Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2018 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2018
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define the Co-operative society. Explain its features.
Answer:
Meaning:
Meaning:
The term “cooperation” is derived from the Latin word “co- operari”. The word “.Co” means “with” and “operari” means “to work”. Thus the term cooperation means working together. Cooperative society is a voluntary association of persons who work together to promote their economic interest.
Definition:
The Indian co-operative societies Act 1912, section (4) defines co-operative society as “a society, which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with co-operative principles”.
Features :
- Voluntary Association: A co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons. That means, persons can join and leave the society when they want.
- Open Membership : The Membership is open to all persons having a common economic interest. Any person can became a member irrespective of his/her caste, creed, religion, colour, sex etc.
- Number of Members : A Minimum qf ’10’ members are
required to form a co-operative Society. In case of multi-state co-operative societies, the minimum number of members should be ’50’ from each state. - State control : Every co-operative society comes under the control and supervision of the Government. Every society has to get its accounts audited from the co-operative Department of the government.
- Capital: The capital of the co-operative society is contributed by its members, it often depends on the loans and grants from state and central Government.
- Democratic set up : The co-operative societies are managed in a democratic manner. The Management of a co-operative society is control by managing committee elected on the basis of “one-man one-vote” irrespective of the number of shares held by any member.
- Service Motive : The primary objective of all co-operative societies is to provide .services to its members, rather than to earn profits.
- Return on capital Investment: The members of co-operative society get returns on their capital investment in the form of dividend.
- Distribution of surplus : After giving dividends to the members of the society, the surplus profit is distributed among the members in the form of bonus.
- Registration of the society: In India, co-operative societies are registered under the co-operative Societies Act. 1912 or the State co-operative Societies Act.
Question 2.
What is Memorandum of Association ? Explain its clauses.
Answer:
Meaning : The Memorandum of Association is the constitution and charter of the company. It defines the scope of the company’s activities as well as its relation with the outsiders. The main purpose of the MOA is intending the share holders before making investment is the company should know about the company.
The memorandum of association must be signed by at least seven members in case of public limited company and two members in case of a private limited company.
Definition:
Section 2 (28) of the companies Act defines a memorandum as “The Memorandum of Association of a company is originally framed or as altered form time to time in pursuance of any previous company laws or of this Act”.
Clauses of Memorandum of Association :
1) Name clause :
A company being a separate legal entity must have a name. A company may select any name which does not resemble the name of any other existing company and it should not contain the words like king, Queen, and name of the government bodies.
The word “Limited” must be used at the end of the name of a public company and “private limited” is used by a private company.
2) Registered office or situation clause :
This clause states the place and address of the registered office of the company. This clause helps the company for communications, notices, circular, etc are sent to the registrar office. If the place is not decided at the time of incorporation, it can be intimated to the Registrar with in 300 days from the date of incorporation.
3) Objective clause :
Objective clause is the important clause of MOA, because it sets out the objects for which a company formed. This clause defines scope of activities and powers of the company. This clause contains (a) main objects (b) other objects.
4) Liability clause :
This clause contains the nature of liability of its members.
It states that the liability of the members is limited to the value of shares held by them. It means that the members are liable to pay only the unpaid balance of their shares and nothing more.
5) Capital clause :
The amount of capital required by the company is stated in this clause. It contains the capital structure of the. company. This capital is divided into small units called shares. This clause mentioned, number of equity and preference shares and their value and also types of share holders have some special rights and privileges.
6) Association clause :
This clause states that the persons subscribing their signatures at the end of the memorandum are desirous of forming them selves into an association in pursurance of memorandum. This clause contains the names, addresses and occupations of the subscribers and witnesses are also given.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Business Finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organisations.
Answer:
Meaning:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called “Business finance”.
Finance is considered as the life blood of any organization. The success of any organization depends on the availability of adequate finance.
Definition :
According to B.O. Wheeler: “Finance is that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of a business enterprise”.
