Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 6th Lesson Plant Growth and Development which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 6th Lesson Plant Growth and Development
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define plasticity. Give an example.
Answer:
- Plasticity: The ability of plants to follow different pathways, in response to the environment or phases of life, to form different kinds of structures is called plasticity.
- Ex: Heterophylly in cotton and coriander.
Question 2.
What is the disease that formed the basis for the identification of gibberellins in plants? Name the causative fungus of the disease.
Answer:
- “Bakane”- foolish seedling disease of rice seedling.
- It is caused by a fungus called Gibberella fujikuroi.
![]()
Question 3.
What is apical dominance? Name the growth hormone that causes it.
Answer:
- Apical dominance: Suppression of growth of lateral buds by the activity of terminal bud is known as apical dominance.
- Auxins are responsible for apical dominance.
Question 4.
What is meant by bolting? Which hbrmone causes bolting? [TS MAY-17, 22]
Answer:
- Bolting: Elongation of internodes just before flowering is called bolting.
- Gibberellins are responsible for bolting.
Question 5.
Define respiratory climactic. Name the PGR associated with it.
Answer:
- Respiratory climactic: The rise in the rate of respiration during the ripening of the fruits is known as respiratory climactic.
- Ethylene is responsible for it.
Question 6.
What is ethephon? Write its role in agricultural practices.
Answer:
- Ethephon is the most widely used compound as a source of ethylene.
- It promotes female flowers in cucumbers, there by increasing the yield.
- Ethephon hastens fruit ripening in tomatoes and apples and accelerates abscission in flowers and fruits.
Question 7.
Which of the PGRs is called stress hormone and why?
Answer:
- ABA (Abscisic acid) is called stress hormone.
- Because it stimulates the closure of stomata in the epidermis and increases the tolerance of plants to various kinds of stresses.
Question 8.
What do you understand by vernalisation? Write its significance.
Answer:
- Vernalisation is the method of inducing flowering in plants by pre-chilling treatment.
- Significance: It prevents precocious reproductive development late in the growing season, and enables the plant to have sufficient time to reach maturity.
![]()
Question 9.
Define the terms quiescence and dormancy. JAP MAR-15|
Answer:
- Quiescence: It is a delayed seed germination which occurs when a seed fails to germinate because the external environmental conditions are too dry or warm or cold for germination.
- Dormancy: It is the innate inhibition of seed germination even a seed is placed in most favourable environment for germination.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on agricultural/horticultural applications of auxins. [AP 17, 22] [TS 20, 22]
Answer:
- Auxins are powerful growth hormones produced in the stem tips of plants.
- In stem cuttings, initiation of roots is noticed. This application is widely used for plant propagation in horticulture.
- Auxins stimulate fruit growth in tomatoes.
- Auxins prevent preharvest fruit drop.
- Auxins control xylem differentiation and help in growth.
- Auxins(2,4—D) are used to prepare lawns.
- Removal of shoot tip results in the growth of lateral buds. This phenomenon is applied in Tea plantations and hedge-making.
Question 2.
Write the physiological responses of gibberellins in plants. [AP MAR-19] [TS MAR-15]
Answer:
- Gibberellins are growth hormones that stimulate fruit repining, stem elongation, termination, flowering, sex expression, enzyme induction, Leaf & fruit senescence.
- Gibberellins are denoted by GA1, GA2, GA3 and so on.
- GA hastens the maturity period of conifers thus leading to early seed production.
- GA3 is used to speed up the malting process in brewing industry.
- Gibberellins increase the length of the axis, thus used to increase the length of grape’s stalks.
- Gibberellins cause fruits like apple to elongate and improve their shape.
- They delay senescence. Thus fruits can be left on the tree for longer time so that the market period can be extended.
- Spraying GA on sugarcane stems, increases the length of stem thus increasing the yield by 20 tonnes per acre.
- Spraying GA on juvenile conifers, hastens the maturity period thus leading the early seed production.
- GAs promote bolting(elongation of intemode) in beet, cabbages.
