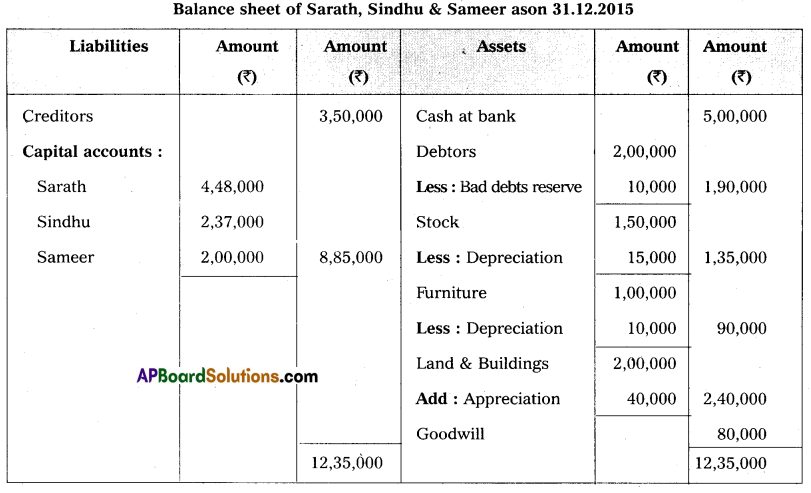
Question 18.
The Balance Sheet of Sarath and Sindhu as of 31-12-2015 who are sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 1 as follows:
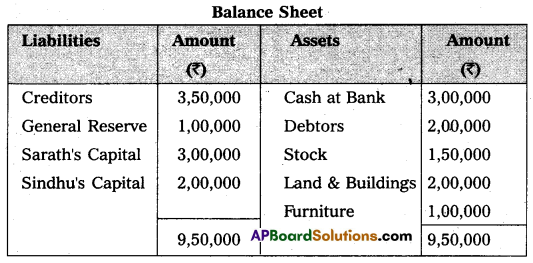
They have agreed to admit Sameer under the following conditions:
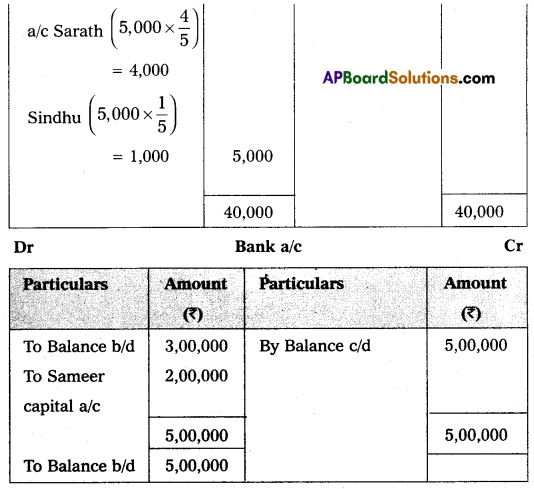
1. Sameer has to bring a capital of ₹ 2,00,000 for his. 1/5th share of profit.
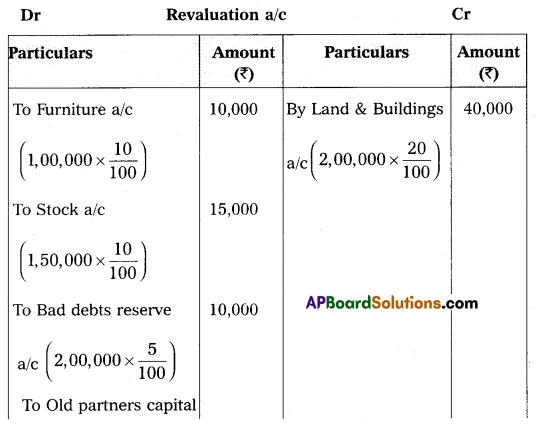
2. Furniture and stock have to be depreciated by 10% and a reserve of 5% has to be created on debtors for bad debts.
3. Land and Buildings have to be appreciated by 20%.
4. Goodwill has to be raised by ₹ 80,000.
Prepare necessary Ledger Accounts and the Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Note: Answer any one of the following questions.
