Thoroughly analyzing AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers Set 5 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
AP Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Paper Set 5 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What is international trade? Discuss various types of international trade.
Answer:
The trade that takes place between nations is international trade. The exchange of goods and services between the traders of two nations is international trade. International trade involves the exchange of not only goods but also currencies between nations. International trade is the process of transferring goods produced by one country for the consumers in another country. The international trade can be divided into three types. They are:
- Import trade
- Export trade
- Entrepot trade
1. Import trade:
The term import is derived from the conceptual meaning as to bring in goods and services into the port city of the country. When purchases are made from another country, goods are said to be imported from that country to the buyer’s country. For example, Japan has the most modern technology for producing electronic products cheaply, so we import these products into our country.
2. Export trade:
The term export is derived from the conceptual meaning as to ship goods and services out of the port of the country. When goods are sold to a trader in another country, goods are exported to that country by the seller’s country. For example, India is a major exporter of tea because of the fertile land in Assam and Darjeeling, so we export tea products to other countries.
3. Entrepot trade:
When goods are imported into a country, not for consumption in that country, but for exporting them to a third country, it is known as ‘Entrepot trade’.
e.g.: India importing wheat from the U.S. and exporting the same to Sri Lanka.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between the capital market and the money market.
Answer:
Distinction between capital market and money market.
| Points of Distinction | Capital Market | Money Market |
| 1. Participants | The participants in the capital market are development banks and investment companies. | The central bank and commercial banks are major participants. |
| 2. Instruments | The main instruments traded in the capital market are equity shares, preference shares, bonds, debentures, etc. | The main instruments are short-term debt instruments such as treasury bills, trade bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposits. |
| 3. Investment Outlay | Investment in the capital market does not necessarily require a huge financial outlay. The value of units of securities is generally low. | In the money market, transactions entail huge sums of money as the instruments are quite expensive. |
| 4. Period | It is a market for long-term funds for more than one year. | It is a market for short-term funds for a period not exceeding one year. |
| 5. Liquidity | Capital market securities are considered liquid investments because they are marketable in the stock exchanges. | Money market instruments, on the other hand, enjoy a higher degree of liquidity as there is formal agreement for this. |
| 6. Safety | Capital market instruments are riskier both concerning returns and principal repayment. | But the money market is generally much safer with a minimum risk of default. This is due to the shorter duration of investing and also to the financial soundness of the issues. |
| 7. Expected Return | Investment in the capital market generally yields higher returns for investors than the money market. | The returns in the money market investments are low when compared with capital markets. |
| 8. Regulator | SEBI regulates the institutions and procedures. | Reserve Bank of India regulates the market. |
Question 3.
What are the responsibilities of a consumer?
Answer:
Various efforts have been made by government or non-government organizations to protect the interest of consumers, but the exploitation of consumers will stop only when the consumer comes forward to safeguard his interest. The consumer has to bear the following responsibilities.
1. Be Quality Conscious:
To put to stop adulteration and corrupt practices of the manufacturers and traders, every consumer must be conscious of the quality of the products they buy. They should look for standard quality certification marks like ISI, Agmark, Woolmark, Ecomark, Hallmark, etc. While making the purchases.
2. Beware of Misleading Advertisements:
The advertisement often exaggerates the quality of the products. Hence the consumers should not rely on the advertisement and carefully check the product or ask the users before making a purchase.
3. Responsibility to inspect a variety of goods before making a selection:
The consumer should inspect a variety of goods before buying the goods and services. For this purpose, he/she should compare their quality, price, durability, after-sales service, etc.
4. Collect Proof of Transaction:
The consumer should insist a valid documentary evidence (Cash memo/invoice) relating to the purchase of goods or availing of any services and preserve it carefully. Such proof of purchase is required for filing a complaint. In the case of durable goods the manufacturers generally provide the warrantee/guarantee card with the product. The consumers must obtain these documents and ensure that they are duly signed, stamped, and dated. The consumer must preserve them till the warranty/guarantee period is over.
5. Consumers must be aware of their Rights:
Consumers must be aware of their rights as stated above and exercise them while buying goods and services. For example, it is the responsibility of a consumer to insist on getting all information about the quality of the product and ensure himself/herself that it is free from any kind of defect.
