Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2015 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2015
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
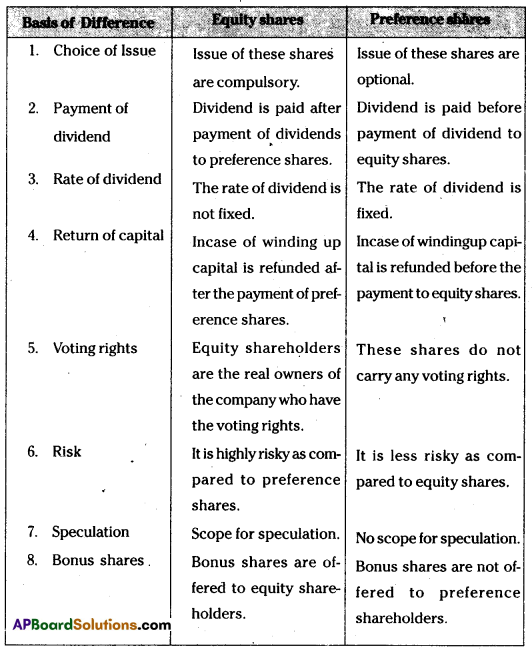
Question 1.
What are the differences between Preference Shares and Equity Shares ?
Answer:
Differences between equity shares and preference shares.
Question 2.
Define partnership. Discuss its merits and demerits.
Answer:
Partnership is defined by section 4 of Indian Partnership Act of 1932 “as the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them act for all”.
Merits:
- Easy formation: It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsory.
- Large resources : The resources of more them one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial power: We can pool capital, organising ability, managerial capacity, technical skill etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making: The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility: The partnership is flexible in nature at any time the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations after taking necessary consent of all the partners.
- Sharing risks: The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach : The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation : All partners actively participate in the business as per their specialisation and knowledge.
Limitations:
- Unlimited liability: The unlimited liability is fundamental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability : The partnership concern suffers from uncertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- Limited resources: There is limitation in raising additional capital for expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners.
- Non-transferability of share: No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust: The mutual distrust among partners is the main cause for dissolution of partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions: Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
![]()
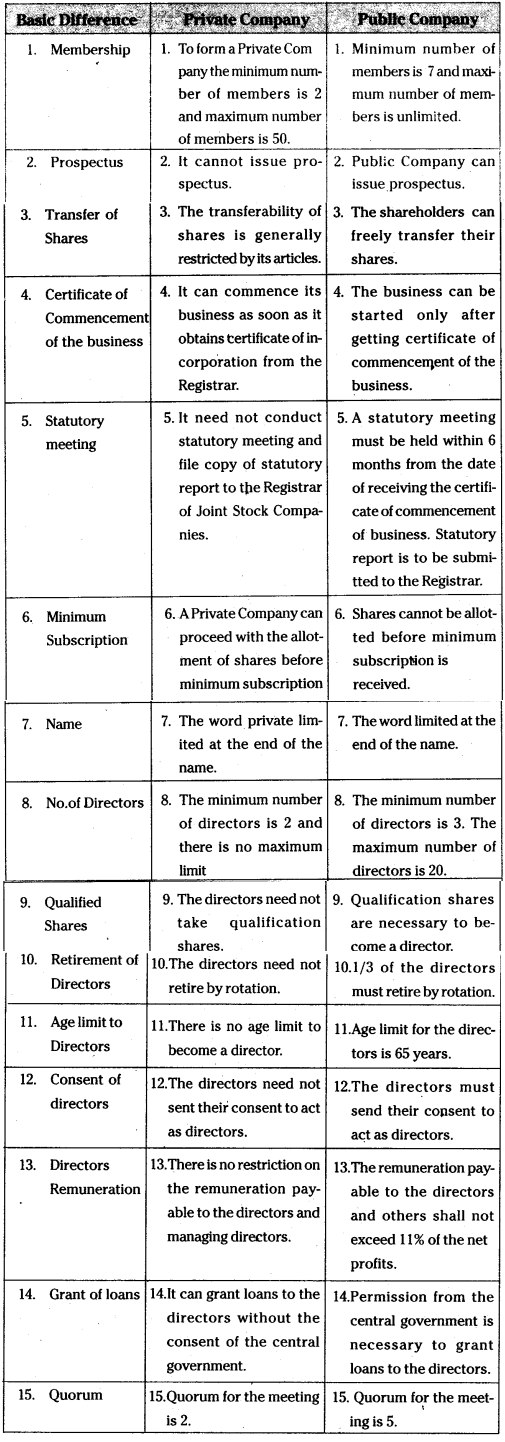
Question 3.
