Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 10th Lesson Biomolecules which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 10th Lesson Biomolecules
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Medicines are either man made (i.e., synthetic ) or obtained from living organisms like plants, bacteria, animals etc. and hence the latter are called natural products. Sometimes natural products are chemically altered by man to reduce toxicity or side effects. Write against each of the following whether they were initially obtained as a natural product or as a synthetic chemical. [AP M-20]
a) Penicillin
b) Sulfonamide
c) Vitamin C
d) Growth Hormone
Answer:
a) Penicillin → Natural product
b) Sulfonamide → Synthetic chemical
c) Vitamin C → Natural product
d) Growth Hormone → Natural product
Question 2.
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond,glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against each of the following.
a) Polysaccharide 5
b) Protein
c) Fat
d) Water
Answer:
a) Polysaccharide → Glycosidic bond
b) Protein → Peptide bond
c) Fat → Ester bond
d) Water → Hydrogen bond [TS May-17]
![]()
Question 3.
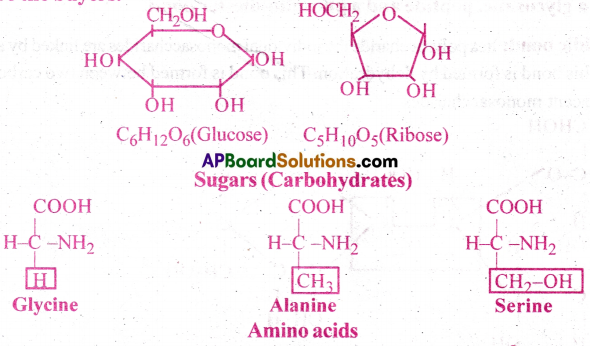
Give one example for each of amino acids, sugars, nucleotides and fatty acids.
Answer:
a) Amino acids Ex: Glycine [IPE Mar-13]
b) Sugars Ex: Glucose [AP May-19] [TS M-16]
c) Nucleotide Ex: Adenylic acid
d) Fatty acids Ex: Lecithin, Glycerol
Question 4.
Explain the Zwitterionic form of an amino acid. [IPE Mar-14]
Answer:
- The amino acid has both acidic (carboxyl fragment) and basic (amino fragment) groups.
- It carries both the positive and negative charges in equal number and exists as dipolar ion.
- Also, the net charge on it is zero. Hence amino acid takes the form of zwitter ion.
Question 5.
What constituents of DNA are linked by glycosidic bond? [AP M-15,17,19]
Answer:
- A Glycosidic bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides.
- Nitrogen base is linked to sugar group laterally by glycosidic bond.
Question 6.
Glycine and Alanine are different with respect to one substituent on the a-carbon.
What are the other common substituent groups? [TS M-19]
Answer:
Common substitutent groups on the a-carbon of Glycine and Alanine are:
Hydrogen, Carboxyl group and Amino group.
Question 7.
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Chitin are polysaccharides found among the following. Choose the one appropriate and write against each. [AP M-17,22] [TS M-15,20]
a) Cotton fibre
b) Exo skeleton of cockroach
c) Liver
d) Peeled Potato
Answer:
a) Cotton fibre – Cellulose
b) Exo skeleton of cockroach – Chitin
c) Liver – Glycogen
d) Peeled potato – Starch.
Question 8.
What are primary and secondary metabolites? Give examples.
Answer:
1) Primary metabolites: The metabolites which have identifiable functions and play known roles in normal physiological processes are called Primary metabolites.
Ex: Amino acids, Sugar.
2) Secondary metabolites: The metabolic products which do not have identifiable functions in the host organism are called secondary metabolites.
Ex: Rubber, drugs, spices, scents etc.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain briefly the metabolic basis for living?
Answer:
- Every living organism use and release energy during various processes.
- The energy is stored in the form of chemical bonds.
- When needed, this bond energy is used for biosynthetic, osmotic and mechanical work.
- The most important form of’energy currency’ in living system is ATP.
- Metabolism is the ‘sum total of chemical reactions’ taking place in cells of the living organisms.
- Metabolic pathways involve the extraction of energy by breaking molecules and using this energy to synthesize the building blocks.
- The metabolic pathway includes making and breaking up of molecules.
- Catabolism: The Breaking up of molecules is called catabolism.
The complex structure is broken down into simpler molecules with release of energy.
Ex: Respiration - Anabolism: The making up of molecules is called Anabolism.
Complex molecules are produced from simpler molecules with input of energy.
Ex: Aminoacids become proteins.
Question 2.
Is rubber a primary metabolite or a secondary metabolite. Write four sentences about rubber.
