Access to a variety of AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2017 helps students overcome exam anxiety by fostering familiarity. question patterns.
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Question Paper March 2017
Note : Read the following instructions carefully.
- Answer all questions of Section ‘A’. Answer any six questions in Section ‘B’ and any two questions in Section ‘C’.
- In Section ‘A’, questions from Sr. Nos. 1 to 10 are of “Very Short Answer Type”. Each question carries two marks. Every answer may be limited to 2 or 3 sentences. Answer all these questions at one place in the same order.
- In Section ‘B’, questions from Sr. Nos. 11 to 18 are of “Short Answer Type”. Each question carries four marks. Every answer may be limited to 75 words.
- In Section ‘C’, questions from Sr. Nos. 19 to 21 are of “Long Answer Type”. Each question carries eight marks. Every answer may be limited to 300 words.
- Draw labelled diagrams wherever necessary for questions in Sections ‘3’ and ‘C’.
Section – A
Note : Answer all questions.
Question 1.
Write any two adverse effects of global warming.
Answer:
Adverse effects of global warming :
- Unseasonal raining.
- Agricultural sector will be badly affected due to global warming.
- Increase the infections diseases.
- Melting of polar ice caps and causing of sealevels to rise.
Question 2.
Define the sink and receptor.
Answer:
- Sink : The medium which retains and interacts with long lived pollutant is called sink.
- Receptor: The medium which is effected by a pollutant is called receptor.
Question 3.
Write the effect of temperature on surface tension and viscosity. Give reason to that.
Answer:
With increase of temperature surface tension decreases.
With increase of temperature viscousity also decreases.
Reasons :
Due to increase in K.E. of molecules.
Due to decrease in intermolecular forces.
![]()
Question 4.
Calculate the oxidation number of ‘Cr’ in K2Cr2O7.
Answer:
K2Cr2O7
2(+1) + 2x + 7(-2) = 0 ‘
2 + 2x – 14 = 0
2x = 12
x = +6
Question 5.
Define the ionic product of water.
Answer:
Ionic product of water : The product of concentrations of H+ ion and OH– ion in water is called ionic product of water (Kw). Kw value at 25°C is 1.008 × 10-14 mole2/lit2
Question 6.
What is plaster of Paris?
Answer:
The hemihydrate of calcium sulphate is called plastor of paris.
The formula of plaster of paris is CaSO2\(\frac{1}{2}\) H20.
Question 7.
Write any four uses of CO2 gas.
Answer:
Uses of CO2 gas :
- Solid CO2 (dryice) is used in ice creams and frozen food.
- CO2 gas is used in the waste water treatment as a cooling medium.
- CO2 gas is used in exting shing fire.
- CO2 gas is used in the food industry, oil industry etc.
- CO2 gas is useful for plants and in the photo synthesis.
Question 8.
Why are alkali metals not found in the free state in nature?
Answer:
Alkali metals are not found in the free state in nature because they readily lose their valency electron to form M+ ion (a nonvalent ion).
![]()
Question 9.
Why the graphite is good conducter of electrocity?
Answer:
In graphite carbon undergoes sp2 hybridisation. Each carbon forms three σ – bonds with three neighbouring carbon atoms. Fourth electron forms π – bond and it is delocalised. Due to the presence of these moving (or) free electrons graphite acts as good conductor.
Question 10.
What is the type of hybridization of each carbon in the following compound?
HC = C – CH = CH2
Answer:
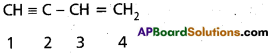
1st carbon – sp – hybridisation
2nd carbon – sp – hybridisation
3rdcarbon – sp2 – hybridisation
4th carbon – sp2 – hybridisation
Section – B
Question 11.
State and explain Graham’s law of diffusion.
Answer:
Graham’s law of diffusion : At a given temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of density, vapour density or molecular weight.
\(r \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{d}} ; r \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{V D}} ; r \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{M}}\)
If r1 and r2 are the rates of diffusion of two gases d1 and d2 are their densities respectively, then
\(\frac{r_1}{r_2}=\sqrt{\frac{d_2}{d_1}}\)
This equation can be written as :
\(\frac{r_1}{r_2}=\sqrt{\frac{d_2}{d_1}}=\sqrt{\frac{V D_2}{V D_1}}=\sqrt{\frac{M_2}{M_1}}\)
Comparison of the volumes of the gases that diffuse in the same time. Let V1 and V2 are the volumes of two gases that diffuse in the same time ‘t’.
