Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 5th Lesson Morphology of Flowering Plants which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 5th Lesson Morphology of Flowering Plants
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate fibrous roots from adventitious roots.
Answer:
| Fibrous roots | Adventitious roots |
| 1) The roots that originate from the base of stem are called fibrous roots. 2) Ex: Monocots like Maize. |
1) The roots which arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle are called adventitious roots. 2) Ex:Velamen, Parasite roots, Ficus |
Question 2.
Define modification. Mention how root is modified in banyan tree and mangrove plants?
Answer:
- A permanent change in the shape, structure of a plant body in order to perform a new function depending upon environment is called modification.
- In banyan, pillar like roots arise from the long heavy branches to give additional support to them.
- In Mangrove plants live Avicennia, Rhizophora the roots corneout of the ground and grow vertically upwards. Such roots are called Respiratory roots. Penumatopores as they help to get oxygen for respiration.
![]()
Question 3.
What type of specialized roots are found in epiphytic plants? What is their function?
Answer:
- Velamen roots are found in epiphytes plants.
- The function of these adventitious roots is to absorb moisture from atmosphere.
Question 4.
How does the sucker of Chrysanthemum differ from the stolon of jasmine?
Answer:
- Sucker of chrysanthemum is an obliquely growing branch of an underground stem.
- But, stolon of Jasmine is an obliquely growing branch of an aerial stem.
- Both serve vegetative propagation when separated from the parent plant.
Question 5.
What is meant by pulvinus leaf base? In members of which angiospermic family do you find them? [TS M-20][APM-17][IPE Mar-14]
Answer:
- The swollen leaf base is called pulvinous leaf base.
- It is seen in ‘Leguminaceae’ family.
Question 6.
Define venation. How do dicots differ from monocots with respect to venation? [AP M-15] [TS-18]
Answer:
Venation: The mode of arrangement of veins and veinlets in the lamina of a leaf is called venation.
| Leaves of Dicots | Leaves of Monocots |
| 1) In dicots reticulate venation is seen. 2) Veinlets are arranged in network manner. Ex: Hibiscus |
1) In monocots parallel venation is seen. 2) Veins are arranged parallely to each other. Ex: Musa |
Question 7.
How is pinnately compound leaf is different from a palmately compound leaf? Explain with one example each.
Answer:
| Pinnately compound leaf | Palmately compound leaf |
| In pinnately compound leaf, the leaflets are arranged on either side of a common axis called rachis. Ex: Murraya, Neem | In palmately compound leaf, the leaflets are arranged at the tip of petiole. Ex: Dolichos, Silk cotton. |
Question 8.
Which organ is modified to trap insects in insectivorous plants? Give two examples.
[AP M-19] [IPE Mar-13]
Answer:
In insectivorous plants, leaves are modified to trap the insects. Ex: Nepenthes, Drosera, Dionea.
Question 9.
Differentiate between Racemose and Cymose infSoreseences. [AP M- 22] [TS M-15]
Answer:
| Racemose | Cymose |
| 1) In Racemose inflorescence, the growth of the main axis is indefinite. 2) The flowers are arranged in acropetal succession. |
1) In Cymose inflorescence, the growth of the main axis is limited 2) The flowers are arranged in a basipetal succession. |
Question 10.
What is the morphology of cup like structure in Cyathium? In which family it is found?
[TS M-17, 22] [AP M-15]
Answer:
In Cyathium, involucre of bracts unite to form a cup like structure. It is found in the family Euphorbiaceae.
![]()
Question 11.
What type of inflorescence is found in fig trees? Why does the insect Blastophaga visits the inflorescence of fig tree? [AP M-16]
Answer:
- The inflorescence found in fig trees is hypanthodium.
- Insect Blastophaga visits the inflorescence for pollination and it leaves the eggs in the gall flowers.
Question 12.
Differentiate actinomorphic from zygomorphic flower. [TS May-17, 19, 22] [AP M-16]
Answer:
| Actinomorphic flower | ‘ Zygomorphic flower |
| Actinomorphic flower can be cut into two equal halves in any vertical plane. | Zygomorphic flower can be cut into two equal halves in one vertical plane. |
| Ex: Datura, Hibiscus | Ex: Bean, Crotalaria. |
Question 13.
How do the petals in pea plant are arranged? What is such type of arrangement called?
Answer:
In pea flowers, there are five petals, the largest (standard) petal over laps the two lateral petals (wings), which in turn overlap the two smallest anterior keel petals. This type of aestivation is called vexillary or papilionaceous.
Question 14.
What is meant by epipetalous condition? Give an example. |TSM-22|| AP M -17,19,22J
Answer:
- When the stamens are attached to the petals, it is called epipetalous condition.
- Ex: Datura Brinjal.
Question 15.
Differentiate between apocarpous and syncarpous ovary.
Answer:
| Apocarpous Ovary | Syncarpous Ovary |
| 1) All the carpels of gynoecium present on the thalamus are free from each other | 1) All the carpels of gynoecium present on the thalamus are fused with each other. |
| 2) Ex: Lotus, Rose. | Ex:Mustard, Tomato. |
Question 16.
Define placentation. What type of placentation is found in Dianthus? [TS M-15,20]
Answer:
- Placentation: The mode of arrangement of ovules in a ovary is known as placentation.
- In Dianthus, the placentation is ‘free central’. [AP M-20]
Question 17.
What is meant by parthenocarpic fruit? How is it useful? [AP May-19][ APM-17J
Answer:
- When a fruit is formed without fertilization of ovary, it is called parthenocarpic fruit.
- It is useful in the Juice industries for commercial production of seedless fruits. Ex: Banana.
![]()
Question 18.
What is the type of fruit found in mango? How does it differ from that of coconut?
Answer:
- The type of fruit found in mango is drupe.
- The mesocarp of mango is fleshy and edible, where as the mesocarp of coconut is fibrous.
Question 19.
Why certain fruits are called false fruits? Name two examples of plants having false fruits. [AP M-19]
Answer:
- A fruit developing from fertilized ovary is called true fruit. Hence, any fruit which is developed from any part of the flower other than the ovary is called as false fruit.
- Ex: Apple, Artacardium.
Question 20.
Name any two plants having single seeded dry fruits. [TS M -19]
Answer:
- Cashew (nut)
- Rice (Caryopsis)
- Tridax (Cypsela)
Question 21.
Define schizocarpic dry fruits. Give an example.
Answer:
Schizocarpic dry fruits: The dry fruits which split into one seeded (bits) mericarps are known as schizocarpic dry fruits. Ex: Acacia, Castor, Coriandrum.
Question 22.
Define mericarp. In which plant you find it? [TSM-16]
Answer:
Mericarp: The one seeded bits of Schizocarpic fruits are called mericarps.
Ex: Acacia, Castor.
Question 23.
What are aggregate fruits? Give two Examples.
