Students must practice these AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Important Questions 8th Lesson Environment and Sustainable Economic Development to boost their exam preparation.
AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Important Questions 8th Lesson Environment and Sustainable Economic Development
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define environment and explain the components of environment.
Answer:
The word environment is derived from the French word ‘environner’ which means to surround or encircle. Everything which surrounds us may collectively be called as environment. We are surrounded by both living things and non-living things. The living things are called as biotic part (Physical environment) and non-living things as abiotic part (biological environment) of the environment. It is a basic life system as it provides the air we breathe, the water we drink, the food we eat and the land where we live in.
Thus, environment is a combination of physical and biological elements that affects the life of an organism. In a wider sense, environment includes man made environment such as social, economic, cultural, political and intellectual activities of the man. The physical and biological components are affected by the man made environment. Components of Environment: According to Rau and Wooten, environment can be viewed in four dimensions as explained below.
1) Physical environment: It covers the physical, chemical and biological elements such as land, climate, vegetation, wild life, surrounding land uses and physical character of the area, infrastructure, air and noise pollution levels.
2) Social environment: It includes a large number of factors such as population and its density, community composition, religious, education, community facilities like schools, parks, hospitals; recreational and cultural facilities. Some Social factors overlap the economic factor.
3) Economic environment; Economic factors like employment, unemployment levels, sources of income, availability of factors of production, demand patterns, poverty levels, inequalities in income and wealth come under economic environment.
4) Aesthetic Environment: This category comprises historical, archeological or architecture of objects or sites, scenic areas, views and landscapes. People derive pleasure by seeing such objects.
As environment consists of all these different components, it is considered to be a completely inter-disciplinary descipline.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the relationship between environment and the economy.
Answer:
Environment acts as the supplier of rawmaterials to the economy and absorbs the wastes discharged by the economy. However, in modern times, the reckless and exploitative behaviour of the economic activity is setting a limit to the efficiency of environment to supply the resoures. The capacity of the environment to absorb the wastes is also declining. In 1966, K.E, Boulding, a British economist warned the World about the consequences of over use of environmental resources. He said that earth is a spaceship with a limited amount of life support resources. He warned the mankind to minimize the consumption rather than to maximise it. The following diagram explaips the relationship between environment and economic activities.
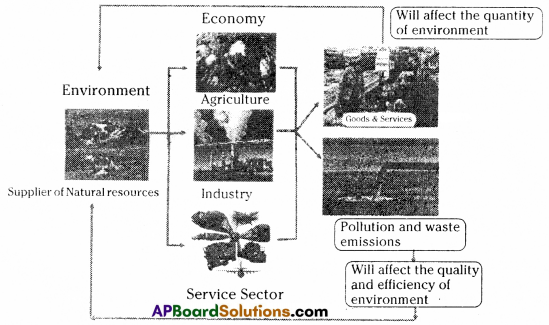
From the above diagram, we can observe that environment is supplying natural resources as the raw materials to different sectors of the economy i.e., to agriculture, industry and service sector. These sectors are using this materials and produce goods and services. Production of goods and services will decrease the quantity of environment. More the production more will be the physical usage of environment and hence decrease in the quantity of resources.
On the otherside, economic activities release wastages and pollution elements in different forms into environment. This adversely affects the quality of environment. It directly reduces the ability of environment to absorb pollution. The environment can bear and tolerate pollution elements to a certain level only. Beyond that, it fails to absorb, which ultimately reduces the quality of environment. To minimise the adverse effects on environment and to maintain a harmony between environment and economic development, we have to control pollution and degradation of environmental assets caused by economic activities.
Question 3.
What is Air pollution ? Explain the causes and consequences of air pollution.
Answer:
“The excessive concentration of contaminated substance in the air, which adversely affects the well being of the individuals, living organisms and property of all forms” is called air pollution.
Causes of Air pollution: It is estimated that 2 billions tonnes of air pollutants are released every year. Besides natural sources, a number of man-made sources causing air pollution. Burning of fire wood for domestic purposes, burning of fossile fuels, industrialisation, agricultural activities, vehicular emmissions, nuclear tests, deforestation, mining, power generation, refrigeration, etc. are the important sources of air pollution.
Consequences (effects) of Air pollution: The air pollution adversely affects people, plants, animals, aquatic life and materials. It leads to health disorders in human beings, damages the leaves of plants and trees, interferes with photosynthesis and plant growth. Air pollution discolours the historical monuments, breaks down the exterior paint on cars and houses and deteriorates the quality of natural beauty sites like Taj Mahal.
