Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Important Questions 3rd Lesson Enzymes which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2ndd Year Botany Important Questions 3rd Lesson Enzymes
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
How are prosthetic groups different form co-factors?
Answer:
- Prosthetic groups are organic compounds that are tightly bound to the apoenzyme.
- But cofactors are non-protein part of holoenzymes which are bound to the enzyme, to make the enzyme catalytically active.
Question 2.
What is meant by ‘Feedback inhibition’?
Answer:
Feed back inhibition is a cellular control mechanism in which an enzyme’s activity is inhibited by the enzyme’s end product.
![]()
Question 3.
Why are ‘oxido reductases’ so named?
Answer:
These enzymes catalyse ‘oxido reduction’ between two substrates S and S’. Hence they are called Oxido reductases.
Ex: S reduced + S’ oxidised → S oxidised + S’ reduced
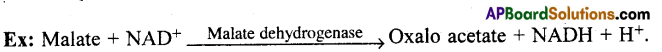
Question 4.
Distinguish between apoenzyme and cofactor. [MAR-14] [TS MAY-17] [TS 20]
Answer:
- Apoenzyme: Protein part of a holo enzyme is called apoenzyme. It is chemically proteinaceous.
- Co-factor: Non-protein part of a holo enzyme is called co-factor.
It makes the enzyme catabolically active.
Question 5.
What are competitive enzyme inhibitors? Mention one example.
Answer:
- The inhibitor that resembles the substrate molecules and prevents the activity of the enzyme are called competitive inhibitors.
- Ex: Malonic acid resembles the substrate succinate and it inhibits the succinic dehydrogenase.
Question 6.
What are non-competitive enzyme inhibitors? Mention one example.
Answer:
- The inhibitors having no structural similarity with the substrate and binding to an enzyme of locations other than the active sites so that the globular structure of the enzyme is changed are called non-competitive enzyme inhibitors.
- Ex: Metal ions of Copper, Mercury.
Question 7.
What do the four digits of an enzyme code indicate?
Answer:
- The four digit code of enzyme helps in identifying the individual enzyme.
- Ex: Enzyme Code (E.C) 2.7.1.2 refers Glucose-6-phospho transferase.
- The first digit indicates the major class of the enzyme.
- The second digit indicates sub-class of the enzyme.
- The third digit indicates sub-sub-class of the enzyme
- The fourth digit indicates the serial number of the enzyme in that sub-sub-class.
Question 8.
Who proposed ‘Lock and Key Hypothesis” and induced fit hypothesis? [ TS MAY-22|
Answer:
- “Lock and key hypothesis” was proposed by Emil Fisher.
- “Induced fit hypothesis ” was proposed by Daniel. E.Koshland
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain bow pH effects enzyme activity with the help of a graphical representation.
Answer:
- The graph of’pH versus enzyme activity’ takes the shape of Parabola.
- Enzymes show their highest activity at a particular pH called optimum pH. This occurs at the vertex of the parabola.
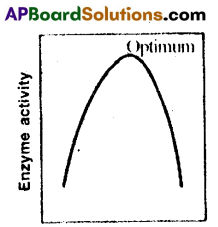
- From the graph it is clear that, the enzyme activity declines both below and above the optimum value.
- Most of the enzymes function near neutral pH.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the importance of [ES] complex formation.
Answer:
The formation of [ES] complex is essential for catalysis.
- Each enzyme has an active site.
- The substrate binds to that active site and forms an enzyme-substrate complex.
- This complex is short-lived and dissociates into its products.
- The enzyme remains unchanged.
- An enzyme product complex is formed.
- The enzyme releases the products and gets free.
- Now the enzyme searches for another substrate molecule.
Question 3.