6. Complaint for Genuine Grievances:
As a consumer, if you are dissatisfied with the product, you can ask for redressal of your grievances. In this regard, you must file a proper claim with the company first. If the manufacturer/company does not respond, then you can approach the forums. But your claim must state the actual loss and the compensation claim must be reasonable. At no cost fictitious complaints should be filed otherwise the forum may penalize you.
7. Proper use of Product/Service:
It is expected from consumers that they use and handle the product/service properly. It has been noticed that during the guarantee period, people tend to recklessly use the product, thinking that it will be replaced during the guarantee period. This practice should be avoided.
Section – B
(4 × 10 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
State commission.
Answer:
The state commission settles the consumer dispute at the state level. The state commission is headed by the judge of the High Court and comprised of other members not less than two and not more than such members as prescribed. The state commission is empowered to call for the records and appropriate orders in respect of any consumer dispute within the state jurisdiction. The state commission shall have jurisdiction to entertain consumer complaints where the value of goods and services for which compensation claimed exceeds ₹ 20 lakhs.
Question 5.
What is an index? Explain SENSEX (Sensitive Index).
Answer:
A stock market index is a barometer of market behavior. It measures overall market sentiment through a set of stocks that are representative of the market. It reflects market direction and indicates day-to-day fluctuations in stock prices. An ideal index number must represent changes in the prices of securities and reflect the price movement of typical shares for better market representation. If the index rises, it indicates that the market is doing well, and vice versa. In the Indian market, the BSE – SENSEX and NSE – Nifty are important indices.
SENSEX (Sensitive Index):
SENSEX is the benchmark index of the BSE. The BSE Sensex is also called the BSE-30. Since the BSE has been the leading exchange of the Indian secondary market, the Sensex has been an important indicator of the Indian stock market. It is the most frequently used indicator while reporting on the state of the market. The SENSEX, launched in 1986 is made up of 30 of the most actively traded stocks in the market. They represent 13 sectors of the economy and are leaders in their respective industries. The index with a base year of 1978-79, and the value base year was 100.
![]()
Question 6.
Advantages of road transportation.
Answer:
Advantages of Road transport: The following are some of the merits of Road transport.
- Low capital: It requires less capital to construct roads. Roads are maintained by government and local authorities.
- Low Maintenance: The maintenance charges of the road carriers are much less than the cost of railways.
- Flexible: Road transport is flexible. The route and timing can be adjusted to the individual requirements.
- Suitable for Short Distance: It is more economical and quicker for carrying goods and people over short distances.
- Door-to-door delivery: Road transport provides door-to-door delivery service for industries. Goods can be loaded at sellers’ doors and unloaded at buyers’ doors.
- Service to Rural Areas: Exchange of goods between villages and towns is made possible by road transport.
- Feeder to other modes of transport: All the movement of goods begins and ultimately ends by making use of roads.
- High Speed: Road transport reduces the effective duration of the transit.
Question 7.
What are the advantages of Life insurance policies?
Answer:
In a life insurance contract, the policy amount is definitely, it is a question of time. The policy may mature during the lifetime of the assured or it may be paid on his death.
Advantages of Life Assurance Policies:
- Encourages Savings: The insured has to pay a premium to the insurance company every year. Otherwise, the policy will be canceled. So, the insurance helps create the habit of saving money.
- Exemption from Income Tax: The amount paid as a premium on a life insurance policy is allowed as a deduction from income for calculating income tax.
- Protection: Life insurance protects the family members if the policyholder dies suddenly. Life insurance builds a fund for the benefit of the dependents.
- Credit Facilities: Insured can get loans against their policies to meet emergency needs. Life Insurance Corporation itself gives a loan against the policy to the insured at a lower rate of interest.
- Surrender: The life insurance company can surrender the life policy if the insured is unable to continue it. The insurance company can return some premium known as ‘surrender value’.
- Meets the Future Needs: An insurance policy can help provide funds for the marriage and educational needs of insured children.
Question 8.
Explain the problems of international trade.
Answer:
Problems of Foreign Trade:
- Currency Problems: Payment between the countries creates complications because every country has its currency. To avoid losses in transactions the rate of exchange has to be carefully determined.