Need and Significance :
1) To meet fixed capital requirement of business :
Business requires finance to meet fixed capital require-ments such as purchase fixed assets like land and building, plant and Machinery, furniture and fixtures etc.
2) To meet working capital requirements :
Working capital is used for holding current assets such as purchase of material, payment of wages, transportation expenses etc. business requires finance.
3) For growth and expansion :
For growth and expansion activities, a business requires finance. It may be required increase production, to install more machines, to set up a R & D centre, etc.
4) For diversification :
Entering into new business and new lines of activities is known as diversification. The Business finance is needed to start any new activity in business.
5) For Survival:
Without the required finance, organizations can not survive for long time. To carry out the various business operations in continuity, business finance is needed.
6) Liabilities :
To meet liabilities of business, may be long-term or short, a business requires sufficient finance, e.g. for payment of loan installments, creditors etc.
7) For payment of expenses
Business finance is needed for payment of expenses like paying salaries, wages, taxes, rent, advertisements etc.
Section-B
(4 × 5 = 20 Marks)
Answer any four of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines each :
Question 4.
Explain Business’s Social Objectives.
Answer:
Business exists in society and it is a part of society. It cannot survive and grow without the support of society. Therefore a business must discharge social responsibilities in addition to earning profits.
Social objectives of business are given below :
1) Supplying desired goods at reasonable prices :
It is the social objective of the business to supply the goods and services required by the society. Goods and services should be of good quality and supplied at reasonable price.
2) Employment generation :
Business should provide opportunities for employment to members of the society. In a country like India unemployment has became a serious problem. Therefore, adequate and full employment opportunities is a significant service to society.
3) Fair remuneration to employees :
It is the obligation of business to provide healthy and safe work environment and fair remuneration to employees. To increase the motivation and efficiency of employees ; the business should be distributed bonus is addition to wages and salary among employees.
4) Social Welfare :
Business should provide support to social, cultural and religions organisations by building or developing schools, colleges, hospitals, sports bodies etc and help to non government organisations (NGos).
5) Payment of Government Dues :
Every business enterprise should pay tax dues like incometax, sales tax, excise duty, customs duty etc, to the government honesty and at the right time.
Question 5.
Explain the classification of Industries.
Answer:
Industry is a business activity, which is related to the extract producing, processing or manufacturing of goods.
Classification / Types of Industries :
1) primary Industry :
Primary Industry is concerned with production of goods with the help of nature and which requires very little human effort. For example : Agriculture ; Farming ; Fishing, etc.
2) Genetic Industry : .
Genetic Industries are engaged, in re-production and multiplication of certain species of plants and animals with, the object of sale to earn profit Eg: plant Nurseries, fish hatcheries, cattle breeding etc.
3) Extractive Industry:
Extractive Industry is concerned with extraction or drawing our goods from the soil, air or water. Generally products of this industry are in raw form and they are used by manufacturing and construction Industries.
Eg : Mining Industry, Coal, Mineral, oil; Iron ore industries etc.
4) Manufacturing Industry: Manufacturing Industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suitable for human use.
Eg: Cement Industry, sugar Industry, Cotton textile industry etc.
5) Construction Industry : construction Industry engaged in the construction of buildings, bridges, roads, dams, canals, etc.
These industries are engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy.
6) Service Industry : In modem times, service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation and therefore it is named as service Industry.
Eg : Hotel. Industry ; Tourism Industry, entertainment industry etc.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the various types of capital required for business enterprises ?
Answer:
Depending up on the nature and purpose; capital may be divided into fixed capital and working capital.
1) Fixed capital:
- The capital which is used to acquire fixed assets such as land and buildings, plant and machinery etc, is called “fixed capital”.
- Business organizations used fixed capital to meet the long term requirements.
- The amount of fixed capital required by the business concern depends on the size and nature of the business.
- The need for fixed capital investment would be greater for a large business as compared to a small business. Ex: A trading concern require small amount of fixed capital than a manufacturing concern.
