Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 4th Lesson Photosynthesis in Higher Plants which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 4th Lesson Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name the processes which take place in the grana and stroma regions of chloroplasts.
Answer:
- Light reaction occurs in grana of chloroplast.
- Dark reaction (carbon fixation) occurs in stroma of chloroplast.
![]()
Question 2.
Can chloroplasts be passed on to progeny? How?
Answer:
- Yes. Chloroplasts can be passed on to progeny.
- Chloroplasts have their own genetic material. They divide by fission and are distributed to daughter cells through cell division.
Question 3.
Where does the photolysis of H2O occur? What is its significance? [AP MAR-17, 20] [TS M AY-22]
Answer:
- Photolysis of H2O occurs in grana of the chloroplast.
- Significance: During photolysis oxygen is evolved.lt is the main source of atmospheric oxygen.
Question 4.
Where is the enzyme NADP reductase located? What is a released if the proton gradient breakdown?
Answer:
- NADP teductase enzyme is located on the stroma side of the lamella or thylakoid of the chloroplast.
- Energy is released if the proton gradient is broken down for the synthesis of ATP.
Question 5.
Which tissue transports photosynthatases? What experiment proves this?
Answer:
- Phloem is the tissue that transports photosynthates.
- Ringing / girdling experiments of phloem prove this.
Question 6.
How many molecules of ATP and NADPH are needed to fix a molecule of CO2 in C3 plants? Where does this process occur?
Answer:
- 3 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADPH are required.
- This process occurs in the §troma of chloroplast.
Question 7.
Explain the terms
(a) Hatch Slack pathway
(b) PEP carboxylase
(c) Calvin cycle
(d) Bundle sheath cells
Answer:
(a) Hatch Slack pathway: ‘CO2 fixation’ in C4 plants was discovered by Hatch & Slack. So C4 pathway is called the Hatch-Slack pathway.
(b) Calvin cycle: ‘CO2 fixation’ in C3 plants was discovered by Calvin . So C3 cycle is called calvin cycle.
(c) PEP carboxylase: In C4 cycle, CO2 is accepted by phosphoenol pyruvate in the presence of an enzyme PEP carboxylase.
(d) Bundle sheath cells: The large cells around the vascular bundles of the C4 pathway plants are called Bundle sheath cells.
Question 8.
What is the role of NADP reductase in the development of proton gradient?
Answer:
- ‘NADP reductase enzyme’ catalyses the oxidation of Fd (ferredoxin) and reduction of NADP+ to NADPH+ + H+.
- As electrons move from PSII to PSI, protons are transported from stroma to lumen.
- Due to activity of NADP reductase enzyme, the proton gradient in stroma declines and results in proton gradient.
Question 9.
Mention the components of ATPase enzyme. What is their location? Which part of the enzyme shows conformational change?
Answer:
Components of ATPase enzyme:
- F0 (Stalk): It is embedded in the membrane and forms a trans membrane channel.
- F1 (Head): It protrudes out into the stroma.
F1 particle of the ATPase shows conformational change.
Question 10.
What products drive calvin cycle? What products regenerate them?
Answer:
- ATP and NADPH + H+ drive ‘calvin cycle’ to reduce CO2 to carbohydrates.
- They are regenerated during light reaction phase .
Question 11.
What is the basis for designating C3 & C4 pathways of photosynthesis?
Answer:
- In C3 pathway, the first stable product formed is PGA. It is a 3-carbon compound.
- In C4 pathway, the first stable product formed is OAA. It is a 4-carbon compound.
- The ‘number of carbon atoms’ in the first stable product of carboxylation is the. basis for designating C3 and C4 pathways.
Question 12.
Distinguish between action spectrum and absorption spectrum. [AP MAR-16]
Answer:
- Action spectrum: It is the graph showing the ‘rate of photosynthesis’ at different wavelengths.
- Absorption spectrum: It is the graph showing the’absorption of light’by pigments at different wavelengths.
Question 13.
Of the basic raw materials of photosynthesis, what is reduced? What is oxidised?
Answer:
CO2 is reduced and H2O is oxidised.
![]()
Question 14.
Define the law of limiting factors proposed by Blackman. [AP MAR-16, 19] [AP MAY-17]
Answer:
Law of limiting factors: In a process participated by a number of separate factors, the rate of the process is limited by the factor which is present in a relatively minimal value.
Question 15.
What is Joseph Priestly’s contribution to the study of photosynthesis?
Answer:
- According to Joseph Priestly, plants restore the air, whatever breathing animals and burning candles remove.
- Priestly proved that plants absorb CO2 and release O2 during photosynthesis.
Question 16.
Comment on the contribution of Van Niel to the understanding of photosynthesis?
Answer:
- Von Niel, demonstrated that photosynthesis is essentially a light-dependent reaction, in which hydrogen from a suitable oxidisable compound reduces CO2 to carbohydrates.
- Niel inferred that the O2 evolved by the green plant comes from H2O, but not from CO2.

Question 17.
With reference to photosystem, bring out the meaning of the terms
a) antennae b) reaction centre.
Answer:
a) Antennae: A group of pigment molecules that absorbs light energy and transfers to a reaction centre complex.
b) Reaction centre: Special chlorophyll which routinely undergoes photooxidation designated as P700 in PSI and P 680 in PS II
Question 18.
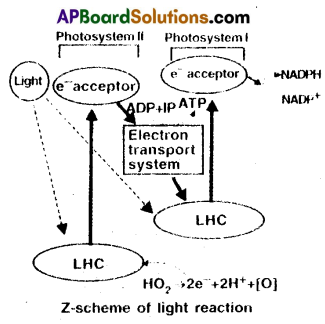
Why is photosynthetic electron transport from H2O to NADP named as Z-scheme?
Answer:
- When all carriers are placed in a sequence on a redox potential scales, the ‘Z shape’ is formed.
- Hence the name Z-scheme is given.
Question 19.
What is the primary acceptor of CO2 in C3 plants? What is first stable compound formed in a Calvin cycle? [MAY-22]
Answer:
- RuBP (Ribulose bi phosphate) is the primary acceptor of CO2 in C3 plants.
- PGA (Phospho Glyceric acid) is the first stable compound in Calvin cycle.
Question 20.
What is the primary acceptor of CO2 in C4 plants? What is the first compound formed as a result of primary carboxylation in the C4 pathway?