Answer:
In Custard Apple, many carpels are present. Each carpel of apocarpous gynoecium develops into a fruitlet. Such bunch of fruitlets are called aggregate fruits. Ex: Annona (Custard Apple), Lotus
Question 24.
Name a plant that has single fruit developing from the entire’inflorescence. What is such a fruit called?
Answer:
The plant which has single fruit developing from the entire inflorescence is ‘Pineapple’ (Ananas sativus) (or) ‘Jackfruit’ (Artocarpus). Such a fruit is called composite fruit.
Question 25.
What is meant by scutellum? I n which type of seeds is it present?
Answer:
- Scutellum: Shield shaped cotyledon present in between embryo of monocots is called Scutellum.
- It is present in monocot seeds like grapes, maize.
- It is specialized for digestion and absorption of the endosperm during germination.
![]()
Question 26.
Define with examples endospermic and non endospermic seeds.
Answer:
1) Endospermic Seeds: Seeds which have an endosperm at maturity are called endospermic seeds. These are also called as albuminous seeds.
- Endospermic monocot seeds. Ex: Rice, wheat, Maize, Barley.
- Endospermic dicot seeds. Ex: Castor, cotton, coffee
2) Non endospermic seeds: Non-endospermic seeds are those which do not have an endosperm in the mature seed. These are also called as ex-albuminous seeds, (cotyledons store food)
- Non-endospermic monocot seed. Ex: Pother, Vallisneria
- Non-endospermic dicot seed. Ex: Pea, gram, Bean.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain different regions of root with neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
A typical young root shows 4 regions:
- Root cap
- Region of meristematic activity
- Region of elongation
- Region of maturity
1) Root cap:
- The root is covered at the apex by a thimble- like structure called the root cap.
- It protects the tender apex of the root as it makes its way through the soil.
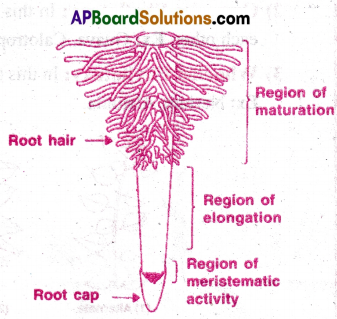
2) Region of meristematic activity:
- The cells of this region are very small, thin walled and with dense protoplasm.
- They divide repeatedly to produce daughter cells.
3) Region of elongation:
- The cells proximal to the meristematic region undergo rapid elongation.
- These responsible for the growth of the root in length.
4) Region of maturity :
- The cells of the elongation zone gradually differentiate and mature.
- Hence the zone proximal to region of an elongation, is called region of maturity.
- From this regions, some of the epidermal cells form very fine delicate thread like structures called root hairs.
- Root hairs absorb water and mineral salts from the soil.
Question 2.
Justify the statement: “Under ground parts of plants are not always roots”.
Answer:
- The under ground part of any plant is generally the root, but it always need not be a root.
- Some times the stems also remain beneath the surface of the soil.
- Such stems are called underground stems.
- The normal stem characters are evident in them.
- The nodes, intemodes, scale leaves, axillary, and terminal buds are clearly seen in them.
- So, under ground parts of plants are not always roots.
Ex : Stem tuber of potato, Bulb of Onion, Rhizome of Zingiber,
Question 3.
Explain with examples different types of phyllotaxy.
Answer:
The mode of arrangement of leaves on the stem is called phyllotaxy. It is of three types.
- Alternate Phyllotaxy
- Opposite Phyllotaxy
- Whorled Phyllotaxy
1) Alternate Phyllotaxy: In this type, single leaf arises at each node in alternate manner.
Ex: Hibiscus, Sunflower.
2) Opposite Phyllotaxy: In this type, a pair of leaves arise at each node and lie opposite to each other. Ex: Guava, Calotropis.
3) Whorled Phyllotaxy: In this type, more than two leaves arise at a node and form a whorl Ex: Nerium, Alstonia.
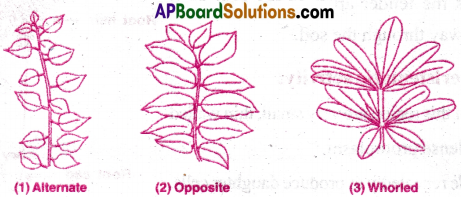
![]()
Question 4.
How do leaf modifications help plants?
Answer:
The normal functions of leaf are photosynthesis, respiration and transpiration. Some times the leaf serves additional functions than the above said and is called a modified leaf.
The modifications are
- Tendrils
- Thoms
- Storage leaves
- Phyllode
- Insectivorous leaves
- Reproductive leaves.
1) Tendrils: In weak stemmed plants, the entire leaf or any part of the leaf modify into a slender, delicate sense organ called tendril. It helps the plant to climb upon the support to expose the leaf to get maximum amount of sunlight. Ex: Pisum.
2) Thorns: Thom is a pointed, sharp, sense organ. When it touches an object it becomes stiff and helps in climbing upon the support. It also reduces the rate of transpiration in xerophytes and also protects the plant from herbivorous animals. Ex: Bougain villia.
3) Storage leaves: Some fleshy leaves store food. Ex: Onion, garlic.
4) Phyllode: Green, photosynthetic petiole is called phyllode. In some xerophytes, normal leaves are modified into spines to reduce the rate of transpiration, then the petiole or rachis is modified into phyllode Ex: Acacia melenoxylon, Parkinsonia.
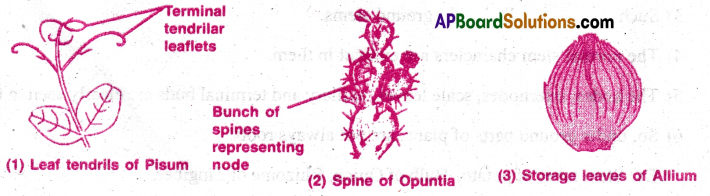
5) Insectivorous leaves: Some plants grow in nitrate deficient soils. In them the leaves are modified to trap the insects and get nitrates from the bodies of insects. Ex: Nepenths, Drosera.
6) Reproductive leaves: Epiphyllous buds are present on the margin of leaves like Biyophyllum. When ever the leaf touches the soil, the buds get accelerated and become new plants.
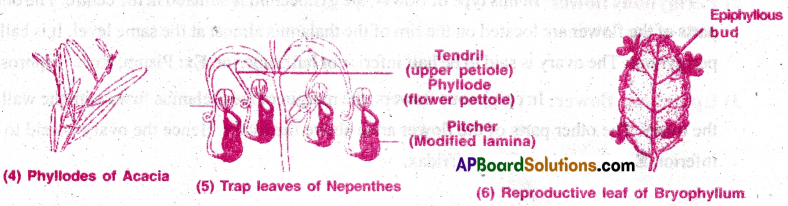
Question 5.
Describe any two special types of inflorescences. [TS M-22]
Answer:
Types of Inflorescences:
1. Cyathium 2. Hypanthodium
1) Cyathium:
- Cyathium is a special type of inflorescence which looks like a cup.