Answer:
- Metabolic products that do not have identifiable functions in host organism are called secondary metabolites.
- Rubber is a secondary metabolite.
- Rubber is produced from latex of Hevea and Ficus elastica.
- Uncured rubber is used as adhesive, insulation and friction tapes.
- Tyres of vehicles are made of vulcanized rubber.
- Other uses of rubber are manufacturing of belts, matting, flooring, medical gloves etc.
- Used rubber tyres are often recycled to make other items like shoes, bags, coats etc.
Question 3.
Schematically represent primary, secondary and tertiary structures of a hypothetical polymer using protein, as an example. [AP M-22]
Answer:
Primary Structure:
- Proteins are heteropolymers containing string of amino acids.
- Each amino acid has hydrogen, carboxyl group, amino group and a variable group.
- When the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (-NH2) group of next amino acid, peptide bonds are formed.
- Many amino acids are j oined by peptide bonds which held them together in a particular sequence and constitute the primary structure of proteins.
- This structure does not make a protein functional.
- It is the linear sequence of amino acids.
Secondary Structure:
- A protein is imagined as a line, the left end is represented by first amino acid and the right end the last amino acid.
- The first amino acid is also called as N- terminal amino acid.
- The last amino acid is called C- terminal amino acid.
- A protein thread does not exist as an extended rigid rod.
- The thread is folded in the form of helix.
- Thus a functional protein has 3-dimensional configuration.
- Secondary protein has a-helicles and (3-sheats held in place of amino acids.
Tertiary Structure:
- The long protein chain is folded like a hollow wooden ball.
- It gives rise to the tertiary structure. This gives us 3-dimensional view of a protein.
- Tertiary structure is absolutely necessary for the many biological activities of proteins.
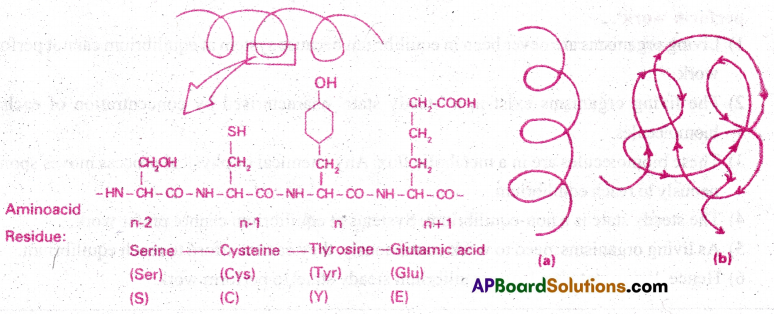
Primary structure of a portion of a hypothetical protein. N and C refer to the two termini of every protein.
a- A secondary structure and
b. A tertiary structure of proteins
![]()
Question 4.
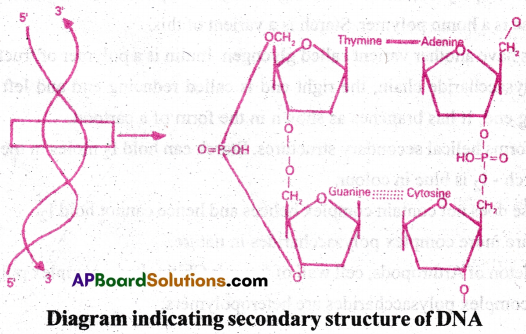
Nucleic acid exhibits secondary structure, justify with example. [TS M-15]
Answer:
- One of the secondary structures exhibited by DNA is of Watson-Crick Model.
- According to this model, DNA exists as double helix.
- The two polynucleotide strands are antiparallel that is run in opposite direction.
- The backbone is formed by the sugar-phosphate-sugar chain.
- N2- bases are projected -perpendicular to the backbone, but face inside.
- Adenine (A) and Guanine(G) of one strand pair with Thymine (T) and Cytosine(C) of other strand, respectively
- Two hydrogen bonds are present in between A and T. Three hydrogen bonds are present in between G and C.
- Each strand looks like a helical stairpase. Each step is represented by a pair of N2-bases.
- At each step of ascent, the strand turns 36°.
- Ten steps or ten base pairs are present in one full turn of the helix.
- The pitch would be 34A°. The distance between two successive base pairs would be 3.4A°.
- This form of DNA with above features is called b-DNA.
Question 5.
Comment on the statement, ‘living state is a non-equilibrium steady state, to be able to perform work’.
Answer:
- Living organisms are never been in equilibrium because system at equilibrium cannot perform work.
- The living organisms exist in a ‘steady state’ characterised by concentration of each of biomolecules.
