Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper May 2017 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper May 2017 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Note: Answer any two questions not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What are the differences between the Money Market and Capital Market?
Answer:
Introduction:
Money Market: The center for dealing mainly of a short-term character, in monetary assets, it meets the short-term requirements of funds.
Capital Market: It is the market where long-term finance is provided to business firms through the sale of securities.
Differences:
| Concept | Money Market | Capital Market |
| 1. Nature | It deals with short-term credit instruments not exceeding one year. | It deals with long-term finance for more than one year. |
| 2. Components | The major players are Commercial Banks, RBI, LIC, GIC, UTI, etc. | The major players are merchant financial institutions, foreign investors, and individuals. |
| 3. Dealing Formation | It deals with credit instruments like Treasury bills, Commercial papers, Call money, etc. | It deals with shares, debentures, bonds, and Government securities. |
Question 2.
Define Banking and explain the functions of Banking.
Answer:
Bank is derived from the French word “Banco” which means a Bench. It is believed that the early bankers, the Jews of Lombardy transacted their business on benches in the marketplace.
Definition: “Banking is defined as accepting for lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft, order of otherwise”. – Banking Regulation Act 1949 – Section 5 (1) (b)
Functions of Banks:
The core functions of a bank are
- Acceptance of money deposits from the public.
- Lending (or) making advances to the public.
- Undertaking Agency Services.
- Rendering General Utility Services.
1. Acceptance of Deposits:
Banks accept money from the public in various forms which constitute borrowings by banks. The deposits are one of the main sources of funds for the banks.
2. Lending (or) Making Advances to the Public:
Banks lending the deposit amounts. It is a profit motive. The bank will not lend the whole of the deposits it keeps a certain amount to meet contingencies and the remaining portion is lent to the business community at a higher rate of interest. The difference between the rate of interest allowed and deposits and the rate charged on the loans is called spread’, it is the main source of income for a bank. An advance is a credit facility provided by a bank to its customers. It is generated for shorter periods. Further, the purpose behind granting an advance is to meet the day-to-day requirements of a business.
3. Agency Functions of Services:
Banks perform these functions for their customers. These are
- To collect or pay bills, cheques, interest, dividends, rent, etc., on behalf of customers. For rendering these services, banks collect charges from their customers.
- To act as executor, trustee, and attorney on the customer’s will.
- To work as a correspondent, agent, or representative of their clients.
4. General Utility Services:
These services are provided to the general public. These are
- A letter of credit may be issued by the bank at the request of the importer to the exporter.
- Bank drafts and traveler’s cheques are issued to provide facilities for fund transfer from one part of the country to another part.
- Acceptance or collection of foreign bills of exchange.
- Banks arrange safe deposit lockers for the safe custody of customers’ securities, valuables, and jewelry.
- Other general public utility services.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the Principles of Management?
Answer:
Generally, management has been defined as “getting things done through others”.
Definitions:
Management is a multipurpose organ that manages a business and manages managers and manages workers and work. – Peter F. Drucker.
Management is the art of knowing what you want to do and then seeing that it is done in the best and cheapest way”. – F.W. Taylor.
To manage is to forecast and to plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control”. – Henry Fayol.
It has been observed that management is used as a collective noun to refer to all those who manage within a particular organization including those who help line managers by performing a staff function. ‘Henry Fayol’ has been rightly called the “Father of administrative management” for his practical approach to management theory. He has identified 14 fundamental principles of management. Those are:
- Division of labour and specialization
- Priority of authority and responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of command
- Unity of direction
- Subordination of individual to general interest
- Remuneration of personnel
- Centralization
- Scalar chain
- Order
- Equity
- Stability of tenure of personnel
- Initiative
- Esperit-de-corps
1. Division of Labour and Specialisation:
Division of labour leads to specialization which increases the efficiency of individual employees. Division of labour is a famous principle of economics. Fayol applied this principle to management. He recommended work of all kinds must be subdivided and allocated to several persons. Subdivision makes each task simpler and results in greater efficiency.
2. Priority of Authority and Responsibility:
According to Fayol, authority and responsibility must flow in the same direction. Responsibility is the natural outcome of authority. A proper balance between authority and responsibility helps to prevent the misuse of authority and promotes a fair fixation of responsibility.