Question 3.
Write any four physiological effects of cytokinins in plants. [APMAR-16] [APMAY-17] [TS MAR-19]
Answer:
- Cytokinins are a class of plant growth hormones that promote cell divisions in plant roots.
- They help to produce new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves
- They help in lateral shoot growth and adventitious shoot formation.
- They promote nutrient metabolism which helps the delay of leaf senescence.
- They help to overcome apical dominance.Thus they promote the growth of lateral branches and help in the bushy growth of the tree.
- Naturally Cytokinins are synthesised in places where rapid cell division occurs.
Ex: Root tips, shoot buds, young fruits.
Question 4.
What are the physiological processes that are regulated by ethylene in plants. [TS MAY-17] [AP MAR-15] [AP 20]
Answer:
- Ethylene is a simple gaseous plant growth-regulating hormone.
- Ethylene effects horizontal growth of seedlings, swelling of axis and apical hook formation in dicot seedlings.
- Ethylene promotes senescence and abscission of leaves and flowers.
- Ethylene is effective in fruit ripening.
- Ethylene rises the rate of respiration and it is called respiratory climactic.
- Ethylene breaks seed and bud dormancy.
- Ethylene initiates germination in pea nut seeds and sprouting of potato tubers.
- In water plants, ethylene promotes rapid petiole and intemode elongation.
- Ethylene also promotes growth of root and root hair formation.
- Ethylene also used to initiate flowering and synchronising fruit set in pine apples.
- Ethylene induces flowering in mango. So it is a widely used PGR in agriculture.
![]()
Question 5.
Write short notes on seed dormancy. [TS MAR-17]
Answer:
- Seed dormancy: The inability or delay of seed to germinate or grow is called seed dormancy.
- It may be due to either external factors or internal factors.
- Dormancy may be due to hard seed coat which prevents the uptake of water or oxygen.
- Certain seeds like tomato contain chemicals like lycopane which inhibit germination.
- Many seeds like polygonum will not germinate for weeks and months until they are exposed to low temperatures in moist conditions.
- The dormancy of such seeds can be lifted by stratification or prechilling treatment.
- The practice of layering the seeds in moist sand and peat during winter is called stratification.
Question 6.
Which one of the plant growth regulators would you use if you are asked to
a) Induce rooting in a twig
b) Quickly ripen a fruit
c) Delay leaf senescence
d) Induce growth in axillary buds
e) ‘Bolt’ a rosette plant
f) Induce immediate stomatal closure in leaves
g) Overcome apical dominance
h) kill dicotyledonous weeds
Answer:
a) Auxins like IBA, NAA
b) Ethylene
c) Cytokinin
d) Cytokinin
e) Gibberellins
f) Abscisic acid (ABA)
g) Cytokinins
h) 2,4 D( Auxin)
Question 7.
Describe briefly
a) Sigmoid growth curve
b)Absolute and relative growth rates.
Answer:
a) Sigmoid growth curve: A sigmoid growth curve is characteristic of all living organisms growing in a natural environment. It is typical for all cells, tissues and organs of a plant.
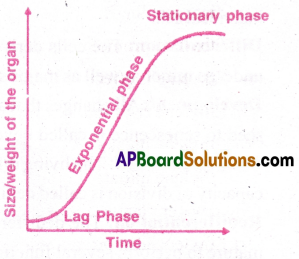
The exponential growth can be expressed as W1 = W0 ert
W1 = final size (weight, height, number etc)
W0 = Initial size at the beginning of the period,
r = growth rate
t = time of growth
e = base of natural logarithms.
Here, r is the relative growth rate and is also the measure of ability of the plant to produce new plant material, referred to as efficiency index. Hence, the final size of W] depends on the initial size, W0.
b) Absolute and relative growth: The measurement and comparison of the total growth per unit time is called the absolute growth rate.
The growth of the given system per unit time expressed on a common basis.
Ex: Per unit initial parameter is called the relative growth rate.

Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate.