- Legal Problems: Laws and customs regulations are affecting the import and export trade because every country has its laws, and customs regulations. These regulations stand in the way of smooth inflow and outflow of goods.
- Credit Problems: The exporter has to take special steps to ascertain the creditworthiness of the buyer as there is no direct contact between the exporter and importer.
- Greater Risk: In foreign trade goods are to be exported to long distances. So exporting the goods creates greater risk.
- Time Gap: In foreign trade, there is a wide gap between the time when the goods are dispatched and the time when the goods are received and paid.
Question 9.
State the opportunities for entrepreneurs in information technology and Automobiles in A.P.
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh, with its rich and abundant natural resources base as well as diverse agricultural and forest wealth, provides tremendous opportunities for entrepreneurs in the state. The various opportunities for entrepreneurs in A.P. are as follows.
1. Information Technology:
The government of A.P. has declared the Information Technology (IT) industry as an essential service under the Essential Services Maintenance Act and the industry has been exempted from power cuts. It aims to transform the state into a knowledge society and make available the benefits of IT to all citizens, especially those in rural areas. People with innovative ideas would be encouraged to set up their IT and IT-enabled services units in the state.
2. Automobiles:
A broad base of automotive equipment manufacturers and a large pool of highly trained, skilled, and disciplined manpower make Andhra Pradesh the desired location for automobile industries. There are more than 100 automotive component manufacturing companies in the state. The industry is highly potential and there is plenty of demand for automobile components, hence the entrepreneurs in the state may grab the opportunities.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
Write one definition of entrepreneurship.
Answer:
In a conference on entrepreneurship held in the United States, the term entrepreneurship was defined as “Entrepreneurship is an attempt to create value through recognition of business opportunity, the management of risk-taking appropriate to the opportunity and through the communication and management skills to mobilize human, financial and material resources necessary to bring a project to function”.
![]()
Question 11.
Export trade.
Answer:
The term export is derived from the conceptual meaning as to ship goods and services out of the port of the country. When goods are sold to a trader in another country, goods are exported to that country by the seller’s country. For example, India is a major exporter of tea because of the fertile land in Assam and Darjeeling, so we export tea products to other countries.
Question 12.
Tele-banking.
Answer:
Customers can perform several transactions from their telephone such as they can check balances and statement information, transferring funds from one account to another, paying certain bills, and ordering statements, checkbooks, etc.
Question 13.
Define insurance.
Answer:
Insurance is the pooling of fortuitous losses by transfer of such risks to insurers, who agree to indemnify the insured for such losses, to provide other pecuniary benefits on the occurrence, or to render service connected with the risk.
Question 14.
Whole life policy.
Answer:
This policy runs throughout the life of the insured. The sum assured under this policy is payable only after the death of the insured. The premium is low and it is meant to protect the family. The insured will have to pay the premium throughout his life even at old age when he is not earning.
Question 15.
Secondary market.
Answer:
It is also known as the stock market or stock exchange. It is a market for the purchase and sale of existing securities. It helps existing investors to disinvest and fresh investors to enter the market. It provides liquidity and marketability to existing securities.
Question 16.
Treasury bills.
Answer:
A treasury bill is an instrument of short-term borrowing by the Government of India maturing in less than one year. These are issued by RBI on behalf of the Government to meet its short-term requirements. The purchase price is less than face value and at maturity govt, will pay full face value.
Question 17.
District Forums.
Answer:
- Composition: The district forum consists of a chairman and two other members one of whom shall be a woman. The district forms are headed by the person of the rank of a District Judge.
- Jurisdiction: A written complaint can be filed before the district forum where the value of goods or services and the compensation claimed does not exceed ₹ 20 lakhs.
