Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions 6th Lesson Biology in Human Welfare which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions 6th Lesson Biology in Human Welfare
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define parasitism and justify this term.
Answer:
- Parasitism is intimate association of two individuals of which one is benefited (parasite) and the other is harmed (host).
- Parasitism means one eating at another ones table.
- Justification; Plasmodium lives as a parasite in humans (Host).
- Then Plasmodium is benefited and human is harmed.
Question 2.
Distinguish between facultative parasite & obligatory parasite.
Answer:
| Facultative parasite | Obligatory parasite |
| 1) A parasite which can survive w ith (or ) without host is called facultative parasite. 2) It can even survive without host. 3) Ex: Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
1) A parasite which is completely dependent on its host is called obligatory parasite 2) It cannot survive without host. 3) Ex: Plasmodium vivax. |
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish between Definitive host & Intermediate host.
Answer:
| Definitive host | Intermediate host |
| 1) It is the host in which parasite undergoes development (or) sexual maturity (or) sexual reproduction. 2) It is a primary host. 3) Ex : Man for wuchereria bancrofti, female anopheles for plasmodium. |
1) It is the host in which parasite undergoes larval (or)immature (or) asexual reproduction. 2) It is a secondary host 3) Ex : Man for plasmodium, female culex for wuchereria |
Question 4.
Distinguish between vector and a reservoir host.
Answer:
| Vector | Reservoir |
| 1) Vector is an organism that transfers the infective stages of a parasite from one host | 1) Reservoir is the host that lodges the parasitic stages without getting infection. |
| 2) Ex: Houseflies, Cockroaches. | 2) Ex: Monkey for plasmodium, African antelope for Trypanosoma |
Question 5.
Distinguish between mechanical vector and biological vector.
Answer:
| Mechanical vector | Biological vector |
| 1) Mechanical vector is a simple carrier of infective stage of parasite. 2) Ex:Housefiles and Cockroaches for Entamoeba. |
1) Biological vector is an organism in which part of life cycle of parasite takes place. 2) Ex: Female culex for wuchereria |
Question 6.
What is a hyper-parasite? Mention the name of one hyper-parasite. [TS M-22]
Answer:
- A parasite which lives on the body of the another parasite is called hyper- parasite.
- Ex: Nosema notabilis is parasite on sphaerospora polymorpha which is a parasite in the urinary bladder of toad fish.
Question 7.
What do you mean by parasitic castration? Give one example.! APM~I7,20|[TSM-16,20|
Answer:
- Degeneration of gonads of the host due to presence of a parasite is called parasitic castration.
- Ex: Sacculina (a crustacean parasite) causes degeneration of ovaries in the crabs.
Question 8.
What are the ‘parasite adaptations’ observed in Ascaris lumbricoides?
Answer:
Parasite adaptations in Ascaris:
- Ascaris develops a ‘protective cuticle’ to withstand the action of the digestive enzymes of the host.
- It lives as a facultative anaerobe. It lives as anaerobic form in the absence of oxygen and in aerobic form in the presence of oxygen.
- Ascaris produces a large number of eggs nearly 2,00,000 per day. This is to ensure that the infection of the parasite to definite host and also to perpetuate their races.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the endo-parasitic adaptations observed in Fasciola hepatica?
Answer:
The endoparasitic adaptations in Fasciola hepatica (sheep liver fluke) are:
- Two Suckers (one oral, another ventral)
- Protective cuticle
- Reproductive system is highly developed.
- Life cycle is complex with many larval stages, (miracidium, sporosyst, redia, cercaria)
- Polyembryony
Question 10.
Define neoplasia. Give one example. [TS M-22J [AP M-19,22]
Answer:
- Neoplasia: Abnormal growth of the host cells in a tissue to form new structures is called neoplasia. Some times it leads to cancer.
- Ex: Carcinoma caused by virus.
Question 11.
Define the most accurate definition of the term ’health’ and write any two factors that affect the health.
Answer:
1) Health is state of complete physical, mental and social well being, not merely absence of any disease or absence of physical fitness.
2) The factors affect that health are
- Genetic disorders
- Infections
- Life style
Question 12.
Distinguish between infectious and non-infectious diseases. Give two examples each.
Answer:
1) Infectious diseases: The diseases that are easily transmitted from one person to other are called infectious diseases. They are caused by pathogens.
Ex: Amoebic dysentery, Malaria, Typhoid, Common cold, Ringworm etc.
2) Non-infectious diseases: The diseases that are not transmitted from one person to other and not caused by pathogens.
Ex: Heart problems, Kidney problems and genetic disorders.
Question 13.
When can you diagnose a healthy person as unhealthy?
Answer:
A healthy person is treated as an unhealthy person when
- The functioning of one (or) more organs (or) system of the body is adversely affected.
- The disease is characterized by various signs & symptoms.
Question 14.
Write any two diagnostic features of trophozoite of Entamoeba histolytica?
Answer:
Diagnostic features of trophozoite of Entamoeba:
- Presence of cart wheel shaped nucleus
- Food vacuoles with RBC.
Question 15.
‘Entamoeba histolytica is an obligatory anaerobe’. Justify.
Answer:
Entamoeba histolytica is an intestinal parasite causing amoebic dysentery. Mitochondria are not present in their body. Oxygen is not available in intestine of man, so they are obligate anaerobes.
Question 16.
Distinguish between precystic stage and cystic stage of E.histoiytica,
Answer:
| Precystic stage | Cystic stage |
| 1)It is spherical, non-motile form. Not , surrounded by cystic wall. 2) It has single nucleus, which doesnot undergo any division. |
1) It is round and surrounded by delicate thin walled resistant cyst wall. 2) Its nucleus undergoes successive mitotic divisions. |
Question 17.
What is the reserve food in the precystic and early cyst stages of Entamoeba histolytica?
Answer:
Glycogen and chromatoid bars are reserve food of cystic and precystic stages of Entamoeba histolytica.
Question 18.
What is a metacystic form with reference to Entamoeba histolytica?
Answer:
The excysted tetranucleated Entamoeba in the luman of the small intestine is called metacystic form.
![]()
Question 19.
A person is suffering from bowel irregularity, abdominal pain, blood and mucus in stool, etc., Based on these symptoms, name the disease and its causative organism. [TS M-15]
Answer:
- The disease showing the given symptoms is amoebic dysentery.
- The causative organism is Entamoeba histolytica.
Question 20.
On the advice of a doctor, a patient has gone to a clinical laboratory for the examination of a sample of faeces. The lab technician, on observing the stool of the patient diagnosed that the patient was suffering from amoebiasis. Write any two characteristic features based on which the technician came to that conclusion.
Answer:
Amoebiasis indicators in stools are (i) Tetranucleate cysts (ii) Blood corpuscles.
Question 21.
Define ‘asymptomatic cyst passers’ with reference to Entamoeba histolytica.
Answer:
Asymptomatic cyst passers are people who lodge the parasite ‘Entamoeba histolytica’ in their intestine without exhibiting any symptoms of amoebiasis. They are just carriers.
Question 22.
Distinguish between primary amoebiasis and secondary amoebiasis?
Answer:
| Primary amoebiasis | Secondary amoebiasis |
| 1) Formation of abscesses in the wall of ‘large intestine’ results in stool with blood and mucous. 2) It is also known as ‘amoebic dysentry’ or ‘intestinal amoebiasis’. 3) Symptoms : Stool with tetranucleate cysts. |
1) Trophozites enter the blood stream by repturing the wall of capillaries and reach the liver to cause abscesses. 2) It is also known as ‘extra – intestinal amoebasis’. 3) Symptoms: Heart, lungs, brain, kidneys, gonads etc., exhibit abscesses in their parts. |
Question 23.
What are the stages of Plasmodium vivax that infect the hepatocytes of man?
Answer:
The stages of plasmodium that infect liver cells are (i) sporozoites (ii) Cryptozoites
Question 24.
What are the stages of plasmodium vivax that infect the RBC of the intermediate host?
Answer:
The stages of plasmodium vivax that infect the RBC of the intermediate hosts are
- Cryptozoites (or) 1st generation merozoites.
