Collaborative study sessions centered around TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2018 can enhance peer learning.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper May 2018
Section – A
(2 × 10 = 20)
Answer any two of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations.
Answer:
Partnership is defined by section 4 of Indian Partnership Act of 1932 “as the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them act for all”.
Merits :
- Easy formation : It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsory.
- Large resources: The resources of more than one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial Capacity : They pool capital, organising ability, managerial capacity etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making : The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility : The partnership is flexible in nature and at any time after mutual consent, the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations.
- Sharing risks : The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach: The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation: All partners actively participate in the business as per their specialisation and knowledge.
Limitations :
- Unlimited liability : The unlimited liability is’the funda-mental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability: The partnership firm suffers from uncertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- Limited resources: There is limitation in raising additional
capital for expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners. - Non-transferability of share : No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust: The mutual distrust among partners is the main cause for the dissolution of the partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions : Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
Question 2.
Distinguish between a private Company and a public company.
Answer:
Introduction :
On the basis of Public Interest, companies may be classified into two types. They are
(1) Private company and
(2) Public company
(1) Private company : According to companies Act, private company is a company which is formed with the association of at least two members but not exceed fifty and with minimum paid up capital of one lakh rupees. It is prohibited from issue of share to the public and also transfer of shares.
(2) Public Company : Public company is a company which is formed with the Association of minimum seven members and there is no limit on maximum number of members. Public companies are required to issue a prospecters for inviting people to purchase their shares. Public company minimum paid up capital is five Lakhs rupees.
Difference between private company and public company :
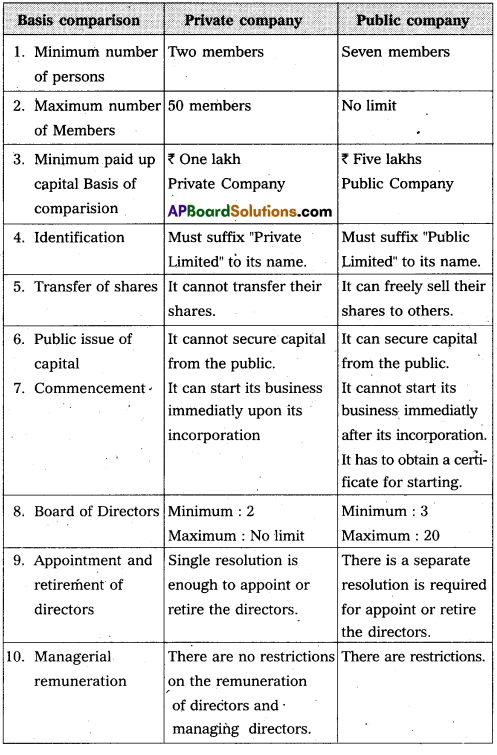
![]()
Question 3.
What are the factors that determine the selection of sources of finance ?
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called Business Finance. R.C.Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
B.O.Wheeler defined business finance as follows : “Finance is that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of a business enterprise”.
Need for business finance :
1. To start a new business : Money is needed to start a business and to procure fixed assets like buildings, plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures etc., working capital is required for holding current assets such as stock of materials, transportation expenses etc. The amount of finance to be procured depends on the type of business, nature of business and usage of technology.
2. To expand the business : Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be improved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technology.
3. To develop and market new products : Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products. Invention and innovation of products should be given much priority to sustain in the market. Marketing research needs more funds.
4. To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
5. To take over another business : Business needs money to overcome competition or to get strengthened. An enterprise may decide to take over another business.
6. To move to new premises: A business unit may be forced to shift the business to new premises according to directions of the government. In such case, finance is needed for expenses like transport, packaging, installation of machinery etc.
7. Pay for the day-to-day running of the business : A business enterprise needs money to meet the day-to-day expenses like wages, taxes advertisement, rent etc. If also needs to meet liabilities like repayment of loan, installments, creditors etc.
The following factors should be considered for selecting the sources of finance.