Answer:
- PEP(Phospho enol pyruvic acid) is the primary acceptor of CO2 in C4 plants.
- OAA (Oxalo acetic acid) is the first compound formed as a result of primary carboxylation in the C4 pathway.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Succulents are known to keep their stomata closed during the day to check transpiration? How do they meet their photosynthetic CO2 requirements?
Answer:
1) Succulent plants have only one kind of photosynthetic cell in which CO2 is fixed during night and used to make glucose during day.
2) In succulent plants there is an alternative pathway of CO2 fixation called Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM). Ex: Cacti Crassulaceaen is one family of Succulent plants.
3) CAM pathway is similar to C4 pathway in that CO2 is trapped by highly efficient PEP carboxylase during nighttime.
4) During day time, the malic acid undergoes oxidative carboxylation to form Pyruvic acid and CO2. CO2 is used for photosynthesis.
Question 2.
Chlorophyll ‘a’ is the primary pigment for light reaction. What are accessory pigments? What is their role in photosynthesis?
Answer:
- Chlorophyll’a’traps sunlight.
- Other accessory pigments such as chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and carotenoids also absorb light and transfer to the energy to chlorophyll a.
- They absorb a higher wavelength of light.
- They also protect the chlorophyll ‘a’ from photooxidation.
Question 3.
Does dark reaction of photosynthesis require light. Explain.
Answer:
- No. Dark reaction does not require light.
- It is a light-independent reaction.
- But the assimilatory power (ATP + NADPH2) produced in light reaction is required to produce starch during the dark phase.
- If the light is not available, dark reaction continues for some time and then stops.
- Then if light is made available, synthesis starts again.
Question 4.
How are photosynthesis and respiration related to each other?
Answer:
- Photosynthesis is an anabolic process whereas respiration is an catabolic process
- In photosynthesis, simple substances like Carbondioxide and water combine and yield complex carbohydrates. Ex: Glucose.
- In respiration, complex carbohydrates are broken into simpler substances like CO2 and H20.
- Photosynthesis is a reductive process whereas respiration is a oxidative process.
- Photosynthesis is an endogenic process whereas respiration is an endergonic process.
- In Photosynthesis O2 is a by-product. In respiration, O2 is utilised.
![]()
Question 5.
What conditions enable KuBisCO to function as oxygenase? Explain the ensuing process?
Answer:
- RuBisCO is.an enzyme which has dual nature.
- It acts as carboxylase, when CO2 concentrations is good enough in the atmosphere.
- But if concentration of oxygen increases and temperature increases, its nature changes and it binds with O2 and acts oxygenase leading to photorespiration and loss of CO2 with ATP utilization.
- In Photorespiration, there is no synthesis of sugar, ATP and NADPH. Hence it is a wasteful process.
Question 6.
Why docs rate of photosynthesis decreases at higher temperatures?
Answer:
- Ezymatic activity is linked with temperature.
- Being enzymatic the dark reactions are temperature controlled.
- Though the light reactions are also temperature sensitive, they are affected to a much lesser extent.
- Tropical plants (C4 plants) respond to higher temperatures than temperature plants (C3 plants)
- At higher temperatures, enzymes get denatured. Hence the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
Question 7.
Explain how during light reaction of photosynthesis, ATE synthesis is a chemiosmotic phenomenon.
Answer:
- ATP synthesis in the chloroplast is a chemiosmotic phenomenon. It was proposed by Mitchell.
- It requires a membrane, proton pump, proton gradient and ATPase.
- In light reaction, H2O splitting takes places on inner side of membrane and releases two protons in the lumen of thylakoid.
- The electrons move through transport chain, protons are transported across membrane into lumen resulting in an increase of proton gradient across the membrane.
- So within chloroplast, protons in stroma decreases. Hence a proton gradient is formed.
- Now ATPase consisting F0 in the membrane, facilitates the diffusion of protons and F1, from lumen to stroma.
- For every passing of 3 protons, some energy is released which helps in synthesis of ATP.
Question 8.
Explain how Calvin worked out the complete biosynthetic pathway for the synthesis of sugar.
Answer:
- The biosynthetic pathway for the synthesis of sugar was traced out by Calvin, Benson and Basshem.
- They used radioactive carbon (14CO2) to the algal cultures.
- This lead to the discovery of the first stable compound PGA, which was a 3-carbon compound.
- Calvin cycle occurs in all Photosynthetic plants.
- Calvin cycle can be described in three phases.
a) Carboxylation phase: During this phase CO2 combines with a five carbon compound called ribulose 1,5 biphosphate and forms 3-Phospho glyceric acid.
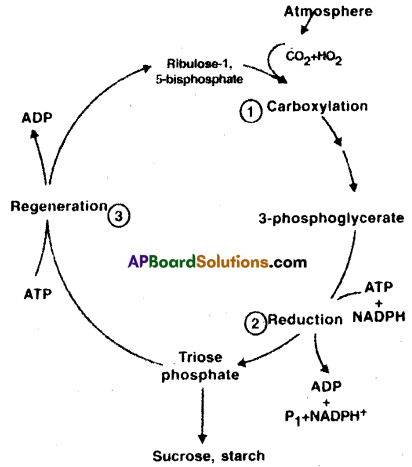
b) Reduction phase: During this phase Carbohydrate is synthesized by utilising the assimilatory power of light reaction Viz, ATP and NADPH.
e) Regeneration phase: During this phase the CO2 acceptor ribulose 1,5 phosphate is formed again to continue the Calvin cycle.
Question 9.
Six turns of calvin cycle are re<|uircd to generate one mole of glucose. Explain. [TS M AY-22, 19]
Answer:
- In Calvin cycle for every CO2 molecule to be fixed, 3ATP and 2 NADPH are required which forms 1/6th of a glucose molecule.
- So to get 1 molecule of glucose, 6CO2 are fixed by using 18ATP and 12 NADPH molecules.
- So to make one glucose molecule, 6 turns of the calvin cycle are required.
Question 10.
With the help of a diagram, explain briefly the process of cyclic photophosphorylation.
Answer:
Cyclic Photophosphorylation:
- The formation of ATP due to cyclic flow of electrons in PSI is called cyclic Photophosphorylation.
- It takes place in PSI, its reaction centre is P700.