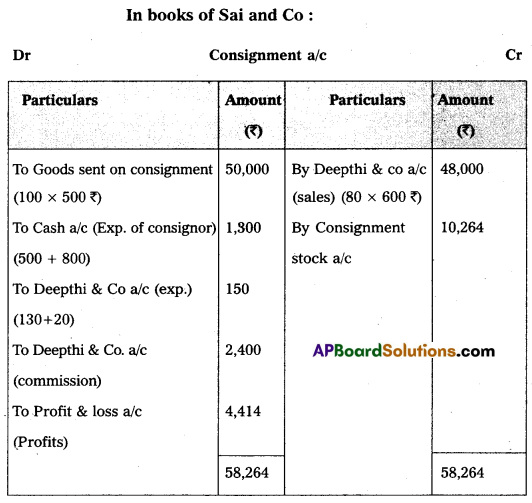
Question 19.
Sai and Co., of China consigned 100 Radios to Deepthi and Co. The cost of each radio was ₹ 500. Sai and Co. paid insurance ₹ 500; and Freight ₹ 800. Account sales were received from Deepthi and Co., showing the sale of 80 Radios at ₹ 600 each. The following expenses were deducted by them:
1. Carriage ₹ 20
2. Selling expenses ₹ 130
3. Commission ₹ 2,400.
Sai and Co. received a bank draft for the balance due. Prepare important Ledger Accounts in the books of Deepthi and Co.
Answer:
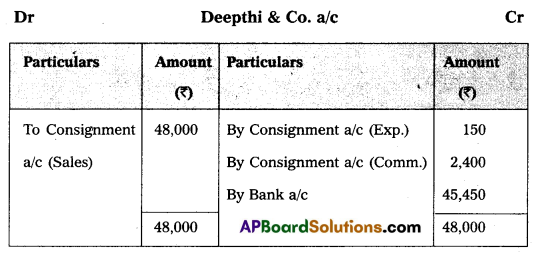
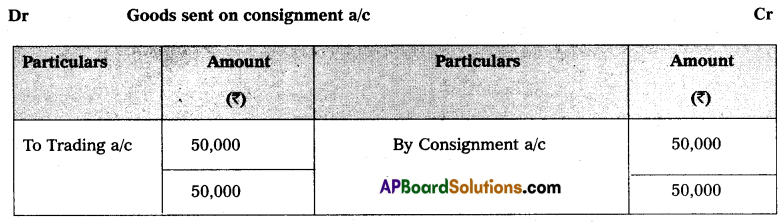
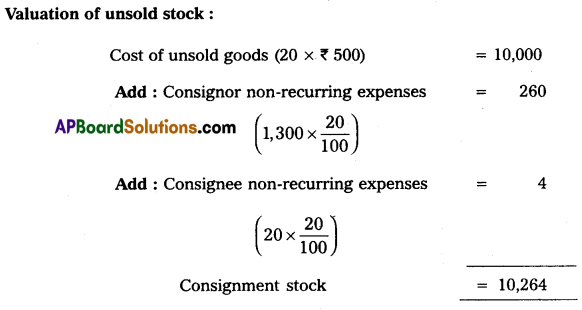
Question 20.
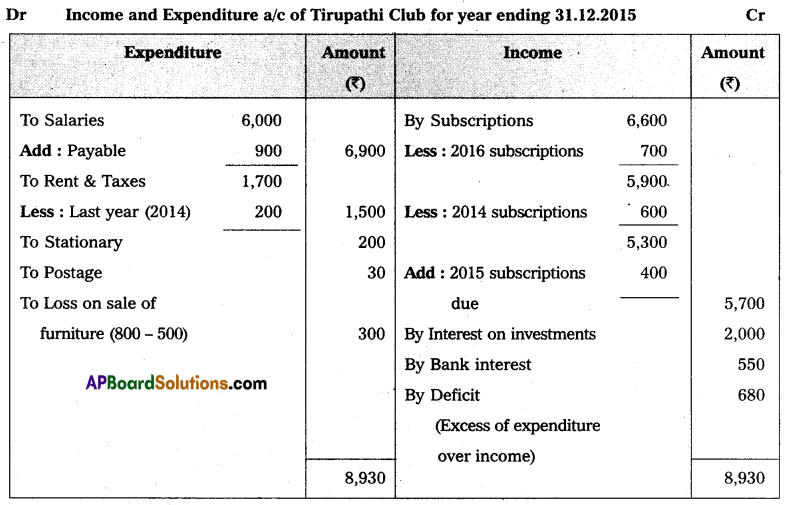
Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c of Tirupati Club from the following Receipts and Payments a/c for the year ending 31-12-2015.
