Thoroughly analyzing TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2017 helps students identify their strengths and weaknesses.
TS Inter 2nd Year Commerce Question Paper March 2017 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
What do you understand by e-banking? Explain the various types of e-banking.
Answer:
The concept of e-banking enables a customer to transact with his/her bank from anywhere such as from home, office, or from any place and time that would be convenient to him/her. We may transact beyond the bank’s working hours, e-banking is a system of banking that is carried out with the use of electronic tools and facilitated through electronic delivery channels. Most banks offer e-banking through ATMs (Automatic Teller Machine), telephonic transactions, etc. Electronic banking provides efficient services at low costs and without any geographical barriers.
Types or Kinds of Services Under e-banking:
- Automatic Teller Machine (ATM)
- Anywhere Banking
1. Automatic Teller Machine (ATM):
ATM is one of the methods of electronic fund transfer. It has removed the time limitations of customer services. ATM is an unattended or unmanned device usually located on or off the bank premises. The operation mechanism begins when the card is inserted into the ATM, the terminal reads and transmits the tape data to the processor, which activates the account. It works for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week (24 × 7). ATMs were used only for withdrawal, electronic transfer of funds, etc. But now they are used for recharging cell phones, bill payments, etc.
2. Anywhere Banking:
With the introduction of ATMs and tele banking financial details can be accessed from anywhere. A customer can operate his account from any branch of his bank situated in India. This is also known as “Core Banking”. The various services provided under Anywhere banking are as follows:
- Tele Banking
- Internet Banking (I-Banking)
(A) Tele Banking:
It refers to banking on the telephone. The customer can dial the branch’s designated telephone number which is connected to the computer. The customer can enquire about his balance, previous transactions, or fund transfers between the accounts. The customer has to choice and facility of calling the bank at any time and it is more beneficial to the majority of customers.
(B) Internet Banking (I-Banking):
Internet banking is one of the popular modes of e-banking. It has made banking not only personalized but also customized. It enables to obtain of general-purpose information by a customer through banks “websites, electronic fund transfers (EFT), Electronic payments such as E-cheque, and card-based payments (credit cards, debit cards, and smart cards) these are called Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS). The RTGS provides continuous processing and enables the settlement of fund transfers.
- Real-Time Gross Settlements (RTGS): Real-time refers to the process of instructions that are executed immediately after they are received. Gross Settlement means settlement of funds transfer and thus payments are considered final and irrevocable.
- Electronic Clearance Service (ECS): This scheme provides an alternative method of effecting bulk payment transactions periodically.
- National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT): NEFT allows individuals and firms to transfer their funds from one bank to another bank. There is no ceiling on the minimum or maximum funds according to RBI.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the principles of management?
Answer:
Generally, management has been defined as “getting things done through others”.
Definitions:
Management is a multipurpose organ that manages a business and manages managers and manages workers and work. – Peter F. Drucker.
Management is the art of knowing what you want to do and then seeing that it is done in the best and cheapest way”. – F.W. Taylor.
“To manage is to forecast and to plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control.” – Henry Fayol.
It has been observed that management is used as a collective noun to refer to all those who manage within a particular organization including those who help line managers by performing a staff function. ‘Henry Fayol’ has been rightly called the “Father of administrative management” for his practical approach to management theory. He has identified 14 fundamental principles of management. Those are:
- Division of labour and specialization
- Parity of authority and responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of command
- Unity of direction
- Subordination of individual to general interest
- Remuneration of personnel
- Centralization
- Scalar chain
- Order
- Equity
- Stability of tenure of personnel
- Initiative
- Esperit-de-corps
1. Division of Labour and Specialisation:
Division of labour leads to specialization which increases the efficiency of individual employees. Division of labour is a famous principle of economics. Fayol applied this principle to management. He recommended work of all kinds must be subdivided and allocated to several persons. Sub-division makes each task simpler and results in greater efficiency.
2. Party of Authority and Responsibility:
According to Fayol, authority and responsibility must flow in the same direction. Responsibility is the natural outcome of authority. A proper balance between authority and responsibility helps to prevent the misuse of authority and responsibility helps to prevent the misuse of authority and promotes a fair fixation of responsibility.
3. Discipline:
Discipline means the observation of certain rules and regulations. People in the organization should be bound to accept certain codes of conduct. The three basic requisites of discipline are disciplined supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreement on goals, and judicious application of penalties.
