These AP 10th Class Maths Chapter Wise Important Questions Chapter 4 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Maths 4thLesson Important Questions and Answers Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Question 1.
What is meant by consistent equations ? Give example.
Solution:
The pair of Linear equations having at least one solution are called consistent.
Question 2.
Find the value of ‘k’ for which the sys-tem of equations x + 2y – 3 = 0 and 5x + ky + 7 = 0 has no solution.
Solution:
Find the value of ’k’ for which the system of equations x + 2y – 3 = 0 and 5x + ky + 7 = 0 has no solutions.
They have no solution means they are parallel.
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 are parallel if
\(\frac{\mathrm{a}_{1}}{\mathrm{a}_{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{b}_{1}}{\mathrm{~b}_{2}} \neq \frac{\mathrm{c}_{1}}{\mathrm{c}_{2}}\)here given
a1 = 1, b1 = 2, C1 = – 3 and a2 = 5, b2 = k, c2 = 7
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{5}=\frac{2}{k}\) ⇒ k = 5(2) = 10
∴ If k = 10 then the above system will have no solution.
![]()
Question 3.
Find the value of k for which the pair of equations 2x + ky + 3 = 0,
4x + 6y – 5 = 0 represent parallel lines.
Solution:
2x + ky + 3 = 0 and 4x + 6y – 5 = 0
∴ a1 = 2, b1 = k, C1 = 3
a2 = 4, b2 = 6, c2 = -5
If the given equations are parallel lines, then
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
Therefore \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\) ⇒ 4k = 12
⇒ k = \(\frac{12}{4}\) = 3
∴ k = 3
Question 4.
The larger of two supplementary angles exceeds the smaller by 58°, then find the angles. *19
Solution:
Let supplementary angles be x and y.
x = y + 58° ⇒ x — y = 58° ……….. (1)
∵ x + y = 180° ……………(2)
By solving (1) and (2)
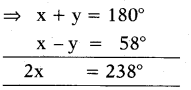
∴ x = 119° and y = 180°- 119° – 61°
∴ The angle| are 119° and 61°.
Question 5.
For what value of ‘k’ the pair of linear equations 2x – ky + 3 = 0, 4x + 6y -5 = 0 represent parallel lines ?
Solution:
If \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\), then the equations are parallel lines.
Since \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\) ⇒ -4k = 12
∴ k = – 3.
Question 6.
Reduce the pair of equations \(\frac{2}{x}+\frac{3}{y}\) = 13 and \(\frac{5}{x}+\frac{4}{y}\) = – 2
(x ≠ 0, y ≠ 0) into a pair of linear equa-tions in two variables ‘a’ and ‘b’.
Solution:
Given equations are \(\frac{2}{x}+\frac{3}{y}\) = 13 ……………..(1)
and \(\frac{5}{x}+\frac{4}{y}\) = – 2 — (2)
Let \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{x}}\) = a and \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{y}}\) = b
then the given equations can be writ¬ten as 2a 4- 3b = 13 and 5a + 4b = -2
Question 7.
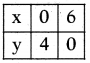
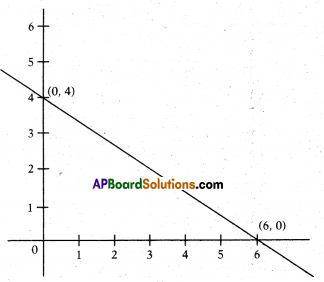
Write the equation of the straight line shown in the graph.
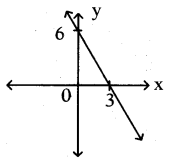
Solution:
Equation of line = \(\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}\) = 1
⇒ \(\frac{x}{3}+\frac{y}{6}\) = 1⇒ \(\frac{2 x+y}{6}\) = 1
⇒ 2x + y = 6AP 10th Class Maths Important Questions Chapter 4 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1
![]()
Question 8.
