Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 11th Lesson Cell Cycle and Cell Division which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 11th Lesson Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Between a prokaryote and a eukaryote, which cell has a shorter cell division time?
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell
Question 2.
Among prokaryotes and eukaryotes, which one has a shorter duration of cell cycle?
Answer:
- Pro-karyotes has shorter duration.
- The Cell cycle duration of prokaryotes is 20 minutes, where as for eukaryotes it is 24 hours.
Question 3.
Which of the phases of cell cycle is of longest duration? [ AP May-19]
Answer:
Interphase of cell cycle has longest duration.
![]()
Question 4.
Which tissue of animals and plants exhibits meiosis? [APM-16]
Answer:
- In animals, Meiosis occurs in gamate producing cells.
- In Thallophyta, meiosis occurs in zygote.
- In Bryophytes, meiosis occurs in spore mother cells (or) reproductive tissue.
Question 5.
Given that the average duplication time of E.coli is 20 minutes. How much time will two E.coli cells take to become 32 cells?
Answer:
- 80 minutes.
- Reason: For every 20 minutes the cells duplicate. 32 = 24. Hence four generations are required. So, they take 20+20+20+20 = 80 minutes time to form 32 cells.
Question 6.
Which part of the human body should be used to demonstrate stages in mitosis?
Answer:
The body cells (cells lining the gut and skin) are the parts of human body used to demonstrate the stages of mitosis.
Question 7.
What attributes does a chromatid require to be classified as a chromosome?
Answer:
A chromatid is said to be a chromosome when it possesses
- Independent existence
- Its own centromere with one DNA molecule.
Question 8.
Which of the four chromatids of a bivalent at prophase-I of meiosis can involve in crossover? [AP M-19] [TS M-16]
Answer:
Non sister chromatids.
Each of separated chromatid consists of 2C DNA.
Question 9.
If a tissue has at a given time 1024 cells. How many cycles of mitosis had the original parental single cell undergone? [AP M-20, 22][TS M-17]
Answer:
- 10 cycles of mitosis.
- Reason: 210 =1024
Question 10.
An anther has 1200 pollen grains. How many pollen mother cells must have been there to produce them? [APM-15,16,17] [IPE-13] [TS M-17, 19, 20, 22]
Answer:
- 300 pollen mother cells.
- Reason: ¼(1200) = 300
Question 11.
At what stage of cell cycle does DNA synthesis occur? [AP, TS M-18]
Answer:
S-phase or Synthesis phase of interphase
Question 12.
It is said that one cycle of cell division in human cells (eukaryotic cells) take 24 hours. Which phase of the cycle, do you think occupies the maximum part of cell cycle?
Answer:
S-phase or Synthesis phase of interphase
Question 13.
It Is observed that heart cells do not exhibit cell division. Such cells do not divide further and exit ………… phase to enter an inactive stage called ….. of cell cycle. Fill in the blanks.
Answer:
- G1 phase
- Quiescent stage (GQ)
Question 14.
Identify the substages of prophased of meiosis in which synapse and desynapse are formed.
Answer:
- Synapsis is pairing of homologous chromosomes.
It occurs in zygotene substage of prophase-1 in meiosis. - Desynapsis is separation of homologous chromosomes.
It occurs in diplotene substage of prophase-1 in meiosis.
Question 15.
Name the stage of meiosis in which actual reduction in chromosome number occurs.
Answer:
Anaphase-I of meiosis.
![]()
Question 16.
Mitochondria and plastids have their own DNA (genetic material). What is their fate during nuclear division like mitosis?
Answer:
During cytokinesis, mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the two daughter cells.
Question 17.
A cell has 32 chromosomes, ft undergoes mitotic divisions. What will be the chromo some number during metaphase? What would be the DNA content (C) during anaphase?
Answer:
- The chromosome number in the cell at metaphase of mitosis is 32 only.
- But each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids
- In anaphase, two sister chromatids of a chromosome is separated and moves to opposite poles.
Question 18.
While examining the mitotic stage in a tissue, one fluids some cells with 16 chromo-somes and some with 32 chromosomes. What possible reasons could you give to this difference in chromosome number?
Answer:
- Mitotic division is also called as equational division.
- Mitotic stage in a tissues at prophase and metaphase contains basic sets of chromosomes.
- But in this condition, anaphase shows two sister chromatids of a chromosome with double number 32.
- So, the cells with 16 chromosomes are arised from cells with 32 chromosomes.