- The cup is formed by the union of involucre of bracts.
- Inside the cup naked, stalked and unisexual flowers are arranged in a cymose manner.
- In the centre of the cup a single female flower with tri carpellary ovary is present.
- The male flowers are arranged in a monochasial pattern around the female flower.
Ex: Members of family Euphorbiaceae-Euphorbia.
2. Hypanthodium:
- Hypanthodium is a fruit like inflorescence. Here, the peduncle is modified into a deep cup like fleshy structure.
- Many sessile, unisexual flowers are arranged irregularly inside the cup.
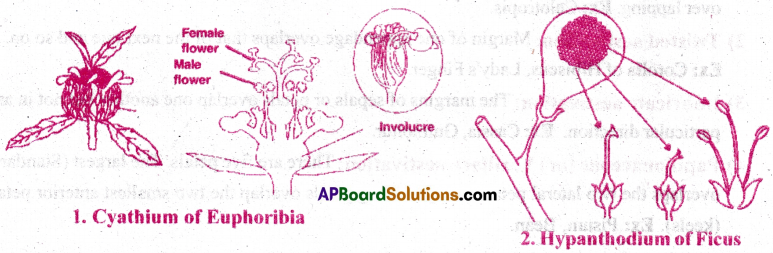
- Male flowers are located near the opening, female flowers at the bottom and sterile female flowers (gall flowers) are between them. Ex: Ficus .
Question 6.
Describe the arrangement of flora! members in relation to their insertion on thalamus.
[TS M-22]
Answer:
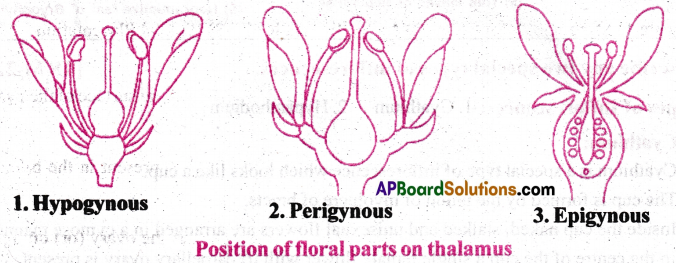
Based on the position of calyx, corolla and insertion of floral members on thalamus, flowers are three types.
- Hypogynous
- Perigynous
- Epigynous.
1) Hypogynous flower: In this type of flower, the gynoecium occupies the highest position. The other parts are situated below it. The ovary in such flowers is superior.
Ex: Mustard, Brinjal, Datura.
2) Perigynous flower: In this type of flower, the gynoecium is situated in the centre. The other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level. It is called perigynous. The ovary is said to be half inferior or half superior. Ex: Pisum, Rose, Tephrosia.
3) Epigvnous flower: In epigynous flowers, the margin of the thalamus fuses with the wall of the ovary. The other parts of the flower arise above the ovary. Hence the ovary is said to be inferior. Ex: Cucumber, Guava, Tridax.
Question 7.
“The flowers of many angiospermic plants which show sepals and petals, differ with respect to the arrangement of sepals and petals in respective whorls”. Explain.
Answer:
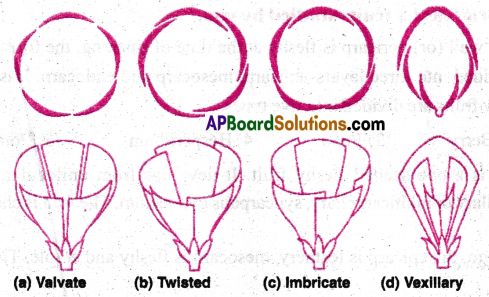
The mode of arrangement of sepals or petals in a floral bud is known as aestivation .
Main types of aestivation:
- Valvate aestivation
- Twisted aestivation
- Imbricate aestivation
- Papilionaceous aestivation
1) Valvate aestivation: Sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margin without over lapping. Ex: Calotropis.
2) Twisted aestivation: Margin of one appendage overlaps that of the next one and so on. Ex: Corolla of Hibiscus, Lady’s Finger.
3) Imbricate aestivation: The margins of sepals or petals overlap one another but not in any particular direction. Ex: Cassia, Gulmohur.
4) Papilionaceous (or) Vexillary aestivation: There are five petals. The largest (Standard) overlaps the two lateral petals (wings). Wing petals overlap the two smallest anterior petals (keels). Ex: Pisum, Bean.
![]()
Question 8.
Describe any four types of placentations found in flowering plants. [TS M-22]
Answer:
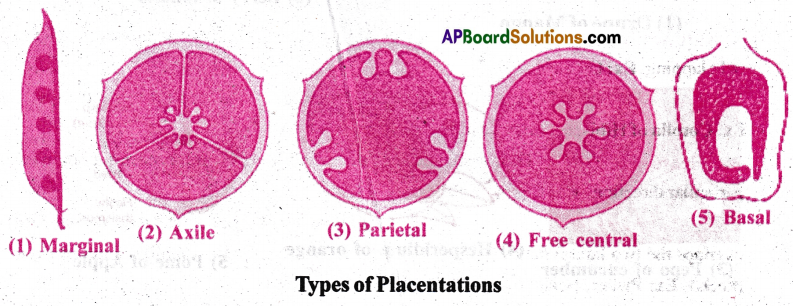
The arrangement of ovules within the ovary is known as placentation. It is of 5 types.
They are
- Marginal Placentation
- Axile Placentation
- Parietal Placentation
- Free central Placentation
- Basal Placentation
1) Marginal Placentation: The ovary is unilocular. Along the ventral surface of the ovary, the ovules are borne on the ridge forming two rows. Ex: Pea, Pisum.
2) Axile Placentation: The ovules are attached to a central axis present in the bilocular to multilocular ovary. Ex: Hibiscus, Lemon, Tomato.
3) Parietal placentation: Ovules are borne on the inner wall of the ovary (or) on a parietal part, The ovary is tricarpellary unilocular in curcurbita. The ovary is one chambered but it becomes two chambered due to the formation of a false septum. Ex: Brassica (Mustard).
4) Free central placentation: The ovules are borne on the central axis without septa. . Ex: Dianthus, Primrose.
5) Basal placentation: Single ovule is attached to placenta at the base of the ovary.
Ex: Sunflower, Marigold, Tridax.
Question 9.
Describe in brief fleshy fruits studied by you.
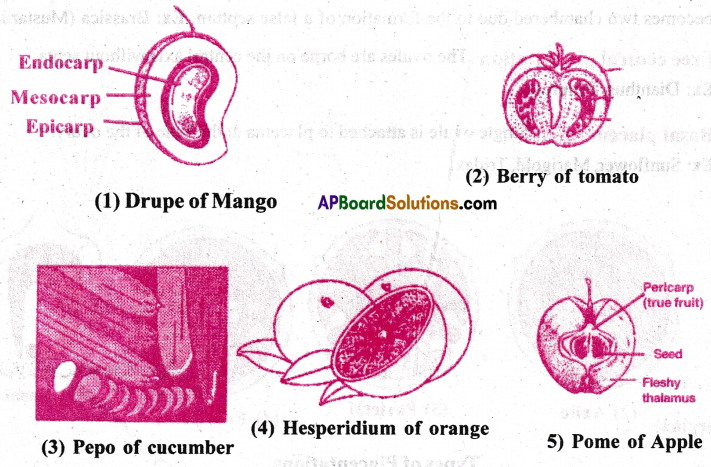
Answer:
When the fruit wall (or) pericarp is fleshy at the time of ripening, the fruit is said to be fleshy.
