Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 8th Lesson Taxonomy of Angiosperms which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Important Questions 8th Lesson Taxonomy of Angiosperms
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is “Omega Taxonomy”? [TS M-18, 20, 22] [AP M-15, 18] [IPE Mar- 13]
Answer:
Omega Taxonomy is an advanced taxonomy which deals with Embryology, Cytology, Palynology, Phytochemistry, Serology etc., along with Morphology.
Question 2.
What is natural system of plant classification? Name the scientists who followed it?
Answer:
- The classification of plants on the basis of all possible Morphological characters and natural relationship is called Natural system of plant classification.
- Bentham and Hooker, de jussieu and de candolle followed this system.
Question 3.
Explain the scope and significance of ‘Numerical Taxonomy’. [AP M-22]
Answer:
- Scope: Numerical taxonomy uses mathematical methods to evaluate observable ‘differences and similarities’ between taxonomic groups. It is easily carried out by using computers.
- Significance: Here, numbers and codes are assigned to all the characters and hence the data is processed. Each character is given equal importance and at the same time hundreds of characters can be considered.
Question 4.
What is geocarpy? Name the plant which exhibits this phenomenon. [AP M-16, 17, 18, 19|[TS M-15, 17]
Answer:
- Formation of fruit inside the soil is called geocarpy.
- Arachis hypogea (ground nut) exhibits this phenomenon.
Question 5.
Name the type of pollination mechanism found in members of Fabaceae. [Mar-14]
Answer:
The pollination mechanism found in Fabaceae is Piston mechanism.
Question 6.
Write the floral formula of solanum plant. [TS M -22] [AP M-20]
Answer:
Floral formula of Solanum plant:

Question 7.
Give the technical description of ovary in Solanum nigrum.
Answer:
- In Solanum nigrum ovary is bicarpellary, syncarpous, bilocular, superior ovary with many ovules on swollen axile, placentation.
- Style terminal, stigma capitate carpels are arranged obliquely at 45°.
Question 8.
Give the technical description of anthers of Allium cepa. [TS M-16]
Answer:
In Allium cepa, anthers are dithecous, basifixed, introrse and dehiscence is longitudinal.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a brief note on semi technical description of a typical flowering plant. [AP M-19]
Answer:
- The description of a flowering plant begins with its habit, habitat, vegetative characters (root, stem, leaves) and then floral characters (inflorescence, flower and its parts) followed by its fruit.
- After describing various parts of a plant, a floral diagram and floral formula are presented.
- Floral diagram provides information about the number of parts of a flower, their arrangement.
- Floral formula represents various floral parts by means of symbols.
- Notation of floral formula:
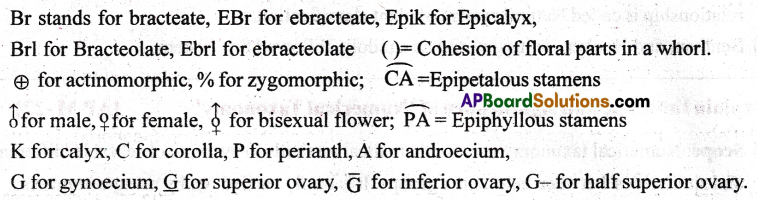
Question 2.
Describe the non-essential floral parts of plants belonging Fabaceae. [IPE Mar-14]
Answer:
- Non-essential floral parts of Fabaceae are Calyx and Corolla. fTSM-16,18)
- Calyx: 5 Sepals, Gamosepalous (united sepals), valvate or imbricate aestivation, odd sepal anterior.
- Corel la: 5 Petals, Polypetalous (petals are free), Papilionaceous consisting of a large posterior petal (Standard), two laterals (Wings); Two anterior fused petals (keels) enclosing the stamens and pistil.
- They show vexillary or descendingly imbricate aestivation.
Question 3.
Give an account of floral diagram. [TS M-22]
Answer:
- The floral diagram provides information about the number of parts of a flower, their arrangement and the relation they have with one another.
- The mother axis represents the posterior side of the flower and is indicated as a dot or circle at the top of the floral diagram.
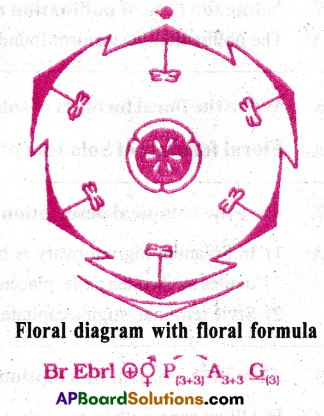
- Calyx, Corolla, androecium and gynoecium are drawn in successive whorls, calyx being the outermost and the gynoecium being in the centre represented by a diagram of T.S. of ovary.
