Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2017 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2017
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Explain any five merits and five demerits of Sole Proprietorship.
Answer:
In this organisation only one individual is at the helm of all affairs of business. He makes all the investments. He bears all risks and takes all profits. He manages and controls the business himself. The business is run with the help of his family members or paid employees. His liability is unlimited. The sole trader is the sole organiser, manager, controller and master of his business.
Kimball and Kimball defines “Sole Proprietorship is a form of business where the individual proprietor is the supreme judge of all matters pertaining to his business”.
Merits :
- Easy to form : It is very easy and simple to form a sole trading business. The capital required is small. There are no legal formalities for starting the business.
- Prompt decisions and quick action : The sole trader is the sole dictator of his business. There is no need to consult any body while taking decisions. So, decisions can be taken quickly.
- Incentive to work hard: The sole trader takes all the profits. There is a direct connection between the effort and reward. So, it is an incentive for him to work hard. He manages the business to the best of his ability.
- Flexibility in operation: Changes in the business are necessary. The sole trading concern is dynamic in its nature. The nature of the business can be easily changed according to charging market conditions.
- Business secrecy : Since the whole business is handled by the proprietor, his business secrets are known to him only. He need not publish annual accounts and there is no need to disclose the information to outsiders. So, he can maintain business secrets.
- Contact with customers : It is easy to maintain personal contact with the customers. He can easily know their tastes, likes and dislikes and adjust his operations accordingly. This results in increase of sales.
Demerits :
- Limited resources : The resources of sole trader are limited. He has only two sources of securing capital, personal savings and borrowing on personal security. Hence, he can raise very limited amount of capital.
- Instability : It has no separate legal status. The business and the owner are inseparable from one another. The business comes to an end on the insolvency, insanity or death of the sole trader.
- Unlimited liability : The liability of a sole trader is un-limited. The creditors can recover the loan amounts not only from the business assets but also from his private property.
- Not suitable for large scale operations : The resources are limited. Therefore, it is suitable only for small business and not large scale operations.
- Limited managerial skill: The managerial ability is lim-ited. A person may not be an expert in all matters. Sometimes, wrong decisions may be taken.
Question 2.
Explain the features of Joint Stock Companies.
Answer:
“A company is an association of many persons who contribute money or money’s worth to a common stock and employ it in some trade or business and share the profits or loss arising there from”.
– L.J. Lindley
A Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association of individuals for profit having a capital divided into transferable shares, the ownership of which is the condition of membership”.
From the above definitions the features of Joint Stock Company is as given below.
Features:
1) Association of persons : A company is an association of persons join hands with a common motive earning profits through business.
2) Separate legal entity : The company is created by law. It has a separate legal entity apart from its members. Eventhough it is invisible and intangible having no body or soul, it can act just like any other human being. It can enter into contracts purchase and sell goods, conduct lawful business in its own name. It can sue and can be sued in a court of law.
3) Perpetual existence : The company has a permanent existence. The shareholders may come or may go but the company will go on forever. The continuity of the company is not affected by death, lunacy or insolvency of shareholders.
4) Common seal: A company being an artificial person cannot put its signature. The law requires every company to have a seal and get its name engraved on it. The seal of the company is affixed on all important documents and contracts as signature.
5) Limited liability : The liability of its shareholders is limited to the value of shares they have purchased.
6) Transferability of shares : The shareholders of the public company are free to transfer their shares. They do not need the consent of other shareholders.
7) Separation of Ownership and Management: The share-holders are the owners of the company. But they are too many. They are widely scattered and cannot take part in the day-to-day affairs of the company. The management is entrusted to Board of Directors who are elected by the shareholders. So, the ownership is separated from management.
8) Membership : To form a Joint Stock Company minimum of 2 members in the case of private company and 7 members in the case of public company. The maximum is 50 members in the case of private company and unlimited in public companies.
9) Formation: The Company comes into existence only when it is registered under the Indian Companies Act, 1956.
10) Submitting annual statements: A Joint Stock Company is required to file annual statements with the Registrar of companies at the end of the financial year. These statements are available for inspection in the office of the Registrar.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Business Finance ? What are the various factors that determine the selection of sources of finance ?