- It receives a light ray of wavelength 700nm.
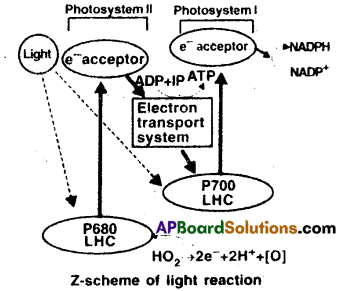
- During this process, the electrons from PSI are conveyed to e– acceptors.
- The excited electron is cycled back to PSI through electron transport system.
- This cyclic flow results in the synthesis of ATP.
Question 11.
In what type of plants do you conic across “Kranz” anatomy? To which conditions they arc better adapted? How are these plahts adapted than the plants which lack this anatomy?
Answer:
- In C4 plants, large cells are present around the vascular bundles called bundle sheath cells and leaves which have such anatomy are said to be Kranz anatomy.
- Kranz means wreath (curl or ring shape) and is a reflection of the arrangement of cells.
- Bundle sheath cells are characterised by a large number of agranal chloroplasts, thick wall impervious to gaseous exchange and no inter-cellular spaces.
- In these plants, CO2 fixation occurs both in mesophyll cells and bundle sheath cells.
- So C4 plants are better equipped to withstand drought and are able to maintain active photosynthesis even under water stress conditions.
![]()
Question 12.
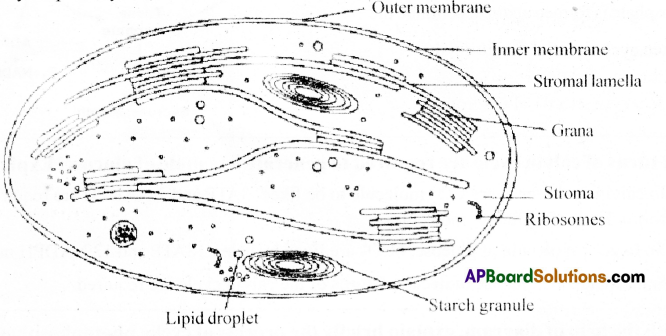
Explain the structure of chloroplast? Draw a neat labelled diagram. [AP MAY-22]
Answer:
- Chloroplasts are double membraned (made of phospho lipids) oval or disc shaped organelles concerned with photosynthesis.
- Inside the chloroplast, the granules thylakoids are arranged in stacks which help to trap sunlight and carry light reactions and help in the synthesis of ATP & NADPH.
- The fluid part is stroma which carries light independent reaction and produces sugar.
- The grana are interconnected by fret lamellar connections.
- The stroma contains many enzymes, ribosomes, starch granules, liquid droplets that helps to carry on photosynthesis.
Question 13.
Explain why 12 molecules of water are used as substrate, instead of 6 molecules of water in the following equation?

Answer:
During photosynthesis, 1 water molecule splits into 2e– + 2H+ and ½O2
In photolysis, 1H2O → 2e– + 2H+ + ½O2
So to produce 6O2 molecules, 12 H2O molecules are required.
Question 14.
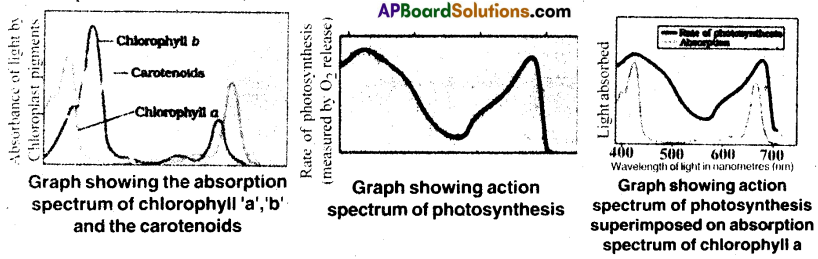
Compare and contrast the absorption spectrum of chlorophylls and carotenoids.
Answer:
- Pigments are substances that has an ability to absorb light at specific wavelengths.
- Most of the photosynthesis takes place in blue and red regions of spectrum.
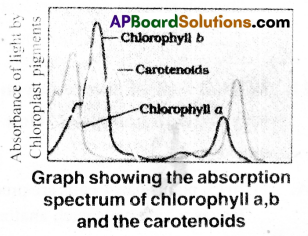
- Chlorophyll a is a major pigment that absorbs light of different wavelengths in visible spectrum. Chlorophyll b, xanthophvl! and carotenoids which are known as accessory pigments, absorb under range of wavelengths of light and transfer to chlorophyll a and protects it from photooxidation.
Question 15.
Which group of plants exhibit.two types of photosynthetic cells? What is the first product of carboxylation? What carboxylating enzyme is present in bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells.?
Answer:
C4 plants exhibit two types of photosynthetic cells. They are mesophyll cells and bundle sheath cells. During first carboxylation in mesophyll cells, OAA is formed as a stable product. In mesophyll cells, PEP carboxylase enzyme is present. In bundle sheath cells, RuBisCO is present.
Question 16.
A cyclic process is occurring in a C3 plant, which is light-dependent and needs O2. This process does not produce energy rather it consumes energy
a) Can you name the given process
b) Is it essential for survival?
c) What are the end products of this process?
d) Where does it occur?
Answer:
a) Calvin cycle or Dark reaction
b) Yes, it is essential for survival
c) Glucose + water + oxygen
d) Occurs in stroma of chloroplast.
Question 17.
Suppose Euphorbia and maize are grown in tropical areas?
a) Which one of them do you think will be able to survive under such conditions?
b) Which one of them is more efficient in terms of photosynthetic activity?
c) What differences do you think are there in leaf?
Answer:
a) Euphorbia
b) Maize
c) In maize leaves, kranz anatomy is seen. Chloroplasts are dimorphic . Two carboxylations occur, one in mesophyll cells and the other in bundle sheath cells.
![]()
Question 18.
