Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 4th Lesson Plant Kingdom which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 4th Lesson Plant Kingdom
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the basis of classification of Algae?
Answer:
Algae are classified into 3 types on the basis of pigments and the type of stored food.
Question 2.
When and where does reduction division take place in the life cycle of a liverwort, a moss, a fern, a gymnosperm and an angiosperm?
Answer:
Reduction division occurs during spore formation within the sporangium in the life-cycle of liverworts, mosses, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate between syngamy and triple fusion.
Answer:
| Syngamy | Triple fusion |
| 1) In syngamy, one of the male gametes released in the embryosac fuses with the egg to form a zygote. 2) It is true fertilisation |
1) In triple fusion, the second male gamete fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus to produce primary endosperm nucleus (PEN). 2) It is double vegetative fertilisation. |
Question 4.
Differentiate between antheridium and archqgonium.
Answer:
| Antheridium | Archcgonium |
| 1) Antheridium is the male sex organ | 1) Archegonium is the female sex organ. |
| 2) It is club shaped. | 2) It is flask shaped. |
| 3) It produces many antherozoids | 3) It produces a single egg cell. |
Question 5.
What are the two stages found in the gametophyte of mosses? Mention the structures from which these two stages develop?
Answer:
- The gametophyte of Mosses consists of two stages:
(i) Juvenile stage-Protonema (ii) Adult leafy stage-Gametophore - Protonema is developed from the spore whereas gametophore is developed from the protonema.
Question 6.
Name the stored food materials found in Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae.
Answer:
- The stored food material in Phaeophyceae is laminarin or mannitol.
- The stored food material in Rhodophyceae is floridian starch.
Question 7.
Name the pigments responsible for brown colour of Phaeophyceae and fed colour of Rhodophyceae.
Answer:
- The pigments Xanthophyll and Fucoxanthin are responsible for brown colour of Phaeophyceae.
- The pigment r-phycoerythrin is responsible for red colour of Rhodophyceae.
Question 8.
Name different methods of vegetative reproduction in Bryophytes. [AP M-15]
Answer:
Fragmentation, gemmae and budding
Question 9.
Name the integumented megasporangium found in Gymnosperms. How many female gametophytes are generally formed inside the megasporangium?
Answer:
- The integumented megasporangium is ovule.
- Inside the megasporangium generally one female gamete is formed.
Question 10.
Name the Gvmnosperms which contain mycorrhiza and corolloid roots respectively.
Answer:
- Pinus contain mycorrhizal roots.
- Cycas contain corolloid roots
![]()
Question 11.
Mention the ploidy of any four of the following
a) Protonemal cell of a moss
b) Primary endosperm nucleus in a dicot
c) Leaf cell of a moss
d) Prothallus of a fern
e) Gemma cell in Marchantia
f) Meristem cell of monocot
g) Ovum of a liverwort
h) Zygote of a fern.
Answer:
a) Haploid
b) Triploid
c) Haploid
d) Haploid
e) Haploid
f) Diploid
g) Haploid
h) Diploid
Question 12.
Name the lour classes of Pteriodophyta with one example each.
Answer:
Class 1: Psilopsida – Ex: Psilotum
Class 2: Lycopsida – Ex: Selaginella, Lycopodium
Class 3: Sphenopsida – Ex: Equisetum
Class 4: Pteridopsida – Ex: Dryopteris, Pteris, Adiantum
Question 13.
What are the first organisms to colonise rocks? Give the generic name of the moss which provides peat?
Answer:
- The first organism to colonise rocks are – Mosses and Lichens.
- The generic name of the moss which provides peat is Sphagnum
Question 14.
Mention the fern characters found in Cycas.
Answer:
Fern characters found in Cycas are:
- Circinate vernation in young leaves.
- Presence of ramenta
- Multiciliated male gametes.
- Presence of archegonia in the female gametophyte
Question 15.
Why are Bryophytes called the amphibians of the plant kingdom?
Answer:
Bryophytes are called amphibians of plant kingdom because these plants live in moist soil and are dependent on water for sexual reproduction.
Question 16.
Name an alga which show (a) Haplo-diplontic and (b) Diplontic (c) Diplobiontic types of life cycles.
Answer:
- Haplo-diplontic life cycle is exhibited by Ectocarpus and Laminaria
- Diplontic life cycle is exhibited by Fucus
- Diplobiontic life cycle is exhibited by Polysiphonia
![]()
Question 17.