Answer:
Growth: It is an irreversible, permanent increase in size of an organism or its parts or even of an individual cell.
Differentiation: The cells derived from root apical and shoot apical meristems and cambium undergo minor as well as major structural changes both in their cell walls and protoplasm. Development: All changes that an organism goes through its life cycle, from germination of the seed to senescence is called development.
Dedifferentiation: The living differentiated cells which lost the capacity to divide can regain the capacity of division is called dedifferentiation.
Kediffcrcntiation: The dedifferentiated cells that once again loose the capacity to divide but mature to perform several functions is called redifferentiation.
Determinate growth: When an organ or part or whose organism reaches a certain size and then stops growing is called determinate growth.
IMeristem: The constantly actively dividing cells present at the root tips and the shoot apex represent the meristem.
(Growth rate: The increased growth per unit time is called growth rate.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe briefly a) Arithmetic growth b) Geometric growth c) Sigmoid growth curve d) Absolute & relative growth rates
Answer:
a) Arithmetic growth: After mitotic cell division, only one daughter cell continues to divide while the other differentiates and matures division, only one daughter cell continues to divide while the other differentiates and matures
Lt= L0 + rt
Lt = Length at time t
L0 = Length at time 0
r= growth rate/ elongation per unit time
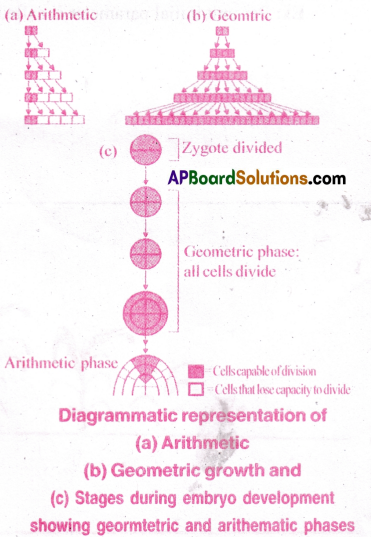
b) Geometric growth: After mitotic cell division both the daughter cells retain their ability to divide and continue to do so.
c) Sigmoid Growth Curve: If a graph is plotted for geometrical growth, it gives typical sigmoid or S-curve. Sigmoid growth curve exhibits three phases.
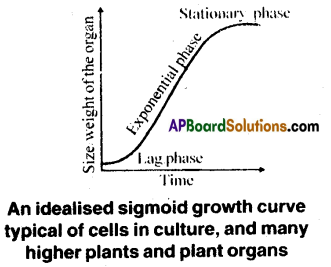
(i) Lag Phase: Initial growth is slow because no of cells is less
(ii) Log or exponential phase: Growth increases rapidly at an exponential rate because the daughter of mitotic cell division retain their ability to divide and coritinue to do so.
Stationary Phase: Due to limited nutrient supply and space, growth slows down leading to a stationary phase.
d) Absolute & Relative Growth Rate:
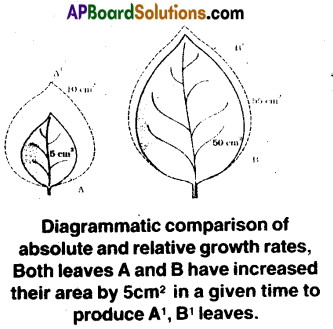
(i) Absolute Growth rate: The measurement and comparison of the total growth per unit time is called the absolute growth rate.
(ii) Relative Growth rate: The growth of the given system per unit time as percentage of initial size is called relative growth rate.

Question 3.
List five natural plant growth regulators. Write a note on discovery, physiological functions and agricultural/horticultural applications of any one of them.