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called Business Finance. R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
B.O. Wheeler defined business finance as follows: “Finance is that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of a business enterprise.”
Need for business finance :
1. To start a new business : Money is needed to start a business and to procure fixed assets like buildings, plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures etc., working capital is required for holding current assets such as stock of materials, transportation expenses etc. The amount of finance to be procured depends on the type of business, nature of business and usage of technology.
2. To expand the business : Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
3. To develop and market new products : Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products. Invention and innovation of products should be given much priority to sustain in the market. Marketing research needs more funds.
4. To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
5. To take over another business : Business needs money to overcome competition or to get strengthened. An enterprise may decide to take over another business.
6. To move to new premises: A business unit may be forced to shift the business to new premises according to directions of the government. In such case, finance is needed for expenses like transport, packaging, installation of machinery etc.
7. Pay for the day-to-day running of the business : A business enterprise needs money to meet the day – to – day expenses like wages, taxes advertisement, rent etc. If also needs to meet liabilities like repayment of loan, installments, creditors etc.
The following factors should be considered for selecting the sources of finance.
1. Cost factor : While deciding the sources of funds that is utilised by the business concern, the cost of procuring the funds and the cost of utilising are to be considered.
2. Sound financial position : In the choice of sources of funds, the business should be financially sound so that it can repay the principle amount together with interest.
3. Form of business organisation : The form of business organisation influences the choice of source for raising money. Ex: A partnership firm cannot raise money by issue of equity shares.
4. Purpose and period of time : While selecting the sources of finance, purpose and period of time is to be taken into account. A short term need can be met by borrowing funds through trade credit, commercial paper etc., with low rates of interest. For long term finance, sources like issue of shares and debentures are more appropriate.
5. Risk factor: Business should evaluate each of the sources of finance in terms of risk involved. Ex: If equity shares are issued, they are to be repaid only at the time of winding up and dividends are not paid if the profits are not available. There is little risk involved. On the other hand, a loan is to be repaid as per schedule and the interest is to be paid whether the firm earn profits or not.
6. Control : A particular sources of funds may affect the control and power of the owners on the management of the firm. As the equity shareholders enjoy voting rights, by the issue of equity shares the financial institutions may take control of the assets or may impose conditions as part of loan agreement.
7. Effect on credit worthiness : Depending on certain sources of finance may affect the credit worthiness in the market. Ex : Issue of secured debentures may affect the interests of the creditors and they may not be willing to extend furthur loans to the company.
8. Flexibility and ease : Another factor which may affect the choice of sources of finance is flexibility and ease of obtaining funds. In order to secure loans from banks, they may impose restrictions and documentation is necessary. If other sources are available traders may not prefer approaching banks and financial institutions.
9. Tax benefits : Tax is not deducted on dividend of preference shares. Interest paid on loans and debentures is tax deductable. In order to take advantage Of tax benefits firms may issue debentures of take loans.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each:
Question 4.
Explain various types of Industries.
Answer:
Classification or types of industries : The industries may be classified as follows.
1) Primary industry : Primary industry is concerned with production of goods with the help of nature. It is nature-oriented industry, which requires very little human effort. E.g: Agriculture, Farming, Fishing, Horticulture etc.
2) Genetic industry : Genetic industry is related to the re-producing and multiplying of certain species of animals and plants with the object of earning profits from their sale. E.g : Nurseries, cattle breeding poultry, fish hatcheries etc.
3) Extractive industry : It is engaged in raising some form of wealth from the soil, climate, air, water or from beneath the surface of the earth. Generally the products of extractive indus-tries comes in raw farm and they are used by manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products. E.g: Min-ing, coal, mineral, iron ore, oil industry, extraction of timber and rubber from forests.
4) Construction industry : The industry is engaged in the creation of infrastructure for the smooth development of the economy. It is concerned with the construction, erection or fabri-cation of products. These industries are engaged in the construc-tion of buildings, roads, dams, bridges and canals.
5) Manufacturing industry: This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw material into semifinished or finished goods. This industry creates form utility in goods by making them suit-able for human uses. E.g : Cement industry, Sugar industry, Cot-ton textile industry, Iron and steel industry, Fertiliser industry etc.