Explanation: This can happen because of mosaicism. Mosaicism denotes the presence of two populations of cells with different genotypes in one individual. Mosaicism can happen because of various reasons, viz. nondisjunction, anaphase lag and endoreplication. Anaphase lag appears to be the prime reason of mosaicism. In this case, the cells with 32 chromosomes must have arisen from those with 16 chromosomes, because the cells are undergoing mitosis and not meiosis.
Question 19.
The following events occur during the various phases of the cell cycle. Fill the blanks with suitable answer against each.
a. Disintegration of nuclear membrane…
b. Appearance of nucleolus.
c. Division of centromere
d. Replication of DNA
Answer:
a) Prophase
b) Telophase
c) Anaphase
d) S-phase
Question 20.
Two key events take place during S-phase in animal cells, DNA replication and duplica¬tion of centriole. In which parts of the cell do these events occur?
Answer:
- DNA replication occurs in nucleus .
- Centriole duplication occurs in cytoplasm.
Question 21.
Name a ceil that is found in arrested in diplotene stage for months and years . Comment in two or three sentences, how it completes its cell cycle.
Answer:
- In oocytes of some vertebrates, diplotene can last for months or years.
- These chromosomes become normal after growth and completes their cell cycle .
- Termination of chiasmata occurs in diakinesis and homologous chromosomes are seperated.
- Subsequently cell enters into other stages of Meiosis I and completes it, thus chromosome number is reduced.
- After meiosis- II 4 daughter cells each with a haploid set are formed.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
In which phase of meiosis are the following formed? Choose the answers from hint points given below.
a) Synaptonemal complex ……..
b) Recombination nodules ………
c) Appearance / activation of Enzyme recombinase
d) Termination of chiasmata
e) Interkinesis.
f) Formation of dyad of cells
Answer:
a) Synaptonemal complex- Zygotene
b) Recombination nodules- Pachytene
c) Appearance /activation of Pachytene Enzyme recombinase
d) Termination of chiasmata Diakinesis
e) Interkinesis- After telophase 1/ before meiosis II
f) Formation of dyad of cells- Telophase 1/ After meiosis I.
Question 2.
Mitosis results in producing two cells which are similar to each other. What would be the consequence if each of the following irregularities occurs during mitosis?
a) Nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate
b) Duplication of DNA does not occur
c) Centromeres do not divide
d) Cytokinesis does not occur
Answer:
a) If the nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate, the chromosomes can not spread through the cytoplasm and metaphase is not continued.
![]()
b) If the duplication of DNA does not occur, the genetic material will not be doubled, the chromosomal number is not doubled and the daughter cells do not get the same number of chromosomes as that of the parent cell.
c) If the centromeres donot divide, chromatids cannot move to opposite poles.
d) If cytokinesis does not occur, after the nuclear division the cell contain two nuclei, but not two daughter cells.
Question 3.
Comment on the statement – Meiosis enables the conservation of specific chromosome number of each species even though the process per sec results in reduction of chromosome number.
Answer:
- In sexually reproducing organisms the chromosome number is reduced to half by meiosis mechanism.
- From a diploid mother cell meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells.
- Fertilization or union sex cells again gives rise to diploid (2n) organisms.
- Hence, conservation of specific chromosome number of each species is achieved across generation by meiosis mechanism.
- It also increases the genetic variability in the population of organisms form one generation to the next, that leads to the evolution.
Question 4.
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Answer:
- Division of mother cells into two daughter cells by a separate process is Called Cytokinesis.
- Cytokinesis is followed by the karyokinesis (division of nucleus)
- In an animal cell, this is followed by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane.
- The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the centre dividing the cell cytoplasm into two plant cells.
- Plant cells are enclosed by a relatively inextensible(rigid) cell wall. So in those cells, wall formation starts in the centre of the cells and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls.
Question 5.
Which division is necessary to maintain constant chromosome number in ail body cells of multicellular organism and why? [IPE Mar-14]
Answer:
- Mitosis is necessary to maintain constant chromosome number in all body cells of multicellular organisms.
- Because mitosis results in the production of diploid daughter cells with genetic employment usually identical to that of the parent cell.
- Mitosis maintains a constant number of chromosomes in all the cells of the body.
- Mitosis helps in wound healing and regeneration of plant parts.
- The daughter cells formed by mitosis are identical with the mother cell.