- The bract represents the anterior side of the flower and is indicated at the bottom of the floral diagram.
Question 4.
Describe the essential floral parts of plants belonging to Liliaceae.|AP M-15,17,18,20|
Answer:
- Essential floral parts of Liliaceae are Androecium and Gynoecium.
- Androecium: Six stamens in two whorls (3+3); epiphyllous, dithecous anthers , basifixed, introrse and longitudinal dehiscence.
- Gynoecium: Tricarpellary, Syncarpous, Trilocular superior ovary with many ovules on axile placentation.
- Style is terminal and stigma is trifid and capitate.
Question 5.
Write a brief account on the class of dicotyledonae of Bentham and Hooker’s classification. [AP M -22] [TS M-17|
Answer:
- According to Bentham and Hooker classification, the dicotyledonae class is divided into 3 sub classes, namely Polypetalae, Gamopetalae and Monochlamydae.
- Polypetalae subclass is divided into 3 series – Thalamiflorae (with 6 cohorts), Disciflorae (with 4 cohorts) and Calyciflorae (with 5 cohorts).
- Gamopetalae subclass is divided into 3 series – Inferae (with 3 cohorts), Heteromerae (3 cohorts) and Bicarpellate (with 4 cohorts)
- Monochlamydae subclass is divided into 8 series (not into cohorts)
- All the cohortsdivided into natural orders are now called families.
- Thus dicotyledonae class includes 165 families.
Question 6.
Describe the essential organs of Solanaceae. [TS M-15, 19, 22]
Answer:
- Essential organs of Solanaceae are Androecium and Gynoecium:
- Androecium: There are five epipetalous stamens, alternating with the petals. Anthers are dithecous, basifixed and introse.
- Gynoecium: The ovary is superior, bicarpellary and syncarpous. It is usually bilocular but occassionally unilocular. It is oblique in position and anterior carpel to the left is at an angle of 45°. There are numerous ovules arranged on axile placentation on swollen placenta.
- The style is terminal and stigma is capitate.
Question 7.
Give economic importance of plants belonging to Fabaceae. [AP M-16] [IPE M-13]
Answer:
Economic importance of Fabaceae plants: [TS M-20] [AP May-19] [AP, TS May-17]
- Pulses – These are the sources of proteins. Ex: Redgram, Black gram, Green gram, Bengal gram.
- Edible oils- Soyabean (Glycine max), Ground nut (Arachis hypogea).
- Vegetables- Pods of bean (Dolichos), Soyabean (Glycine max), leaves of Menthi.
- Timber – Red sanders, Indian rose wood.
- Fiber- Sun hemp (crotalaria)
- Blue dye- Indigofera tinctoria, yellow dye- Butea monosperma.
- Fodder – Crotalaria, phaecealous
- Green manure – Sesbania, Tephroshia 9) Medicinal – Derris indica
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
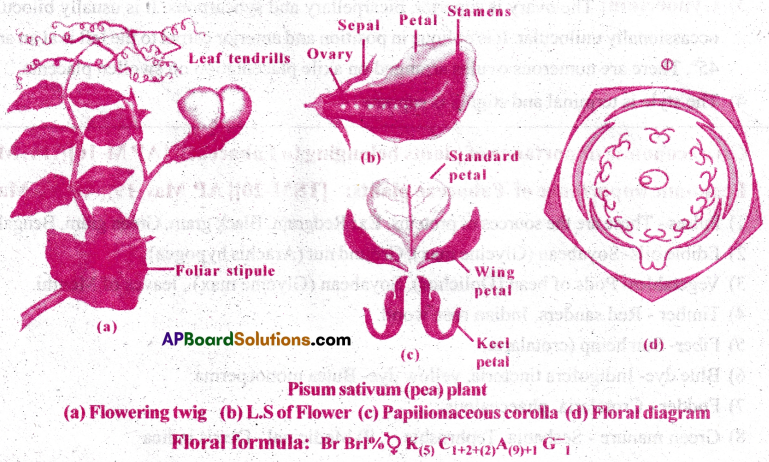
Describe the characteristics of plants belonging to Fabaceae,
Answer:
I) Vegetative Characters:
Habit: The plants are annual herbs. Some are shrubs, trees, weak stemmed twinners or tendril climbers.
Root system: It is a tap root system. The roots bear root nodules in which the symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria Rhizobia are present.
Stem: Aerial, prostrate or erect, herbaceous or woody climbers.
