Students can go through AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Notes 4th Lesson Union Legislature will help students in revising the entire concepts quickly.
AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Notes 4th Lesson Union Legislature
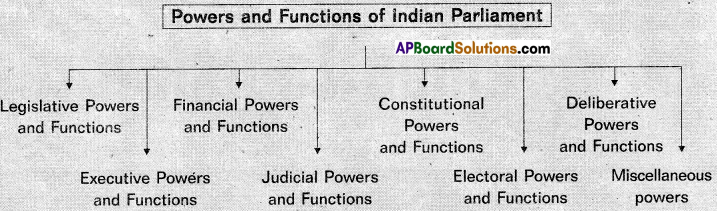
→ Indian Constitution provided Parliamentary System to our country.
→ Indian Parliament is Bi-cameral. It consists of two Houses.
- Rajya Sabha
- Lok Sabha.
→ The Lok Sabha is the Lower House. Rajya Sabha is the Upper House.
→ The Lok Sabha meets at least twice in a year.
→ The Speaker presides over the meetings of Lok Sabha.
→ The Lok Sabha enjoys superior powers in money matters.
→ There are many committees in our Parliament. They act as advisory bodies to the Parliament.
![]()
→ There will be a Chairman and Deputy Chairman for the Rajya Sabha.
→ The Vice President of India is the Ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha.
→ The Rajya Sabha gives representation to the States. It is also known as ‘The Council of States’.
→ The members of Parliament enjoy certain privileges.
→ Bills passed by the Parliament are of two types
- Public bills
- Private bills.
→ Ordinary bills can be introduced in any house of the Parliament.
→ Money bills shall be introduced only in Lok Sabha.
→ All the bills approved by the Union Legislature become Laws only with the assent of the President.
Synopsis
- The Union Legislature (Parliament) is the highest Legislative organ of the Union Government.
- The Union Legislature is bicameral legislature in structure.
- The Lok Sabha is popularly known as the House of the people or the Lower House.
- Rajya Sabha is known as the Council of States or the Upper House.
- The Vice-President of India acts as the Ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
- The Union Legislature has some nominated members in both the houses.
- The Constitution provides for a speaker for Lok Sabha.
- The President is not a member of the Parliament but he is regarded as integral part of the Parliament.
- The Legislative procedure ¡s identical in both the Houses of the Parliament.
- The Primary function of the Parliament is to make laws for the governance of the country.
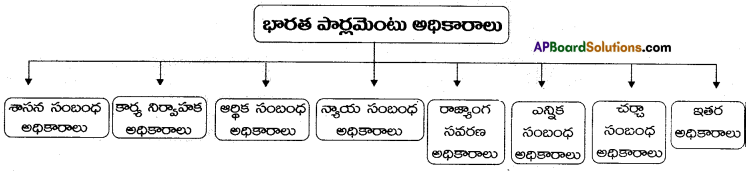
→ భారత రాజ్యాంగం పార్లమెంటరీ పద్ధతిని సూచించింది. భారత పార్లమెంటులో రెండు సభలు కలవు. అవి :
1) లోక్సభ 2) రాజ్యసభ.
→ పార్లమెంటులో లోక్ సభ దిగువసభ. రాజ్యసభ ఎగువసభ.
→ లోక్సభ సంవత్సరానికి కనీసం రెండుసార్లు సమావేశమవుతుంది.
→ లోక్సభ సమావేశాలకు స్పీకర్ అధ్యక్షత వహించును.
→ ఆర్థిక విషయాలలో లోకసభకే ఎక్కువ అధికారాలు ఉన్నాయి.
→ పార్లమెంటులో కొన్ని ముఖ్యమైన కమిటీలు కలవు. అవి పార్లమెంటుకు సలహా సంస్థలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి. ఉదా : అంచనాల కమిటీ, పబ్లిక్ అకౌంట్సు కమిటీ, ప్రభుత్వ రంగ సంస్థల కమిటీ, సభా కార్యక్రమాల సలహా కమిటీ, నిబంధనల కమిటీ మెదలగునవి ముఖ్యమైనవి.
→ రాజ్యసభ సమావేశాలను నిర్వహించడానికి ఒక ఛైర్మన్, డిప్యూటీ చైర్మన్ ఉంటారు.
→ ఉపరాష్ట్రపతి రాజ్యసభ ఛైర్మన్గా వ్యవహరించును.
![]()
→ రాజ్యసభ రాష్ట్రాలకు ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహించును. రాజ్యసభను “క్రాస్ ఆఫ్ స్టేట్స్” అని కూడా అంటారు.
→ పార్లమెంటు సభ్యులకు ప్రత్యేక హక్కులు ఉన్నాయి.
→ పార్లమెంటు రూపొందించే బిల్లులు ప్రధానంగా రెండు రకాలు. అవి :
- పబ్లిక్ బిల్లులు
- ప్రైవేట్ బిల్లులు.
→ సాధారణ బిల్లులను ఏ సభలోనైనా ప్రవేశపెట్టవచ్చును.
→ ఆర్థిక బిల్లులను ముందుగా లోక్సభలోనే ప్రవేశపెట్టాలి.
→ రాష్ట్రపతి ఆమోదం పొందిన తరువాతనే బిల్లులు చట్టాలుగా మారుతాయి.