4. Unity of Command:
The principle states that a subordinate should receive orders and be accountable to one and only one superior. No employee, therefore, should receive instructions from more than one person. The principle is necessary to avoid confusion and conflict.
5. Unity of Direction:
Unity of direction is essential for achieving unity in action, in the pursuit of common goals by a group of persons. For this, Foyal advocates one head and one plan’. Unity of direction (one head, one plan) is not the same as unity of command (one employee receives orders from one superior).
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest:
According to this principle, the fulfillment of individual objectives, in the long run, is contingent upon the attainment of common objectives in the short run. Thus, in case the need arises, an individual must sacrifice in favor of larger group objectives.
7. Remuneration of Personnel:
Remuneration is the price paid to the personnel for the services rendered by them. According to Fayol, the system of remunerating personnel should be fair and satisfactory to both the employees and the employer. It should be attractive to employ and retain the best personnel
8. Centralization:
It refers to the extent to which authority is concentrated or dispersed. The appropriate degree of centralization will vary with different concerns. It is a problem of finding the measure that will give the best overall yield. Under centralization managers or executives play an important role.
9. Scalar Chain:
It refers to the line of authority from the highest to the lowest executive for communication. However, in the routine course of business, employees at the same level can communicate with each other following the principle of ‘Gangplank’.
10. Order:
Fayol has classified order into two categories.
- Material Order: Material order is described as a place for everything and everything in its place.
- Social Order: Social order demands the employment of a “right man in the right place”.
11. Equity:
Equity is a combination of kindliness and justice. It seeks to elicit loyalty and devotion from personnel. Managers should show kindness and justice in dealing with their subordinates.
12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel:
High turnover increases inefficiency. An employee needs time to adjust to the new work. Its environment demonstrates efficiency. Therefore, stability of tenure is a desirable principle for ensuring efficiency. Unnecessary employee turnover is the cause and effect of bad management.
13. Initiative:
The initiative is the freedom to propose and execute a plan. To have freedom in this respect is the greatest satisfaction for an intelligent person. A manager, who induces his subordinates to think and act on their own is always better and more successful than the one who does not.
14. Esperit-de-corps:
It is a French phrase which means “Union is Strength.” It means the union is strong. There should be loyalty and concern for the honor of the organization to which one belongs. This can be achieved through the adoption of the principle of unity of command.
Question 3.
What is SEBI? What are its functions and powers?
Answer:
Securities and Exchanges Board of India (SEBI) was established to overcome undesirable practices in the stock exchanges. It is a controller of capital issues and it was established in the year 1988 and derived authority from the Capital Issues Act 1947. Later on, SEBI came into existence through the SEBI Act, 1992 the Indian Parliament Act Was given statutory powers.
Functions of SEBI:
SEBI has three functions rolled into one body.
- Quasi legislative
- Quasi-judicial
- Quasi executive
It drafts regulations in its legislative capacity, conducts investigation and enforcement action in its executive function and it passes rulings and orders in its judicial capacity. Their functions may be summarised as
- Regulating the business in stock exchanges.
- Registering and regulating the working of stock brokers, subbrokers, issue bankers, underwriters, and other intermediaries who may be associated with securities markets in any manner.
- Registering and regulating the working of collective investment schemes including mutual funds.
- Promoting and regulating self-regulatory organizations.
- Prohibiting fraudulent and unfair trade practices relating to the securities market.
- Promoting investor’s education and training of intermediaries of the securities market.
- Prohibiting inside trading in securities.
- Regulating substantial acquisition of shares and takeover of companies.
- Calling for information from, undertaking inspections, conducting inquiries, and audits of the stock exchanges.
- Performing such functions may be delegated to it by the Central Government.
Powers of SEBI:
The SEBI ordinance has given it the following powers:
- It may be called periodical returns from stock exchanges.
- It has the power to prescribe maintenance of certain documents by the stock exchange.
- SEBI may call upon the exchange or any member to furnish explanations or information relating to the affairs of the stock exchange or any members.
- It has the power to approve the laws of the stock exchange for regulation and control of the contracts.
- It can amend the bylaws of the stock exchange.
- In certain areas, it can grant to license the dealers in securities.
- It can compel a public company to list its shares.