3. Discipline:
Discipline means the observation of certain rules and regulations. People in the organization should be bound to accept certain codes of conduct. The three basic requisites of discipline are disciplined supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreement on goals, and judicious application of penalties.
4. Unity of Command:
The principle states that a subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to only the superior. No employee, therefore, should receive instructions from more than one person. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict.
5. Unity of Direction:
Unity of direction is essential for achieving unity in action, in the pursuit of common goals by a group of persons, (one head, one plan) is not the same as unity of command (one employee receives orders from one superior).
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest:
According to this principle, the fulfillment of individual objectives, in the long run, is contingent upon the attainment of common objectives is contingent upon the attainment of common objectives in the short run. Thus, in case the need arises, an individual must sacrifice in favor of larger group objectives.
7. Remuneration of Personnel:
Remuneration is the price paid to the personnel for the services rendered by them. According to Fayol, the system of remuneration personnel should be fair and satisfactory to both the employees and the employer. It should be attractive to employ and retain the best personnel.
8. Centralization:
It refers to the extent to which authority is concentrated or dispersed. The appropriate degree of centralization will vary with different concerns. It is a problem of finding the measure that will give the best overall yield. Under centralization managers or executives play an important role.
9. Scalar Chain:
It refers to the line of authority from the highest to the lowest executive for communication. However, in the routine course of business, employees at the same level can communicate with each other following the principle of ‘Gangplank’.
10. Order:
Fayol has classified order into two categories.
- Material Order: Material order is described as a place for everything and everything in its place.
- Social Order: Social order demands the employment of a “right man in the right place”.
11. Equity:
Equity is a combination of kindliness and justice. It seeks to elicit loyalty and devotion from personnel. Managers should show kindness and justice in dealing with their subordinates.
12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel:
High turnover increases inefficiency. An employee needs time to adjust to the new work, and its environment and demonstrate efficiency. Therefore, stability of tenure is a desirable principle for ensuring efficiency. Unnecessary employee turnover is the cause and effect of bad management.
13. Initiative:
The initiative is the freedom to propose and execute a plan. To have freedom in this respect is the greatest satisfaction for an intelligent person. A manager, who induces his subordinates to think and act on their own, is always better and more successful than the one who does not.
14. Esperit-de-corps:
It is a French phrase which means “Union is Strength.” It means the union is strength. There should be loyalty and concern for the honor of the organization to which one belongs. This can be achieved through the adoption of the principle of unity of command.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Note: Answer any FOUR questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Bulls and Bears?
Answer:
Bull:
A Bull or Tejawalla is an operator who expects a rise in the prices of securities in the future. In anticipation of a price rise, he makes purchases of shares and debentures to sell at higher prices in the future. He being a speculator has no intention of taking delivery of securities but deals only in difference of prices. Such a speculator is called ‘Bull’ because of the resemblance of his behavior with the bull. A bull tends to throw his victims up in the air. Similarly, a bull speculator tries to raise the prices of securities by placing big purchase orders.
Bears:
Bear or Mandiwala speculators expect prices to fall in the future and sell securities at present to purchase them at lower prices in the future. A bear does not have securities at present but sells them at higher prices in anticipation that he will supply them by purchasing at present but sells them at higher prices in anticipation that he will supply them by purchasing at lower prices in the future. If the prices move down as per the expectations of the bear, he will earn profits out of these transactions. A bear does not take the delivery of securities but takes the difference if prices fall. In case the prices do not fall as expected by the bears then they may start speculator rumors to pressurize prices downwards, it is known as ‘bear said’.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the differences between Goods and Services.
Answer:
Goods are objects of value over which ownerships are established or exchanged. Ownership of goods can be transferred and can be transmitted. Goods are often made in factories, workshops, etc, and stored till they are exchanged for money or other commodities. The important characteristics of goods are the outcome of repetitive processes, durable, tangible, movable, and transferable.
Differences between Goods and Services:
| Goods | Services |
| 1. It is a physical commodity. | 1. It is a process or an activity. |
| 2. It is tangible. | 2. It is intangible. |
| 3. It is homogenous. | 3. It is heterogeneous. |
| 4. Transfer of ownership is possible. | 4. Transfer of ownership is not possible. |
| 5. Goods are consumable. | 5. Services are usable. |
| 6. Production and Distribution are separate from their consumption. Goods can be stored. | 6. It cannot be stored. |
Question 6.