Tabulate eight differences between C3 cycles and C4 cycles. [AP MAR – 15]
Answer:
| C3 Cycles | C4 Cycles |
| 1) First stable product of carbon pathway is C3 compound (PGA-Phospho glyceric acid) 2) This occurs mostly in Temperate plants. 3) Leaves do not show Kranz anatomy. 4) Chloroplast dimorphish is not seen. 5) Photo respiration is very high. 6) In C3 plants, transpiration is more. 7) Less efficient in utilising atmospheric CO2. 8) Biomass is produced in less quantity. Ex: Almost all dicot plants |
1) First stable product of carbon pathway is C4 compound (OAA-Oxalo acetic acid) 2) This occurs only in Tropical plants. 3) Leaves show Kranz anatomy. 4) Chloroplast dimorphish is seen. 5) Photo respiration is not detectable. 6) In C4 plants, transpiration is less. 7) More efficient in utilising atmospheric CO2. 8) Biomass is produced in high quantity.Ex: Maize, Sugarcane, Sorghum |
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
The entire process of photosynthesis consists of number of reactions. Where in the cell do each of these take place?
a) Synthesis of ATP and NADPH
b) Photolysis of Water
c) Fixation of CO2
d) Synthesis of sugar molecule
e) Synthesis of starch
Answer:
a) Grana thylakoid
b) Innerside of thylakoid membrane
c) Stroma
d) Cytoplasm
e) Cytoplasm
Question 2.
Which property of pigments is responsible for its ability to initiate the process of photosynthesis? Why is rate of photosynthesis higher in red and blue regions of spectrum of light?
Answer:
A chromatographic separation of leaf pigments shows the colour we see in leaves is not due to single pigment but due to four pigments-
- Chlorophyll ‘a’ (bright blue or green)
- Chlorophyll ‘b’ (yellow green)
- Xanthophylls (yellow)
- Carotenoids (yellow to yellow orange)
1) Pigments are substance that have an ability to absorb light at specific wavelengths chlorophyll ‘a’ is chief pigment of photosynthesis which absorbs blue and red wavelengths of light and is shown in graph by measuring the amount of O2 released.
2) Maximum photosynthesis occurs in blue and red lights and least in green light.
3) This is because other accessory pigments (chlorophyll ‘b’ and carotenoids) also absorb light and transfer to chlorophyll ‘a’.
4) They not only absorb under range of wavelengths of light but also protect chlorophyll ‘a’ from photooxidation.
Question 3.
Under what conditions are C4 plants superior to C3?
Answer:
C4 plants are superior to C3 plants in the following conditions:
| Conditions | C4 plants | C3 plants |
| 1) CO2 fixation rate under light condition | High | Low |
| 2) Photorespiration present at low light intensities | Negligible | High |
| 3) Photorespiration present at high light intensities | Negligible | High |
| 4) Photorespiration would be present at low CO2 | Negligible | High |
| concentration | ||
| 5) Photorespiration would be present at high CO2 | Negligible | High |
| concentration | ||
| 6) Optimum Temperature | 30°C-40°C | 20°C-25°C |
| 7) Primary Acceptor of CO2 | PEPA | RUBP |
| 8) Stable Primary products | OAA | PGA |
| (4 carbon compound) | (3-carbon compound) | |
| 9) Plants having RuBISCO? | In bundle Sheath cells only |
Yes |
| 10) Plants having PEP case | Yes | No |
Question 4.
a) How can wc plot an action spectrum? What does an action spectrum indicate? Explain with an example.
Answer:
- A graph showing the rate of photosynthesis and function of the wavelength of light is called action spectrum.
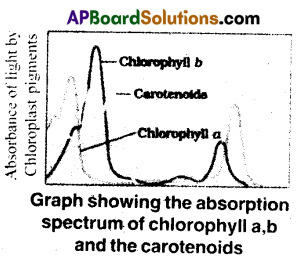
- To plot a graph, rate of photosynthesis should be taken on X-axis and wavelengths on Y-axis.
- The action spectrum indicates wavelengths at which maximum photosynthesis occurs in blue and red lights.
![]()
b) How can we derive an absorption spectrum for any substance?
Answer:
- Pigments are substances that have the ability to absorb light at specific wavelengths.
- In the graph, the ability of chlorophyll-a pigment to absorb light of different wavelengths in the visible light is VIBGYOR.
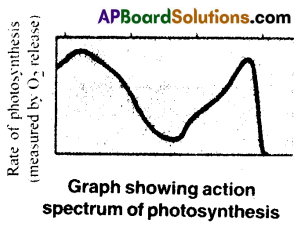
c) If chlorophyll ‘a’ is responsible for light reaction of photosynthesis, why do action spectrum and absorption spectrum not overlap?
Answer:
- In the graph, it shows that the most of the photosynthesis takes place in the blue and red regions of the spectrum.
- Some photosynthesis does not take place at the other wavelength regions of visible spectrum.
- The graph shows that there is complete one to one overlap between absorption spectrum of chlorophyll ‘a’ and the action spectrum of photosynthesis.
Question 5.
What arc the important events and end products of light reactions?
Answer:
Important events of light reaction are light absorption, photolysis end products are ATP, NADPH and O2.
Light absorption: Pigment molecules absorb light. The Chi ‘a’ contain two photo systems, PSI and PSII. Its reaction centres are P700 and P 680 respectively. The process of formation of ATP in the presence of light is called photophosphorylation. It is of two types a) Cyclic and b) Non-Cyclic photophosphorylation.
a) Cyclic Photophsophorylations:
- Formation of ATP due to cyclic flow of electrons in PSI is called cyclic Photophosphorylation.
- It takes place in PSI, its reaction centre is P700.
- It receives a light ray of wave length 700nm.
- During this process the electrons from PSI are conveyed to e– acceptors.
- The excited electron is cycled back to PSI through electron transport system.
- This cyclic flow results in the synthesis of ATP.
b) Non-cyclic Photo Phosphorylations:
- PSII and PSI are involved in Non-cyclic photo phosphorylation.
- P680 of PSII absorbs a light ray of 680nm.
- The excited PSI releases electrons, which are picked by e– acceptor.
- At the same time P700 of PSI also gets excited by receiving a light ray of 700nm.
- The excited PSI also releases electrons, which reduce NADP to NADPH.
- As the electron are travelling in the shape of ‘z’, the non-cyclic photophosphorylation is also named as z-scheme.
Photolysis of water:
- In the first step electrons are removed from PSI.
- They are recharged by PSII. Now PSII loses electrons.
- Splitting of water molecules by oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) release electrons.
2H2O → 4H+ + O2 + 4e–
These electrons are supplied to PSII.
Thus the end products of light reaction are ATP, NADPH and O2.