Solve the following equations by sub-stitution method
i) 2x – 7y = 3
ii) 4x + y = 21
Solution:
The given two linear equations are
2x – 7y = 3 …………. (1)
4x + y = 21 …………..(2)
From the equation (2) we get
y = 21 – 4x now we substitute this Y value in equation (1)
We get
2x – 7(21 – 4x) = 3
⇒ 2x- 147 + 28 x – 3
⇒ 30 x = 147 + 3 = 150
then x = \(\frac{150}{30}\) ∴ x = 5
Now put x = 5 in equation (2) we get
4(5) + y = 21
20 + y = 21
y = 21 – 20 = 1
So x = 5 and y = 1 are the solutions of the system.
Question 9.
10 students of 10th class participated in a Quiz programme. The number of girls participated in it is 4 more than boys. So find the number of boys and girls participated in Quiz.
Solution:
Let the number of girls = x (say)
and the number of boys = y (say)
then total students = x + y
-10 …………… (1)
and also
The number of girls = number of boys + 4
x = y + 4 …………….(2)
Put this ‘x’ value in equation (1), we get
y + 4 + y = 10
⇒ 2y + 4 = 10
⇒ 2y = 10 – 4 = 6
∴ y = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 }\) = 3
So y = 3 then
x + y = 10 becomes
x + 3 = 10
⇒ x = 10-3
∴ x = 7
So the number of girls = 7 and the number of boys = 3.
Question 10.
Is the pair of linear equations 3x – y = 40, 4x – 2y = 50 consistent or inconsis-tent ? Why ?
Solution:
Given equations are consistent.
Reason : Given equations are 3x – y = 40, 4x – 2y = 50
\(\frac{\mathrm{a}_{1}}{\mathrm{a}_{2}}=\frac{3}{4} ; \frac{\mathrm{b}_{1}}{\mathrm{~b}_{2}}=\frac{1}{2} ; \frac{\mathrm{a}_{1}}{\mathrm{a}_{2}} \neq \frac{\mathrm{b}_{1}}{\mathrm{~b}_{2}}\)
Hence the linear equations are consis-tent.
Question 11.
“Dependent pair of linear equations in two variables is always consistent”. Is it TRUE or FALSE ? Justify.
Solution:
“Dependent pair of linear equations in two variables is always consistent”.
This is true because dependent pair of linear equations represent coincident lines which have infinite number of solutions. Hence they are consistent.
Question 12.
Draw a rough diagram (graph) of lin-ear equation x = 2.
Solution:
Linear equation x = k represents a line, which is parallel to Y-axis at a distance of ‘k’ units.
∴ x = 2 can be represented as follows :
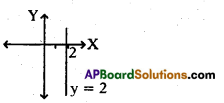
Question 13.
Solve x + 2y = 5 and 2x – y = 0 using any non-graphical method.
Solution:
x + 2y = 5 …………… (1)
2x-y = 0 ………… (2)
2x = y ⇒ x = \(\frac{y}{2}\)
This value substitute in equation (1)
\(\frac{y}{2}\) + 2y = 5 ⇒ y + 4y = 10
5y = 10 ⇒ y = 2
This value substitute in equation (2)
2x – 2 = 0 ⇒ 2x = 2 ⇒ x = 1
∴ x = 1, y = 2.
![]()
Question 14.
Vamsi bought 9 kg of onions and 2 kg of potatoes for Rs. 247. If the cost of 1 kg of onion is Rs. 3 more than that of potatoes, find their cost per kg.
Solution:
Let the cost of 1 kg of potato be x.
Then cost of 1 kg of onion is x + 3
x + x + 3 = 247
2x + 3 = 247
2x = 244 ⇒ x = \(\frac{244}{2}\) = Rs. 122.
The cost of potatoes per kg = Rs. 122
The cost of onions per kg = x + 3
= 122 + 3 = Rs. 125
Question 15.
Solve the given pair of linear equations by elimination method.
i) 2x + y – 5 = 0 and
ii) 3x – 2y – 4 = 0.
Solution:
In this elimination method, we solve this pair of linear equation by making either of coefficients equal.