Leaves: Cauline, alternate, stipulate, base pulvinate, petiolate, simple or pinnately compound leaf, venation reticulate.
II) Floral characters:
Inflorescence: Mostly a raceme.
Flower: Bracteate, bracteolate or ebraeteolate, pedicillate, zygomorphic, complete, bisexual, pentamerous, perigynous, cupshaped thalamus.
Calyx: Sepals five, gamosepalous, valvate or imbricate aestivation, odd sepal anterior.
Corolla: Petals five, polypetalous, papilionaceous consisting ofa large posterior petal (Standard), two lateral (wings), two anterior fused petals (keels) enclosing the stamens and pistil, vexillary / descendingly imbricate aestivation.
Androecium: 10 Stamens, diadelphous [(9)+l] as in pisum; or monadelphous as in Arachis, crotalaria, anthers dithecous.
Gynoecium: Monocarpel lary unilocular half- superior ovary with many ovules on marginal placentation, style single, long, terminal; stigma simple.
Pollination: Flowers are protandrous, usually entomophilous cross pollination with “Piston mechanism” self pollination in Pisum and Lathyrus.
Fruit: Mostly legume or pod, geocarpic, indehiscent in Arachis.
Seed: One to many, non -endospermic, two cotyledons which store mostly proteins but also oil in Arachis.
Question 2.
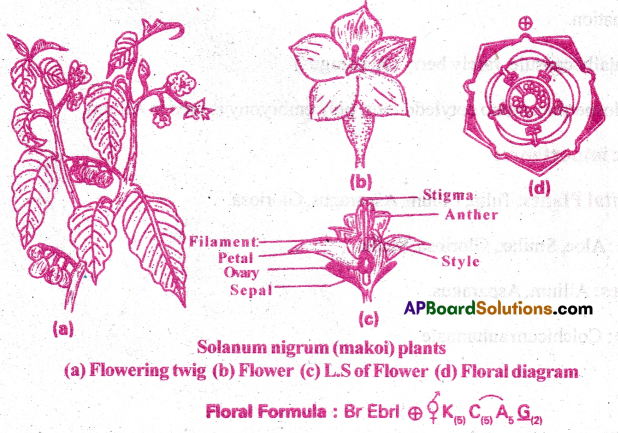
Write about the key characteristics of Solanaceae?
Answer:
I) Vegetative Characters:
Habit: Mostly annula or perennial herbs. Some are shrubs. (Cestrum sps).
Root system: Tap root system.
Stem: It is aerial, erect and mostly herbaceous. Stem is an underground tuber in Solanum tuberosum (potato). Bicollateral vascular bundles are present in the stem.
Leaves: Leaves are exstipulate, petiolate and show alternate phylloatxy. They are simple or rarely pinnately compound leaf with reticulate venation.
II) Floral characters:
Inflorescence: It is usually cymose type. It may be terminal or axillary in position. In some species of Solanum, it is an axillary. In Datura, it is solitary and terminal, panicle in tobacco. Flower: The flowers are bracteate or ebracteolate, pedicillate, actinomoiphic, complete, bisexula, pentamerous, hypogynous.
Calyx: It consists of 5 sepals which are fused (gamosepalous) and persistent (Capsicum, Solanum). The aestivation is valvate.
Corolla: It consists of 5 petals and is gamopetalous. The aestivation is valvate or twisted Androecium: There are 5 epipetalous stamens alternating with the petals. Anthers are dithecous, basifixed and introse. The dehiscence may be longitudinal (Datura) or porous (Solanum).
Gynoecium: The ovary is superior, bicarpellary and syncarpous. It is oblique in position due to the tilting of posterior carpel. Carpels are arranged obliquely at 45°. The style is terminal and stigma is capitate.
Pollination: Flowers are usually protandrous. But some species of Solanum are protogynous. Cross pollination through insects (entomophily) is common.
Fruit: The fruits are mostly berry (Capsicum, Solanum, Lycopersicon, Physalis etc.,). Some are capsule (Datura and Nicotiana)
Seed: The seeds are endospermic and dicotyledonous.
Question 3.