\(\frac{r_1}{r_2}=\frac{\frac{v_1}{t_1}}{\frac{v_2}{t_2}}\)
When time of flow is same then : \(\frac{r_1}{r_2}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}\)
When volume is the same then : \(\frac{r_1}{r_2}=\frac{t_2}{t_1}\)
Applications :
- This principle is used in the separation of isotopes like U235 and U238.
- Molar mass of unknown gas can be determined by comparing the rate of diffusion of a known gas molecular mass.
- Ansil’s alarms which are used in coal mines to detect the explosive marsh gas works on the principle of diffusion.
Question 12.
A carbon compound contains 12.8% carbon, 2.1 % hydrogen, 85.1% bromine. The molecular weight of the compound is 187.9. Calculate the molecular formula (At. wt C = 12, H = 1,Br = 80).
Answer:
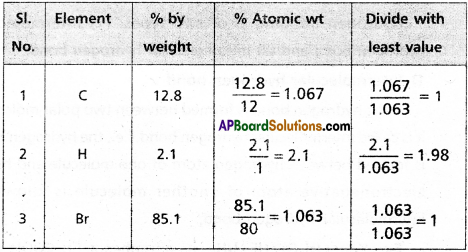
∴ Emperical formula of the compound = C1 H2 Br
Molecular formula = n (Emperical formula)
n = \(\frac{\text { Molecular wt }}{\text { Emperical wt }}=\frac{187.9}{94}\)
Given molecular wt = 187.9
∴ Molecular firmula = 2 (CH2Br)
Emperical Wt = 94 (CH2 Br)
= C2H4Br2
![]()
Question 13.
What is hydrogen bond ? Explain the different types of hydrogen bonds with examples.
Answer:
Hydrogen bond is a weak electrostatic bond formed between partially positive charged hydrogen atom and an highly electronegative atom of the same molecule or another molecule.
Hydrogen- bond is formed when the Hydrogen is bonded to small, highly electronegative atoms like F, O and N. A partial positive charge will be on hydrogen atom and partial negative charge on the electronegative atom.
The bond dissociation energy of hydrogen bond is 40 KJ/mole. Hydrogen bond is represented with dotted lines (……). Hydrogen bond is stronger than Vander Waals’ forces and weaker than covalent bond.
Hydrogen bonding is of two types. (1) Intermolecular hydrogen bond and (2) Intramolecular hydrogen bond.
1) Intermolecular hydrogen bond:
If the hydrogen bond is formed between two polar molecules it is called intermolecular hydrogen bond, i.e., the hydrogen bond is formed between hydrogen atom of one molecule and highly electronegative atom of another molecule is known as intermolecular hydrogen bond.
Ex.: Water (H2O); HF: NH3; p – nitrophenol, CH3COOH, ethyl alcohol
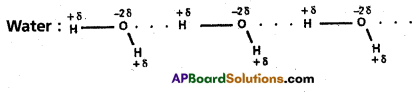
Water molecule forms an associated molecule through inter- molecular hydrogen bond. Due to molecular association water possess high boiling point.
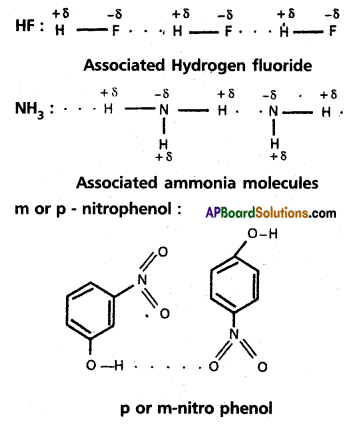
2) Intramolecular hydrogen bond:
If the hydrogen bond is formed within the molecule it is known as intramolecular hydrogen bond.
Ex. : o – nitrophenol; o – hydroxy benzaldehyde.