Pericarp is divided into three layers- epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Based on the nature of pericarp, fleshy fruits are divided into five types.
- Drupe
- Berry
- Pepo
- Hesperidium
1) Drupe: It is a one seeded fleshy fruit. It develops from unilocular, superior ovary of monocarpellary or multicarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium. The fruit is characterised by stony endocarp.
Ex: In Mango, the epicarp is leathery, mesocarp is fleshy and edible. The inner endocarp is hardstony.
In cocos, the epicarp is leathery, mesocarp is fibrous. The inner endocarp is hardstony. The edible part is the endosperm of seed[copra].
2) Berry: It is a fleshy fruit having one or more seeds. It develops from ovary of bi or multi carpellary syncarpous gynoecium. The pericarp is differentiated into epi, meso and endocarps. The meso and endocarps fuse to form pulp. Seeds are the hard portions and are scattered in the pulp. Ex: Tomato, Grapes, Guava.
3) Pepo: It develops from a tricarpellay, syncarpous unilocular inferior ovary. The epicarp is like a rind, the mesocarp is fleshy and the endocarp is smooth. Ex: Cucumber.
4) Hespcridium: It develops from multicarpellary, syncarpous, multilocular superior ovary. The epicarp is leathery with volatile oil glands, mesocarp is papery and endocarp wall bears juicy hairs. Ex: Citrus, Orange.
5) Pome: It develops from inferior ovary of bi or multicarpellary gynoecium and is surrounded by fleshy thalamus. The endocarp is cartilagenous. Ex: Apple.
Question 10.
Describe with examples the various dry fruits studied by you.
Answer:
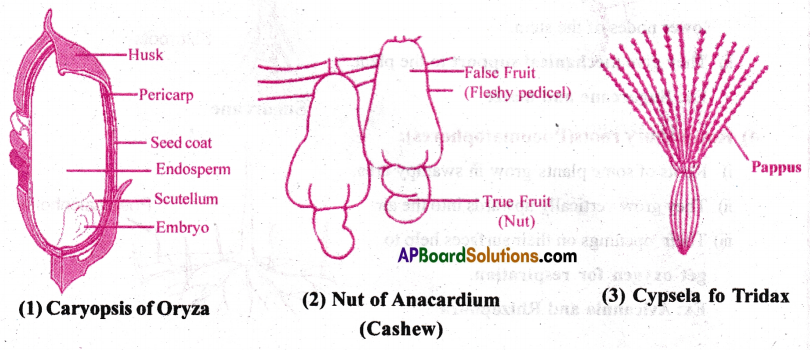
When the fruit wall or pericarp is dry at the time of ripening the fruit is said to be dry. The dry fruits are of three types.
- Dry dehiscent
- Dry indehiscent fruits
- Schizocarpic fruits
1) Dry dehiscent: These dry fruits break open and liberate seeds. They are of different types.
a) Legume: The fruit breaks dorsiventrally into two halves and liberate the seeds.
Ex: Pea, bean
b) Capsule: It dehisces in different ways to liberate the seeds. Ex: Cotton, Datura.
2) Dry indehiscent fruits: In this type, the fruit remain unopened and liberate the seeds only after disintegration Of pericarp. They are of the following types.
a) Caryopsis: In this the pericarp and seed coat fuse together. It is characteristic of the family poaceae. Ex: Grass, Rice.
b) Nut: It is developed from a multicarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular ovary and the pericarp is stony. Ex: Cashew.
c) Cypsela: It is a single seeded fruit, characterised by persistent pappus like calyx.
Ex: Tridax.
3) Schizocarpic fruits: When a fruit splits into one- seeded bits, it is said to be a schizocarpic fruit. Ex: Acacia, Castor.
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define root modification. Mention the types of root systems. Explain how root is modified to perform different functions. [AP May-19] [ AP, TS M-15, 17] [TS M- 20]
Answer:
Root: The under ground part of the flowering plant is called root.
Roots are of two types: (i) Tap Roots (ii) Fibrous Roots
Main functions of roots are fixation, absorption and conduction of water, Minerals.
Root modification: Roots in some plants change their shape and structure to perform some additional functions other than fixation, absorption and conduction.
Such modification of roots is called Root Modification.
Types of Root modifications and Functions:
1) Storage roots:
- Roots of some plants store food material.
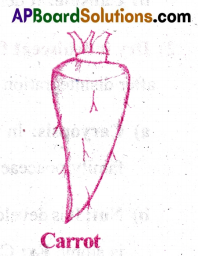
- Due to this, the roots become swollen.
Ex:Tap roots in carrot;
Adventitious roots in sweet potato; Fibrous roots in Asparagus.
2) Proproots:
- Roots of some trees arise from heavy branches.
- They hang in air and enter into soil.
Ex: Banyan Tree

3) Stilt roots:
- Roots of some plants arise from the lower nodes of the stem.
- They give mechanical support to the plant. Ex: Sugarcane and maize
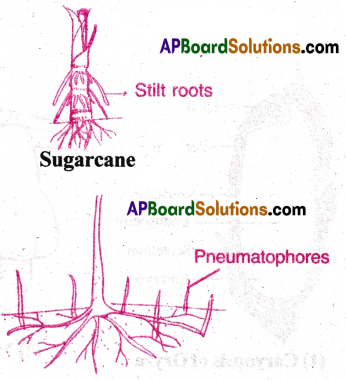
4) Respiratory roots(Pneumatophores):
- Roots of some plants grow in swampy area.
- They grow vertically upwards into the air.
- Their openings on their surfaces help to get oxygen for respiration.
Ex: Avicannia and Rhizophora
5) Velamen roots:
- Roots of some plants are found on the branches of some other plants (epiphytes).
- The function of these adventitious roots is to absorb moisture from atmosphere.
Ex: Vanda.
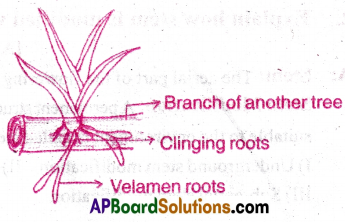
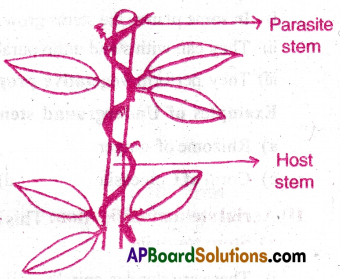
6) Parasitic roots(or) Hailstorm roots:
- The plants that depend upon some other plants for their food and water are Called parasite plants
- They are two types.
a) Complete parasites Ex: Cuscuta
b) Partial parasites: Ex: Viscum, Striga.
