Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 9th Lesson Cell: The Unit of Life which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 9th Lesson Cell: The Unit of Life
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the significance of vacuole in a plant Cell? [AP M -16,17,22]
Answer:
- Vacuoles play an important role in osmo regulation of plant cells.
- In some plant cells, vacuolar sap contain pigments like anthocyanin which impart colour to its flower.
Question 2.
What does’S’refer in a 70S & and 80S ribosome? [TS M-17, 20]
Answer:
- ‘S’ refers to sedimentation coefficient (Expressed in Svedberg unit)
- It is indirectly a measure of density and size of ribosome.
Question 3.
Mention a single membrane bound organelle which is rich in hydrolytic enzymes. [TS M-15, 22]
Answer:
Lysosomes, Vacuoles.
![]()
Question 4.
What are gas vacuoles? State their functions.
Answer:
- Gas vacuoles: These are the aggregates of number of small hollow cylilndrical vesicles found in the cytoplasm of the ‘floating purple and green photosynthetic’ bacteria.
- Functions: They store reserve materials in prokaryotes.
They help the bacteria to float on the surface of water.
Question 5.
What is the function of a polysome? [TS M-19] [AP May-19]
Answer:
The ribosomes of a polysome translate the mRNA into proteins.
Question 6.
What is the feature of a metacentric chromosome? [AP M-18]
Answer:
The meta centric chromosome has middle centromere forming two equal arms of the chromosome.
Question 7.
What is referred to as satellite chromosome? [AP M-20][AP,TS May-17]
Answer:
- Some chromosomes contain a small segment called satellite which is separated from the main body of the chromosome by a secondary constriction.
- Such chromosomes are called satellite chromosomes.
Question 8.
What are microhodies? What do they contain?
Answer:
Microbodies: Peroxysomes and glyoxysomes are called micro bodies.
- Peroxysomes are involved in the convertion of fatty acids into phospholipids and in Photo respiration
- Glyoxysomes contain enzymes of glyoxylate cycle. They convert stored lipids to carbohydrates.
Question 9.
What is middle lamella made of ? What is its functional significance? [AP M-15]
Answer:
- Middle lamella is pectin layer which made of calcium pectate. [TS M-16]
- It holds the neighbouring cells together.
Question 10.
What is Osmosis?
Answer:
Osmosis: Movement of molcules or ions or water from a region of higher concentrated place to a region of lower concentrated place through a semi permeable membrane is called osmosis. Movement of water by diffusion across the membrane is called Osmosis.
Question 11.
Which part ofthe bacterial cell is targeted in gram staining? [IPE Mar-14]
Answer:
The chemical composition of’cell envelopes’ is responsible in gram staining.
Question 12.
Which of the following is not correct?
a) Robert Brown discovered the cell.
b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory.
c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing cells.
d) A unicellular organism carries out its life activities within a single cell.
Answer:
(a) is not correct [The Cell was discovered by Robert Hook]
Question 13.
New cells generate from
a) bacterial fermentation
b) regeneration of old cells
c) from pre-existing cells
Answer:
c) from pre-existing cells
Question 14.
Match the following [AP MAR-19]
a) Cristae – i) Flat membranous sacs in stroma
b) Cisternae – ii) Infoldings in mitochondria
c) Thylakoids – iii) Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus
d) abiotic materials
Answer:
a) ii
b) iii
c) i
![]()
Question 15.
Which of the following is correct:
a) Cells of ail living organisms havea nucleus.
b) Both animal and plant cells have a well defined cell wall.
c) In prokaryotes, there are no membrane bound organelles.
d) Cells are formed de novo from abiotic materials.
Answer:
(c) is correct.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Discuss briefly the role of nucleolus in the cells actively involved in protein synthesis?
Answer:
- Spherical body present in the nucleoplasm is called nucleolus.
- It is not a membrane bounded structure. In some nucleus, one or more nucleoli may be present.
- Nucleolus actively synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- rRNA synthesizes proteins.
- Several ribosomes attach with a mRNA (messenger RNA) to form a chain are referred to as a polyribosome or polysome .
- The ribosomes of a polysome translate the mRNA into proteins.
- Larger and more numerous nucleoli present in cells actively carryout protein synthesis.
Question 2.
Explain the association of carbohydrate to the plasma membrane and its significance.
Answer:
- Carbohydrates form about 1-5% of the total chemical composition of the plasma membrane.
- The lipid component of plasma membrane consists of phosphoglycerides.
- Cell membranes consist of carbohydrates.
- Carbohydrates are found only on the outer surface of plasma membrane.
- The main carbohydrates present in the plasma membrane are oligosaccharides.
- Molecules of carbohydrates are covalently linked to the polar heads(hydrophilic) of some lipid molecules (glycolipids) and most of the proteins are exposed at the outer surface (glyco-proteins)
- Carbohydrates function as adhesion.