6) Service industry : In modem times, service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation and therefore it is named as service industry. These are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. E.g : Banking, transport, insurance etc.
Question 5.
Explain the features of partnership firm.
Answer:
A partnership is an association of two or more persons formed with the object of sharing profits arising out of business. Partnership is defined by Indian Partnership Act, 1932 as “The relation between the persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them acting for all”.
Features :
- Agreement: Partnership is the result of an agreement. It is created by mutual consent and voluntary agreement.
- Lawful business : The partnership can only be for some kind of lawful business. An agreement indulge in smuggling, black marketing etc., cannot be called as partnership.
- Unlimited liability : The liability of the partners is individual, several and unlimited.
- Principle and agent relationship: Every partner is owner by himself and act as agent for other partners.
- Voluntary registration : The partnership may or may not be registered. But registered firms gets some privilages and facilities.
- Legal entity: There is no legal entity for partnership firms.
- Transfer of share: No partner can transfer his share without the consent of the other partners.
- Membership : The minimum number is 2 and maximum number is 10 in case of banking business and 20 in other cases.
- Mutual trust : The partnership deed depends upon mutual trust.
Question 6.
Explain any five advantages of equity shares.
Answer:
Advantages of equity source of finance :
- Equity shares do not create any obligation to pay a fixed rate of dividend.
- Equity shares can be issued without creating any charge over the assets of the company.
- It is a permanent source of capital and the company need not to repay it except under liquidation.
- Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company who have the voting, rights.
- Incase of profits, equity shareholders are the real gainers by way of increased dividends and appreciation in the value of shares.
Question 7.
Differentiate between a share and a debenture.
Answer:
The following are the differences between shares and De-bentures.
| Shares | Debentures |
| 1. A share is a part of owned capital. | 1. A debenture is an acknowledgement of debt. |
| 2. Shareholders are paid dividend on the shares held by them. | 2. Debenture holders are paid interest on debentures. |
| 3. The rate of dividend depends upon the amount of divisible profits and policy of the company. | 3. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures irrespective of profit or loss. |
| 4. Dividend on shares is a charge against profit and loss appropriation account. | 4. Interest on debentures is a charge against profit and loss account. |
| 5. Shareholders have voting rights. They have control over the management of the company. | 5. Debenture holders are only creditors of the company. They cannot participate in management. |
| 6. Shares are not redeemable except redeemable preference shares during the life time of the company. | 6. The debentures are redeemed after a certain period. |
| 7. At the time of liquidation of the company, share capital is payable after meeting all outside liabilities. | 7. Debentures are payable in priority over share capital. |
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the disadvantages of MNCs for the host country.
Answer:
The following are the disadvantages of MNC to host country.
- Threat to sovereignty : MNCs pose a danger to the independence of host countries. These corporations tend to interfere in the political affairs of the host nation.
- Spread of foreign culture : MNCs tend to vitiate the cultural heritage of local people. They propagate their own culture to sell their products.
- Depletion of natural resources : MNCs cause rapid depletion of the some of the resources of the host nation.
- Retard growth of employment : They create relatively few job opportunities and fail to solve chronic problems like unemployment etc.
Question 9.
Define e-business. Explain any four benefits of e-business to consumers.
Answer:
E-business : The term E-Business was first used by IBM in 1997. It defined E-business as “The transformation of key business processses through the use of internet technologies”. E-business is defined as the application of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) which support all the activities of the business with customers. It also enables enterprises to link their internal and external data processing systems more efficiently and flexibly and serve better to the needs and expectations of their customers. E-Business uses web based technology to improve relationships with customers.
The following are the benefits of E-Business to consumers.
- Purchasing made easy r E-Business enables consumers to shop or to do any other transactions 24hours a day, round the year from any location.
- Wide choice: Customers will have more choices as more alternative products and services are available.
- Saving in prices : E-Business provides customers with less expensive products and services which allows them to shop in many places and conduct quick comparisons. E-business facilitates competition, which results in substantial discounts.
- Exchange of information: E-Business allows customers to interact with other customers and exchange their opinions and experiences on products purchased by them.
