Collaborative study sessions centered around TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2016 can enhance peer learning.
TS Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper March 2016
Part – I (Marks 50)
Section – A
Question 1.
Define the Co-operative Society. Explain its features.
Answer:
The Indian Co-operative Societies Act, 1932 Section 4 defines co-operatives as a “society which has its objectives for the promotion of economic interests of its members in accordance with cooperative principle”.
Features of Co-operative Society:
- Voluntary membership : A Co-operative society is a voluntary association of persons. Everyone is at liberty to enter or leave the co-operative society as and when he likes. Any person can become a member irrespective of his/ her caste, creed, religion, colour, sex etc.
- Democracy and equality : It is organised on the basis of democracy and equality. Every member has a right to participate in the management. Every member has only one vote.
- State control : A co-operative society is subject to the control and supervision. In India, all co-operatives are registered under Indian Co-operative Societies Act or respective state co-operative laws.
- Service motto : The primary objective of co-operative society is to provide service to the members. The aim is not to earn profits. The societies earn small amount of profits to cover administration expenses.
- Knowledge of the principles of co-operation : Every person joining a co-operative society must be familiar with the fundamentals of co-operation. The important aim is to serve common man. The spirit is “Each for all and all for each”.
- Cheaper and better commodities : A Co-operative society aims at service rather than profit. The consumers can get goods of better quality at reasonable price.
- Privileges: The government has granted several privileges to co-operative society. The government provide finance at concessional rates of interest.
- Elimination of middlemen : A Co-operative society purchases goods directly from the producers and sells directly to its members. Hence, middlemen are eliminated.
- Aim at mutual prosperity : Co-operatives function on the principle of “Each for all and all for each” with the aim of mutual prosperity.
Question 2.
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Joint Stock Company.
Answer:
The following are the advantages of Joint Stock Company:
- Large financial services: As there is no limit on the number of shareholders in public company, it can collect large amount of capital.
- Limited liability: The liability of the shareholders is limited to the face value of the shares held by them. If a member pays entire amount on shares, he will not be called upon to pay even a single rupee.
- Perpetual succession: A company has continuous existence. It does not come to an end with the death, lunacy or insolvency of members.
- Transfer of shares : Transferability of shares acts as an added incentive to investors. The shares of public company are traded easily in stock exchange.
- Economies of large scale production: A company has large amount of capital. It can organise production on large scale. It will result in economies in production, purchase, marketing, management etc.
- Efficient professional management: A company has large resources at its disposal. So, it can appoint highly qualified persons and secure their services.
- Diffused risk: In case of companies, there are large number of shareholders. So risk is shared by large number of persons and risk is reduced to each member.
- Tax benefits: Although the companies are required to pay tax at higher rates, their tax burden is low as they enjoy many tax exemptions under Income tax Act.
The following are the disadvantages of Joint Stock Company:
1) Difficulty in formation : Promotion of company is not an easy task. There are so many legal formalities are to be compiled with. Large amount is to be spent.
2) Lack of motivation : A company is managed by Board of Directors and paid officials. They do not have share in profits. They do not have any incentive to work hard.
3) Economic oligarchy: The management of the company is supposed to carried on in according to the collective will of its members. But there is rule by few, often the directors try to mislead the members and manipulate voting power to maintain their control.
4) Fradulent (corrupt) management: In companies, there is often danger of fraud and misuse of property by dishonest management. Unscrupulous person may manipulate annual accounts to show artificial profits or losses for their personal gain.
5) Delay in decisions: Quick decisions cannot be taken as all important decisions are taken either by the Board of Directors or referred to general house.
6) Unhealthy speculation : As the liability of the members is limited, the management is tempted to get into speculative business activities.
7) Excessive government control : At every Stage, the management of the company has to follow several legal provisions and reports are to be filed. A lot of time and money is wasted.
8) Social evils : The growth of companies encouraged monopolies. It may become a cause of political corruption. The company influences the policies of the government by giving donations to the political parties.
![]()
Question 3.
What is business finance ? Explain its need and significance in the business organizations.
Answer:
The requirement of funds by business firm to accomplish its various activities is called business fnance.
R.C. Osborn defines business finance as “The process of acquiring and utilising funds by business”.
Significance of business finance:
- To commence a new business: Money is needed to start a new business and to procure fixed assets like land and buildings etc., working capital is required to meet the day – to – day expenses and holding current assets like cash, stock-in-trade etc.