- Micro – meta cryptozoites
- Hypnozoites
Question 25.
Define prepatent period. What is its duration in the life cycle of plasmodium vivax?
Answer:
- Prepatent period: The duration between first entry of sporozoites into blood and second entry in the form of cryptozoites is called prepatent period.
- The duration of life cycle of plasmodium vivax is nearly 8 days.
![]()
Question 26.
Define incubation period. What is its duration in the life cycle of plasmodium vivax?
Answer:
- Incubation period: The period between the entry of sporozoites into blood of a man and appearance of clinical symptoms of malaria is called incubation period.
- Its duration is about 10-14 days.
Question 27.
What are Schuffner’s dots? What is their significance?
Answer:
- Schuffner’s dots are small red coloured dots, appear in the cytoplasm of RBC when the parasite is in schizont stage of erythrocytic cycle.
- They are supposed to be the antigens released by plasmodium. The parasite develops immunity against these antibodies.
Question 28.
What are haemozoin granules? What is their significance?
Answer:
- The malaria parasite digests the globin part of the ingested haemoglobin and converts the soluble haem into an insoluble crystalline haemozoin granules.
- When erythrocyte bursts, haemozoin is released into blood, it causes malaria fever.
Question 29.
Distinguish between schizogony and sporogony?
Answer:
| Schizogony | Sporogony |
| 1) In the life cycle of plasmodim in man, the asexual reproduction is called schizogony. 2) It occurs both in liver cells and RBC. |
1) In the life cycle of plasmodium in mosquitoes the formation of sporozoites in the oocysts is called sporogony. 2) It occurs in stomach wall of female Anopheles mosquito. |
Question 30.
What is exfiagellation and what are the resultant products called?
Answer:
- Exfiagellation: The process of liberation of male gametes from the cytoplasm of microgametocyte by exhibitting lashing movements like flagella is called exfiagellation.
- The resultant products are called male gametes.
Question 31.
Why is the syngamy found in Plasmodiu m called anisogamy?
Answer:
- In plasmodium, the male and female gametes are dissimilar in size.
- Hence, the process of fusion is called Anisogamy.
Question 32.
What is ookinete? Based on the ‘sets of chromosomes’ how do you describe it?
Answer:
- Long, slender, motile vermiform structure of Plasmodium formed in the lumen of crop of female Anopheles mosquito during sexual life cycle of plasmodium is called ookinete.
- Ookinete is a diploid stage which contains two sets of chromosomes.
Question 33.
What is tertian fever, with reference to the types of malaria you have learnt about? Give the name of the causative species of the pathogens concerned?
Answer:
Tertian fever: A fever which occurs on every third day is called ‘Tertian fever’.
Causative species of pathogens and types of malaria:
a) Plasmodium vivax causes ‘Benign tertian malaria’.
b) Plasmodium falciparum causes ‘Cerebral malaria’ (or) ‘Malignant tertian malaria’.
c) Plasmodium Ovale causes ‘Mild tertian malaria’.
d) Plasmodium malariae causes ‘Quartan malaria’.
Question 34.
What is the significance of hypnozoites with reference to malarial fever?
Answer:
- Significance: Initiating fresh erythrocytic cycle is the significance of hypnozoites with respect to malaria. This is referred as ‘relapse of malaria’
- Hypnozoites are the ‘dormant stage’ of the macro-meta cryptozoites.
- These may survive for a long period in liver
Question 35.
A person is suffering from chills and shivering and high temperature. These symptoms are cyclically followed by profuse sweating and return to normal body temperature. Based on these symptoms, name the disease and its causative organism.
Answer:
The disease is malaria. The causative organism is plasmodium.
Question 36.
Describe the methods of biological control of mosquitoes.
Answer:
Methods of Biological control of mosquitoes:
- Spraying insecticides like DDT, BHC at mosquito breeding places.
- Introduction of larvivorous fishes like Gambusia.
- Introduction insectivorous plants like utricularia.
- Spraying of kerosene, pyrethrum oil on stagnant waters.
![]()
Question 37.
The eggs of Ascaris are called ‘mammillated eggs’. Justify. [AP,TS M-19]
Answer:
The eggs of Ascaris have a protein outer coat which has papillae hence looks rippled. So it is called mamillated egg.
Question 38.
Write the route of extra intestrial migration followed by the juveniles of Ascaris lumbricoides.
Answer:
Small intestine → Hepatic portal vein → Liver → Post caval vein → dieart → pulmonary arteries→Lungs → Bronchi → trachea → daiynx → glottis → pharynx → oesophagus → stomach → Small intestine.
Question 39.
Write any two difference between male and female worms of Wuchereria bancrafti
Answer:
| 1) It is shorter than female. | 1) It is longer than male. |
| 2) It’s posterior end is curved with a cloacal aperture. | 2) It’s posterior end is straight with Anus. |
| 3) A pair of unequal, chitinous copulatory spicules are present | 3) ‘Pineal Spicules’ or ‘Copulatory species’ are absent. |
Question 40.
What is meant by nocturnal periodicity with reference to the life history of a nematode parasite you have studied? [TS Mar, May-17) |AP M-15|
Answer:
Migration of sheathed microfilaria larva from deeper vessels to peripheral blood vessels during night sleeping time between 10.00 PM and 4 AM is referred to as nocturnal periodicity.
Question 41.
Distinguish between lymphadenitis and lymphangitis?
Answer:
- Inflammation of lymph glands is Lymphadenitis.
- Inflammation of lymph vessels is known as Lymphangitis.
Question 42.
‘Elephantiasis is the terminal condition of filariasis’. Justify.
Answer:
Elephantiasis is caused by filarial parasite. It is the last stage of the disease.
The stages are
- Headache, depression and rise of temperature.
- Lymphangitis.
- Lymphadenitis.
- Blocking of lymph vessels.
- Elephantiasis is the ultimate stage.
Question 43.
Mention the pathogens that cause ringworm.
Answer:
- Ringworm is an infectious disease in man caused by fungi.
- The pathogens that cause ring worm are Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton.
Question 44.
Explain any three preventive measures to control microbial infections.
Answer:
Preventive measures to control microbial infections:
- Immunization by using vaccines. This eradicates diseases like small pox, polio, diptheria, pneumonia & tetanus.
- Use of antibiotic and other drugs to treat infectious diseases effectively.
- Use of newer and safer vaccines developed by biotechnological methods.
Question 45.
Maintenance of personal and public hygine is necessary for prevention and control of many infectious disease”. Justify the statement giving suitable examples.
Answer:
- Use of ‘boiled and filtered water’ prevents some infectious disease like cholera.
- Washing hands, fruits and vegetables properly prevent infectious diseases like ascariasis, amoebiasis.
- Using septic tank toilets prevents ‘Amoebiasis’.
Question 46.
Diseases like amoebic dysentery, ascariasis, typhoid etc are more common in over crowded human settlements. Why?
Answer:
- In over crowded human settlements the given diseases spread easily due to poor sanitation.
- Drinking water is only available from water sources like tanks, lakes and ponds where cleaning of cattle, washing of clothes is also done.
- Due to these conditions the contaminated water, food and air spread the diseases like typhoid, ameobic dysentery and Ascariasis.
Question 47.
In which way does tobacco affect the respiration? [AP May-17]
Name the alkaloid found in tobacco.
Answer:
- Tobacco effects the respiration because when tobacco is smoked then smoking increases the carbon monoxide level and reduces the oxygen level in the blood.
- Alkaloid found in tobacco is Nicotine.
![]()
Question 48.
Define drug abuse. [AP M-22]
Answer:
- Drug abuse is taking of a drug in excess for a purpose other than its medicinal use.
- It leads to physical, psychological disturbances. Sometimes irrepairable damage to the body.
Question 49.
From which substances ‘Smack* and ‘Coke’ are obtained? [AP M-16]
Answer:
- Smack (Heroin) is obtained by the acetylation of morphine.
- Coke (Crack) is obtained from Cocaine.
Question 50.
‘Many secondary metabolites of plants have medicinal properties. It is their misuse that creates problems’. Justify the statement with an example.