- These biomolecules are in a metabolic flux. Any chemical or physical process moves sponta-neously to reach equilibrium.
- The steady state is a non-equilibrium. Systems at equilibrium cannot prefer work.
- As living organisms need to work continuously, they cannot afford to reach equilibrium.
- Hence living state is a ‘non- equilibrium steady state’ to perform work.
Question 6.
Dynamic state of body constituents is a more realistic concept than the fixed concentra¬tions of body constituents, at any point of time. Elaborate.
Answer:
- Living organisms like simple bacterial cell, a plant or an animal contain thousands of biomolecules.
- The biomolecules have certain concentrations.
- During metabolism breaking and making up of compounds involve conversion of biomolecules from one form to another.
- The metabolic pathways are either linear, circular or they may be criss-cross to each other.
- The metabolic pathway has definite rate and direction.
- The metabolic flow is called ‘dynamic state of body constituents’.
- As biochemical reactions continues all the time, the bio molecules have ‘varied concentrations’.
- Hence dynamic state of body constituents is a more realistic concept than the fixed concentra¬tion of body constituents at any point of time.
Question 7.
Write a brief account on polysaccharides.
Answer:
- Polysaccharides are long chains of sugars.
- They are threads containing different monosaccharides as building blocks.
- Cellulose is a polysaccharide consisting of only one type of monosaccharide ie., glucose.
- Cellulose is a homo polymer. Starch is a varient of this.
- Animals have another varient called glycogen. Inulin is a polymer of fructose.
- In a polysaccharide chain, the right end is called reducing end and left end is called non¬reducing end. It has branches as shown in the form of a cartoon.
- Starch forms helical secondary structures. Starch can hold I2 moles in the helical portion.
- The starch -I2 is blue in colour.
- Cellulose does not contain complex helices and hence cannot hold I2.
- There are more complex polysaccharides in nature.
- Exoskeleton of Arthropods, cell wall of fungi is Chitin. It is a complex polysaccharide.
- These complex polysaccharides are heteropolymers.
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are secondary metabolites? Enlist them indicating their usefulness to man.
Answer:
Metabolic products that do not have in the host organism are called secondary metabolites. They are Alkaloids, Flavinoids, Rubber, Essnetial oils, Antibiotics, Coloured pigments, Scents, Gums and Spices.
Alkaloids:
- Alkaloids from plants have been used as ingredients in portions (liquid medicine) and poisons.
- Ancient people used plant extracts containing alkaloids for treating a large number of ailments including snake bite, fever and insanity.
Flavinoids:
These are widely distributed group of polyphenolic compounds with health related properties which include anticancer, antiviral, anti inflamatory activities, effects on capillary fregility and can ability to inhibit human platelet aggregation.
Rubber:
- Uncured rubber is used for cements for adhesive, insulating and friction tapes. The flexibility of rubber is often used in hose, tires and rollers for a wide variety of devices.
- Its elasticity makes it suitable for variouis kinds of shock absorbers.
- It is impermeable to gases, it is useful in the manufacture of articles such as air hoses, balloons, bulls and cushions.
Essential oils:
- An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from plants.
- These are also known as volatile oils, etheral oils or aertherolea. These are used in aromatherapy.
Antibiotics:
- Antibiotics are defined as chemicals of natural organic origin that will kill certain harmful pathogens.
- They should not be toxic or have side effects to the host.
- An antibiotic is a substance that harms or destroys the bacteria that cause infection and disease. We take antibiotics to fight bacterial infections.
Spices:
- Asafoetida is a good remedy for whooping cough and stomach ache caused due to gas.
- Candamon(elachi) helps to control bad breath and digestive disorder.
Question 2.
What are the processes used to analyse elemental composition, organic constituents and inorganic constituents of living tissue? What are the inferences on the most abundant constituents of living tissue? Support the inferences with appropriate data.
Answer:
Analysing elemental composition, organic constituents and inorganic constituents of living tissues is done by chemical analysis.
I) Analyse Organic Compounds:
- Take any living tissue (a vegetable or a piece of liver) and grind it in tirchloro acetic acid (CH3 CCOOH) using a mortar and pestle.
- We obtain a thick slurry
- If we were to strain this through a cheese cloth or cotton, we would obtain two fractions. One is called filtrate or the acid-soluble tool and the second is the acid -insoluble fraction.
- Subject the extract to various separation techniques and separate an organic compound from the rest.
- Analytical techniques, when applied to the compound give us an idea of the molecular formula
and probable structure of the compound. - All the carbon compounds that we get from living tissues can be called ‘biomolecules’.
2) Analyse inorganic compounds:
- Weigh a small amount of a living tissue say a leaf or liver and this is called wet weight.