- To expand the business : Huge amount of funds are required for purchasing sophisticated machinery and for employing technically skilled labour. The quality of the product can be im-proved and cost per unit can be reduced by adopting new technol-ogy.
- To develop and market new products : Business needs money to spend on developing and marketing new products.
- To enter new markets : Creation of new markets leads attracting new customers. Business spend money on advertisement and retail shops in busy areas.
- To take over another business : In order to overcome competition, an enterprise may decide to take over another business.
- To more to new premises : Sometimes a business may be forced to shift the business in another place.
- Day to day running: A business needs money to meet the day – to – day requeirements like wages, taxes etc.
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions not exceeding 20 lines each.
Question 4.
Define trade and explain various types of aids to trade.
Answer:
All the human activities engaged in buying and selling of goods and services comes under trade. Therefore trade includes sale, transfer or exchange of goods and services with the intention of making profit. The object of trade is to make goods available to those who need them and willing to pay for them. Trade is the final stage of business activities and involves transfer of ownership.
Aids to trade : Trade or exchange of goods and services involves several difficulties which can be removed by aids to trade. Aids to trade refer to those activities which directly or indirectly facilitate smooth exchange of goods and services.
Aids to trade includes transport, warehousing, banking, insurance, advertising and communication.
1) Transport: All the goods are not consumed at the same place where they are produced. Goods are to be moved from the places of production to the places where they are demanded. The activity concerned with the movement of goods is called transpor-tation. It can be done by rail, road, water and air.
2) Warehousing : Goods are produced in anticipation of demand. There is time gap between production and consumption. Hence, it became necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. Agricultural products like wheat and rice are seasonal in nature but they are consumed throughout the year. On the other hand, goods such as umbrellas and woollen cloths are produced throughout the year but they are demanded only during particular season. Therefore, these goods need to be stored in warehouses till they are demanded. Warehousing creates time utility.
3) Insurance : Business is subject to risks and uncertainities. Risks may be due to theft, fire, accident or any other natural ca-lamity. Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Insurance compa-nies who act as risk bearers covers risks.
4) Banking: Producers and traders require money for carrying on production and trade. Banks are the institutions which supply funds for industries and trade. They pool savings from the public and make them available to industries. So, banking is an important function of commerce.
5) Advertising: Exchange of goods is possible when the con-sumers have the knowledge about the existence of the product. Through advertisement, producers communicate all information about the goods to prospective consumers. It creates a strong desire to buy the product. Advertising is done through T.V, radio, newspapers, magazines, hoarding, wall posters etc.
6) Communication : Communication means exchange of information from one person to another. It is necessary to finalise and settle terms such as price, discount, facility of credit etc. Modem means of communication like telephone, telex, e-mail, teleconference etc., play an important role in establishing contact between businessmen, producers and consumers.
Question 5.
What is partnership deed ? Explain its contents.
Answer:
The written agreement can contain as much, or as little, as partners want. The law does not say what it must contain. The usual contents of partnership deed are listed as here under.
- Name of the partnership firm.
- Names, addresses and occupation of all the partners.
- Nature, object and duration of business.
- Amount of capital to be contributed by each partner.
- Drawings if any, allowed for private purposes.
- Sharing of profits and losses.
- Rate of interest on capital and drawings.
- Rights, duties and liabilities of each partner.
- Method of keeping books of accounts and audit.
Question 6.
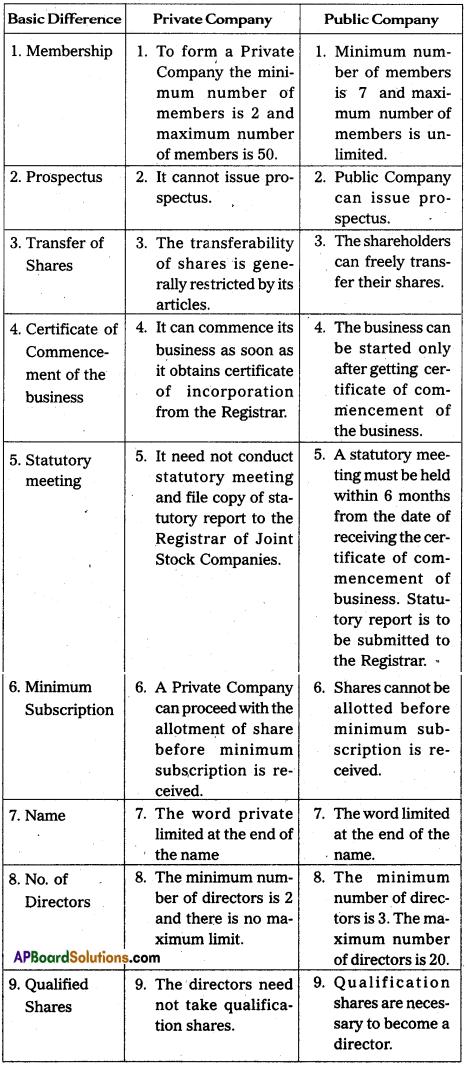
Distinguish between a private company and a public company.