Answer:
- Secondary metabolites show various medicinal properties.
- When they are misused, they can create problems in physical or psychological functions of the person leading to mental illness like depression, insomnia etc.
Question 51.
Write the scientific names of any two plants with hallucinogenic properties.
Answer:
- Atropa belladonna & Datura
- Erythroxylum coca
Question 52.
Why are cannabinoids and anabolic steroids banned in sports and games?
Answer:
- Cannabinoid and anabolic drugs are called steroid drugs.
- They mimic the effect of testosterone and dihydro testosterone. They increase protein synthesis which develop muscular tissue enhancing the performance of sportsmen. So they are banned.
Question 53.
Mention the names of any four drugs which are used as medicines to treat patients with mental illness like depression, insomnia, etc. that are often abused.
Answer:
Drugs used to treat mental illness are
- Lysergic acid diethyl amide(LSD)
- Benzpdiazepines(tranquilizers)
- Barbiturates (sleeping pills)
- Amphetamines
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What, is the need for parasites to develop special adaptations? Mention some special adaptations developed by the parasites. [TSM-19]
Answer:
- Parasites depend on hosts for their survival. The hosts tend to reject and resist the parasites.
- So parasites have evolved adaptations to counteract and neutralise host’s defence system. The adaptations are loss of unnecessary sense organs, development of organs of attachment, high reproductive capacity etc.
Special Parasitic adaptations:
- In order to live in the host, some parasites develop attachment organs are Hooks, suckers, rostellum etc.
- Some parasites develop protective covering like tough ‘cuticle’ tegument to withstand digestive juices. Ex: Ascaris, Fasciola.
- Some parasites produce large number of eggs.
Ex: Taenia has 700-900 proglottids, each producing 3500 eggs. - Some parasites produce anti enzymes to neutralise host’s digestive juices. Ex: Taenia.
- Some parasites develop complex life cycles with many larval stages. Ex: Fasciola.
- Some parasites show development of cysts. Ex: Entamoeba.
- Some parasites change the surface antigens to escape from vaccines. Ex: Plasmodium, HIV
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the effects of parasites on the host?
Answer:
Parasites cause weakening of the body of their hosts by causing the deprivation of nutrients, fluids and metabolites.
Effects of parasites on hosts:
- Parasitic castration : Some parasites cause the degeneration of gonads of the host, making it sterile.
Ex: Sacculina causes the degeneration of gonads in the crab Carcinus maenas. - Neoplasia : Some parasites cause an abnormal growth of the host cells in a tissue to form new structures. This effect leads to cancers.
Ex: Some viruses. - Gigantism : Some parasites cause an abnormal increase in the size of the host.
Ex: The larval stages of Fasciola hepatica cause gigantism in snail (an intermediate host) - Hyperplasia Some parasites cause increase in the number of cells.
Ex: Fasciola hepatica in the bile duct of sheep - Hypertrophy : Some parasites cause an abnormal increase in the Volume / size of the infected host cells.
Ex: RBC of man infected by Plasmodium
Question 3.
Distinguish between hypertrophy and hyperplasia with an example for each.
Answer:
1) Hypertrophy: Some parasites cause abnormal increase in the size of the host cell which finally ruptures. [AP,TS M-20]
Ex: Plasmodium causes increase in the size of RBC which finally bursts.
2) Hyperplasia; Some Parasites cause increase in the size of the organ by increasing the number of cells. This causes inconvenience or death to the host.
Ex: Fasciola hepatic lives in bile ducts of sheep. It blocks the passage of bile duct by increasing the cells.
Question 4.
Write any four types of parasitic diseases. Mention the primary and secondary hosts of these parasites.
Answer:
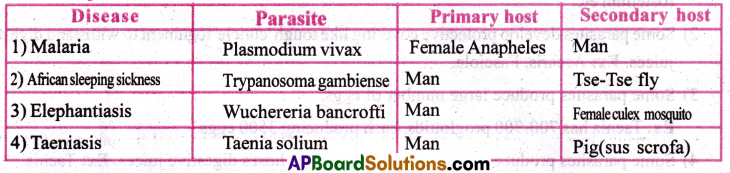
Question 5.
Describe the structure of a trophozoite of Entamoeba histolytica.
Answer:
Structure of E histolytica in trophozoite stage;
- This is the most active, motile, feeding and pathogenic stage.
- It lives in mucous and submucous layers of large intestine of man.
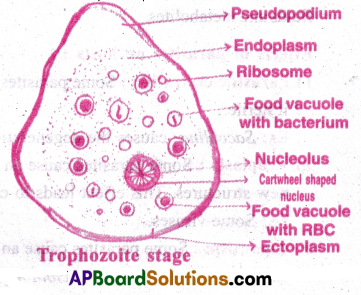
- Its body is surrounded by plasmalemma.
- Its Cytoplasm is differentiated into an outer clear inner fluid with granular endoplasm.
- Endoplasm contains ribosomes, food vacuoles with RBC, a cart wheel shaped nucleus.
- It respires anaerobically.
- It produces the proteolytic enzyme called histolysin to dissolve host tissue.
- The mode of nutrition is holozoic.
Question 6.
ExplaIn the life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica.
Answer:
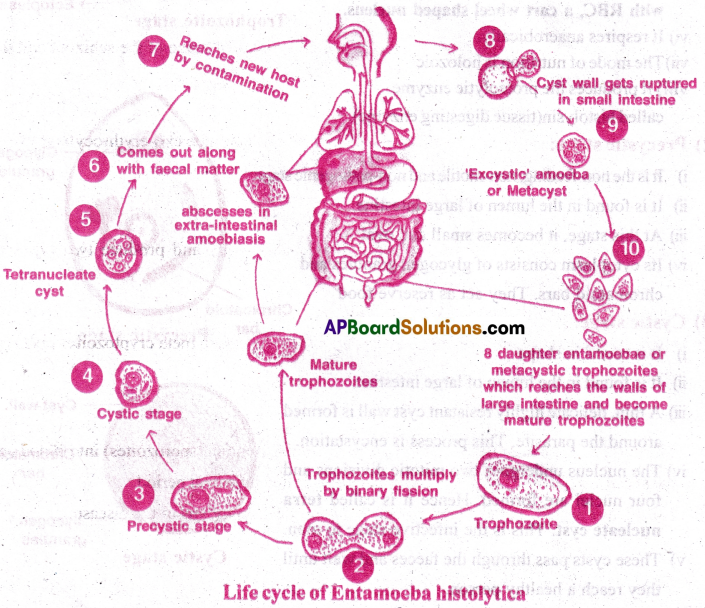
Life cycle of Entamoeba:
- Entamoeba histolytica is a protozoan, monogenetic histozoic parasite living in the wall of large intestine of man.
- The infection is through contaminated food and water or by mechanical vectors like housefly and cockroach.
- Tetranucleated stage is the infective stage when it enters the small intestine the cyst wall breaks and encystic amoeba or metacyst is released.
- The nucleus divides followed by cytoplasm to produce 8 daughter entamoeba.
- They reach the wall of the large intestine and grow into mature trophozoites.
- Trophozoites multiply by binary fission.
- Trophozoites become precystic stages.
- A cyst wall develops and the parasite becomes cystic stage.
- Nucleus divides in to four and the cystic stage becomes tetra nucleate cyst. Tetra nucleate cysts come out along with faeces and remain alive for 10 days. Through contaminated food and water they reach another host and the cycle continues.
Question 7.
Write a short note on the pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica.
Answer:
Pathogenicity of Entamoeba:
- Entamoeba causes ulcers in large intestine.
- The ulcers ooze blood cells, cellular debris and bacteria.
- Ultimately there will be blood and mucus motions. It is called intestinal amoebiasis or amoebic desentry.
- Sometimes the trophozoites enter the blood stream and reach lungs,heart, kidneys and brain causing abscesses in those organs leading to severe pathological conditions. It is called extra intestinal
- Some people do not exhibit symptoms such people are called carriers or asymptomatic cyst passers as their stool contains the tetranucleate cysts.
![]()
Question 8.
Describe the structure of sporozoite of Plasmodium vivax.