Section – C
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each :
Question 10.
Define Business.
Answer:
The word business literally means a state of being busy. In the words of Haney “Business may be defined as human activities directed towards providing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods”. According to Wheeler “Business is an institution organised and operated to provide goods and services to the society under the incentive of private gain”.
Question 11.
What is entrepot trade ?
Answer:
When goods are imported from one country and the same are exported to another country, such trade is called entrepot trade.
E.g.: India importing wheat from U.S. and exporting the same to Srilanka.
Question 12.
Define cooperative society.
Answer:
Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons started with the objective of service but not profit. It encourages self-help, mutual help and thrift among members.
The Indian Co-operative Societies Act 1932 defines co-operatives in Section 4 as “a society which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with co-operative principle”.
According to H.C. Calvert, a co-operative society is “a form of organisation where in persons voluntarily associate together as human beings on the basis of equality for the promotion of economic interest of themselves”.
Question 13.
Who is ‘Kartha’?
Answer:
The senior most male member of the family is Karta. All the affairs of the Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Karta or Manager. The liability of the Karta is unlimited. He acts on behalf of the other members of the family. He is not accountable to anyone. He is the great master of the grandshow.
Question 14.
What is Memorandum of Association ?
Answer:
The Memorandum of Association is the constitution of the company. If the charter of the company. It provides the foundation on which the company structure is built. It defines the scope of company activities as well as the relation with the outside world. The purpose of memorandum is to enable the shareholders, creditors and those who deal with the company to know the permitted range of activities of the enterprise. Section 2(38) of the Companies Act defines memorandum as “The Memorandum of Association of a company as originally framed or altered from time to time in pursuance of any previous laws or of this Act”.