Give examples for unicellular, colonial and filamentous algae.
Answer:
- Unicellular algae – Chlamydomonas
- Colonial algae – Volvox
- Filamentous algae- Spirogyra, Ulothrix
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between red algae and brown algae. |TS M-17, 19, 22] [AP M-16, 19]
Answer:
| Red Algae | Brown Algae |
| 1) Red algae belongs to Rhodophyceae class. 2) Their red colour is due to the red pigment called r-phycoerythrin 3) Major pigments in them are chlorophyll a,d and phycoerythrin. 4) Reserve food material is Floridian starch. 5) Asexual reproduction is by non-motile spores. 6) Sexual reproduction is by non-motile gametes. Ex: Gracilaeria, Gelidium |
1) Brown algae belongs to Phaeophyceae class. 2) Their brown colour is due to the brown pigment xanthophyll. 3) Major pigments in them are chlorophyll a,c, carotenoids and xanthophylls 4) Reserve food material is laminarin (or) mannitol. 5) Asexual reproduction is by biflagellate zoospores. 6) Sexual reproduction is by motile gametes. Ex: Ectocarpus, Laminaria, Fucus. |
Question 2.
Differentiate between liverworts and mosses. [AP Mar, May-17]
Answer:
| Liverworts | Mosses |
| 1) Plant body in liverworts is thalloid. 2) Liverworts are amphibians. 3) Sporophyte is complete parasite on gametophyte. 4) Sporophyte is small or reduced. 5) Elaters help in the dispersal of spores. Ex: Marchantia |
1) Plant body in Mosses is upright structure and divided into root like, stem like and leaflike. 2) Mosses are the advanced bryophytes. 3) Sporophyte is semi parasite tm gametophyte 4) Sporophyte is more elaborate. 5) Peristomial teeth help in the dispersal of spores. Ex:Polytrichum,Spagnum,Funaria. |
Question 3.
What is meant by homosporous and heterosporous pteridophytes? Give two examples. [APM-15,22] [IPE Mar-13]
Answer:
1) Homosporous pteridophytes; The plants which produce only one kind of spores are called homosporous pteridophytes.
Ex: Psilotum, Lycopodium
2) Heterosporous pteridophytes: The plants which produce two kinds of spores on the same plant are called heterosporous pteridophytes.
Ex: Selaginella, Salvinia.
Question 4.
What is heterospory? Briefly comment on its significance. Give two examples. [TS M-15, 20]
Answer:
Heterospory: Production of two kinds of spores on the same plant is called heterospory.
Ex: Selaginella, Salvinia
Significance:
- Two types of spores are seen
(i) Microspores – germinate into male gametophyte
(ii) Megaspores – germinate into female gametophyte. - Sex organ in male gametophyte is Antheridia. It gives antherozooids as male gametes.
- Sex organ in female gametophyte is Archegonia. It produces egg as female gametes.
- Fusion of Antherozoids to egg results zygote.
- Development of zygote into young embryo takes place within the female gametophytes.
- This event is precursor to the seed habit. This is considered as important step in evolution.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a note on economic importance of Algae and Bryophytes. [TS M-16] [AP M-19]
Answer:
I) Economic importance of Algae:
- Fixation of carbondioxide on Earth is mainly carried out by algae.
- Brown algae produces Algin
- Red algae produces carrageen.
- Agar Agar is obtained from Gelidium.
- Chlorella and spirulina are used as food supplements by space travellers.
- Laminaria and sargassum are used as food for fauna of sea.
II) Economic importance of Bryophytes:
- Mosses provide food for herbivorous mammals and birds.
- Sphagnum provides peat, which is used as fuel.
- They play significant role in plant succession.
- They prevent soil erosion.
- They are used as packing material for trans-shipment.
Question 6.
How would you distinguish monocots from dicots?
Answer:
| Monocots | Dicots |
| 1) The seed has only one cotyledon. 2) Root system is adventitious type. 3) Leaves have parallel venation. 4) Leaves are isobilateral. 5) Sheathing leaf base is present. 6) Secondary growth is absent. 7) Vascular bundles are scattered and closed. Ex: Rice, Maize |
1) The seed has two cotyledons. 2) Root system is taproot system 3) Leaves show reticulate venation. 4) Leaves are dorsiventral 5) Sheathing leaf base is absent. 6) Secondary growth is present. 7) Vascular bundles are arranged in ring & open. Ex:Mango, Coffee. |
Question 7.