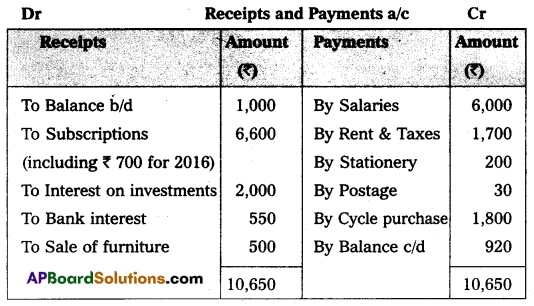
Adjustments:
1. Rent paid included ₹ 200 for 2014.
2. Salaries payable ₹ 900.
3. Subscriptions received included ₹ 600 for the year 2014.
4. Subscriptions due for the year 2015, ₹ 400.
5. Cost of furniture sold ₹ 800.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Note: Answer any Two of the following questions.
Question 21.
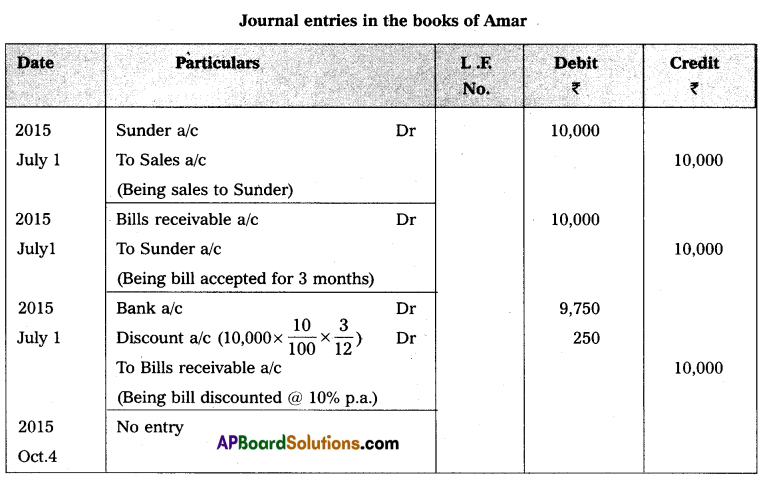
Amar sold goods for ₹ 10,000 to Sunder on credit on 1st July 2015. Amar draws a bill of exchange on Sunder for the same amount for three months. Sunder accepted the bill and returned it to Amar. Amar discounted the bill with his bank @ 10% per annum on the same day. Sunder met his acceptance of maturity. Pass necessary Journal entries in the books of Amar.
Answer:
Question 22.
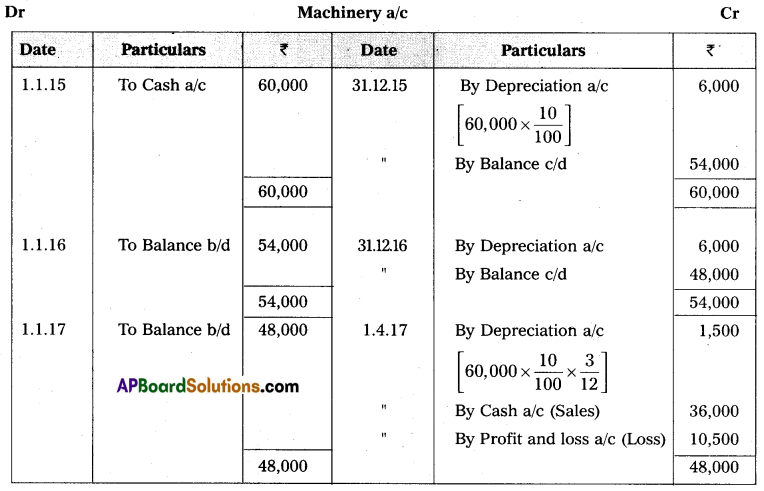
Ranadheer & Co. purchased a machine for ₹ 60,000 on 1st January 2015. Depreciation is calculated @ 10% on the Straight Line method. On 1st April 2017, the company sold the machine for ₹ 36,000. Prepare Machinery account assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year.
