Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions 5th Lesson Locomotion and Reproduction in Protozoa which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions 5th Lesson Locomotion and Reproduction in Protozoa
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Draw a labelled diagram of T.S of flagellum.
Answer:
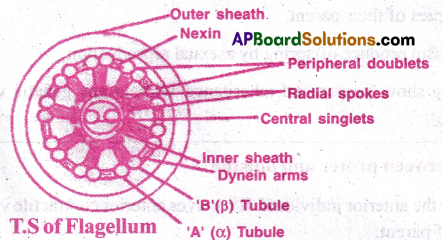
Question 2.
List any two differences between a flagellum and cilium. [APM-17,19,20] [TS M-16,18,20]
Answer:
- Flagellum is long whip like locomotor organelle whereas Cilium is small hair like structure.
- Flagellum performs undular movement and cilium performs pendular movement.
- Flagellum helps in locomotion where as cilium helps in locomotion, food collection, movement of materials and also sensory.
![]()
Question 3.
What are dynein arms? What is their significance? [TSM-19]
Answer:
- Dynein arms: In cross section of flagellum , the ‘A’ tubule of each peripheral doublet bears
paired arms along its length. They are called dynein arms. - Significance: Dynein arms bring about sliding movement of microtubules utilising ATP so that flagellum or celium bends.
Question 4.
What is a kinety? [AP M-22][AP, TS M-19][TS May-17][AP, TS M-16] [IPE-14]
Answer:
- A longitudinal row of kinetosomes and their inter connecting kinetodesmata are collectively called kinety.
- Kinety is a part of infra ciliary system of ciliates.
Question 5.
Distinguish between synchronous and metachronous movements.
Answer:
There are two different types of movements of cilia.
- Synchronous movement: The cilia in transverse row beat once at a time in one direction.
- Metachronous movement: The cilia in a longitudinal row beat one after another.
- It looks like winds passing over paddy field producing waves.
Question 6.
Why do we refer to the offspring, formed by asexual method of reproduction, a clone?
[APM-19,20][TSMar-17]
Answer:
- The term clone is used to describe morphologically and genetically similar individuals which are exact copies of their parent.
- Lower organism produce offspring by asexual reproduction.
- The offspring show ‘uniparental inheritance’ without any genetic variation, hence they are called a clone.
Question 7.
Distinguish between proter and opisthe. [AP,TS M-15,17]
Answer:
- The proter is the anterior individual. It receives anterior contractile vacuole, cytopharynx and cytostome of parent.
- The opisthe is the posterior individual. It receives posterior contractile vacuoles and develop other organelle.
Question 8.
How is sexual reproduction advantageous in evolution?
Answer:
- Sexual reproduction results in the formation zygote by the union of female and male gametes.
There is genetic recombination. - The offspring are not photocopies of their parents because of variations.
- Variations accumulate in course of time, generation after generation, leading to the formation of new species. So sexual reproduction is the basis for evolution.
Question 9.
Distinguish between lobopodium and filopodium.Give an example to each of them.
Answer:
- Blunt finger like pseudopodia are called Lobopodia. Ex: Amoeba, Entamoeba. [APM-15,16,17]
- Long and fibre like pseudopodia are called Filopodia. Ex: Euglypha [TS M-17,20]
Question 10.
Define conjugation with reference to ciliates. Give two examples. [AP,TS-18][TSM-15]
Answer:
- Conjugation is a temporary union between two senile ciliates, that belong to different mating types, for the exchange of nuclear material and reorganization, to restore vigour and vitality.
- Ex: Paramecium and Vorticella.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name the system that controls the fastest swimming movement of protozoans and write its components.
Answer:
Fastest protozoans are ciliates. The system that helps in locomotion is infraciliary system
Infraciliary system:
- It is located in the ecto plasm below the pellicle of ciliates.
- It consists of kinetosomes, kinetodesmata and motorium.
- Kinetosomes are arranged in longitudinal and transverse rows.
- Kinetodesmal fibrils are connected to kinetosomes and run along right side of each row of kinetosomes as a cord of fibres called kinetodesmata.
- A longitudinal row kinetosomes together with connected kinetodesmata is called a kinety.
- All the kineties together form the infraciliary system.
- The system is connected to a motorium
- The infraciliary system and motorium form the neuro motor system which controls and coordinates the ciliary movement.
Question 2.
Write the mechanism of bending of flagellum and explain effective and recovery strokes.