- Growth in organism is caused by mitosis and it restores the surface-to-volume ratio of the cell
Question 6.
Though redundantly described as a resting phase, interphase does not really involve rest. Comment. [ TS M-17,22] [AP Mar-15,16,17,19,20,221 [IPE Mar- 13]
Answer:
Interphase: The state of cell cycle, at which, the nucleus is not in a state of division, is called Inter phase. It is the period of preparation for cell division. This stage occurs between two successive cell divisions.
The inter phase is called resting phase. But during this time, the cell prepares for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. The inter phase is divided into 3 sub stages-G1 phase, S phase and G2 phase.
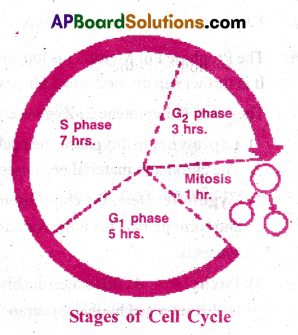
1) G1 phase: This is the phase between mitosis phase and initiation of DNA replication. During G1 phase the cell is metabolically active and it grows continuously; but does not replicate its DNA.
This G1 phase includes
a) Increase in the size of the cell, b) Synthesis of RNA and proteins.
2) S Phase: In this phase, DNA replication takes place. During this time the amount of DNA per cell doubles.
However, there is no increase in the chromosome number.
3) G2 phase: During G2 phase, the synthesis of proteins and RNA continues. Various cell organelles are newly synthesized.
In view of the above 3 phases, we say interphase does not really involve rest.
Question 7.
Mention the key features of meiosis.
Answer:
Key features of Meiosis:
- Meiosis involves two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell division called meiosis I and Meiosis II, but only a single cycle of DNA replication.
- Meiosis I is initiated after the parental chromosomes have replicated to produce identical sister chromatids at the S-Phase.
- Meiosis involves pairing of homologous chromosomes and recombination between them.
- Four haploid cells are formed at the end of meiosis II. Meiotic events can be grouped under the following phases.
Meiosis I Meiosis II Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II
![]()
Question 8.
Explain prophase I of meiosis. [TS M -19] [TS May-17]
Answer:
- In sexually reproducing organisms the chromosome number is reduced to half by meiosis mechanism.
- From a diploid mother cell meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells.
- Fertilization or union sex cells again gives rise to diploid (2n) organisms.
- Hence, conservation of specific chromosome number of each species is achieved across generation by meiosis mechanism.
- It also increases the genetic variability in the population of organisms form one generation to the next, that leads to the evolution.
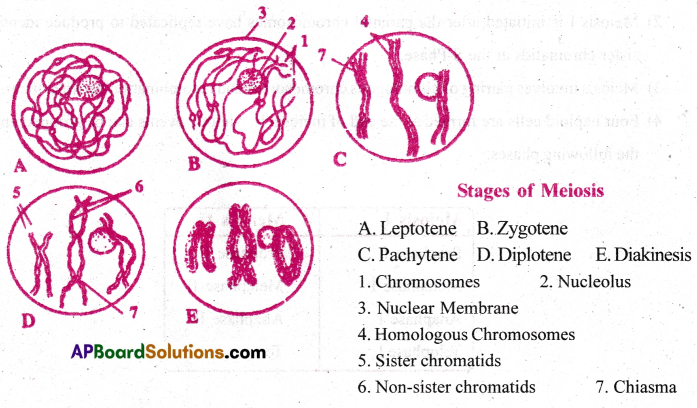
The Prophase I of Meiosis I is ionger and more complex when compared to prophase of mitosis.
It is further sub divided into 5 phases based on the chromosomal behaviour
They are
- Leptotene
- Zygotene
- Pachytene
- Diplotene and
- Diakinesis.
1) Leptotene: In this phase, the nucleus increases in size by absorbing water from the cytoplasm. The chromatin material organises into a constant number of chromosomes.
2) Zygotene: Here, the chromosomes become shorter and thicken. They approach each other and form pairs. This homologous pair is called bivalent and the process of pairing is called synapsis.
3) Pachytene: At this stage, the bivalent chromosomes are clearly visible as tetrads. This stage is characterised by the appearance of recombination nodules.
Crossing over is mediated by recombinase enzyme. Crossing over leads to recombination of genetic material.
4) Diplotene: Here, dissolution of synaptonemal complex occurs. The homologous chromosomes of bivalents separate from each other except at the sites of cross overs. Here, the x-shaped structures are called chiasmata.