1. Cost factor : While deciding the sources of funds that is utilised by the business concern, the cost of procuring the funds and the cost of utilising are to be considered.
2. Sound financial position : In the choice of sources of funds, the business should be financially sound so that it can repay the principle amount together with interest.
3. Form of business organisation : The form of business organisation influences the choice of source for raising money.
Ex: A partnership firm cannot raise money by issue of equity shares.
4. Purpose and period of time: While selecting the sources of finance, purpose and period of time is to be taken into account. A short term need can be met by borrowing funds through trade credit, commercial paper etc., with low rates of interest. For long term finance, sources like issue of shares and debentures are more appropriate.
5. Risk factor: Business should evaluate each of the sources of finance in terms of risk involved. Ex: If equity shares are issued, they are to be repaid only at the time of winding up and dividends are not paid if the profits are not available. There is little risk, involved. On the other hand, a loan is to be repaid as per schedule and the interest is to be paid whether the firm earn profits or not.
6. Control : A particular sources of funds may affect the control and power of the owners on the management of the firm. As the equity shareholders enjoy voting rights, by the issue of equity shares the financial institutions may take control Of the assets or may impose conditions as part of loan agreement.
7. Effect on credit worthiness : Depending on certain sources of finance may effect the credit worthiness in the market.
Ex : Issue of secured debentures may effect the interests of the creditors and they may not be willing to extend further loans to the company.
8. Flexibility and ease : Another factor which may effect the choice of sources of finance is flexibility and ease of obtaining funds. In order to secure loans from banks, they may impose restrictions and documentation is necessary. If other sources are available traders may not prefer approaching banks and financial institutions.
9. Tax benefits: Tax is not deducted on dividend of preference shares. Interest paid on loans and debentures is tax deductable. In order to take advantage of tax benefits firms may issue debentures of take loans.
Section – B
Answer any FOUR of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
What is meant by Industry ? Explain four types of Industries.
Answer:
Refer Q.No : 4 T.S/A.P.2018 March Paper.
Question 5.
Briefly explain the different types of co-operative societies.
Answer:
According to the needs of people different types of co-operative societies are started in India. They are :
1) Consumers Co-operative Society : These are started to help lower and middle class people. These societies protect weaker sections from the clutches of profit hungry businessmen.
These societies make bulk purchases directly from producers and sells these goods to members on retail basis. The commission and profit of the middlemen are eliminated. The members contribute capital and membership is open to all irrespective of caste, creed, colour etc.
2) Producers Co-operative Society : Small producers find it difficult to collect various factors of production they also face marketing problem. The production of goods is undertaken by members in their houses or at common place. They are paid wages for their services. They are supplied raw material and equipment by the society. The output is collected and sold by the society. The profits are distributed among members after retaining some profit in the general pool. Ex: Appco, Co-Optex, Emniganur weavers co-operative society.
3) Marketing Co-operative Society : These societies are established by producers for selling their products at remunerative prices. These societies pool production from different members and undertake to sell these products by eliminating middlemen. The goods are sold when the market is favourable. The societies provide some advance money to the members for helping them in meeting their urgent needs. The sale proceeds are shared among members according to their contributions. These societies provide services like grading, warehousing, insurance, finance etc.
4) Co-operative Credit Society: The people with moderate means are formed with the object of extending short term credit to their members. They also develop thrift among the members. The funds are contributed by the members. These societies are divided into rural credit co-operative societies and urban credit co-operative societies.
5) Co-operative Housing Society: The low and middle income group of people are not able to construct their own house for want of money. Co-operative society arrange loans for their members from financial institutions and government agencies against security of the houses. These societies helps the members to become owners of house over a period of time. Ex: Housing Board Colonies.
6) Co-operative Farming Societies : These societies are basically agricultural co-operatives. These are formed by the small land owners. They pool their resources to achieve the benefits of large scale farming and maximising agricultural product. They solve the problems of finance, irrigation seeds, fertilizers etc.