Answer:
Mechanism of Bending movement of Flagellum:
- Bending movement of flagellum is brought about by sliding of microtubules by dynein arms using ATP.
- Dynein anns show a complex cycle of movements.
- They are the sites of ATPase activity.
- The dynein arms of doublet attach to the adjacent doublet and pull it.
- The arms are released and reattached to the next site and again pull.
- A series of such pullings bend the flagellum.
- Side wise- lash movement: This movement consists of effective and recovery strokes.
- Effective Stroke: Flagellum becomes rigid. It starts bending to one side beating against water. The beating is at right angles to the body axis. The organism moves forward.
- Recovery StrokesrFlagellum becomes soft and moves backwards to its original position. It is called recovery’ stroke.
Question 3.
What are lateral appendages? Based on their presence and absence, write the various types of flagella giving at least one example for each type. [AP,TS M-15, 17]
Answer:
Lateral appendages: One or two or many rows of short, lateral hair like fibrils found on some flagella are called lateral appendages or mastigonemes. Based on the arrangement of mastigonemes five types of flagella are recognised.
Types of Flagella:
- Stichonematic: This flagellum bears one row of mastigonemes. Ex: Euglena, Astasia.
- Pantonematic: The flagellum has two or more rows of mastigonemes .
Ex: Peranema and Monas - Acronematic: There are no mastigonemes on this flagellum. The tip of axoneme is naked without any sheath Ex: Chlamydomonas and polytoma
- Pantacronematic: The flagellum has two or more rows of mastigonemes and a naked terminal filament Ex: Urceolus
- Anematic (simple) : Mastigonemes are absent. There are no terminal filaments.
Ex: Chilomonas and cryptomonas
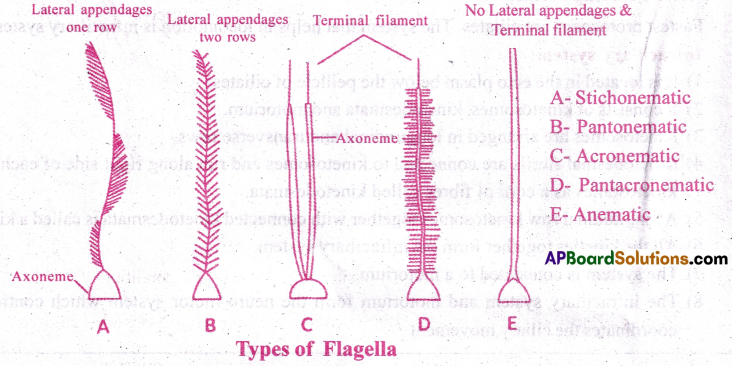
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the process of transverse binan’ fission in Paramecium. [AP,TS M-19]
Answer:
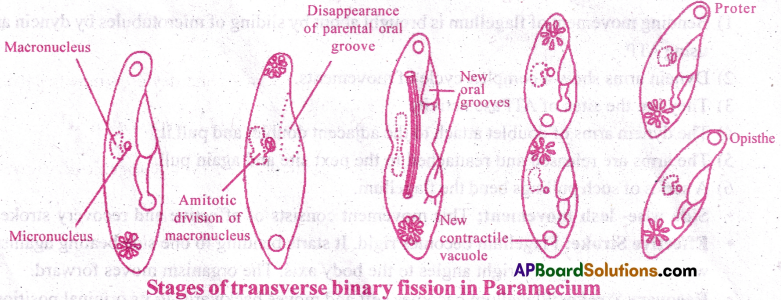
Binary fission in Paramecium: [TSM-20]
- Paramecium undergoes transverse binary fission during favourable conditions.
- Before binary fission, it stops feeding and the oral groove disappears.
- The micro nucleus divides in to two by mitosis.
- The macro nucleus divides into two by amitosis.
- A transverse constriction appears in the middle.
- It deepens and divides the parent into two daughter individuals.
- The anterior is called proter and posterior is opisthe.
- Each daughter gets one contractile vacuole ofthe parent and a second vacuole is newly formed in both.
- Opisthe receives the posterior contractile vacuole along with macro and micro nuclei.
- The missing organelle are newly developed by both.
- Binary fission is completed in two hours.
- In a day, the paramecium can produce 4 generations of offspring.
- The transverse binary fission is called homothetogenic fission (at right angle to kineties) and perkinetal (across kinetia).
Question 5.