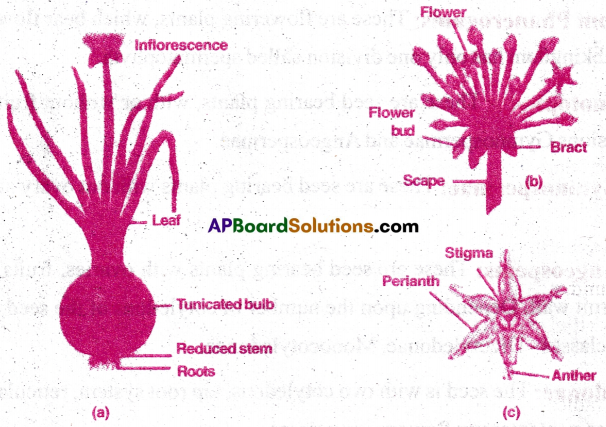
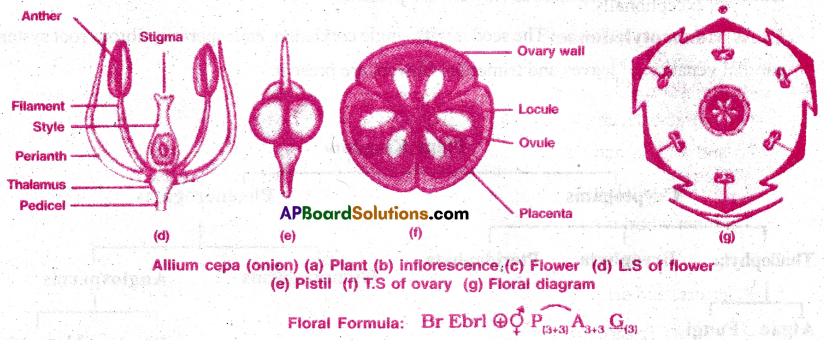
Give an account of the family Liliaceae.
Answer:
The family of Liliacea is commonly called ‘Lily family’.
It belongs to class Monocotyledonae and series Coronariae
Vegetative Characters:
Habit: Mostly perennial herbs with underground stems such as bulbs, corms, rhizome. Some are shrubs, some are tree like (Yucca, Dracaena, Agave), some are climbers (Gloriosa, Smilax) Root system: Adventitious roots, fasciculated and tuberous in Asparagus.
Stem: Underground, perennial, bulb (Allium), corm (Colchicum), rhizome (Gloriosa), some are aerial, weak, tendril climbers (Gloriosa, smilax) branches modified into cladophylls (Ruscus, Asparagus).
Leaves: Mostly radical (Allium) or cauline (Smilax), simple, alternate, linear exstipulate, parallel venation, exceptionally reticulate venation in Smilax.
Floral characters:
Inflorescence: Solitary cyme or umbel or raceme.
Flower: Bracteate, ebracteolate, pedicillate, complete, bisexual or exceptionally unisexual as in smilax and Ruscus, actinomorphic, trimerous, hypogynous, homochlamydeous.
Perianth: Six petals in two whorls (3+3), odd tepal of outer whorl is anterior in position and odd petal of inner whorl is posterior in position, valvate aestivation.
Androecium: Six stamens in two whorls (3+3), free or epiphyllous, anthers dithecous, basi fixed, introrse and dehiscence longitudinal.
Gynoecium: Tricarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, trilocular with many ovules on axile placentation, style terminal, stigma trifid and capitate.
Pollination: Flowers may be protandrous( Allium) or protogynous (Colchicum), entomophilous cross pollination.
Fruit: Usually capsule, rarely berry (Asparagus)
Seed: Endospermic, mono cotyledonous, poly embryony is seen in Allium.
Economic importance:
Ornamental Plants: Tulip, Lilium, Asparagus, Gloriosa.
Medicine: Aloe, Smilax, Gloriosa, Scilla.
Vegetables: Allium, Asparagus.
Colchicin: Colchicum autumnale.
Question 4.
Write the characteristics of plants that are necessary for classification. Describe them in brief.
Answer:
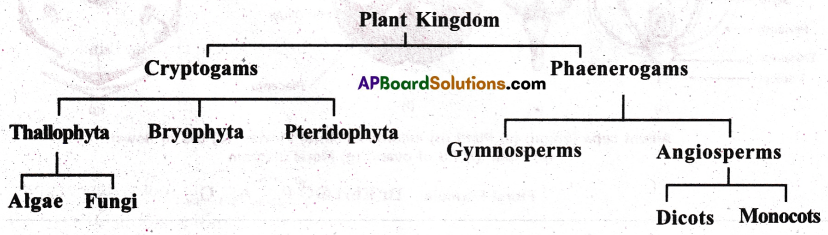
Based on flower, plants are classified as cryptogams and phanerogams.
I) Sub kingdom Cryptogams: These are non flowering plants, donot produce flowers, fruits and seeds. Based on the type of plant body, they are divided into Thallophyta, Bryophyta and Pteridophyta.
Division -Thallophyta: The plant body is thallus, which is not divided into root, stem and leaf. This division is divided into Algae and Fungi.