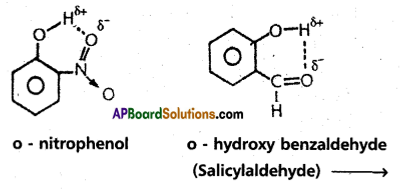
Abnormal behaviour due to hydrogen bond :
- The physical state of substance may alter. They have high melting and boiling points.
- Ammonia has higher boiling point than HCl eventhough nitrogen and chlorine have same electronegativity values (3.0). Ammonia forms an associated molecule through inter- molecular hydrogen bond.
- p – hydroxy benzaldehyde have higher boiling point than o- hydroxy benzaldehyde. This is due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding in para isomer.
- Ethyl alcohol is highly soluble in water due to association and co-association through intermolecular hydrogen bonding
Question 14.
State and explain Hess’s law of constant heat summation. Give an example.
Answer:
Hess’s law states that the total amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction is always same whether the reaction is carried out in one step (or) in several steps.
Illustration:
This means that the heat of reaction depends only on the initial and final stages and not on the intermediate stages through which the reaction is carried out. Let us consider a reaction in which ∆ gives D. The reaction is brought out in one step and let the heat of reaction be ∆H
A → D; ∆H
Suppose the same reaction is brought out in three stages as follows
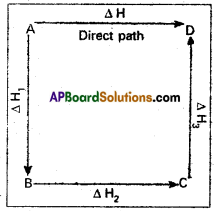
A → B : ∆H1
B → C : ∆H2
C → D : ∆H3
The net heat of reaction is ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3.
According to Hess law AH = ∆H1 + ∆H2+ ∆H3.
Ex: Consider the formation of CO2. It can be prepared in two ways.
1) Direct method : By heating carbon in excess of O2.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g); ∆H1 = -393.5 kj
2) Indirect method : Carbon can be converted into CO2 in the following two steps.
C(s) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)O2 → CO2(g); ∆H1 = -110.5 Kj
CO(g) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)O2 → CO2(g); ∆H2 = -283.02 kj
Total ∆H = -393.52 Kj (∆H1 + ∆H2)
The two ∆H values are same.
![]()
Question 15.
What are homogenous and heterogenous equilibria? Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Homogenous:
It the physical states of the participating substances are same they the equilibrium is homogeneous equilibrium.
e.g : H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Heterogenous:
If the physical states of all (or) some of the participating substances are same then the equilibrium is Het-erogeneous equilibrium.
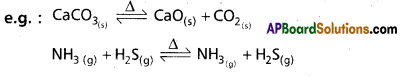
Question 16.
Write any four uses of dihydrogen (H2).
Answer:
Hydrogen as a fuel :
- The heat of combustion of hydrogen is high i.e about 242kj/mole. Hence hydrogen is used as industrial fuel,
- The energy released by the combustion of dihydrogen is more than the petrol (3 times).
- Hydrogen is major constituent in fuel gases like coal gas and water gas.
- Hydrogen is also used in fuel cells for the generation of electric power. 5% dihydrogen is used in CNG for running four-wheeler vehicles.
By hydrogen economy principle the storage and transportation of energy in the form of liquid (or) gaseous state. Here energy is transmitted in the form of dihydrogen and not as electric power.
Question 17.
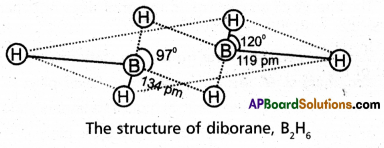
Explain the structure of diborane.
Answer:
Diborane is an electron deficient compound. It has ’12’ valency electrons for bonding purpose instead of ’14’ electrons. In diborane each boron atom undergoes sp3 hybridization out of the four hybrid orbitals one is vacant.
Each boron forms two, a – bonds (2 centred – 2 electron bonds) bonds with two hydrogen atoms by overlapping with their’1s’orbital. The remaining hybrid orbitals of boran used for the forma¬tion of B-H-B bridge bonds
In the formation of B-H-B bridge, half filled sp3 hybrid orbitaj of one boron atom and vacant sp3 hybrid orbital of second boron atom overlap with 1s orbital of H-atom. These three centred two electron bonds are also called as banana bonds. These bonds are present above and below the plane of BH2 units.
