Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 8th Lesson Viruses which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 8th Lesson Viruses
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention living and non-living characters of Viruses.
Answer:
Living Characters:
- They contain nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
- They live as obligate parasites.
- They can undergo mutations.
- They reproduce in host cells.
Non-living characters:
- They do not show cellular organization. They are acellular.
- They do not show metabolic activities.
- They exist as crystals outside the host.
- They do not exhibit some life processes like growth, or irritability.
Question 2.
What is the shape of T4 phage? What is its genetic material?
Answer:
- The shape of T4 phage virus is Tadpole shape (Polyhedral symmetry with head & tail)
- Its Genetic material is double stranded DNA
![]()
Question 3.
What are virulent phages. Give an example.
Answer:
- The Viruses which attack the bacteria like E.coli are called virulent phages.
- They kill the host soon after penetration. Ex: Oncogenic viruses,T-even phages
Question 4.
What is lysozyme and what is its function? [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
- The viral enzyme which dissolves the plasma membrane of host cell is called lysozyme.
- It breaks the bacterial cell wall and releases the newly produced phase particles (or) virons.
Question 5.
Define ’lysis’ and ’brust size’ with reference to viruses and their effects on host cells,
Answer:
- Lysis: The dissolving of plasma membrane of a host cell which releases virons is called Lysis.
- Brust size: The number of newly synthesized phase particles released from a Single cell is called “burst size”. It usually ranges from 50-200.
Question 6.
What is a prophage?
Answer:
Prophage: The phage DNA which is incorporated into the host DNA, during hydrogenic cycle is called prophage.
Question 7.
What are temperate phages? Give one example.
Answer:
- Temperate phages: The phages whose DNA is incorporated into host DNA, to produce prophages are called temperate phages.
- It occurs during the lysogenic cycle and does not cause lysis of the of the host cell.
Ex: Coliphage λ
Question 8.
Mention the differences between virulent phages and temperate phages. [AP MAR-15]
Answer:
- Virulent Phages: Phages that replicate only through lytic cycle are called Virulent phages.
Ex: T-even phages. - Temperate Phages: Phages that replicate both lytic and lysogen cycles are called Temperate phages. Ex: Coliphage λ.
Question 9.
What is the shape of TMV? What is its genetic material?
Answer:
- The shape of TMV is rod shaped.
- The genetic material is single stranded RNA consisting of 6500 nucleotides.
- TMV stands for Tobacco mosaic virus.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is ICTV? How are viruses named? [TS MAR-19] [TS 20]
Answer:
- ICTV means – International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses.
- It regulates the classification and nomenclature of viruses.
- ICTV has three hierarchial levels namely family, genus and species.
- The family names end with the suffix Viridae
- The genus names end with virus.
- The species names are common english expressions describing their nature.
- Sometimes viruses are named after the disease they cause. Ex: Polio virus.
- According to ICTV, the virus that causes AIDS in man is classified as follows:
Family: Retroviridae, Genes: Lentivirus, Species: Human Immunodeficiency virus(HIV)
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the chemical structure of viruses.
Answer:
- All viruses consist of two basic components, a) Core b) Capsid
- Core of nucleic acid forms the genome.
- Capsid is the surrounding protein coat.
- Capsid gives shape and protection to the virus.
- Capsid is madeup of protein subunits called capsomeres.
- The genome of virus is either single stranded DNA (or) double stranded DNA.
- In general, plant virus has ssRNA and animal virus has dsDNA.
- Viral nucleic acid molecules are either circular or linear.
- Most viruses have a single nucleic acid molecule, but a few have more than one.
- Ex: HIV has two identical molecules of RNA.
Question 3.
Write briefly about the symmetry of viruses.
Answer:
Symmetry of the virus depends upon ‘mode of arrangement of capsomeres’ in the capsid.
Types of Symmetry:
1) Helical symmetry: Helical viruses have helical symmetry. They resemble long rods.