The given equations are
2x + y = 5 …………….(1)
3x – 2y = 4 ………..(2)
To make the coefficients of ‘x’ equal let us multiply the equation (1) by 3 and the equation (2) by (2) on both sides. We get
(2x + y = 5) 3; (3x – 2y = 4) 2
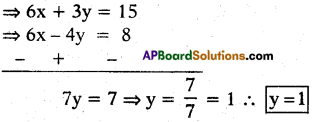
then 2x + y = 5 becomes
2x + 1 = 5
⇒ 2x = 5 – 1 = 4
∴ x = \(\frac{4}{2}\) = 2 So x = 2
x = 2 and y = 1 are the solutions of the given equations.
Verification : Put x = 2 and y = 1 in equation (1) and (2)
2x + y = 5
2(2) + 1 = 5
4 + 1 = 5
5=5
LHS = RHS
3x – 2y = 4
3(2) – 2(1) = 4
6 – 2 = 4
4 = 4
LHS = RHS
Question 16.
Solve the following equations graphically.
\(\frac{1}{3} x+\frac{1}{2} y\) = 1; \(2 x-\frac{1}{3} y=-\frac{2}{3}\)
Solution:
First we convert above given equations into linear equation form.
So \(\frac{1}{3} x+\frac{1}{2} y\) = 1 can be written as \(\frac{2 x+3 y}{6}\)= 1
⇒ 2x + 3y = 6 ………. (1)
and 2x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)y = \(\frac{-2}{3} \Rightarrow \frac{6 x-y}{3}=\frac{-2}{3}\)
⇒ 6x – y = – 2 ………….. (2)
now we find the points through which the above lines passes.
i) 2x + 3y = 6 ⇒ y = \(\frac{6-2 x}{3}\)

So (0, 2) (3, 0) are two points lie on 2x + 3y = 6
ii) 6x – y = – 2 ⇒ y = 6x + 2

So (0, 2) (1, 8) are two points lie on 6x – y = -2
I’m 5
now we plot a,ove points A(0, 2),
B(3,0) and join \(\stackrel{\leftrightarrow}{\mathrm{AB}}\) again÷ve plot (0, 2) (1, 8) and join the line \(\stackrel{\leftrightarrow}{\mathrm{CD}}\) . Now we observe (0, 2) is intersection of two lines.
Hence the solution of given equations = (0, 2)
So x = 0; y = 2 is the solution.
![]()
Question 17.
Solve the following pair of equations by eliminating method.
2x + y – 5 = 0; 3x – 2y – 4 = 0
Solution:
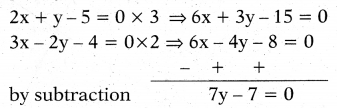
substitute y = 1 in 2x + y -5 = 0
2x + 1 – 5 = 0
2x = 4
x = 2
Question 18.
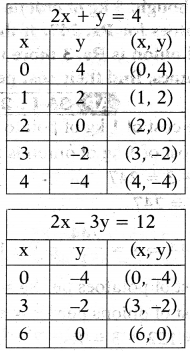
Solve the following pair of linear equations graphically.
2x + y = 4 and 2x – 3y = 12
Solution:
Given equations are
2x + y – 4 = 0 and 2x – 3y – 12 = 0
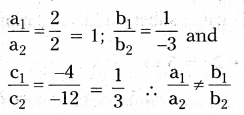
The equations are consistent.
∴ They intersect at one point giving only one solution.
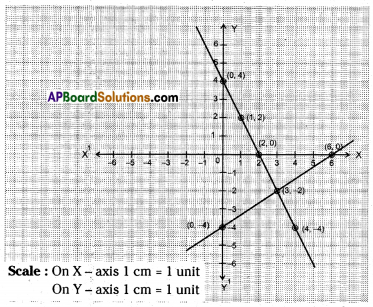
From the observing of above graph the solution is x = 3 and y = -2
Question 19.
6 pencils and 4 notebooks together cost Rs. 90/- whereas 8 pencils and 3 note-books together cost Rs. 85/-. Find the cost of one pencil and that of one note-book.
Solution:
Let the cost of each pencil be ₹ x and the cost of each pen be ₹ y.
By problem,
6 pencils and 4 notebooks together cost ₹90.
∴ 6x.+ 4y = 90 ……………. (1)
8 pencils and 3 notebooks together cost, ₹85.