- The fluid mosaic layer describes membranes as ‘fluid lipid bilayer of floating proteins’ and carbohydrates.
Question 3.
Comment on the cart wheel structure of centriole.
Answer:
- Centrosome is a cell organelle containing two central cylindrical structures called centrioles.
- The centrosome is surrounded by amorphous pericentriolar materials.
- Both the centrioles lie perpendicular to each other.
- Each centriole has an organisation like the cart wheel.
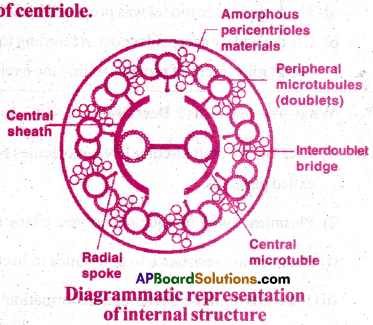
- They are made up of nine evenly spaced peripheral fibrils of tubulin.
- Each peripheral fibril is a triplet.
- The adjacent triplets are also linked.
- The central part of the centriole is also proteinaceous and it is called the hub.
- The hub is connected with tubules of the peripheral triplets by radial spokes made of protein.
- The centrioles form the basal body of cilia or flagellae and spindle fibres that give rise to spindle apparatus during cell division in animal cells.
![]()
Question 4.
Briefly describe the cell theory. [AP M – 22]
Answer:
A German Botanist Schleiden and a British Zoologist Schwann proposed the cell theory.
The statements of the cell theory:
- All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells.
- The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells (R-Virchow)
Question 5.
Differentiate between Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). [AP M- 17]
Answer:
| Rough Endoplasmic reticulum (RER) | Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) |
| 1) The ER bearing ribosomes on their surface is called RER. 2) RER observed in cells actively involves in protein synthesis and secretion. |
1) The ER which does not bear ribosomes on their surface is called SER. 2) SER is the site for synthesis of lipids and lipid like steroidal hormones in animal cells. |
Question 6.
Give the biochemical composition of plasma membrane. How are lipid molecules arranged in the membrane?
Answer:
- Biochemical investigations reveal that the cell membrane possess protein and carbohydrates.
- The cell membrane is composed of lipids arranged in a bilayer.
- Within the membrane, the polar (hydrophilic) head is towards the outer side and the hydrophobic tail is towards the inner part.
- This ensures that non polar tail of saturated hydrocarbons is protected from the aqueous environment.
- The fluidmosaic model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson.
- It is the widely accepted model. According to this model, the quasi-fluid nature of lipid enables lateral movement of proteins within the overall bilayer.
Question 7.
What are plasmids? Describe their role in bacteria? ’
Answer:
1) Plasmids: Small circular DNA molecules found outside genomic DNA in many bacteria are called plasmids.
2) Plasmids confer ‘unique phenotypic characters’ to bacteria.
- Plasmids are resistance to antibiotics in bacteria.
- Plasmids monitor ‘bacterial transformation’ with foreign DNA.
- Plasmids take part in the production of toxins.
- Plasmids take part in the synthesis of cell surface structures required for adhering or colonization
Question 8.
What are histones? What are their functions?
Answer:
Histones:
- Histones are the main proteins in chromatin. DNA wrapped around a core of histone octomer which contains H2A, H2B, H3 & H4.
- The DNA that continues between two succesive nucleosomes is called linker DNA.
- The association between negatively charged DNA and oppositely charged histones allows for meaningful DNA packaging inside the nucleus.
Functions:
- Their function is to package DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. Chromatin is a combination of DNA and protein which makes up the contents of a cell nucleus.
- Because DNA wraps around histones, they also play a role in gene regulation.
Question 9.
What is Cytoskeleton? What functions is it involved in? [AP M-20]
Answer:
- The network of filamentous proteinaceous structures in the cytoplast is collectively called as cytoskeleton.
- It has three components micro filaments, intermediate filaments and micro tubules.
- The cytoskeleton is involved in mechanical support and in the maintenance of cell shape, cell motility, intra cellular transport and karyo kinesis, signalling across the cell.
![]()
Question 10.
What is endomembrane system? What cell organelles are not included in it? Why?
Answer:
- The membranous organelles is distinct in terms of its structure and function.
- Many of these are considered together as endo membranous system because their functions are coordinated.
- Endomembrane system includes ER, Golgi complex, lysosomes and vacuoles.
- The functions of mitochondria, chloroplast and peroxysomes are not coordinated.
- So they are not considered as part of the endomembrane system.
Question 11.
Distinguish between active transport and passive transport.