Here, capsomers are systematically arranged in helical manner around core of nucleic acid.
Ex: TMV Virus, Rabies Virus.
2) Polyhedral symmetry : The capsid is in polyhedral shape and capsomeres are arranged in isohedral symmetry. Ex: Many animal and plant viruses like Poliovirus, Herpes simplex.
3) Binal Symmetry: Bacteriophages have both (i) polyhedral symmetry in the head and (ii) helical symmetry in the tail sheath.
4) Spherical Symmetry: Enveloped viruses have spherical symmetry Ex: Influenza virus.
Question 4.
Explain the structure of TMV. [AP MAY-17, 22] [TS MAR, MAY-17|
Answer:
- TMV stands for Tobacco mosaic virus.
- TMV is a ssRNA virus that infects tobacco plants.
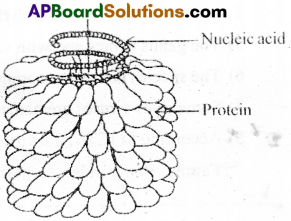
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus is a rod shaped virus. It is about 300 nm long and 18 nm in diameter, with a molecular weight of 39 x 106 Daltons.
- Its capsid is made of 2,130 proteins sub units called capsomeres.
- The capsomeres are arranged in a helical manner around a central hollow core of 4 nm.
- Each protein sub unit is made of 158 amino acids.
- Inside the capsid, there is single stranded spirally coiled RNA with 6,500 nucleotides.
Question 5.
Explain the structure of T-even bacteriophages.
Answer:
- The viruses which attack bacteria are called bacteriophages.
- Bacteriophages are tadpole-shaped with a large head and a tail.
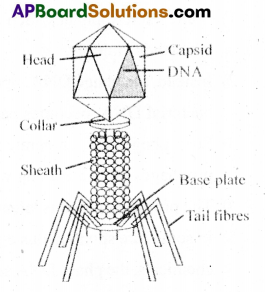
- The head is hexagonal and is capped by hexagonal pyramid.
- The tail is composed of a tail sheath, a base plate, pins and tail fibres.
- The tail helps injecting viral DNA into the host cell.
- The head and tail are joined by collar .
- At the tip of the tail, hexagonal tail plate is present with six tail pins and tail fibres.
- With the help of tail fibres the virus attaches to the host cells.
Question 6.
Explain the lytic cycle with reference to certain viruses.
Answer:
- The viruses T- even phages attack the bacterium E.coli.
- They cause lysis of host cells and are called virulent phages.
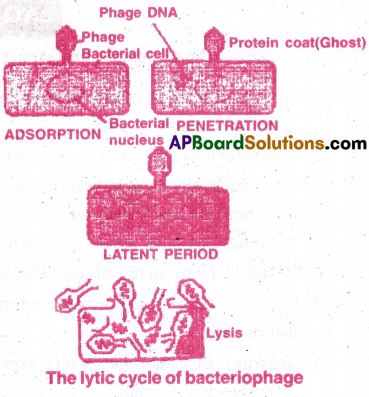
- The lytic cycle consists of following five steps.
Attachment: The tail fibres of the virus attach, to the complementary receptor sites on the bacterial cell wall.
Penetration:
- The in jection of phage nucleic acid into bacterium cell is called penetration.
- The tail core is driven in through the bacterial cel! wall.
- The DNA of bacterio phage passes through the plasma membrane and enters into the bacterial cell.
- The phage particle functions like a hypodennic syringe and injects its DNA into the bacterial cell.
- The capsid out side the bacterial cell is called as the Ghost.
![]()
Biosynthesis:
- Once the phage DNA reaches the Cytoplasm of the host cell, many copies of phage DNA, enzymes and capsid proteins are synthesized using the cellular machinery of the host cell.
- Complete phages can not be found in the host cell.
Maturation:
- In this process, the phage DNA and capsids are assembled into complete virons.