Question 15.
Define promotion.
Answer:
A promoter conceives an idea for setting up a particular business at a given place and performs various formalities required for starting a company. He is an individual, or a firm or association of persons or a company.
Question 16.
What is preference share ?
Answer:
As the name suggests, these shares have certain preferences as compared to equity shareholders. There is a preference for payment of dividend and also repayment of capital at the time of liquidation when the company has distributable profits, the dividend is first paid to preference shares. In the event of liquidation, after the payment of outside creditors, preference share capital is returned. Because of these preferences they are called as preference shares. These shares do not carry any voting rights. Hence they cannot participate in the management.
![]()
Question 17.
Define medium enterprises.
Answer:
In case of Manufacturing Enterprises, a medium enterprise is an enterprise where investment in Plant and Machinery is more than ₹ 5 crores, but does not exceed ₹ 10 crores.
In case of service enterprises, a medium enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 2 crores but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D (1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question :
Question 18.
From the following Trial Balance of Mr. Paramesh, prepare the Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31.03.2016.
Trial Balance as on 31.03.2016
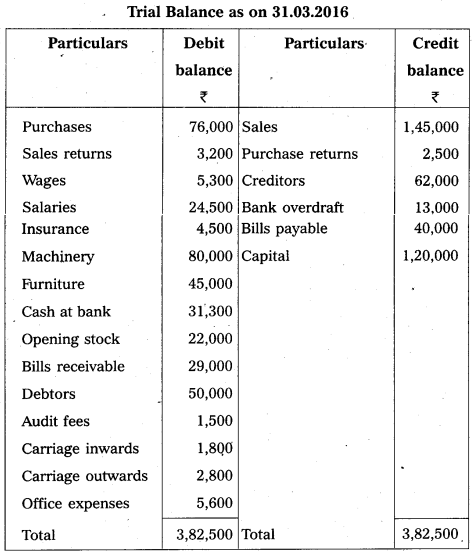
Adjustments :
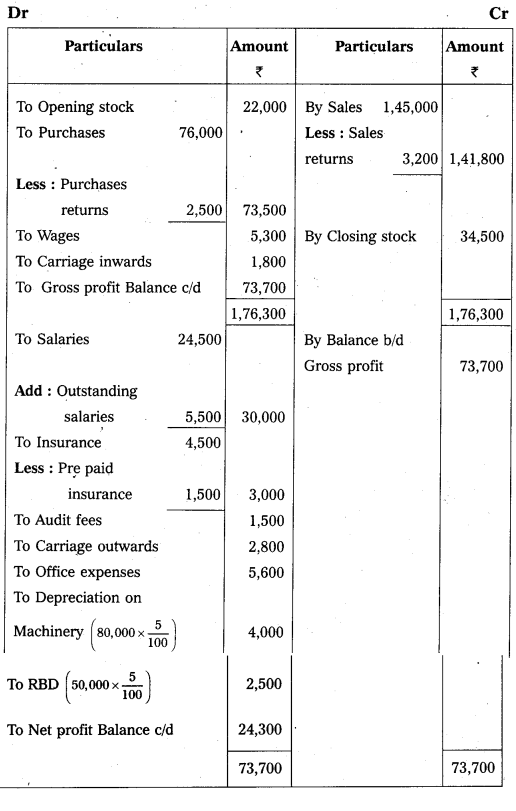
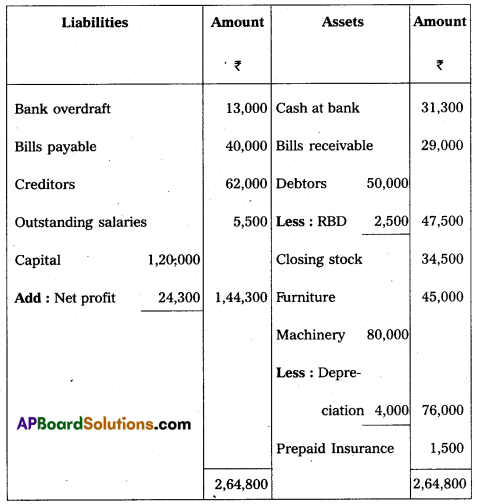
i) Closing stock ₹ 34,500/-.
ii) Outstanding salaries ₹ 5,500/-.
iii) Depreciate machinery by 5%.
iv) Prepaid insurance ₹ 1,500/-.
v) 5% provision is to be made for bad debts on debtors.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss a/c of Mr. Paramesh for the year ending on 31.3.2016.
Balance Sheet of Mr. Paramesh as on 31.3.2016
Section – E (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions :
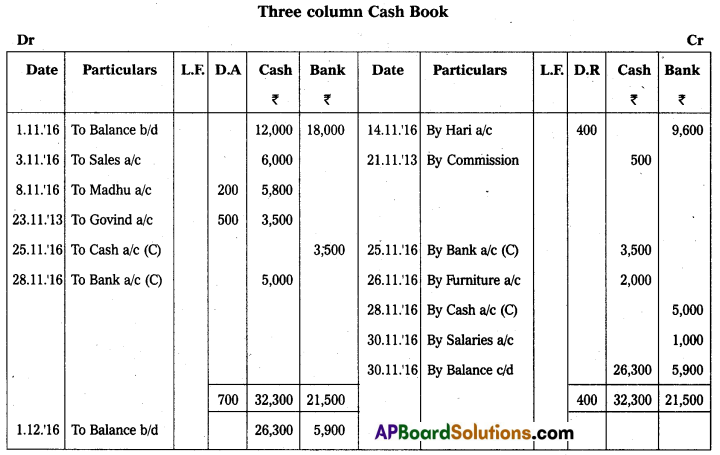
Question 19.
Prepare a three-column cashbook from the following transactions :
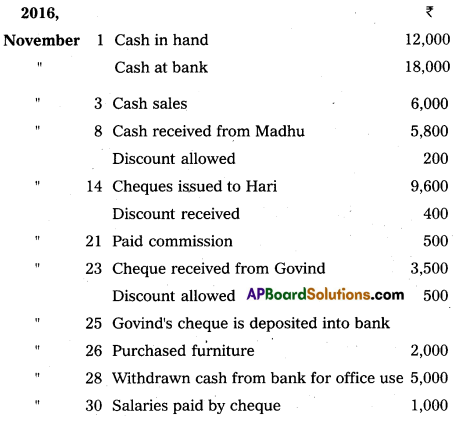
Answer:
Question 20.