Answer:
| Active transport | Passive Transport |
| 1) Movement of molecules (or) ions across the membrane through carrier proteins by utilizing metabolic energy is called Active transport. | 1) Movement of molecules across the membrane without utilizing metabolic energy is called Passive transport. |
| 2) It is carried against concentration gradient that is from lower to higher concentration. | 2) It is carried across concentration gradient that is from higher to lower concentration. |
| 3) Metabolic energy ATP is utilized in this process. Ex: Polar | 3) Metabolic energy ATP is not utilized Ex: Neutral solution. |
Question 12.
What are mesosomes? What do they help in?
Answer:
- The plasma membrane extends into the cell to form special membranous structures called mesosomes.
- These extensions are in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
- They help in cell wall formation, DNA replication, respiration, secretion, increase the surface area of plasma membrane and enzymatic content.
Question 13.
What are nucleosomes? What are they made of? [AP,TSMay-17][APM-16,19]
Answer:
- Nucleosome is a structural unit of eukary otic chromosome, consisting of a length of DNA coiled around a core of histones.
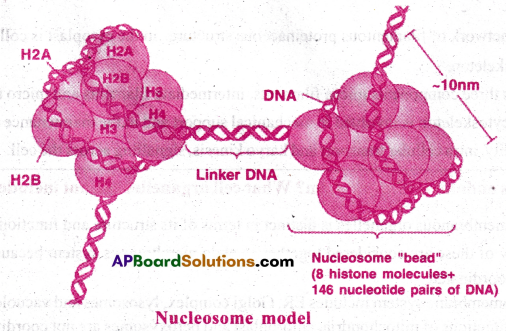
- A typical nucleosome contains 2Q0bp of DNA double helix wrapped (Two turns) around a core of histone octomer.
- It has two copies of each of four types of histone proteins viz., H2A, H2B, H3 and H4.
Question 14.
How do neutral solutes move across the plasma membrane? Can the polar molecules also move across it in the same way? It not, then how are these transported across the membrane?
Answer:
- Neutral solutes move across the membrane by diffusion along the concentration gradient ie., from higher concentration to the lower.
- No, the polar molecules cannot pass through the non polar lipid bilayer.
- The polar molecules require a carrier protein of the membrane to facilitate their transport across the membrane.
- A few’ ions are transported across the membrane against the concentration gradient.
- It is an energy dependent process. ATP is utilised and is known as active transport.
![]()
Question 15.
Name two cell-organelles that are double membrane bound. What are the characteristics of these two organelles? State their functions and draw labelled diagrams of both.
Answer:
Chloroplasts, Mitochondria and nucleus are double membrane bound cell organelles.
Question 16.
What are the characteristics of prokaryotic cell? [AP M-18]
Answer:
Characteristics of prokaryotic cell:
- Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, surrounding the cell membrane.
- There is no well defined nucleus. The nuclear membrane is absent.
- They are smaller, multiply more rapidly and vary greatly in shape and size.
- Its organization is fundamentally similar, even though they vary in the shape.
- The fluid matrix of the cell is the cytoplasm.
- The genetic material is naked, it is in the form of a single chromosome or circular DNA.
- Smaller circular DNA called plasmids are present out side the genome.
- The cell organelles, which are found in eukaryotes are absent, except in ribosomes.
- The infoldings of plasma membrane called mesosomes are present.
- The prokaryotic cells are seen in bacteria, blue-green algae, mycoplasma and PPLO.
Question 17.
Multicellular organisms have division of labour. Explain.
Answer:
- The organism with several cells in the body is called multicellular organism.
- Any multicellular organism, including man has to start its life with the division of a single cell called zygote.
- Similar cells unite to form a tissue and serves a particular function.
- Epithelial cells of animals covers the body of the animal and protect it from bacteria.
- Nervous tissue is meant for control and co-ordination.
- The conducting tissue, i.e., xylem and phloem of plants is meant for conduction of water and food materials respectively.
- Different functions are carried out by different tissues in multicellular organisms.
- This is known as division of labour.
Question 18.
Cell is the basic unit of life. Discuss in brief.
Answer:
- The cell theory states that cell is the basic structural and functional unit of the organism.
- The life of all multicellular organisms begins with a single cell.
- The body of unicellular organisms is made up of a single cell.
- In multicellular organisms, cells are grouped into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems.
- Each cell is made up of several organelles.
- Each organelle performs a particular function.
- So cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
Question 19.
What are nuclear pores? State their function.
Answer:
- The nucleus of a cell is surrounded by a double membrane called nuclear envelope.
- At a number of places the nuclear envelope is interrupted by minute pores called nuclear pores.
- Through these pores movement of RNA and protein molecules take places in both directions between nucleus and cytoplasm.
Question 20.
Both lysosomes and vacuoles are endomembrane structures, yet they differ in terms of their functions. Comment.
Answer:
I) Lysosomes: These cell organelles are vesicular structures, surrounded by a single membrane, found in animal cells.
