These TS 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics will help the students to improve their time and approach.
TS 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Question 1.
Can you name some objects made of metals?
Answer:
Platinum jewellery, gold Iewellerv, silver ornaments, silver plates, silver bangles, iron machinery, iron cots, iron tables, copper boilers, copper wires, aluminium cookers, aluminium cooking ware, aluminium cables, tungsten filament. iron rails, iron ships, anchors, mercury thermometers, etc. There are a number of objects made of metals and alloys of metals.
Question 2.
Observe the fig. Try to name the metals of which the objects are made. Add names of more metals that you know to the list.
Answer:
- The jewellery is made of silver and gold.
- The ‘avatar bucket is made of aluminium.
- The spade is made of iron. Some other metals: Copper. tin, zinc, calcium, mercury, lead, platinum, magnesium, etc.

Question 3.
a) Did any of your friends add steel to the list of metals?
b) Do you think that steel is a metal?
Answer:
a) No.
b) Steel is not a pure metal. It is a mixture of some metals and non-metals. It mainly contains iron, The other metals can be nickel, chromium, manganese, etc. The non-metals can be carbon, phosphorus. etc. So steel is called an alloy. It is a mixture of metals or a mixture of metals and non-metals.
Question 4.
Why are wooden bells not used In temples?
Answer:
Bell should be sonorous to hear sound. So it must make with metal not with wood. Because wood is not sonorous.
![]()
Question 5.
Do all materials produce sound when they dropped on hard surface?
Answer:
No, all materials did not produce sound when they dropped on hard surface. Only most of the materials are sonorous.
Question 6.
We use wires in different situations in our daily life. Look at the samples given in the table.
Have you ever seen the wires made up of materials mentioned in table. Write yes if you have seen wires made of them elsewhere.
Table
| Sample | Wires (Yes/No) |
| Iron | Yes |
| Zinc | No |
| Copper | Yes |
| Sulphur | No |
| Aluminium | Yes |
| Graphite | No |
| magnesium | Yes |
| Iodine | No |
Question 7.
Is ductility the only property of metal to use them as connecting wires In electric circuits?
Answer:
- No.
- The metal should be a very good conductor of electricity.
- The metal should also be not too costly.
Note: Tungsten is a metal. It is highly ductile. But it is a poor conductor of electricity. So this metal is not used as connecting wire in electric circuits.
Electrical Conductivity:
Question 8.
You might have seen an electrician while using his screwdriver. What materials does it contain?
Answer:
Iron and wood/plastic.
Question 9.
Why does not screwdriver used by electricians has metal handle?
Answer:
Metals are good conductors of electricity, So while using the screwdriver, if it touches a live wire, electricity passes into his body through the handle. It is dangerous to him. So to prevent such a possibility, handles of screwdrivers are made of a non-conducting material like wood or plastic.
Question 10.
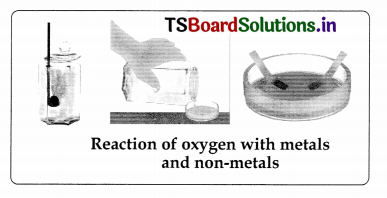
Conduct an experiment to know the reaction of oxygen with metals and non-metals.
Answer:
Aim: To know the reaction of oxygen with metals and non-metals Material required: Two metals samples (copper and magnesium) and one non-metal sample (sulphur), spirit lamp or bunsen burner and litmus papers, etc.
Procedure:
i. Take a piece of copper wire. If the wire is covered with plastic then remove it with sandpaper or pliers. Note the colour of the wire. Hold the wire with a pair of tongs and heat it for some time over a spirit lamp or bunsen burner. Cool the wire and note the colour.
ii. Take a small strip of magnesium and note its appearance. Burn it. Collect the ashes of magnesium in a test tube and add some distilled water to it. Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
iii. Take a small amount of powdered sulphur in a deflagrating spoon and heat it. As soon as sulphur starts burning introduce the spoon into a gas jar tumbler. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time but try to keep the jar covered. Add a small quantity of avatar into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well. Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
![]()
iv. Note the results of above activities in a table.
| Sample | Appearance before reaction | Appearance after reaction | Effect on moist litmus paper |
| Copper | shiny, reddish brown | Black powder, Coating | |
| Magnesium | Silvery white | White ash | Red → Blue |
| Sulphur | Yellow | Colourless gas | Blue → Red |
From these activities, we can conclude that
a. Non-metals react with oxygen to give out oxides that are acidic in nature.
b. Metals react with oxygen to give out oxides that are basic in nature.
Question 11.
What is happening in the above experiment?
Answer:
1. When we burn the samples, they react with the oxygen in air to give different products.
Copper + oxygen → Copper oxide
Magnesium + oxygen → Magnesium oxide
Sulphur + oxygen → Sulphur dioxide.