Describe the process of longitudinal binary fission in Euglena.[TS M-16][IPE-14]
Answer:
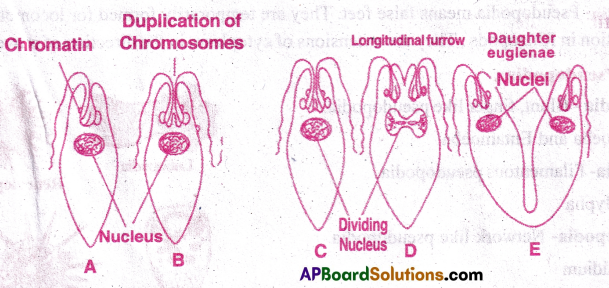
Binary fission in Euglena:
- Euglena undergoes longitudinal binary fission during favourable conditions.
- During this process the stigma, paraflagellar body and contractile vacuoles disappear.
- Nucleus, basal granules, chromatophores and cytoplasm undergo division.
- A longitudinal groove appears in the central part of anterior end.
- It gradually extends to posterior and divides the organism into two.
- One daughter Euglena retains parental flagella, the other daughter develops new flagella.
- Stigma, paraflagellar body and contractile vacuole develop freshly in new individuals.
- As daughter forms look like mirror images, the fission is called ‘symmetrogenic division’.
Question 6.
Write a short note on multiple fission.
Answer:
Multiple Fission:
- Multiple fission is the division of parent into many daughter individuals.
- Multiple fission generally takes place in unfavourable conditions.
- The nucleus undergoes repeated mitotic divisions.
- Many daughter nuclei are formed.
- The cytoplasm divides into as many number of bits as there are nuclei.
- Each bit of cytoplasm surrounds a nucleus forming many small individuals.
- Different forms of multiple fissions are schizogony, male gametogony and sporogony in plasmodium, sporulation in Amoeba.
Question 7.
Give an account of pseudopodia. [AP M-19, 20, 22]
Answer:
Pseuodpodia: Pseudopodia means false feet. They are temporarily formed for locomotion and food collection in Rhizopods . They are extensions of cytoplasm in the direction of movement.
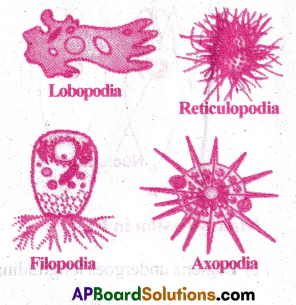
Types of Pseudopodia:
- Lobopodia – Blunt, finger like pseudopodia.
Ex: Amoeba and Entamoeba - Filopodia- Filamentous pseudopodia.
Ex: Euglypha - Reticulopodia- Network like pseudopodia.
Ex: Elphidium - Axopodia or Heliopodia – Ray like pseudopodia Ex: Actinophrys
Process of formation:
- Pseudopodium is formed by conversion of gel cytoplasm to sol cytoplasm and vice versa (Sol to gel)
- Sol-gel theory is the most accepted theory.
- Allen’s theory ‘Front contraction’ or ‘fountain zone’ theory is more appropriate.
- Actin and myosin molecules also have a role.
- Pseudopodial movement or amoeboid movement is performed by Amoeba, Entamoeba macrophages, neutrophils etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Give an account of the ultra structure of an axoneme.
Answer:
1) Ultra structure of Axoneme: Axoneme is the central microtubular structure of flagellum or cilium. It surrounded a membrane which is continuous with plasma membrane.
2) Microtubules:Axoneme has 2 central tubules (singlets) and 9 peripheral doublets (2 tubules). The tubules are formed of protein tubulin. Each peripheral doublet has two tubules A &B. Tubule A is small and complete. B Tubule is large and incomplete. The doublets are interconnected by linkers called nexins.
3) Dynein arms: A pair of arms along the length of tubule are present attached to tubule A. They are the dynein arm. They are protein motor molecules. They are made of the protein dynein. They help in bending of flagellum.
4) Outer Sheath: Around the peripheral doublets there is other sheath.
5) Radial spokes: These are elastic fibres that connect the inner sheath to the ‘A’ tubule.
6) Basal granules (kinetosome/ basal body/ blepharoplast): Basal granule is a modified centrioles. It is formed of 9 triplet tubules ABC.
A and B are continued as peripheral doublets. ‘C’ terminates at pellicle.
7) Mastigonemes: There are short hair like fibrils attached to the side of flagellum.
Question 9.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Euglena.