Answer:
Structure of Sporozoite of Plasmodium:
- Structure of sporozoite of plasmodium was studied by Gamham.
- Sporozoite is sickle shaped. It is swollen in the middle and pointed at ends.
- Its length is 15 microns and width is 1 micron.
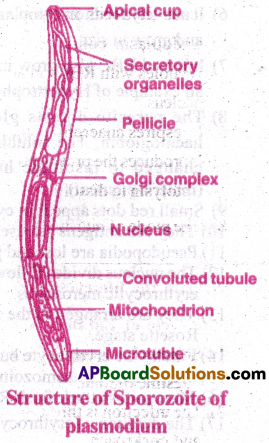
- The pellicle is provided with microtubules. They help in wriggling movement of sporozoite.
- The cytoplasm contains Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and a nucleus.
- Convoluted tubules of unknown function are present.
- An apical cup containing a pair of secretory organelles is present at the anterior end.
- The secretory organelles produce cytolytic enzyme.
- It helps to penetrate liver cells.
Question 9.
What do you know about the exo erythrocytic cycle of piasmodium vivax?
Answer:
Exoerythrocytic cycle of piasmodium is nothing but like pre – erythrocytic cycle
Exo-erythrocytic Cycle:
- The cryptozoites that enter liver cells undergo schizogony and produce two types of metacryptozoites within two days.
- Some are small called micro meta cryptozoites enter blood stream and attack fresh RBC to continue erythrocytic cycle.
- Others are large and called macro meta cryptozoites. The macro meta cryptozoites continue hepatic schizogony.
- This process is completed approximately in 2 days.
Question 10.
Describe the cycle of Golgi in the life history of Plasmodium vivax.
Answer:
Cycle of Golgi Erythrocytic cycle of piasmodium is also called ‘cycle of Golgi’ because it was first described by Golgi.
- The cryptozoites of pre erythrocytic cycle or micrometa cryptozoites of exoerythrocytic cycle enter the fresh RBC.
- In RBC the parasite becomes the trophozoite.
- A small vacuole appears at the centre and gradually grow in size pushing the nucleus to one side.
- Then the stage of parasite is called signet ring stage as it resembles a finger ring.
- Soon the vacuole is lost and pseudopodia appear then the stage is called amoeboid stage.
- It actively feeds on cytoplasm of RBC and grow in size.
- Infected RBC also grow in size. It is an example of Hypertrophy.
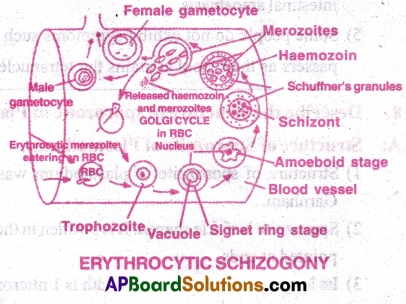
- The parasite digests globin part haemoglobin. The soluble haem is changed to insoluble haemozoin (malaria pigment)
- Small red dots appear in cytoplasm of RBC called Shuffner’s dots.
- They are antigens released by parasite.
- Pseudopodia are lost and piasmodium occupies the entire RBC and becomes a schizont.
- The nucleus divides followed by the division of cytoplasms (schizogony) forms 12 to 24 erythrocytic merozoites.
- They are arranged in the form of the petals of a rose in the RBC. This stage is called the Rosette stage.
- Finally the erythrocyte bursts and releases merozoites and haemozoin into the blood.
- The release of haemozoin causes chill, fever.
- Merozoites attack fresh RBC and continue the erythrocytic cycle.
- The duration of erythrocytic cycle is 48 hours.
Question 11.
Describe the process ofSporogony in the life cycle of plasmodium vivax. What is the significance of sporozoites?
Answer:
Sporogony: The oocyst enlarges in size and begins sporogony.
- According to Bano, the nucleus of the oocyst first undergoes reduction division.
- Then the nucleus divides repeatedly by mitosis and produces a number of nuclei.
- Each bit of nucleus is surrounded by a little bit of the cytoplasm and it transforms into a sickle shaped sporozoite. Oocyst with such sporozoites (about 10,000) is called sporocyst.
- When Sporocysts are ruptured spindle shaped sporozoites are liberated into haemocoel.
- From there, they travel into the salivary glands and become ready for infection of a healthy person.
- The life cycle of plasmodium in mosquito is completed in about 10 to 24 days.
Significance : Sporozoites formed in sporogony are ready for infection. These are infective stages of malarial fever.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain the pathogenicity of Wuchereria bancrofti in man. [TS M-22]
Answer:
Pathogenicity of Wuchereria bancrofti:
- Wuchereria bancrofti is the filarial worm.
- Light infection causes fever, headache, depression.
- Generally filarial worm causes inflammation of lymph vessels and glands.
- Lymph vessel inflammation is called Lymphangitis.
- Lymph gland inflammation is lymphadenitis.
- When there is heavy infection, the dead worms clog the lymph vessels, and lymph glands causing swelling of drooping parts.
- Fibrous tissue accumulate near these parts.
- The sweat glands disintegrate and skin becomes rough.
- This condition is Elephantiasis.
Question 13.
Write short notes on typhoid fever and its prophylaxis.
Answer:
Typhoid Fever: Typhoid is caused by salmonella typhi (gram negative bacterium).
- It lives in the small intestine of man.
- It reaches the other parts of the body through blood circulation.
- Widal test confirms the presence of salmonella.
- Mode of Infection: Contaminated food and water.
- Symptoms: Continuous fever, weakness, stomach pain, constipation, head ache and loss of appetite.Intestinal perforations (hole) and death occurs in severe cases.
- Prophylaxis: Immunization by vaccines, drinking safe water, using septic tank toilets.
Question 14.
Write short notes on pneumonia and its prophylaxis.
Answer:
Pneumonia: It is a bacterial disease.
- It is caused by gram positive bacteria; streptococcus pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza.
- They infect the lung alveoli.
- Mode of Infection: Contamination is by inhaling aerosols released by infected person.
- Symptoms: Severe problems in respiration.
- Prophylaxis: Use of masks, boiled utensils, use of vaccines and antibiotics.
Question 15.
Write short notes on common cold and its prophylaxis.
Answer:
Common cold: Common cold is a viral disease caused by Rhinovirus.
- It infects the nose and respiratory passage but not lungs.
- Mode of Infection: Contamination is by inhalation of droplets from infected person through cough and sneeze or coming into contact with contaminated articles.
- Symptoms: Nasal congestion, running nose, sore throat, cough, headache etc.
- Prophylaxis: Use of masks, use of boiled water, use of antibiotics.
Question 16.
Write short notes on ‘ringworm’ and its prophylaxis.
Answer:
- Ringworm is an infectious disease caused by fungi belong to Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton.
- People living in hot humid climates get the infection.
- It grows in skin folds of groin, armpits, and in between toes.
- Mode of Infection:Contamination is by using towels, clothes or combs of infected persons or from wet soil.
- Symptoms: Dry, scaly circular patches appear on the body. It causes intense itching. Fungicides help in treatment.
- Prophylaxis: Clothes of infected persons should be avoided, use safer vaccines and antibiotics.
Question 17.
What are the adverse effects of tobacco? [TS May-17,22] [APM-16,19][IPE-14]
Answer:
Adverse effects of Tobacco:
- Tobacco is smoked, chewed as gutkha or snuffed.
- Smoking increases carbon monoxide level in blood and reduces oxygen level.
- Tobacco contains Nicotine, an alkaloid.
- Nicotine stimulates adrenal gland.
- The hormones adrenaline and nor-adrenaline increase blood pressure and heart rate.
- It causes bronchitis, emphysema, coronary heart disease and gastric ulce.rs.
- It increases the incidence of cancer of throat, lungs and urinary bladder.
Question 18.
Write short notes on Opioids.
Answer:
- Opioids are drugs obtained from poppy plant papaver somniferum.
- These drugs bind to specific receptors of CNS and alimentary canal.
Two important opioids are (i) Morphine (ii) Heroin.
(i) Morphine: It is produced from dried latex or unripe fruits of poppy plant.