The Securities Contract Act empowers the Central Government to delegate some of its powers to SEBI they are:
- Power to grant recognition to a stock exchange.
- Power to direct any stock exchange to amend the rules relating to the constitution of the stock exchange, admission of new members, etc.
- Power to supersede the governing body of any stock exchange.
- Power to suspend the business of a recognized stock exchange.
- Power to prohibit contracts in certain cases.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any four of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
What are the differences between the primary market and the secondary market?
Answer:
| Concept | Primary Market | Secondary Market |
| 1. Nature | It is concerned with the issue of new shares. | It is concerned with the marketing of existing shares. |
| 2. Sale of Securities | It enables the company to sell securities to the investors directly or through intermediaries. | It helps the holders of securities to exchange their securities. |
| 3. Capital Formation | It is directly connected with the promotion of capital formation. | It is indirectly connected with the promotion of capital formation. |
| 4. Securities Dealing | It deals with the buying of securities. | It enables both buying and selling of securities. |
| 5. Value of Securities | It enables the management of the company to decide the value of the securities. | It enables the demand and supply to determine the price of securities. |
| 6. Location | It has no fixed geographical location. | It is located at specific places. |
Question 5.
What are the merits and demerits of road transport?
Answer:
Merits:
- Cheapness: All forms of animal-driven, man-driven, and motor-driven transport are cheaper compared to the other forms.
- Safety: Damage due to the handling of goods is lesser in the form of transport.
- Flexibility: This advantage could be claimed only by road transport. It may go the place of loading and delivery of goods at the place of use.
Demerits:
- Irregular operation: Most of the transporting systems operating on roads are not coordinated.
- Limited carrying capacity: Limited load-carrying capacity is one of the drawbacks of road transport.
- Slow speed: Speed is an essential element in marketing but it is not possible in road transport.
- Rates: The rate structure is often oscillating in character.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the Danhof classification of entrepreneurs.
Answer:
Danhof has classified entrepreneurs into four categories:
- Innovating Entrepreneurs
- Adoptive (or) Imitation Entrepreneurs
- Fabian Entrepreneurs
- Drone Entrepreneurs
1. Innovating Entrepreneurs:
He introduces new products, and new methods of production and opens new markets. Innovating entrepreneur experiments.
2. Adoptive (or) Imitative Entrepreneurs:
This type of entrepreneur instead of innovating new things just adopts the successful innovations innovated by others. In such cases, the imitative innovations may make some changes in the innovations made by the innovative entrepreneur to suit their requirements.
3. Fabian Entrepreneurs:
These are entrepreneurs’ rigid and fundamental approaches. They follow in the footsteps of their successors. They are shy to introduce new methods and ideas. Fabian entrepreneurs are no risk-takers.
4. Drone Entrepreneurs:
They resist changes. They are laggards. They may close down their business but they don’t accept changes.
Question 7.
Explain the special support extended by the government of Telangana to the SC/ST entrepreneurs in our state.
Answer:
Special support to SC/ST entrepreneurs is offered through TS-PRIDE. Some of the activities are as follows:
- A special direct funding programme for financing SC/ST entrepreneurs.
- Payment of margin money on behalf of SC/ST entrepreneurs by the Government and creation of ₹ 5 crores for margin money refund scheme.
- Preferential allotment of plots in industrial parks.
- Supplier diversity opportunities in large industries.
- State departmental procurement policy in tune with GOI’s SME procurement policy of 20%.
- Organizing intensive entrepreneur and skill development.
- Subsidy eligibility if funded by CRISIL-rated NBFCs.
- Representation in all the districts and state-level committees.
Question 8.
What are the benefits of international trade?
Answer:
The benefits of international trade are discussed below:
- It leads to better use of available resources.
- It reduces the wastage of resources.
- It equalizes the prices of goods throughout the world.
- It helps countries to sell those goods which they have in surplus.
- It creates healthy competition.
- It brings about an international division of labour and specialization.
- It increases employment opportunities.
- It increases foreign exchange reserves.
Question 9.
What are the steps in the process of organizing?
Answer:
The process of organizing are following steps.
1. Identification and Division of Work:
The first step in the process of organizing involves identifying and dividing the work that has to be done by previously determined plans. The burden of work can be shared among the employees.
2. Departmentalization:
Once work has been divided into small and manageable activities then those activities which are similar are grouped. Such sets facilitate specialization. This grouping process is called departmentalization.