7) Nodular roots:
- Roots having nodules are called nodular roots.
- These are present in the members of Fabaceae.
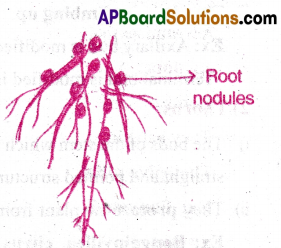
- Rhizobium bacteria live in the root nodules and they fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- Ex: Ground Nut
8) Photosynthetic roots:
- Roots of some plants become chlorophyllous (green).
- In these plants, normal, green leaves are reduced.
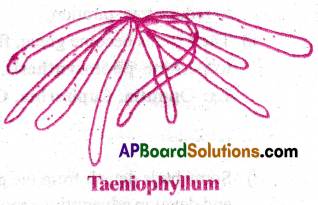
- They perform photosynthesis.
- Ex: Taeniophyllum.
Question 2.
Explain how stem is modified variously to perform different functions. [AP Mar-19,20] [AP May-17,22] [TS M-16, IPE-14]
Answer:
Stem: The aerial part of the flowering plant is called stem.
Stem Modification : A permanent structural change in the stem to perform some special functions suitable to the environment is called stem modification. This is of three types.
I) Underground stem modification
II) Aerial stem modification
III) Sub-aerial stem modification.
I) Underground stem modification:
- In some plants, the stems grow into soil.
- They can with stand unfavourable conditions and become Perennial plants.

- They perform vegetative propagation. They store food material.
Examples of Underground stems:
a) Rhizome of ginger
b) Bulb of Onion
c) Corm of Colocasia
d) Stem tuber of Potato
II) Aerial stem modification: This is of four types.
1) Stem tendrils:
- These are slender, spirally coiled structure,

- They help in climbing up.
Ex: Axillary bud is modified into a tendril in cucumber, watermelon.
Terminal bud is modified into a tendril in grape vines.
2) Thorns:
- The buds of the stem which modify into woody, straight and pointed structures are called thorns.
- They protect the plant from grazing animals.
Ex: Bougainvillea, citrus.

3) Phylloclades:
- In some xerophytes, the leaves are modified to reduce transpiration.
- Their stems become green, flat and photosynthetic to perform photosynthesis.
Ex: Opuntia, Euphorbia, Casuarina.
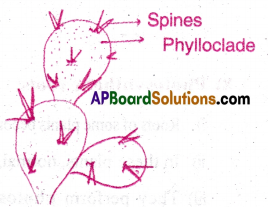
![]()
4) Bulbils:
- Some buds, detach from the parent plant, and develop adventitious roots(buds) to store food.
- Such buds are called bulbils.
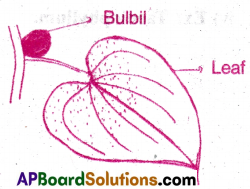
- This helps in vegetative reproduction.
Ex: Floral buds (Agave),
Vegetative buds (Diascoria)
III) Sub-aerial stem moditlcat ioti: Here the stems are partly aerial and partly underground.
They help in vegetative propagation. They are four types.
I) Runner:
- In some plants, subaerial stems spread to new niches and form new plants when older parts die.
- Such plants are called runners.
Ex: Strawberry, Oxalis
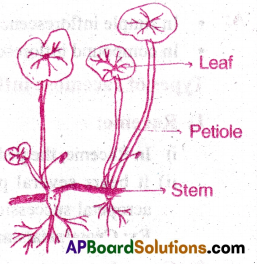
2) Stolon:
- In some plants, a slender lateral branch grows aerially.
- After some time, it arches downwards to touch the ground and produce adventitious roots.
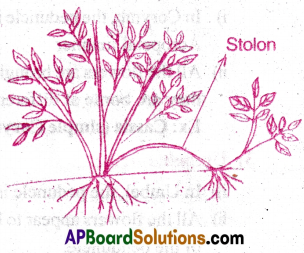
- Such branches are called stolons.
- When detached from the parent plant they lead independent life.
Ex: Jasmine, Nerium
3) Offset:
- ‘One intemode length’ of a lateral branch of acquatic plants is called ‘offset’.
- It bears a rosette of leaves at each node and a tuft of balancing roots .
Ex: Pistia and Eichhornia

4) Sucker:
- In some plants, a part of the stem lies in the underground.
- Some lateral branches originate from the main stem.
- They grow horizontally and then come out obliquely upwards giving rise to leafy shoots.
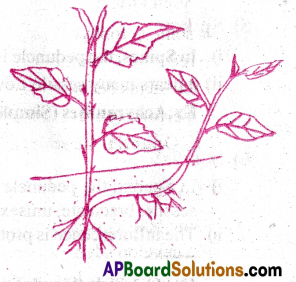
- These branches are called suckers.
Ex: Banana, Chrysanthemum
Question 3.
Explain different types of racemose inflorescences. [TS M-19] [AP M-16]
Answer:
- In simple inflorescence, the flowers grow on the Main Peduncle (Main axis).
- In compound inflorescence, the flowers grow on their branches.
Types of racemose inflorescences:
1) Raceme:
- In Raceme, the peduncle grows indefinitely,
- It bears several pedicellate, bracteate flowers in an acropetal succession.
Ex: CrotaIaria(simple raceme), Mangifera (compound)
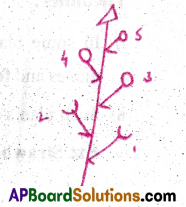
2) Corymb:
- In Corymb, the peduncle is long. It bears many flowers in Acropetal manner
- All the flowers are brought to the same level even though they are borne at different nodes.
Ex: Cassia (simple Corymb), Cauliflower(Compound)

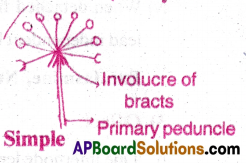
3) Umbel:
- In Umbel, the peduncle is condensed.
- All the flowers appear to have arisen from the same point of the pendunele.
- At the base of flowers, involucre of bracts form a whorl.
Ex: Onion (simple umbel), Carrot (Compound Umbel)
4) Head:
- In Head, unisexual and bisexual sessile flowers develop centripetally on a condensed receptacle.
- Such an arrangement of flowers is called head inflorescence.
Ex: Tridax and Sunflower.
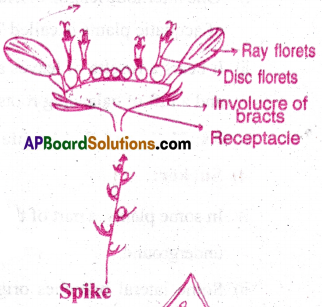
5) Spike:
- In Spikes, the peduncle is long.
- It bears many sessile flowers arranged acropetally.