Diborane contains two coplanar BH2 groups. The four hydrogen atoms are called terminal hydrogen atoms and the remaining two hydrogens are called bridge hydrogen atoms.
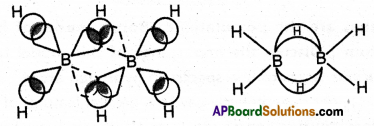
Bonding in diborane, Each B atom uses sp3 hybrids for bonding. Out of the four sp3 hybrids on each B atom, one is without an electron shown in broken lines. The terminal B-H bonds are ormal 2-centre-2-electron bonds but the two bridge bonds are 3-centre-2- electron bonds. The 3-centre-2-electron bridge bonds.
Question 18.
Define the dipole moment. Why the BF3 molecule dipole moment is zero?
Answer:
Dipolemoment : The product of magnetude of charge and the distance between the two poles (bond length) is called dipolemoment (p).
Units – Debyl
μ = q × d
q = charge;
d = bond length
BF3 molecule is a symmetrical molecule. In symmetrical molecules bonds moments vectorial sum is zero. SO BF3 has zero dipole moment.
![]()
Question 19.
What are the postulates of Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom? Discuss the importance of this model to explain various series of line spectra in hydrogen atom.
Answer:
Niels Bohr quantitatively gave the general features of hydrogen atom structure and it’s spectrum. His theory is used to evaluate several points in the atomic structure and spectras. The postulates of Bohr atomic model for hydrogen as follows Postulates:
1. The electron in the hydrogen atom can revolve around the nucleus in a circular path of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits (or) stationary states. These circular orbits are concentric (having same center) around the nucleus.
2. The energy of an electron in the orbit does not change with time. When an electron moves from lower stationary state to higher stationary state absorption of energy takes place.
3. When an electron moves from higher stationary state to lower stationary state emission of energy takes place.
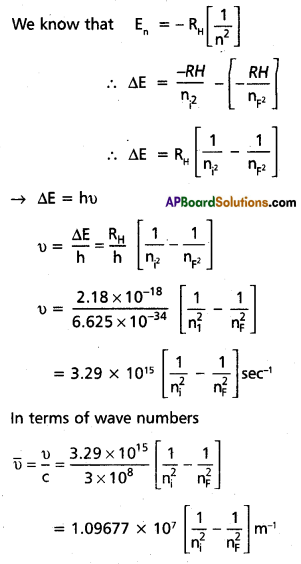
4. When an electronic transition takes place between two sta¬tionary states that differ in energy by
∆E = E2 – E1 = hυ
∴ The frequency of radiation absorbed (or) emitted υ = \(\frac{E_2-E_1}{h}\)
E1 and E2 are energies of lower, higher energy states respectively.
4. The angular momentum of an electron is given by mvr = \(\frac{\mathrm{nh}}{2 \pi}\)
An electron revolve only in the orbits for which it’s angular momentum is integral multiple of \(\frac{h}{2 \pi}\)
Line spectra of Hydrogen – Bohr’s Theory :
In case of hydrogen atom line spectrum is observed and this can be explained by using Bohr’s Theory.
According to Bohr’s postulate when an electronic transition takes place between two stationary states that differ in energy is given by
ΔE = Ef – Ei
Ef = final orbit energy
Ei = initial orbit energy
- In case of absorption spectrum nf ni → energy is absorbed (+Ve)
- In case of emission spectrum ni > nf → energy is emitted (-ve)
- Each spectral line in absorption (or) emission spectrum associated to the particular transition in hydrogen atom
- In case of large no.of hydrogen atoms large no.of transitions possible they results in large no.of spectral lines.
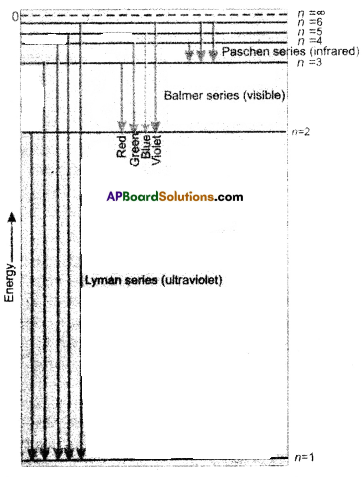
The series of lines observed in hydrogen spectra are
| ‘n’ value | Series | Region |
| 1 | Lyman series | UV region |
| 2 | Balmer series | visible |
| 3 | Pachen series | Near I.R. |
| 4 | Brackette series | I.R. |
| 5 | pfund series | Far I.R. |
Question 20.