Give a brief account of prothallus. [AP M- 20]
Answer:
Prothallus:
- The gametophytic plant body of pteridophytes is called prothallus.
- The haploid spore germinates and gives rise to prothallus.
- It is a heart shaped thallus like structure, green, dorsiventral with a notch.
- The rhizoids produced on ventral surface are unicellular.
- Prothallus grows on shady, damp and wet soil.
- Male sex organs antheridia are produced on the lower part of prothallus.
- Female sex organs archegonia are produced near the notch.
- The antherozoids are ciliated, require water to reach the egg.
- The zygote develops into an embryo, which develops into a diploid sporophyte with in the female gametophyte.
![]()
Question 8.
Draw labelled diagrams of (a) Female thallus and male thallus of a liverwort.
(b) Gametophyte and sporophyte of Funaria.
Answer:
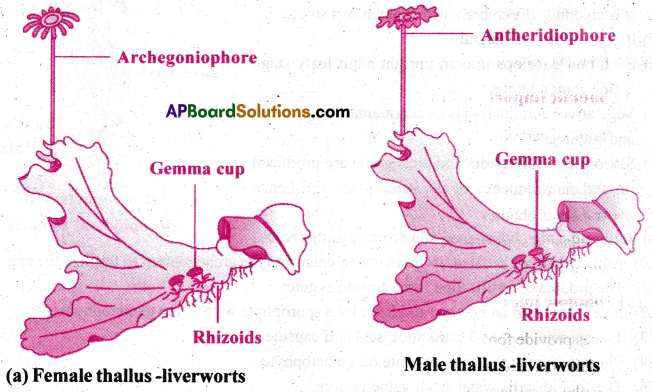
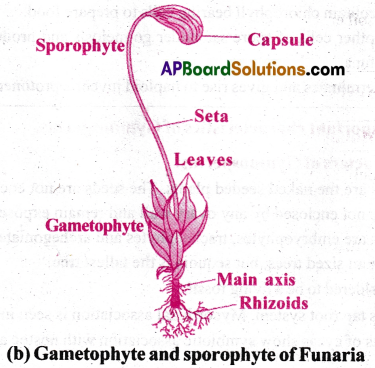
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name three groups of plants that bear arehegonia, Briefly describe the life cycle of any one of them.
Answer:
The plant groups which bear arehegonia are Bryophytes, Pteridophytes and gymnosperms.
Life cycle of Bryophytes-Funaria (Moss plant):
- The life cycle includes two phages – gametophyte and sporophyte.
- The gametophyte also has two stages – protonema and adult stages.
- The haploid spore germinates and gives rise to a juvenile stage called protonema.
- It is creeping, green branched filamentous stage.
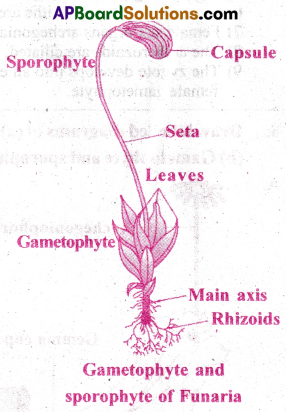
- It possess several lateral buds.
- Each bud develops into an upright adult leafy stage called gametophore.
- Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation, gemmae and budding.
- Sex organs – antheridia and arehegonia are produced on separate branches of the same plant and hence monecious.
- Antheridia are club shaped and produce antherzoids.
- Antherzoids are ciliated, swim in water, enter into the archegonium to fertilize the egg.
- The product of fertilization is the diploid zygote.
- It develops into an embryo and there by a sporophyte with in the gametophyte.
- The sporophyte has 3 parts foot, seta and capsule.
- The sporophyte is a semi parasite on gametophyte.
- The foot absorbs water from gametophore.
- The capsule contain chlorophyll bearing cells to prepare food.
- The spore mother cells of spore sac under go meiosis and produce haploid spores of one kind. Hence funaria is homosporous.
- Each spore germinates and gives rise to haploid juvenile protonema
Question 2.
Describe the important characteristics of Gymnosperms.
Answer:
Important characters of Gymnosperms:
- Gymnosperms are the naked seeded plants. The seeds are not enclosed inside the fruit.
- The ovules are not enclosed by any ovary wall and remain exposed.
- Gymnosperms are embryophytes, tracheophytes and archegoniate phanerogams.
- They are medium sized trees, but sequoia is the tallest tree.
- Ginkgo is considered to be a living fossil.
- Root system is tap root system. Mycorrhizal association is seen in the roots of pinus.