- Dry it. All the water evaporates. The remaining material gives dry weight.
- Fully bum the tissue, all carbon compounds are oxidised to gaseous form and are removed.
- The remaining is called ash. This ash contain inorganic materials like Ca, Mg etc.
- Inorganic compounds like sulphate, phosphate are also seen in acid-soluble fraction.
3) Elemental analysis:
- Elemental analysis gives elemental composition of living tissues in the form of hydrogen, carbon, oxygen and chlorine.
- Analysis of compounds gives an idea of the kind of organic and inorganic constituents present in living tissues.
![]()
Question 3.
Nucleic acids exhibit secondary structure. Describe through Watson-Crick model.
Answer:
- Nucleic acids exhibit a wide variety of secondary structures.
- One of the secondary structures exhibited by DNA is Watson and Crick model.
- According to this model, DNA exists as a double helix.
- The two strands are anti parallel i.e., run in opposite direction.
- The back bone is formed by the sugar- phosphate – sugar chain.
- The nitrogen bases are projected perpendicular to back bone but face inside.
- A and G of one strand base pairs with T and C respectively, on the other strand.
- Each strand appears like a helical stair case.
- Each step is represented by a pair of bases.
- Coiling occurs at an angle of 360°. At each step turn is 36°.
- One full turn of the helical strand involves 10 base pairs.
- The length of each turn is 34A°.
- The distance between two successive steps is 3.4 A°.
- This form of DNA with the above mentioned salient features is called B- DNA.
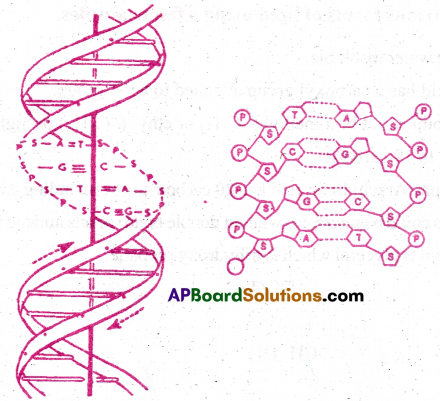
Watson and Cricks’ double helix model of DNA
P= Phosphate, S= Sugar, A=Adenine, T= Thymine, G= Guanine, C= Cytosine
Question 4.
What is the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside? Give two examples of each with their structure.
Nucleotide
- Nucleotide is made up of nitrogen base + Sugar + Phosphoric acid
- Nucleotide of RNA is called ribonucleotide.
- Nucleotide of DNA is called deoxy ribo nucleotide.
- Ex: Adenylic acid, Guanylic acid, cytidyolic acid, thymidylic acid, uridylic acid, AMP.
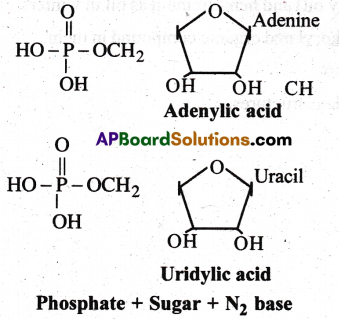
Nucleoside
- Nucleoside is made up of nitrogen base + sugar.
- Nucleoside of RNA is called ribonucleoside
- Nuceloside of DNA is called deoxy ribo nucleoside.
- Ex: Adenosine, Guanosine, Cytidine, Thymidine and Uridine.
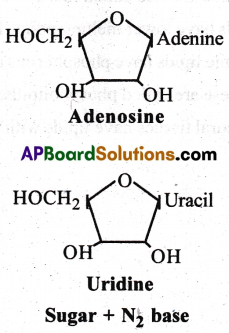
Question 5.
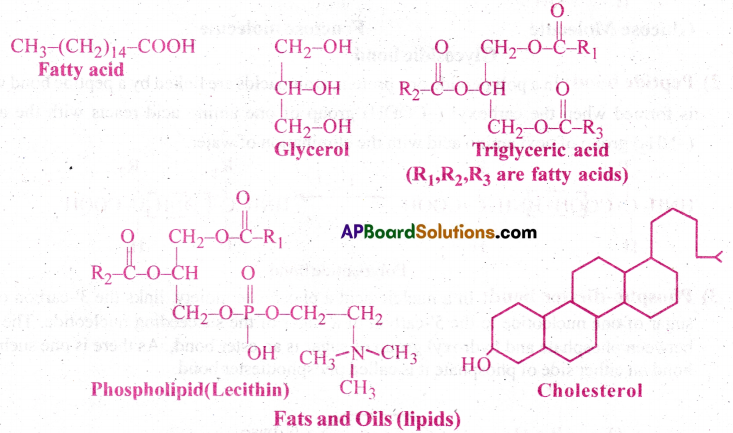
Describe various forms of lipid using a few examples.