5) Diakinesis: This is the final stage of prophase I of meiosis I. This is marked by terminalisation of chiasm ata. By the end of diakinesis, the nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope also breaks down.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Discuss on the statement – Telophase is reverse of prophase.
Answer:
- The changes occurring in telophase are almost reverse to those which take place in late prophase.
- The daughter chromosomes arrived at the poles of the cells, lengthen and their visibility decreases due to decondensation of chromatin.
- The kinetochore fibres disappear.
- The nuclear membrane reappears and nucleoli are reorganised.
- At the end of telophase two independent daughter nuclei are organised in the same mother cell.
- Nuclear membrane, Nucleolus, Golgi complexes, Endoplasmic reticulum disappears. Thats why telophase is the reverse phase to prophase.
Question 2.
What are the various stages of meiotic prophase-I? Enumerate the chromosomal events during each stage?
Answer:
- In sexually reproducing organisms the chromosome number is reduced to half by meiosis mechanism.
- From a diploid mother cell meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells.
- Fertilization or union sex cells again gives rise to diploid (2n) organisms.
- Hence, conservation of specific chromosome number of each species is achieved across generation by meiosis mechanism.
- It also increases the genetic variability in the population of organisms form one generation to the next, that leads to the evolution.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate between the events of mitosis and melosis
Answer:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| 1) It occurs in both haploid and diploid cells | 1) It occurs in diploid cells only. |
| 2) It occurs in somatic cells. | 2) It occurs in reproductive cells. |
| 3) Nucleus divide once. | 3) Nucleus divide twice. |
| 4) Daughter cells are identical. . | 4) Daughter cells not identical. |
| 5) Two daughter cells are formed. | 5) Four daughter cells are formed. |
| 6) Prophase is simple. | 6) Prophase is complicated and divided into five sub phases. |
| 7) Pairing of chromosomes does not occur. | 7) Homologous chromosomes pair to form bivalents. |
| 8) Both chiasmata and crossing over are absent. | 8) Both chiasmata and crossing over occur between non-sister chromatids. |
| 9) Centromere undergo division in anaphase. | 9) Centromere donot divide in anaphase I, but divides in anaphase II. |
| 10) Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite poles. | 10) Bivalents are disjunctedto opposite poles in anaphase I. |
| 11) The chromosomal number of daughter nucleoli is unchanged. | 11) The chromosomal number of daughter nucleoli is reduced to half. |
| 12) Duration of time is less. | 12) Duration of time is more. |
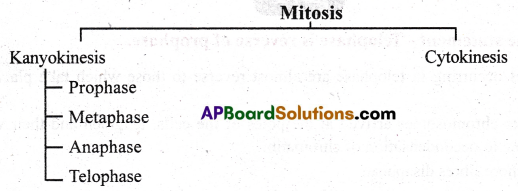
Events of Mitosis
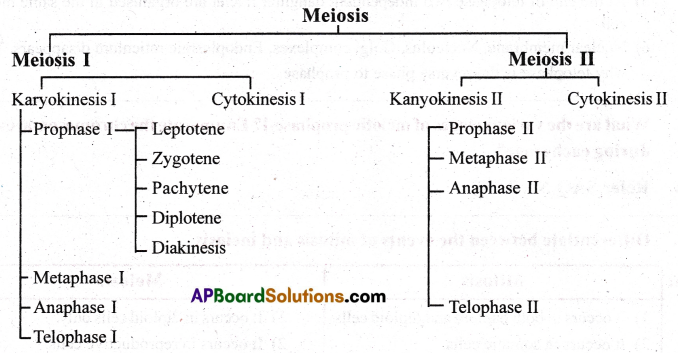
Events of Meiosis
Question 4.
Write brief note on the following:
a. Synaptonemal complex
b. Metaphase plate
Answer:
a) Synaptonemal complex: During zygotene stage chromosomes start pairing together and this process of association is called synopsis.
- Such paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.
- Chromosome synapsis is accompanied by the formation of complex structure called synaptonemal complex.
- The complex formed by a pair of homologous chromosomes is called bivalent or tetrad of chromatids.
b) Metapahse plate:
- Metaphase is characterised by two important changes.
- Formation of bipolar spindle fibres and attach the same to the kinetochores of chromosomes.
- Orientation of chromosomes on the equatorial region and forming a equatorial plate or metaphoric plate.