Write briefly about enzyme inhibitors. [AP MAY 17][AP\TS MAR-17] [AP MAR-15,19]
Answer:
Enzyme Inhibitors: These are the chemicals that stop the activity of the enzymes. Those
chemicals are called “inhibitors” and the process is called inhibition. The inhibitors are three types. They are a) Competitive inhibitors b) Non-competitive inhibitors c) Feed back inhibitors.
a) Competitive inhibitors: The inhibitors that resemble the substrate molecules and prevent the activity of the enzyme are called competitive inhibitors.
Ex: Malonic acid resembles the substrate succinate and it inhibits the succinic dehydrogenase.
b) Non-competitive inhibitors: The inhibitors having no structural similarity with the sub-strata and binding to an enzyme of locations other than the active sites so that the globular structure of the enzyme is changed are called non-competitive enzyme inhibitors.
Ex: Metal ions of Copper, Mercury.
c) Feedback inhibitors: Feedback inhibition is a cellular control mechanism in which an enzyme’s activity is inhibited by the enzyme’s end product.
It is a part of homeostatic control metabolism.
Question 4.
Explain different types of cofactors. [AP,TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-19] [AP MAR-16]
Answer:
The non-protein part of the holo enzyme is called co-factor.
The co-factors are three types.
a) Prosthetic groups
b) Co-enzymes
c) Metal ions.
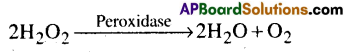
a) Prosthetic groups: These are organic compounds that are tightly bound to the apoenzyme Ex: Peroxidase is the enzyme which breaks hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
In this regard, “Haem” in the prosthetic group which is tightly bound to the enzyme peroxidase.
b) Co-enzymes: These are organic compounds, which are loosely attached to the apoenzyme. These co-enzymes are derived from water-soluble vitamins.
Ex: Both co-enzymes NAD and NADP contain the vitamin niacin.
c) Metal ions: A number of enzymes require metal ions for their activity. They form coordination bonds with side chains at the active site.
Ex: Zinc is the co-factor for the proteolytic enzyme carboxypeptidase.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write an account oF the classification of enzymes.
Answer:
Enzymes are divided into 6 classes as follows:
1) Oxidoreductases/ dehydrogenases: Enzymes that catalyze oxidoreduction between two substrates S and S’.
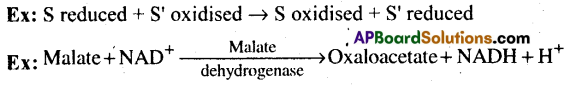
2) Transferases: These enzymes catalyze the transfer of a group G (other than hydrogen) between a pair of substrates S and S’.
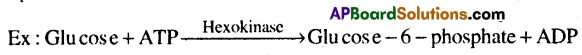
3) Hydrolases: These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of ester, ether, peptide, glycosidic, C-C, C- haltde or P-N bonds.

4) Lyases: These enzymes catalyze removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds.
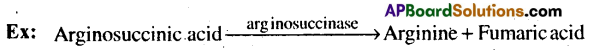
5) Isomerases: These enzymes include all enzymes catalysing interconversion of optical, geometrical or positional isomers.
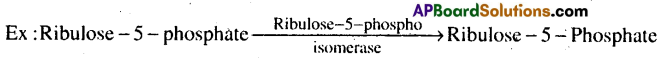
6) Ligases: These enzymes catalyse the linking together of 2 compounds, i.e joining of C-0, C-S, C-N, P-0 bonds.
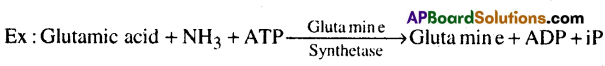
Question 2.
Explain the mechanism of enzyme action. [AP 20]
Answer:
1) Each enzyme (E) has substrate (S) binding site in its molecule with in a given cleft.
2) The substrate has to diffuse towards the active site leading to formation of an enzyme-substrate complex with in a short time.
3) This transition state structure soon dissociates into enzyme product complex.
4) The energy required for the substrate to get converted into products is called activation energy which is available from heat, ATP’s etc.
![]()
5) The structure of substrate gets transformed into the structure of products.