Question 6.
What is Article of Association ? Explain its contents.
Answer:
The rules and regulations framed for the internal management of a company are set out in a document is called as “Articles of Association”. It is a supplementary document to the Memorandum of Association”.
The Articles must be printed, divided in paragraphs, stamped adequately and signed by each subscriber to the memorandum of Association.
According to section 2(2) of the Companies Act “Articles of Association of the company as originally framed or as altered from time to time in pursuance of any previous companies law or of this Act”.
The contents of Articles of Association :
- Procedure of issuing share capital.
- Procedure for transfer and forfeiture of shares.
- Procedure for issue of debentures and stocks
- Powers of after as well as reduce share capital and its procedure of alternation.
- The appointment of directors, their powers, duties and remuneration.
- The appointment of the managing director.
- Provisions regarding conducting the general meeting special meetings, noting proxies, resolutions etc.
- Provisions related to dividends and reserves
- Rules for preliminary contracts
- Provisions related to use of common seal
- Preparation of Accounts and audit maintenance of Bank accounts.
- Procedure for winding up the company.
![]()
Question 7.
Differentiate between the equity shares and preference shares.
Answer:
Difference between Equity shares and preference shares :
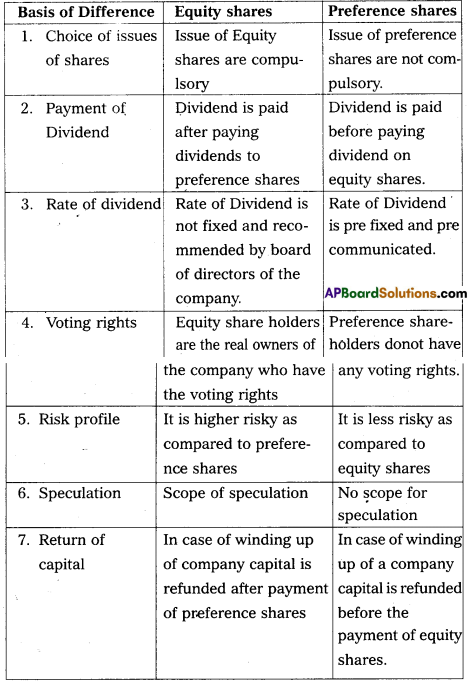
Question 8.
What are the sources of short term finance ?
Answer:
The following are the sources of short-term finance :
1. Bank credit : Commercial banks extend short term financial assistance to business in the form of loans, cash credits, overdrafts and discount bills. Bank loans are provided for a specific short period. Such advance is credited to loan account and the borrower has to pay interest on the entire amount of the loan sanctioned. Bank grants cash credits upto a specific limit. The firm can withdraw any amount within that limit. Interest is charged on the actual amount withdrawn. In overdraft, the customer can overdraw his current account. The arrangement is for short period only. Commercial banks finance the business houses by discounting the bills of exchange and promissory notes.
2. Trade credit: Just as firm grants credit to customers, so it often gets credit from suppliers. It is known as trade credit. It does not make available funds in cash but it facilitates the purchase of goods without immediate payment of cash.
3. Installment credit: Business firm gets credit from equip-ment suppliers. The supplier may allow the purchase of equipment with payments extended over a period of 12 months or more. Some portion of the cost price is paid on delivery and the balance is paid in number of instalments. The supplier charges interest on unpaid balance.
4. Customers advance : Many times, the manufacturer of goods insist on advance by customers, in case of big orders. The customers advance represent a part of the price of the product which will be delivered at a later date.
5. Commercial Paper : Commercial paper is an unsecured promissory note issued by a firm to raise funds for shorter period, varying from 90 days to 365 days. It is issued by one firm on another firm. The amount raised by C.P is large. As the debt is totally unsecured, firms having good credit rating can issue commercial paper.
Question 9.
List out the features of MNCs.