Distinguish between a Private Company and a Public Company.
Answer:
Section – B (4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each:
Question 4.
Explain various types of industries.
Answer:
Industry: Industry is concerned with making or manufacturing goods. It is the part of production which is involved in changing form of goods at any stage from raw material to the finished product.
Ex : Weaving yarn into cloth.
Classification of Industires:
1) Primary industry: Primary industry is concerned with production of goods with the help of nature. It is nature-oriented industry, which requires very little human effort.
E.g : Agriculture, Farming, Fishing, Horticulture etc.
2) Genetic industry : Genetic industry is related to the reproducing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale.
E.g : Nurseries, cattle breeding poultry, fish hatcheries etc.
3) Extractive industry : It is engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive industries comes in raw farm and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products. E.g: Mining, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil industry, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
4) Construction industry : The industry is engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabrication of products. These industries are engaged in the construction of buildings, roads, dams, bridges and canals.
5) Manufacturing industry : This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human uses. E.g : Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cotton textile industry, Iron and steel industry, Fertiliser industry etc.
6) Service industry : In modern times, service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation and therefore it is named as service industry. These are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. E.g: Banking, transport, insurance etc.
Question 5.
Briefly explain the different types of Co-operative Societies. Differentiate between a share and a debenture.
Answer:
According to the needs of people the following of co-operative societies are started in India.
1. Consumers Co-operative Society: These are started to help lower and middle class people. These societies protect weaver sections from the clutches of hungry business men. These societies make bulk purchases directly from the producers and sells these goods to the members on retail basis. The commission and profits of the middle men are eliminated. The members contribute capital and membership is open to all irrespective of caste, creed, colour etc.
2. Producers Co-operative Society : Small producers find it difficult to collect various factors of production and they also face marketing problems. The production of’goods is undertaken by members in their houses or at common place. They are paid wages for their services. They are supplied raw material and equipment by the society. The output is collected and sold by the society. The profits are distributed among members after retaining some profits in the general pool. Ex : Apco, Co-optex, Emmiganur weavers co-operative society.
3. Marketing Co-operative Society : These societies are established by producers for selling their products at remunerative prices. These societies pool production from different members and undertake to sell these products by eliminating middle men. The goods are sold when the market is favourable. These societies provide some advance money to the members for helping them in meeting their urgent needs. The sale proceeds are shared among members according to their contributions. These societies provide services like grading, werehousing, insurance, finance etc.
4. Co-operative Credit Societies: These societies are voluntary associations of people. They are formed with the objectives to provide the short time financial accommodation to their members. These societies are formed with the idea of saving their members from the clutches of money-lenders.
5. Co-operative Housing Societies : Such societies are formed to provide residential accomodation to their members either on ownership basis or at fair rents. They are organized by poor and middle class people in big cities where housing is a serious problem. Housing co-operative buys and land and constructs flats which are alloted to members.
Question 6.
What are the sources of finance ?
Answer:
The following are the differences between shares and Debentures.
| Shares | Debentures |
| 1. A share is a part of owned capital. | 1. A debenture is an acknowledge of debt. |
| 2. Shareholders are paid dividend on the shares held by them. | 2. Debenture holders are paid interest on debentures. |
| 3. The rate of dividend depends upon the amount of divisible profits and policy of the’company. | 3. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures irrespective of profit or loss. |
| 4. Dividend on shares is a charge against profit and loss appropriation account. | 4. Interest on debentures is a charge against profit and loss account. |
| 5. Shareholders have voting rights. They have control over the management of the company. | 5. Debenture holders are only creditors of the company. They cannot participate in management. |
| 6. Shares are not redeemable except redeemable preference shares) during the life time of the company. | 6. The debentures are redeemed after a certain period. |
| 7. At the time of liquidation of the company, share capital is payable after meeting all outside liabilities. | 7. Debentures are payable in priority over share capital. |
Question 7.
Explain the functions of promoters.
Answer:
Sources of finance can be classified on the basis of period, ownership and generation.
On the basis of period: On the basis of period, sources of funds are divided into long term, medium term and short term finance. Long term sources fulfill the financial requirements for a period exceeding five years and include sources such as shares, debentures and long term borrowings. Medium term finance is required for a period of more than one year and these includes borrowings from commercial banks, public deposits, lease financing. Short term funds are required for a period of less than one year and the sources are trade credit, bank credit, instalment credit, advances, bank overdraft, cash credit and commercial paper.