∴ 8x + 3y = 85 ………….(2)
By solving the eqns (1) and (2)
6x + 4y = 90 ⇒ 3(6x + 4y) = 90 x 3
⇒ 18x + 12y = 270
8x + 3y = 85 ⇒ 4(8x + 3y) = 85 x 4
⇒ 32x + 12y = 340
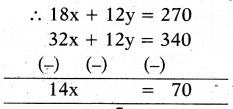
x = 5
From (2) ⇒ 8(5) + 3y = 85
⇒ 3y = 85 – 40 = ₹ 45
∴ y = ₹15
∴ Cost of each pencil be = x = ₹ 5
Cost of each pen be = y = ₹ 15
Question 20.
Solve the pair of equations
\(\frac{3}{x+y}+\frac{2}{x-y}\) = 2 and \(\frac{9}{x+y}-\frac{4}{x-y}\) = 1
Solution:
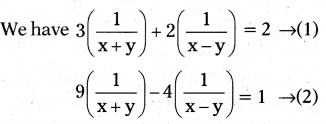
If we substitute \(\frac{1}{x+y}\) = p and \(\frac{1}{x-y}\) = q
We get the following pair of linear equations
3p + 2q = 2 …………………(3)
9p – 4q = 1 ……………………(4)

Substitute the value of q in equation (3)
3p + 2(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) = 2
⇒3p + 1 = 2 ⇒ 3p = 1
P = \(\)\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
But \(\frac{1}{x+y}\) = p = \(\frac{1}{3}\) x + y = 3 ……………. (5)
\(\frac{1}{x-y}\) = q = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x – y = 2 …………… (6)
By solving (5) and (6)
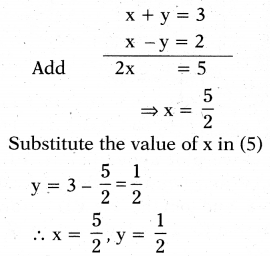
Question 21.
Solve the following pair of linear equations graphically.
2x-3y + 13 = 0, 3x-2y + 12 = 0
Solution:
Given equations are 2x – 3y + 13 = 0 and 3x – 2y + 12 = 0
i.e., 2x – 3y = – 13 and 3x – 2y = – 12
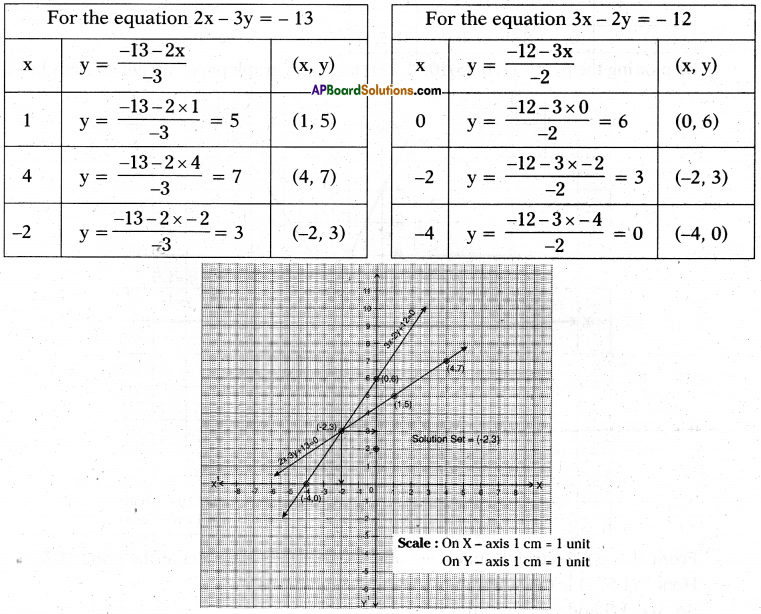
The unique solution of this pair of equations = (-2, 3)
![]()
Question 22.
Solve the equations 2x + y = 4 and 3x – 2y = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\) graphically.