Answer:
MNCs means Multinational Corporations. The word “Multinational” is a combination of words “Multi” which refers to many and ” national” refers to a country. So multinationals means a company which operates in more than one country. MNC refers to an enterprise whose managerial headquarters are located in one country, while it carries out operations in a number of other countries.
According to David E. Liliental, defines the MNCs as “Corporations which have their home in one country but operate and live under the laws and customs of other countries as well”.
Features of MNCs:
- Giant size ; The assets aind sale of MNCs are very large. These companies operate on large scale as they trade in more than one country. Sometimes their sales turnover exceeds the Gross National product (GNP) of developing countries.
- International Operation : A MNC operates and sells their products in different countries. It operates through a network of branches and subsidiaries in host countries.
- Professional Management : A Multinational corporation employees professional experts, specialized people. MNCs try to keep their employees updated by training from time to time to handle the advance in technology effectively.
- Oligo polistic powers : Oligopoly means power in the hands of few companies only. Due to their gaint size, the MNCs occupy dominating position in the market.
- Centralized control : MNC’s will have managerial head-quarters in the home country. All the subsidiary and branches work under the supervision, guidance and control of the head office.
- Sophisticated Technology : Multinational companies make use of latest, advanced and innovative technology to produce quality goods.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Commerce ?
Answer:
Commerce is concerned with exchange of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to transfer of goods from the places of production to the ultimate consumer. Commerce enables all these processes which helps to break the barriers between producers and consumers. It is sum of those processes which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of persons, place and time in exchange.
Question 11.
What is Sole Proprietorship.
Answer:
Sole trade is the oldest and most commonly used form of business organisation. It is also known as sole proprietorship, individual partnership, single entrepreneurship. In sole trade concern a single individual introduces his own capital, skill and intelligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is the easiest to form and is also the simplest in organisation. All that is required is that the individual concerned should decide to carry on particular business and find the necessary capital. For this purpose, he may depend mostly on his own savings or he may borrow part or whole from his friends or relatives. He can start business in his own house or on rented premises. He may run the business on his own or may obtain the assistance of his family members or paid employees.
A sole trader is a person who sets up the business with his own resources, manages the business himself by employing persons for his help and alone bears all gains and risks of the business.
Question 12.
Coparcener.
Answer:
In Joint Hindu Family business Organisation, family members of three successive generations own the business Jointly. This interest in inheritence is called coparcenary interest. Hence the members of the joint Hindu family firm are called “coparceners.
Question 13.
What is a Government Company.
Answer:
- Any company in which not less than “51” percent of the paid up share capital is held by the central government or state Government is called a Government company.
- For example: ONGC, NTPC
Question 14.
Define fixed capital.
Answer:
The capital which is used to acquire fixed assets such as land and buildings, plant and machinery etc., is called fixed capital. Capital used by the business organisations to meet the long term requirements is called fixed capital or block capital. The amount of fixed capital required by the business concern depends on the size and nature of business.
Question 15.
Retained earnings.
Answer:
Retained earnings or ploughing back of profits refers to the process of reinvestment of the earning of the year after year. In this technique all the profits are not distributed to share holders. A part of the profit is retained in the business as a reserve which are used for financing long term and short term needs of the company.
![]()
Question 16.
Define Service Enterprises.
Answer:

Question 17.
Define E-Banking.
Answer:
E-banking means “Electronic Banking” which is one of the most successful online business. E-Banking allows customers to access their accounts, and execute orders through use of website. With the help of e-banking a customer can view their accounts, transfer funds and can pay bills. Eg : Net Banking.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
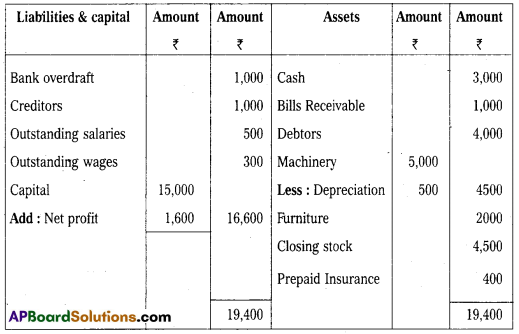
From the following Trial Balance, Prepare final accounts of sachin company as on 31-12-2016.