- Appeal: If a consumer is not satisfied by the decision of the District Forum, he can challenge the same before the state commission, within 30 days of the order.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
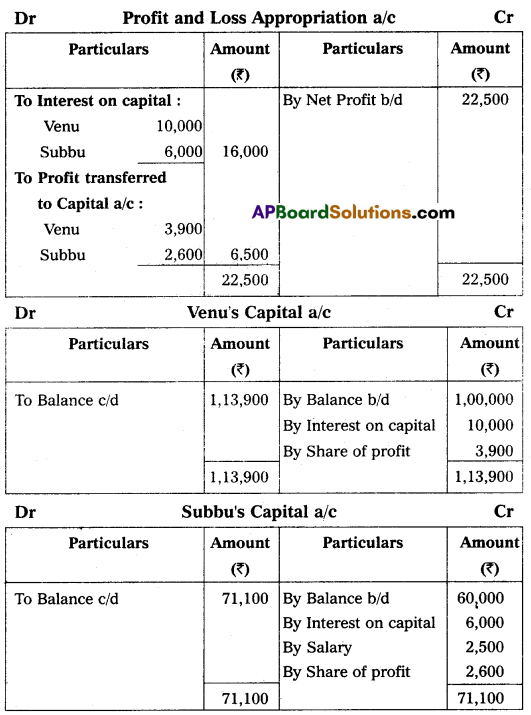
Venu and Subbu are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2, with capitals of ₹ 1,00,000 and ₹ 60,000 respectively. Interest on capital is agreed @ 10% p.a. Subbu is to be allowed an annual salary of ₹ 2,500. During the year 2014-15, the profits before the calculation of interest on capital but after charging Subbu’s salary amounted to ₹ 22,500. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and the partners’ capital accounts for the year ending March 31, 2015.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
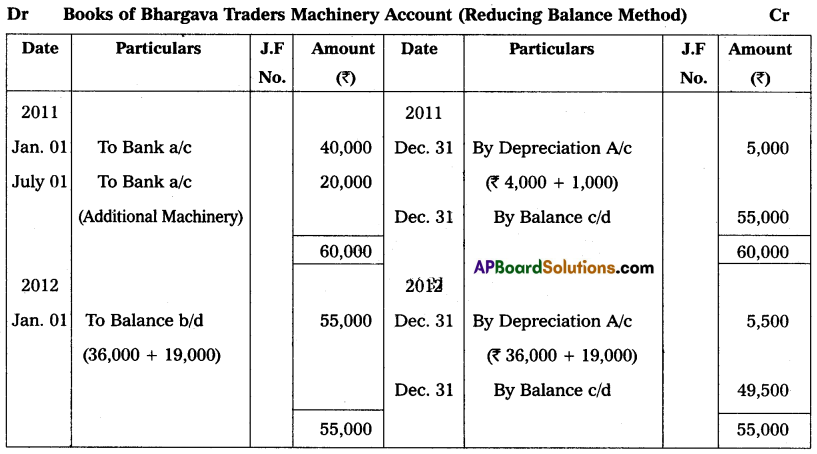
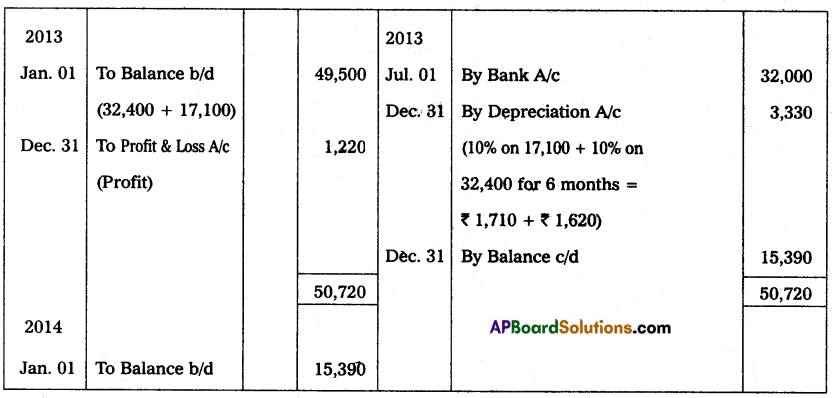
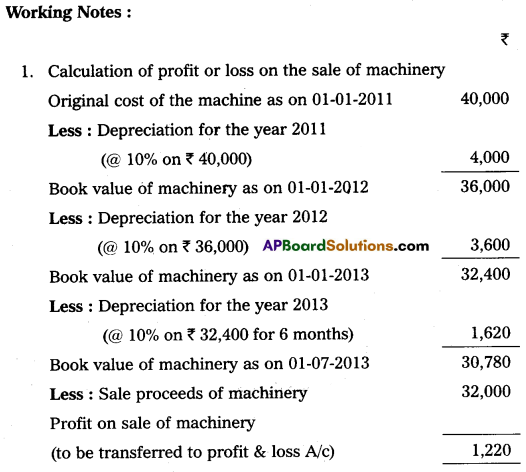
On 1st January 2011, Bhargava traders purchased machinery for ₹ 40,000. On 1st July in the same year the firm purchased additional machinery for ₹ 20,000. On 1st July 2013, the machinery purchased on 1st January 2011 having become obsolete, it was sold for ₹ 32,000. The books are closed on 31st December every year. Prepare Machinery Account for three years providing depreciation @ 10% p.a. on Reducing Balance Method.