Explain the functions of Entrepreneurs.
Answer:
The functions of Entrepreneur are:
1. Innovation:
Innovation is also different from invention. Invention implies the discovery of new ideas, new articles, and new methods, whereas innovation means the application of inventions and discoveries to make new and desired products and services that can be successfully sold in the market.
2. Risk Bearing:
Entrepreneurs in the game of business where risks and rewards are plenty will be ready to accept them.
3. Organisation and Management:
As rightly said by Alfred Marshall organization and management of the enterprise is the main function of an entrepreneur. He makes required alternations in the size of the business, its location, techniques of production, etc. The entrepreneur also undertakes managerial functions like formulation of production plans, organization of sales, and personnel management.
4. Business Planning:
The entrepreneur must provide logical and scientific basics for planning the business operations, the need for raw materials and men, production schedules, etc. For systematic business planning, the entrepreneur must be able to formulate goals, policies, procedures, programs, and budgets.
5. Decision Making:
Another important function discharged by the entrepreneur is decision-making. He has to make decisions regarding the activities of the enterprise.
Question 7.
Explain the special provisions enacted by the Telangana state for the MSMEs.
Answer:
The special provisions for the micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are as follows:
- An adequate number of smaller plots in industrial parks for SMEs and developed sheds.
- Special funds for addressing incipient sickness.
- Special fund for IP registration assistance.
- Special fund for anti-pirating assistance.
- Special fund for technology transfer and modernization of the MSME sector.
- Reimbursement of land conversion charges for units in own land.
- Marketing assistance to participate in national.
- Consultant panel to respond to MSME entrepreneur needs.
- Separate state-level bankers committee for industries.
Question 8.
List out the advantages of SEZs.
Answer:
The following are the major benefits of SEZs.
- Employment generation: SEZs are viewed as highly effective tools for job creation.
- Economic development: SEZs are viewed as the engines for economic development.
- Growth of labor-intensive manufacturing industry: The establishment of SEZs would lead to feist growth of labor-intensive manufacturing and service industries in the country.
- Balanced regional development: SEZs are beautifully crafted initiatives for achieving balanced regional development.
- Capacity building: SEZs are important for stronger capacity building.
Question 9.
Explain the principles of Directing.
Answer:
The principles are explained below.
- Maximum individual contribution: This principle emphasizes that directing techniques must help every individual in the organization to contribute to his maximum potential for achievement of organizational objectives.
- Harmony of Objectives: Good directing provides harmony by convincing that employee rewards and work efficiency are complementary to each other.
- Appropriateness of Direction Technique: According to these people, appropriate motivational and leadership techniques should be used while directing the people based on the needs of subordinates’ capabilities, attitudes, and other situational variables.
- Unity of Command: This principle insists that a person in the organization should receive instructions from one superior only.
- Managerial Communication: Effective managerial communication across all the levels in the organization makes direction effective. Directing should convey clear instructions to create toted understanding subordinates.
- Use of Informed Organization: A manager should realize that informal groups of organization exist within every formal organization.
- Leadership: Managers should exercise good leadership as it influences the subordinates positively while directing the subordinates without causing dissatisfaction among them.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any five questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What is a Lame duck?
Answer:
He is a speculator when the expectations of Bear do not come true and the price of security does not fall, he cannot fulfill his commitment, and he is said to be a lame duck.
Question 11.
Define Endowment Policy.
Answer:
It runs only for a limited period or upto a particular age. The policy money becomes due at the end of the period specified in the policy. In case, however, the assured dies before the specified time the policy money is paid at the time of death.
![]()
Question 12.
Define Entrepreneurs.
Answer:
He is an economic agent who unites all means of production, labour, capital, and land and who finds the value of products that result from their employment.
Question 13.
What are Bridge Loans?
Answer:
It is a short-term loan that enables the entrepreneur to continue with the implementation of the project till the term loan is applied and obtained.
Question 14.
What is a Letter of Credit?
Answer:
It is a letter that is obtained by an exporter to satisfy himself about the creditworthiness of an importer.
Question 15.
What is the exchange rate?
Answer:
The rate at which the currency of one country is exchanged for the currency of another country is known as the exchange rate.
Question 16.
What is meant by Internal Trade?
Answer:
Internal trade: Internal trade is conducted within the political and geographical boundaries of a particular country. It can take place at the local regional or national level.