Ex:Achyranthes (Simple), Grass-Poaceae (Compound)
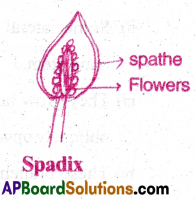
6) Spadix:
- In Spadix, the peduncle is fleshy and it produces many sessile, bracteate, unisexual flowers acropetally.
- The inflorescence is protected by a modified bract called spathe.
Ex: Colocasia (Simple Spadix), Cocos (Compound Spadix)
Exercise
Question 1.
In which plant, the underground stem grows horizontally in soil and helps in perennation?
Answer:
Zingiber (ginger), Curcuma (turmeric)
Question 2.
Needle like phylloclades are found in which plant?
Answer:
Casuarina
![]()
Question 3.
Why do plants like Nepenthes trap insects?
Answer:
For their nitrogen requirement, as they are living in nitrate deficient soils.
Question 4.
What is the characteristics inflorescence found in members of Asteraceae?
Answer:
Head inflorescence
Question 5.
Can you name a plant that has least number of flowers in its inflorescence?
Answer:
Hibiscus and Datura (One flower in one inflorescence)
Question 6.
Which family shows naked flowers?
Answer:
Family: Euphorbiacea
Question 7.
In which flowers of the fig trees does the insect Blastophaga lay its eggs?
Answer:
Gall flowers (sterile female flowers)
Question 8.
What type of symmetry is shown by the flowers of Canna?
Answer:
Asymmetry (irregular)
Question 9.
On which side of the flower do the flowers of pea have the keel petals?
Answer:
Anterior side
Question 10.
What is the ratio of overlapping margins of petals to overlapped ohes in imbricate aestivation?
Answer:
1:1
Question 11.
How many ovules are found attached in basal placentation? VHAS
Answer:
One ovule
Question 12.
Which part of the flower in cashew plant forms the false fruit? ?!
Answer:
Pedicel
Question 13.
Which plant has hard, stony endocarp and fleshy edible mesocarp?
Answer:
Mango
Question 14.
What is the morphology of’spathe’ in Spadix inflorescence?
Answer:
Bract
Question 15.
What is the type of fruit known as if it develops from apocarpus ovary of a single flower?
Answer:
Aggregate fruit
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Adventitious roots are
1. Lateral roots
2. Tap roots
3. Roots formed from radicle
4. Roots formed from other parts but not from radicle
Answer:
4. Roots formed from other parts but not from radicle
![]()
Question 2.
Bacterium found in the root nodules is
1. Clostridium
2. Rhizobium
3. Mycobacterium
4. Salmonella
Answer:
2. Rhizobium
Question 3.
Cuscuta is a
1. Complete stem parasite
2. Incomplete stem parasite
3. Complete root parasite
4. Incomplet root parasite
Answer:
1. Complete stem parasite
Question 4.
Stent is . …….
1. Negatively phototropic
2. Positively phototropic
3. Positively geotropic
4. Diageotropic
Answer:
2. Positively phototropic
Question 5.
The primary function of stem is to
1. bear and hold leaves and branches
2. help in vegetative propagation
3. anchor the plant in the soil
4. absorption of water and minerals
Answer:
1. bear and hold leaves and branches
Question 6.
Flower is the modification of
1. Stem
2. Leaf
3. Shoot
4. Rachis
Answer:
3. Shoot
Question 7.
…………. is not a common function of leaf
1. Transpiration
2. Photosynthesis
3. Gaseous exchange
4. Reproduction
Answer:
4. Reproduction
Question 8.
Example for leafless plant
1. Vanda
2. Striga
3. Taeniophyllum
4. Viscum
Answer:
3. Taeniophyllum
Question 9.
Insect eating plant is
1. Alstonia
2. Dionea
3. Bombax
4. Acacia
Answer:
2. Dionea
Question 10.
Plant with Thorns is
1. Casuarina
2. Bougainvillea
3. Opuntia
4. Gourd
Answer:
4. Gourd
Question 11.
Asparagus is a
1) Plant with storage tap root
2) Xerophyte with assimilatory root
3) Hydrophyte with balancing roots
4) Xerophyte with fibrous roots storing food
Answer:
4) Xerophyte with fibrous roots storing food
![]()
Question 12.
A pome fruit is said to be false because
1) The pericarp is inconspicuous
2) The endocarp is cartilaginous
3) the fruit is present in fleshy edible thalamus
4) the fruit is derived from inferior ovary
Answer:
3) the fruit is present in fleshy edible thalamus
Question 13.
Prop roots in Banyan arc
1. Positively geotropic
2. Negatively geotropic
3. Positively phototropic
4. Negatively phototropic
Answer:
1. Positively geotropic
Question 14.
Roots found in Taeniophyllum are
1. Tuberous
2. Photosynthetic roots
3. Pneumatophores
4. Nodular roots
Answer:
2. Photosynthetic roots
Question 15.
Nitrogen fixing nodular roots are found in
1. Malvaceae
2. Liliaceae
3. Fabaceae
4. Solanaceae
Answer:
3. Fabaceae
Question 16.
Roots found in Asparagus are
1. Tuberous roots
2. Pneumatophores
3. Nodular roots
4. Haustorial roots
Answer:
1. Tuberous roots
Question 17.
Fibrous tuberous roots are found in
1. Carrot
2. Radish
3. Turnip
4. Asparagus
Answer:
4. Asparagus
Question 18.
Adventitious root becomes tuberous in
1. Carrot
2. Radish
3. Tumip
4. Ipomoea
Answer:
4. Ipomoea
Question 19.
Lateral roots arise from
1. Root cap region
2. Region of elongation
3. Root hair region
4. Matured region
Answer:
4. Matured region
Question 20.
Positive geotropism is exhibited by
1. Stem
2. Roots
3. Leaf
4. Flower
Answer:
2. Roots
Question 21.
Short -lived primary root is found in
1. Dicots
2. Monocots
3. Angiosperms
4. Gymnosperms
Answer:
2. Monocots
Question 22.
Vanda is a/an …………
1. Saprophyte
2. Parasite
3. Epiphyte
4. Climber
Answer:
3. Epiphyte
![]()
Question 23.
Avicennia and Rhizophora are
1. Epiphytes
2. Xerophytes
3. Mangroves
4. Parasites
Answer:
3. Mangroves
Question 24.
Nodular roots are inhabited by
1. Viruses
2. Fungi
3. Bacteria
4. Algae
Answer:
3. Bacteria
Question 25.
Nodular roots are found in
1. Avicennia
2. Rafflesia
3. Vanda
4. Crotalaria
Answer:
4. Crotalaria
Question 26.
Type of roots found in Fabaceae
1. Nodular roots
2. Haustorial roots
3. Epiphytic roots
4. Stilt roots
Answer:
1. Nodular roots
Question 27.
Respiratory roots are found in
1. Asparagus
2. Rhizophora
3. Taeniophyllum
4. Rafflesia
Answer:
2. Rhizophora
Question 28.