Air pollution affects the stratosphere and climatic conditions, global warming, acid rains, depletion of ozone layer, changes in the distribution of solar energy, rising temperatures, occurance of droughts, changes in the natural plants, crops, insects, live stock and increased ultraviolet radiation, etc. are the effects of air pollution.
Question 4.
Briefly discuss the sources, effects of water pollution.
Answer:
Like air, water is also very essential for the existence of all the living organisms. It accounts for about 70 per cent of the weight of the human body. In the toted available water in various forms on 0.003 per cent is available to us.
Increased human and economic activities make the water polluted. Water pollution is defined as, “the addition of some substance or factor present in water which degrades its quality so that it becomes health hazard or unfit for use”. If water loses its quality and get polluted it becomes unfit for drinking or even for agriculture and industrial purposes.
Causes of water pollution: Domestic wastes and sewage, silt, industrial effluents, fertilizers and pesticides production and consumption, oil spills, compounds of toxic metals, mining wastes, etc. are the major pollutants that make water impure.
Effects of water pollution: Water pollution has the following effects. They are:
- Transmits the water – born diseases and cause heavy economic burden in the form of medical expenses.
- Deteriorates the quality of drinking water which makes it unfit for direct use in economic activities.
- Seafood becomes contaminated and effects the country’s foreign exchange earnings with decreased exports.
- Depletes oxygen in water brings undesirable changes in temperature and breeding of fish, which is having serious repercussions on country’s acquatic resources.
- Water pollution leads to losaof man days due to illness of workers, which will cause slow down of production.
![]()
Question 5.
Define noise pollution and explain how it affects the quality of environment.
Answer:
Generally, we have different sounds in and outside of our surroundings. Sound is a form of energy. Any vibration can produce sound. The sound spreads through the solid and liquid medium. Some sounds are pleasant and some are not. The intensity of sound is measured in decibles (dB).
Noise is different from sound. Any thing between 50 to 90 dB a deep, loud and unpleasant sound is called noise. As per the Environment (protection) Rules, 1997, the permitted noise level is 125 dB for human beings.
“Any noise generated above 125 dB and produces harmful effects in environment and causes health hazards to human beings” is called noise pollution.
Causes of noise pollution: The noise pollution may be indoor or outdoor. The sounds generated from home appliances, living room etc. are indoor noise pollution, and the noise generated by the transport vehicles, loud speakers, industries etc. are outside noise pollution. Sound pollution is mainly generated by Thermal power plants, mining activities, aerodromes and various means of transportation.
Effects of Noise pollution: The noise pollution affects the quality of environment as well as life on earth. Noise pollution has the following effects. They are:
- Pollutes the essence of music and speech.
- Affects communication.
- Leads to hearing loss temporarily or permanently.
- Affects the functioning of various systems in the human body. Hypertension, sleeplessness, digestive disorders etc. are some of the bad effects of noise pollution.
- It causes irregular or faster pulse beats and increases blood pressure levels.
- Causes irrepairable loss/damage to unborn babies.
Question 6.
What are the economic implications of environmental degradation ?
Answer:
Economic development and environmental degradation i.e., pollution move in the same direction. Mindless and ruthless exploitation of natural resources causes degradation of physical environment. The economic impact of environmental degradation is explained below.
A) Effects on Human health: Environmental degradation has adverse effects on human health, which may increase the labour absenteeism, decrease in the efficiency of labour which in turn leads to low productivity.
- Air pollution spoils human health. Diseases like lung cancer, bronchitis, eye irritation, skin irritation, etc. are caused by air pollution.
- Water pollution causes dysentry, typhoid, cholera and infections hepatitis.
- Sound pollution affects human health in manyways. Loud noise causes disturbances in sleep, damage of hearing, diversion of concentration, hypertension, fast heart beat, irritation etc.
B) Effects on Agriculture: Environmental degradation negatively af f ects the agricultural sector. Agricultural productivity as well as the quality of agricultural products will be deteriorated due to environmental degradation.
1) Air pollution most commonly damages leaves of plants and this adversely affects agricultural production. Air pollution also brings a change in climate. Acid rain is a result of air pollution which affects agricultural production.
2) Water pollution highly affects the productivity of agriculture, particularly irrigated lands. If inorganic salts, particularly chlorides, salt, etc. are accumulated through irrigation, the fertility of land deteriorates and the land may become barren.