Answer:
(Or)
Question 20.
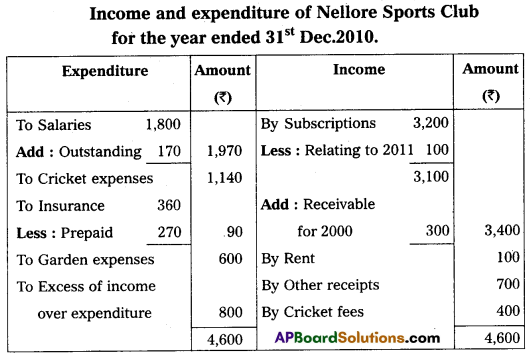
Nellore Sports Club started on 01-01-2010. Their Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ended 31-Dec-2010.
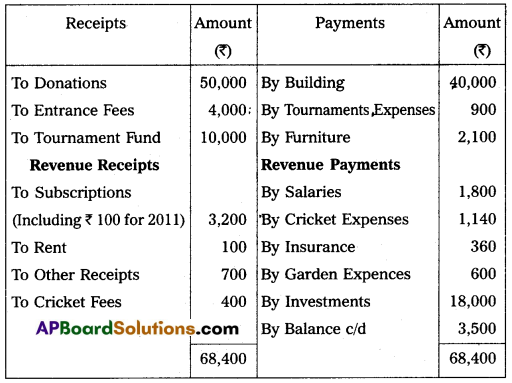
Additional Information:
(a) Subscription receivable for the 2010 – ₹ 300.
(b) Salaries Unpaid – ₹ 170.
(c) Entrance fees are to be capitalized.
(d) Insurance includes 9 months premium for 2011.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Question 21.
Define depreciation. What are the main causes of depreciation?
Answer:
Spicer and Pegler define depreciation as follows:
‘Depreciation is the measure of exhaustion of the effective life of an asset from any cause during a given period’. Depreciation means a decline in the value of a fixed asset due to use, passage of time, obsolescence, or any other cause.
Causes of Depreciation:
The main causes of depreciation include the following:
- Wear and Tear: When the fixed assets are put to use in business operations for earning revenue, the value of such assets may decrease. Such a decrease in the value of assets is said to be due to wear and tear.
- Physical Forces: When the assets are exposed to the forces of nature like weather, winds, rains, etc. The value of such assets may decrease even if they are not being put to use.
- Expiration of Legal Rights: When the use of assets like patents, copyrights, leases, etc., is governed by a time-bound agreement, the value of such assets may decrease with time.
- Obsolescence: Obsolescence implies an existing asset becoming out of date on account of the availability of a better type of asset due to technological changes or improvements in production methods.
- Accidents: A decline in the usefulness of the asset may be caused by accidents due to fire, earthquakes, floods, etc. Accidental loss is permanent.
- Depletion: Assets of wasting character such as mines, quarries, oil wells, etc., get depleted with the extraction of raw materials.
![]()
Question 22.
Sandhya sold goods for ₹ 14,000 to Rajeswari on 1st March 2014 and drew upon her a bill of exchange payable after 2 months. Rajeswari accepted the bill and handed over the same to Sandhya. Sandhya immediately discounted the bill with her bank @ 12% p.a. On the due date, Rajeswari met her acceptance. Pass the necessary journal entries in the books of Sandhya and Rajeswari.