- Corolloid roots of cycas show symbiotic association with nostoc and anaebaena.
- The stem is unbranched in cycas, branched in pinus.
- Leaves may be simple or compound.
- In cycas pinnate persistant leaves and in pinus needle like leaves are present.
- Leaves adapted to with stand extremes of temperature, Sunken stomata are also present.
- Anatomically the stem is eustele, vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and open.
- Vessels are generally absent in xylem. Companion cells are absent in phloem.
- Secondary growth occurs in stem and root.
- The Gymnosperms are heterosporous, produce micro and mega sporangia.
- The microsporangia are produced on niicrosporophylls which are arranged to form compact cones.
- The microspores are the pollen grains which are produced in microsporangia.
- Megaspores are produced in megasporangia, which are integumented ovules.
- Ovules are borne on mega sporophylls and have three layered integument.
- Micropyle is the opening on ovule. Pollination is direct.
- Fertilization is siphonogamy. The male gametes travel in the pollen tube.
- Zygote is the fertilization product, which becomes an embryo.
- The body of female gametophyte becomes the endosperm.
- The endosperm is a pre fertilization tissue and is haploid.
- Seeds are naked without any covering of fruit wall.
- Germination is epigeal. Polyembryony is noticed.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the salient features of Pteridophytes. .
Answer:
- Pteridophytes are the first terrestrial plants to possess vascular tissues.
- They are embryophytic, archegoniate, vascular cryptogams.
- They are found in cool, damp, shady places.
- They are soil-binders, grown as ornamentals and used for medicinal purposes.
- The main plant body is sporophyte and is differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- The roots are adventitious, stem shows internally epidermis, cortex and stele.
- Stele may be a protostele or spiphonostele or solenostele or dictyostele.
- Leaves may be microphylls as in selaginella and macrophylls as in ferns.
- The sporophyte bear sporangia, that occur on leaf like appendages called sporophylls.
- The development of sporangium may be lepto-sporangiate or eusporangiate.
- Majority of pteridophytes are homosporous, produce one kind of spores.
- Genera like selaginella, salvinia are heterosporous, produce two kinds of spores.
- Sporophylls form compact structures called strobili or cones.
- Spores germinate and produce small, multicellular, photosynthetic gametophytes called prothalli.
- Prothallus may be monoecious or dioecious
- Sex organs are antheridia or archegonia.
- Antheridia produce male gametes which are uninucleate, biflagellate or multiflagellate.
- Archegonium contain egg.
- Fusion of male and female gamete results in diploid zygote.
- Zygote develops into diploid embryo with in the female gametophyte.
- The embryo produces a multicellular sporophyte which is a dominant phase in pteridophytes.
Question 4.
Give an account of plant life cycles and alternation of generations.
Answer:
A) Life Cycles.
I) Hapiontic life cycle:
- The dominant photosynthetic phase of the plant is free living gametophyte.
- Sporophytic generation is represented by one-celled diploid zygote.
- Sporophyte is not free living.
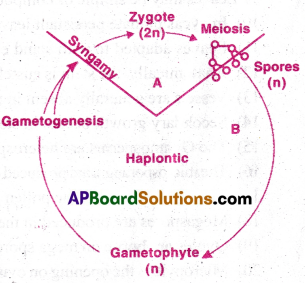
- Meiosis in zygote results haploid spores and germinate into a gametophyte.
- This kind of life-cycle is called hapiontic.
Ex: Algae like Volvox and Spirogyra.
II) Diplontic life cycle:
- The diploid sporophyte is the dominant, photosynthetic, independent phase of the plant.
- Haploid phase is represented by gametes only.
- This type of life cycle is called diplontic.
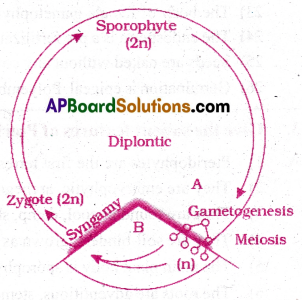
- When the life cycle is represented by only independent sporophyte with few celled gametophyte, life cycle is called diplo-haplontic
Ex: Pteridophyte and seed-bearing plants.
![]()
III) Haplo-diplontic life cycle:
- Bryophytes exhibit an intermediate conditior called haplo-diplontic.
- Both phases are multicellular.
- Dominating phase in gametophytic generation It is independent.
- Sporophyte is photosynthetic, but dependent or gametophyte.