2) Working capital:
- The capital required by a business enterprise to run its day to day operations is called ‘Working capital”.
- Working capital is used for holding current assets such, as stock of material, bills receivables and for meeting expenses like salaries, wages, taxes and rent.
- The amount of working capital requirement is various from one business enterprises to another depending on various factors.
- For Example : A business unit selling goods on credit or having a slow sales turnover, would require more working capital as compared to a business unit selling its goods on cash basis or having a high turnover.
Question 7.
Differences between Shares and Debentures.
Answer:
The capital of a company is divided into small units called “share”. “Debentures” are important instruments for raising long term debt capital.
The following are the differences between shares and debentures.
| Shares | Debentures |
| 1. A share is a part of owned capital. | 1. A Debenture is an acknowledge of debt. |
| 2. Share holders are paid dividend on the shares held by them. | 2. Debenture holders are paid interest on debentures. |
| 3. The rate of dividend depends upon the amount of divisible profits and policy of the company. | 3. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures irrespective of profit or loss. |
| 4. Dividend on shares is a charge against profit and loss Appropriation account. | 4. Interest on debenture is a charge against profit and Loss account. |
| 5. Share folders have voting rights. They have control over the management of the company. | 5. Debenture holders are only creditors of the company. They cannot participate in management. |
| 6. At the time of liquidation of the company, share capital is payable after meeting all out side liabilities. | 6. Debentures are payable in priority over share capital at the time of liquidation of the company. |
Question 8.
List out the features of MNCs.
Answer:
MNCs means Multinational Corporations. The word “Multinational” is a combination of words “Multi” which refers to many and ” national” refers to a country. So multinationals means a company which operates in more than one country. MNC refers to an enterprise whose managerial headquarters are located in one country, while it carries out operations in a number of other countries.
According to David E. Liliental, defines the MNCs as “Corporations which have their home in one country but operate and live under the laws and customs of other countries as well”.
Features of MNCs:
- Giant size ; The assets aind sale of MNCs are very large. These companies operate on large scale as they trade in more than one country. Sometimes their sales turnover exceeds the Gross National product (GNP) of developing countries.
- International Operation : A MNC operates and sells their products in different countries. It operates through a network of branches and subsidiaries in host countries.
- Professional Management : A Multinational corporation employees professional experts, specialized people. MNCs try to keep their employees updated by training from time to time to handle the advance in technology effectively.
- Oligo polistic powers : Oligopoly means power in the hands of few companies only. Due to their gaint size, the MNCs occupy dominating position in the market.
- Centralized control : MNC’s will have managerial head-quarters in the home country. All the subsidiary and branches work under the supervision, guidance and control of the head office.
- Sophisticated Technology : Multinational companies make use of latest, advanced and innovative technology to produce quality goods.
Question 9.
What are the benefits of e-business to organizations ?
Answer:
“E – business” is defined as the application of information and communication technologies (ICT) which support all the activities of business.
Benefits to organization:
- Reach beyond boundaries : E business extends the market place to national and international market.
- Cost savings: It Reduces the cost of processing, distributing, storing, inventories and over heads.
- Competitive Benefits : E Business reduced processing time allows for customization of products and services for achieving competitive advantages.
- Earlier capital collection : It reduces the time between the outlay of capital and the receipt of products and services.
Section – C
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each: (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 10.
Define Business.
Answer:
- Business is an economic activity involving production, exchange, distribution and sale of goods and services with an objective of making profits.
- L.H. Haney Defined Business as “a Human activity directed towards producing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods.
Question 11.
Entrepo-trade.
Answer:
- Importing of goods with the intention to export the same to other country is called as entrepo trade.
- Example : England imports, Tea from India and Exports to Europe.
Question 12.
Active partner.
Answer:
- The partner who .actively participate in the day to day operations of the business is called as “Active partner”.
- Active partner is also called as “working partner” or “Managing partner”.
Question 13.
Coparceners.