Answer:
- Lipids are water insoluble.
- A fatty acid has a carboxyl group attached to an R-group.
- The R-group could be a methyl (-CH3) or ethyl (-C2H5) or higher number of -CH2 groups (1 carbon to 19 carbons)
- For example, Arachidonic acid has 20 carbon atoms including carboxyl carbon.
- Fatty acids could be saturated (without double bond) or unsaturated with one or more C=C bonds.
- Simple lipid is glycerol which is trihydroxy propane.

- Many lipids have both glycerol and fatty acids.
- Here fatty acids are found esterified with glycerol.
- They can be then called as monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides.
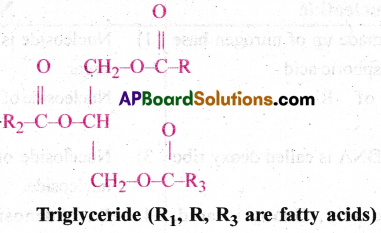
- These are also called fats and oils based on melting point.
- Oils have lower melting point (Ex: Gingerly oil) and hence remain as oil in winters.
- Some lipids have phosphorous and a phosphorylated organic compound in them. These are called phospholipids. Ex: Lecithin.
- Neural tissues have lipids with more complex structures.
![]()
Exercise
Question 1.
What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Answer:
Large size biomolecules having high molecular weight of above 800 dalton are called macro
molecules. They have lower solubility and complex molecular structure and occur in colloidal state. They are formed by the polymerisation of large number of micro molecules. They belong to four types of organic compounds, i.e., proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides and lipids.
Question 2.
Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho-d tester bond.
Answer:
1) Glycosidic bond: In a polysaccharide the individual monosaccharides are linked by a glycosidic bond. This bond is formed by dehydration. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides.
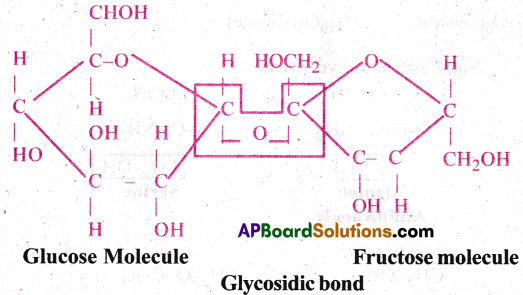
2) Peptide bond: In a polypeptide or a protein, aminoacids are linked by a peptide bond which is formed when the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (—NH2) group of next amino acid with the elimination of water.

3) Phospho-diester bond: In a nucleic acid a phosphate moiety, links the 3′-carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide to the 5′-carbon of a sugar of the succeeding nucleotide. The bond between phosphate and hydroxyl group of sugar is an ester bond,. As there is one such ester bond on either side of phosphate it is called phosphodiester bond.
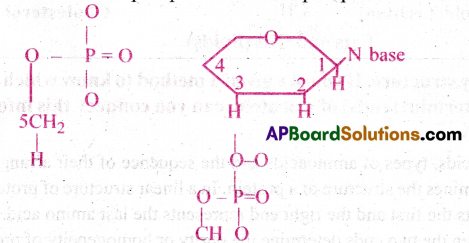
Question 3.
What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins?
Answer:
- Long protein chain of secondary structure is folded upon it self like a hollow wroolen ball, giving rise to the tertiary structure.
- ‘This gives us a 3-dimensional view of protein.
- Tertiary structure is necessary for many biological activities or proteins.
Question 4.
Find and write down structures of 10 interesting small molecular weight biomolecules.
Find if there is anTIndustry which manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers.
Answer:
Question 5.
Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein?
Answer:
The number of amino acids, types of aminoacids and the sequence of their arrangement in the polypeptide chain determines the structure of a protein. In a linear structure of protein chain, the left end of line represents the first and the right end represents the last amino acid. The number of amino acids in between the two ends determine the purity or homogeneity of proteins.
Question 6.
Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., Cosmetics etc.,)
Answer:
- List of proteins used as therapeutic agents -thrombin, fibrinogen, enkephalins, antigens, antibodies, streptokinase, protein tyrosine kinax, diastase, renin, insulin, oxytocin, vasopressin etc.
- Other applications are – Proteins also used as cosmetics, dairy industries, textile industries, research techniques etc.
Question 7.
Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Answer:
Fatty acids are found esterified with glycerol. They can be monoglycerids, diglycerids and triglyeerids. In a triglyceride single molecule of glycerol and 3 fatty acids are present. In a glycerol 3 carbon atoms are present along with 30n groups. Fatty acids consists of long chain hydrocarbon with a carboxyl group at the end. Both of them form ester bond. This bond is saturated when simple bonded carbons are present and unsaturated when double bonded carbon atoms are present.
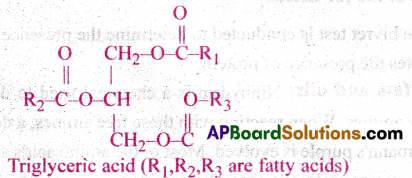
Question 8.
Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt, based on your understanding of proteins.
Answer:
Denaturation of protein occur during the conversion of milk into curd. During this process the configuration of protein is lost. In denaturation process, secondary, tertiary structure leads to the conversion of globular proteins into fibrous protein. This involves a change in physical, chemical and biological proportion of protein molecules.
![]()
Question 9.
Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models).
Answer:
Yes, models of bio molecules can be prepared. Atomic models are available in the market. Bell and stick models and space filling models are 3D models. They serve to display the structure of chemical products (or) bio molecular. In the ball stick model, the centres of atoms are connected by straight lines which represent covalent bond. Double and triple bonds are represented by spinner. The bond angles and bond lengths reflects actual relationships.
Question 10.
Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Answer:
By the titration curves one can understand the existence of different ionic forms of amino acids.
The number of dissociating functional groups is one in case of neutral and basic amino acids and two in case of acidic amino acids.
Question 11.
Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
Answer:

Question 12.
What are gums made of? Is Fevicol different?
Answer:
- Gums are secondary metabolics -made up of compounds present in plants, fungi and microbial cells.
- Yes, fevicol is different from gum. It is a synthetic resin made by polymerisation manufactured by esterification of organic compounds.
Question 13.
Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
Answer:
- Test for protein: The bivret test is conducted to determine the presence of peptide bonds.
A violet colour indicates the presence of protein. - Ninhydrin test for fats and oils: Ninhydrin is a chemical used to detect ammonia or primary and secondary amines. When reacting with these free amines, a deep blue or purple colour known as Ruhemann’s purple is evolved. Most of the amino acids are hydrolysed and reacted with ninhydrin except proline (a secondary amine)
- Solubility test for fats and oils: Fat dissolves in lighter fluid and not in water. In this test 5 drops of fat are added in 10 drops of lighter fluid in a test tube. It gets dissolved.
- Fruit, juice: Fruit juice contains sugar. So it cannot be tested for proteins and amino acids.
- Saliva test: It contain proteins, minerals and amylase. So it can be tested for proteins and amino acids.
- Sweat test: It contains salts and sodium chloride.
- Urine test: It contains proteins. So it can be tested for protein.
Question 14.
Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much of paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man annually. What a loss of vegetation?
Answer:
- Nearly 100 billion tonnes of cellulose is prepared and used in manufacture of paper every year. Increase in industrialization increased the use of paper.
- Because of this reason vegetation is lost to a great extent.
Question 15.
All life forms exhibit ‘unity in diversity’-Give reasons.
Answer:
- Wide diversity is seen in all living forms. But their chemical composition and metabolic activities appear to be similar. The most abundant chemical in all living forms is water.
- All living forms contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen an inanimate matter.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
ATP
1) nucleotide
2) nucleoside
3) nucleic acid
4) vitamin
Answer:
1) nucleotide
Question 2.
Biomolecules are
1) Inorganic compounds
2) Organic compounds
3) carbon compounds obtained from living tissue
4) only DNA and RNA
Answer:
3) carbon compounds obtained from living tissue
Question 3.
Trihydroxy propane is
1) Palmitic acid
2) Arachidonic acid
3) Glycerol
4) Glycine
Answer:
3) Glycerol
Question 4.
Primary structure of protein is formed by
1. Phospodiester bonds
2. Peptide bonds
3. Glycosidic bonds
4. Hydrogen bonds
Answer:
2. Peptide bonds
Question 5.
Secondary structure of protein is
1. α-helix
2. β-helix
3. γ-helix
4. Triple helix
Answer:
1. α-helix
Question 6.
Most abundant protein found in the human body is
1. Haemoglobin
2. Immunoglobin
3. Keratin
4. Collagen
Answer:
4. Collagen
![]()
Question 7.
The polymers of amino acids are
1. Nucleic acids
2. Proteins
3. Lipids
4. Polysaccharides
Answer:
2. Proteins
Question 8.
The polymers of proteins are
1. Nitrogen bases
2. Nucleotides
3. Aminoacids
4. Heterocyclic organic acids
Answer:
3. Aminoacids
Question 9.