Question 5.
Write briefly the significance of mitosis and meiosis in multicellular organism.
Answer:
I) Significance of Mitosis:
- Growth in organisations is caused by mitosis and it restores the surface or volume ratio of the cell.
- The daughter cells formed by mitosis are identical with the mother cell. Hence it is important in conserving the genetic integrity of the organism.
- In unicellular organisms, mitosis helps in reproduction.
- Mitosis helps in wound healing and regeneration of lost plant parts.
- Mitosis helps for grafting in vegetative reproduction.
- It maintains a constant number of chromosomes in all the cells of the body.
II) Significance of Meiosis:
- It helps in the maintenance of a constant chromosome number from one generation to the next.
- Due to crossing over, genetic recombinations are caused which help in the origin of new species and lead to evolution.
![]()
Exercise
Question 1.
Name a stain commonly used to colour chromosome.
Answer:
Acetocaramine
Question 2.
Name the pathological condition when uncontrolled cell division occurs,
Answer:
Cancer
Question 3.
An organism has two pairs of chromosomes (i.e., chromosome number =4). Diagrammatically represent the chromosomal arrangement during different phases of meiosis-II.
Answer:
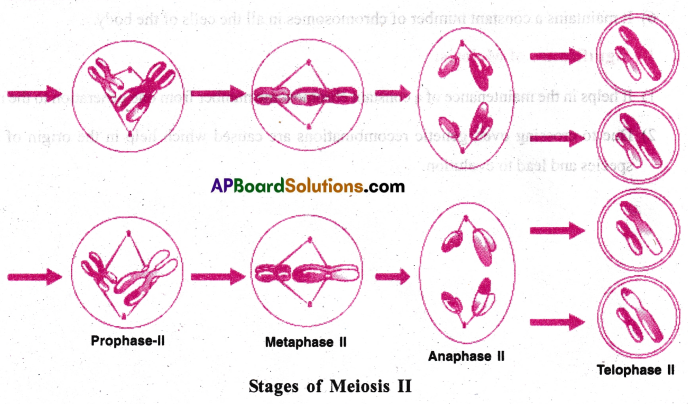
Question 4.
Meiosis has events that lead to both gene recombinations as well as mendelian recombinations. Discuss.
Answer:
- In pachytene stage both chiasmata and crossing over occur between non-sister chromatids.
Due to crossing over, genetic recombinations are caused. - During Anaphase I of Meiosis I, Mendelian recombination takes place.
Question 5.
Both unicellular and multicellular organisms undergo mitosis. What are the differences, if any, observed between the tw o processes?
Answer:
- In unicellular organisms like Amoeba and Paramecium asexual reproduction occurs by binary
fission. The cell divides by mitosis and produces two daughter cells. - Stages like Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase are present in multicellular organisms but absent in unicellular organisms.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The number of major phases in the cell cycle are
1. 4
2. 8
3. 2
4. 5
Answer:
3. 2
Question 2.
Interphase is the gap between
1) Karyokinesis and cytokinesis
2) G1 and G2
3) Replication and Karyokinesis
4) Two mitotic cell divisions
Answer:
2) G1 and G2
Question 3.
In a typical cell cycle, the longest phase is ,
1. Interphase
2. Mitotic phase
3. Karyokinesis
4. Cytokinesis
Answer:
1. Interphase
![]()
Question 4.
The least time consuming sub-stage of interphase is
1. 5 phase
2. G1 phase
3. G2 phase
4. GQ phase
Answer:
2. G1 phase
Question 5.
Best stage to observe chromosomes with different shapes having one chromatid is
1) Interphase
2) Prophase
3) Metaphase
4) Anaphase
Answer:
4) Anaphase
Question 6.
Phase of cell cycle when DNA polymerase is active in
1) G1
2) S
3) G2
4) M
Answer:
2) S
Question 7.
The phase corresponding to the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication is
1) G1 – phase
2) G2 – phase
3) S – Phase
4) M – Phase
Answer:
1) G1 – phase
Question 8.
In meiocytes, interphase is immediately followed by
1. Prophase-II
2. Prophase-I
3. Telophase-I
4. Telophase-II
Answer:
2. Prophase-I
Question 9.
The ratio of number of chromatids in mitotic metaphase and chromosomes in mitotic anaphase is
1) 1:2
2) 2:1
3) 1:4
4) 1:1
Answer:
4) 1:1
Question 10.