Answer:
In Joint Hindu Family business Organisation, family members of three successive generations own the business Jointly. This interest in inheritence is called coparcenary interest. Hence the members of the joint Hindu family firm are called “coparceners”.
Question 14.
What is Government Company ?
Answer:
- Any company in which not less than “51” percent of the paid – up share capital is held by the central government or state Government is called a Government company.
- For example : ONGC, NTPC
Question 15.
Define promotion.
Answer:
- Promotion is the first state in the formation of a company. It involves identification of a business opportunity or idea, analysis of its prospects, gathering the relevant information and taking steps to implement it.
- L.H. Haney “Promotion is the process of organizing and planning the finance of a business enterprise under the corporate form”.
Question 16.
Equity shares.
Answer:
- Equity shares are also known as “ordinary shares” represent the ownership of a company.
- As per section 85 of companies Act 1956, equity shares fulfils the following conditions.
a) Having right to vote
b) Dividend is not fixed
c) No right to repayment of capital before paid to preference shares.
Question 17.
Define Service Enterprises.
Answer:
- The enterprises involve in providing or rendering services are called service enterprises.
- There are 3 types of service enterprises based on investment in equipment.
a) Micro service Enterprise: Investment in equipment does not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs
b) Small service Enterprise : Investment in equipment is more than ₹ 10 lakhs but does not exceeds ₹ 2 crore.
c) Medium service Enterprise : Investment and equipment is more than ? 2 crore but does not exceed ₹ 5 crore.
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Kapil, prepare the Trading , Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31.03.2015.
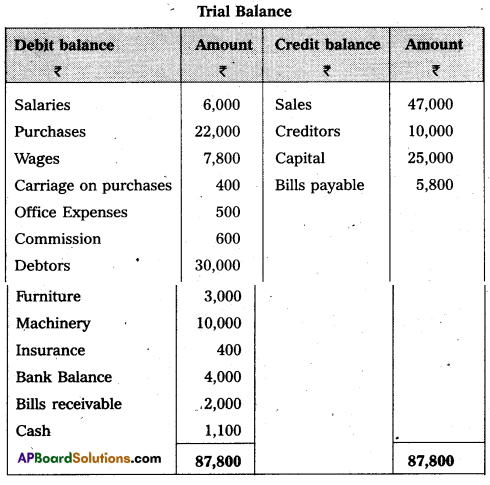
Adjustments :
i) Outstanding wages – ₹ 2,000.
ii) Outstanding salaries – ₹ 1,000.
iii) Prepaid Insurance – ₹ 50.
iv) Create 5% reserve for bad debts on debtors.
v) Depreciation on furniture ₹ 150, depreciation on machinery ₹ 500.
vi) Closing stock – ₹ 11,000.
Answer:
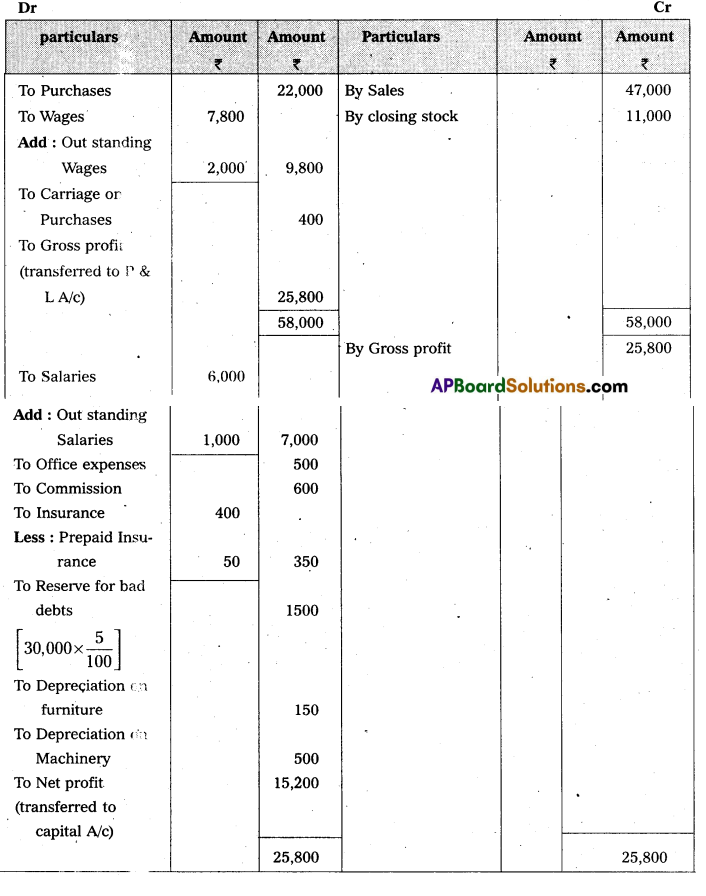
Balance Sheet of Mr. Kapil as on 31-3-2015
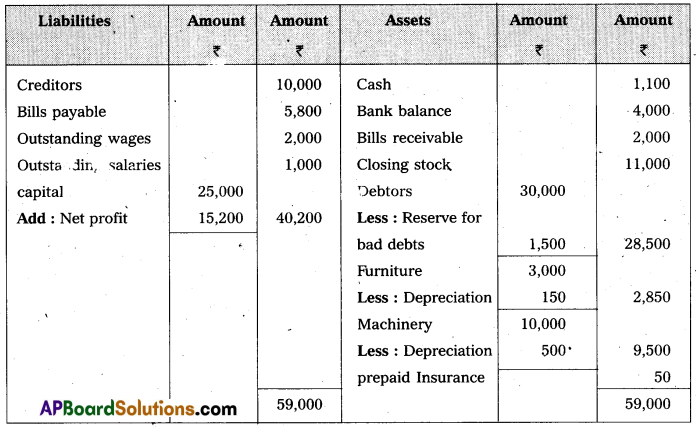
Section – E (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
Prepare three-column cash Book from the following :

Answer:
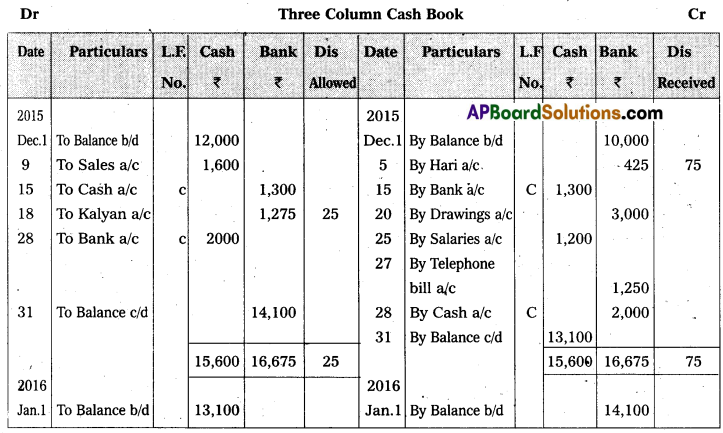
![]()
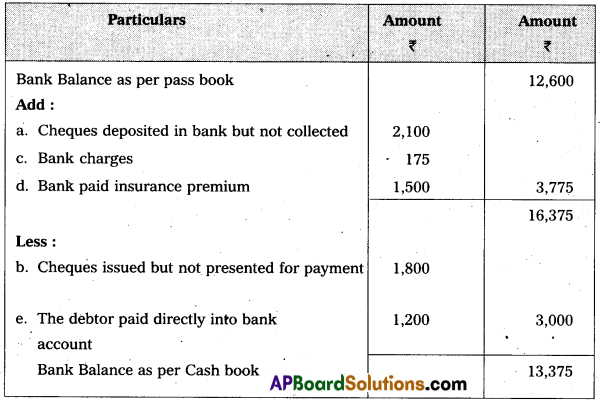
Question 20.