Answer:
![]()
Question 23.
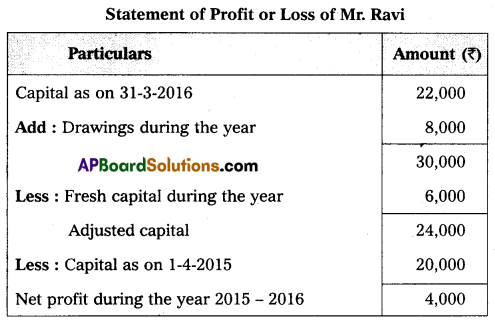
Mr. Ravi maintains his books on single entry method. He gives you the following information:
Capital on 1-04-2015 – ₹ 20,000
Drawings during the year – ₹ 8,000
Capital on 31-3-2016 – ₹ 22,000
Fresh capital during the year – ₹ 6,000
Prepare the Statement of Profit or Loss.
Answer:
Question 24.
Explain the advantages of computerized accounting.
Answer:
Computerized accounting offers the following advantages:
- Speed: Computer accounting processes accounting data much faster than manual accounting.
- Accuracy: The possibility of error is eliminated in a computerized accounting system because the primary accounting data is entered for all the subsequent usage and the process is preparing the accounting reports.
- Reliability: Computers are more reliable than human beings because computers perform repetitive operations without tiredness or boredom.
- Upto-date Information: The accounting records in a computerized accounting system are updated automatically as and when accounting data is entered and stored.
- Automated Document Production: Computerised accounting system reports such as Cashbook, Trial balance, and Statement of accounts by one click of a mouse.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any five questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 25.
Days of Grace.
Answer:
For making the payment of the bill, the drawee is allowed three extra days after the normal due date. Such 3 days are known as “Days of Grace”.
Question 26.
Rate of Depreciation formula.
Answer:
Rate of Depreciation = \(\frac{\text { Annual depreciation }}{\text { Original cost of asset }} \times 100\)
Question 27.
Additional commission or overriding commission.
Answer:
It is an extra commission allowed over the normal commission. This commission is generally offered when an agent is required to work hard either to introduce a new product in the market.
Question 28.
Special Donations.
Answer:
If the donation is for a specific purpose it is called specific donations or special donations.
Eg.: Donations for the construction of buildings, donations for the library, etc.
Question 29.
Ready-to-use.
Answer:
Ready to use is accounting software that is suited to organizations running small businesses where the frequency of accounting transactions is low. The cost and installation are low for this accounting software.
Question 30.
What is Equity Shares?
Answer:
Shares that do not have any preferential rights in the payment of dividends or repayment of capital are called “Equity shares”. Equity shareholders are owners and they have voting rights.
![]()
Question 31.
Any two advantages of a single entry system.
Answer:
- A single-entry system is a simple method of recording transactions.
- It is less expensive when compared to double-entry system bookkeeping.
- It is suitable for small business concerns.
- Ascertainment of profit or loss is very easy.
Question 32.
Akshay and Bharat are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. They admit Dinesh as a new partner for 1/5th share with future profits of the firm. Calculate the new profit-sharing ratio of Akshay, Bharat, and Dinesh.
Answer:
The old ratio of Akshay and Bharath is 3 : 2
New partner Dinesh share = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Take total share of the firm is 1.
Remaining share of profits = 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Akshay new share = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{12}{25}\)
Bharath new share = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{2}{5}=\frac{8}{25}\)
Dinesh new share = \(\frac{1}{5} \times \frac{5}{5}=\frac{5}{25}\)
∴ New ratio of Akshay, Bharath & Dinesh = \(\frac{12}{25}: \frac{8}{25}: \frac{5}{25}\) = 12 : 8 : 5