Question 17.
Define Staffing.
Answer:
It is the management process concerned with obtaining, utilizing, and maintaining a satisfactory and satisfactory work.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Note: Answer the following question.
Question 18.
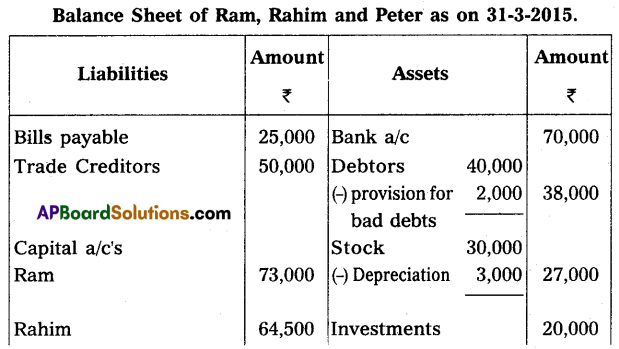
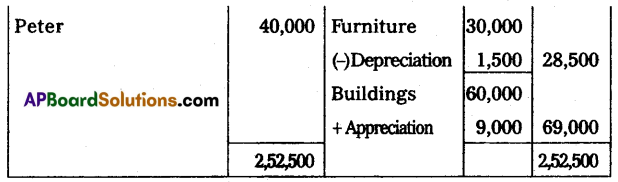
The following is the balance sheet of Ram and Rahim who are sharing profit/loss in the ratio of 2 : 3. Their balance sheet as of 31st March 2015:
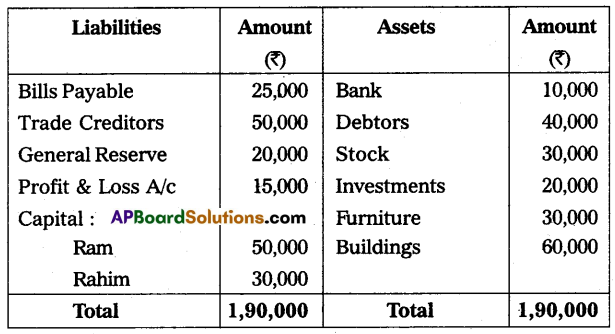
On 1st April 2015, they agreed to admit Mr. Peter as a new partner for 1/5th share in profits on the following terms:
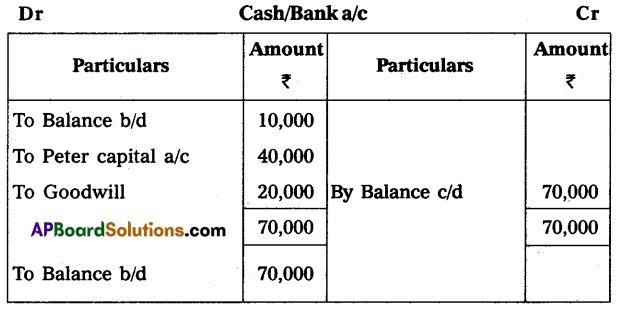
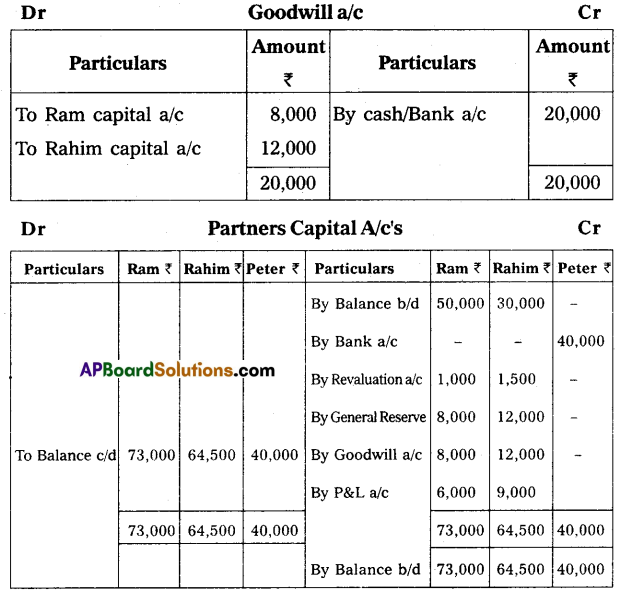
(a) Peter should bring ₹ 40,000 for capital and ₹ 20,000 for goodwill in cash.