3. Assignment of Duties:
It is necessary to define the work of different job positions and accordingly allocate work to various employees. Jobs are then allocated to the members of each department by their skills and competencies.
4. Establishing Reporting Relationships:
Merely allocating work is not enough. Each individual should also know to whom he has to take orders and to whom he is accountable. The establishment of such clear relationships helps to create a hierarchical structure and helps in coordination among various departments.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What is the call rate?
Answer:
Commercial banks are required to maintain a minimum cash balance known as the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR). with the effect of changes in the cash reserve ratio by RBI, the banks with cash reserves below the statutory requirement borrow from such banks having surplus cash reserves. For the services rendered by the lending bank, interest is paid which is known as the call rate.
Question 11.
Write about the endowment policy.
Answer:
It runs only for a limited period or upto a particular age. The policy money becomes due at the end of the period specified in the policy. In case, however, the assured dies before the specified time the policy money is paid at the time of death.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain Balanced Regional Development.
Answer:
Entrepreneurs in the public and private sectors help to remove regional disparities by setting up industries in the backward areas. The government gives various concessions and subsidies to the entrepreneurs.
Question 13.
What are bridge loans?
Answer:
It is a short-term loan that enables the entrepreneur to continue with the implementation of the project till the term loan is applied and obtained.
Question 14.
Write about Hawkers and Pedlars.
Answer:
Hawkers and Pedlars:
These itinerants move from place to place to search for their customers. Features are:
- They sell low-cost products.
- They usually sell unbranded products.
Question 15.
What are multiple shops?
Answer:
Multiple Shops: Multiple shops are identical shops that sell standardized products in different parts of a particular place city or town.
E.g.: Bombay dyeing.
Question 16.
What is a bill of lading?
Answer:
It is an official receipt of the shipping company acknowledging the receipt of goods on board.
Question 17.
Define staffing.
Answer:
It is the process of management that is concerned with obtaining, utilizing, and maintaining a satisfactory and satisfactory work.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
(1 × 20 = 20)
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
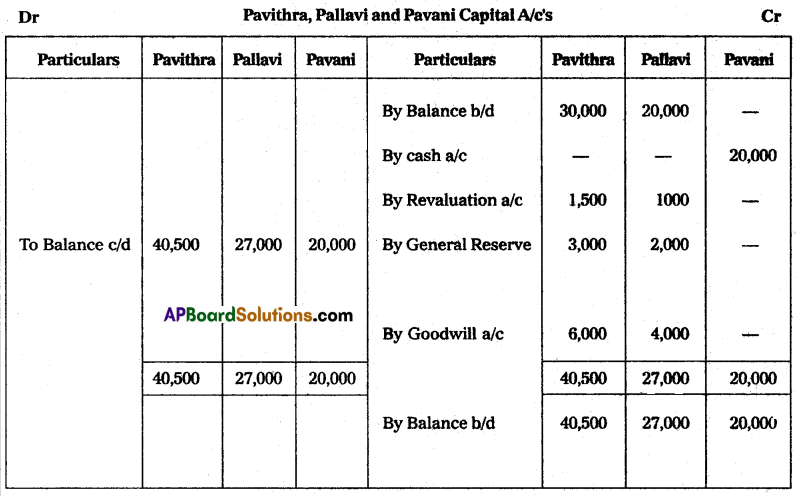
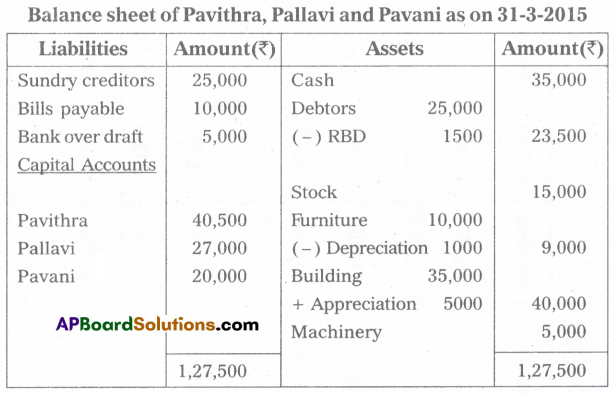
Pavithra and Pallavi are the partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their Balance Sheet as of 31st March 2015 was asunder:
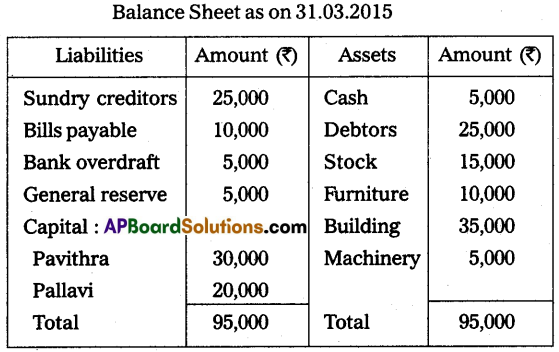
On 1st April 2015, they decided to admit Miss Pavani for 1/5th share in the profits. The terms of admission are:
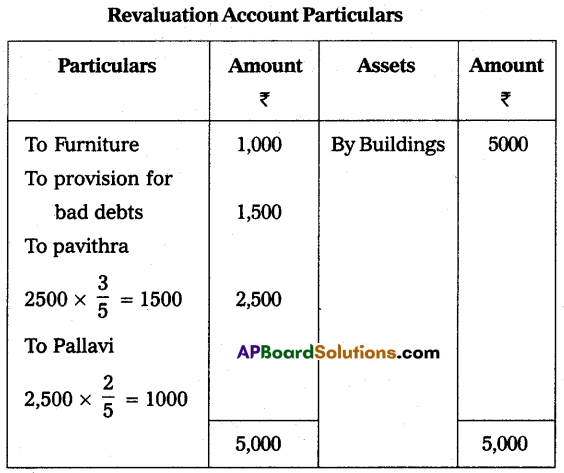
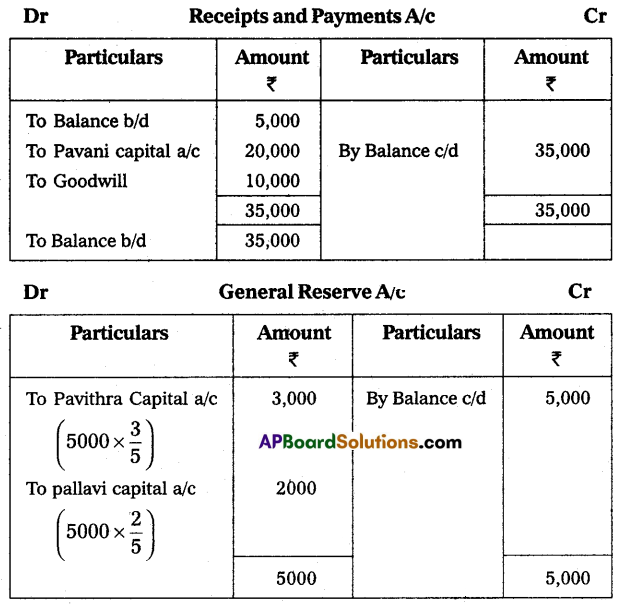
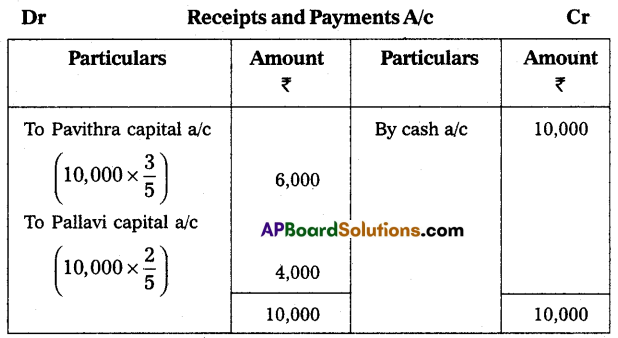
(i) She has to bring ₹ 20,000 towards capital and ₹ 10,000 towards goodwill in cash.
(ii) Furniture is to be depreciated ₹ 1,000.
(iii) Create a provision of ₹ 1,500 for bad debts on debtors.
(iv) Appreciate the value of Buildings by ₹ 5,000.
Prepare the necessary ledger accounts and show the balance sheet of the new firm.
Answer:
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any one of the following questions.
Question 19.