On the basis of ownership : On the basis of ownership, the sources can be classified into owners funds and borrowed funds. Owners funds and borrowed funds. Owners funds are those which are provided by the owners which include issue of share and retained earnings. Borrowed funds refer to the funds raised through loans or borrowings which include loans from commercial banks, financial institutions, issue of debentures and public depends.
On the basis of generation: Sources of finance can be generated from internal source or external source. Internal sources of funds are generated within the business such retained earnings, collection of receivables, depreciation fund, disposing surplus stock etc. External sources lie outside the business and include shares, debentures, public deposits, borrowings from banks and financial institutions etc.
Question 8.
Find out the features of MNC’s.
Answer:
A promoter conceives an idea for setting up a particular business at a given place and performs various formalities required for starting a company. A promoter may be an individual, a firm, association of persons or a company. Promoter takes lead for bringing money, men, machinery and material together for establishing an enterprise.
Promoter performs the following functions.
- A promoter conceives an idea for the setting up of a business.
- He makes preliminary investigations and ensures about the future prospects of the business.
- He brings together various persons who agree to associate with him and share the business responsibilities.
- He prepares various documents and gets the company incorporated.
- He raise the required finances and gets the company going.
Question 9.
Find out the features of MNC’s.
Answer:
Characteristics or features of Multi National Corporations (MNC’s):
- Global Operations :,Multi National Corporation carry production and marketing operations in different countries of the world. They possess all the infrastructural facilities in all the countries of the their operations.
- Giant Size : The assets and sales of MNC are quite large. The sales turnover of Some MNC’s extend the gross national product of several developing countries.
- Centralised Control : It has its head office’in the home country. It exercises control over all branches and subsidiaries.
- Dominant Position and Status : They occupy a dominant position in the market due to their giant size. They also takeover the firms to acquire a huge economic power.
- Internationalised Research and Development: These are intended to capture the quality and serve according to the requirements of the host nation.
- Sophisticated Technology : MNC has advanced technology so as to provide world class products and services. It employees capital intensive technology in manufacturing, marketing and other area of business.
- Professional Management: A MNC employees professional managers to integrate and manage world wide operations.
Section – C (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines each:
Question 10.
Explain the E – Banking.
Answer:
Electronic banking (E-banking) is one of the most successful online business. E-Banking allows customers to access their accounts and execute orders through website.online banking allows the customers to get their money from an Automatic Teller Machines instead of walking upto the cash desk in the bank. The customers can view their accounts, transfer funds and can pay bills. Ex : Internet banking.
Question 11.
Define manufacturing enterprise.
Answer:
Manufacturing enterprises are those business enterprises which are engaged in the manufacture or production of goods and services. The manufacturing enterprises are defined in terms of investment made in plant and machinery.
| Enterprise | Investment in plant and machinery |
| Micro | Does not exceed ₹ 25 lakhs. |
| Small | More than ₹ 25 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores |
| Medium | More than ₹ 5 crores but does not exceed ₹ 10 crores. |
Question 12.
What do you mean by Karta ?
Answer:
The Senor most male member of the family is Karta. All the affairs to joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Karta or Manager. The liability of Karta is unlimited. He acts on behalf of other members of two family. He is not accountable to anyone.
Question 13.
Who is active partner ?
Answer:
An active partner is one who fakes active part in the day-to-day working of the business. He may act in various capacities as manager, advisor or organiser. He is also known as working partner or managing parther.
Question 14.
Business Finance
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called business finance.
R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business.
Question 15.
Commercial Banks
Answer:
Commercial Banks occupy a vital position as they provide funds for different purposes as well as for different periods. Banks extends loans to forms of all sizes in many ways like cash credits, overdrafts, purchase, discounting of bills and issue of letters of credit. The loan is repaid in lumpusum or in instalments. The borrower is required to provide some security or create a charge before the loan is sanctioned.
Question 16.
Define Business
Answer:
The word business literally means a state of being busy. In the words of Honey “Business may be defined as human activities directed towards providing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods”. Accourding to wheeler “Business is an institution organised and operated to provide goods and services – to the society under the incentive of private gain”.
Question 17.
Entrepot-Trade
Answer:
When the goods are imported from one country and the same is exported to another country, such trade is called entrepot trade. E.g.: India importing wheat from U.S.A. and exporting the same’ to Srilanka.
Part – II (Marks 50)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question :
Question 18.