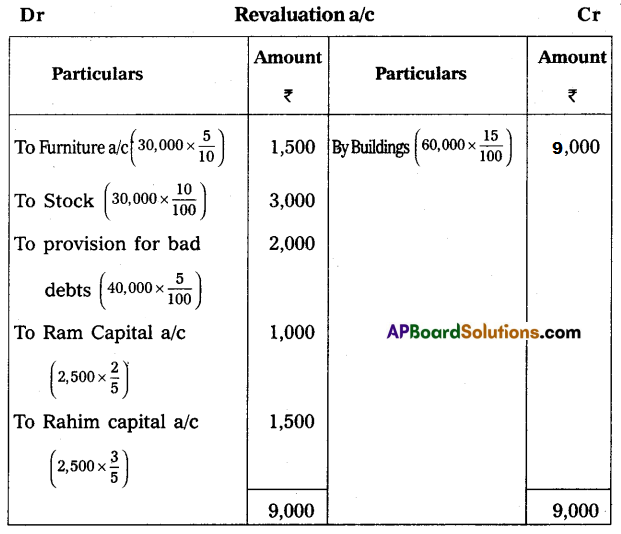
(b) Depreciation on furniture by 5% and stock by 10%.
(c) Appreciate building value by 15%.
(d) Provide for bad debts at 5% on debtors.
Give necessary ledger accounts and open the balance sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Note: Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
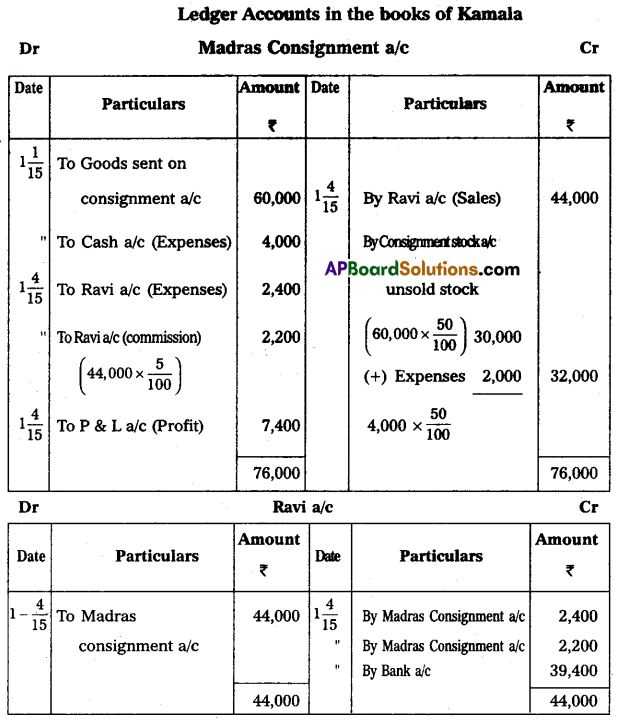
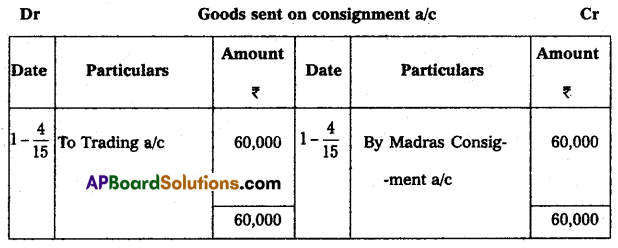
On 1-1-2015, Kamala of Hyderabad consigned goods valued at ₹ 60,000 to Ravi of Madras. Kamala paid cartage and other expenses ₹ 4,000. On 1-4-2015, Ravi sent the account sales with the following information:
(a) 50% of the goods sold for ₹ 44,000.
(b) Ravi incurred expenses amounting to ₹ 2,400.