2. Each oxide is shaken separately with a little water in a test tube. Except copper oxide, the remaining two oxides dissolve in water. Solutions are formed.
3. Magnesium oxide turns red litmus, and blue. So the solution is basic. Hence magnesium is a metal. Sulphur dioxide turns blue litmus, red, so the solution is acidic. Hence sulphur is a non-metal. Copper oxide is not soluble in water.
Question 12.
Reaction with Acids Take the samples given in the below table in separate test tubes. Add
5 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid to each of the test tubes with the help of a dropper. Observe the reactions. If you find no reaction, heat the test tube gently.
If you still see no reaction, add 5 drops of Conc. Hydrochloric acid. Now bring a burning match stick near the mouth of the test tube and observe what happens. Record your observations in the table.
Table
| Sample | Reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid | Reaction with dilute sulphuric acid |
| Iron | A pop sound | Do |
| Zinc | A pop sound | Do |
| Copper | No pop sound | No pop sound |
| Sulphur | No pop sound | No pop sound |
| Aluminium | Pop Sound | No pop sound |
| Graphite | No pop sound | Do |
| Magnesium | Pop sound | Pop sound |
| Iodine | No pop sound | Do |
Questions based on the above experiment
a. Do non-metals react with water?
Answer:
Non-metals generally do not react with water.
b. Do you find any difference in these reactions?
Answer:
A pop sound indicates the presence of hydrogen gas.
c. When do you notice a pop sound with a burning matchstick?
Answer:
A pop sound is produced when there is hydrogen gas.
(Reason: The hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas of air at that temperature. Water vapour forms. Then energy liberates. This liberated energy appears as sound).
Question 13.
Take five beakers and label them a, b, c, d and e. Take 50m1 of water in each beaker and dissolve a spoonful of copper sulphate in a and b beakers each. Dissolve a spoonful of zinc sulphate, iron sulphate and zinc sulphate each in c, d and e beakers.
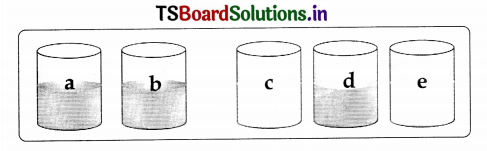
Now put:
- Zinc granules in beaker ‘a’
- Iron nails in beaker ‘b’
- Copper turnings in beaker ‘c’
- Copper turnings in beaker ‘d’
- Iron nails in beaker ‘e’
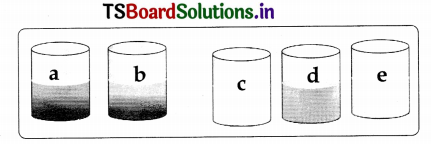
Leave the beakers undisturbed. Record the changes in the colour of the solutions in the table below.
Table
| Solutions | Observations |
| Beaker ‘a’ | A red mass of copper deposits at the bottom of the beaker |
| Beaker ‘b’ | Do |
| Beaker ‘c’ | No change |
| Beaker ‘d’ | No change |
| Beaker’e’ | No change |
a. What could be the reasons behind these changes?
Answer:
In beaker a, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate. Then copper deposits. Zinc sulphate is formed. Copper sulphate + Zinc → Zinc sulphate + Copper↓.
In beaker ‘b, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. Then copper deposits. Iron sulphate is formed.
Copper sulphate + Iron → Iron sulphate + Copper ↓.
No reactions occur in the remaining beakers c, d and e.
Question 14.
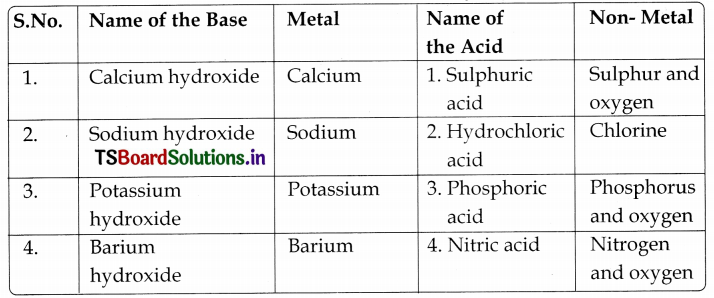
Recall the names of the some of the laboratory acids and bases that you know. Write down their names and identify metal/non-metal present In them, which form oxides when react with oxygen. Take the help of your teacher.
Question 15.
Try to find the metals and non-metals that you came across in the chapter on the periodic table.
Answer:
Periodic table is a table showing the classification of elements in rows and columns. Rows are called as periods. Columns are called as groups. Metals and non-metals arc not separated in this table. We find metals sodium and potassium in the first group. calcium, magnesium in second group and aluminium in the thirteenth group.
We find non-metals carbon in 14 group nitrogen. phosphorous in 15 groups. oxygen, sulphur in 16 groups. From this, we can say that metallic property decreases from left to right of the periodic table.
![]()
Question 16.