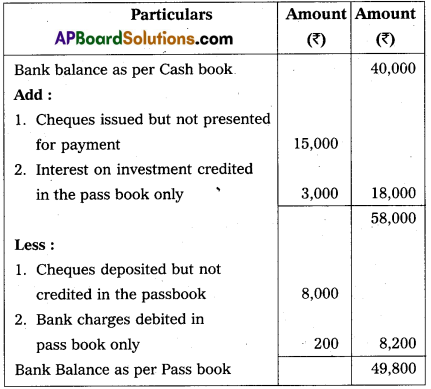
From the following information prepare a Bank Reconcilia-tion Statement of M/s. Narayana Agro Industries as on December 31st 2016.
a) Bank balance as per cashbook ₹ 40,000.
b) Cheque issued but not presented for payment ₹ 15,000.
c) Cheques deposited into bank but not credited upto December 31st 2016 ₹ 8,000.
d) Interest on investment ₹ 3,000 was collected and credited by bank but no entry is made in the cashbook.
e) Bank charges debited in the passbook only ₹ 200.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of M/S Narayana Agro Industries as on December 31, 2016.
Section – F (2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions :
Question 21.
Explain the different types of accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
Answer:
The accounts are broadly divided into two types.
1) Personal Accounts
2) Impersonal accounts.
1) Personal Accounts : These accounts which relate to the persons, group of persons or institutions are called personal accounts. Ex. : Rama’s a/c, Andhra Bank a/c., LIC a/c, Infosys Ltd. The rule in personal accounts is ‘Debit the receiver and credit the giver. According to this, benefit receivers account is debited and benefit givers account is credited.
2) Impersonal Accounts : Impersonal accounts are those accounts which are not personal accounts. They are again divided into
i) Real Accounts
ii) Nominal Accounts.
i) Real Accounts: These accounts related to the assets and properties of the business firm. Ex. : Building, machinery, stock, goodwill etc.
The rule in real accounts is “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”. When an asset is received the asset account is debited and when the asset goes out of the business, the asset is credited.
ii) Nominal Accounts : These accounts relate to expenses, incomes or gains or losses. Ex. : Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Commission received a/c etc.
The rule in nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains”.
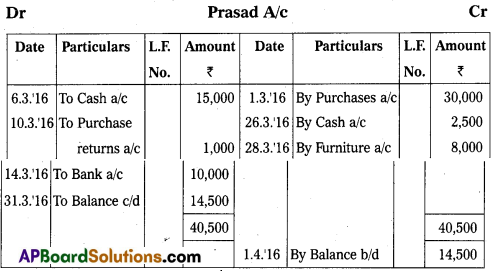
Question 22.
Prepare Prasad account from the following particulars :

Answer:
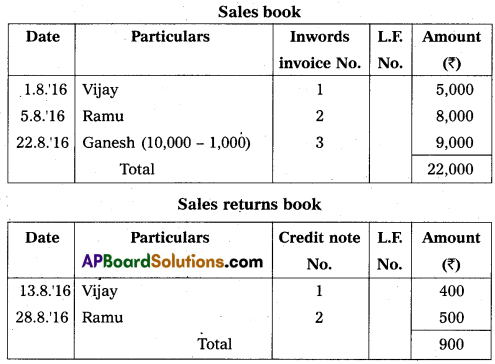
Question 23.
Prepare sales book and safes return book from the following particulars.

Answer:
Question 24.
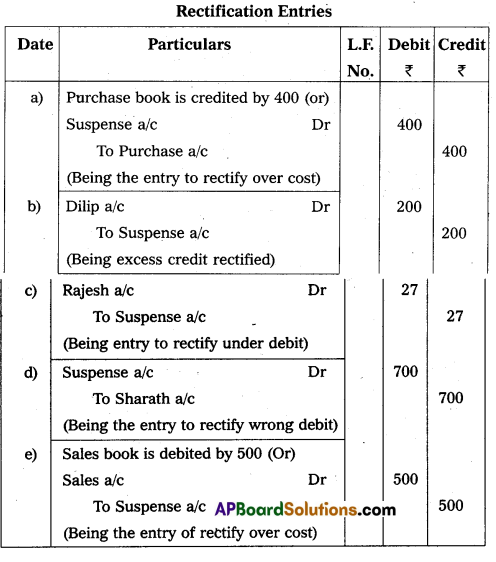
Rectify the following errors which are found after the preparation of trial balance.
a) Purchase book over cost by ₹ 400.
b) Credit side of Dilip account over cost by ₹ 200.
c) Goods sold to Rajesh for ₹ 296 was posted to his account as ₹ 269.
d) ₹ 350 received from Sharath has been posted to the debit side of his account.
e) Sales book was over cost by ₹ 500.