- This period of time between the infection by a virus and the appearance of mature virus with in the cell is called eclipse period.
Release:
- The final stage of viral multiplication is the lysis phage of the host cell.
- The plasma membrane of the host cel! gets dissolved by the host enzyme called lysozyme.
- The host cell wall breaks, releasing newly produced phage particles (or) Virus.
Question 7.
Explain how temperate phages play a role in transduction
Answer:
- Some bacteriophages such as λ (Lambda^phages dp not cause lysis and death of host cell when they multiply.
- Instead, the phage DNA, upon penetration into an E.Coli cell gets integrated into the circular bacterial DNA, becomes part of it and remains latent.
- Such phages are temperate phages. The inserted phage DNA is now called prophages. The prophages replicate along with the bacterial genetic material.
- The prophage remains latent within the progeny cells.
- In some rare spontaneous events, or when the host cell is exposed to UV light or due to come chemicals, the phase DNA separates from the bacteria genetic material leading to the initiation of the lytic cycle. This lysogenic cycle facilitates transduction.
Question 7.
Mention the differences between lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle.
Answer:
| Lytic Cycle | Lysogenic Cycle |
| 1) At the end of lytic cycle, bacterial cell undergoes lysis. | 1) Bacterial cell does not undergo immediate lysis. |
| 2) The entry of viral DNA brings about the degradation of bacterial DNA. | 2) Bacterial DNA is not destroyed and viral DNA gets incorporated. |
| 3) Prophages are not formed and virulent phages do not allow bacteria to survive. | 3) Prophages persist in close relationship for long period even when bacterial cell undergoes many division cycles. |
| 4) The viruses are called virulent. Ex: T-even phages. | 4) There viruses are called temperate phages. Ex: Coliphage-λ |
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention the differences between lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle.
Write about the discovery and structural organization of viruses.
Answer:
- From ancient times Viruses have been causing many diseases in humans, but economically useful to plants and animals.
- Even after the proposal of germ theory’ of disease, an identifiable agent was not noticed.
- Russian pathologist Iwanowski (1892) studied tobaccomosaic disease.
- He filtered the sap of diseased tobacco leaf through filter.
- The infectious agent passed through the pores of the filter.
- He infected this sap to a healthy plant and found symptoms of mosaic disease in it.
- He is not able to see the micro organism and reported that filterable agent was responsible for that disease.
- Beijerinck repeated Iwanow’ski’s expect and concluded that disease causing agent was a “Contagious living fluid”.
- W.M.Stanley (1935) was able to crystallise the virus causing tobaccomosaic disease.
- It was named as Tobacco Mosaic Virus.
- Fraenkel Conrat (1956) confirmed that the genetic material of TMV is RNA.
- By using ultra centrifugation, x-ray crystallography and electron microscopy, a number of new viruses were reported and their ultra structure was elucidated.
Question 2.
Describe the process of multiplication of viruses.
Answer:
Multiplication of virus occur in two ways. Virulent phages follow lytic cycle of replication where as temperate phages follow lysogenic cycle of replication.
- T- even phages attack the bacterium E.coli.
- They cause lysis of host cells and are called virulent phages.
- They show lytic cycle which consists of five steps.
1) Attachment: Attachment or adsorption occurs between phage particles and bacteria after a contact.
The tail fibres of the virus attach to the complementary receptor sites on the bacterial cell wall.
2) Penetration:
- The injection of phage nucleic acid into bacterium cell is called penetration.
- The tail core is driven in through the bacterial cell wall.
- The DNA of bacterio phage passes through the plasma membrane and enters into the bacterial cell.
- The phage particle functions like a hypodermic syringe and injects its DNA into the bacterial cell.
- The capsid out side the bacterial cell is called as the Ghost.
3) Biosynthesis:
- Once the phage DNA reaches the Cytoplasm of the host cell, many copies of phage DNA, enzymes and capsid proteins are synthesized using the cellular machinery of the host cell.