Solution:
To solve the equations
2x + y = 4 and 3x – 2y = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\) graphically
We can rewrite the given equations as follows
2x + y = 4 ⇒ y = 4 – 2x ……….. (1)
3x – 2y = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\) ⇒ 6x – 4y = 5 ⇒ y = \(\frac { 6x-5 }{ 4 }\) ………… (2)
Now we choose the co-ordinates of the points lie on the straight lines represented by above (1) & (2)
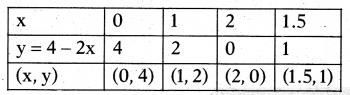
So we plot the points (0, 4), (1, 2), (2, 0) and (1.5, 1) on graph paper and connect them to get its straight line and
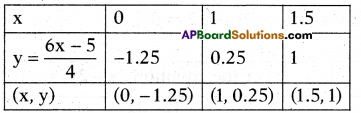
By plotting the points (1, 0.25) (0, -1.25) (1.5, 1) on graph paper we get its straight line.
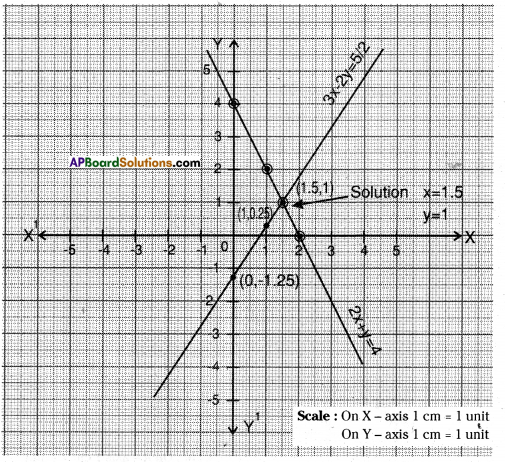
From above two straight lines, we observe that they intersect at the point (1.5, 1). Hence (1.5, 1) is the solution of given two equations So, x = 1.5 and y = 1 are the solution.
Question 23.
Solve the pair of equations by reduc¬ing them to a pair of linear equations.
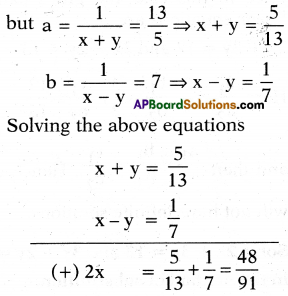
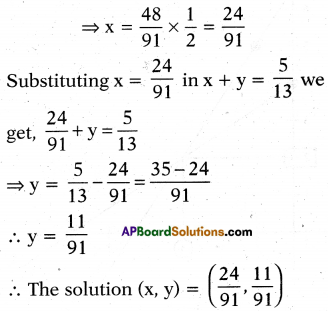
\(\frac{5}{(x+y)}-\frac{2}{(x-y)}=-1\)
\(\frac{15}{x+y}-\frac{7}{x-y}\) = -10, where x ≠ 0 and y ≠ 0
Solution:
Given \(\frac{5}{(x+y)}-\frac{2}{(x-y)}=-1\) and
\(\frac{15}{x+y}-\frac{7}{x-y}\) = -10
Take \(\frac{1}{x+y}\) = a and \(\frac{1}{x-y}\) = b, then the given equations reduce to
5a – 2b = – 1 ………. (1)
15a – 7b = – 10 ………..(2)
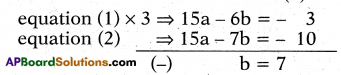
∴ b = 7
Substituting b = 7 equation (1)
we get
5a – 2(7) = – 1 ⇒ 5a = – 1 + 14
⇒ 5a = 13 ⇒ a = \(\frac { 13 }{ 5 }\)
Question 24.
Cost of Mathematics textbook is Rs. 10 less than twice of cost of English text book. Write this in linear equation.
Solution:
Let the cost of English textbook = Rs. x
Twice of it = 2x Rs. 10 less to above = 2x – 10
Then cost of Mathematics textbook y = 2x – 10 is the required linear , equation.
Question 2.
Solve the pair 2x + 3y = 12 and
3x + 2y = 13 in elimination method.
Solution:
2x + 3y = 12 …………(1)
3x + 2y = 13 …………. (2)
Multiply the equation (1) with 3 on both sides, and the equation (2) on both sides.