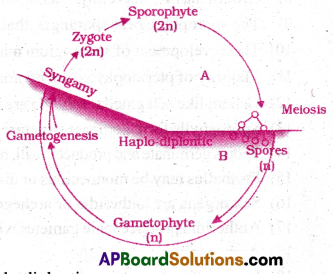
- This life cycle is called haplo diplontic.
- Most algal forms are hapiontic.
- Some forms like Ectocarpus, Laminaria are haplo-diplontic.
- Fucus in diplontic and polysiphonia is diplo-biontic.
B) Alternation of generations;
- There are two generations in the life of a plant body. They are gametophyte and sporophyte.
- The haploid gametophyte produces gametes by mitosis.
- Fusion of gametes result in the formation of diploid zygote.
- Zygote divides by mitosis and produces a diploid sporophytic plant body.
- Sporophytes produces sporemother cells, which undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores.
- These spores in turn divide by mitosis to form haploid plant body once again.
- Thus during the life cycle of any sexually reproducing plant, there is an alternation of generation between gamete producing haploid gametophyte and spore producing diploid sporophyte.
Question 5.
Both Gyimiosperms and Angiosperms bear seeds, then why are they classified separately?
Answer:
Though both Gymnosperms and Angiosperms bear seeds, because of their following differences they are classified separately.
Exercise
Question 1.
How far does Selaginella, one of the few living members of Lycppodiales (Pteridophytes) fall short of seed habit.
Answer:
- Pteridophytes like selaginella are heterosporous. It produces two kinds of spores – mega and micro spores.
- The sporophylls form distinct compact structures called strobili or cones.
- Micro spores germinate to give rise to inconspicuous male gametophyte contain sex organs called antheridia which produce antherzoids.
- Mega spores germinate to give rise to inconspicuous female gametophyte, contain sex organs called archegonia which produce eggs or female gametes.
- Fusion of male and female gametes results in the formation of zygote in side the archegonium.
- The development of zygote into young embryos takes place with in the female gametophyte.
- This event is a precussor of seed habit, but not a true seed habit.
- Thus members of lycopodinae fall short of seed habit.
![]()
Question 2.
Each plant or group of plants has some phylogenetic significance in relation to evolution.
Answer:
Cycas, one of the few living members of Gymnosperms is called as the relic of past. Can you establish a phylogenetic relationship of Cycas with any other group of plants that justifies the above statement?
Cycas is a member of Gymnosperm. It shows some resemblances with the ferns and on the other hand shows several angio spermic features. Thus it is treated as the “relic of the past”.
Fern characters of Cycas are:
- Young leaves show circinate vernation.
- Sporophylls are leaf like.
- Sporophylls are arranged in the form of a cone or strobilus.
- Micro sporangia are produced on the abaxial side of microsporophyll.
- Presence of ramenta.
- Persistant leaf bases.
- Stem underground in young condition.
- Xylem with trachieds only.
- Phloem without companion cells.
- Archegonia are present in the female gametophyte.
- Sperms are multiciliate.
Question 3.
The male and female reproductive organs of several Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms are comparable to floral structures of angiosperms. Make an attempt to compare the various reproductive parts of Pteriodophytes and Gymnosperms with reproductive structures of Angiosperms.
Answer:
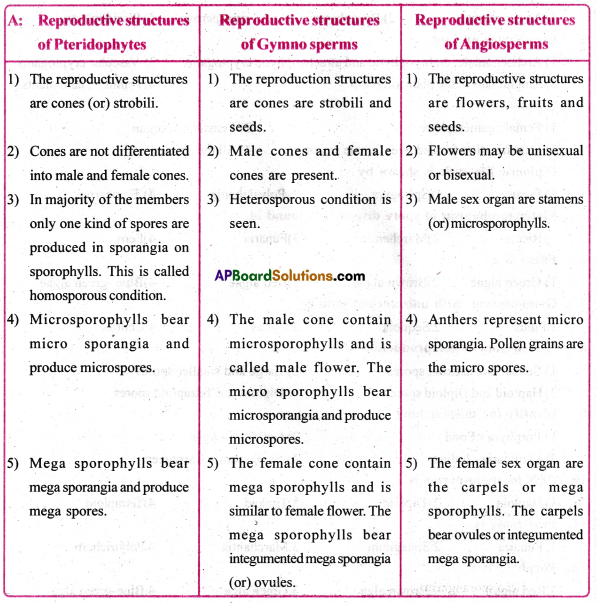
Question 4.