Answer:
Question 7.
Explain the classification of sources of finance.
Answer:
Sources of finance can be classified on the basis of period, ownership and generation.
On the basis of period : On the basis of period, sources of funds are divided into long term, medium term and short term fi-nance. Long term sources fulfill the financial requirements for a period exceeding five years and include sources such as shares, debentures and long term borrowings.
Medium term finance is re-quired for a period of more than one year and these includes bor-rowings from commercial banks, public deposits, lease financing. Short term funds are required for a period of less than one year and the sources are trade credit, bank credit, instalment credit, advances, bank overdraft, cash credit and commercial paper.
On the basis of ownership : On the basis of ownership, the sources can be classified into owners funds and borrowed funds. Owners funds are those which are provided by the owners which include issue of shares and retained earnings. Borrowed funds refer to the funds raised through loans or borrowings which include loans from commercial banks; financial institutions, issue of de-bentures and public deposits.
On the basis of generation: Sources of finance can be generated from internal source or external source. Internal sources of funds are generated within the business such as retained earnings, collection of receivables, depreciation fund, disposing surplus stock etc. External sources lie outside the business and include shares, debentures, public deposits, borrowings from banks and financial institutions etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Differentiate between a share and a debenture.
Answer:
| Shares | Debentures |
| 1. A share is a part of owned capital. | 1. A debenture is an acknowledgement of debt. |
| 2. Shareholders are paid dividend on the shares held by them. | 2. Debentureholders are paid interest on debentures. |
| 3. The rate of dividend depends upon the amount of divisible profits and policy of the company. | 3. A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures irrespective of profit or loss. |
| 4. Shares are not redeemable except redeemable preference shares during the life time of the company. | 4. The debentures are redeemed after a certain period. |
| 5. At the time of liquidation of the company, share capital is payable after meeting all outside liabilities. | 5. Debentures are payable in priority over share capital. |
Question 9.
Find out the features of MNC’s.
Answer:
Characteristics or features of Multi NationalCorporations :
- Global Operations : Multi National Corporations carry production and marketing operations in different countries of the world. They possess all the infrastructural facilities in all the countries of their operations.
- Giant Size : The assets and sales of MNC are quite large. The sales turnover of some MNCs extend the gross national product of several developing countries.
- Central ised Control: It has its head office in home country. It exercises control over all-branches and subsidiaries.
- Dominant Position and Status : They occupy a dominant position in the market due to their giant size. They also takeover the firms to acquire huge economic power.
- Internationalised Research and Development: These are intended to capture the quality and serve according to the requirements of the host nation.
- Sophisticated Technology: MNC has advanced technology so as to provide world class products and services. It employs capital intensive technology in manufacturing, marketing and other areas of business.
- Professional Management: A MNC employs professional managers to integrate and manage world wide operations.
Section – C
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions not exceeding 5 lines each.
Question 10.
What is profession ?
Answer:
Profession is an occupation involving the provision of personal services of a specialised and expert nature. The service is based on professional education, knowledge, training etc. The specified service is provided for a professional fees charged from the clients. For example, a doctor helps his patients though his expert knowledge of science of medicine and charges a fee for the service.
Question 11.
What is sole proprietorship ?
Answer:
Sole trade is the oldest and most commonly used form of business organisation. It is also, known as sole proprietorship (or) individual partnership (or) single entrepreneurship. In sole trade concern a single individual introduces his own capital, skill and intelligence in the management of its affairs and is solely responsible for the results of its operations. It is the easiest to form and is also the simplest in organisation.