(c) Ravi is entitled to commission @ 5% on sales. A bank draft was enclosed for the balance. Prepare the necessary Ledger Accounts in the Books of Kamala.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
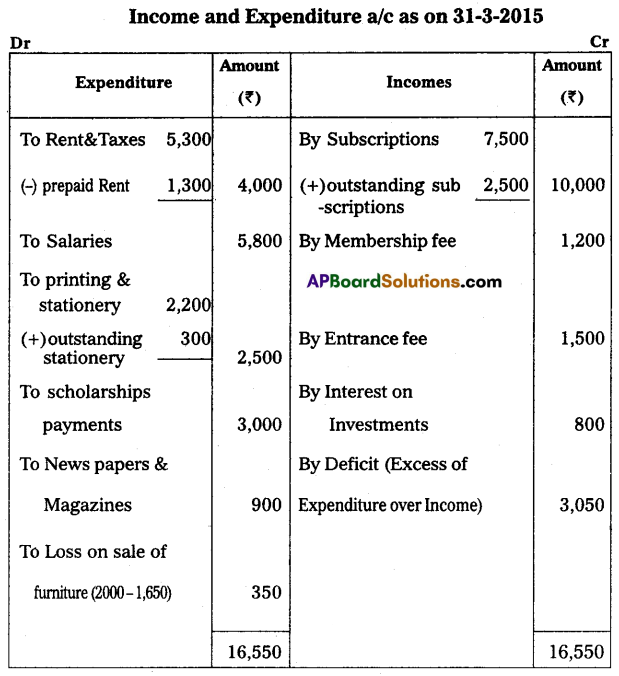
From the following Receipts and Payments Account, prepare the Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March 2015:
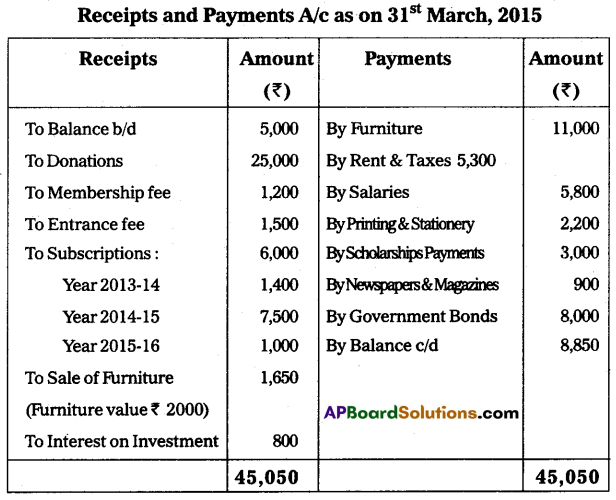
Other Information:
1. Outstanding subscriptions for the year 2014-15 ₹ 2,500.
2. Prepaid Rent ₹ 1,300.
3. Outstanding stationery bill ₹ 300.
4. Capitalize the Donations.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Note: Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
What are the differences between consignment and sales?
Answer:
| Point of Difference | Consignment | Sale |
| 1. Parties | There are two parties here consignor and consignee. | There are two parties here: Seller and Buyer. |
| 2. Ownership of Goods | The ownership of the goods does not transfer from consignor to consignee. | The ownership of the goods is transferred from the seller to the buyer. |
| 3. Relationship | The relationship between the consignor and the consignee is the principal and agent. | In case of credit sale the relationship. |
| 4. Account Sales | The consignee sends the account sales to the consignor. | The buyer need not send the account sales to the seller. |
| 5. Return of Goods | The consignee can return the unsold stock to the consignor. | The buyer cannot return the goods to the seller. |
| 6. Risk of Loss of Goods | In case the goods are destroyed, the consignor has to bear the loss. | In case the goods are destroyed after the sale, the buyer has to bear the loss. |
| 7. Profit/Loss | The profit/loss belongs to the consignor. | The profit or loss on sales belongs to the seller. |
| 8. Order/Indent | There is no order from the consignee. | There must be an order from the buyer to the seller. |
Question 22.
Ganesh bought a machine for ₹ 17,000 and paid for its installation charges ₹ 3,000 on 30th Sep. 2011. Depreciation is provided at 10% under the straight-line method. His accounts were closed every year on 31st March. Prepare Machine A/c. upto 31st March 2015.