- Complete phages can not be found in the host cell.
4) Maturation:
- In this process the phage DNA and capsids are assembled into complete virons.
- This period of time between the infection by a virus and the appearance of mature virus with in the cell is called eclipse period.
5) Release:
- The final stage of viral multiplication is the lysis phage of the host cell.
- The plasma membrane of the host cell gets dissolved by the host enzyme called lysozyme.
- The host cell walls breaks, releasing newly produced phage particles (or) Virus.
![]()
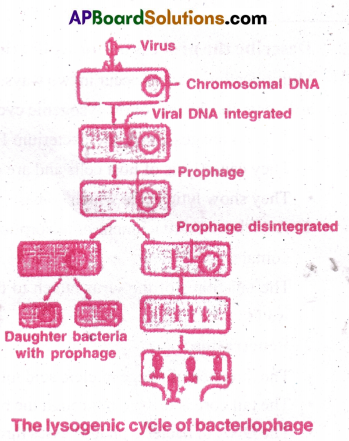
The Lysogenic Cycle:
- Transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another through bacteriophages is called transduction.
- Temperate phages play a role in transduction.
- λ phages donot cause lysis and death of the host cells when they multiply.
- The phage DNA upon penetration into E.Coli, gets integrated to the bacterial DNA.
- It becomes a part of bacterial DNA, remains latent and such phages are called temperate phages.
- This phage DNA is now called prophage.
- Every time the bacterial genetic material replicates.
- The prophage also undergoes replication.
- The prophage remains latent within progeny cells.
- In some rare events when the host cell is exposed to UV light, the phage DNA separates from bacterial genetic material, leading to the initiation of lytic cycle.
Exercise
Question 1.
When discussing the multiplication of viruses, Virologists prefer to call the process as replication, rather than reproduction. Why?
Answer:
- Reproduction of virus occur only in a living host cell but not outside.
- The normal mitotic machinery of cell division is not seen in viral reproduction.
- The host cell infected with the virus may die immediately (lytic cycle) or after some time (lysogenic cycle)
- Hence it is better to call the multiplication of virus as replication rather than reproduction.
Question 2.
In dealing with public health, the approach to deal with bacterial diseases is treatment. Can you guess the nature of the general public health approach to viral diseases? What example do you cite to support your answer?
Answer:
- The medical approach to a viral disease is only vaccination.
- Vaccination develops immunity to a particular disease.
- Antiviral therapy is to overcome drug resistance.
- Antibiotics do not have any effect on virus.
Eg: Hepatitis, AIDS, Encephalitis.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The complete virus particle is called
1. Viroid
2. Capsid
3. Virion
4. Prion
Answer:
3. Virion
Question 2.
‘Biological entities’ known to infect every type of cell are called
1. Bacteria
2. Fungo
3. Protozoans
4. Viruses
Answer:
4. Viruses
Question 3.
The nucleic acid of viruses is enclosed by a protein coat called
1. Viroid
2. Virion
3. Capsid
4. Core
Answer:
3. Capsid
Question 4.
A virus particle in its core contains
1. Capsomeres
2. Peplos
3. Both DNA & RNA
4. Either DNA or RNA
Answer:
4. Either DNA or RNA
Question 5.
Viruces are
1. Obligate intracellular parasites
2. Facultative extracellular parasites
3. Obligate saprophytes
4. Facultative saprophytes
Answer:
1. Obligate intracellular parasites
![]()
Question 6.
The scientist, who confirmed that the genetic material of TN1V ¡s RNA is
1. Fraenkel conrat
2. Jwanowski
3. Beijerinck
4. W.M.Stanley
Answer:
1. Fraenkel conrat
Question 7.
The family names in virus classification ends ith
1. Virus
2. Virion
3. Prion
4. Viridae
Answer:
4. Viridae
Question 8.
The genus name of virus ends with
1. Viridae
2. Virion
3. Prion
4. Virus
Answer:
4. Virus
Question 9.