All that is required is that the individual concerned should decide to carry on particular business and find the necessary capital. For this purpose, he may depend mostly on his own savings or he may borrow part or whole from his friends or relatives. He can start business in his own house or on rented premises. He may run the business on his own ormay obtain the assistance of his family members or paid employees.
A sole trader is a person who sets up the business with his own resources, manages the business himself by employing persons for his help and alone bears all gains and risks of the business.
Question 12.
Define Karta.
Answer:
The senior most male member of the family is Karta. All the affairs of the Joint Hindu Family are controlled and managed by one person. He is known as Karta or Manager. The liability of Karta is unlimited. He acts on behalf of the other members of the family. He is not accountable to anyone.
Question 13.
What is a government company ?
Answer:
A Company in which not less than 51% of the paid up share capital is held by the Central Government or State Government or partly by Central Government and partly by State Government is called Government Company.
e.g.: Hindustan Machine tools, ONGC, NTPC.
Question 14.
What is meant by working capital ?
Answer:
The capital required by business entreprise to run its day-today operations such as purchase of raw material, payment of wages and holding current assets like of raw materials, bills receivable is called working capital. The amount of working capital required varies from business to business. Generally trading concerns require more working capital as compared to manufacturing concerns.
Question 15.
What are retained earnings ?
Answer:
Retained earnings or ploughing back of profits refers to the process of reinvestment of the earning of the year after year. In this technique all the profits are not distributed to shareholders. A part of the profit is retained in the business as a reserve which are used for financing long term and short term needs of the company.
Question 16.
Define service enterprises.
Answer:
Service enterprises : These enterprises involve in providing or rendering service. Service sector may be defined in terms of investment made in equipment.
- A Micro enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment does not exceed ₹ 10 lakhs.
- A Small Enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 10 lakhs but does not exceed ₹ 2 crores.
- A Medium Enterprise is an enterprise where the investment in equipment is more than ₹ 2crores but does not exceed ₹ 5 crores.
Question 17.
What is e-banking ?
Answer:
Electronic banking (e-Banking) is one of the most successful online business. E-Banking allows customers to access their accounts and execute orders through website. Online banking allows the customers to get their money from an Automatic Teller Machines instead of walking upto the cash desk in the bank. The customers can view their accounts, transfer funds and can pay bills.
Ex: Internet banking.
Part – II (50 Marks)
Section – D
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
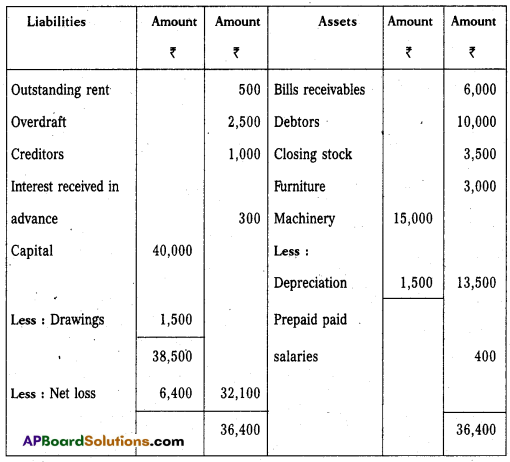
From the following Trail Balance of Ramakrishna Traders, prepare the final accounts for the year ended 31.12.2015.
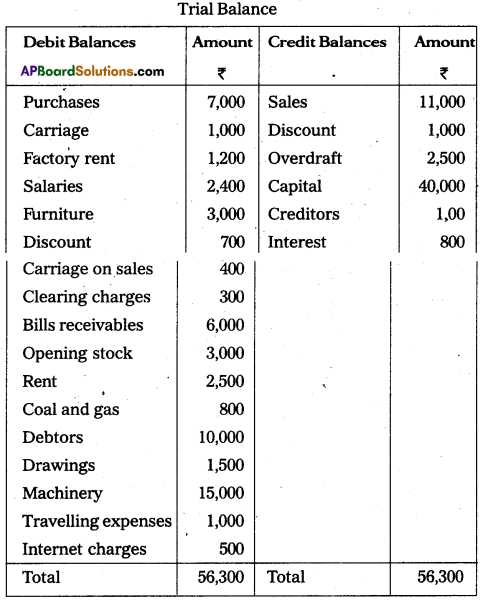
Adjustments:
i) Closing stock value ₹ 3,500.
ii) Outstanding rent ₹ 500.
iii) Prepaid salaries ₹ 400.
iv) Interest received in advance ₹ 300.
v) Depreication on machinery 10%.