Answer:
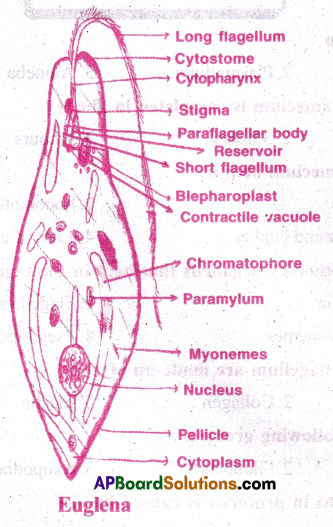
Question 10.
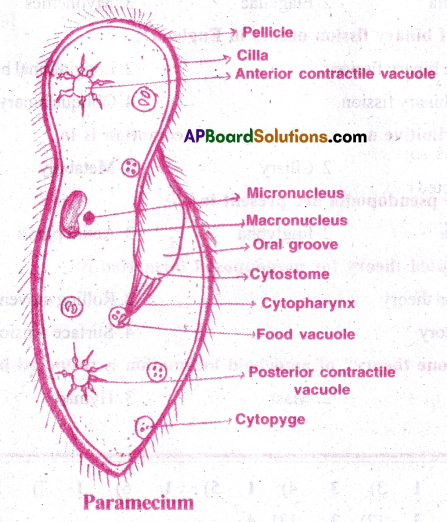
Draw a neat diagram of Paramecium and label its important structures/components. [AP M-22]
Answer:
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Anisogamy is seen in
1. Monocystis
2. Plasmodium
3. Amoeba
4. Paramecium
Answer:
2. Plasmodium
Question 2.
Binary fission in Paramecium is completed in about
1. 2 hours
2. 3 hours
3. 4 hours
4. 5 hours
Answer:
1. 2 hours
Question 3.
Conjugation in Paramecium help in
1. Metamorphosis
2. Locomotion
3. Restoration of vigour and vitality
4. Loss of chromosomal balance
Answer:
3. Restoration of vigour and vitality
![]()
Question 4.
In protozoa, the locomotory organells that help in the ingestion of food are
1. Pseudopodia and cilia
2. Flagella and cilia
3. Pseudopodia and myonemes
4. Pseudopodia and flagella
Answer:
1. Pseudopodia and cilia
Question 5.
The microtubules of flagellum are made up of
1. tubulin
2. Collagen
3. Elastin
4. Fibrin
Answer:
1. tubulin
Question 6.
The odd one in the following group is
1. Undulipodia
2. Filopoaia
3. Axopodia
4. Lobopodia
Answer:
1. Undulipodia
Question 7.
The zig-zag movement in protozoa is caused by
1. Pseudopodia
2. Flagellae
3. Myonemes
4. Cilia
Answer:
3. Myonemes
Question 8.
Paddle movement is exhibited by
1. Pseudopodia
2. Flagellae
3. Myonemes
4. Cilia
Answer:
4. Cilia
Question 9.
What type of binary fission occurs in Euglena?
1. Transverse binary’ fission
2. Longitudinal binary fission
3. Tangential binary fission
4. Oblique binary’ fission
Answer:
2. Longitudinal binary fission
Question 10.
The most primitive and slowest type of locomotion is in
1. Flagella
2. Ciliary
3. Metaboly
4. Amoeboid
Answer:
4. Amoeboid
![]()
Question 11.
Sun ray like pseudopodia are present in
1. Globigerina
2. Euglypha
3. Actinophrys
4. Entamoeba
Answer:
3. Actinophrys
Question 12.
Widely accepted theory for pseudoposial formation is
1. Contraction theory
2. Rolling movement
3. Sol-gel theory
4. Surface tension theory
Answer:
3. Sol-gel theory
Question 13.
“Fountain zone theory” of amoeboid locomotion is proposed by
1. Pantin
2. Mast
3. Flyman
4. Allen
Answer:
4. Allen
Question 14.
The arms of mircotubules attached to outer doublets are made of
1. Flagellin
2. Tubulin
3. Dynein
4. Fibroin
Answer:
3. Dynein
Question 15.
Type of flagellum without terminal filament and lateral appendages is present in
1. Urceolus
2. Peranema
3. Astasia
4. Chilomonas
Answer:
4. Chilomonas
Question 16.