E+S → ES → EP → E+P
6) When we represent this pictorially through a graph by taking potential energy on Y-axis and progress of reaction on X-axis, we notice the energy level difference between ‘S’ and ‘P’.
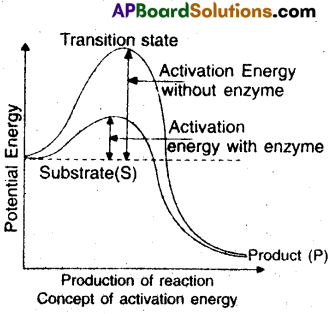
7) If ‘P’ is at lower level than S, it is an exothermic reaction. One need not supply energy to form the product.
8) If ‘P’ has higher energy level then ‘S’ it is an endothermic or energy-requiring reaction.
9) Then ‘S’ has to go through a much higher energy state or transition state.
10) Each enzyme E has a substrate (S) binding site in its molecule so that a highly reactive enzyme-substrate complex (ES) is produced.
11) This complex is short-lived a dissociates into products and the unchanged enzyme with an intermediate formation of the enzyme product complex
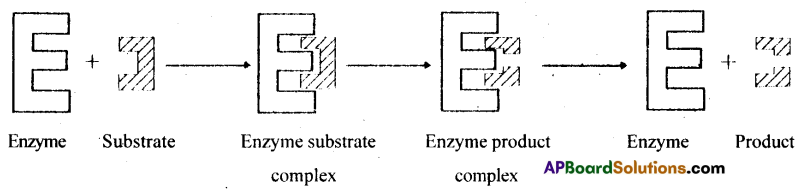
The formation of ES complex has been explained with lock & key hypothesis by Emil fisher and much later with induced bit hypothesis by Daine E.Koshland
The catalytic cycle of an enzyme action can be described under four steps:
- The substitute binds to active site of the enzyme, fitting into the active site.
- The binding of the substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape, fitting more tightly around the substrate.
- The active site of an enzyme now in close proximity to the substrate, breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate and the new enzyme product complex is formed.
- The enzyme releases the products of the reaction and free enzyme is ready to bind another molecule of the substrate and runs through the catalytic cycle once again.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The vitamin present in coenzymes like NAD and NADP is
1) Thiamine
2) Riboflavin
3) Naicin
4) Biotin
Answer:
3) Naicin
Question 2.
Select the correct statement
1) Enzymes denature at low temperature
2) All proteins are enzymes but not all enzymes are proteins
3) Km value represents the inverse measures the affinity of the enzyme for a substrate
4) A single enzyme can catalyse the different types of reactions on different substrates
Answer:
3) Km value represents the inverse measures the affinity of the enzyme for a substrate
Question 3.
Transient phenomenon involves the
1) formation of enzyme inhibitor complex
2) formation of Enzyme Substrate complex
3) formation of active sites
4) release of product from the enzyme
Answer:
2) formation of Enzyme Substrate complex
Question 4.
Ribozyines are
1) Non proteinaceous part of an enzyme
2) Nucleic acids behave as enzymes
3) Proteins & nucleic acids behave as enzymes
4) secondary structure of protein
Answer:
2) Nucleic acids behave as enzymes
Question 5.
Active sites of enzymes appear in
1) Primary structure of protein
2) secondary structure of protein
3) tertiary structure of protein
4) quartemary structure of protein
Answer:
3) tertiary structure of protein
Question 6.
Nucleic acids which behave like enzymes are
1) Ribose acid
2) Ribozymes
3) Catalyst
4) Deoxyribose acid.
Answer:
2) Ribozymes
![]()
Question 7.
Hydrolysis of starch into glucose is a
1) Inorganic chemical reaction
2) Organic chemical reaction
3) Inorganic physical reaction
4) Organic physical reaction
Answer:
1) Inorganic chemical reaction
Question 8.
Rates of physical & chemical processes are influenced by
1) temperature
2) pressure
3) light
4. CO2
Answer:
1) temperature
Question 9.