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Rama Krishna Traders as on 31.12.2015
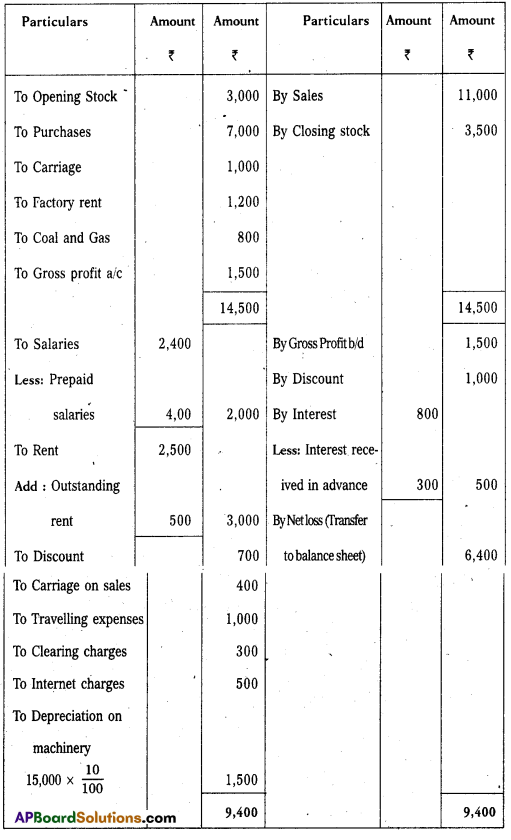
Balance Sheet of Rama Krishna Traders as on 31.12.2015
Section – E
(1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
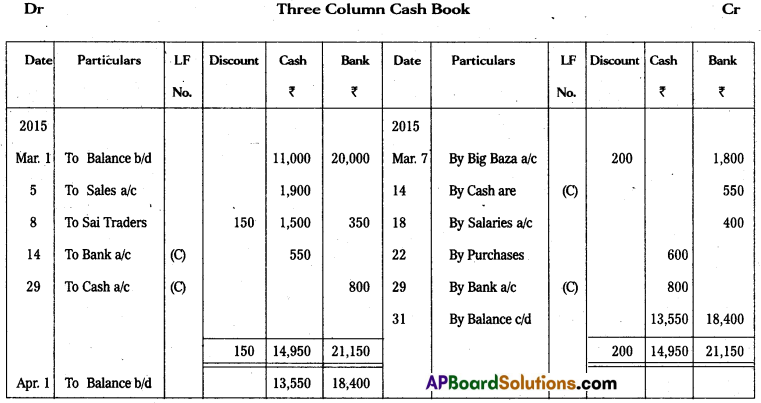
Question 19.
Prepare three column cash book from the following particulars:
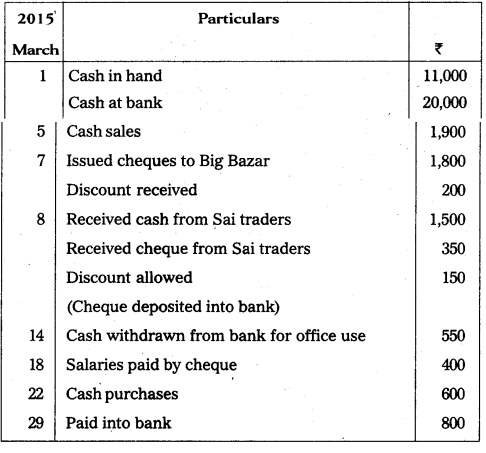
Answer:
Question 20.
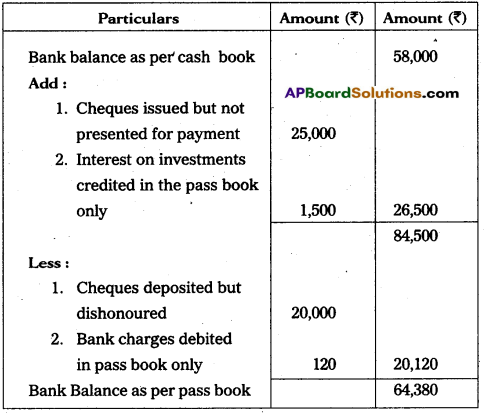
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement of S.V. Traders and find the balance as per the passbook as on 31.12.2015.
i) Cash book balance as on 3 1.12.2015 is ₹ 58,000.
ii) Cheques amounting to ₹ 25,000 issued on 25.12.15 were presented for payment on 5.1.16.
iii) A cheque for ₹ 20,000 deposited on 25.12.15 was returned dishonoured on 8.1.16.
iv) Interest on investments ₹ 1,500 was collected and credited by bank but no entry is in the cashbook.
v) Bank charges debited in passbook only 120.