- It is in the form of colourless crystals or white crystalline powder.
- It is taken orally or by injection.
- It is an effective sedative and pain killer.
- It is useful for surgery patients and who suffer from painful ailments.
(ii) Heroin: It is produced from morphine by acetylation. It is a white bitter powder.
- Chemically it is diacetyl morphine.
- It is also called ‘smack’.
- It is taken in by snorting and injection.
- Heroin causes depression and slows down the body functions.
Question 19.
Write short notes on Cannabinoids.
Answer:
Cannabinoids::These drugs are obtained from Indian hemp plant Cannabis sativa (ganjai mokka)
- The flower tips, leaves and resin of these plant are used in various combination to produce marijuana, hashish, charas and ganja.
- These drugs are used by sports person to enhance their performance.
- These drugs are taken in either orally or inhalation.
- Cardio vascular system is effected.
Question 20.
Write short notes on Cocaine.
Answer:
Cocaine: Cocaine is a white crystalline alkaloid.
- It is obtained from coca plant erythroxylum.
- Coca found in South America. It is commonly known as Coke or crack.
- It is taken through nose (snorting).
- It interferes with the transport of neuro transmitter dopamine.
- It produces a sense of euphoria and increased energy.
- Excess consumption causes hallucinations.
![]()
Question 21.
Why in adolescence is considered vulnerable phase? [AP M-15,22]
Answer:
- Adolescence is the teenage between 12 to 18 years .
- It is a bridge between childhood and adulthood.
- During this period a child becomes mature.
- Several biological and behavioural changes take place during this period.
- So Adolescence is said to be a vulnerable phase of mental and psychological development of an individual.
Question 22.
Why do some adolescents start taking drugs? How can this be avoided?
Answer:
- The age between 12-18 years is known as adolescence period
- During this period youngsters show curiosity, desire for adventure and excitement, experimentation etc.,
- They also suffer from some mental stress, physical stress and harmonal imbalance.
- Due to such reasons they start taking drugs (or) alcohol.
Measures to avoid drug usage(TDA):
- Seeking help from peers: If classmates find some one getting into trap of TDA, it should be brought to the notice of their parents or. teachers.
- Education and counselling: There must be a continuous process of educating the children regarding TDA, at every level in the form of lessons.
- Seeking professional and medical help: A lot of help is available in the form of highly qualified psychologists, psychiatrists and de-addiction and rehabilitation programmers.
Question 23.
Distinguish between addiction and dependence.
Answer:
Addiction:
- It is a psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria.
- The inherent addictive nature of alcohol, drugs and tobacco force the people to use them.
- Repeated use of these drugs increases the tolerance level of the receptors in the human body. As a result, receptors respond only to higher doses leading to greater intake of these drugs and addiction.
- It should be clearly borne in mind that use of drugs even once, can be a fore -runner to addiction.
- Addictive potential of tobacco, drugs, alcohol pull the users in to a vicious circle leading to their regular use (Abuse) from which they may not able to get out.
- In the absence of any guidance (or) counselling, people get addicted and become dependent on them.
Dependence:
- It is the tendency of the body to manifest characteristic and unpleasant condition (with drawal syndrome), if the regular dose of drugs (or) alcohol is abruptly discontinued.
- The withdrawal syndrome is characterised by anxiety, shakiness, (tremors), nausea and sweating which may be relieved when the regular use is resumed again.
- Dependence leads to patient to ignore all social norms.
Question 24.
‘Prevention is better than cure’. Justify with regard to TDA abuse. [AP, TS-18]
Answer:
TDA abuse stands for Tobacco Drug and Alcohol Abuse . [TS-15,16j
The proverb, ‘Prevention is better than cure’ holds true in case of TDA .
Measures useful for prevention:
- Avoid undue parental pressure: All children have their own choices, capacities and , personalities. The parents should not force their children to perform beyond their capacity.
They should not compare them with others in studies, games etc. - Responsibility of parents and teachers: They have to advise, counsel and help the children who are likely to get into the trap of TDA.
- Seeking help from peers: If classmates find some one getting into trap of TDA, it should be brought to the notice of their parents or teachers.
- Education and counselling: There must be a continuous process of educating the children regarding TDA, at every level in the form of lessons.
- Seeking professional and medical help: A lot of help is available in the form of highly qualified psychologists, psychiatrists and de-addiction and rehabilitation programmers.
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the structure and life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica with the help of neat labelled diagrams. [TSM-191[APM-15]
Answer:
Entamoeba histolytica is a monogenetic histozoic parasite.
It inhabits in the large intestine of man.
It causes amoebic dysentery (or intestinal amoebiasis).
I) Structure of E histolytica in its life cycle: It consists of 3 stages. They are
- Trophozoite stage
- Precystic stage
- Cystic stage
1) Trophozoitestage:
- This is the most active, motile, feeding and pathogenic stage.
- It lives in mucous and submucous layers of large intestine of man.
- Its body is surrounded by plasmalemma.
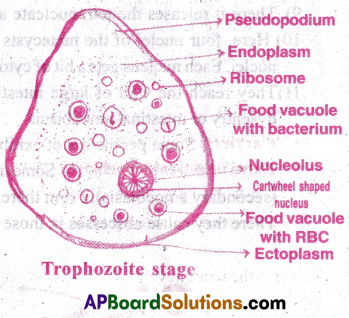
- Its Cytoplasm is differentiated into (i) an outer clear viscous, non-granular ectoplasm and (ii)the inner fluid with granular endoplasm.
- Endoplasm contains ribosomes, food vacuoles with RBC, a cart wheel shaped nucleus.
- It respires anaerobically.
- The mode of nutrition is holozoic
- It produces the proteolytic enzyme called histolysin(tissue digesting enzyme).
2) Precystic stage:
- It is the non-feeding, non-motile and non-pathogenic stage.
- It is found in the lumen of large intestine.
- At this stage, it becomes small and oval.
- Its cytoplasm consists of glycogen granules and chromatoid bars. They act as reserve food

3) Cystic stage:
- It is round in shape
- It is found in the lumen of large intestine.
- A thin, delicate highly resistant cyst wall is formed around the parasite. This process is encystation.
- The nucleus undergoes two mitotic divisions and four nuclei are formed. Hence it is called tetra nucleate cyst. This is the infective stage to man.
- These cysts pass through the faeces and wait until they reach a healthy person.
II) Life Cycle of E histolytica:
- The trophozoites undergo binary fissions and produce a number of daughter Entamoeba.
- They feed upon the bacteria and host’s tissues. They grow in size and multiply by binary fissions.
- Some of these, enter the lumen of the large intestine and transform into precystic stage.
- Here, the precystic stage transforms into cystic stage.
- There they intum develop into tetranucleate cysts.This entire process is completed in a few hours.
- These tetranucleate cysts (infective stage to man) come out along with the faecal matter and can remain alive for about 10 days.
- These cysts then reach new host through contaminated food and water.
- The cyst wall gets ruptured by enzyme trypsin in the small intestine of a new human host.
- There it releases the tetranucleate amoebae. These are called metacysts.
- Here, four nuclei of the metacysts undergo mitotic divisions and produce eight daughter nuclei. Each nucleus gets a bit of cytoplasm and thus eight daughter entamoebae are produced.
- They reach the wall of large intestine and become mature trophozoites causing amoebic dysentry or intestinal amoebiasis.
- Carriers: Some people donot exhibit any symptoms, such people are called carriers.
- Extra intestinal amoebiasis: Some times, the trophozoites reach the liver and cause ‘abscesses’ (secondary amoebiasis). From there they may go to lungs, heart, brain and kidneys.
- There they cause abscesses in those parts leading to severe pathological conditions.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the life cycle of Plasmodium vivax in man. [AP M-17] [TS May-17]
Answer:
Plasmodium vivax is the malarial parasite of man.
It is digenetic intra cellular parasite that lives in the liver cells and RBC of man.