Question 6.
Explain various aspects of Mitchell chemiosmotic hypothesis, with the help of diagrams.
Answer:
1) Chemiosmotic hypothesis is proposed by Mitchell to explain ATP synthesis.
2) ATP synthesis is linked to development of proton gradient across the membrane.
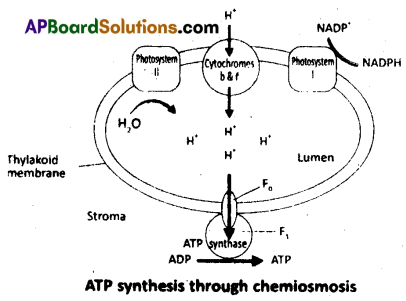
3) Splitting of the water molecule takes place on the inner side of the membrane, the protons or hydrogen ions that are produced by the splitting of water, accumulate within the lumen of the thylakoids.
4) As electrons move through the transport chain, protons are transported across the membrane. This happens because the primary acceptor of electrons which are located towards the outer side of the membrane transfers its electron not to electron carrier, but to (H ) proton carrier (PQ). Hence it removes protons, from the stroma which transports an electron.
5) When this molecule passes its electron, to the electron carrier on the inner side of the membrane, the proton is released into the inner side or lumen of the membrane. Then proton gradient across the membrane increases due to quinones.
6) The NADP reductase enzyme is located on the stroma side of the membrane. Along with the electrons that come from the acceptor of electrons of PS I, protons are necessary for the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH + H+.
7) These protons are also removed from the stroma. Thus protons in the stroma decrease in number. Where as in lumen protons are accumulated. This creates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane and the pH in the lumen decreases.
8) The proton gradient is broken down due to the movement of protons across the membrane to the stroma through the transmembrane channel of ATPase.
ATPase consists of two parts.
(i) One is F0. F0 is embedded in the membrane that forms the transmembrane channel it carries
facilitated diffusion of protons across the membrane.
(ii) Other one is F0. It produces on the outer surface of the thylakoid membrane.
Diffusion of protons across the membrane releases enough energy to activate ATPase enzyme that catalyses the formation of ATP
Question 7.
Comment on the dual role of RuBiSC’O. What is the basis for its oxygenation activity? Why is this activity absent or negligible in C4 plants?
Answer:

- RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme in the world.
- Its active site can bind to both CO2 and O2. It acts as both oxygenase and carboxylase
- RuBisCo has a much greater affinity for CO2 than for O2.
- If O2 concentration is more, RuBisCo functions as oxygenase, and binds with O2.
- Instead of forming two molecules of PGA, it forms one molecule of phosphoglycerate and one molecule of phosphoglycolate.
- This pathway is called photo respiration.
- In photorespiration pathway there is synthesis of neither sugar nor ATP nor NADPH.
- Moreover, there is a release of CO2 with the utilisation of ATP.
- Therefore photorespiration is a wasteful process.
- In C4 plants the bundle sheath cells have more RuBisCo than PEPase.
- Photorespiration does not occur because C4 plants have a mechanism that increases the concentration of CO2 at enzyme site.
- It takes place when C4 acid from mesophill cells is broken down in the bundle sheath cells to release CO2.
- This results in increasing the intra cellular concentration of CO2.
![]()
Question 8.
Describe in brief photorespiration [TS 20]
Answer:
- RuBisCO is the most abundant enzyme in the world.
- Its active site can bind to both CO2 and O2. It acts as both oxygenase and carboxylase
- RuBisCo has a much greater affinity for CO2 than for O2.
- If O2 concentration is more, RuBisCo functions as oxygenase, and binds with O2.
- Instead of forming two molecules of PGA, it forms one molecule of phosphoglycerate and one molecule of phosphoglycolate.
- This pathway is called photorespiration.
- In photorespiration pathway there is synthesis of neither sugar nor ATP nor NADPH.
- Moreover, there is a release of CO2 with the utilisation of ATP.
- Therefore photorespiration is a wasteful process.
- In C4 plants the bundle sheath cells have more RuBisCo than PEPase.
- Photorespiration does not occur because C4 plants have a mechanism that increases the concentration of CO, at enzyme site.
- It takes place when C4 acid from mesophill cells is broken down in the bundle sheath cells to release CO2.
- This results in increasing the intra cellular concentration of CO2.
Exercise
Question 1.
By looking at a plant externally, can you tell whether a plant is C3 or C4? Why and how?
Answer:
Differences based on external points.
| Cvplants | C4 plants |
| 1. They occur in Temperate plants. 2. Optimum temperature is low (15°C-25°C.) 3. Photo respiration is very high. 4. In C3 plants, transpiration is more. 5. Biomass is produced in less quantity. Ex: Almost all dicot plants |
1. They occur in Tropical plants. 2. Optimum temperature is high (30°C-45°C.) 3. Photo respiration is not detectable. 4. In C4 plants, transpiration is less. 5. Biomass is produced in high quantity. Ex: Maize, Sugarcane, Sorghum |
Question 2.
By looking at which internal structure of a plant can you tell whether a plant is C3 or C4? Explain.
Answer:
- If the leaf shows kranz anatomy, the plant is C4 plant.
- The cells participating will have two types of chloroplasts i.e., chloroplast dimorphism is seen, the plant is C4 plant.
- The cells participating will have only one type of chloroplast -the plant is C3 plant.
- Bundle sheath cells have thick walls and impervious to gases- the plant is C4 plant.
- The anatomy of leaf does not show kranz-anatomy – the plant is C3 plant.
Question 3.
Even though a very few cells in a C4 plant carry out the hiosynthetie -Calvin pathway, yet they are highly productive can you discuss why?
Answer:
- RuBisCO has a much greater affinity for CO2 than for O2.
- In C3 plants some O2 binds to RuBisCO leading to photo respiration and hence CO2 fixation is decreased.
- In C4 plants photorespiration does not occur.
- In C4 plants CO2 concentration is more in bundle sheath cells.
- Hence productivity is high.
Question 4.
RuBisCO is an enzyme that acts both as a carboxylase and oxygenase. Why do you think RuBisCO carries out more carhoxylation in C4 plants?