The plant body in higher plants is well differentiated and well developed. Roots are organs used for the purpose of absorption. What are the equivalent of roots in the less developed lower plants?
Answer:
In the some members of bryophyta like Riccia and Marchantia the rhizoids are unicellular whereas the rhizoids of Funaria are multicellular. The rhizoids ofprothallus of Fern are also unicellular, but in the sporophyte of pteridophytes adventitious root system is present. All these structures are meant for the absorption of water and salts in lower plants.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Amphibians of the plant kingdom are
1) Angiosperms
2) Bryophytes
3) Gymnosperms
4) Pteridophytes
Answer:
2) Bryophytes
Question 2.
Bryophytes are not
1) Archaegoniate, embryophytic and atracheophytic cryptogams
2) Vascular cryptogams
3) Amphibians of the plant kingdom
4) Primitive land plants
Answer:
4) Primitive land plants
Question 3.
Carpogonhim is a
1) Female gametophyte
2) Female sex organ
3) Fructification formed over female sex organ
4) All the above
Answer:
2) Female sex organ
Question 4.
Diplontic life cycle is shown by —
1) Fucus
2) Spirogyra
3) Polysiphonia
4) Ectocarpus
Answer:
1) Fucus
Question 5.
Elater mechanism of spore dispersal is found in
1) Riccia
2) Marchantia
3) Funaria
4) Fem
Answer:
2) Marchantia
Question 6.
Focus is a
1) Green algae
2) Brown algae
3) Red algae
4) Blue -green algae
Answer:
2) Brown algae
![]()
Question 7.
Gymnosperm with unbranched stem is
1. Pinus
2. Sequoia
3. Cycas
4. Cedrus
Answer:
3. Cycas
Question 8.
Heterospory is the production of
1) Sexual and asexual spores
2) Large and smaller spores
3) Haploid and Diploid spores
4) Diploid and Tetraploid spores
Answer:
2) Large and smaller spores
Question 9.
Identify the mismatching
1) Porphyra – Food
2) Gelidium – Agar
3) Laminaria – Iodine
4) Sargassum – Carrageen
Answer:
4) Sargassum – Carrageen
Question 10.
PEN in angiosperms is
1) Haploid
2) Diploid
3) Triploid
4) Tetraploid
Answer:
3) Triploid
Question 11.
Peat moss is
1. Funaria
2. Sphagnum
3. Marchantia
4. Polytrichum
Answer:
2. Sphagnum
Question 12.
Porphyra is a
1. Red alga
2. Brown alga
3. Green alga
4. Blue-green alga
Answer:
1. Red alga
Question 13.
Pyrenoid contains
1) Proteins and starch
2) Protein and lipid
3) starch and lipid
4) starch and cellulose
Answer:
1) Proteins and starch
![]()
Question 14.
Protonema is
1) haploid and found in mosses
2) diploid and is found in liver worts
3) diploid and is found in pteridophytes
4) haploid and is found in pteridophytes
Answer:
1) haploid and found in mosses
Question 15.
Agar is
1. obtained from green algae
2. used in tissue culture medium
3. stored food in brown algae
4. pigment present in red algae
Answer:
2. used in tissue culture medium
Question 16.
Food storage bodies of green algae are
1. ER
2. Nucleus
3. Chloroplasts
4. Mitochondria
Answer:
3. Chloroplasts
Question 17.
Female sex organ is called carpogonium in
1. Cyanobacteria
2. Phaeophyceae
3. Rhodophyceae
4. Chlorophyceae
Answer:
3. Rhodophyceae
Question 18.
The following plant provides peat which is used as fuel located in
1. Marchantia
2. Sphagnum
3. Riccia
4. Anthoceros
Answer:
2. Sphagnum
Question 19.
Identify the mismatching
1. Liverwort – Marchantia
2. Hornwort – Anthoceros
3. Mosses – Polytrichum
4. Hepacticopsida – Funaria
Answer:
4. Hepacticopsida – Funaria
![]()
Question 20.
Pseudo – elaters are found in
1. Marchantia
2. Anthoceros
3. Sphagnum
4. Polytrichum
Answer:
2. Anthoceros
Question 21.
The following plants are used as soil binders
1. Algae
2. Bryophytes
3. Pteridophyetes
4. Lichens
Answer:
3. Pteridophyetes
Question 22.
Mlcrophylls are found ¡n
1. Selagineila
2. Pteris
3. Diyopteris
4. Azolla
Answer:
1. Selagineila
Question 23.