Answer:
Bank Reconciliation Statement of SN. Traders as on 31.12.2015
Section – F
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
Question 21.
Explain the different types of accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
Answer:
The accounts are broadly divided into two types.
1. Personal Accounts
2) Impersonal accounts.
1. Personal Accounts : These accounts which relate to the persons, group of persons or institutions are called personal accounts. Ex.: Rama’s a/c, Andhra Bank a/c., LIC a/c, Infosys Ltd. The rule in personal accounts is “Debit the receiver and credit the giver”. According to this, benefit receivers account is debited and benefit givers account. According to this, benefit receivers account is debited and benefit givers account is credited.
2) Impersonal accounts : Impersonal accounts are those accounts which are not personal accounts. They are again divided into
i) Real Accounts
ii) Nominal Accounts.
i) Real Accounts : These accounts are related to the assets and properties of the business firm. Ex.: Building, machinery, stock, goodwill etc.
The rule in real accounts is “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”. When an asset is received the asset account is debited and when the asset goes out of the business, the asset is credited.
ii) Nominal Accounts : These accounts relate to expenses, incomes or gains or losses. Ex.: Salary a/c, Rent a/c, Commission received a/c etc.
The rule in nominal accounts is “Debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains”.
![]()
Question 22.
Prepare Jyothi account from the following particulars :
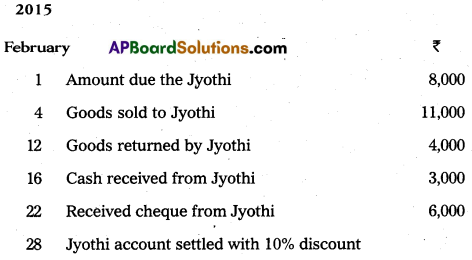
Answer:
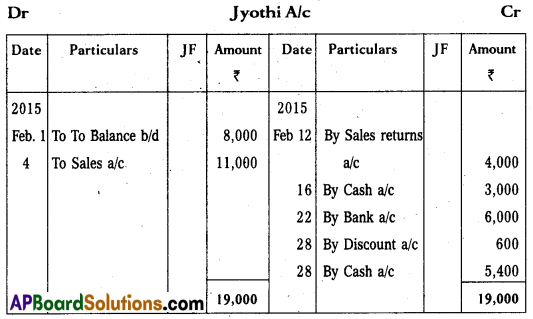
Question 23.
Enter the following transactions in the proper subsidiary books.

Answer:
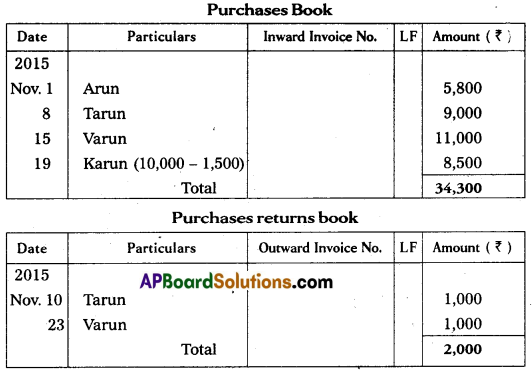
Question 24.
Explain the various types of errors.
Answer:
Errors are classified into two types.
1) Error of principle
2) Clerical errors
1) Error of principle: Error of principle occurs where errors are made due to defective knowledge of accounting principles. These may arise, when distinction is not made between capital and revenue nature items.
2) Clerical errors : When mistake is committed while recording them in the books of original entry or posting them in the ledger is called clerical errors. They are again divided into following types of errors.
a) Errors of omission : These errors occur due to omission of some transactions in any subsidiary books.
b) Errors of commission : These errors arises because of mistakes in calculations, totalling, carry forward or balancing.
c) Compensating errors: These errors arise when one error is compensated by any other error or errors.
Section – G
(5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
Question 25.