Answer:
RuBisCO can bind to CO2 and O2. It acts both as a carboxylase and an oxygenase. In C4 plants RuBisCO is present only in bundle sheath cells. In C4 plants photorespiration does not occur. This is because they have a mechanism that increases the concentration of CO2 at the enzyme site. So RuBisCO carries out more carboxylation in C4 plants.
Suppose there were plants that had a high concentration of chlorophyll b, but lacked chlorophyll a, would it carry out photosynthesis? Then why do plants have chlorophyll b and other accessory pigments?
- If the plants have high chl ‘b’ and no chi ‘a’, does not carry out photosynthesis.
- ChL ‘b’ and other necessary pigments absorb light and transfers into chL ‘a’.
- ChL ‘a’ is the chief photosynthetic pigment and that only carries out photosynthesis.
- In addition accessory pigments protect chl ‘a’ from photo-oxidation.
Question 6.
Why is the colour of a leaf kept in the dark frequently yellow, or pale green? Which pigment do you think is more stable?
Answer:
- If a plant is kept in dark the leaf loses its green colour and gets pale yellow or orange colour due to Etiolation.
- Etiolation – loss of colour of leaf or death of the plant part is called etiolation. It is due to keeping the plant in dark.
- The following pigments are responsible for different colouration.
- Chi ‘a’- bright green
- Chl’b’-yellow green.
- Xanthophylls – yellow
- Carotenoids – yellow (or) orange.
Question 7.
Look at leaves of the same plant on the shady side and compare it with the leaves on the sunny side. Or, compare the potted plants kept in the sunlight with those in the shade. Which of them has leaves that are darker green? Why?
Answer:
- The plant kept in sunny side prepare more food and the leaves appear to be dark green.
- The plant kept in shady side prepare less amount of food and the leaves appear to be pale.
- There is a direct relation between the amount of chlorophyll in the leaf and rate of photosynthesis.
Question 8.
The figure shows the effect of light on the rate of photosynthesis. Based on the graph, answer the following
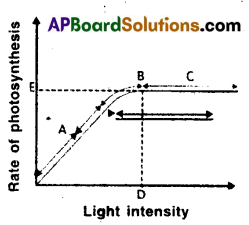 questions:
questions:
a. At which points (A, B or C) in the curve is light at limiting factor?
b. What could be the limiting factors in region A?
c. What do C and D represent on the curve?
Answer:
a) A and B
b) Light
c) Saturation of light ‘C.
The photosynthetic rate will not increase by increasing the intensity of light ‘D’.
![]()
Question 9.
Give comparison between the following:
a. C3 and C4 pathways
b. Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
c. Anatomy of leaf in C3 and C4 plants.
Answer:
a. C3 and C4 pathways:
| C3 pathway | C4 pathway |
| 1. C3 pathway is seen in C3 plants. | 1. C4 pathway is seen in C4 plants. |
| 2. It occurs in mostly by in temperate plants and some tropical plants. | 2. It occurs in subtropical and tropical plants. |
| 3. Kranz anatomy is not shown by the leaves. | 3. Leaves exhibit kranz anatomy. |
| 4. Cells participating will have only type chloroplasts. | 4. Cells participating will have two types of chloroplasts (agranual and granual) |
| 5. Chloroplast dimorphism is not present. | 5. Chloroplast dimorphism is present. |
| 6. Only Calvin cycle occurs. | 6. C4 pathway in mesophyll cells and Calvin cycle in bundle sheath cells takes place. |
| 7. The primary CO2 acceptor is RuBP (5C). | 7. The primary CO2 acceptor is PEP(C3) |
| 8. Less efficient in utilising the atmospheric CO2 | 8. More efficient in utilising the atmospheric CO2 |
| 9. Photorespiration is very high. | 9. Photo respiration is not detectable. |
| 10. The optimum temperature for this path-way is 15°C-25°C. | 10. The optimum temperature for this pathway is 30°C-45°C. |
| 11. Photosynthetic yield is low to average. | 11. Photosynthetic yield is high. |
| 12. For the synthesis of one glucose mole, 18 ATP are required. | 12. For the synthesis of one glucose mole, 30 ATP are required. |
| 13. Water use efficiency is low. | 13. Water use efficiency is high. |
| 14. CO2 compensation point is very high. | 14. CO2 compensation point is low. |
b. Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
| Cyclic Photophosphorylation | Non Cyclic Photophosphorylation |
| 1. Only one photosystem (PSI) is involved. | 1. Two photo systems (PSI & PSII) operate simultaneously in series. |
| 2. Utilises only longer wave length of light. | 2. Utilises both longer and shorter wave lengths of light. |
| 3. Electrons move fn a closed circle. | 3. Electrons move in a zig-zag manner (Z- scheme) |
| 4. Photolysis of water does not occur, hence no O2 is evolved. | 4. Water is oxidised, thus oxygen is evolved. |
| 5. Process is not inhibited by DCMV. | 5. Process is inhibited by DCMV. |
| 6. Only one ATP is formed without any NADPH. | 6. Two ATP moles are formed along with one NADPH. |
c. Anatomy of leaf in C4 and C4 plants:
| Anatomy of C4 leaf | Anatomy of C4 leaf |
| 1. Leaves does not show kranz anatomy. 2. Chloroplasts are only one type. 3. Chloroplast dimorphism is not seen. |
1. Leaves show kranz anatomy. 2. Chloroplasts two types (agranular and granular) 3. Chloroplasts show dimorphism. |
Question 10.
Cyanobacteria and some other photosynthetic bacteria do not have chloroplasts. How do they conduct photosynthesis?
Answer:
- In bacteria like chlorobium and chromatium – a type of chlorophyll called chlorobium chlorophyll is present. It conducts photosynthesis.
- In bacterial xanthophyll and phycobilins chlorophyll pigments are present. They conduct photosynthesis in cyanobacteria.
Question 11.
Why photorespiration does not occur in C4 plants?
Answer:
- In C4 plants RuBisCO is present in the bundle sheath cells.
- CO2 concentration is more in bundle sheath cells.
- So there is no possibility for the O2 to bind with RuBisCO.
- Thus photophosphorylation does not occur in C4 plants.
Question 12.
Tomatoes, chillies and carrots are red in colour due to the presence of one pigment. Name the pigment. Is it a photosynthetic pigment?
Answer:
- Carotenoids.