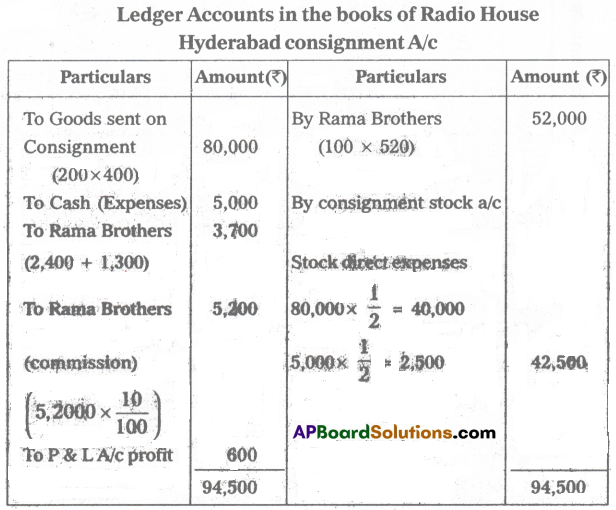
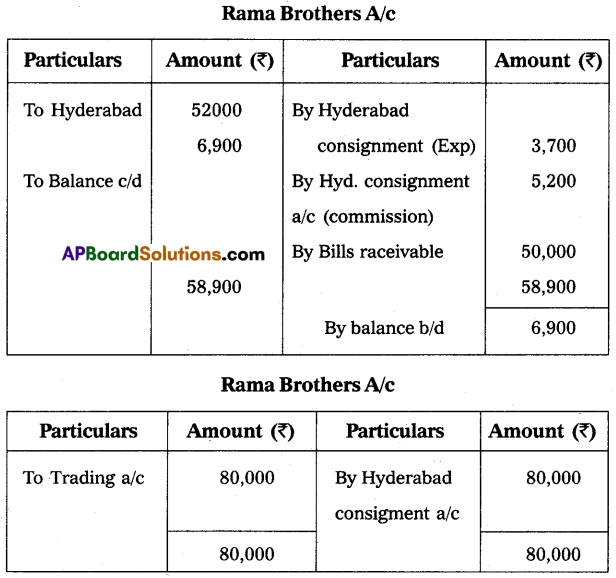
Western Radio House of Madras consigned 200 radios to Rama Brothers of Hyderabad. The cost of each radio was ₹ 400. Radio House paid ₹ 5,000 for freight and insurance. Rama Brothers accepted a three-month bill drawn upon them by Radio House for ₹ 50,000. Rama Brothers paid ₹ 2,400 as rent and ₹ 1,300 for advertisement. They sold 100 radios at ₹ 520 each. Rama Brothers is entitled to a commission of 10% on sales. Prepare the necessary ledger account in the book of Radio House assuming that Rama Brothers sent a bank draft for the balance due to Radio House.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
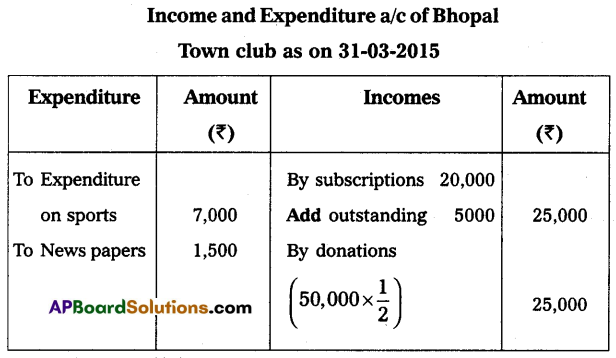
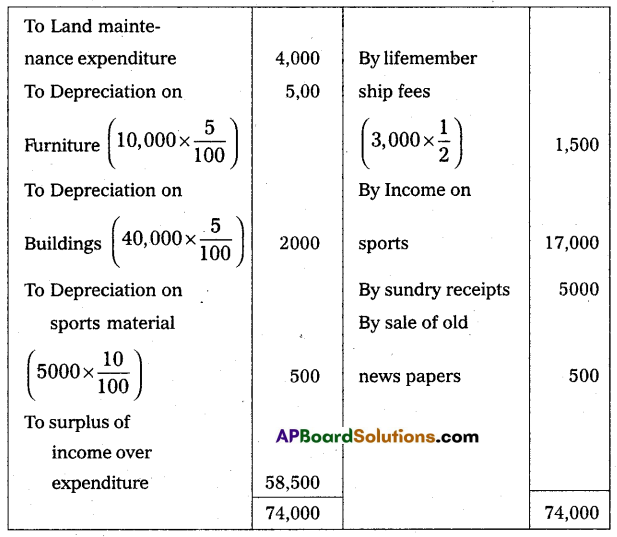
From the following information, prepare the Income and Expenditure account for the year ended on 31-03-2015 of Bhopal Town Club.