Sub division- Algae:These are green, photo autotrophic, aquatic thallophytes.
Sub division fungi: These are non-green heterotrophic thallophytes.
Division Bryophyta: These are amphibians of plant kingdom. These are green, autotrophic, embryophytic, non vascular cryptogams.
Division Pteridophyta: These are true land plants, green, autotrophic, embryophytic, vascular cryptogams.
II) Sub Kingdom Phanerogams: These are flowering plants, which bear flowers, fruits and seeds. This subkingdom has only one division called spermatophyta.
Division Spermotophyta: These are seed bearing plants, with or without fruits and divided into two sub divisions Gymnospermae and Angeospermae.
Sub division Gymnospermae: These are seed bearing plants with out ovary and fruit. Seeds are naked.
Sub division Angeospems: These are seed bearing plants with ovaries, fruits and seeds are enclosed in the fruit walk Depending upon the number of cotyledons of the seed, the plants are divided into two classes – Dicotyledonae, Monocotyledonae.
Class Dicotyledonae: The seed is with two cotyledons, tap root system, reticulate venation of leaves and tetra or pentamerous flowers are present.
Class Monocotyledonae: The seed is with single cotyledon, endospermic, fibrous root system, parallel venation of leaves and trimerous flowers are present.
Question 6.
Give an account of Bentham and Hooker’s classification of plants.
Answer:
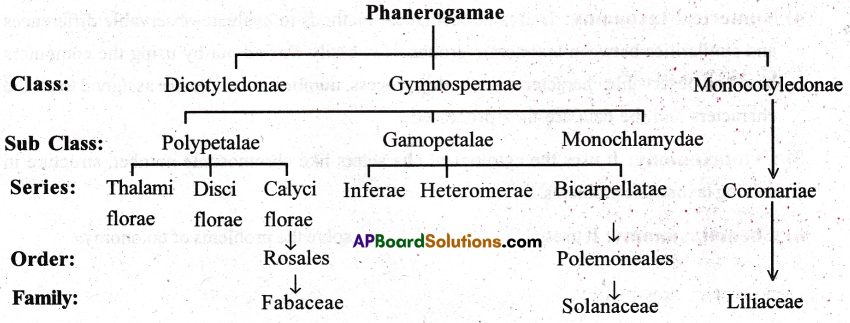
Natural system of classification is also known as Bentham and Hooker’s system. They divided the flowering plants into three classes namely Dicotyledonae, Gymnospermae and Monocotyledonae.
I) Class-Dicotyledonae: Seed with two cotyledons, Tap root, reticulate venation in leaves and tetra or pentamerous flowers. This class is divided into three sub classes – Polypetalae, Gamopetalae and Monochlamydae.
1) Sub class- Polypetalae: Petals are free, perianth in two whorls. This sub class is divided into three series.
a) Series- Thalamiflorae: Thalamus is conical or elongated. The flowers are hypogynous. This series has 5 cohorts or orders.
b) Series – Disciflorae: Thalamus is disc shaped. Flowers are hypogynous. This series has 4 cohorts (or) orders.
c) Series- Calciflorae: Thalamus is cup shaped. Flowers are epigynous. This series has 5 cohorts, (or) orders.
The family: Fabaecae belongs to order Rosales. It is included in our syllabus.
2) Sub class Gamopetalae: Petals are united, perianth in two whorls, stamens are epipetalous. Based on the nature of ovary and merosity of the flower, the sub class is divided into 3 series.
a) Series- Inferae: Ovary is inferior. It includes 3 cohorts.
b) Series – Heteromerae: Ovary is superior and more than two carpels. It has 3 cohorts.
c) Series- Bicarpellatae: Ovary is superior two carpels in the ovary. It has 4 cohorts.
The family solanaceae belongs to order polemoniales.
3) Sub class- Monochlamydeae: Perianth is not divided into calyx or corolla. It has 8 series and no cohorts.
II) Class- Gymnospermae: Naked seeded plants are included. It is divided into 3 families. Cycadaceae, Conifera and Gnetaceae.
III) Class Monocotyledonae: Single cotyledon in the seed, Adventitious root system, parallel venation, trimerous flowers. It has 7 series and no cohorts. Families are directly placed under the series. The family liliacea comes under the series coronariae.
Question 7.
What is taxonomy? Give a brief account of different types of plant classification.
Answer:
Assigning the plants to specific groups on the basis of their similarities and dissimilarities is called classification. The classification of plants is called Taxonomy. It includes four basic components viz, characterization, identification, nomenclature and classification. There are three systems of classification.