In general, the ratio of time spent in interphase and divisional phases of cell cycle is
1) 6:4
2) 10:1
3) 19:1
4) 2:1
Answer:
3) 19:1
Question 11.
Membrane bound new cell organelles are developed in
1. Prophase
2. G1 phase
3. S phase
4. G2 phase
Answer:
4. G2 phase
Question 12.
A bivalent consists of
1) 2 chromatids and 2 DNA molecules
2) 4 chromatids and 8 DNA molecules
3) 4 chromatids and 2 chromosomes and 4 telomeres
4) 4 chromatids, 2 centromeres, 8 telomeres
Answer:
4) 4 chromatids, 2 centromeres, 8 telomeres
Question 13.
Well organised chiasmata are first seen in
1. Pachytene
2. Zygotene
3. Diplotene
4. Leptotene
Answer:
3. Diplotene
![]()
Question 14.
Cell plate is grown
1. Centrifugally
2. Centripetally
3. Either centripetally or centrifugally
4. Periclinally
Answer:
1. Centrifugally
Question 15.
Different phases of meiosis can be best observed in
1. Root apex
2. Shoot apex
3. Anther
4. Fertilizedovaries
Answer:
3. Anther
Question 16.
A transitional stage from prophase-I to metaphase-I is represented by
1. Anaphase-I
2. Pachytene
3. Diakinesis
4. Diplotene
Answer:
3. Diakinesis
Question 17.
The spindle fibres are chemically composed of
1. Actin
2. Myosin
3. Collagen
4. Tubulin
Answer:
4. Tubulin
Question 18.
Bulk of RNA is synthesised in a cell during
1. S-phase
2. G2 phase
3. G1 phase
4. M-phase
Answer:
3. G1 phase
Question 19.
Duplication of centriole in animal cell occurs during
1) G1 – phase
2) S – phase
3) G2 – phase
4) G0 – phase
Answer:
2) S – phase
Question 20.
G1 phase is not characterised by
1) Continuous growth
2) Active metabolism
3) DNA replication
4) Non – replication of DNA
Answer:
3) DNA replication
Question 21.
Number of spindles formed in meiosis-1 is
1. 2
2. 3
3. 4
4. 1
Answer:
4. 1
Question 22.
Meiosis II performs
1) Separation of sex chromosomes
2) Synthesis of DNA and centromere
3) Separation of homologous chromosomes
4) Separation of chromatids
Answer:
3) Separation of homologous chromosomes
![]()
Question 23.
The ratio of the amount of DNA in pachytene to that at Anaphase-H
1. 1:4
2. 4:1
3. 1:2
4. 1:1
Answer:
4. 1:1
Question 24.
Non-dividing cells like heart cells and nerve cells are in
1. G1 phase
2. S phase
3. G2 phase
4. G0 phase
Answer:
4. G0 phase
Question 25.
Mitosis differs from meiosis in
1. Formation of spindle
2. Separation of chromatids
3. Lack of crossing over
4. Disappeamce of nuclear membrane at the end of prophase
Answer:
3. Lack of crossing over
Question 26.
The daughter cells of meiocytes always divide by
1. Budding
2. Meiosis
3. Binary fission
4. Mitosis but never by meiosis
Answer:
4. Mitosis but never by meiosis
Question 27.
Number of meiocytes found in each ovule of Pisum sativum
1. 7
2. 14
3. Many
4. 1
Answer:
4. 1
Question 28.
Activity of ligase enzyme is found in
1. Leptotene
2. Zygotene
3. Pachytene
4. Diplotene
Answer:
3. Pachytene
Question 29.
The stage of cell cycle present after the end of G1 and before the beginning of G2 is
1. Go
2. S
3. M
4. D
Answer:
2. S
Question 30.
During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at 4C level if the initial amount is denoted as 2C?
1) G0 and G1
2) G1 and S
3) Only G1
4) G1 and M
Answer:
4) G1 and M
Question 31.
Yeast completes cell cycle in
1) 30 min
2) 60 min
3) 90 min
4) 120 min
Answer:
3) 90 min
Question 32.
To observe mitotic stages which of the plant material can be suitable for identification ?
1) Shoot apex of onion
2) Root apex of onion
3) Leaf apex of onion
4) Flower of onion
Answer:
2) Root apex of onion
Question 33.