Infraciliary system is located in
1. Ectoplasm of ciliates
2. Endoplasm of ciliates
3. Ectoplasm of flagellates
4. Endoplasm of ciliates
Answer:
1. Ectoplasm of ciliates
![]()
Question 17.
Infraciliary system of Paramoecium consists of
1. Neurofibrils + Motorium
2. Neurofibrils + Kinetosomes
3. Kinetia + Neuromotor system
4. Kinetodesmata only
Answer:
2. Neurofibrils + Kinetosomes
Question 18.
Cilia and Flagella are named as undulopodia by
1. Lamarck
2. Hyman
3. Berthold
4. Mast
Answer:
2. Hyman
Question 19.
Kinety is
1. Longitudinal row of kinetosomes and interconnecting kinetodesmata in ciliates
2. Longitudinal row of kinetosomes and inter connecting kinetodesmata in flagellates
3. Horizontal row ofkinetosomes and interconnecting kinetodesmata in ciliates
4. Horizontal row ofkinetosomes and interconnecting kinetodesmata in flagellates
Answer:
1. Longitudinal row of kinetosomes and interconnecting kinetodesmata in ciliates
Question 20.
Undulation from base to tip causes pushing force which is like
1. the propeller of a boat
2. the propeller of an aeroplane
3. 1 and 2
4. gyration
Answer:
1. the propeller of a boat
Question 21.
If undulation passes from tip to base, flagellate
1. moves forwards
2. moves backwards
3. rotates on its own axis
4. rotates in opposite direction
Answer:
1. moves forwards
Question 22.
The sequential movement of cilia in longitudinal row in Paramecium is
1. Synchronous movement
2. Metachronous movement
3. Gliding movement
4. Undulation in a cilium
Answer:
2. Metachronous movement
Question 23.
Small zig zag movement in the protozoans caused by contracation and relaxation of myonemes is called –
1. Gliding movement
2. Gyration
3. Amoeboid movement
4. Metaboly
Answer:
1. Gliding movement
Question 24.
Asexual reproduction during favourable conditions in Amoeba takes place by
1. Conjugation
2. Sporulation
3. Binary fission
4. Regeneration
Answer:
3. Binary fission
Question 25.
The organelle that divides in binary fission of Euglena are
1. Cytopharynx
2. Basal granules
3. Contractile vacuoles
4. Stigmas
Answer:
2. Basal granules
![]()
Question 26.
During longitudinal binary fission which structure is retained by one daughter Euglena and other develops new one
1, Reservoir
2. Nucleus
3. Chromatophore
4. Flagella
Answer:
4. Flagella
Question 27.
Photoreceptor organelle of Euglena is
1. Stigma
2. Paraflagellar body
3. tentacles
4. Ocelli
Answer:
2. Paraflagellar bod
Question 28.
Homothetogenic binary fission is seen in
1. Euglena
2. Paramecium
3. Amoeba
4. Vorticella
Answer:
2. Paramecium
Question 29.
Number of times a Paramecium can undergo binary fission in a day is
1. 5 times
2. 8 times
3. 9 times
4. 4 times
Answer:
4. 4 times
Question 30.
Number of generations of progeny formed from Paramecium by binary fission is
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
Answer:
2. 2
Question 31.
At the end of binary fission which daughter form contains the parental anterior contractile vacuole
1. Opisthe
2. Proter
3. Both (1) & (2)
4. None
Answer:
2. Proter
Question 32.
……….. in Paramecium during binary fission the micronucieus undergoes
1. Amitosis
2.Meiosis
3. Mitosis
4. Endomixis
Answer:
3. Mitosis
Question 33.
Under unfavourable conditions, the Amoeba reproduces by
1. Binary fission
2. Conjugation
3. Sporulation
4. Schizogamy
Answer:
3. Sporulation
Question 34.
Syngamy means
1. fusion of gametes
2. fusion of cytoplasms
3. fusion of two similar spores
4. fusion of two dissimilar spores
Answer:
1. fusion of gametes
![]()
Question 35.
The fusion of similar gametes is called
1. Isogamy
2. Anisogamy
3. Polygamy
4. Plasmotomy
Answer:
1. Isogamy
Question 36.
Isogamy is seen in
1. Monocystis
2. Vorticella
3. Plasmodium
4. Amoeba
Answer:
1. Monocystis
Question 37.
The fusion of pronuclei of two mature organisms which do not form gametes but behave as gametes is called
1. Isogamy
2. Anisogamy
3. Hologamy
4. Cytogamy
Answer:
3. Hologamy