1) Artificial system of classification:It is based only on gross superficial morphological characters such as habit, colour, number and shape of leaves etc. In this system only a few characters were selected and plants were arranged into groups. Classification of plants into three groups is done by basing on the habitat such as herbs, shrubs and trees in the book of Theophrastus. In the sexual system of classification on Linnaeus classified plants into 24 groups based on the number, length and union of stamens and carpels.
2) Natural system of classification: All important morphological characters and their relations were taken into consideration while grouping the plants. Ex: Bentham and Hooker system, classification of decondolle.
3) Phylogenetic systeip of classification: This is the classification of post-darwinian period. Evolutionary trends in plants are taken into consideration as phylogenic systems. Primitive and advanced characters are recognised in a phylogenic system. Evolution may be progressive or retrogressive. While considering the status of a taxon, a comprehensive picture of all the characters is taken into account. One system is proposed by Engler and Prantl in their book “Die Naturlichen Planzen families”. Another system is by J. Hutchinson in his book “Families of Flowering plants”. The latest phylogenic classification is APG (Angiospermic Phylogenetic Group) system.
Other types:
4) Numerical taxonomy: It uses mathematical methods to evaluate observable differences and similarities between taxonomic groups. It is easily carried out by using the computers based on observable characteristics. In this process, number and codes are assigned to all the characters and the data are then processed.
5) Cytotaxonomy: It uses the cytological characters like chromosome number, structure in solving taxonomic problems.
6) Cheniofaxonomy: It uses phytochemical data to solve the problems of taxonomy.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Aloe vera belongs to the family
1. Solanaceae
2. Liliaceae
3. Fabaceae
4. Malvaceae
Answer:
2. Liliaceae
Question 2.
Berry is the fruit in
1. Datura
2. Arachis
3. Nicotiana
4. Asparagus
Answer:
4. Asparagus
Question 3.
Cestrum is a
1. Herb
2. Tree
3. Climber
4. Shrub
Answer:
4. Shrub
Question 4.
Draw back of natrual system of classification is
1) Classified the plants upto species level
2) Floral characters are given equal importance
3) Evolutionary importance is not considered
4) Vegetative characters are not considered
Answer:
3) Evolutionary importance is not considered
Question 5.
Earliest system of plant classification is
1. Natural system
2. Artificial system
3. Phylogenetic system
4. APG system
Answer:
2. Artificial system
Question 6.
Fundamental requisite information for classification of plants is
1. Palynology
2. Palaeobotany
3. Morphology
4. Cytology
Answer:
3. Morphology
Question 7.
Father of Taxonomy is
1. Theophrastus
2. Parasara
3. Linnaeus
4. Gaspard Bauhin
Answer:
3. Linnaeus
Question 8.
Sexual system of classification was proposed by
1. Theophrastus
2. Linnaeus
3. de Candolle
4. Bentham & Hooker
Answer:
2. Linnaeus
Question 9.
Sexual system of Linnaeus is found in
1. Historia plantarum
2. Species plantarum
3. Genera plantarum
4. Vrikshayurveda
Answer:
2. Species plantarum
Question 10.
Authors of Genera plantarum
1. Engler & Prand
2. Bentham & Hooker
3. Sutton and Boveri
4. Knoll & Ruska
Answer:
2. Bentham & Hooker
Question 11.
Sexual system of classification is a kind of
1. Natural system
2. Artificial system
3. Phylogenetic system
4. APG system
Answer:
2. Artificial system
Question 12.
Closely related natural orders are placed under
1. Cohort
2. Genus
3. Class
4. Phylum
Answer:
1. Cohort
Question 13.
Scientific name of Red sanders is
1. Dalbergia latifolia
2. Butea monosperma
3. Derris indica
4. Pterocarpus santalinus
Answer:
4. Pterocarpus santalinus
Question 14.
Placentation in Fabaceae is
1. Marginal
2. Basal
3. Parietal
4. Axile
Answer:
1. Marginal
Question 15.
Pulses belong to the family
1. Solonaceae
2. Liliaceae
3. Caesalpiniaceae
4. Fabaceae
Answer:
4. Fabaceae
Question 16.
Scientific name of Rosewood plant is
1. Pterocarpus santalinus
2. Butea monosperma
3. Dalbergia latifolia
4. Derris indica
Answer:
3. Dalbergia latifolia
Question 17.
Cohesion of stamens is exhibited by
1. Pisum
2. Solanum
3. Allium
4. Datura
Answer:
1. Pisum
Question 18.