Pneumatophores are helpful for
1. Transpiration
2. Photosynthesis
3. Respiration
4. Climbing
Answer:
3. Respiration
Question 29.
Edible part of Sweet potato is
1. Underground stem
2. Aerial Stem
3. Tap Root
4. Tuberous Adventitious Root
Answer:
4. Tuberous Adventitious Root
Question 30.
Edible part of Banana is
1) Epicarp
2) Epicarp and endocarp
3) Endocarp and mesocarp
4) Epicarp and mesocarp
Answer:
3) Endocarp and mesocarp
Question 31.
Tap root is developed from
1. Plumule
2. Radicle
3. Epicotyl
4. Hypocotyl
Answer:
2. Radicle
![]()
Question 32.
Lateral roots arise from
1. Epidermis
2. Endodermis
3. Pericycle
4. Cortex
Answer:
3. Pericycle
Question 33.
Shape of the tuberous root in Turnip
1. Conical
2. Fusifrom
3. Napiform
4. Irregular
Answer:
3. Napiform
Question 34.
Which in not an example for tuberous roots
1. Carrot
2. Aspagarus
3. Vanda
4. Radish
Answer:
3. Vanda
Question 35.
Select the correct pair
1. Vanda,Turnip
2. Viscum,strigna
3. Stringa,Cuscuta
4. Rafflesia,Viscum
Answer:
2. Viscum,strigna
Question 36.
Select the wrong statement
1. Fibrous root system is found in Monocots
2. Primary root is long lived in Dicotyledons
3. Monocotyledons show Taproot system
4. Roots derived from radicle are normal roots
Answer:
3. Monocotyledons show Taproot system
Question 37.
Which of the following does not have a root modification?
1. Carrot
2. Sweet potato
3. Potato
4. Radish
Answer:
3. Potato
Question 38.
Velamen roots are found in
1. Cuscuta
2. Vanda
3. Ceratophyllum
4. Avicennia
Answer:
2. Vanda
Question 39.
Part of the stem, from which leaf arises is
1. Axil
2. Intemode
3. Node
4. Tip
Answer:
3. Node
Question 40.
Modified stem that helps in climbing is
1. Phyllode
2. Stem tuber
3. Bulb
4. Stem Tendril
Answer:
4. Stem Tendril
![]()
Question 41.
The modified stem found in onion is
1. Aerial
2. Sub-aerial
3. Underground
4. Tuberous
Answer:
3. Underground
Question 42.
Stem modification found in Curcuma,Ginger
1. Rhizome
2. Conn
3. Bulb
4. Stem tuber
Answer:
1. Rhizome
Question 43.
Climbing organ in Gourds and Grapewines
1. Hook
2. Tendrill
3. Thom
4. Sucker
Answer:
2. Tendrill
Question 44.
An example for Stem Tdber is
1. Solanum xanthoCarpum
2. Solamum tuberosum
3. Solanum trilobatum
4. Solanum melongena
Answer:
2. Solamum tuberosum
Question 45.
Function of Bulbils is
1. Photosynthesis
2. Protection
3. Storage
4. Climbing
Answer:
3. Storage
Question 46.
Stem is developed from
1. Epicotyl
2. Hypocotyl
3. Radicle
4. Plumule
Answer:
4. Plumule
Question 47.
Phylloclade is the modification of
1. Root
2. Stem
3. Leaf
4. Inflorescence
Answer:
2. Stem
Question 48.
Example for suckers
1. Nerium
2. Pineapple
3. Dioscorea
4. Watermelon
Answer:
2. Pineapple
Question 49.
The stem modification in Curcuma is
1. Corm
2. Bulb
3. Rhizome
4. Stem tuber
Answer:
3. Rhizome
![]()
Question 50.
Vegetative reproduction in Musa is brought about by
1. Offset
2. Stolon
3. Sucker
4. Runner
Answer:
3. Sucker
Question 51.
Stem modification helpful in climbing is
1. Phyllode
2. Stem tuber
3. Bulb
4. Tendril
Answer:
4. Tendril
Question 52.
Underground stem in Allium cepa is
1. Bulbil
2. Bulb
3. Rhizome
4. Corm
Answer:
2. Bulb
Question 53.
Plant with an offset is
1. Colocasia
2. Pineapple
3. Pistia
4. Nerium
Answer:
3. Pistia
Question 54.
Bulbil is found in
1. Pistia
2. Agave
3. Allium
4. Lilium
Answer:
2. Agave
Question 55.
Bulbs arc present in
1. Pteridophytes
2. Gymnosperms
3. Dicots
4. Monocots
Answer:
4. Monocots
Question 56.
Number of internodes in the Offset
1. Two
2. One
3. Four
4. Three
Answer:
2. One
Question 57.
Which is not a modification of stem
1 .Corm of Colocasia
2. Rhizome of ginger
3. Tuber of sweetpotato
4. Tuber of Potato
Answer:
3. Tuber of sweetpotato
Question 58.
Identify the correct pair
1. Opuntia & Euphorbia
2. Causarina & Bougainvillea
3. Asparagus & Citrus
4. Agave & Onion
Answer:
1. Opuntia & Euphorbia
Question 59.
Axillary bud is modified into a tendril in
1. Bougainvillea
2. Pisum
3. Grapewine
4. Watermelon
Answer:
4. Watermelon
Question 60.
A tendril climber with nodular roots
1. Crotalaria
2. Phaseolus
3. Lathyrus
4. Arachis
Answer:
2. Phaseolus
![]()
Question 61.
In Pea, the leaf modifications is
1. Thom
2. Tendril
3. Hook
4. Flower
Answer:
2. Tendril
Question 62.
Epiphyllous buds are found in
1. Ceratophyllum
2. Bougainvillea
3. Bryophyllum
4. Bulbophyllum
Answer:
3. Bryophyllum
Question 63.
Stalk of the leaf is known as
1. Petiolule
2. Rachis
3. Petiole
4. Pedicel
Answer:
3. Petiole
Question 64.
Spines are present in
1. Cucurbita
2. Bongainvillea
3. 0puntia
4. Causuarina
Answer:
3. 0puntia
Question 65.
Pinnately compound leaf is found in
1. Guava
2. Ceiba
3. Neem
4. Hibiscus
Answer:
3. Neem
Question 66.
In Calotropis and Guava, phyllotaxy is
1. Alternate
2. 0pposite
3. Whorled
4. Decussate
Answer:
2. 0pposite
Question 67.
Which part of the plant bears stipules?
1. Flower
2. Fruit
3. Stem
4. Leaf
Answer:
4. Leaf
Question 68.
Epiphyllous buds arise from
1. Axil of leaf
2. Tip of the stem
3. Lamina of leaf
4. Petiole
Answer:
3. Lamina of leaf
Question 69.
Leaves serve the function of storage in
1. Dionea
2. Acacia
3. Garlic
4. Cactus
Answer:
3. Garlic
Question 70.