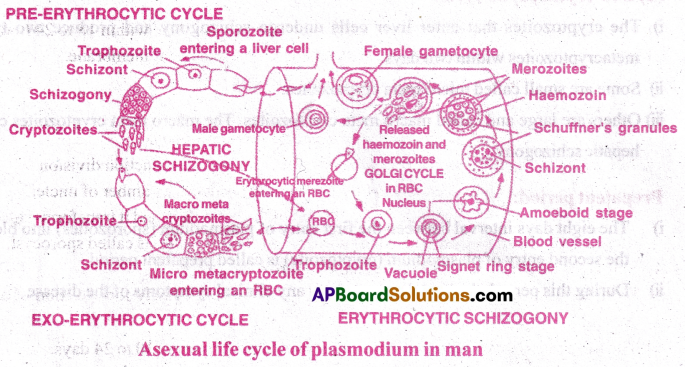
Life cycle of Plasmodium in man (Human phase):
- In man, plasmodium reproduces by asexual reproduction called schizogony.
- It is of two types:
(I) Hepatic schizogony(occurs in liver cells) (II) Erythrocytic schizogony (occurs in RBC)
(I) Hepatic Schizogony: It was discovered by Shortt and Gamham
When an infected mosquito bites a healthy person, the sporozoites enter the blood of man. With in half an hour they reach liver cells. In liver cells, the parasites increase their number in two cycles. They are Pre-erythrocytic and Exo-erythrocytic cycles.
(1) Pre-erythrocytic cycle:
- The sporozoites enter liver cells and transform into trophozoites.
- They become round and grow in size and are called schizonts.
- The nucleus divides several times. It is followed by the cytoplasm divisions, producing 12,000 cryptozoites (or first generation merozoites).
- They enter the sinusoids of the liver by rupturing the cell membrane of the schizont and the liver cells.
- The duration of pre-erythrocytic cycle is 8 days.
- The cryptozoites may enter into either fresh liver cells to continue exo-erythrocytic cycle or they can enter into RBC to continue erythrocytic cycle.
(2) Exo-erythrocytic cycle:
- The cryptozoites that enter liver cells undergo schizogony and produce two types of metacryptozoites within two days.
- Some are small called micro meta cryptozoites.
- Others are large and called macro meta cryptozoites. The macro meta cryptozoites continue hepatic schizogony.
Prepatent period:
- The eight days interval between the first entry of plasmodium (sporozoites) into blood and the second entry of plasmodium (cryptozoite) is called prepatent period.
- During this period, the host does not show any clinical symptoms of the disease.
(II) Erythrocytic schizogony:
(1) Golgi cycle: It was described by Golgi.
- The cryptozoites or micro meta cryptozoites enter into the fresh RBC.
- They transform into trophozoites.
- A small vacuole appears in trophozoite.
- It enlarges by pushing the cytoplasm and nucleus to one side.
- The parasite looks like a finger ring and hence it is called signet ring stage.
- Here, the vacuole disappears, Pseudopodia develop and the parasite changes to amoeboid stage.
- At this stage parasite exhibits hypertrophy condition (RBC grows almost double the size).
- It feeds on globin part of haemoglobin and grows in size.
- It converts the soluble haem into insoluble haemozoin called malaria pigment.
- Small red colour dots appear in the cytoplasm of RBC called Schuffner’s dots.
- They are beleived to be the antigens produced by the parasite.
- It becomes a round schizont.
- It undergoes schizogony and produces 12 to 24 erythrocytic merozoites.
- They are arranged in the form of the petals of a rose in the RBC.This stage is called the Rosette stage.
- Finally the erythrocyte bursts and releases merozoites and haemozoin into the blood.
- The release of haemozoin causes chill, fever.
- Merozoites attack fresh RBC and continue the erythrocytic cycle, xviii) The duration of erythrocytic cycle is 48 hours.
- Incubation period: The period between the entry of plasmodium (sporozoite) and the first appearance of symptoms of Malaria is called incubation period. Its duration is 10 to 14 days.
2) Formation of Gametocytes:
- After several erythrocytic schizogonies, some merozoites enter the RBC and transform into gametocytes instead of continuing the erythrocytic cycle.
- There are two types of gametocytes.
(a) Macrogametocyte or female gametocyte (b) Micro gametocyte or male gametocyte. - The gametocytes do not develop further in man. They have to reach female Anopheles. ,
- They die if they do not reach the mosquito within a week.
Question 3.
Describe the life cycle of Plasmodium vivax in mosquito. [AP,TS M-16,17] [IPE-14]
Answer:
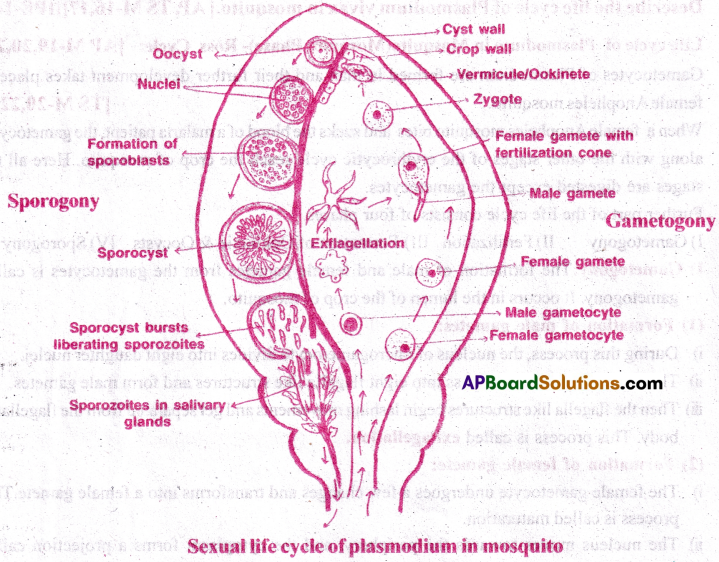
Life cycle of Plasmodium in Mosquito(Mosquito Phase)-Ross Cycle: [AP M-19,20,22]
- Gametocytes of Plasmodium are formed in man and their further development takes place in female Anopheles mosquito. [TS M-20,22]
- When a female Anopheles mosquito bites and sucks the blood of a malaria patient, the gametocytes along with the other stages of the erythrocytic cycle reach the crop of mosquito. Here all the stages are digested except the gametocytes.
Further part of the life cycle consists of four phases.
- Gametogony
- Fertilization
- Formation of Ookinetie & Oocysts
- Sporogony
(I) Gametogony: The formation of male and female gametes from the gametocytes is called gametogony. It occurs in the lumen of the crop of mosquito.
![]()
(1) Formation of male gametes:
- During this process, the nucleus of microgametocyte divides into eight daughter nuclei.
- The eight daughter nuclei pass into eight flagella like structures and form male gametes.
- Then the flagella like structures begin lashing movements and get separated from the flagellated body. This process is called exflagellation.
(2) Formation of female gamete:
- The female gametocyte undergoes a few changes and transforms into a female gamete.This process is called maturation.
- The nucleus moves towards the periphery, and the cytoplasm forms a projection called fertilization cone.
II) Fertilization: The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization.
- One of the active male gamete comes in contact with the ‘fertilization cone’ of the female gamete and enters into it.
- The pronuclei and cytoplasm of these two gametes fuse with each other. As a result the zygote is formed.
- These gametes are dissimilar in size and hence the process is called anisogamy.
III) Formation of Ookinete & Oocysts:
- The zygote elongates and becomes motile and is called ookinete within 18 to 24 hours.
- It pierces the wall of the crop and settles beneath the basement membrane.
- It becomes round and secretes a cyst around its body.
- This encysted ookinete is now called oocyst
IV) Sporogony: The oocyst enlarges in size and begins sporogony.
- According to Bano, the nucleus of the oocyst first undergoes reduction division.
- Then the nucleus divides repeatedly by mitosis and produces a number of nuclei.
- Each bit of nucleus is surrounded by a little bit of the cytoplasm and it transforms into a sickle shaped sporozoite. Oocyst with such sporozoites (about 10,000) is called sporocyst.
- Sporocysts are formed into spindle shaped sporozites.
- From there, they travel into the salivary glands and become ready for infection of a healthy person.
- The life cycle of plasmodium in mosquito is completed in about 10 to 24 days.
Question 4.
