Collaborative study sessions centered around AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Model Papers and AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper April 2022 can enhance peer learning.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Question Paper April 2022
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 100
Part – I (50 Marks)
Section – A
Answer any TWO of the following questions in not exceeding 40 lines each.
Question 1.
Define partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations.
Answer:
Partnership has been defined by Haney as “The relation existing between persons to make contracts who agree to carry on a lawful business with a view to private gains.” Partnership is defined by Section-4 of Indian Partnership Act of 1932 as “The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of the business carried on by all or any of them acting for all”.
Merits:
- Easy formation : It is very easy and simple to form a partnership. There are no legal formalities to start the business. No formal documents are required. A simple agreement among partners is sufficient to start the business. Even the registration is not compulsory.
- Large resources : The resources of more than one person are available for the business. The partners can contribute to start a moderately large scale concern.
- Higher managerial power : We can pooi capital, organising ability, managerial capacity, technical skill etc., in the partnership. It will leads to work efficiently among partners.
- Promptness in decision making : The partners meet frequently and they can take prompt decisions.
- Flexibility The partnership is flexible in nature. At any time the partners can decide the size or nature of business or area of its operations after taking necessary consent of all the partners.
- Sharing risks : The risk of business is shared by more persons.
- Cautions and sound approach : The principle of unlimited liability induces the partners to work hard for the success of the business. They take keen interest in the affairs of the business.
- Business secrecy : Annual accounts are not published and audit report is also not required. So, business secrets can be maintained.
- Benefits of specialisation : All partners actively participate in the business as per their specialisation and knowledge.
Limitations:
- Unlimited liability : The unlimited liability is fundamental drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts of the firm.
- Instability : The partnership concern suffers from uncertainity of duration because it can be dissolved on the death, lunacy or insolvency of the partner.
- Limited resources : There is limitation in raising additional capital for expansion purposes. The business resources are limited to the personal funds of the partners.
- Non-transferabifity of share : No partner can transfer his share to third party without the consent of other partners.
- Mutual distrust : The mutual distrust among partners is the main cause for dissolution of partnership firms.
- Delay in decisions : Before any decision is taken all the partners must be consulted. Hence quick decisions cannot be taken.
Question 2.
What are the various factors that determine the selection of sources of finance ?
Answer:
The following factors should be considered for selecting the sources of finance.
- Cost factor: While deducting the sources of funds that is utilised by the business concern, the cost of procuring the funds and the cost of utilising are to be considered.
- Sound financial position: In the choice of source funds, the business should be financially sound so that it can repay the principle amount together with interest.
- Form of business organisation : The form of business organisation influences the choice of source raising money. Ex: A partnership firm cannot raise money by issue of equity shares.
- Purpose and period of time: While selecting the sources of finance, purpose and period of time is to be taken into account. A short term need can be met by borrowing funds through trade credit, commercial paper etc., with low rates of interest. For long term finance, sources like issue of shares and debentures are more appropriate.
- Risk factor: Business should evaluate each of the sources of finance in terms of risk involved. Ex: If equity shares are issued, they are to be repaid only at the time of winding up and dividends are not paid if the profits are not available. There is little risk involved. On the other hand, a loan is to be repaid as per the schedule and the interest is to be paid whether firm earns profits or not.
- Control : A particular sources of funds may affect the control and power of the owners on the management of the firm. As the equity shareholders enjoy voting rights, by the issue of equity shares the financial institutions may take control of the assets or may impose conditions as per loan agreement.
- Effect on credit worthiness : Depending on certain sources of finance may affect the credit worthiness in the market. Ex : Issue of secured debentures may affect the interests of the creditors and they may not be willing to extend furthur loans to the company.