Viruses are named
1. basing on their type of multiplication
2. basing on the nucleic acid type in their core
3. basing on the disease they cause
4. basing on their host
Answer:
3. basing on the disease they cause
Question 10.
The largest virus in size is approximately equal to the size of
1. largest bacterium
2. Mycoplasma
3. 70S ribosome
4. 80S ribosome
Answer:
2. Mycoplasma
Question 11.
The smallest virus will have the same diameter as that of
1. largest bacterial cell
2. Mycoplasma
3. Smallest bacterial cell
4. Ribosome
Answer:
4. Ribosome
Question 12.
The poiio virus belongs to morphological type
1. Polyhedral virus
2. Helical virus
3. Long rods
4. Spherical
Answer:
1. Polyhedral virus
Question 13.
The shape of the virus is given by
1. Core
2. Capsid
3. Genome
4. Cell wall
Answer:
2. Capsid
Question 14.
The viruses that infect animals generally have
1. dsDNA
2. ss DNA
3. ds RNA
4. ssRNA
Answer:
1. dsDNA
Question 15.
Number of nucleotides present in the RNA molecule of TIMV is
1. 6500
2. 5600
3. 3500
4. 158
Answer:
1. 6500
Question 16.
The head and tail of T4 bacteriophage is joined by
1. Spikes
2. Tail fibres
3. Collar
4. Tail plate
Answer:
3. Collar
Question 17.
The function of tail fibres of T4 phage is to
1. attach to host cell
2. attach to other virus particle
3. join head and tail
4. inject viral DNA into the hose cell
Answer:
1. attach to host cell
Question 18.
The multiplication process of virulent phages is referred to as
1. Lysogenic cycle
2. Lytic cycle
3. Haplontic cycle
4. Diplontic cycle
Answer:
2. Lytic cycle
![]()
Question 19.
Attachment of the virion to the host bacterium is called
1. Penetration
2. Maturation
3. Adsorption
4. Lysis
Answer:
3. Adsorption
Question 20.
The viral disease that may lead to cancer is
1. AIDS
2. Hepatitis B
3. Polio
4. Rabies
Answer:
2. Hepatitis B
Question 21.
Oncoviruses causes
1. Ebola
2. Neonatal rubella
3. Cancer
4. AIDS
Answer:
3. Cancer
Question 22.
The disease caused bv prions in cow is
1. Bovine Spongiform Encephalitis
2. Epstein-Barr
3. Human papilloma
4. Neonatal rubella
Answer:
1. Bovine Spongiform Encephalitis
Question 23.
The mad cow disease causing prion may reach man through beef and cause
1. Bovine Spongiform Encephalitis
2. Epstein-Barr
3. Human papilloma
4. Creutzfeldt – Jacob disease
Answer:
4. Creutzfeldt – Jacob disease
Question 24.
The largest virus among the following is
1. Vaccinia virus
2. Would tumor virus
3. TMV
4. Papova virus
Answer:
1. Vaccinia virus
Question 25.
………… is a complex virus
1. TMV
2. Bacteriophage
3. Polio virus
4. Rabies virus
Answer:
2. Bacteriophage
Question 26.
The virion is enveloped by peplos in
1) TMV
2) Bacteriophage
3) Influenza virus
4) Lambda phage
Answer:
3) Influenza virus
Question 27.
According to ICTV, the HIV is included under genus
1) Retroviridae
2) Human immune deficiency virus
3) Lentivirus
4) Spherical virus
Answer:
3) Lentivirus
Question 28.
Number of polynucleotide strands in 14 bacteriophage is
1) One
2) Two
3) 2130
4) Many
Answer:
2) Two
Question 29.
Ccnctie material in HIV’ virion is
1) ssRNA
2) ds RNA
3) ss DNA
4) ds DNA
Answer:
1) ssRNA
Question 30.