- They are formed by a process of packing in the golgi apparatus.
- They contain hydrolytic enzymes (hydrolases)
- They digest carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
- Under starvation conditions, lysosomes digest own cellular contents and cause the death of the cell.
- So they are called “Suicidal bags of the cells”. This process is autolysis.
II) Vacuoles:
- The vacuole is the membrane bound space found in the cytoplasm and common in plant cells. It is surrounded by single membrane called tonoplast.
- It contains cell sap composed of water, metabolic bye products, excretion and other waste materials.
- Vacuolar sap also contain some pigments like anthocyanin which impart colour to the plant part.
- In plant cells vacuoles occupy 90% of cell volume and play an important role in osmoregulation.
![]()
Question 21.
Briefly give the contributions of the following scientists in formulating the cell theory
a) Rudolf Virchow
b) Schleiden and Schwann
Answer:
a) Rudolf Virchow:
- Rudolf Virchow first explained that cells divide and new cells are formed from pre-existing cells.
- He modified hypothesis of Schleiden and Schwann and gave a final shape to cell theory .
- All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells (R-Virchow)
b) Schleiden and Schwann:
- Schleiden is a German Botanist, examined a large number of plants.
- All plants are composed of different kinds of cells which form the tissues of the plant.
- Schwann is a British Zoologist, studied different types of animal cells.
- He reported that cells had a thin outer layer called plasma membrane.
- Based on his studies on plant tissues, he concluded that presence of cell wall is a unique feature of the plant cells.
- On this basis Schwann proposed cell theory, stating that the bodies of plants and animals are composed of cells and products of cells.
- Schleiden & Schwann together formulated cell theory.
- This theory did not explain how new cells are formed.
- Rudolf Virchow first explained that cells divide and new cells are formed from pre-existing cells.
Question 22.
Is extra genomic DNA present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? If yes, indicate their location in both the types of organisms.
Answer:
- Yes.
- In prokaryotes like bacteria the genomic DNA is in the form of a single chromosome or circular DNA. Where as the extra genomic DNA is in the form of small circular DNA moles outside the genomic DNA. These small circular DNA molecules are called plasmids.
- In Eukaryotes extra genomic DNA is present in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Nucleolus also contain small amount of DNA.
Question 23.
Structure and function are correctable in living organisms. Can you justify this by taking plasma membrane as an example?
Answer:
- Plasma membrane is the double membrane which surrounds the cytoplasm of cell and almost all the cell organelles.
- It is a double layer of lipids with protein molecules sand witched.
- The hydrophilic heads of lipids are towards the outer sides and hydrophobic tails towards the inner part.
- The function of plasma membrane as semipermeable membrane is similar in all living organisms.
- All neutral solutes like water move across the membrane passively towards their concentration gradient.
- With the help of carrier proteins ions move across the membrane against their concentration gradient. This process is called active transport.
Question 24.
Describe the cell organelle which contains chlorophyll pigments. [TS M-16, 22]
Answer:
- The cell organelles which contain chlorophyll pigment are called chloroplasts.
- They are double membrane bound structures.
- The space limited by the inner membrane is called the stroma.
- A number of flattened membranous sacs called thyalcoids are present in stroma.
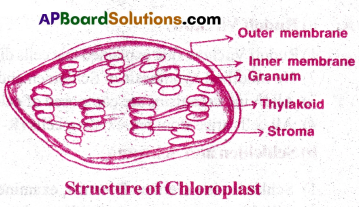
- Thylacoids are arranged in stacs like the piles of coins called grana.
- Jatmembranous tubules, called stroma lamellae connect the thylacoids of different grana.
- The membrane of the thylacoids encloses a space called lumen.
- The stroma of chloroplast contains enzymes required for the synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins.
- Chloroplasts also contain small, double stranded circular DNA molecules and ribosomes.
- Function: Chloroplasts perform photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 25.
Describe the structure and function of power houses of cell. [TS M-17]
Answer:
- Mitochondria are the power houses of cell.
- These cell organelles are bounded by a double membrane.
- Typically, a mitochondria is sausage shaped or cylindrical in shape.
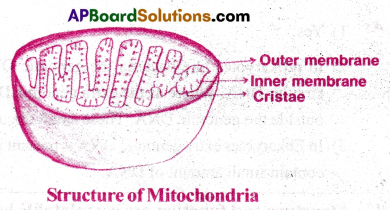
- The inner membrane divides its lumen ‘ into two compartments.
- The inner compartment is called matrix.
- The matrix contains single stranded circular DNA, 70S ribosomes and RNA.
- The outer membrane forms the continuous limiting boundary.
- The inner membrane forms a number of infoldings called cristae.
- The cristae increases the surface area.
- The two membranes have their own specific enzymes related to their function.