3) Soil pollution i.e., soil erosion, salination, desertification, etc. reduces the qantity and quality of cu.u viable land. This adversely affects the agricultural production.
C) Effects on Industry: Environmental pollution affects the quality of industrial products.
- Air pollution causes depreciation of machinery and deterioration of quality of products.
- Water pollution reduces the utility of water for industrial purposes, polluted water causes high costs for industries.
- Soil pollution, due to indiscriminate exploitation of mineral resources hampers industrial development.
D) Effects on livestock: Environmental degradation has evil effects on the health of – livestock which in turn reduce the animal products. Contaminated water affects badly the digestive system and reproductive system of live stock.
E) Effect on Aquatic food resources: Water pollution has negative effects on fisheries. The eating of fish affected by pollution of water in dangerous to human health.
F) Other Effects: Apart from the above economic impacts, environmental degradation, biodiversity will be affected and the interrelationship among the species get disturbed. The food chain relationship among the various creatures break or weaken.
With the degradation of environment, the levels of green house gases rise in the atmosphere, the ozone layer becomes think and get holes. All these lead to global warming.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the various factors resulting in environmental pollution ?
Answer:
The basic factors for environmental pollution are explained below.
A) Social factors: The social factors that are responsible for environmental pollution are:
1) Population: Though population is an important source of development, but it is a major source of pollution when it exceeds the threshold limits of the support systems.
2) Poverty: Poverty is both cause and effect of environmental pollution. Poor people who depends on natural resources more than rich, deplete natural resources faster.
3) Urbanisation: Rapid and unplanned expansion of cities due to migration resulted in the degradation of urban environment.
B) Economic factors: To a large extent, environmental degradation in the result of market failure i.e., the non-existent or poorly functioning markets for environmental goods and services.
Transport activities have a wide variety of effects on the environment such as air pollution, noise pollution, oil spills from marine shipping, etc.
Agricultural development has a direct impact on the environment arising from soil erosion, land salination and loss of nutriants. The spread of green revolution accompanied by over exploitation of land and water resources, and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides are also responsible for environmental pollution.
C) Institutional factors: Due to corruption and weak administration, the loop holes in the legal system, the environmental protection laws are strictly enforced in India. The capabilities of environmental institutions both at the central and the state levels are weak and ineffective. There is no effective coordination among the various ministries/ Institutions regarding the integration of environmental concerns in the planning stage of the project.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain various concepts of environment.
Answer:
To understand the environment and its nature, a primary information of its basic concepts is necessary. Eco-system, biodiversity, green house effect, global warming, acid rain, ozone layer depletion, etc. are some of the basic concepts of the environment. They are discussed below.
1) Eco-system: The living and non-living components of the environment constitute as eco-system. It includes plants, trees, animals, birds, fish, micro organisms, water, soil and people of that region.
2) Biodiversity: The variety and variability among the living organisms is called as – biodiversity. So far, the science identified 1.75 million species in which various types of plants, insects, fungi, bacteria, virus, algae, etc. are included.
3) Green house effect: It is a phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps radiation emitted by the sun, caused by gases such as carbondioxide, water vapour and methane that allows incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the planet’s surface. Green house effect may lead to many serious environmental issues such as radiation, climate change, monsoon direction and its efficiency and so on.
4) Global warming: Global warming is the increase of Earth’s average surface temperature due to the effect of green house gases, which trap heat that would otherwise escape from earth.
5) Acid Rain: Acid rain is a broad term referring to a mixture of wet and dry deposition from the atmosphere containing higher than normal amounts of nitric and suphuric acids.
6) Ozone depletion: Reduction in the amount of Ozone (O3) in the stratosphere is called ozone depletion. It happens due to high levels of chlorine and bromine compounds in that layer. As ozone depletes, more ultraviolet radiation comes to earth and causes damage to all the living organisms. It causes skin cancer and other skin complications.
Question 2.
Causes for soil or land pollution.
Answer:
Soil pollution is defined as, “Unfavourable alteration of soil quality by disturbing the natural composition which decreases soil productivity.
Causes for soil pollution:
- Soil erosion, in which the fertile upper surface of land erode and land becomes barren. It happens due to deforestation, extensive cultivation, mining activities, etc.
- Desertification makes the land lifeless sea of sand. Desertification spreads due to over grazing, extensive use of poor soils, alkalization of soil.