What is an accounting cycle?.
Answer:
- Transactions
- Journal
- Ledger
- Trail Balance
- Tradings, Profit and Loss a/c
- Balance sheet
Question 26.
Explain money measurement concept.
Answer:
While recording the business transactions we do not record them in terms of kgs, metres, litres etc. We record them in a common denomination so as to see that they become homogeneous and meaningful. Money does this function. It is adopted as the common measuring unit.
Question 27.
What is posting ?
Answer:
Posting is the process of entering in the ledger the entries given in the journal. Posting into the ledger is done periodically, may be weekly or fortnightly as per the convenience of the business.
Question 28.
What is imprest system ?
Answer:
Under imprest system, the petty expenditure for period, say a week or a month, is estimated and a cheque for an equal amount is issued to petty cashier. All the payments made by the petty cashier are recorded in the petty cash book. Periodically, say a week or a month, a copy of it (petty cash book) is submitted to the head cashier along with concerned vouchers by the petty cashier. After verifing all the vouchers, the head cashier, issues a cheque equals to the amount spent by the petty cashier in that period. This cheque amount and the balance with petty cashier becomes the opening balance for the next period.
![]()
Question 29.
What is meant by BRS ?
Answer:
A bank reconciliation statement is a statement prepared at periodical intervals indicating the various items, that cause the disagreement between bank balance as per cash book and as per pass book on any given date.
Question 30.
Journalise the following transactions.

Answer:
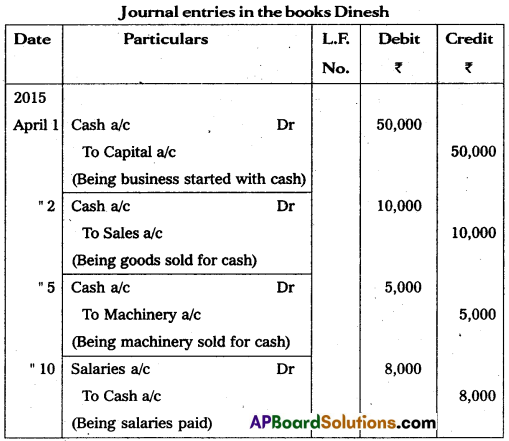
Question 31.
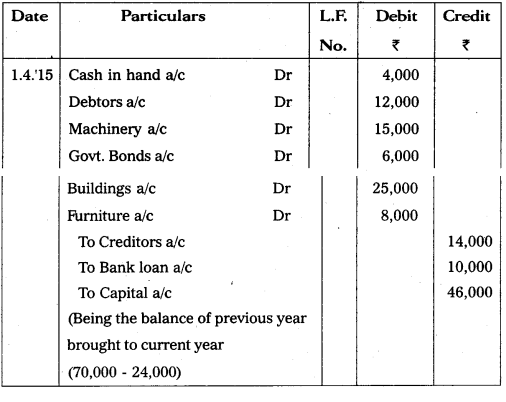
Write the opening entry as on 1.4.2015 from the following Particulars :
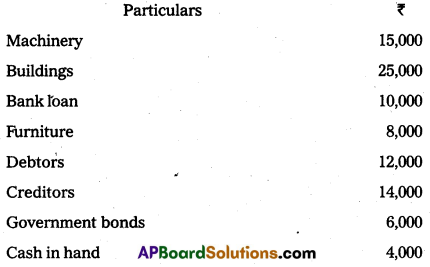
Answer:
Question 32.
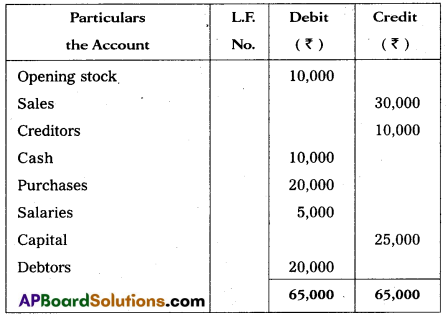
Prepare a Trial Balance of Satish from the following as on 31.12.15.
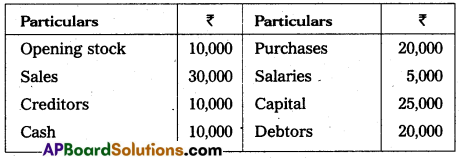
Answer:
Trial Balance of Satish as on 31.12.2015