Functions:
- Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration.
- They produce cellular energy in the form of ATP. Hence they are called power houses of the cell.
Question 26.
Describe the structure of nucleus.
Answer:
Structure of Nucleus: Nucleus has four main parts. They are
I) Nuclear envelope II) Nuclear matrix III) Chromatin material IV) Nucleolus
I) Nuclear envelope: It consists of two parallel membrane with nucleoplasm inside.
The outer membrane is continuous with ER, which is coated by ribosomes. Minute pores are present on the membrane called nuclear pores.
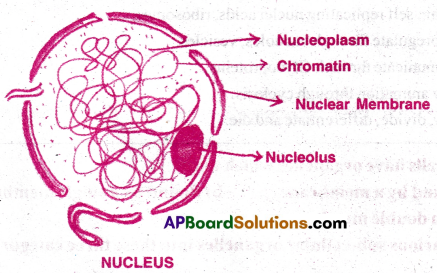
II) Nuclear matrix (or) Nucleoplasm: It is homogeneous, semi solid substance filled inside the nucleus. It is composed of glycoproteins, ribonucleo proteins, hydrolyzing enzymes, DNA and RNA polymerase.
III) Chromatin material: The darkly stained network like substance in nucleoplasm is called chromatin material. It contains DNA and histones.
IV) Nucleolus: One (or) more spherical bodies present in the nucleoplasm are called nucleoli.
Question 27.
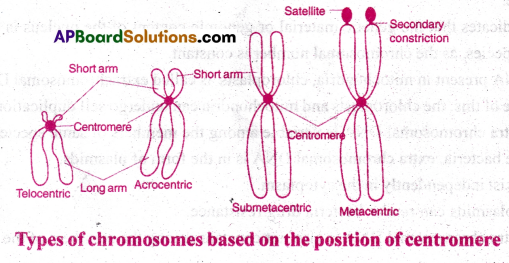
Give a brief account of the types of chromosomes based on the position of centromere. Answer: Based on the position of centromere, chromosomes are four types. [TS M-16,18,20]
Answer:
- Metacentric: This chromosome has a middle centromere with two equal arms.
- Sub metacentric: The centromere is nearer to one end of the chromosome, resulting in one shorter arm and one longer arm.
- Acrocentric: Centromere is close to its end forming one extremely short and one very long arm.
- Telocentric: This chromosome has a terminal centromere.
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What structural and functional attributes must a cell have to be called a living cell?
Answer:
Living cells have different organelles and perform different functions:
- Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
- The cell with a nucleus is called living cell. The cell without nucleus is the dead cell.
- Nucleus is the cell brain of the cell. Nucleus controls the functions of all the cell organelles.
- The chromosomes of the nucleus contain genes. Thus nucleus is involved in heredity.
- Nucleus plays important role in cell division and reproduction in unicellular organism.
- The fluid matrix of the cell is called cytoplasm. Several metabolic activities occur in the cytoplasm of a living cell.
- Cells obey laws of energies that is they transform energy.
- Cells contain self replicating nuclei acids, ribosomes.
- Cells osmoregulate through vacuoles, vesicles.
- Cells communicate through Glycoproteins.
- Cells show animation through cyclosis.
- Cells grow, divide, differentiate and die.
Question 2.
Eukaryotic cells have organelles which may
a) Not be bound by a membrane
b) Bound by a single membrane
c) Bound by a double membrane
Answer:
Group the various sub-cellular organelles into these three categories.
a) Cell organelles not bound by any membrane: Ribosomes, nucleolus.
b) Cell organelles bound by single membrane: Lysosomes, Vacuoles, Microbodies.
c) Cell organelles bound by double membrane: Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Nucleus, ER and Golgi complex .
Question 3.
The genomic content of the nucleus is constant for a given species where as the extra chromosomal DNA is found to be variable among the members of a population. Explain.
Answer:
- The total number of genes present in a haploid set of chromosomes of a living cell is called genome.
- This indicates that the genetic material or genomic content of the nucleus is constant for a given species, as the chromosomal number is constant.
- The DNA present in mitochondria, chloroplasts is called extrachromosomal DNA.
- Because of this, the chloroplasts and mitochondria can undergo self duplication.
- This extra chromosomal DNA is variable among the members of same species.
- In some bacteria, extra chromosomal DNA is in the form of plasmids.
- They exist independently in the cytoplasm.
- These plasmids can render bacteria drug resistance.
- This extra chromosomal DNA is also not constant among the members of the same species.
![]()
Question 4.
Justify the statement. “Mitochondria are power houses of the cell”. [AP M – 15]
Answer:
- Mitochondria are the cell organelle found in the eukaryotic cells. [TS M-22]
- Each mitochondrion is surrounded by a double membrane.
- The outer membrane forms a limiting boundary of the organelle.