Answer:
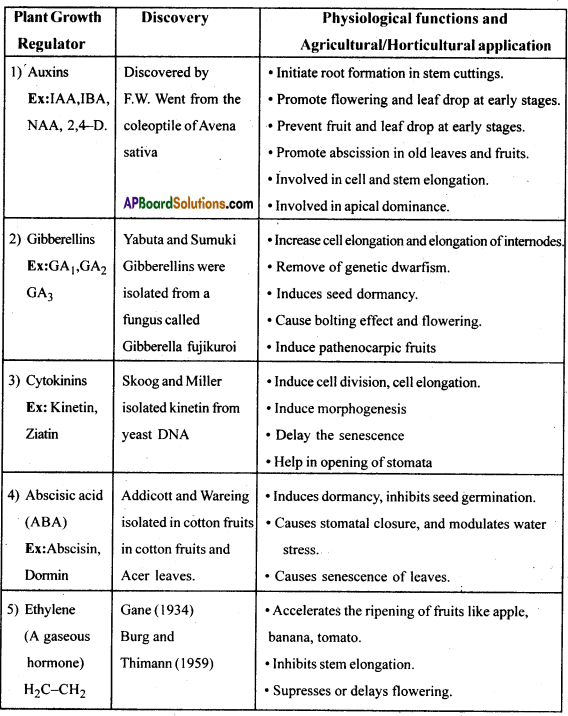
Exercise
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate word/words.
a. The phase in which growth is most rapid is …………..
b. Apical dominance as expressed in dicotyledonous plants is due to the presence of more ………… in the apical bud than in the lateral ones.
c. In addition to auxin, a …………. must be supplied to the Culture medium to obtain a good callus in plant tissue culture.
d. …………. of vegetative plants are the sites of photoperiodic perception.
Answer:
a) Log phase
b) Auxins
c) Cytokinins
d) Leaves
![]()
Question 2.
Gibberellins promote the formation of …………. flowers on genetically ………… plants in cannabis whereas ethylene promotes formation of ………… flowers on genetically ………… plants.
Answer:
a) Male
b) dwarf
c) female
d) dwarf
Question 3.
Classify the following plants into long-day plants (LDP), Short day plants (SDP) and Day Neutral plants (NDP).
Xanthium, Spinach, Henbane (Hyoscyamus niger), Rice, Strawberry, Bryophyllum, Sunflower, Tomato, Maize.
Answer:
Xanthium – Short day plant
Spinach – Long day plant
Herbane – Short day plant
Rice – Short day plant
Strawberry – Short day plant
Bryophyllum – Short day plant
Sunflower – Day neutral plant
Tomato – Day neutral plant
Maize – Long day plant
Question 4.
A farmer grows cucumber plants in his field. He wants to increase the number of female flowers. Which plant growth regulator can be applied to achieve this?
Answer:
Auxins
Question 5.
Where are the following hormones synthesized in plants?
a. IAA
b. Gibberellins
c. Cytokinins.
Answer:
a. IAA is synthesized by the growing apices of stems and roots.
b. Gibberellins: Gibberellins are synthesised from Acetyl Co.enzyme A. They are also synthesised in germinating seeds, fruits, young leaves of apical bud.
c. Cytokinins: Cytokinins are synthesised from root apices, young embryonic tissues.
Question 6.
Light plays an important role in the life of all organisms. Name any three physiological processes in plants which are influenced by light.
Answer:
a) Photosynthesis
b) Photoperiodisih
c) Growth
Question 7.
Growth is one of the characteristics of all living organisms. Do unicellular organisms also grow? If so, what are the parameters?
Answer:
- Yes,
- If we plot the parameter of growth against time, we get a typical sygmoid growth curve.
Question 8.
Rice seedlings infected with fungus Gibberella fujikuroi are called foolish seedlings. What is the reason?
Answer:
- During that time of disease, the rice plant grew excessively tall with very little grain production.
- The plants were taller, thinner and paler with little tillering as compared to healthy plants.
- This is called bakame (or) foolish seedling disease.
Question 9.
Why isn’t any one parameter good enough to demonstrate growth throughout the life of a flowering plant?
Answer:
Because growth depends upon cell division, nutrient supply, time, light, temperature etc.
Question 10.
‘Both growth and differentiation in higher plants are open’. Comment.
Answer:
- Plant growth is unique because plants retain the capacity through out their life.