Protein that acts as hormone is
1. Glut-4
2. Insulin
3. RUBrsco
4. Trypsin
Answer:
2. Insulin
Question 10.
Which of the following is normally not a function of proteins
1. Structural integrity of the cell
2. Regulation of metabolism
3. Defense mechanism
4. Hydrolysis of energy provision
Answer:
4. Hydrolysis of energy provision
Question 11.
The simplest and least carbon containing amino acid is
1. Glycine
2. Serine
3. Lysine
4. Alanine
Answer:
1. Glycine
Question 12.
The molecular formula of Glycine is
1. C2H5O2N
2. C3H7O2N
3. C3H7O2N
4. C5H10O5N
Answer:
1. C2H5O2N
Question 13.
Identify the mismatch from the following
1. Chitin-Heteropolymer
2. Cellulose-Does not hold I2
3. Inulin-Polymer of glucose
4. Insulin-polymer of amino acids
Answer:
3. Inulin-Polymer of glucose
Question 14.
Which of the following biomolecuies are not heteropoiymers?
1. Protein
2. Chitin
3. Cellulose
4. Nucleic acid
Answer:
3. Cellulose
Question 15.
Proteins that have more than one polypeptide chains are said to be in
1. Secondary structure
2. Primary structure
3. Tertiary structure
4. Quatemary structure
Answer:
4. Quatemary structure
Question 16.
Fatty acids without double bonds between carbon atoms are called
1. Saturated fatty acids
2. Unsaturated fatty acids
3. Adenylic acid
4. Glycerides
Answer:
1. Saturated fatty acids
Question 17.
Lipids which are in liquid state at room temperature are called
1. Oils
2. Fats
3. Esterified solution
4. Glycolipids
Answer:
1. Oils
Question 18.
The building block of nucleic acids are
1. Nucleosides
2. Nucleotides
3. Nitrogen bases
4. Monosaccharide sugar and phosphate
Answer:
2. Nucleotides
Question 19.
The types of monosaccharide sugars found in nucleic acids are
1. 3
2. 4
3. 2
4. 5
Answer:
3. 2
![]()
Question 20.
Abrin and Ricins are
1 .Toxic secondary metabolites
2. Lectin type secondary metabolites
3. Terpenoid secondary metabolites
4. Alkaloid secondary metabolites
Answer:
1 .Toxic secondary metabolites
Question 21.
The secondary metabolites used as drugs are
1. Abrin, Ricin
2. Rubber, gums, cellulose
3. Morphine, codeine
4. Vinblastin, curcumin
Answer:
4. Vinblastin, curcumin
Question 22.
The monomers repeating V number of times are called
1. Homopolymers
2. Heteropolymers
3. Low molecular weight heteromers
4. High molecular weight heteromers
Answer:
1. Homopolymers
Question 23.
The polymer units in nucleic acids are
1. Nucleosides
2. Nucleotides
3. Nitrogen bases
4. Monosaccharides
Answer:
2. Nucleotides
Question 24.
The length of pitch of each coil of DNA is
1) 3.4 A
2) 0.34 A
3) 34 A
4) 2.0nm
Answer:
3) 34 A
Question 25.
The most important form of energy currency in a living system is
1. GTP
2. ATP
3. TPP
4.UTP
Answer:
2. ATP
Question 26.
Amines are formed by
1. Removal of amino group in a nucleotide base
2. Removal of carboxyl group form amino acids
3. Removal of CO2 from amino acids
4. Hydrolysis of glycosidic bond in a disaccharide
Answer:
3. Removal of CO2 from amino acids
Question 27.
Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
1. Gluconic acid
2. Galactose
3. 3methylgalactoside
4. Sucrose
Answer:
2. Galactose
Question 28.
The four elements that make up 99% of all elements found in a living system are
1) C, H,Q and P
2) C, H, O and S
3) C, H, O and N
4) C, N, O and P
Answer:
3) C, H, O and N
Question 29.
The percentage of abundant chemical present in the living organism is
1) 95-9.8%
2) 70-90%
3) 80 – 85 %
4) 60-90%
Answer:
2) 70-90%
![]()
Question 30.
Which of the following is incorrect.
1) Glycerol is trihydroxy propane
2) Palmitic acid has 16 carbons including carboxyl carbon
3) Arachidonic acid has 20 carbons including the carboxyl carbon
4) Lipids are generally water soluble.
Answer:
4) Lipids are generally water soluble.
Question 31.