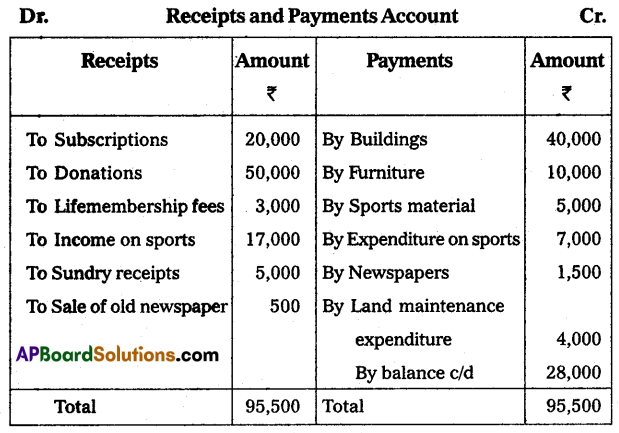
Additional Information:
(i) Capitalize 50% of donations and life membership fees.
(ii) Outstanding subscriptions ₹ 5,000.
(iii) Provide for depreciation on furniture and buildings 5% and on sports materials 10%.
Answer:
Section – F
(2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any two of the following questions.
Question 21.
What is donation? Explain the types of donations.
Answer:
Donations are the amount received by the organizations from individuals and institutions as a gift. Donations are of two types:
- General Donations: A general donation is the amount given by the individuals without mentioning the purpose. So that the amount can be utilized for any purpose by the not-for-profit organizations.
- Special Donations (or) Specific Donations: A donation received by the organization for a specific purpose.
Question 22.
Raghu & Co. purchased furniture on 1st April 2010 for ₹ 40,000. Depreciation is provided at the rate of 10% under straight-line method. On 31st March 2014 furniture was sold for ₹ 18,000. Prepare furniture account. Assume that the accounts are closed by 31st March every year.
Answer:
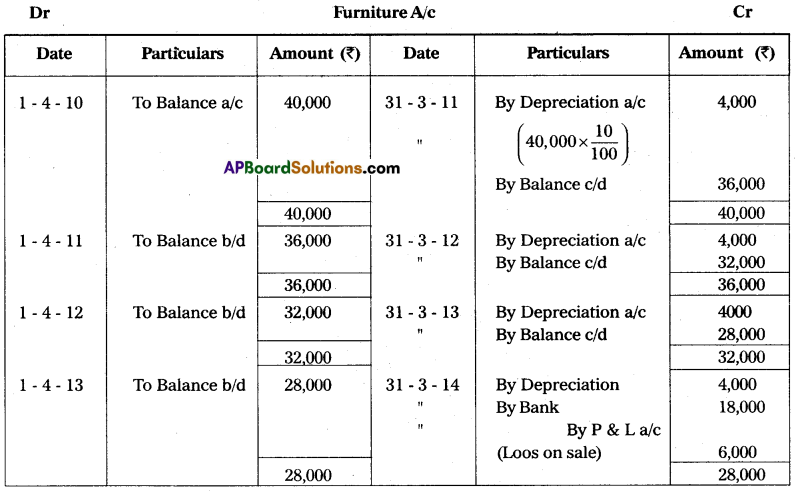
Question 23.
Ascertain the profit earned by M/s. Jagathi and Co., who keep books under a single entry system.
Capital at the beginning of the year ₹ 13,000
Capital at the end of the year ₹ 19,000
Drawing during the year ₹ 6,000
Further capital introduced during the year ₹ 3,000
Answer:
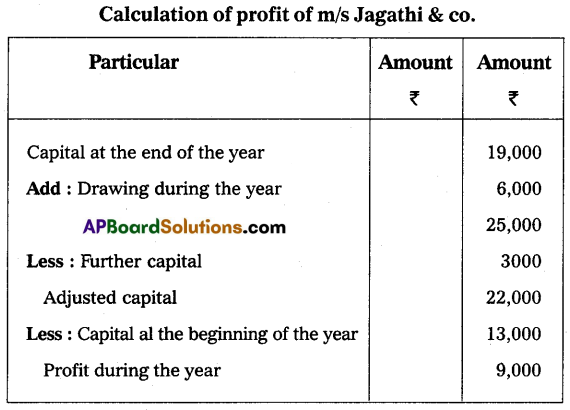
Question 24.