- Carotenoids are photosynthetic pigments, which absorb light rays of different wavelengths and transfers it to Chl ‘a’. They also protect Chl ‘a’ from photo-oxidation.
![]()
Question 13.
If a green plant is kept in dark with proper ventilation, can this plant carry out photosynthesis? Can anything be given as supplement to maintain its growth or survival?
Answer:
- No, It cannot carry photosynthesis.
- Yes, artificial light may be provided.
Question 14.
Photosvnthetic organisms occur at different depths in the ocean. Do they receive qualitatively and quantitatively the same light? How do they adapt to carry out photosynthesis under these conditions?
Answer:
- No, they do not receive qualitatively and quantitatively the same light.
- Diffuse light is received.
Question 15.
In tropical rainforests, the canopy is thick and shorter plants growing below it, receive filtered light. How are they able to carry out photosynthesis?
Answer:
- If the canopy is thick in tropical rain forests, short plans under the trees donot get proper sunlight.
- There is no possibility for the survival of normal herbs. Modified plants like epiphytes may survive.
Question 16.
Why do you believe chloroplast and mitochondria to be semi-autonomous organelle.
Answer:
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain circular DNA. It can replicate.
- Thus these cell organelles are semi-autonomous.
Question 17.
Is it correct to say that photosynthesis occurs only in the leaves of a plant? Besides leaves, what are the other parts that may be capable of carrying out photosynthesis? Justify.
Answer:
- Besides the leaves, the young stems which are green in colour can perform photosynthesis.
- Phylloclades, phyllodes, photosynthetic roots perform photosynthesis.
Question 18.
What can we conclude from the statement that the action and absorption spectrum of photosynthesis overlap? At which wavelengths do they show peaks?
Answer:
- By observing the action spectrum and absorption spectrum we can conclude that maximum absorption by chlorophyll ‘a’ is in the blue and red regions.
- The rate of photosynthesis is also maximum at this regions only.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The first event in photosynthesis is
1) Synthesis of ATP
2) Photoexcitation of chlorophyll
3) Photolysis of water
4) Release of oxygen
Answer:
2) Photoexcitation of chlorophyll
Question 2.
Cell organelle concerned in Photosynthesis is
1) Nucleus
2) Leucoplast
3) Chloroplast
4) Chromoplast
Answer:
3) Chloroplast
Question 3.
Primary source of food on earth is due to
1) Respiration
2) Photosynthesis
3) Transpiration
4) Protein Synthesis
Answer:
2) Photosynthesis
Question 4.
In the Half-leaf experiment, which part of leaf showed positive for starch test?
1) Part in the test tube
2) Exposed part
3) Entire leaf
4) Petiole
Answer:
2) Exposed part
Question 5.
Source of Carbon for Autotrophs is
1) Soil
2) Organic Molecules
3) Carbon dioxide
4) Inorganic Molecule
Answer:
3) Carbon dioxide
Question 6.
Oxygen released during Photosynthesis comes from
1) Water
2) Carbondioxide
3) Carbohydrate
4) O3
Answer:
1) Water
Question 7.
Site of Dark reaction of Photosynthesis is
1) Stroma Lamellae
2) Matrix
3) Grana Lamellae
4) Stroma.
Answer:
4) Stroma.
Question 8.
Chief Pigments found in leaves of higher plants are
1) Chlorophylls
2) Xanthophyll
3) Carotenoiods
4) Phycobilins
Answer:
1) Chlorophylls
![]()
Question 9.
How many turns of Calvin cycle are required to make one molecule of glucose?
1) One
2) Two
3) Three
4) Six
Answer:
4) Six
Question 10.
During Photosynthesis
1) Water gets oxidized and CO2 gets reduced
2) Water gets reduced and CO2 gets oxidized
3) Both H20 and CO2 get reduced
4) Both C2 and CO2 get oxidized
Answer:
1) Water gets oxidized and CO2 gets reduced
Question 11.
Photorespiration is absent in
1) C3 plants
2) C4 Plants
3) Both C3&C4 plants
4) All green plants
Answer:
2) C4 Plants
Question 12.
Plants which show both Calvin and Hatch Slack path ways are
1) C3 plants
2) C4 Plants
3) Both C3&C4 plants
4) Both C4&CAM plants
Answer:
4) Both C4&CAM plants
Question 13.
Carbon fixation in C4 Plants was revealed by
1) Calvin
2) Benson
3) Hatch and Slack
4) Calvin and Benson
Answer:
3) Hatch and Slack
Question 14.
Major limiting factor for photosynthesis is
1) Water
2) Chlorophyll
3) Light
4) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
4) Carbon dioxide
Question 15.
ATP and NADPH in photosynthesis are used during
1) Carboxylation phase
2) Reduction Phase
3) Regeneration Phase
4) Starch synthesis
Answer:
2) Reduction Phase
Question 16.
C4 plant are more efficient in carbon fixation than C3 plants because
1) Carboxylation occurs twice
2) Absence of photorespiration
3) Both 1&2
4) They absorb less CO2
Answer:
3) Both 1&2
Question 17.
The ratio of ATP utilization of CO2 fixation between C3 and C4 plants is
1) 1:1
2) 5:3
3) 3:5
4) 2:3
Answer:
3) 3:5
Question 18.
Photosynthesis is a …………. process
1) Anabolic, exergonic
2) Anabolic, endergonic
3) Catabolic, exergonic
4) Catabolic, endergonic
Answer:
2) Anabolic, endergonic
Question 19.
Photolysis of water takes place in
1) Stroma
2) Thylakoid membrane
3) Lumen of thylakoid
4) Peri plastidial space
Answer:
3) Lumen of thylakoid
Question 20.
Which of the following would not be a limiting factor in photosynthesis
1) O2
2) CO2
3) Chlorophyll
4) Light
Answer:
1) O2
Question 21.
During light phase, ……… are formed
1) ATP and sugar
2) Hydrogen donor, O2 and sugar
3) ATP, Hydrogen donor and O2
4) ATP, O2 and oxidized coenzyme
Answer:
3) ATP, Hydrogen donor and O2
![]()
Question 22.
Most effective light for photosynthesis is
1) Blue
2) Red
3) Violet
4) Green
Answer:
2) Red
Question 23.
Accessory pigments include
1) Chl-b
2) Carotenes
3) Xanthophylls
4) All
Answer:
Question 24.