- Flexibility and ease : Another factor which may affect the choice of sources of finance is flexibility and ease of obtaining funds. In order to secure loans from banks, they may impose restrictions and documentation is necessary. If other sources are available, traders may not prefer approaching banks and financial institutions.
- Tax benefits : Tax is not deducted on dividend on preference shares. Interest paid on loans and debentures is tax deductable. In order to take advantage of tax benefits, firms may issue debentures of take loans.
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish between a private company and a public company.
Answer:
The following are the differences and a Public Company between Private Company and a Public Company.
| Private Company | Public Company |
| 1. To form a Private company the minimum number of members is 2 and maximum number of members is 50. | 1. Minimum number of members is 7 and maximum number of members is unlimited. |
| 2. It cannot issue prospectus. | 2. Public company can issue prospectus. |
| 3. The transferability of shares is generally restricted by its articles. | 3. The shareholders can freely transfer their shares. |
| 4. It can commence its business as soon as it obtains certificate of incorporation from the registrar. | 4. The business can be started only after getting certificate of commencement of the business. |
| 5. If need not conduct statutory meeting and file copy of statutory report to the registrar of Joint Stock Companies. | 5. A statutory meeting must be held within 6 months from the date of receiving certificate of commencement of business. Statutory report is to be submitted to the registrar. |
| 6. A private company can proceed with the allotment of shares before minimum subscription is received. | 6. Shares cannot be allotted before minimum subscription is received. |
| 7. The word private limited at the end of the name. | 7. The word limited at the end of the name. |
| 8. The minimum number of directors is 2 and there is no maximum limit. | 8. The minimum number of directors is 3. The maximum number of directors is 20. |
| 9. The directors need not take qualification shares. | 9. Qualification shares are necessary to become a director. |
| 10. The directors need not retire by rotation. | 10. 1/3 of the directors must retire by rotation. |
| 11. There is no age limit to become a director. | 11. Age limit for the directors is 65 years. |
| 12. The directors need not sent their consent to act as directors. | 12. The directors must send their consent to act as directors. |
| 13. There is no restriction on the remuneration payable to the directors and managing directors. | 13. The remuneration
payable to the directors and others shall not exceed 11% of the net profits. |
| 14. It can grant loans to the directors without the consent of the central government. | 14. Permission from the central government is necessary to grant loans to the directors. |
| 15. Quorum for the meeting is 2. | 15. Quorum for the meeting is 5. |
Section – B
(4 × 5 = 20)
i) Answer any FOUR of the following questions in not exceeding 20 lines.
ii) Each question carries 5 marks.
4. Explain any five types of industries.
5. Explain any five merits of sole proprietorship.
6. Explain the classification of sources of finance.
![]()
7. Define service enterprises as per MSME Act, 2006.
8. Explain the merits of MNCs to home country.
9. What are the benefits of e-business to customers ?
Section – C (5 × 2 = 10)
i) Answer any FIVE of the following questions in not exceeding 5 lines.
ii) Each question carries 2 marks.
Question 10.
Employment
Answer:
Employment: Employment involves working under a contract of employment for or under some one known as employer in return for a salary. The person engaged under employment works as per the directions of the employer.
11. Commerce
12. Sleeping Partner
13. Partnership deed
![]()
14. What do you mean by a statutory company ?
15. Define MOA (Memorandum of Association)
16. Fixed Capital
17. Define FDI
Part – II (1 × 20 = 20)
Section – D
Answer the following question.
Question 18.
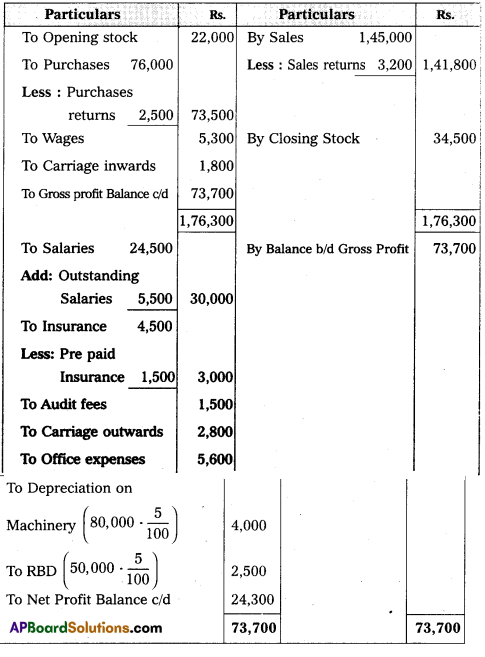
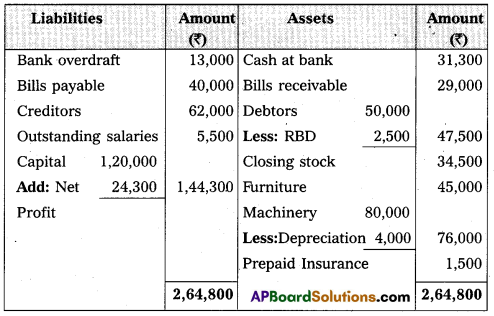
From the following Trial Balance, Prepare Trading, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
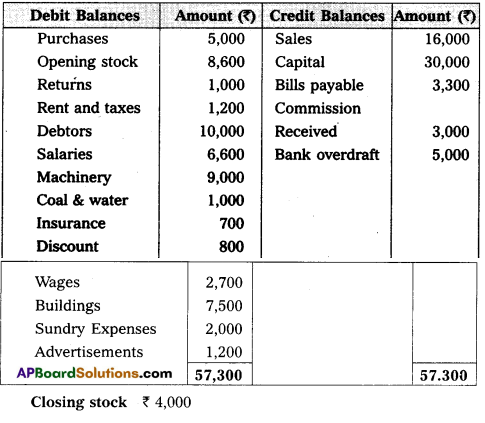
Answer:
Balance Sheet of Mr Paramesh as on 31.3.2016
Section – E (1 × 10 = 10)
Answer any ONE of the following questions.
Question 19.
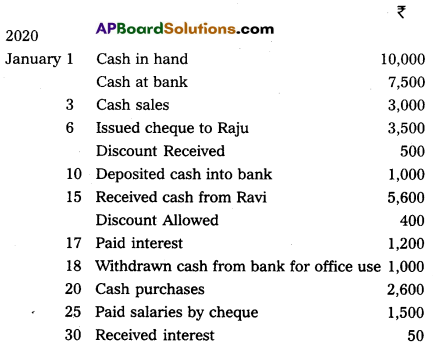
Prepare three column Cash Book from the following information :
20. Reddy Limited’s Pass Book showed a balance ₹ 20,000 as on 31.12.2020. On comparing the cash book the following discrepancies were noted.

Prepare a bank Reconciliation statement showing balance as per Cash Book.
Section – F (2 × 5 = 10)
Answer any TWO of the following questions.
21. Write different types of Accounts along with their debit, credit rules.
22. Prepare Kavya’s account from the following particulars :

23. Record the following transactions in proper subsidiary Books.

![]()
24. Explain the merits and demerits of Trial Balance.
Section – G (5 × 2 = 10)
Answer any FIVE of the following questions.
25. Define Accounting.
26. Explain money measurement concept.
27. Journalise the following transactions in the books of Mr. Balu :

30. Prepare Trial Balance from the following :

31. Capital income.
32. Drawings