From the following Trial Balance of Pallavi Traders, prepare fined accounts as on 31-03-2014.
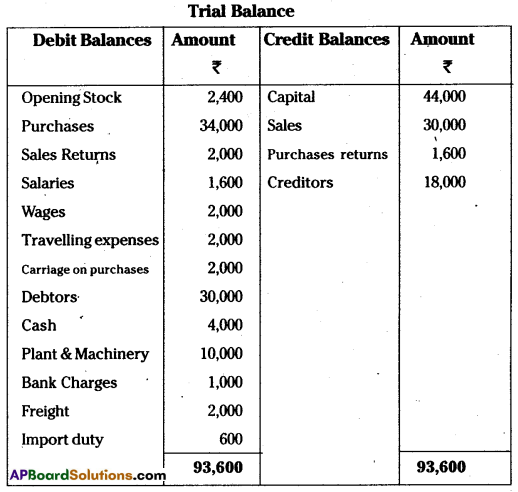
Adjustments:
i) Closing Stock ₹ 20,000
ii) Reserve for Bad Debts 10%
iii) Depreciation on machinery 20%
iv) Depreciation on furniture at 10%
Answer:
Trading and profit and Loss Account of
Pallavi Traders as on 31-03 -2014.
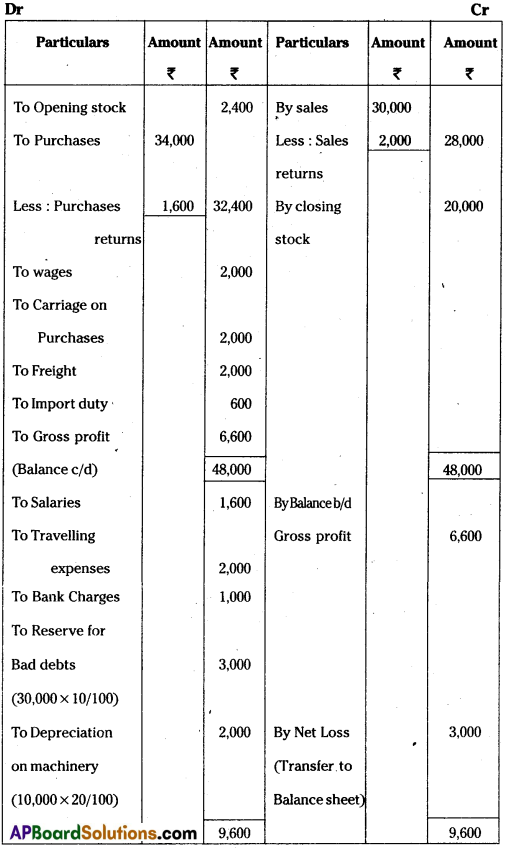
Note: Depreciation of furniture at 10% was given in the problem but there is no furniture in the Trial Balance.
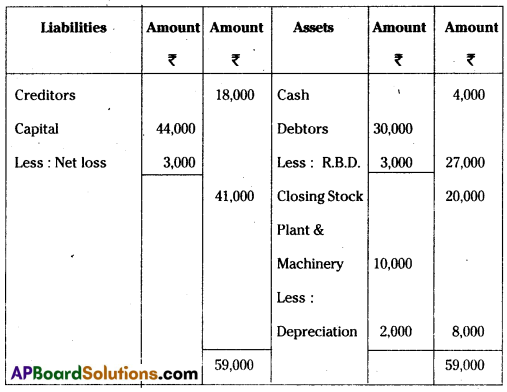
Balance sheet of Pallavi Traders as on 31-3-2014
Section – E (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions :
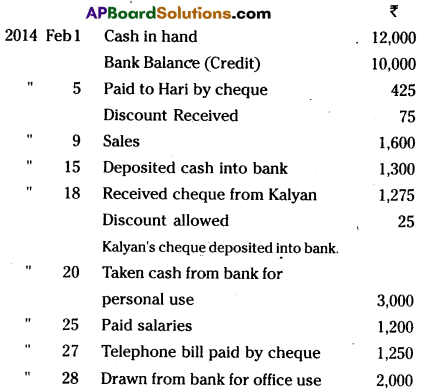
Question 19.