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Filling of wastages and other disposable into the land also causes the degradation of soil.
Question 3.
Types of natural resources with suitable examples.
Answer:
The resources available in the environment, which are useful for living organisms are called Natural Resources. Water, land, minerals, air etc. are natural resources.
Natural resources are classified into, A) Renewable resources, and B) Non-renewable resources.
A) Renewable Natural Resources: The, natural resources which can be used continuously/permanently without depletion, are called renewable resources. They are not exhaustible. They can regenerate for themselves with in a short period. Renewable resources are also known as non-conventional resources. For e.g.: solar, wind, tidal, geothermal energy, etc.
B) Non-renewable Natural resources: The natural resources which will exhaust by use are called as non-renewable resources. They cannot be regenerated, once they are exhausted. They are also called conventional resources. For e.g. gold, silver, copper, fossil fuel, oil, gas etc.
![]()
Question 4.
What is pollution? Explain the types of pollution. [Mar ’19 (TS)]
Answer:
Pollution is an undesirable change in the physical and biological characteristics of the environment. This environmental pollution can take several forms such as air pollution, water pollution, soil pollution, noise pollution etc.
A) Air pollution: The excessive concentration of contaminated substances in the air which adversely affects the well-being of individuals, living organisms and property of all forms” is called air pollution.
B) Water Pollution: “The addition of some substance or factor present in water which degrades its quality, so that it becomes health hazard or unfit for use” is called water pollution.
C) Soil Pollution: Unfavourable alternation of soil quality by disturbing the natural composition which decreases soil productivity is called soil or land pollution.
D) Noise Pollution: Any noise generated above 125 dB that produce harmful effects in the environment and causes health hazards to human beings is called sound/noise pollution.
The other forms of pollution are solid waste pollution, thermal pollution and radioactive pollution.
Question 5.
What do you mean by “sustainability”? Explain the components of sustainability.
Answer:
The Brundtland Commission, 1987 defined sustainable development as “the development that seeks to meet the needs and aspirations of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” The concept of “sustainable development aims at maximizing the net benefits of economic activities, subject to maintaining the stock of productive assets overtime and providing safety net to meet the basic needs of the poor.
Components of sustainability: There are three basic components of sustainable development. They are economic, social and environmental components. These three components are interdependent. A balance is to be achieved among these three components for achieving the sustainable development. The balance is shown in the
A) Economic Component: Economic components of sustainability require that the society pursues growth path that generate optimum flow of income while maintaining the basic stock of man-made capital, human capital and natural capital.
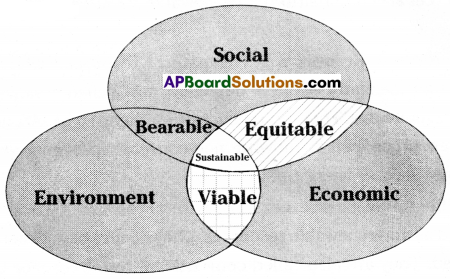
B) Social Components: Social components of sustainability are built on the twin principles of justice and equality. For development path to be sustained, wealth, resources and opportunities should be equally shared. All citizens should have access to minimum standards of security, human rights and social benefits such as food, education, health and opportunities of self-development.
C) Environmental Components: Environmental components of sustainability require sustainable resource use, efficient sink function and maintenance of natural capital. Environment should be able to perform its three functions efficiently and uninterrupted so that ecological stability and resilience are not affected.
Question 6.
Explain the effects of pollution on human health.
Answer:
Effects on Human health: Environmental degradation has adverse effects on human health, which may increase the labour absenteeism, decrease in the efficiency of labour which in turn leads to low productivity.
- Air pollution spoils human health. Diseases like lung cancer, bronchitis, eye irritation, skin irritation, etc. are caused by air pollution.
- Water pollution causes dysentry, typhoid, cholera and infections hepatitis.
- Sound pollution affects human health in many ways. Loud noise causes disturbances in sleep, damage of hearing, diversion of concentration, hypertension, fast heart beat, irritation etc.
![]()
Question 7.
Measures for the conservation of forests. [Mar ’19 (AP); Mar ’18, ’17; May ’18 ’17]
Answer:
Forests are the carbon sinks and treasures of scenic beauty. The following are some protective measures for the conservation of forests. They are:
- Forest land should not be allotted to poor for house sites.
- Specific areas must be developed under social forestry programmes.