- The inner membrane forms a number of infoldings called cristae.
- Stalked particles are present on cristae. They are F0 and F1 particles.
- The inner space is filled with matrix.
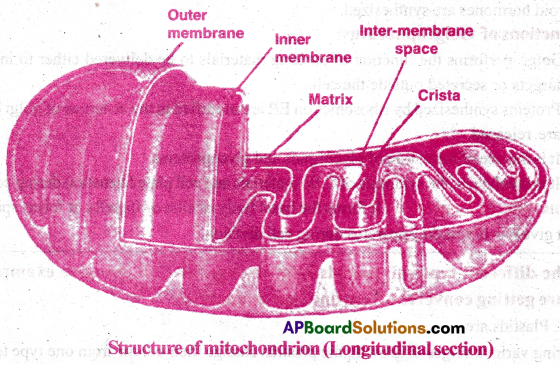
- The matrix consists of a single circular DNA molecule, a few RNA molecules, 70S ribosomes.
- The matrix also contains the compartments required for the synthesis of proteins.
- Kreb’s cycle occurs on cristae and Electron transport occurs in matrix.
- Mitochondria are involved in cellular aerobic respiration.
- This leads to oxidation of food material & hence the release of energy.
- The potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and stored in ATP
- As the mitochondria produce energy in the form of ATP(Adenosine Tri Phosphate), they are considered as power houses of the cell.
Question 5.
Is there are species specific or region specific type of plastids? How does one distinguish one from the other?
Answer:
Plastids bear some specific pigments, which impart specific colours to the part of the plant which possesses them.
Based on the type of pigments, plastids can be classified into three types:
- Chloroplasts
- Chromoplasts
- Leucoplasts.
1) Chloroplasts: These green coloured plastids help in the synthesis of food materials by photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments which trap light energy.
2) Chromoplasts: They are coloured pigments which were in yellow, orange or red in colour. In these plastids, fat soluble carotenoids like carotene and xanthophylls are present which imparts orange, red or yellow colour.
3) Leucoplasts: The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids of varied shapes and sized with stored nutrients. Based on the storage product, they are of three types namely amyloplasts (store starch) claioplasts (store oils) and alearoplasts (Store proteins).
Question 6.
Write the functions of the following
a) Centromere b) Cell Wall c) Smooth ER d) Golgi Apparatus e) Centrioles
Answer:
a) Functions of Centromere: Each chromosome has a primary constriction called centromere.
Centromere divides the chromosomes into two equal arms (or) two unequal arms based on its position in the chromosomes. On the sides of each centromere, disc shaped structures called kinetochores are present. These are helpful in the formation of daughter chromosomes during cell division.
b) Functions of Cell wall: Cellwall gives a shape to the cell. It protects the cell from mechanical damage. Cell wall is permeable and allows substances to pass through.
c) Functions of Smooth ER: It performs the synthesis of lipids. In animal cells, lipid like steroid hormones are synthesized.
d) Functions of Golgi apparatus:
- Golgi performs the function of packing materials to be delivered either to intra cellular targets or secreted outside the cell.
- Proteins synthesized by ribosomes on ER are modified in the cistemae of golgi before they are released.
- It is the site of formation of glycolipids and glycoproteins.
- It is involved in the synthesis of C. W. materials and cell plate formation during cell division.
e) Functions of Centriole : It forms the basal body of cilia or flagella. It forms spindle fibres that give rise to spindle apparatus during cell division.
![]()
Question 7.
Are the different types of plastids inter changeable ? If yes, give examples where they are getting converted from one type to another.
Answer:
- Yes, Plastids are interchangeable.
- During various stages of growth, the plastids change their colour from one type to other.
- For example, in potato when tubers are exposed to air, leucoplasts convert into chloroplasts.
- In tomato and chillies, the ovaries contain leucoplasts which change into chloroplasts.
- After fertilization and in ripe condition, the chloroplasts are transformed into chromoplasts.
Question 8.
Describe the structure of the following with the help of labeled diagrams.
i) Nucleus
ii) Centrosome
Question 9.
What is a centromere? How does the position of centromere form the basis of classification of chromosomes. Support your answer with a diagram showing the position of centromere on differen t types of chroiw asomes.
Answer:
Centromere is a region of chromosome where the two chromatids are held together.
Special proteins surround the centromere which form a disc shaped structures called kinetochores.
Each chromosomes shows centromere at a specific position.
Based on the position of centromere, monocentric chromosomes are four types.
1) Metacentric: Centromere present in the middle point of the chromosome. It is ‘V’ shaped and consists of two equal arms.
2) Sub-metacentric: Centromere is slightly away from the centre ofthechromosome.lt is ‘L’ shaped, and consists of two unequal arms.