Trial Balance
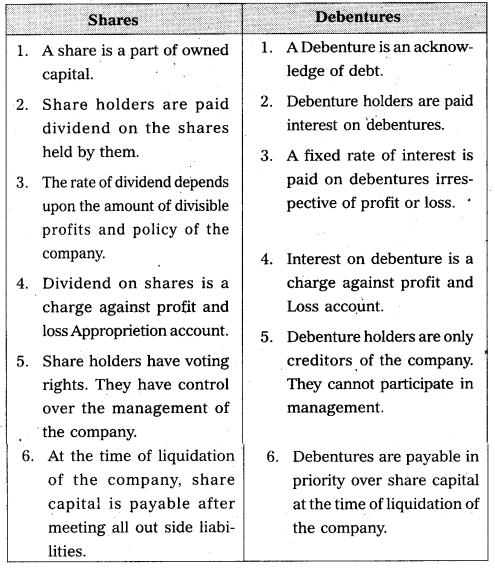
Adjustments :
1. Outstanding salaries ₹ 500.
2. Closing stock ₹ 4,500.
3. Prepaid Insurance ₹ 400.
4. Outstanding wages ₹ 300.
5. Depreciation on Machinery 10%.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Sachin company for year ending 31.12.2016
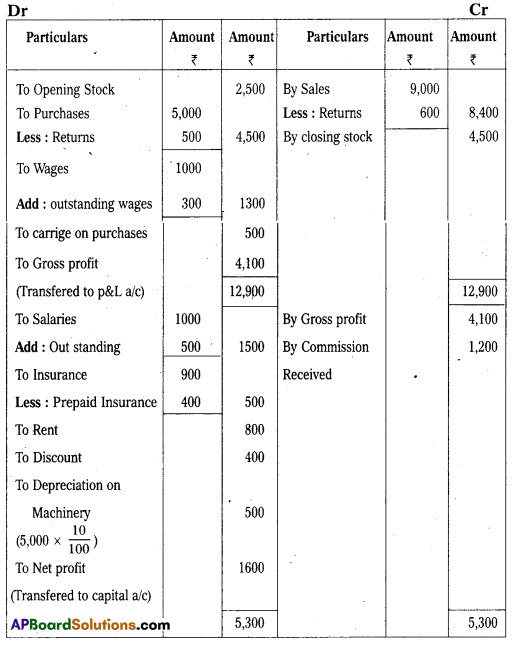
Balance Sheet of Sachin Company as on 31.12.2016
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
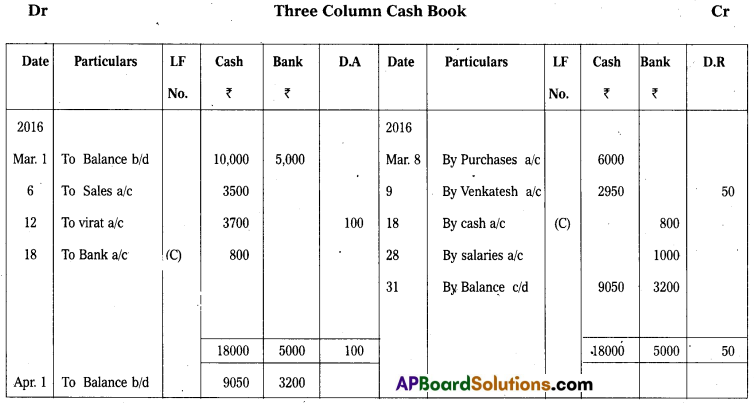
Question 19.
Prepare Three Column Cash Book from the following :

Answer:
Question 20.