Ascaris lumbricoides with the help of a neat labelled diagram. [AP May-17,19] [TS M-15] [IPE- 13] [AP-18]
Answer:
Ascaris lumbricoides:
- Ascaris lumbricoides is commonly called the ‘common round worm’.
- It lives in the intestine of man (mostly children)
- Mode of infection is through contaminated food and water.
- The infective stage is the embryonated egg with the 2nd stage rhabditiform larva.
- It is dimorphic, monogenetic pseudocoelomate, enterozoic parasite.
I) Structure of Ascaris lumbricoides:
- Sexes are separate and the sexual dimorphism is distinct.
- In both males and females, the body is elongated and cylindrical.
- In both forms mouth is at the anterior end surrounded by Chitinous lips.
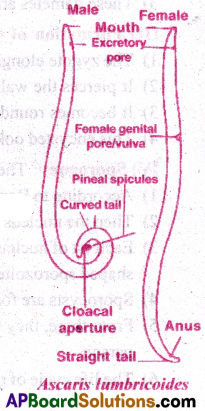
- Excretory pore is present ventrally close to the mouth.
A) Male: It is short with posterior curved end. There is cloaca in the curved end bearing equal sized a pair of copulatory spicules or pineal spicules.
B) Female: The body is long with a straight posterior end. Anus is subterminal. Female genital pore is at about one third the length from anterior end.
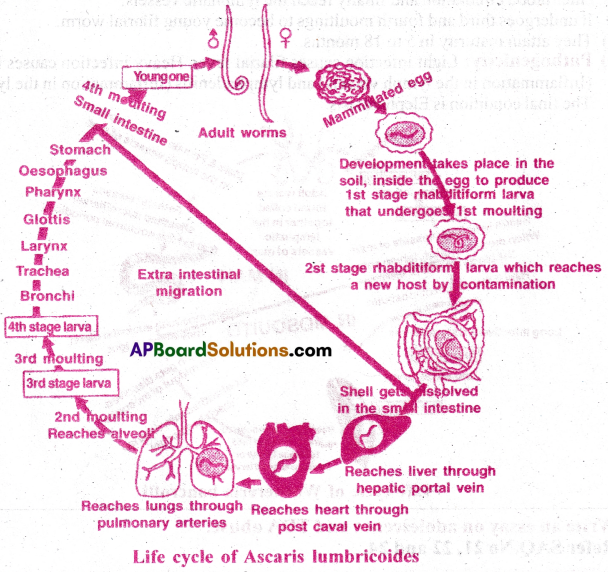
II) Life cycle of Ascaris iumhricoides:
- After copulation in the small intestine the female releases about two lakh eggs daily.
- Each egg is surrounded by a rippled protein coat and hence it is called mammillated egg.
- These mammillated eggs are passed out along with faecal matter.
- In the moist soil, development takes place inside the eggs and first stage rhabditiform larva is produced.
- It undergoes first moulting and 2nd stage rhabditiform larva is formed. The 2nd stage larva is the infective stage to man formed by first moulting.
- These eggs reach a new host through contaminated food and water.
- In the small intestine, the shell gets dissolved and larva is released. Here larva undertakes extra intestinal migration.
- It reaches the liver through hepatic portal vein.
- Then it goes to heart through post caval vein.
- It reaches lungs through pulmonary arteries.
- The second moulting take place in alveoli of lungs and 3rd stage larvae are formed.
- The third moulting take place in alveoli of lungs and 4th stage larvae are formed.
- It reaches the small intestine through bronchi, trachea, larynx, glottis, pharynx, oesophagus and stomach.
- Fourth moulting (final moulting) takes place in small intestine and then becomes young round worm.
- It attains sexual maturity in 8 to 10 weeks.
- Pathogenicity: Ascaris causes ascariasis. When the infection is heavy it can cause Nutritional deficiency, severe abdominal pain and stunted growth in children.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the life cycle of Wuchereria bancrofti with a neat diagram.
Answer:
Wuchereria bancrofti:
- Wuchereria bancrofti is called commonly called the filarial worm.
- It is digenetic, dimorphic, histozoic, pseudocoelomate parasite
- It lives in lymph vessels of man. Its secondary host is female culex mosquito.
I) Structure:
- Sexes are separate and the sexual dimorphism is distinct.
- The body is long and filiform. The anterior end is blunt and posterior end is pointed.
- Mouth is anterior without any lips.
- Male: It has posterior curved end with cloaca and a pair of unequal copulatory spicules.
- Female: It has anus at the posterior straight end. Female genital pore is about one third the length from the mouth. It is ovoviviparous.
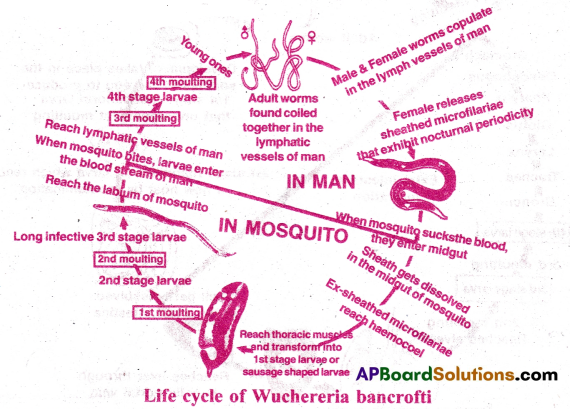
II) Life cycle: Wuchereria completes its life cycle in two hosts. Man and female culex mosquito.
1) In man: Male and female worms remain coiled in lymph vessels.
- After copulation the female releases ensheathed microfilaria larva. The larva is 0.2 to 0.3 mm in length.
- It is surrounded by loose cuticular sheath. It lives in deep blood vessels during day time and comes to periphery during night between 10 PM and 4 AM. This is called nocturnal periodicity.
- The larva can live for 70 days, before which, it has to enter a mosquito.
2) In female cluex mosquito:
- When female culex bites the infected person, the micro filarial enter the mid gut of mosquito.
- The sheath is dissolved in midgut.
- The larva penetrates the gut wall and reach the thoracic muscles.
- In two days, it becomes sausage shaped larva or first stage microfilaria.
- It undergoes two moults to become long slender infective, third stage microfilaria.
- The 3rd stage goes to the labium of mosquito and waits to enter man.
3) In man after infection: When infected mosquito bites a healthy person, the 3rd stage larva enter blood circulation and finally reach the lymphatic vessels.
- It undergoes third and fourth moultings to become young filarial worm.
- They attain maturity in 5 to 18 months.
4) Pathogenicity: Light infection causes filarial fever. Heavy infection causes Lymphangitis (Inflammation in the lymph vessels) and lymphadenitis (Inflammation in the lymph glands). The final condition is Elephantiasis.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Abnormal increase in the size of the host due to parasite is called
1. Castration
2. Gigantism
3. Hypertrophy
4. Hyperplasia
Answer:
2. Gigantism
Question 2.
Chronic malaria causes the enlargement of
1. Liver
2. Spleen
3. Prostate
4. Bursa of fabrici
Answer:
2. Spleen
Question 3.
Drug which induces dreamy state of consciousness is
1. sedative
2. stimulant
3. depressant hallucinogen
4. hallucinogen
Answer:
4. hallucinogen
Question 4.
The parasites which live within the cells of host are called
1. Cytozoic parasites
2. Intercellular parasites
3. Facultative parasites
4. Coelozoic parasites
Answer:
1. Cytozoic parasites
Question 5.
In the absence of regular hosts, some parasites survive in
1. Reservoir hosts
2. Intermediate hosts
3. Vectors
4. Paratenic hosts
Answer:
1. Reservoir hosts
![]()
Question 6.
Plasmodium is a
1. Digenetic parasite
2. Coelozoic parasite
3. Monogenetic parasite
4. Intermittent parasite
Answer:
1. Digenetic parasite
Question 7.
Discharge of blood and mucus in faeces of man is the symptom of
1. Taeniasis
2. Amoebiasis
3. Malaria
4. Filaria
Answer:
2. Amoebiasis
Question 8.