In Fabaceae, essential organs are enclosed by
1. Vexillum
2. Wings
3. Keel petals
4. Alae
Answer:
3. Keel petals
Question 19.
Inflorescence in Tobacco is
1. Compound corymb
2. Compound spike
3. Compound umbel
4. Compound raceme (panicle)
Answer:
4. Compound raceme (panicle)
Question 20.
Atropa belongs to this Cohort
1. Rosales
2. Poales
3. Rubiales
4. Polemoniales
Answer:
4. Polemoniales
Question 21.
Night queen and Day king belong to the genus
1. Petunia
2. Withania
3. Datura
4. Cestrum
Answer:
4. Cestrum
Question 22.
Petiole is adnate to the stem in
1. Brassicaceae
2. Fabaceae
3. Liliaceae
4. Solanaceae
Answer:
4. Solanaceae
Question 23.
Stem tuber is seen in
1. Solanum tuberosum
2. Solanum nigrum
3. Capsicum fruitescens
4. Solanum melongena
Answer:
1. Solanum tuberosum
Question 24.
Protogynous flowers are seen in
1. Colchicum and Solanum
2. Allium and Solanum
3. Pisum and Colchicum
4. Pisum and Solanum
Answer:
1. Colchicum and Solanum
Question 25.
Swollen placenta is seen in
1. Solanaceae
2. Fabaceae
3. Liliaceae
4. Brassicaceae
Answer:
1. Solanaceae
Question 26.
Fasciculated tuberous roots are found in
1. Solanum tuberosum
2. Arachis hypogea
3. Asparagus racemosus
4. Aloe vera
Answer:
3. Asparagus racemosus
Question 27.
The ratio of tepals, staments, carpels in the flower of Allium cepa is
1. 1:2:2
2. 1:2:1
3. 2:2:1
4. 2:1:2
Answer:
3. 2:2:1
Question 28.
Polyembryony is seen in
1. Allium
2. Datura
3. Nicotiana
4. Pisum
Answer:
1. Allium
Question 29.
Liliaceae plant with reticulate venation is
1. Gloriosa
2. Smilax
3. Asparagus
4. Ruscus
Answer:
2. Smilax
Question 30.
Flowers are homochlamydeous in
1. Solanaceae
2. Liliaceae
3. Brassicaceae
4. Fabaceae
Answer:
2. Liliaceae
Question 31.
Colchicine is obtained from
1. Aloe
2. Garlic
3. Glorylily
4. Meadow saffron
Answer:
4. Meadow saffron
Question 32.
Odd tepai of outer whorl is anterior in
1. Garlic
2. Solanum
3. Arachis
4. Pisum
Answer:
1. Garlic
Question 33.
Liliaceae plant with protandry is
1. Colchicum
2. Allium
3. Solanum
4. Nicotiana
Answer:
2. Allium
Question 34.
Liliaceae plants with bulb are
1. Allium, Lilium
2. Colchicum
3. Gloriosa
4. Asparagus
Answer:
1. Allium, Lilium
Question 35.
Mesophytes of Liliaceae are
1. Asparagus
2. Ruscus
3. Aloe
4. Allium, Lilium
Answer:
4. Allium, Lilium
Question 36.
Fruit in Datura and Nicotiana is
1. Legume
2. Berry
3. Capsule
4. Caryopsis
Answer:
3. Capsule
Question 37.
The ratio of tepals and sporophylls in the flower of Allium respectively is
1. 3:2
2. 2:3
3. 1:3
4. 1:2
Answer:
2. 2:3
Question 38.
Stamens are epipetalous in
1. Dolichos
2. Allium
3. Asparagus
4. Datura
Answer:
4. Datura
Question 39.
Seeds are non-endospermic in
1. Datura
2. Aloe
3. Allium
4. Arachis
Answer:
4. Arachis
Question 40.
The classification of plants into herbs, shrubs and trees was done by
1. Parasara
2. Theophrastus
3. Linnaeus
4. Bauhin
Answer:
2. Theophrastus
Question 41.
The carpels in Solanaceae flower tilt in the angle
1. 90°
2. 30°
3. 180°
4. 45°
Answer:
4. 45°
Question 42.
Bicollateral vascular bundles are present in part of Solanaceae plants
1. Root
2. Stem
3. Fruit
4. Petiole
Answer:
2. Stem
Question 43.
A ’sub-class’ without cohorts in Bentham and Hooker’s classification is
1) Monocotyledonae
2) Monochlamydeae
3) Gymnospermae
4) Polypetal ae
Answer:
2) Monochlamydeae
Question 44.