The aromatic aminoacid, Acidic aminoacid and aminoacid with methyl as R group respectively are
1) Alanine, Glutamic acid Tyrosine
2) Tryptophan, Glutamic acid and Alanine
3) Phenyl alanine, Alanine and valine
4) Glycine, lysine and Alanine
Answer:
2) Tryptophan, Glutamic acid and Alanine
Question 32.
Which one of the following fats contains unsaturated fatty acids?
1) Ghee
2) Curd
3) Gingelyoil
4) Fish oil
Answer:
3) Gingelyoil
Question 33.
Most abundant enzyme of biosphere is located in
1) Starch factory
2) Protein factory
3) ATP factory
4) Ribosome factory
Answer:
1) Starch factory
Question 34.
An alkaloid is
1) Collagen
2) Algin
3) Carragen
4) Codeine
Answer:
4) Codeine
Question 35.
A segment of DNA has 120 adenine and 120 cytosine bases. The total number of nucleotides present in the segment is
1) 480
2) 240
3) 120
4) 60
Answer:
1) 480
Question 36.
The Compounds found in the acid soluble pool of molecular weight ranging from
1) 180 to 800 (Da)
2) 800 to 180(Da)
3) 18 to 800 (Da)
4) more than 800 (Da)
Answer:
3) 18 to 800 (Da)
Question 37.
Identify a set in the given list in which all are polymeric secondary metabolites
1) Protein, Nucleic acid, Rubber
2) Rubber, Lipid, Cellulose
3) Cellulose, Gum, Rubber
4) Nucleic acid, Protein, Polysaccharide
Answer:
3) Cellulose, Gum, Rubber
Question 38.
Mark the true matching
1) Trichloro acetic acid – Amino acid
2) Glutamic acid – Fatty acid
3) Arachidonic acid – Resin
4) Uredylic acid – Nucleotide
Answer:
4) Uredylic acid – Nucleotide
Question 39.
………… is not an enzyme
1) RUBISCO
2) Insulin
3) Trypsin
4) Pepsin
Answer:
2) Insulin
Question 40.
Non polymeric substances present in retentate
1) Proteins
2) Nucleic acids
3) Lipids
4) All the above
Answer:
3) Lipids
![]()
Question 41.
Most complex lipids are found in
1) Muscles
2) Neural tissues
3) Adipose tissue
4) Membranes
Answer:
2) Neural tissues
Question 42.
An essential oil is
1) Lemon grass oil
2) Gingelly oil
3) Turpentine oil
4) Palm oil
Answer:
1) Lemon grass oil
Question 43.
Select the correct statement
1) All molecules in organisms are biomolecules
2) All biomolecules are heteropolymers
3) All biomolecules are hemopolymers
4) Organelles are present in retentate
Answer:
4) Organelles are present in retentate
Question 44.
Which are united by phosphodiester bonds?
1) Nitrogen bases of RNA
2) Nucleotides of DNA
3) Monosaccharides of glycogen
4) Fatty acids and glycerol
Answer:
2) Nucleotides of DNA
Question 45.
In metabolic pathways
1) Only complex structures are formed
2) Metabolites are converted into each other through a series of linked reactions
3) Only simple structures are formed
4) The biochemical reactions are catalyzed by inorganic catalyst
Answer:
2) Metabolites are converted into each other through a series of linked reactions
Question 46.
Read the following statements and find out the incorrect statement
1) Oils have lower melting point (e.g. gingely oil) and hence remain as oil in winters
2) Adenosine, guanosine, cytosine, uridine and thymidine are nucleosides
3) Adenylic acid, thymidylic acid, guanylic acid, uridylic acid and cytidylic acid are nucleotides
4) Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA consists of nucleosides only
Answer:
4) Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA consists of nucleosides only
Question 47.
Aromatic amino acids are
a) Glycine
b) Tyrosine
c) Tryptophan
d) Phenyl alanine
1) a & b only
2) c & d only
3) b & c only
4) b, c & d
Answer:
4) b, c & d
Question 48.
Lecithin is
a) Phospholipid
c) The component of cell membrane
b) Phosphorylated organic compound
d) Polysaccharide
1) a and b only
2) b and c only
3) a, b and c only
4) All of the above
Answer:
3) a, b and c only
![]()
Question 49.
Assertion (A): The amino acids which possess both +ve and -ve charges to their R groups are called Zwitter ionic forms.
Reason (R): The particular property of a particular amino acid depends on the ionizable nature of amino group and carboxyl group.
1) Both A & R are true & R is the correct explanation of A
2) Both A & R are true & R is not the correct explanation of A
3) A is true but R is false
4) A is false but R is true
Answer:
1) Both A & R are true & R is the correct explanation of A