Answer:
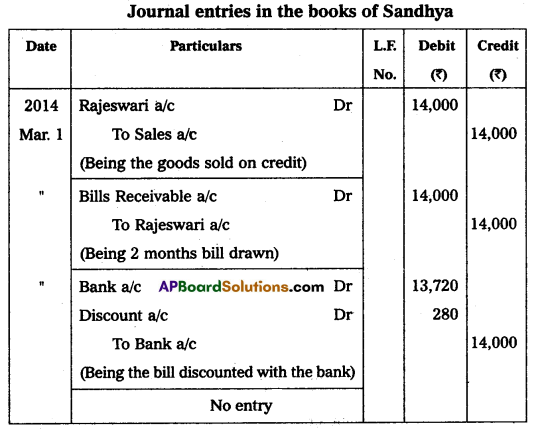
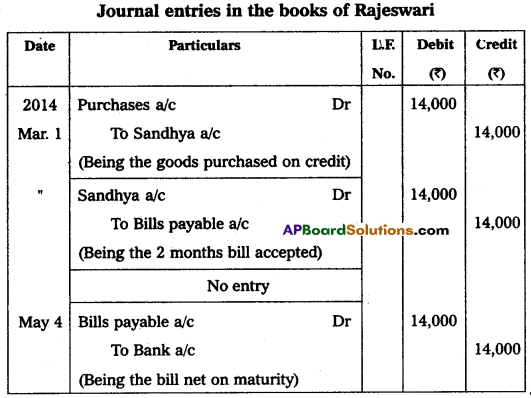
Question 23.
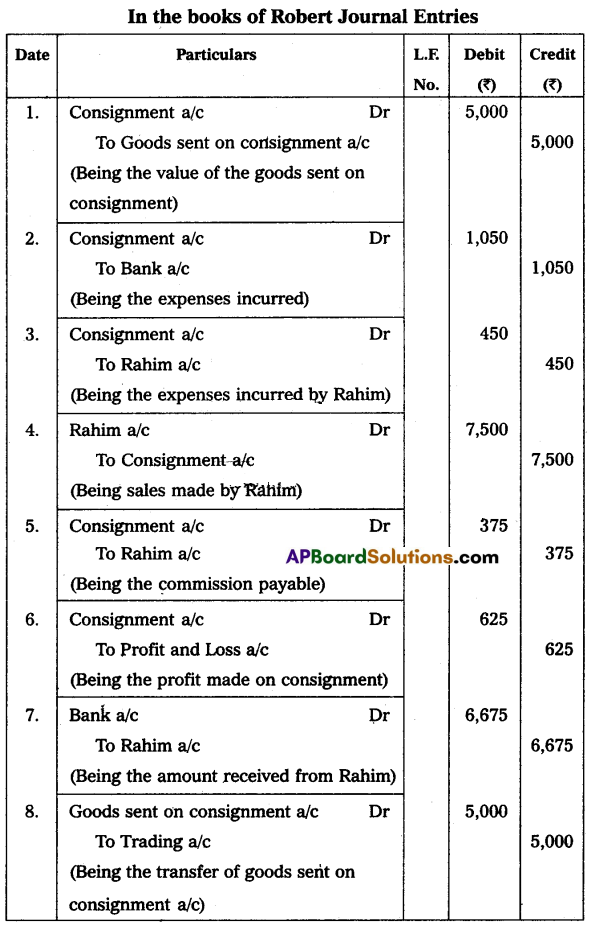
Robert consigned goods to Rahim valued at ₹ 5,000 to be sold on a 5% commission basis. Robert has paid ₹ 500 freight and ₹ 550 towards insurance. Robert received account sales and a draft for the balance from Rahim showing the following particulars.
Gross Sales – ₹ 7,500
Selling Expenses – ₹ 450
Commission – ₹ 375
Pass necessary journal entries in the books of Robert.
Answer:
Question 24.
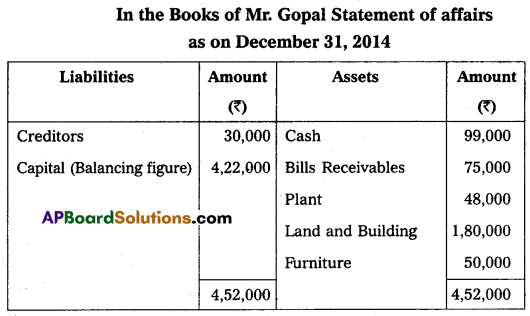
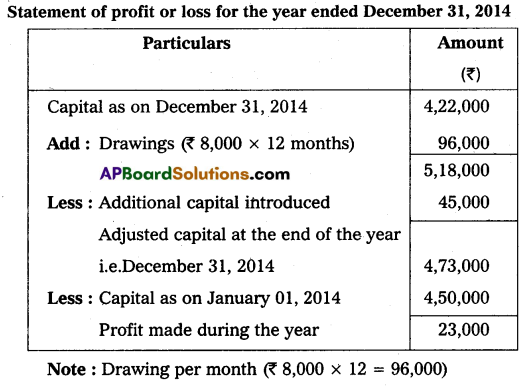
Gopal started his business on January 01, 2014, with a capital of ₹ 4,50,000 on December 31, 2014, his position was as under.