We get
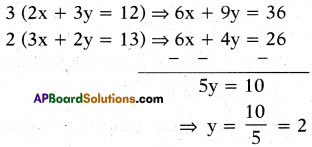
2x + 3y = 12
⇒ 2x + 3(2) = 12
⇒ 2x + 6 = 12
⇒ 2x + 12 – 6 = 6
then x = 6/2 = 3
∴(2x + 3y = 12)
∴ x = 3 and y = 2 are the solution .
Question 25.
Solve the linear equations 2x + 3y = 12 and 3x + 2y = 13 by graph method.
Solution:
A linear equation can be expressed by a straight line on a graph.
The intersecting point of two straight lines is the solution of linear equation represented by them.
Now let us find the points on 2x + 3y = 12
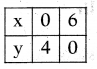
So the line represented by the equa¬tion 2x + 3y = 12 passes through the points (0, 4) and (6, 0).
Similarly 3x + 2y = 13 passes through the points (1, 5) and (3, 2)
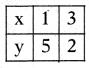
Now, see the graph
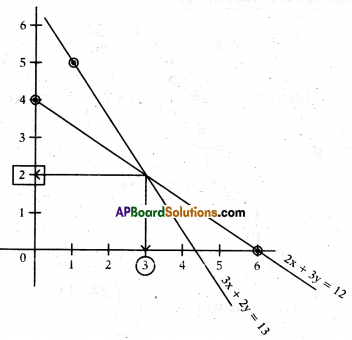
So x = 3, and y = 2 is the solution of above system.
Question 26.
Say whether the solution for 2x + 3y = 12 and 3x + 2y = 13 is exist or not basing on the coefficients.
Solution:
The two linear equations a1x + b1y + C1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 are consistent then their solution exists if and only if
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}} \neq \frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\)
In the given two linear equations
2x + 3y = 12 and 3x + 2y = 13
\(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{2}{3} \neq \frac{3}{2}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}\)
Hence they are consistent and their solution exists.
![]()
Question 27.
Check whether the number of solutions of 2x + 3y = 12 and 3x + 2y = 13 are Infinity or not. Give reasons.
Solution:
The number of solutions to the pair of
linear equationsa1x + b1y + c1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 are infinity if and only if \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}}=\frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}}=\frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
Here in this case the given pair of linear equations are
2x + 3y = 12 and 3x + 2y = 13
Here \(\frac{\mathrm{a}_{1}}{\mathrm{a}_{2}}=\frac{2}{3}, \frac{\mathrm{b}_{1}}{\mathrm{~b}_{2}}=\frac{3}{2}, \frac{\mathrm{c}_{1}}{\mathrm{c}_{2}}=\frac{12}{13}\)
and then \(\frac{a_{1}}{a_{2}} \neq \frac{b_{1}}{b_{2}} \neq \frac{c_{1}}{c_{2}}\)
Hence they will not have infinite solutions.
Question 28.
Solve 2x + 3y = 12 and 3x + 2y = 13 in the method of substitution.
Solution:
The given equations are
2x + 3y – 12 ………….. (1)
3x + 2y = 13 ………….. (2)
∴ 2x = 12 – 3y [∵From (1)]
x = \(\frac{12-3 y}{2}\) ……….. (3)
Substitute this value of x in given equa¬tion (2) we get
3 (\(\frac{12-3 y}{2}\)) + 2y = 13
\(\frac{36-9 y+4 y}{2}\) = 13
⇒ 36 – 5y = 13 x2 = 26
⇒ -5y = 26 -36 = – 10
∴ 5y = 10 and y = \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) = 2
Then from equation (3)

∴ x = 3 and y = 2 are the solution for given pair of linear equations.
Question 29.
Why there exist infinite solutions to the straight line 2x + 3y = 12 ?
Solution:
2x + 3y = 12 can be represented by a straight line on x-y coordinate system.
Now the points lie on this straight line are infinite. All the points on the line satisfy the condition 2x + 3y = 16. Hence all
Such points are solutions to this straight line. Hence they are infinite.
For example
2x + 3y = 12