- This ability of plants is due to the presence of meristems in their body.
- The cells of such meristems have the capacity to divide and self-perpetuate.
- The product soon loses the capacity to divide and such cells make up the plant body.
- This form of growth, wherein new cells are always added to the plant body by the activity of meristem is called open form of growth.
- The cells derived from meristem of shoot apex, root apex, cambium differentiate and mature to perform specific functions. .
- This act leading to maturation is called differentiation.
- Differentiation in plants is open, because cells arising out of the same meristem have different structures at maturity.
- The final structure at maturity is also determined by the location of the cell.
- For eg: Cells positioned away from root apex meristem differentiate as root cap cells.
- While those pushed to the periphery mature as epidermis.
![]()
Question 11.
‘Both a short day plant and a long day plant can produce flowers simultaneously in a given place’. Explain.
Answer:
- Long day plants require the exposure of light for a period more than the critical duration.
- Short day plants require the exposure of light for a period less than the critical duration.
- It is concluded that flowering in certain plants depends not only on light and dark combination, but also on the duration of exposure.
- This is called photo periodism.
- When we place both long day and short day plants at one place, artificial conditions are to be provided to expose them to the necessary inductive photoperiod. Then both the plants produce flowers.
Question 12.
Would a defoliated plant respond to photoperiodic cycle? Why?
Answer:
No, a defoliated plant would not respond to photoperiodic cycle. Because, the site of perception of light/dark duration is the leaves. In defoliated plant leaves are absent. Hormonal substances are responsible for flowering (florigens). These substances migrate from the leaves to shoot apices for inducing flowering only when the plants are exposed to the necessary inductive photo period.
Question 13.
What would be expected to happen if:
a. GA3 is applied to rice seedlings
b. Dividing cells stop differentiating
c. A rotten fruit gets mixed with unripe fruits
d. You forget to add cytokinin to the culture medium.
Answer:
1) Elongation of coleoptile occurs.
2) Un differentiated mass of cells are formed.
3) All fruits come to ripening state.
4) Shoot growth is inhibited.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A plant cell gets elongated by
1. Taking up water
2. increase of cytoplasm
3. increasing size of prot oplast
4. increasing thickness
Answer:
1. Taking up water
Question 2.
Gibberellins are most effective in the following parts of plants
1. Roots
2. Stems
3. Flowers
4. Fruits
Answer:
2. Stems
Question 3.
Which process of growth is mostly affected by Auxins?
1. Stem elongation
2. Elongation of cells
3. Celldivison
4. Cell maturation
Answer:
2. Elongation of cells
Question 4.
‘Apical dominance’ means
1. Apical bub inhibits the growth of lateral buds
2. Apical bud induces the growth of lateral buds
3. Lateral buds suppress the growth of apical bud
4. Removal of apical bud prevents the growth of lateral buds
Answer:
1. Apical bub inhibits the growth of lateral buds
Question 5.
‘Scarification’ means
1. Keeping seeds between sand layers
2. Making seed coat permeable to oxygen and water
3. Washing seeds with hormones
4. Washing seeds with chemicals
Answer:
2. Making seed coat permeable to oxygen and water
Question 6.
Cytokinins induce
1. Cell divison
2. Cell elongation
3. Dormancy
4. Root formation
Answer:
1. Cell divison
Question 7.
When the apical bud is removed, the plant
1. becomes more tall
2. appears more bushy
3. grows slowly
4. ceases to grow
Answer:
2. appears more bushy
Question 8.
Fruit ripening hormone is
1. Indole Butyric Acid
2. Zeatin
3. Ethylene
4. Kinetin
Answer:
3. Ethylene
![]()
Question 9.
The most widely used compound as a source
1. Tryptophan
2. Ethephon
3. Ethanol
4. Dormin
Answer:
2. Ethephon
Question 10.
Seed and bud dormancy can be broken by
1. Ethyl
2. Gibberellin
3. Zeatin
4. Auxin
Answer:
1. Ethyl
Question 11.