Non-character of conifers is
1. Needle like leaves
2. Thick cuticle
3. Seeds covered by fruit
4. Sunken stomata
Answer:
1. Needle like leaves
Question 24.
The pollination is direct and anemophilous in
1. Bryophytes
2. Pteridophytes
3. Gymnosperms
4. Angiosperms
Answer:
3. Gymnosperms
![]()
Question 25.
The giant red wood tree belongs to
1. Angiosperms
2. Dicots
3. Gymnosperms
4. Monocots
Answer:
3. Gymnosperms
Question 26.
Reserve food of brown algae is
1. Fucoxanthin
2. Floridean starch
3. Carrageen
4. Laminarin
Answer:
4. Laminarin
Question 27.
Algae, that is a rich source of protein is
1. Nostoc
2. Ectocarpus
3. Chlorella
4. Spirogyra
Answer:
3. Chlorella
Question 28.
In mosses, meiosis occurs
1. During spore formation
2. In the zygote
3. In the gametangium
4. In the gametes
Answer:
1. During spore formation
Question 29.
In bryophytes
1. both sporophyte and gametophyte are independent
2. sporophyte is dependent on gametophyte
3. both sporophyte and gametophyte are dependent on one another
4. gametophyte is dependent on sporophyte
Answer:
3. both sporophyte and gametophyte are dependent on one another
Question 30.
Double fertilization is a characteristic of
1. Pteridophytes
2. Angiosperms
3. Bryophytes
4. Gymnosperms
Answer:
2. Angiosperms
![]()
Question 31.
Life cycle in Marchantia is
1. Haplo-diplontic
2. Diplontic
3. Diplo-haplontic
4. Haplontic
Answer:
1. Haplo-diplontic
Question 32.
Reserve food in porpyra is
1. oil droplets
2. Marmitol
3. Floridean starch
4. Glycogen
Answer:
3. Floridean starch
Question 33.
The commerical product agar is produced by
1. Ectocarpus
2. Gelidium
3. Laminaria
4. Chlorella
Answer:
2. Gelidium
Question 34.
Align is the cell wall material in
1. Blue green lagae
2. Red algae
3. Green algae
4. Brown algae
Answer:
4. Brown algae
Question 35.
Kelp is
1. Laminaria
2. Volvox
3. Lycopodium
4. Adiantum
Answer:
3. Lycopodium
Question 36.
Much of the global photosynthesis is carried out by
1. Algae
2. Bryophytes
3. Pteridophytes
4. Angiosperms
Answer:
1. Algae
Question 37.
Fronds are seen in
1. Green algae
2. Blue-green algae
3. Porphyra
4. Laminaria
Answer:
4. Laminaria
![]()
Question 38.
In gymnsperm, the endosperm is
1. Haploid
2. DiPloid
3. Triploid
4. Polyploid
Answer:
1. Haploid
Question 39.
A gymnosperm having vessels in xylem is
1. Cednis
2. Gnetum
3. Cycas
4. Pinus
Answer:
2. Gnetum
Question 40.
Spermatozoid of cycas is
1. Biflagellate
2. Non-flagellate
3. Uniflagellate
4. Multiciliate
Answer:
4. Multiciliate
Question 41.
Megasporophyll of Cycas has the same nature as
1. Stamen
2. Petal
3. Sepal
4. Carpel
Answer:
4. Carpel
Question 42.
Spores of Funaria on germination, give rise to
1. Antheridia
2. Protonema
3. Archegonia
4. Vegetative body
Answer:
2. Protonema
Question 43.
………….. plants play an important role in plant succession on bare rocks/soil
1. Bryophytes
2. Pteridophytes
3. Fungi
4. Bacteria
Answer:
1. Bryophytes
![]()
Question 44.
Number of stages in the life cycle of a moss
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
Answer:
2. 2
Question 45.
Chlorophyll – bearing, simple, thalloid and autotrophic plants arc
1) Bryophytes
2) Algae
3) Pterodohyptes
4) Fungi
Answer:
2) Algae
Question 46.
Non-flagellated isogametes are formed during sexual reproduction in
1) Chlamydomonas
2) Fucus
3) Spirogyra
4) Volvox
Answer:
3) Spirogyra
Question 47.
The most common cell wall materials in green algae are
1) cellulose, hemicellulose
2) Hemicellulose, pectin
3) Cellulose, pectin
4) Pectin and xylan
Answer:
3) Cellulose, pectin
Question 48.