In order to control bacterial pathogens, often-used inhibitors are
1) Feed back inhibitors
2) Competetive inhibitors
3) Non-competetive inhibitors
4) Pro-inhibitors
Answer:
2) Competetive inhibitors
Question 10.
The prosthetic group which is a part of the active site of the enzyme is
1) globin
2) globulin
3) haem
4) protein
Answer:
3) haem
Question 11.
The essential chemical components of many coen/.ymc are
1) Vitamins
2) Minerals
3) Lipids
4) Proteins
Answer:
1) Vitamins
Question 12.
A non-proteniaceous enzyme is
1) Ribozyme
2) Coenzyme
3) Apoenzyme
4) Conjugated enzyme
Answer:
2) Coenzyme
Question 13.
Feedback inhibition of enzyme action is affected by
1) Enzyme
2) Substrate
3) End product
4) Intermediate product
Answer:
3) End product
Question 14.
Glutamine synthetase is an example for
1) Isomerases
2) Ligases
3) Transferases
4) Hydrolases
Answer:
2) Ligases
Question 15.
Chemically enzymes are
1) Fats
2) Proteins
3) Aminoacids
4) Hydrocarbons
Answer:
2) Proteins
Question 16.
A true statement about enzymes
1) All enzymes are proteins
2) All proteins without active sites are called enzymes
3) All enzymes are non proteins
4) All enzymes are minerals
Answer:
1) All enzymes are proteins
Question 17.
If three enzymes are physically A, chemically B and functionally C then A, B,C are respectively
1) Colloids, Proteins, Nucleic acids
2) Nucleic acids, Proteins, Colloids
3) Colloids, Proteins, Catalysts
4) Colloids, Nucleic acids, Catalysis
Answer:
3) Colloids, Proteins, Catalysts
Question 18.
An enzyme can perform is catalytic activity in structure
1) Primary
2) Secondary
3) Tertiary
4) Quartemary
Answer:
3) Tertiary
Question 19.
Active site is a
1) part of inactive to which substrate binds
2) cleft or crevice on DNA double helix
3) cleft or crevice on enzyme into which substrate fit
4) part of anti body
Answer:
3) cleft or crevice on enzyme into which substrate fit
Question 20.
Enzymes with two sites are called
1) Apoenzymes
2) Holoenzymes
3) Allosteric enzymes
4) Conjugate enzymes
Answer:
2) Holoenzymes
![]()
Question 21.
Enzymes isolated from organisms which live in extreme high temperatures (Fix: Hot vents and sulphur springs) show catalytic activity in a rage of
1) 40° – 60°C
2) 60° – 80°C
3) 80°-90°C
4) 40°-45°C
Answer:
3) 80°-90°C
Question 22.
Identify the false statement regarding enzymes
1) They are specific
2) They are made of globular proteins
3) They are most active at maximum temperature
4) They are most active at optimum temperature
Answer:
3) They are most active at maximum temperature
Question 23.
Kibozyme is
1) RNA with enzyme activity
2) RNA without sugar
3) RNA without phosphate
4) RNA without extra phosphate
Answer:
3) RNA without phosphate
Question 24.
Enzymes are different from catalysts in
1) being proteinaceous
2) not used up in reaction
3) functional at high temperature
4) having high rate of diffusion
Answer:
1) being proteinaceous
Question 25.
The number of carbonic acid molecules formed every second in the presecc of carbonic anhydrase enzyme is
1) 5 Lakhs
2) 3 Lakhs
3) 6 Lakhs
4) 2 Lakhs
Answer:
3) 6 Lakhs
Question 26.
Which of the following options represents correct set of steps for an ‘enzyme catalysed reaction’
1) E+S → ES → [EP] → E+P
2) E → ES → EP
3) S → P
4) 1 and 3
Answer:
1) E+S → ES → [EP] → E + P
Question 27.