Prepare Three Column Cash Book from the following:
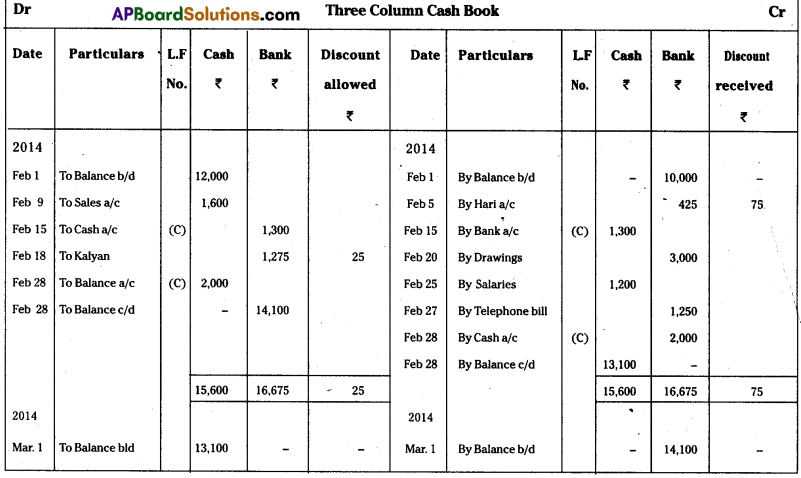
Answer:
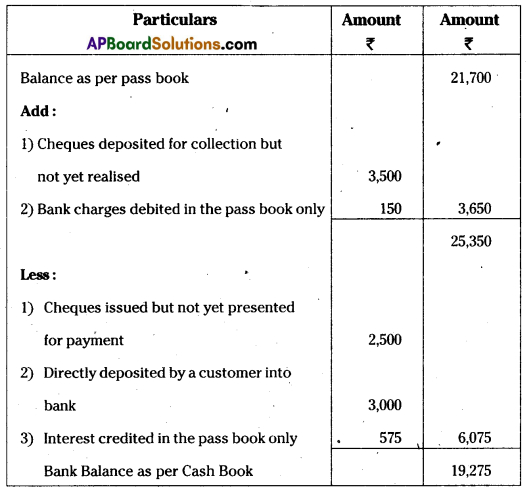
Question 20.
Murali & Sons Pass Book showed a balance of 21,700 as on 30th September 2014. On comparing the cash book the following discrepancies were noted:

Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement showing balance as per cashbook.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation statement of Murali & Sons as on 30.09.2014.
Section – F (2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions :
Question 21.
Explain different types of accounts along with their debit and credit rules.
Answer:
Accounts are broadly divided into two types.
1) Personal Accounts
2) Impersonal Accounts.
1) Personal Accounts : These accounts relate to persons or firrps. Ex.: Rama’s a/c, Andhra Bank a/c., LIC a/c, InfosysLtd. The rule in personal accounts is “Debit the receiver and credit the giver”.
2) Impersonal Accounts : Impersonal Accounts are those accounts which are not personal accounts. They are again divided into
i) Real Accounts
ii) Nominal Accounts.
i) Real Accounts: These accounts related to the assets and properties Ex.: Building, machinery, stock, goodwill etc.
The rule in real account is “Debit what coihes in and credit what goes out”.
ii) Nominal Accounts : These accounts relate to expenses, incomes and gains; losses. Ex.: Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Interest received a/c etc.
The rule in nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains”.
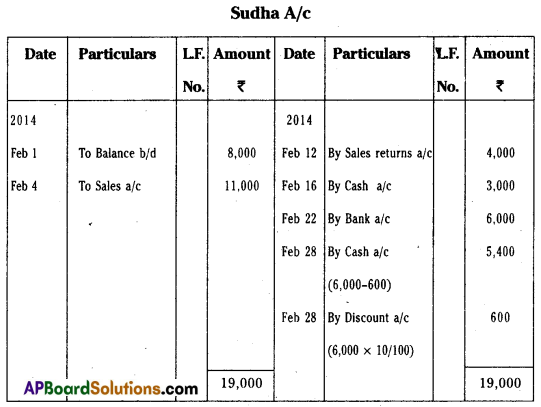
Question 22.
Prepare Sudha account from the following :

Answer:
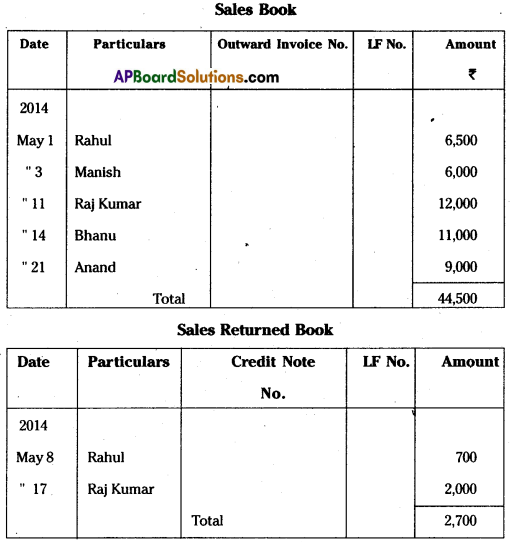
Question 23.