Gibberellin yielding gibberella is a (an)
1. alga
2. fungus
3. lichen
4. bacterium
Answer:
2. fungus
Question 12.
‘Stress-hormone’ is
1. Ethylene
2. ABA
3. Auxin
4. Zeatin
Answer:
2. ABA
Question 13.
Dormancy causing phytohormone is
1. ABA
2. Ethylene
3. Kinetin
4. Cytokinin
Answer:
1. ABA
Question 14.
In most of the plants, auxin is produced in
1. Flowers
2. Stem apex
3. Leaves
4. Buds
Answer:
2. Stem apex
Question 15.
Which of the following is not considered as growth?
1. increases of surface area of leaf
2. increase in the length of stem
3. increase in the size of a wooden piece placed in water
4. increase in the radius of the stem
Answer:
3. increase in the size of a wooden piece placed in water
Question 16.
Cell division is stimulated by
1. Gibberellins and Cytokinins
2. Auxins and Abscissic acid
3. Gibberellins and Auxins
4. Auxins and Cytokinins
Answer:
4. Auxins and Cytokinins
Question 17.
A plant bushy with
1. Decapitation
2. Dedifferentiation
3. Deforestation
4. Decondensation
Answer:
1. Decapitation
Question 18.
Ethephon causes
1. Fruit ripening
2. Cell elongation
3. stem elongation
4. Cell divison
Answer:
1. Fruit ripening
Question 19.
Stratification involves the use of
1. Moist sand and peat
2. Hormones and acids
3. Scalpels and blades
4. Hay and sponges
Answer:
1. Moist sand and peat
Question 20.
Geometrical growth occurs rapidly at an exponential rate during
1. Lag phase
2. Log phase
3. Stationary phase
4. Senescene phase
Answer:
2. Log phase
Question 21.
‘Cells derived from meristem differentiate and get matured to perform specific function’. This is known as
1) Redifferentiation
2) Dedifferentiation
3) Differentiation
4) Adifferentiation
Answer:
3) Differentiation
![]()
Question 22.
Measurement and comparison of the total growth per unit time is called
1) Absolute growth rate
2) Relative growth rate
3) Development rate
4) Differentiation rate
Answer:
1) Absolute growth rate
Question 23.
Growth slows down due to limited nutrient supply leading to phase of growth
1) Lag phase
2) Log phase
3) Stationary phase
4) Senescence phase
Answer:
3) Stationary phase
Question 24.
Which of the following can be used as a parameter to measure growth
1) Increase in cell number
2) Increase in cell size
3) Increase in length and weight
4) All the above
Answer:
4) All the above
Question 25.
Which one of the following pairs is not eorreetly matched
1) Adenine derivative-kinetin
2) Caroteniod derivative-ABA
3) Terpenes-IAA
4) Indole compounds-IBA
Answer:
3) Terpenes-IAA
Question 26.
Adding of new cells always to the plant body by the activity of mcristeni is called
1) direct form of growth
2) open form of growth
3) closed form of growth
4) indirect form of growth
Answer:
2) open form of growth
Question 27.
Growth rate means
1) Increased growth per unit area
2) Increased growth per unit time
3) Increased growth in total length
4) Increased growth in total girth
Answer:
2) Increased growth per unit time
Question 28.
Character of phase of elongation is
1) Cell wall is thin and cellulosic
2) Abundant plasmodesmatal connections
3) Increased vacuolation of cell
4) Cell wall becomes very much thickened
Answer:
3) Increased vacuolation of cell
Question 29.
Formulae of growth which can be represented in linear curve is
1) L1 = L0 + rt
2) L0 = L1 + rt
3) W1 = W0 ert
4) W0 = W1 ert
Answer:
1) L1 = L0 + rt
Question 30.
The cells of the following /one attain their maximal size in terms of wall thickening and protoplasmic modifications.
1) Meristematic phase
2) Elongation phase
3) 1 and 2
4) Maturation phase
Answer:
2) Elongation phase
Question 31.