……….. character can be represented only in floral diagram
1) Fusion of floral parts
2) Position of gynoecium
3) Adhesion of floral parts
4) Aestivation
Answer:
4) Aestivation
Question 45.
Number of cohorts are present in Bentham and Hooker’s classification in Dicotyledonae members having two whorls of perianth and fused petals.
1) 25
2) 21
3) 15
4) 10
Answer:
1) 25
Question 46.
Fodder plant(s) in Fabaceae is
1) Crotalaria
2) Pisum
3) Trifolium
4) 1 and 3
Answer:
1) Crotalaria
Question 47.
In pea flower, the positions of odd sepal and odd petal respectively are
1) Anterior, posterior
2) Posterior, anterior
3) Anterior, anterior
4) Posterior, posterior
Answer:
1) Anterior, posterior
Question 48.
Medicinal plants in Fabaceae are
1) Sesbania
2) Derris
3) Crotalaria
4) Tndogofera
Answer:
2) Derris
Question 49.
Members of solanaceae differ with members of Liliaceae by having
1) Axile placentation
2) Hypogynous flowers
3) Penta merous flowers
4) Inferio ovary
Answer:
1) Axile placentation
Question 50.
The ratio of tepals, stamens and carpels of a flower in Allium is
1) 1:2:2
2) 2:2:1
3) 1: 1: 1
4) 1:1:2
Answer:
2) 2:2:1
Question 51.
Similarities between self pollinated plants in Fabaceae is (are)
1) Foliaceous stipules
2) Leaf tendril
3) Complete, actinomorphic flowers
4) 1 and 2
Answer:
4) 1 and 2
Question 52.
Ornamental shrub of solanaceae is
1) Kamanchi (Makoi)
2) Atropa
3) Datura
4) Cestrum
Answer:
4) Cestrum
Question 53.
Bicarpellary syncarpous gynoecium with bilocular ovary, axile swollen placentation and oblique septum occurs in
1) Brassicaceae
2) Solanaceae
3) Fabaceae
4) Liliaceae
Answer:
2) Solanaceae
Question 54.
The floral formula of pea is represented by

Answer:
1)
Question 55.
The floral formula represents
1) Tobacco
2) Tulip
3) Soyabean
4) Sunhemp
Answer:
1) Tobacco
Question 56.
Type of placentation in the ovary of plants which arc source of proteins
1) Basal
2) Axile
3) Free central
4) Marginal
Answer:
1) Basal
Question 57.
In which of the following family, bacteria fix nitrogen, in soil by symbiosis
1) Solanaceae
2) Brassicaceae
3) Fabaceae
4) Liliaceae
Answer:
3) Fabaceae
Question 58.
Character common between Liliaceae, solanaceae is
1) Axile placentation
2) Cohesion of stamens
3) Adhesion of stamens
4) 1 and 3
Answer:
1) Axile placentation
Question 59.
The ratio of locules in the mature ovaries of Capsicum, Solatium and Allium respectively is-
1) 1 : 2 : 1
2) 1 : 2: 3
3) 1 : 3 : 2
4) 1 :1:3
Answer:
2) 1 : 2: 3
Question 60.
Tricyclic trimerous flowers are found in
a) Smilax b) Dracaena c) Ruscus d) Yucca
1) a,b
2) c,d
3) a,c
4) b,d
Answer:
3) a,c
Question 61.
Stipulate tendrillar plant of Liliaceae shows
1) Parallel venation
2) Solitary flower
3) Berry
4) Unisexual flowers
Answer:
4) Unisexual flowers
Question 62.
Mustard flower is
1) Actinomorphic, Pentamerous, Bisexual
2) Zygomorphic, Tetramerous, Bisexual
3) Ebracteate, Ebracteolate, Pentamerous
4) Ebracteate tetramerous, Actinomorphic and bisexual
Answer:
4) Ebracteate tetramerous, Actinomorphic and bisexual
Question 63.
Arrange the following in ascending order with reference to Bentham and Hooker classification
a) Total number of cohorts
b) Natural orders in Monocotyledonae
c) Cohorts in polypetalae
d) Total number of series
e) Series in Dicotyledonae
1) e, c, d, a, b
2) b, a, d, c, e
3) e, d, a, b, c
4) c, e, d, b, a
Answer:
1) e, c, d, a, b
Question 64.
Which of the following characters of flowers cannot be represented in floral formula?
a) Sexuality of the flower
b) Symmetry of the flower
c) No of floral organs in the flower
d) No of the locules in the ovary
e) Cohesion of sepals
f) Type of aestivation
1) a,b,c
2) d and f
3) d alone
4) a,c,e and f
Answer:
2) d and f