Write any five features of computerized accounting.
Answer:
Computerized accounting is nothing but replacing the manual accounting system of maintaining the books of account with the use of relevant software packages for accounting on a computer. “As its name suggests “Computerised Accounting” is an accounting done with the support of a computer. It lends to involve dedicated accounting software and digital spreadsheets to keep track of a business or client’s financial transactions. Features of computerized accounting are:
1. Fast, Powerful, Simple and Integrated:
Computerized accounting is developed to automate and integrate all accounting transactions. All the accounting information, that is recorded will be at the fingertips of the user. It is very simple to operate with a greater speed.
2. Total Visibility:
The company will have greater visibility into the day-to-day business operations.
3. Improved User Free Experience:
Computerized accounting permits companies to enter into data through various ways. It makes the work a pleasure. The company can adopt specific company needs with this feature.
4. Accuracy and Error-Free:
Computerized accounting provides users with definable templates with which they can get accurate and error-free data within no time as and when the button is clicked by the user.
5. Scalability:
Computerized accounting is designed to meet the current and future needs of the companies irrespective of their size and style.
6. Supremacy:
Computerized accounting is capable of storing huge volumes of transactions with greater retrieval capacity and efficiency.
7. Improved Business Performance:
Integrated and enhanced features of computerized accounting cover accounting inventory and reporting.
8. Rapid Decision Making:
Critical management information system reports instantly to make appropriate decisions at the right time.
9. Absolute Reliability:
Computerized accounting provides accurate critical financial information.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any five of the following questions.
Question 25.
What are the two causes of depreciation?
Answer:
Causes of depreciation are:
- Wear and Tear
- Depletion
- Accidents
- Obsolescences
- Effluxion of time/passage of time
- Fluctuations
Question 26.
Define a single entry system of bookkeeping.
Answer:
- Single entry is a simple method of recording business transactions.
- Profit or loss can be easily ascertained by comparing the opening capital with the closing capital.
- For keeping records in a single entry one does not require expert knowledge.
- It is less expensive when compared to double-entry system of bookkeeping.
- It is easy to follow and understand.
- No principles are required in this system.
Question 27.
What is the Delcredere commission?
Answer:
Remuneration or additional commission paid to the consignee for taking the responsibility of collecting the amount on credit sales made by him.
Question 28.
Define Legacy.
Answer:
Legacy is the amount received by the organization as per the “will” of a person.
Question 29.
What is a partnership deed?
Answer:
It is a document that defines the rights and liabilities of partners of the firm besides containing other matters about be conduct and management of the firm.
Question 30.
What are spreadsheets?
Answer:
A spreadsheet is an interactive computer application program. It helps the organization with the analysis and storage of data in tabular form. It is a table of values arranged in rows and columns. Each value can have a pre-defined relationship to the other values.
![]()
Question 31.
What is Marg?
Answer:
Marg was launched in 1992 by Compu Soft Private Ltd., This software provides customized solutions depending upon the needs of each industry like pharmaceuticals, trading real industry, etc.
Question 32.
Radha and Rani share profits in the ratio 4 : 3. Roja admitted into business for 1/8th share in the future profits. Calculate a new profit-sharing ratio.
Answer:
Old profit-sharing ratio of Radha and Rani = 4 : 3
Roja new share = \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Remaining share = 1 – \(\frac{1}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{8}\)
\(\frac{7}{8}\) will be given to Radha and Rani in their old profit-sharing ratio
New profit sharing ratio of Radha = \(\frac{7}{8} \times \frac{4}{7}=\frac{28}{56}\)
New profit sharing ratio of Rani = \(\frac{7}{8} \times \frac{3}{4}=\frac{21}{56}\)
New profit sharing ratio of Roja = \(\frac{1}{8} \times \frac{7}{7}=\frac{7}{56}\)
Radha, Rani and Roja new profit sharing Ratio = \(\frac{28}{56}: \frac{21}{56}: \frac{7}{56}\) = 28 : 21 : 7 = 4 : 3 : 1