Answer:
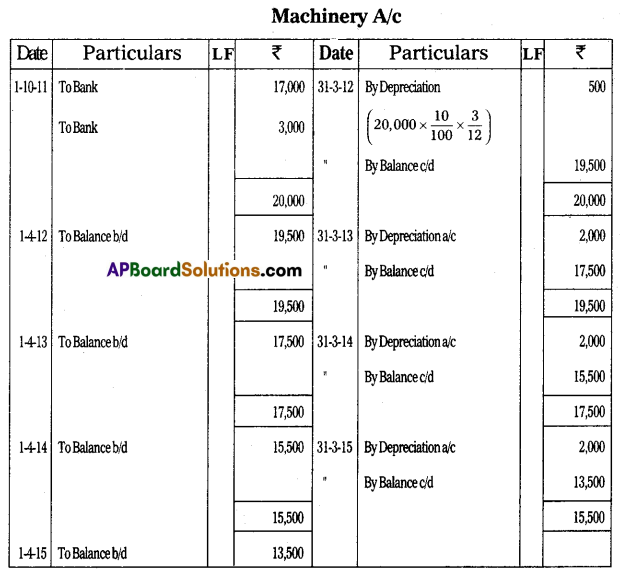
Question 23.
Rama keeps his books under a single entry system. From the given information find out his Profit/Loss.
Capital as on 1st April 2014 – ₹ 1,25,000
Capital as on 31st March 2015 – ₹ 1,70,000
He introduced further capital ₹ 15,000 and his drawings during the year are ₹ 20,000.
Answer:
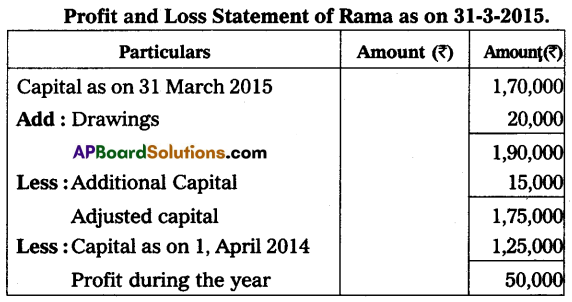
Question 24.
Explain any five advantages of Computerised Accounting.
Answer:
The following are some of the advantages of using computerized accounting:
- Automation: Since all the calculations are handled by the software, computerized accounting eliminates many of the routines.
- Accuracy: This accounting system is designed to be accurate to the minute detail.
- Data Access: Using accounting software, it becomes much easier for different individuals to access accounting data outside of the office securely.
- Reliability: Because of the accurate calculations, the financial statements prepared by computers are highly reliable.
- Speed: Using accounting software, the entire process of preparing an account becomes faster.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Note: Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines.
Question 25.
Define Depletion.
Answer:
It refers to the physical deterioration by the exhaustion of natural resources.
Question 26.
What is account sales?
Answer:
Account sales is a statement that shows the net result of a purchase or sale transaction made by one person on another’s behalf, including commission and other charges.
Question 27.
What is a Subscription?
Answer:
It is an amount paid by the members regularly at periodical intervals. Subscriptions are a regular source of income for the organization.
Question 28.
Define Recon Xpert.
Answer:
Recon Xpert is a rule-based financial and investment transaction reconciliation tool.
Question 29.
Define Single Entry System.
Answer:
- Single entry is a simple method of recording business transactions.
- Profit or loss can be easily ascertained by comparing the opening capital with the closing capital.
- For keeping records in a single entry one does not require expert knowledge.
- It is less expensive when compared to the double-entry system of bookkeeping.
- It is easy to follow and understand.
- No principles are required in this system.
Question 30.
What is spreadsheets?
Answer:
A spreadsheet is an interactive computer application program. It helps the organization for analysis and storage of data in tabular form. It is a table of values arranged in rows and columns. Each value can have a pre-defined relationship to the other values.
![]()
Question 31.
X and Y are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2, they decided to admit, Mr. Z for 1/5 share in profit. Calculate the new profit-sharing ratio of X, Y, and Z.
Answer:
Old Ratio of X & Y = 3 : 2
‘Z’ New Share = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Remaining Profit = 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
New profit sharing ratio of X = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{12}{25}\)
New profit sharing ratio of Y = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{2}{5}=\frac{8}{25}\)
New profit sharing ratio of Z = \(\frac{1}{5} \times \frac{5}{5}=\frac{5}{25}\)
New ratio of X, Y & Z = \(\frac{12}{25}\) : \(\frac{8}{25}\) : \(\frac{5}{25}\) (or) 12 : 8 : 5
Question 32.
What is goodwill?
Answer:
Goodwill is the reputation or good name associated with the name of a firm. Firms that have goodwill will enjoy continuous patronage of customers.