Condensation and decondensation of chromosomes occurs respectively in
1) Prophase and Metaphase
2) Anaphase and Metaphase
3) Prophase and Anaphase
4) prophase and Telophase
Answer:
4) prophase and Telophase
![]()
Question 34.
Which one is not possible due to mitosis?
1) Wound healing
2) Regeneration
3) Grafting
4) Reduction of chromosome number
Answer:
4) Reduction of chromosome number
Question 35.
End of prophase is marked by
1) Complete disintegration of nuclear membrane
2) Disappearance of ER, GB, nucleolus and nuclear envelope
3) Initiation of condensation of chromosomal material
4) Chromosomes aligns at the equatorial plate
Answer:
2) Disappearance of ER, GB, nucleolus and nuclear envelope
Question 36.
Daughter cells formed as a result of meiosis are not similar to that of parent cell because
1) Meiosis is completed in two stages
2) Prophase is the longest phase
3) Nucleus size increases in daughter cells
4) Crossing over takes place and chromosome number is halved
Answer:
4) Crossing over takes place and chromosome number is halved
Question 37.
Homologous chromosomes separate during
1) Metaphase I
2) Anaphase I
3) Metaphase II
4) Anaphase II
Answer:
2) Anaphase I
Question 38.
Microtubules of opposite poles of spindle get attached to kinetochores of sister chromatids during
1) Anaphase II
2) Prophase II
3) Metaphase II
4) Metaphase I
Answer:
4) Metaphase I
Question 39.
Synapsis occurs between
1) Spindle fibres and centromeres
2) mRNA and ribosomes
3) A male and female gamete
4) Two homologous chromosomes
Answer:
4) Two homologous chromosomes
Question 40.
In onion root tip during metaphase stage of mitosis the number of kinetochores will be
1) 4
2) 8
3) 16
4) 32
Answer:
4) 32
Question 41.
Tetrad is made of
1) Four homologous chromosomes with four chromatids
2) Two homologous chromosomes, each with two chromatids
3) F our nonhomologous chromatids
4) F our nonhomologous chromosomes
Answer:
2) Two homologous chromosomes, each with two chromatids
Question 42.
Select the correct sequence of stages of meiotic – 1 .prophase
1) Zygotene -Leptotene – Diplotene – Diakinesis – Pachytene
2) Leptotene – Zygotene – Pachytene – Diplotene – Diakinesis
3) Leptotene – Diplotene – Pachytene – Diakinesis – Zygotene
4) Diakinesis – Diplotene – Pachytene – Zygotene – Leptotene
Answer:
2) Leptotene – Zygotene – Pachytene – Diplotene – Diakinesis
![]()
Question 43.
During diplotene stage in meiosis
1) Chromosomes replicate
2) Chromosomes segregate
3) Homologous chromosomes pair
4) Chaismata are seen
Answer:
4) Chaismata are seen
Question 44.
Which statement best explains the evolutionary advantage of meiosis?
1) Meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction
2) Genetic recombinations are possible from generation to generation
3) Meiosis alternates with mitosis from generation to generation
4) The same genetic system is passed on from generation to generation
Answer:
2) Genetic recombinations are possible from generation to generation
Question 45.
Synaptonemal complex is found associated with
1) Paired meiotic chromosomes
2) Lampbrush chromosomes
3) Polytene chromosomes
4) Mitotic chromosomes
Answer:
1) Paired meiotic chromosomes
Question 46.
Disjunction refers to
1) The separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase-II
2) The type of chromosomal aberration in which there is loss of a part of chromosome.
3) In compatibility in fungi and other thallophytes
4) The separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase-I
Answer:
4) The separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase-I
Question 47.
Zygotic meiosis occur in
1) Dryopteris
2) Marchantia
3) Pinus
4) Chlamydomonas
Answer:
4) Chlamydomonas
Question 48.
Crossing over in diploid organisms is responsible for
1) dominance of genes
2) linkage between genes
3) segregation of alleles
4) recombination of alleles
Answer:
4) recombination of alleles
Question 49.
The following stage is incorrect with reference to meiosis
1) Nucleus divides twice
2) Chromosomes divide twice
3) Chromosomes divide once
4) Centromere divides once
Answer:
2) Chromosomes divide twice
![]()
Question 50.
Answer: The M – phase represents the phase when the actual cell division occurs R: Interphase represents the phase between two successive M – phases
1) A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
2) A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
3) A is true, R is false
4) A is false, R is true
Answer:
2) A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A