Cash – ₹ 99,000
Bills Receivables – ₹ 75,000
Plant – ₹ 48,000
Land and Buildings – ₹ 1,80,000
Furniture – ₹ 50,000
Creditors – ₹ 30,000
He owned ₹ 45,000 from his friend Sukumar on that date. He withdrew ₹ 8000 per month for his household purposes. Ascertain his profit or loss for this year ended December 31, 2014.
Answer:
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is meant by the dishonor of a bill?
Answer:
When the drawee or acceptor of the bill fails to make payment of the bill on the date of maturity it is called ‘Dishonour of the bill’.
Question 26.
Write different methods of providing depreciation.
Answer:
The following are the different methods of providing depreciation:
- Straight line method
- Reducing balance method
- Annuity method
- Depreciation fund method
- Insurance policy method
- Revaluation method
- Depletion method
- Machine hour rate method
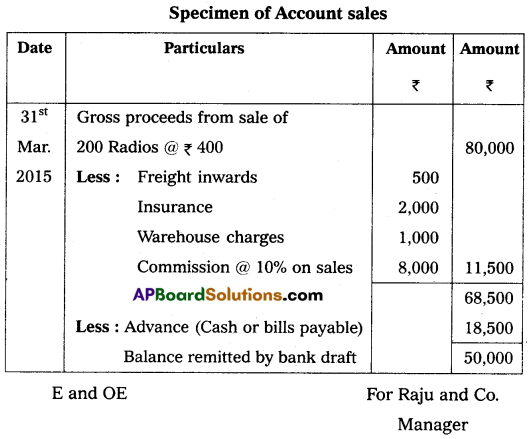
Question 27.
Specimen of Account Sales.
Answer:
Question 28.
Subscription and life membership.
Answer:
Subscriptions are a major recurring source of income for non-profit entities that are paid by members periodically. Subscriptions relating to the current year are shown as income. It is paid to a member once in a lifetime. So it should be capitalized and shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
![]()
Question 29.
Goodwill.
Answer:
Over some time, a well-established business develops the advantage of a good name and reputation which helps the business to earn more profits. The monetary value is called goodwill. It is regarded as an intangible asset. So, goodwill is the value of the reputation of a firm concerning profits expected in the future over and above the normal profits.
Question 30.
Ranjana, Sadhana, and Kamana are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 4 : 3 : 2. Ranjana retired, and Sadhana and Kamana decided to share future profits in the ratio of 5 : 3. Calculate the gaining ratio.
Answer:
Old Profit Sharing Ratio = 4 : 3 : 2
New Ratio = 5 : 3
Sadhana Gaining Ratio = New Ratio – Old Ratio
= \(\frac{5}{8}-\frac{3}{9}\)
= \(\frac{45-24}{72}\)
= \(\frac{21}{72}\)
Kamana Gaining Ratio = \(\frac{3}{8}-\frac{2}{9}\)
= \(\frac{27-16}{72}\)
= \(\frac{11}{72}\)
∴ Gaining Ratio = 21 : 11
Question 31.
Explain the issue of shares at a premium.
Answer:
When a company issues its shares at a price higher than the face value, it is said to have been issued at a premium. The money collected more than the face value is called the premium.
Ex: If the face value of a share is ₹ 100 it is issued for ₹ 110.
Question 32.
Customized accounting software.
Answer:
Accounting software may be customized to meet the special requirements of the user. For example, standardized accounting software may contain the sales voucher and inventory status as separate options. However, when the user requires that inventory status be updated immediately upon entry of sales voucher and report be printed, the software needs to be customized.