Select the typical symptom of amoebic dysentery
1. Alkaline stools
2. Severe pain in abdomen
3. Severe pain in anus
4. Stools with metacysts
Answer:
2. Severe pain in abdomen
Question 9.
Infective stage of Plasmodium to man is
1. Trophozoite
2. Gametocyte
3. Sporozoite
4. Merozoite
Answer:
3. Sporozoite
Question 10.
A mosquito that transmits the malarial parasite from one person to the other is termed as
1. definitive host
2. secondary host
3. paratenic host
4. Vector
Answer:
4. Vector
Question 11.
The incubation period of Plasmodium vivax is
1. 8 days
2. 10-14 days
3. 48 hours
4. 3 days
Answer:
2. 10-14 days
Question 12.
Intertian malaria, fever occurs
1. After every 96 hours
2. After every 24 hours
3. After every 48 hours
4. After every 72 hours
Answer:
3. After every 48 hours
Question 13.
The malarial symptoms occur because of
1. Schuffner’s dots
2. Haemozoin
3. Sporozoite
4. Signetring stage
Answer:
2. Haemozoin
Question 14.
High fever, increased heart beating and pulse rate are some symptoms of
1. First stage malaria
2. Cold stage malaria
3. Hot stage malaria
4. Sweating stage malaria
Answer:
3. Hot stage malaria
Question 15.
Mamillated eggs are seen in
1. Wuchereria
2. Taenia
3. Ascaris
4. Plasmodium
Answer:
3. Ascaris
Question 16.
Cloaca and pineal spicules are characteristic of
1. Tapeworms
2. Earthworms
3. Male round worms
4. Female round worms
Answer:
3. Male round worms
Question 17.
Female Culex acts as an intermediate host of
1. Plasmodium vivax
2. Wuchereria bancrofti
3. Leishmania donovani
4. Fasciola hepatica
Answer:
2. Wuchereria bancrofti
![]()
Question 18.
In mosquito, the microfilaria under goes
1. One moulting
2. Two moultings
3. Three moultings
4. Four moultings
Answer:
2. Two moultings
Question 19.
Widal test confirms
1. pneumonia
2. common cold
3. typhoid
4. ringworm
Answer:
3. typhoid
Question 20.
Typhoid is infected through
1. Mosquito bite
2. Inoculation
3. contaminated food and water
4. Anopheles
Answer:
3. contaminated food and water
Question 21.
Pneumonia is caused by
1. Salmonella typhi
2. Rhino virus
3. Trichoderma spp
4. Haemophilus influenzae
Answer:
4. Haemophilus influenzae
Question 22.
Severe itching, circular dry lesions on skin are characteristic features of
1. Pneumonia
2. Malaria
3. Ringworm
4. Filaria
Answer:
3. Ringworm
Question 23.
Ring worm disease is caused by
1. Roundworms
2. Bacteria
3. virus
4. Fungi
Answer:
3. virus
Question 24.
Nicotin stimulates the secretion of
1. Adrenaline
2. Thyroxine
3. Vasopressin
4. Insulin
Answer:
1. Adrenaline
Question 25.
The adolescent period comes at the age of
1. 12-18 years
2. 15-20 years
3. 20-26 years
4. 10-15 years
Answer:
1. 12-18 years
Question 26.
Cytozoic parasite which lives in the liver cells of man is
1. Plasmodium
2. Trichomonas
3. Taenia
4. Paramecium
Answer:
1. Plasmodium
Question 27.
Nosema notabilis, which is in association with Sphaerospora, a parasite in the urinary bladder of toad fish is a ,
1. predator
2. hyperparasite
3. host
4. commensal
Answer:
2. hyperparasite
Question 28.
Digenetic trematode parasite completes the life cycle in
1. two hosts of same species
2. single host in one form
3. two hosts of different species
4. single host in different forms
Answer:
3. two hosts of different species
Question 29.
Nucleus is cart-wheel-shaped in
1. Entamoeba histolytica
2. Enterobius vermicularis
3. Ancylostomaduodenale
4. Echinococcus granulosus
Answer:
1. Entamoeba histolytica
![]()
Question 30.
One of the following is a symptom of amoebic dysentery
1. Presence of uninucleate metacystic forms in faeces
2. Blood and mucous in faeces
3. Sporozoites in the faeces
4. Presence of octanucleated cysts in faeces
Answer:
2. Blood and mucous in faeces
Question 31.
Plasmodium reproduces asexually by
1. gametogony
2. binary fission
3. budding
4. schizogony
Answer:
4. schizogony
Question 32.
Anticoagulant present in the saliva of mosquito is
1. hirudin
2. histolysin
3. haemolysin
4. histamine
Answer:
3. haemolysin
Question 33.
One of the following scientists first discovered the oocyst stages of Plasmodium in crop-wall of female
1. Ross
2. Golgi
3. Manson
4. Grassi
Answer:
1. Ross
Question 34.
Ascaris lives in the
1. blood cells of man
2. blood plasma of man
3. small intestine of man
4. liver cells of man
Answer:
3. small intestine of man
Question 35.
Infective stage of Ascaris to man
1. stage of rhabditiform larva
2. 2nd stage of rhabditiform larva
3. 3rd stage of rhabditiform larva
4. 4 stage of rhabditiform larva
Answer:
3. 3rd stage of rhabditiform larva
Question 36.
Total number of moultings In the life history of Ascaris Is
1. four
2. three
3. two
4. one
Answer:
1. four
Question 37.
Ovovivlparous pseudocoelomate in the following ¡s
1. Ascaris
2. Enterobius
3. Ancylostoma
4. Wuchereria
Answer:
4. Wuchereria
Question 38.
Third moult in the life cycle Wuchcreria occurs ¡n the
1. lymph vessels of man
2. blood vessels of man
3. mid gut of mosquito
4. thoracic muscles of mosquito
Answer:
1. lymph vessels of man
Question 39.
Inflammation of lymph glands caused fly the filarial worm in man is called
1. lymphangitis
2. lymphadenitis
3. lymphoedema
4. myeloma
Answer:
2. lymphadenitis
Question 40.
Chemical test that is used in diagnosis of Typhoid is
1. ELISA test
2. ESR test
3. mantoux test
4. widal test
Answer:
4. widal test
Question 41.
Tobacco contains the alkaloid
1. cocaine
2. morphine
3. codeine
4. nicotine
Answer:
4. nicotine
![]()
Question 42.
Harmful effect of cigarette smoking is
1. baldness
2. yellowing of eyes
3. lung cancer
4. fever
Answer:
3. lung cancer
Question 43.
Opium is obtained from
1. Oryza sativa
2. Thea sinensis
3. Coffea arabica
4. Papaver somniferum
Answer:
4. Papaver somniferum
Question 44.
Morphine obtained from Opium is a(an)
1. latex
2. pome
3. alkaloid
4. tannin
Answer:
3. alkaloid
Question 45.
Diacetyl morphine is commonly known as
1. morphine
2. Cannabis
3. heroin
4. cocaine
Answer:
3. heroin
Question 46.
Heroin acts as a
1. Stimulant
2. depressant
3. hallucinogen
4. intensifier
Answer:
2. depressant
Question 47.
Cannabinoids interact with cannabinoid receptors present principally in the
1. gut
2. lungs
3. liver
4. brain
Answer:
4. brain
Question 48.
Chemical obtained from Cannabis sativa is
1. codeine
2. cocaine
3. cannabinoid
4. caffeine
Answer:
3. cannabinoid
Question 49.
Coca plant belongs to genus
1. Papaver
2. Atropa
3. Erythroxylum
4. Datura
Answer:
3. Erythroxylum
Question 50
Narcotic drugs like bhang, ganja and charas are obtained from
1. hemp plant
2. poppy seed
3. coco plant
4. ergot fungus
Answer:
1. hemp plant
Question 51.
The synthetic drugs structurally similar to adrenaline are
1. amphetamines
2. barbiturates
3. hallucinogens
4. nicotinic derivatives
Answer:
1. amphetamines
![]()
Question 52.
LSD is obtained from
1. Erythroxylon coca
2. Papaver somniferum
3. Cannabis sativa
4. Claviceps purpurea
Answer:
4. Claviceps purpurea