The growth in plants and animals are respectively
1) Determinate, indeterminate
2) Indeterminate, determinate
3) Determinate, determinate
4) Indeterminate, Indeterminate
Answer:
2) Indeterminate, determinate
Question 32.
A pair of hormones which can remove apical dominance
1) Auxins & Cytokinins
2) Cytokinins & Ethylene
3) GA & ABA
4) ABA & Ethylene
Answer:
2) Cytokinins & Ethylene
![]()
Question 33.
Indole 3-acetic acid, called as auxin was first isolated from
1) Human urine
2) Com germ oil
3) Herring sperm DNA
4) Coleorhiza tips of oat seddlings
Answer:
1) Human urine
Question 34.
Delay of fruit senescence and delay of leaf senescence are caused by
1) Auxins and Gibberellins
2) Gibberellins &cytokinins
3) Cytokinins and ABA
4) ABA and ethylene
Answer:
2) Gibberellins &cytokinins
Question 35.
Cytokinins were first isolated from
1) Oat seedlings
2) Coconut milk
3) Sperms of Herring fish
4) Maize leaves
Answer:
3) Sperms of Herring fish
Question 36.
PGR that acts both as growth promoter as well as growth inhibitor is
1) Auxins
2) Gibberellins
3) ABA
4) Ethylene
Answer:
4) Ethylene
Question 37.
Genetic dwarfism can be removed by using
1) Auxin
2) Cytokinin
3) GA
4) ABA
Answer:
3) GA
Question 38.
Natural cytokinins are syntherised in tissues that are
1) storing food
2) differentiating
3) dividing
4) senescent
Answer:
3) dividing
Question 39.
Increase in the yield of sugarcane crops can be achieved by the application of
1) GA
2) IAA
3) Kinetin
4) Ethylene
Answer:
1) GA
Question 40.
In drought, which hormone plays a protective role
1) ABA
2) GA
3) IAA
4) Cytokinin
Answer:
1) ABA
Question 41.
Flowering in short day plants is stimulated by
1) short nights
2) long day with interrupted night
3) short day and uninterrupted long night
4) short days and interrupted long nights
Answer:
3) short day and uninterrupted long night
Question 42.
The ability of producing different kinds of structures at different phases of life is called
1. Plasticity
2. Re-differentiation
3. Plasmacity
4. Maturation
Answer:
1. Plasticity
Question 43.
PGR which induces the formation of new leaves and chloroplasts in plants
1. Cytokinins
2. Ethylene
3. Gibberellins
4. Abscisic acid
Answer:
1. Cytokinins
![]()
Question 44.
The secondary tissue present in woody dicotyledonous plants (secondary Xylem and secondary Phloem) are formed through
1. Differentiation
2. Dedifferentiation
3. Redifferentiation
4. Plasticity
Answer:
3. Redifferentiation
Question 45.
Which of the following is formed after dedifferentiation
1) Secondary phloem
2) Secondary cortex
3) Parenchyma
4) Interfassicular vascular cambium
Answer:
4) Interfassicular vascular cambium
Question 46.
Vernalisation takes place in response to
1) Low light intensity
2) High light intensity
3) Low temperature
4) High temperature
Answer:
3) Low temperature
Question 47.
The phenomenon which shortens vegetative period and hastens flowering is
1) Etiolation
2) Vermalisation
3) Photoperiodism
4) Parthenocarpy
Answer:
2) Vermalisation
Question 48.
Plant hormone that causes apical hook formation in dicot seedlings is
1) Abscisic acid
2) Ethylene
3) Cytokinins
4) Gibberellins
Answer:
2) Ethylene
![]()
Question 49.
Fruit and leaf drop at early stages can be prevented by the application of
1) Ethylene
2) Auxins
3) Gibberellic acid
4) Cytokinins
Answer:
2) Auxins
Question 50.
The site of perception of light in plants during photoperiodism is
1) leaf
2) shoot apex
3) stem
4) axillary bud
Answer:
1) leaf