Prepare Sales Book and Sales Return Book from the following:

Answer:
Question 24.
Explain the various kinds of errors.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors.
1) Error of principle : Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors: When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is caused clerical errors. They are given divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of Omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of Commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors: These errors arise when one error is compensated by other error or errors.
Section – G (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions :
Question 25.
What is Book Keeping ?
Answer:
Book-keeping is the art of recording business transactions in regular and systematic manner. According to carter “Book-keeping is the science and art of correctly recording books Of accounts all those business transactions that result in transfer of money or money’s worht.
Question 26.
What is the Business Entity Concept ?
Answer:
Business is treated as separate from the proprietor. All the transactions are recorded in the books of business but not in the books of proprietor. The proprietor is also treated as creditor of the business when he contributes capital he is treated as a person who has invested amount in business. So, capital appears on the liabilities side in the Balance sheet.
Question 27.
What is Revenue Expenditure ?
Answer:
Revenue expenditure consists of expenditure of the benefit of which is not carried over to the several accounting periods. It is expenditure incurred in one accounting period the full benefit of which is consumed in the same period. Such expenditure is necessary for the maintenance of earning capacity including the up keep 6f the fixed assets.
Eg:
- Office & administration expenses
- Selling expenses.
Question 28.
Suspense Account.
Answer:
Suspense account is an imaginary account, opened and used as a temporary measure to make the two side of the tried balance agree. As and when the errors which causes the disagreement in trial balance is detected, rectification entries should be passed through suspense account.
Detection and rectification of all the errors will result in automatic closure of suspense account.
Question 29.
Single Entry System.
Answer:
Single Entry system is a system where the scientific method of double entry system is not followed. It is more appropriate to call it as “Incomplete Accounting system”.
Definition According to carter: “Single Entry is a method or a veriety of methods employed for recording of transactions, which ignores the two-fold aspect and consequently fails to provide the businessman with the information necessary for him to be able to ascertain the position”.
Question 30.
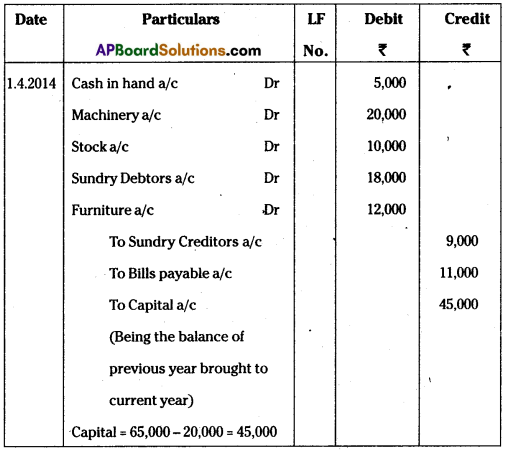
Record the opening entry from the following particulars on 1st April, 2014.

Answer:
Opening entry as on 1-4-2014.
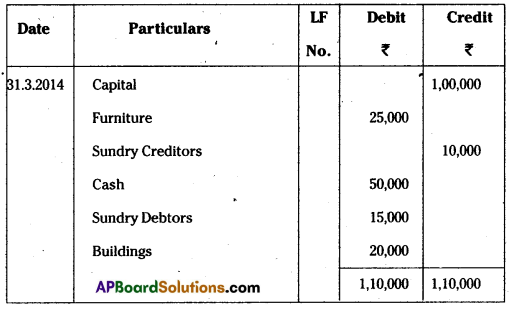
Question 31.
What is Double Entry System ?
Answer:
According to J.R.Batliboi “Every business transaction has a two sold effect and than it affects two accounts in opposite direction and if a complete record were to be made of each such transaction, it would be necessary to debit one accunt and credit another account. This recording of two fold effect of every transaction has given rise to the term Double entry system of book-keeping is that “for every debit there must be corresponding value of credit”.
Question 32.
Prepare Trial Balance of Susmitha from the following balances as on 31-3-2014.

Answer:
Trial Balance of Susmitha as on 31.3.2014