- Wastelands must be brought under plantations.
- Forests must be protected from fire, particularly during the summer.
- Measures should be taken to refill the depleted forest areas.
- Establishment of Joint Forest Management communities is necessary.
- Cattle grazing and illegal cutting of trees should not be allowed.
- Local communities must be involved in the conservation of forests.
Question 8.
Need for environmental preservation. [May 2017]
Answer:
Environment is a common property. It belongs to the total living organisms of the world. Everyone humans, animals, plants and trees, birds and fish is using, enjoying and experiencing the products of environment. Particularly human beings, out of their greed are overusing this public resource. As a result, it is becoming weak and even unable to discharge its natural functions. So, environment must be protected.
Need for environmental protection:
- To meet the needs of present and future generations.
- For distributional equity (environment and economic activity).
- To preserve physical, human and natural capital.
- To avoid threats for floral and formal species and biological diversity.
- To prevent further degradation of delicate eco-system.
- To protect the environment, the Government of India has taken a large number of constitutional, legal and administrative steps.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Environment. [May 2017]
Answer:
Everything which surrounds is collectively called an environment.
Question 2.
Eco-system [Mar ’19 (AP)]
Answer:
The combination of natural and physical environments in a given geographical area is called ecosystem.
Question 3.
Greenhouse effect [March 2017]
Answer:
It is a phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps the radiation emitted by the sun, caused by gases such as carbondioxide, water vapor and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the surface of the planet.
Question 4.
Air pollution
Answer:
The excessive concentration of contaminated substance in the air which adversely affects the well being of the individuals, living organisms and property of all forms is called as air pollution.
Question 5.
Water pollution [Mar. 2018, ’17; May ’18]
Answer:
The addition of some substance or factor present in water that degrades its quality so that it becomes health hazard or unfit for use is called water pollution.
Question 6.
Ozone layer [Mar ’19 (AP); Mar ’18, ’17; May ’18]
Answer:
The layer in the stratosphere protecting the earth and all living organisms on it from the ultraviolet rays of the sun is called Ozone layer.
Question 7.
Global Warming
Answer:
Global warming means the increase of Earth’s average surface temperature due to the effect of greenhouse gases which trap heat that would otherwise escape from earth.
![]()
Question 8.
Sustainable development. [Mar ’19 (AP&TS); Mar ’18, May ’17]
Answer:
The process of development which sustains human wellbeing in future also is called sustainable development.
Question 9.
Cost-benefit analysis of the environment
Answer:
The evaluation and comparison of capital and environmental costs of a project to estimate its relative merits and demerits is called cost-benefit analysis.
Question 10.
Reasons for deforestation.
Answer:
Growth of population, poverty and unemployment raise the demand for land for the purpose of cultivation, housing, firewood. Overgrazing by the cattle stock brings pressure on forests. Construction of dams, roads, and railway tracks destroy forests. Forest fires, podu cultivation, etc. are some other reasons for deforestation.
Question 11.
Biodiversity [Mar ’19 (AP); Mar ’18, ’17; May ’18 ’17]
Answer:
The totality of genes, species and ecosystem of a region is called biodiversity.
Question 12.
What is Noise’? [May 2018]
Answer:
A deep, loud and unpleasant sound which is undesirable and unwanted is called noise.
Question 13.
What is land degradation?
Answer:
Unfavorable alteration of soil quality by disturbing the natural composition which decreases soil productivity is called soil or land pollution.
Question 14.
Environmental externalities
Answer:
An externality is a consequence of an economic activity that is experienced by the environment. An environmental externality can be either positive or negative, For e.g.: water pollution caused by a factory spoils the health of nearby residents, cattle and fish is a negative externality.
Question 15.
Swachh Bharat Abhiyan [May 2017]
Answer:
Prime Minister Sri Narendra Modi launched “Swachh Bharat Abhiyan” on 2nd October. 2014. He asked people to devote 100 hours every year to make ‘India clean’.
Question 16.
Renewable natural resources
Answer:
The natural resources which can be used continuously and permanently are called renewable resources. For e.g.: solar, wind, tidal, and geothermal energy.
![]()
Question 17.
Non-renewable natural resources
Answer:
The natural resources which will exhaust by use and which cannot be regenerated are called non-renewable natural resources. For e.g.: gold, silver, copper, oil, gas, etc.
Question 18.
Pollution
Answer:
The undesirable changes in the basic features of the environment is called pollution.