Identify the True statement regarding Photosynthesis
1) Oxidation of CO2 and reduction of HO2
2) Process which connects the biotic and abiotic world
3) Exergonic process
4) Oxidation of Glucose
Answer:
2) Process which connects the biotic and abiotic world
Question 25.
The Scientist who experimentally proved that oxygen is evolved from water by using isotope technique, is
1) Van Neil
2) Ruben and Kamen
3)RoberHi!l
4) Melvin Calvin
Answer:
1) Van Neil
Question 26.
The correct sequence of How of electrons in the light reaction is
1) PSII, plastoquinone , cytochromes, PSI, ferredoxin
2) PSI, plastoquinone, cytochromes, PSI, ferredoxin
3) PSI, ferredoxin , PSII
4) PSI, plastoquinone cytochromes, PSII, ferredoxin
Answer:
1) PSII, plastoquinone , cytochromes, PSI, ferredoxin
Question 27.
Which one of the following is not a ‘down hill movement’ of electrons in Z-scheme
1) Pheophytin to PSI
2) LHC II to pheophytin
3) Ferrdoxin to NADPH
4) Both 1 & 3
Answer:
2) LHC II to pheophytin
Question 28.
Identify the false statement
1) O2 is evolved from water in green plants
2) O2 is evolved during light reaction of photosynthesis
3) CO2 is reduced during dark reaction of photosynthesis
4) The light dependent ATP synthesis is called oxidative phosphorylation
Answer:
4) The light dependent ATP synthesis is called oxidative phosphorylation
Question 29.
Choose incorrect statement with respect to photosynthesis
1) It is a physico-chemical process
2) Oxygen is evolved as a by product in all photosynthetic organisms.
3) Occurs in unicellular and multicellular photoautotrophs
4) Anabolic and reductive process
Answer:
2) Oxygen is evolved as a by product in all photosynthetic organisms.
Question 30.
A mile stone contribution to the understanding of photosynthesis was made by Cornelius Van Niel, which was based on the studies of
1) Bacteria
2) Algae
3) Angiospermicplant
4) Lower plant
Answer:
1) Bacteria
Question 31.
Moll’s half leaf experiment demonstrates the importance of
1) H2O for photosynthesis
2) Chlorophyll for photosynthesis
3) Light for photosynthesis
4) CO2 for photosynthesis
Answer:
4) CO2 for photosynthesis
![]()
Question 32.
Movement of H+ from lumen to stroma through the Fo portion of ATP ase is
1) According to cone, gradient
2) By simple diffusion
3) By active transport
4) Against cone, gradient
Answer:
1) According to cone, gradient
Question 33.
In non-cyclic e- transport, down hill movement of e- s occurs between
1) P680 and Phephytin
2 ) PSI P700 and A
3) A0 – Fd
4) PS-I – PS-II
Answer:
3) A0 – Fd
Question 34.
Two compounds that accepts both electrons and protons during noncyclic electron transport are
1) Plastosemiquinone and NADP–
2) Plastocyanin and NADP+
3) Plastosemiquinone and plastocyanin
4) P680 and P700
Answer:
1) Plastosemiquinone and NADP–
Question 35.
Isotopes employed to study the process of photosynthesis reaction are
1) C12 & O16
2) N14 & C12
3) C14 & O18
4) N14 & C18
Answer:
3) C14 & O18
Question 36.
Chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in chloroplasts is based on
1) accumilation of £+ ions
2) Proton gradient
3) Accumilation of Na ions
4) Accumilationof Ca2+ ions
Answer:
2) Proton gradient
Question 37.
In which cells of leaf, pyruvate is converted into PEP in C4 pathway
1) Epidermal cells
2) Mesophyll cells
3) Bundle sheathcells
4) 1 & 3
Answer:
2) Mesophyll cells
Question 38.
In calvin cycle, formation of I, 3 Bis PGA from RUBP require
1) ATP
2) NADPH + H+
3) ATP & NADPH + H+
4) FADH2
Answer:
3) ATP&NADPH + H+
Question 39.
Number of ATP molecules utilized in excess in C4 plants when compared to plants to synthesis one glucose molecule is
1) 12
2) 30
3) 18
4) 24
Answer:
1) 12
Question 40.
Bundle sheath cells have following characters except
1) large in size
2) large no.of chloroplasts
3) thick wall impervious to gaseous exchange
4) with intercellular spaces
Answer:
4) with intercellular spaces
Question 41.
Assimilatory power required to reduce one molecule of CO2 in calvin cycle is
1) 18ATP, 12NADPH+ H+
2) 3ATP, 2NADH + H+
3) 3ATP, 2NADPH + H+
4) 18ATP+ 12NADH + H+
Answer:
3) 3ATP,2NADPH + H+
![]()
Question 42.
Tomato and bell pepper are
1) C3 and C4 plants respectively
2) C4 and C3 plants respectively
3) C3 plants
4) C4 plants
Answer:
3) C3 plants
Question 43.
Which of the following statements are true regarding photorespiration?
1) no synthesis of ATP
2) no synthesis of NADPH
3) release of CO2
4) all the above
Answer:
4) all the above
Question 44.
Photorespiration occurs
1) during day time
2) in C3 plants
3) in co-operation with chloroplast, peroxisome & mitochondria
4) all the above.
Answer:
4) all the above.
Question 45.
Which of the following is not related to photorespiration
1) Lysosome
2) Chloroplast
3) Peroxisome
4)Mito chondria
Answer:
1) Lysosome
Question 46.
For every CO2 molecule entering into Calvin cycle, the number of ATP and NADPH required in regeneration phase
1) 1 ATP + 1 NADPH
2) 2ATP + 2NADPH
3) 2ATP + 1 NADPH
4) 1ATP + 0 NADPH
Answer:
4) 1ATP + 0 NADPH
Question 47.
The net requirement of assimilatory power for the formation of 6 Hexose molecules in maize plant is
1) 72 ATP, 48 NADPH
2) 72 ATP, 60 NADPH
3) 108 ATP, 72 NADPH
4) 180 ATP, 72 NADPH
Answer:
4) 180 ATP, 72 NADPH
![]()
Question 48.
Which of the following is not a product of light reaction of photosynthesis?
1) ATP
2) NADH
3) NADPH
4) Oxygen
Answer:
2) NADH