Write the classification of elements into s, p, d and f blocks in long form of periodic table.
Answer:
According to the electronic configuration of elements, the elements have been classified into four blocks. The basis for this classification is the entry of the differentiating electron into the subshell. They are classified into s, p, d and f blocks.
‘s’ block elements : If the differentiating electron enters into ‘s’ orbital, the elements belongs to ‘s’ block. In every group there are two ‘s’ block elements. As an ‘s’ orbital can have a maximum of two electrons, ‘s’ block has two groups IA and IIA.
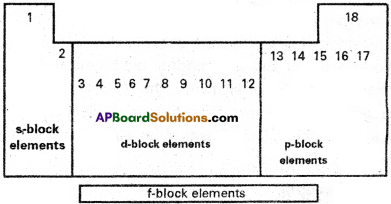
‘p‘ block elements : If the differentiating electron enters into ‘p’ orbital, the elements belongs to ‘p’ block. ‘p’ block contains six elements in each period. They are MIA to VII A and zero group elements. The electronic configuration of “p” block elements varies from ns2np1 to ns2np6.
‘d’ block elements :
It the differentiating electron enters into (n – 1) d – orbitals the elements belongs to’d’ block. These elements are in between ‘s’ and ‘p’ blocks. These elements are also known as transition elements. In these elements n and (n – 1) shells are incompletely filled. The general electronic configuration of’d’ block elements is (n – 1) d1-10 ns1-2. This block consists of NIB to VIIB, VIII, IB and MB groups.
f block elements :
If the differentiating electron enters into f orbitals of antipenultimate shell (n – 2) of atoms of the elements belongs to T block. They are in sixth and seventh periods in the form of two series with 14 elements each. They are known as lanthanides and actinides and are arranged at the bottom of the periodic table. The general electronic configuration is (n – 2) f1-14 (n -1) d0-1 ns2.
In these shells the last three shells (ultimate, penultimate and anti penultimate) are incompletely filled. Lanthanides belongs to 4f series. It contains Ce to Lu. Actinides belong to 5f series. It contains Th to Lr.
Advantages of this kind of classification :
As a result of this classification of elements were placed in correct positions in the periodic table. It shows a gradual gradation in physical and chemical properties of elements. The metallic nature gradually decreases and non – metallic nature gradually increases from ‘s’ block to ‘p’ block. This classification gave a special place for radioactive elements.
![]()
Question 21.
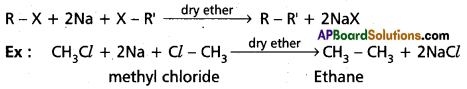
a) Wurtz’s reaction
Answer:
Wurtuz reactions : Alkylhalides reacts with sodium metal in presence of dry ether to form alkanes.
b) Polymerization of ethylene
Answer:
Polymerization : A large molecular weight complex compound which is formed by the repeated combination of smaller units is called polymer. The process of formation of polymer is called polymerisation.
Ex : Ethylene undergo polymerisation at 200°C and 1500 – 200 atm pressure gives polythene.

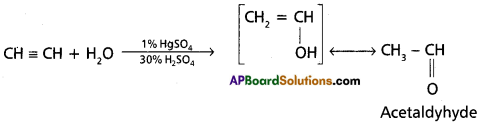
c) Addition of water to acetylene
Answer:
Addition of water: Acetylene undergoes addition reaction with water in the presence of mercuric sulphate and sulphuric acid. Vinyl alcohol formed in the reaction undergoes rearrangement gives acetaldehyde.
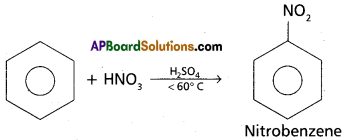
d) Nitration of benzene
Answer:
Nitration : Benzene when heated with a mixture of cone. H2SO4 and cone. HNO3 below 60°C to give Nitrobenzene.