Choose the wrong statement with reference to phaeophyceae
1) Pear shaped biflagellated zoospores and flagellae are unequal and laterally attached
2) Pyriform shaped gametes bearing two laterally attached flagellae
3) Union of gametes occurs in the oogonium
4) Carotenes and xanthophylls are absent
Answer:
4) Carotenes and xanthophylls are absent
Question 49.
Identify the mismatching
1) Chara – Monoecious
2) Marchantia – Dioecious
3) Funaria – Monoecious
4) Salvinia – Terrestrial moss plant
Answer:
4) Salvinia – Terrestrial moss plant
Question 50.
Archaegoniophore is present in
1) Marchantia
2) Chara
3) Adiantum
4) Funaria
Answer:
1) Marchantia
![]()
Question 51.
Which of the following is responsible for peat formation
1) Marchantia
2) Riccia
3) Funaria
4) Sphagnum
Answer:
4) Sphagnum
Question 52.
Chlamydomonas, Ciadophora, Chloreila, Ectocarpus, Ocdogonium., Spirogyra, Volvox and Ulothrix. Among this howmany are green filamentous algae
1) 5
2) 4
3) 2
4) 1
Answer:
3) 2
Question 53.
…………. algae are used as food
a) Porphyra
b) Sargassum
c) Laminaria
1) a,c only
2) c, b only
3) a, b only
4) a,b,c
Answer:
4) a,b,c
Question 54.
Choose the wrong statement with reference to pteridophytes
1) First terrestrial plants to have vascular tissues
2) Embryophytic, archaegoniate trachaeophytic cryptogams
3) Main plant body is a sporophyte with tap roots
4) Deveiopoment of sporangium may be leptosporangiate or eusporangiate
Answer:
3) Main plant body is a sporophyte with tap roots
Question 55.
Heterosporous ferns are
1) Salvinia, selaginella
2) Equisetum, selaginella
3) Azolla, salvinia
4) Dryopteris, pteris
Answer:
1) Salvinia, selaginella
Question 56.
The bryophyte which provides peat used as fuel and also used as packing material for transshipment of living material is . .
1) Funaria
2) Sphagnum
3) Anthoceros
4) Marchantia
Answer:
2) Sphagnum
![]()
Question 57.
Sex organs are multicellular, jacketed and sessile in
1) Bryophytes
2) Pteridophytes
3) Algae
4) Fungi
Answer:
2) Pteridophytes
Question 58.
Identify the mismatching
1) Haplontic life cycle – Spirogyra
2) Haplodiplontic life cycle – Ectocarpus, Laminaria, Bryophytes
3) Diplontic life cycle – Gymnosperms and Angiosperms, Fucus
4) Diplo Haplontic – Chlamydomonas
Answer:
4) Diplo Haplontic – Chlamydomonas
Question 59.
A fern differs from a mass in having
1) Swimming archegonia
2) Swimming antherozoids
3) Independent gametophytes
4) Independent sporophytes
Answer:
4) Independent sporophytes
Question 60.
Mark the correct statement
1) All archegoniates are tracheophytes
2) All protistans are heterotrophic
3) All algae show chlorophyll a
4) All tracheophytes are archegoniate
Answer:
3) All algae show chlorophyll a
Question 61.
In chlorophyceae, the mode of sexual reproduction is
1) Anisogamy
2) Oogamy
3) Isogammy
4) All of these
Answer:
4) All of these
Question 62.
First terrestrial plants possessing vascular tissues are
1) Bryophytes
2) Pteriodophytes
3) Gymnosperms
4) Angiosperms
Answer:
2) Pteriodophytes
![]()
Question 63.
Strobili cones are found in
1) Salvinia
2) Pteris
3) Marchantia
4) Equisetum
Answer:
4) Equisetum
Question 64.
Which of the following algae produce Carrageen?
1) Blue-green algae
2) Green algae
3) Brown algae
4) Red algae
Answer:
4) Red algae
Question 65.
Protonema occurs in the life cycle of
1) Riccia
2) Funaria
3) Anthoceros
4) Spirogya
Answer:
2) Funaria
Question 66.
An alga, very rich in protein is
1) Chlorella
2) Nostoc
3) Spirogyra
4) Ulothrix
Answer:
1) Chlorella
![]()
Question 67.
Mannitol is the stored food in
1) Porphyra
2) Fucus
3) Gracillaria
4) Chara
Answer:
2) Fucus