At low temperature, an enzyme is
1) Slightly activated
2) Killed
3) Coagulated
4) Inactivated
Answer:
4) Inactivated
Question 28.
When the temperature is increased by lrt”C the rate of a reaction increases
1) two times
2) three times
3) four times
4) remains unchanged
Answer:
1) two times
Question 29.
Which part of enzyme determine specificity of enzyme?
1) Inorganic factor
2) Co enzyme
3) Protein part
4) Holo enzyme
Answer:
3) Protein part
Question 30.
The catalytic efficiency of two different enzymes can be compared by .
1) pH optimum value
2) Km value
3) Molecular size of the enzyme
4) Molecular weight of enzyme
Answer:
2) Km value
Question 31.
A competetivc inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase is
1) a – Keto glutarate
2) Malate
3) Malonate
4) Oxaloacetate
Answer:
3) Malonate
![]()
Question 32.
Lock and Key model of enzyme action was proposed by
1) Paul fields
2) D.D. Woods
3) Emil fischer
4) Koshland
Answer:
3) Emil fischer
Question 33.
A cofactor which is tightly binded with coordinated bond to the Apoenzyme, is
1) Co enzyme
2) Prosthetic group
3) Inorganic cofactor
4) Apoenzyme
Answer:
3) Inorganic cofactor
Question 34.
The activity of an enzyme can be affected by a change in the conditions which can alter the
1) primary structure
2) Secondary structure
3) Teritary structure
4) All the above
Answer:
3) Teritary structure
Question 35.
Enzymes catalysing removal of groups & formation of double bond are
1) Transferases
2) Ligases
3) Lyases
4) Oxidoreductases
Answer:
3) Lyases
Question 36.
Select the type of enzyme involved in the reaction: S -G + S’ → S + S’-G
1) Lygase
2) Liase
3) Isomerase
4) Transferase
Answer:
4) Transferase
Question 37.
A working combination of an apoenzyme and a co-enzyme is termed as
1) prosthetic group
2) enzyme-substrate complex
3) holoenzyme
4) enzyme product complex
Answer:
3) holoenzyme
Question 38.
The enzyme needed in biological systems for joining two molecules is called
1) lyases
2) ligases
3) isomerases
4) hydrolases
Answer:
2) ligases
Question 39.
A substance unrelated to substrate but capable of reversibly changing activity of enzyme by binding to a site other than active site is called
1) Competitive inhibitor
2) Noncompetitive inhibitor
3) CatalyStic inhibitor
4) Allosteric modulator / inhibitor
Answer:
4) Allosteric modulator / inhibitor
Question 40.
Lock and key theory (Template theory) of enzyme action indicates
1) Enzyme specificity
2) Turnover number
3) Inhibitors
4) Enzyme classification
Answer:
1) Enzyme specificity
Question 41.
The inorganic part of enzyme is known as
1) Holoenzyme
2) Inorganic cofactor
3) Activator
4) b and c
Answer:
2) Inorganic cofactor
Question 42.
Naicin is a vitamin present in the coenzyme of
1) NAD+
2) NaDP+
3) FAD+
4) 1 and 2
Answer:
4) 1 and 2
Question 43.
Feed back inhibition of an enzymatic reaction is caused by accumulation of
1) Substrate
2) Enzyme
3) End product
4) Rise temperature
Answer:
3) End product
![]()
Question 44.
According to ‘induced fit theory of enzyme action’
1) substrate induces conformation change in enzyme
2) substrate changes its shape after binding
3) conformational change takes place in substrate
4) there is no conformation change in enzyme
Answer:
1) substrate induces conformation change in enzyme
Question 45.
Km value represents
1) Affinity of enzyme for substrate
2) Affinity of enzyme for product
3) Affinity of enzyme for inhibitor
4) Affinity of enzyme for reactants
Answer:
1) Affinity of enzyme for substrate
Question 46.
Feed back inhibition is due to accumulation of
1) Substrates
2) Products
3) Metal ions
4) Pathogens
Answer:
2) Products