Pass Book of a trader shows a balance of ₹ 12,600 on comparing the Pass Book with the Cash Book, the following discrepancies were noted :
a) Cheques deposited in bank but not collected ₹ 2,100
b) Cheques issued but not presented for payment ₹ 1,800
c) Bank charges ₹ 175
d) Bank paid insurance premium ₹ 1,500
e) The debtor paid directly into bank account ₹ 1,200
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement
Section – F (2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain the different types of accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
Answer:
Accounts are classified into 3 types. Which are
1) Personal Accounts
2) Real Accounts and
3) Nominal Accounts.
1) Personal Accounts : The accounts which are related to persons, firms and companies are called “personal accounts”. Ex : Ramu a/c , State Bank of India a/c etc.
Rule : Debit The receiver
Credit the giver.
2) Real Accounts : Accounts related to properties and assets of
business are called “Real accounts”. Ex : Cash a/c, Furniture a/c, land & building a/c ; goodwill a/c etc
Rule : Debit what comes in
Credit what goes out.
3) Nominal Accounts: The accounts related to expenses, losses, incomes and gains are called as “Nominal Accounts”. Ex : Wages a/c , salaries a/c, commission a/c, rent a/c, discount received a/c etc.
Rule : Debit all expenses and losses
Credit all incomes and gains.
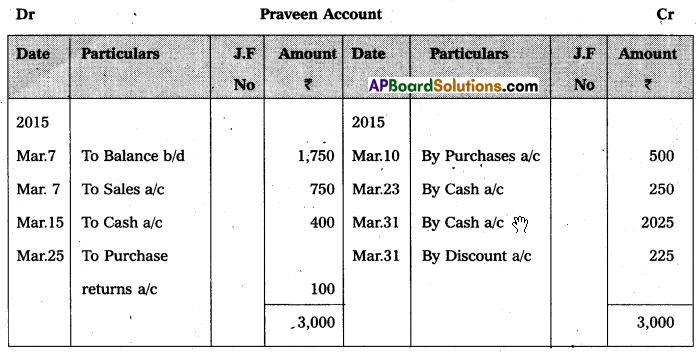
Question 22.
From the following information, Prepare Praveen’s Account as on 31-03-2015 :

Answer:
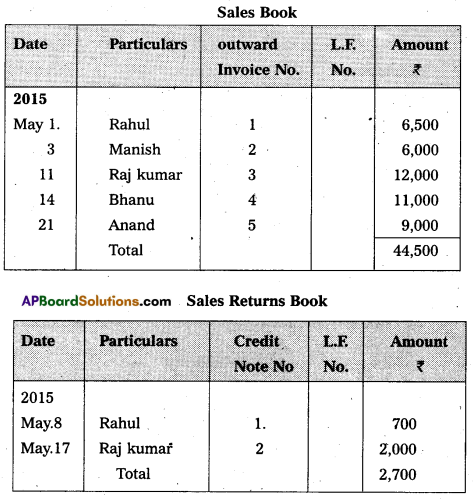
Question 23.
Prepare Sales Book and Sales returns Book from the following :

Answer:
Question 24.
Explain any five types of Errors.
Answer:
Types of Errors :
- Errors of Principles: Errors which are committed by violating accounting principles is called as errors of principles.
Eg : Purchased land and buildings debited to purchases account instead of land and buildings account. - Errors of omission : When a transaction is completely or partly omitted from the books of accounts such error is known as error of omission.
Eg: Purchase of goods are not recorded in the books of accounts. - Error of commission : The errors arise due to wrong recording, wrong casting, wrong balancing etc are errors of commission.
Eg : sold goods to Rama of ₹ 150 recorded as ₹ 50. - Compensating Errors : If two or more errors are committed and, one error nullifieds the another error.
Eg : Amount of excess sales will compensate the amount of excess purchases of same amount. - Writing to wrong head of account: Instead of recording in one account; recorded in another account is known as “writing to wrong head of account”.