Mosaic disease on floral leaves is found in
1) Tobacco
2) Papaya
3) Cauliflower
4) Tulipa
Answer:
4) Tulipa
Question 31.
A substance that is produced in the body of vertebrates against viruses, is
1) Antibody
2)Antibiotic
3) Interferon
4) Pheromone
Answer:
3) Interferon
Question 32.
Lysogenic cycle can be changed to lytic cycle by exposing to
1) UV Radiation
2) I.R. radiations
3) PAR
4) Visible light
Answer:
1) UV Radiation
Question 33.
NI’V is an example for
1) Zoophage
2) Phytophage
3) Bacteriophage
4) Viroid
Answer:
1) Zoophage
Question 34.
Burst size refers to
1) Size of virion
2) Size of bacterium
3) Number of bacteriophages
4) Number of bacteria
Answer:
3) Number of bacteriophages
![]()
Question 35.
Viral diseases which lead to long term debility are
1) Rabies and Polio
2) Ebola and AIDS
3) Polio and neonatal rubella
4) Polio adn Tetanus
Answer:
3) Polio and neonatal rubella
Question 36.
Viruses are best described as
1) Non infectious particles
2) Infectious penticles
3) Intercellular parasites
4) Infectious prokaryotes
Answer:
2) Infectious penticles
Question 37.
Glycoproteins projections called spikes are present in the envelop of
1) Adenovirus
2) Papava virus
3) Measles virus
4) Bacterio phage
Answer:
3) Measles virus
Question 38.
A host bacterial cell infeeted by a T2 – phage becomes dead
1) immediately after penetration
2) after eclipse phase
3) due to lysis at the end
4) before penetration
Answer:
3) due to lysis at the end
Question 39.
One of the following viral disease is considered beneficial in horticulture
1) Bhendi vein clearing
2) Tulip Mosaic break
3) Swollen shoot of cocoa
4) Tomato spotted wilt
Answer:
2) Tulip Mosaic break
Question 40.
The symmetry of Herpes simplex and polio viruses is
1) Radial symmetry
2) Polyhedral symmetry
3) Binal symmetry
4) Helical symmetry
Answer:
2) Polyhedral symmetry
Question 41.
Number of capsomcrcs, aniinoacids & RNA nucleotides in TMV respectively is
1) 2,500, B8,6, 130
2) 2, 158, 130,6500
3) 2,130,336540,6,500
4) 2,130,138,6,500
Answer:
3) 2,130,336540,6,500
Question 42.
The viruses which cause long term debility is
1) Rabies
2) AIDS
3) Polio
4) Ebola
Answer:
3) Polio
Question 43.
Bacteriophages which become prophage are called
1) Temperate phages
2) Virulent phage
3) Cyanophage
4) Zymophage
Answer:
1) Temperate phages
Question 44.
The feature of viruses, which indicates that they are non-living is
1) Viruses can undergo mutation
2) Viruses maintain genetic continuity
3) Viruses are made up of proteins and nucleic acid
4) Viruses can be crystallised
Answer:
3) Viruses are made up of proteins and nucleic acid
![]()
Question 45.
During the lytic cycle phage, proteins |of the capsid| are synthesized during
1) Eclipse period
2) Maturation phage
3) Lysis
4) Penetration period
Answer:
1) Eclipse period
Question 46.
Identify the false statement regarding viruses
1) All are parasites
2) Antibiotics have no effect on them
3) All of them have helical symmetry
4) They are made up of proteins and Nucleic acids
Answer:
3) All of them have helical symmetry
Question 47.
‘Viruses arc particulate and not a liquid’. This statement was proposed by
1) Beijerinck
2) Pasteur
3) Stanley
4) None
Answer:
3) Stanley
Question 48.
Cancer causing agents in humans and animals are
1) Epstein – Barr virus
2) Human papillomavirus
3) Tobacco mosaic – virus
4) Both 1 and 2
Answer:
4) Both 1 and 2