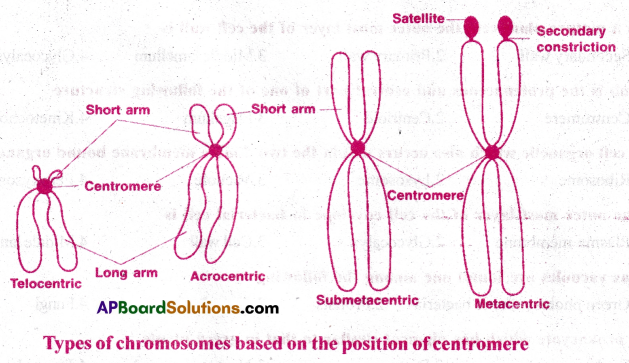
3) Acrocentric: Centromere is situated at the subterminal position of a chromosome. It is ‘J’ shaped. It consists of a very long arm and a very small arm.
4) Telocentric : Centromere is situated at the terminal position of a chromosome. It is T shaped and has only one arm.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Cell was discovered by
1. Robert White
2. Robert Brown
3. Robert Hooke
4. Rudolf Virchow
Answer:
3. Robert Hooke
Question 2.
Cell nucleus was discovered by
1. Leeuwenhoek
2. Robert Brown
3. Rudolf Virchow
4. Palade
Answer:
2. Robert Brown
Question 3.
Which one of the following dosot have a cellular structure
1. Diatoms
2. Bacteria
3. Actinomycetes
4. Viruses
Answer:
4. Viruses
Question 4.
Element necesary for the middle lamella is
1) Ca
2) Zn
3) K
4) Cu
Answer:
1) Ca
![]()
Question 5.
The smallest known living cell is
1. Yeast
2. Chlorella
3. Egg of an Ostrich
4. Mycoplasma
Answer:
4. Mycoplasma
Question 6.
Cells with centrally located nucleus are
1) Sclerenchymatous cells
2) Parenchymatous cells
3) Meristamatic cells
4) Collenchymatous cells
Answer:
3) Meristamatic cells
Question 7.
Conversion of fats into carbohydrates is carried out by
1) Lysosomes
2) Peroxisomes
3) Glyoxysomes
4) Chloroplasts
Answer:
3) Glyoxysomes
Question 8.
Prokaryotic cell does not contain
1) Ribosome
2) Mesosome
3) Plasma membrane
4) Nuclear membrane
Answer:
4) Nuclear membrane
Question 9.
Which of the following is an energy dependent process
1. Passive transport
2. 0smosis
3. Diffusion
4. Active transport
Answer:
4. Active transport
Question 10.
In a mature plant cell, the outer most layer of the cell wall is
1. Secondary wall
2. Primary wall
3. Middle lamellum
4. Glycocalys
Answer:
3. Middle lamellum
Question 11.
Hub is the protenaceous and central part of one of the following structure
1. Centromere
2. Centriole
3. Flagellum
4. Kinetochore
Answer:
2. Centriole
Question 12.
A cell organelle which also occurs within the two double membrane bound organelles is
1. Ribosome
2. Lysosome
3. Vacuole
4. Peroxysome
Answer:
1. Ribosome
![]()
Question 13.
The outer most layer of the cell envelope in bacterial cell is
1. Plasma membrane
2. Glycocalyx
3. Cell wall
4. Middle lamellum
Answer:
2. Glycocalyx
Question 14.
Gas vacuoles are found one among the following
1. Green photosynthetic bacteria
2. Protists
3. Amoeba
4. Fungi
Answer:
1. Green photosynthetic bacteria
Question 15.
A prokaryote which has pigment similar to that in green plants
1. Euglena
2. Diatoms
3. Nostoc
4. Desmids
Answer:
3. Nostoc
Question 16.
In which of the following organisms the genome occurs in the form of a single circular DN A .
1. Protistans
2. Bacteria
3. Fungi
4. Plants
Answer:
2. Bacteria
Question 17.
Movement of chromosomes during cell division is called
1. Cytokinesis
2. Cell motility
3. Karyokinesis
4. Karyogamy
Answer:
3. Karyokinesis
Question 18.
Which of the following eukaryotes with nucleus has chromosomes but without histones
1. Plant cell
2. Fungi
3. Desmids
4. Dinoflagellates
Answer:
4. Dinoflagellates
Question 19.
Which of the following non-cellular organisms gives the meaning of poisonous fluid
1. Virus
2. Viroid
3. Prion
4. My coplasma
Answer:
1. Virus
Question 20.
The organisms which show inert crystalline structure outside the living cell are
1. Viroids
2. Prions
3. Viruses
4. Protistans
Answer:
3. Viruses
Question 21.
The infectious agents which cause ‘scrapie disease’ are
1. Non-cellular
2. Unicellular
3. Prokaryotic
4. Multicellular
Answer:
1. Non-cellular
Question 22.