Recall the names of the some of the laboratory acids and bases that you know. Write down their names and identify metal/non-metal present in then which form oxides, when react with oxygen. Take the help of your teacher.
Answer:
Laboratory acids:
| Name | Symbol | Non-metal present in it |
| 1. Hydrochloric acid | HCl | Chlorine |
| 2. Sulphuric acid | H2SO4 | Sulphur |
| 3. Nitric acid | HNO3 | Nitrogen |
| 4. Phosphoric acid | H3PO4 | Phosphorus |
| 5. Carbonic acid | H2CO3 | Carbon |
Laboratory bases:
| Name | Symbol | Metal present in it |
| 1. Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | Sodium |
| 2. Magnesium hydroxide | Mg(OH)2 | Magnesium |
| 3. Calcium hydroxide | Ca(OH)2 | Calcium |
| 4. Zinc hydroxide | Zn(OH)2 | Zinc |
| 5. Potassium hydroxide | KOH | Potassium |
Question 17.
Which substance liberates hydrogen when reacts with metals?
Answer:
Metals react with acids, liberating hydrogen gas.
Eg: Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride’ Hydrogen.
Mg + 2 HCl → MgCl2 + H2 (g)
Question 18.
Discuss the acidic and basic nature of the metals and non-metals with suitable experiments.
Answer:
Basic nature of metals
- A piece of magnesium (a metal) wire is held with tongs.
- It is burnt to ash on a bunsen flame.
- The ash is shaken well with a little distilled water. It dissolves slightly. A solution is formed.
- This solution is tested both, with red and blue litmus papers.
- The solution turned red litmus, blue. So the solution is basic. This shows that metals are basic in nature.
Acidic nature of non-metals:
- A small amount of powdered sulphur (a non-metal)is taken in a deflagrating spoon.
- The spoon is heated Sulphur starts burning.
- The spoon is noise introduced into a gas jar. The jar is covered with a lid so that the gas does not escape out.
- The spoon is removed after some time, keeping the jar always covered.
- A small quantity of water is added into the jar and the lid is replaced quickly.
- The jar is shaken well. Then the gas dissolves in water, A solution is formed.
- The solution is tested, both with the red and blue litmus papers.
- Blue litmus turned red. So the solution is acidic. This shows that non-metals are acidic in nature.

diagrams
1.

2.
3.
Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Phosphorus is stored in ( )
A) kerosene
B) petroleum
C) water
D) none
Answer:
C) water
Question 2.
Sodium is stored in ( )
A) kerosene
B) water
C) none
D) acids
Answer:
A) kerosene
Question 3.
Metals generally react with acids and produce the gas ( )
A) O2
B) N2
C) H2
D) none
Answer:
C) H2
![]()
Question 4.
The non-metal used in the purple-coloured solution which is applied on wounds as an antiseptic is ( )
A) nitrogen
B) bromine
C) iodine
D) none
Answer:
C) iodine
Question 5.
Chlorophyll, the green colouring material in plants contains the metal ( )
A) calcium
B) magnesium
C) zinc
D) none
Answer:
B) magnesium
Question 6.
The haemoglobin of blood contains the metal ( )
A) calcium
B) magnesium
C) iron
D) none
Answer:
C) iron
Question 7.
Copper sulphate + Zinc → Zinc sulphate + Copper. This is a ……… reaction. ( )
A) combination
B) double decomposition
C) displacement
D) decomposition
Answer:
C) displacement
Question 8.
The best conductor of electricity is ( )
A) aluminium
B) copper
C) gold
D) silver
Answer:
D) silver
Question 9.
Metals are electropositive in nature. They show a tendency to form.( )
A) anions
B) cations
C) anions or cations
D) none
Answer:
A) anions
Question 10.
Metals have generally ………………. valency electrons. ( )
A) a large number
B) a few
C) eight
D) no
Answer:
C) eight
Question 11.
The liquid metal used in clinical thermometers is ( )
A) bromine
B) water
C) mercury
D) glass
Answer:
C) mercury
Question 12.
In the vulcanisation (hardening) of rubber the non-metal used is ( )
A) carbon
B) phosphorus
C) sulphur
D) iron
Answer:
C) sulphur
![]()
Question 13.
Tungsten is used as filament in ‘filament bulbs because the metal is( )
A) a good conductor of electricity
B) a poor conductor of electricity
C) cheap
D) sonorous
Answer:
A) a good conductor of electricity
Question 14.
Aluminium oxide is an ( )
A) acidic oxide
B) basic oxide
C) amphoteric oxide
D) black in colour
Answer:
C) amphoteric oxide
Question 15.
Rust is ( )
A) ferric oxide
B) hydrated ferric oxide
C) a non-metal
D) a pure metal
Answer:
A) ferric oxide
Question 16.
Noble gases have …………. electrons in their valence shell. So they are least reactive. ( )
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
Answer:
D) 8