1. Thom
2. Cladophyll
3. Phyliode
4. Phylloclade
Answer:
3. Phyliode
![]()
Question 71.
Leaves help in Vegetative propagation in
1. Alstonia
2. Bryophyllum
3. Nepenthes
4. Allium
Answer:
2. Bryophyllum
Question 72.
Arrangement of leaves on the stem is called
1. Anthotaxy
2. Phyllotaxy
3. Venation
4. Vematon
Answer:
2. Phyllotaxy
Question 73.
Rachis is found in the leaves of
1. Neem
2. Bryophyllum
3. Bombax
4. Hibiscus
Answer:
1. Neem
Question 74.
Plant with fleshy leaves is
1. Allium
2. Acacia
3. Alstonia
4. 0puntia
Answer:
1. Allium
Question 75.
Plant that possesses balancing roots is
1. Dioanea
2. Nepenthes
3. Pistia
4. Hydrilla
Answer:
3. Pistia
Question 76.
In an inflorescence, flowers are arranged on
1. Petiole
2. Pedicel
3. Peduncle
4. Phyllode
Answer:
3. Peduncle
Question 77.
A plant with a simple raceme
1. Tridax
2. Ficus
3. Crotalaria
4. Vinca
Answer:
3. Crotalaria
Question 78.
inflorescence in Allium is
1. Umbel
2.Corymb
3. Spadix
4. Spike
Answer:
1. Umbel
Question 79.
Spadix inflorescence is found in
1. Poaceae
2. Achyranthus
3. Apiaceae
4. Colocasia
Answer:
4. Colocasia
Question 80.
A special type of inflorescence is
1. Cymule
2. Head
3. Hypanthodium
4. Umbel
Answer:
3. Hypanthodium
Question 81.
Gall flowers are
1. Male flowers
2. Female flowers
3. Sterile Male flowers
4. Sterile Female Flowers
Answer:
4. Sterile Female Flowers
Question 82.
In Cauliflower, inflorescence is
1. Raceme
2. Compound Umbel
3. Compound Corymb
4. Head
Answer:
3. Compound Corymb
Question 83.
Panicle is the name given to
1. Compound Spadix
2. Compound Corymb
3. Compound Umbel
4. Compound Receme
Answer:
4. Compound Receme
Question 84.
Plant that shows edible inflorescence is
1. Cassia
2. Cauliflower
3. Cabbage
4. 0nion
Answer:
2. Cauliflower
![]()
Question 85.
In Sunflower, the type of inflorescence ………… is
1. Receme
2. Capitulum
3. Spike
4. Spadix
Answer:
2. Capitulum
Question 86.
The inflorescence which externally appears as a fruit …………..
1. Capitulum
2. Verticellaster
3. Hypanthodium
4. Compound Corymb
Answer:
3. Hypanthodium
Question 87.
Number of nodes’of the floral axis is
1. Four
2. Three
3. Two
4. One
Answer:
1. Four
Question 88.
Smallest flowers are found in
1. Raffiesia
2. Hamelia
3. Wolfa
4. 0ryza
Answer:
3. Wolfa
Question 89.
Asymmetrical flowers are found in
1. Cassia
2. Canna
3. Pisum
4. Datura
Answer:
2. Canna
Question 90.
In Citrus, the stamens are
1. Monoadelphous
2. Diadelphous
3. Polyadelphous
4. Polyandrous
Answer:
3. Polyadelphous
Question 91.
An ovary with false septum is found in
1. Pea
2. Nicotiana
3. Datura
4. Tridax
Answer:
3. Datura
Question 92.
Plant whose haustoria enter into xyleni and pholoent of root of the host is
1) Striga
2) Cuscuta
3) Loranthus
4) Rafflesia
Answer:
4) Rafflesia
![]()
Question 93.
Which roots of Vanda help in absorbing mineral water ?
1) Haustoria
2) Velamen roots
3) Tap roots
4) Clinging roots
Answer:
2) Velamen roots
Question 94.
Identify the correct statement;
1) Stem of Pistia has one intemode
2) Runners of grasses are aerial
3) Leaves are produced at intemode
4) Stolons are found in mint plant
Answer:
1) Stem of Pistia has one intemode
Question 95.
Aerial stem modification that helps in vegetative reproduction-
1) Bulb
2) Bulbil
3) Thom
4) Rhizome
Answer:
2) Bulbil
Question 96.
Cladophyll with one internodai length is found in
1) Asparagus
2) Opuntia
3) Euphorbia
4) Casuarina
Answer:
1) Asparagus
Question 97.
In how many of the following plants, Stamens are in two different heights in each flower.
Solanum, Salvia, Brassica, Datura, Allium, Lilium, Asparagus, Euphorbia
1) 2
2) 4
3) 5
4) 7
Answer:
1) 2
Question 98.
When the stem or its branch ends into floral buds
1) Vegetative growth starts
2) Reproductive growth starts
3) Lateral branch is given out
4) Apical growth is promoted
Answer:
3) Lateral branch is given out
Question 99.
An inflorescence always forms a
1) Multiple or composite fruit
2) Simple fruit
3) Dry dehiscent fruit
4) Aggregate fruit
Answer:
1) Multiple or composite fruit
![]()
Question 100.
Mark the incorrect match
1) Stilt root-turnip
2) Tap root – carrot
3) Adventitious root – sweet potato
4) prop root – banyan tree
Answer:
1) Stilt root-turnip
Question 101.
Axillary buds are modified into tendrils in
a) Cucumber
b) Pumpkin
c) Citrus
d) Bougainvillea
1) a, b, c
2) a, d only
3) a, b only
4) a, b, c, d
Answer:
3) a, b only
Question 102.
Which roots amongst the following grow against gravitational force?
1) Prop roots
2) Stilt roots
3) Pneumatophores
4) 1 & 3
Answer:
3) Pneumatophores
Question 103.
The plant that stores food reserves in leaves is
1) Mango
2) Sweet potato
3) Onion
4) Sugar cane
Answer:
3) Onion
Question 104.
In Nepenthes, the pitcher like structure is formed by the modification of
1) Leaf margin
2) Leaf-blade
3) Stipules
4) Petiole
Answer:
2) Leaf-blade
Question 105.
Correct arrangement of the modifications of Nepenthes leaf in sequence from base to apex is …………
1) Tendril, Phyllode, Pitcher
2) Pitcher, Tendril, Phyllode
3) Tendril, Pitcher, Phyllode
4) Phyllode, Tendril, Pitcher
Answer:
4) Phyllode, Tendril, Pitcher
![]()
Question 106.
Bisexual flowers, naked flowers and gall flowers found in special inflorescences respectively
1) Verticellaster – Cyathium – Hypanthodium
2) Cyathium – Hypanthodium – Verticellaster
3) Cyathium – Verticellaster – Hypanthodium
4) Hypanthodium – Cyathium – Verticellaster
Answer:
1) Verticellaster – Cyathium – Hypanthodium