Applications of concepts and techniques of physics & chemistry in understanding biology is called
1) Functional biology
2) Environmental biology
3) Evolutionary biology
4) Reductionist biology
Answer:
4) Reductionist biology
Question 23.
In which group all are membrane bound?
1) Nucleus, Nucleolus, Vacuole
2) Chioroplast, peroxisome, ribosome
3) Glyoxisome, Lysosome, Mitochondria
4) G.C., E.R,, Centriole
Answer:
3) Glyoxisome, Lysosome, Mitochondria
![]()
Question 24.
Organelle lacking l)NA but capable of duplication is
1) Ribosome
2) Centriole
3) Chioroplast
4) Mitochondria
Answer:
2) Centriole
Question 25.
The seat of nucleases, proteases, lipases and carbohydrases in the eukaryotic cell.
1) Lysosome
2) Vacuole
3) E.R
4) Golgi complex
Answer:
1) Lysosome
Question 26.
Cell organelle with only one type of nucleic acid is
1) Ribosome
2) Mitochondria
3) Chioroplast
4) Vacuole
Answer:
1) Ribosome
Question 27.
Diameter of a nucleosome bead is
1) 200nm
2) 10nm
3) 146 run
4) 20nm
Answer:
2) 10nm
Question 28.
Common cell wall material in primary wall, secondary wall and middle lamellum is
1) Cellulose
2) Suberin
3) Pectin
4) Lignin
Answer:
3) Pectin
Question 29.
Ratio of Ht ,I12 and Hj protein molecules iin nucleosomes
1) 1 : 2 :2
2) 1 : 1 : 2
3) 2 : 1 : 2
4) 1 : 4 : 2
Answer:
4) 1 : 4 : 2
Question 30.
In eukaryotic cells, there is a extensive compartmentaliiation of cytoplasm due to
1) Presence of fibres
2) Presence of different types of molecules
3) Presence of membrane bound cell organelles
4) All the above
Answer:
3) Presence of membrane bound cell organelles
![]()
Question 31.
Which of the following wall is capable of growth in plant cell?
1) Primary cell wall
2) Secondary cell wall
3) Middle lamellum
4) 1 & 3
Answer:
1) Primary cell wall
Question 32.
Experimental material used for the study chemical structure of cell membrane was
1) White blood cells
2) Red blood cells
3) Platelets
4) Lymph cells
Answer:
2) Red blood cells
Question 33.
Similar character between prokaryotic cell & eukaryotic cells is
1) Cell wall composition
2) Presence of slime layer
3) Composition of cell membrane
4) Nature of nucleus
Answer:
3) Composition of cell membrane
Question 34.
Cis face of golgi cisternae is always
1) Nearer to the nucleus
2) Nearer to the nucleolus
3) Away from the nucleus
4) Away from the nucleolus
Answer:
1) Nearer to the nucleus
Question 35.
Hydrolytic enzymes present in the lysosome are optimally active at
1) Acidic pH
2) Basic pH
3) Neutral pH
4) No influence of pH
Answer:
1) Acidic pH
Question 36.
hoptosynthetic structu res of proka ryotes
1) Chromatophores
2) Chromoplasts
3) Inclusion bodies
4) Chioroplasts
Answer:
1) Chromatophores
![]()
Question 37.
Plasmodesmata connections help in
1) Cytopiasmic streaming
2) Synchronous mitotic divisions
3) Locomotion of univellular organisms
4) Movement of substances within cells
Answer:
1) Cytopiasmic streaming
Question 38.
Organclle associated with packing of secretary substances is
1) RER
2) GC
3) Lysosome
4) Ribosome
Answer:
2) GC
Question 39.
A → B → Lysosomc, A and B are respectively
1) GC and ER
2) GC and NM
3) ER and NM
4) ER and GC
Answer:
4) ER and GC
Question 40.
Number of longitudinal peripheral fibres found in a centriole is
1) 2
2) 9
3) 5
4) 7
Answer:
2) 9
Question 41.
Tonoplasm is made-up of
a) H2O
b) Metabolic bye products
c) Secretory substances
d) Excretory materials
1) a only
2) a, d only
3) a,b,d only
4) a,b,c&d
Answer:
2) a, d only
Question 42.
Living cells without nuclei
a) RBC of mammals
b) Mature sieve tubes
e) WBC of mammals
d) Sciereids
1) a,b,c,d
2) a,b,c
3) a,d
4) a,b only
Answer:
4) a,b only
![]()
Question 43.
Lipids and proteins act a structural units in
a) Plasma membrane
b) Cloroplast membranes
e) Thylakoid membranes
d) Endo membrane system
e) Nuclear membrane
1) a & b only
2) b & c only
3) c & d only
4) All are correct
Answer:
4) All are correct