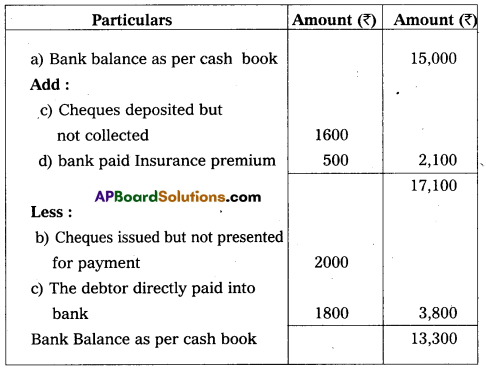
From the following information prepare a Bank Reconci-liation statement of Shiva Traders as on 31-12-2016.

Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of Shiva Traders as on 31.12.2015
Section – F
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain different types of accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
Answer:
The accounts are broadly divided into two types.
1. Personal Accounts
2) Impersonal accounts.
1) Personal Accounts : These accounts which relate to the persons, group of persons or institutions are called personal accounts. Ex.: Rama’s a/c, Andhra Bank a/c., LIC a/c, Infosys Ltd. The rule in personal accounts is “Debit the receiver and credit the giver”. According to this, benefit receivers account is debited and benefit givers account is credited.
2) Impersonal accounts : Impersonal accounts are those accounts which are not personal accounts. They are again divided into
i) Real Accounts
ii) Nominal Accounts.
i) Real Accounts : These accounts are related to the assets and properties of the business firm. Ex.: Building, machinery, stock, goodwill etc.
The rule in real accounts is “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”. When an asset is received the asset account is debited and when the asset goes out of the business, the asset is credited.
ii) Nominal Accounts : These accounts relate to expenses, incomes or gains or losses. Ex.: Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Commission received a/c etc.
The rule in nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains”.
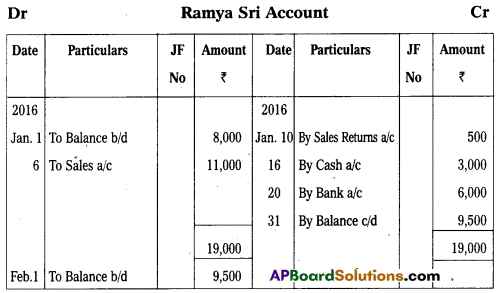
Question 22.
Prepare Ramya Sri account from the following.

Answer:
Question 23.
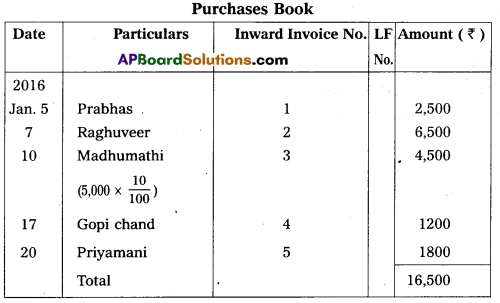
Record the following transactions in the purchases book.

Answer:
Question 24.
What are the errors disclosed by the Trial Balance?
Answer:
The errors which affect the agreement of Trial Balance are called Errors disclosed by the Trial Balance.
The following are the errors disclosed by Trial Balance :
- Posting of Transaction to wrong side of an account: Posting of transaction to wrong side of account affect the agreement of Trial Balance.
Eg : Discount allowed posted to credit side of discount account. - Posting of wrong amount to an account: Posting of wrong amount affect the agreement of Trial Balance.
Eg : Sales of ₹ 5000 posted as ₹ 500 to sales account. - Errors in totaling : Errors in totaling it may be over cast or undercast affects the agreement of trial Balance. Eg: Sales Returns Book Overcast by ₹ 100.
- Errors of carrying forward: If a mistake in carrying forward a total of one page to the next page. This error affect the agreement of Trial Balance. Eg: purchase Book total is carried forward as ₹ 1,500 instead of ₹ 150.