Eg : Paid to Mahesh ₹ 1000 is debited to Mohan account.
Section – G (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following question.
Question 25.
What is Book-keeping ?
Answer:
Book keeping is the branch of knowledge that reveals how to keep a record of business transactions. It covers all activities i.e Identifying, measuring, recording and classifying all business transactions.
Question 26.
What is business entity concept ?
Answer:
As per this concept, Business organisation are treated as a separate entity which can be distinguished from the “owners” or stakeholders who provide capital to it. This concept helps in keeping private affairs of the owners and stakeholders separate from the business affairs.
![]()
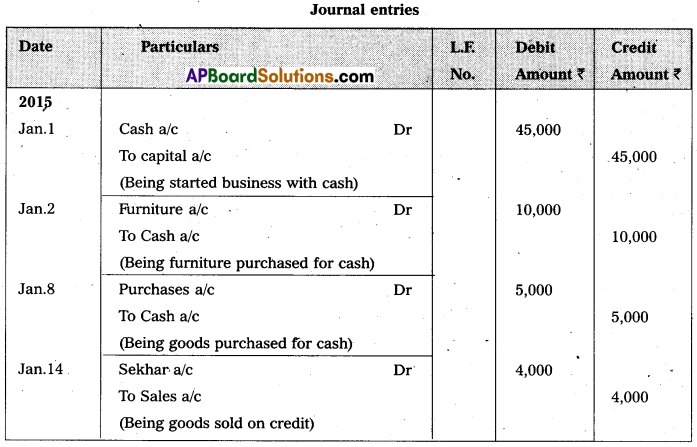
Question 27.
Journalize the following transactions.

Answer:
Question 28.
Contra Entry.
Answer:
An Entry which appears on both the sides (debit side as well as credit side of the tree column Cash Book is called “contra Entry ? For contra entries letter “c” is written is L.F. column.
Question 29.
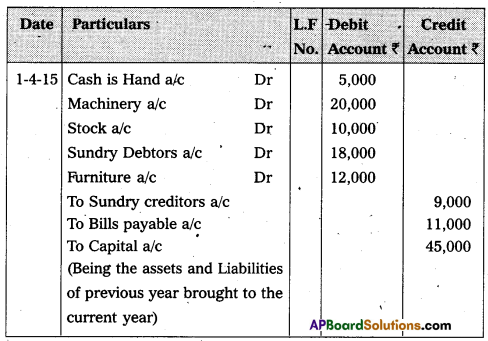
Record the opening entry form the following particulars on 1st April, 2015 :

Answer:
Opening entry on 1-04-2015
Question 30.
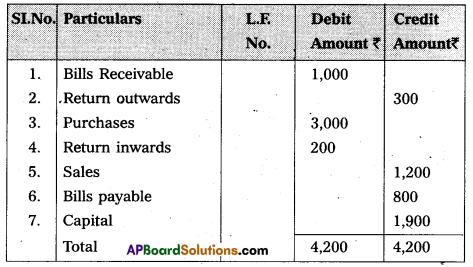
Prepare the Trial Balance of Manasa as on 31-12-2015 :
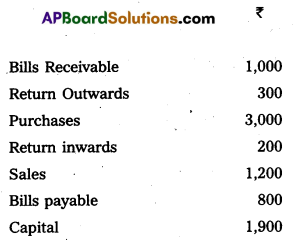
Answer:
Trial Balance of Manasa as on 31-12-2015
Question 31.
Compensating Errors.
Answer:
- If two or more errors are committed and, one error nullifieds the another error, they are called “compensating errors”.
- Example : amount of ₹ 100 excess in sales will compensate the amount of excess ₹ 100 in purchases.
Question 32.
Depreciation.
Answer:
The value of fixed assets such as machinery, furniture, loose tools etc., will decrease year after year due to various reasons such as wear and tear, obsolescence etc. Such decline in the value of fixed asset is called “Depreciation”.