Answer:
Section-G (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
Define Accounting.
Answer:
The American Institute of Public Accountants defined accounting as the art of recording, classifying and summerising in significant manner and Interms of money transaction’s and events which are in part, atleast of financial character and interpreting the results thereof”.
![]()
Question 26.
What is business entity concept ?
Answer:
Business is treated separate from the proprietor. All the transactions are recorded in the books of business but not in the books of proprietor. The proprietor is also treated as creditor of the business. When he contributes capital he is treated as a person who has invested his amount in the business. Therefore, capital appears on the liabilities side of the balance sheet of the business.
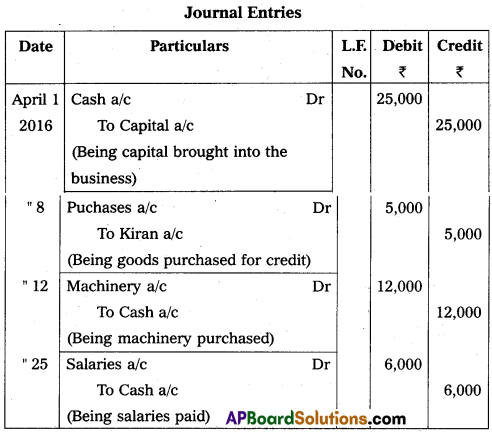
Question 27.
Journalize the following transactions.

Answer:
Question 28.
What is Invoice ?
Answer:
It is a statement sent by the supplier along with the goods or in advance, to the trader, stating that the goods are supplied along with the price, discount offered and other terms and conditions. The document is called ‘Inward Invoice’, as it is received by the trader from the supplier.
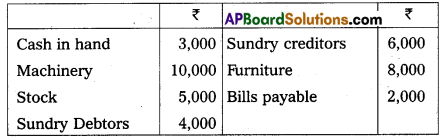
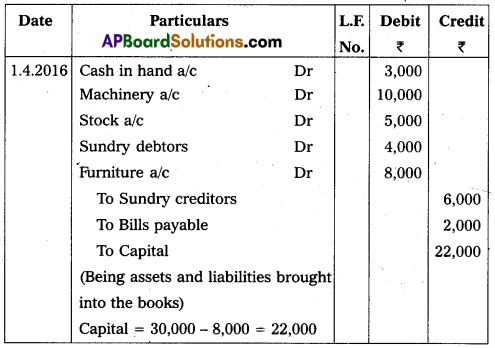
Question 29.
Write the opening entry as on 01.04.2016 from the following particulars.
Answer:
Opening entry as on 01.04.2016
Question 30.
Prepare Trial Balance from the following balances.
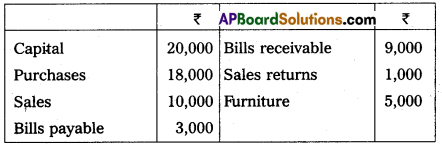
Answer:
Question 31.
What is suspense account ?
Answer:
Suspense account is an imaginary account, opened and used as a temporary measure to make the two side of the trial balance agree. As and when the errors which causes the disagreement in trial balance is detected, rectification entries should be passed through suspense account. Detection and rectification of all the errors will result in automatic closure of suspense account.
Question 32.
What is revenue expenditure ?
Answer:
Revenue expenditure consists of expenditure of the benefit of which is not carried over to the several accounting periods. It is expenditure incurred in one accounting period the full benefit of which is consumed in the same period. Such expenditure is necessary for the maintenance of earning capacity including the up keep of the fixed assets.
Eg:
- Office & administration expenses,
- Selling expenses.