- Posting of only one aspect of Journal Entry into ledger :
Some times accountant may post only one aspect of entry to the ledger account, it affect the Agreement of Tril Balance. Eg: Sale of goods to Ramesh ₹ 200 Posted to sales book only. - Recording one aspect twice :
An accountant may be record one aspect twice it affect the Agreement of Trial Balance.
Eg : Paid salaries ₹ 600 debited twice in salaries account.
Section -G
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is an Account ?
Answer:
An Account is a summary of relevant transactions at one place related to a person asset expense revenue named is the heding. An account is a brief history of financial transactions of a particular person or item which has two sides called debit side and credit side.
Question 26.
Explain money measurement concept.
Answer:
According to Money Measurement concept, we record all transactions which can be measured in terms of money. The transactions and events which cannot be expressed in term of money are not recorded in books of Accounts.
![]()
Question 27.
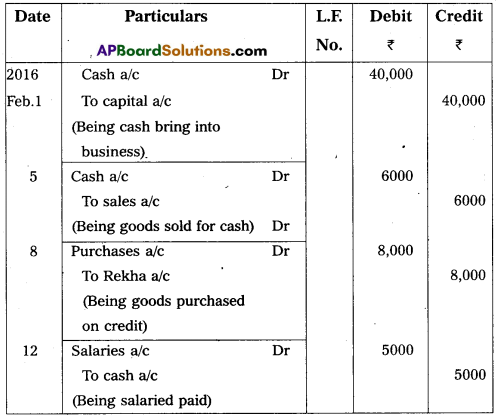
Journalize the following transactions. In the books of Dhoni.

Answer:
Journal entries is the books of Dhoni
Question 28.
What is Contra Entry ?
Answer:
An Entry which appears on both the sides (debit side as well as credit side of the tree column Cash Book is called “contra Entry ? For contra entries letter “c” is written is L.F. column.
Question 29.
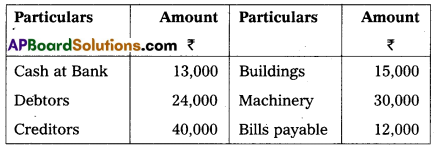
Pass Opening Entry from the following particulars as on 01-01-2015.
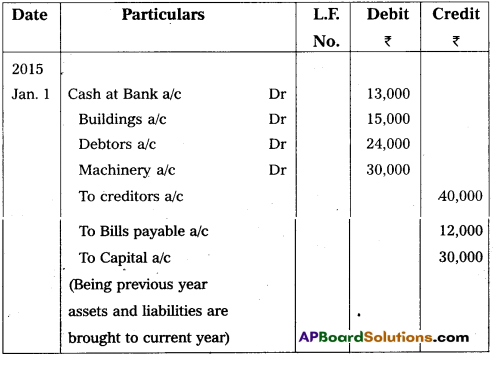
Answer:
Opening Entry as on 1-1-2015
Question 30.
What is Overdraft ?
Answer:
Bank overdraft is an arrangement made by the customer with banker to drawn an excess amount of what the customer has in his bank account balance subject to a specific predetermined limit.
Question 31.
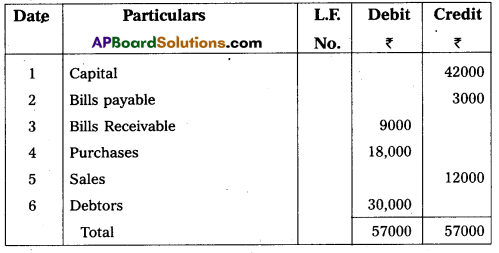
Prepare Trial Balance of Raviteja from the following balances as on 31-3-2016.
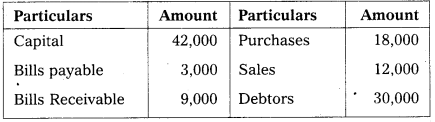
Answer:
Trial Balance of Ravi Teja as on 31-3-2016
Question 32.
Define Drawings.
Answer:
It is the amount of cash or value of goods withdrawn from the business by the proprietor for his personal use. It is deducted from the capital.