Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Physics Important Questions 9th Lesson Gravitation which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Physics Important Questions 9th Lesson Gravitation
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
State the unit and dimension of the universal gravitational constant(G). Units of ‘G’: [Imp.Q]
Answer:
C.GS unit: dyne. cm²/gm²
S.l unit : Nm²/kg²
Dimensional formula: [M-1L³T-2]
Question 2.
State the vector form of Newton’s law of gravitating. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
The vector form of Newton’s law of gravitation is
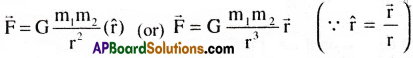
Where G is the universal gravitational constant, \(\hat{r}\) is the unit vector from m] to m, and r is the distance between the two bodies.
Question 3.
If the gravitational force of the earth on the moon is F, what is the gravitational force of the moon on the earth? Do these forces form an action-reaction pair?
Answer:
The gravitational force of the earth on the moon is F.
The gravitational force of the moon on the earth is -F.
Yes, these forces will form an action-reaction pair.
Question 4.
What would be the change in acceleration due to gravity (g) at the surface, if the radius of Earth decreases by 2% keeping the mass of Earth constant?
Answer:

∴ As R decreases by 2%, the value of g increases by 4%.
Question 5.
As we go from one planet to another how will (a) the mass (b) the weight of a body change? jlmp.QI
Answer:
(a) The mass of the body remains same
(b) Weight W = mg ⇒ W ∝ g
As ‘g’ changes from planet to planet.
So, weight of the body is proportional to mass of the planet and inversely proportional to square of its radius.
Thus, weight of the body changes from one planet to another planet.
![]()
Question 6.
Keeping the length of a simple pendulum constant, will the time period be the same on all planets? Support your answer with reason.
Answer:
No.
For a Simple Pendulum, Time period T = πJ\(\sqrt{\frac{l}{g}}\)
If l is kept constant then T ∝ \(\frac{l}{\sqrt{g}}\)
Since, ‘g’ varies from one Planet to another Planet. So time period also varies from one planet to another planet.
Question 7.
Give the equation for the value of g at a depth ‘d’ from the surface of Earth. What is the value of ‘g’ at the centre of Earth?
Answer:
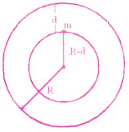
gd = g(1-\(\frac{d}{R}\))
Where d = depth from the surface of earth.
R = radius of the earth.
At the centre of the earth d = R. Hence, gd = 0.
Question 8.
What are the factors that make ‘g’ the least at the equator and maximum at the poles?
Answer:
The factors that make ‘g’, the least at the equator and maximum at the poles due to
- Non sphericity (shape of the earth )
- rotation of the earth
Question 9.
“Hydrogen is in abundance around the sun but not around the earth.” Explain.
Answer:
The r.m.s velocity of hydrogen molecules is around 2km/s.
The escape velocity on the surface of earth is 11,2km/s.
But the escape velocity on the surface of sun is 620km/s.
The escape velocity of sun is greater than escape velocity of earth and r.m.s velocity of hydrogen
Also, the gravitational attraction of the sun is more than the earth.
Hence hydrogen is in abundance around the Sun and less around the earth.
Question 10.
What is the time period of revolution of a geostationary satellite? Does it rotate from West to East or from East to West?
Answer:
The time period is equal to 24 hours. It rotates from West to East in an equatorial plane.
![]()
Question 11.
What are polar satellites?
Answer:
The low altitude (500 to 800km) satellites, which go around the poles of the earth in a north-south direction are known as polar satellites.
The time period of polar satellite is around 100 minutes.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
State Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. [Imp. Q; TS 17, 20]
Answer:
1) Law of orbits :
All planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun situated at one of the foci.
2) Law of areas :
The line that joins any planet to the sun sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
3) Law of periods :
The square of the time period of revolution of a planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the ellipse traced out by the planet.
Question 2.
Derive the relation between acceleration due to gravity(g) at the surface of a planet and Gravitational constant(G). [AP 19; Imp. Q]
Answer:
Relation between g and G :
Consider a body of mass ‘m’ is placed on the surface of a planet of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’. The distance between the centres of the planet and the body is equal to the radius of the planet(R).
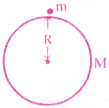
According to Newton’s law of gravitation the gravitational force on the body is
F = \(\frac{GMm}{R^2}\) ………. (1),
Where ‘G’ is universal gravitational constant.
The force acting on the body due to gravitational pull of the planet is F = mg ………. (2)
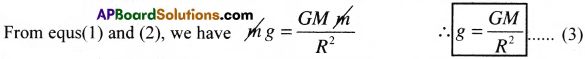
Question 3.
How does the acceleration due to gravity(g) change for the same values of height (h) and depth(d)? [Imp.Q]
Answer:
a) At small heights and small depths :
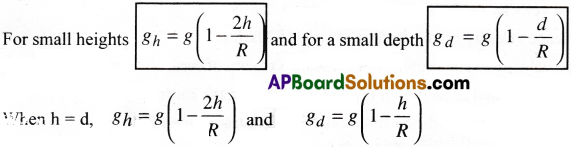
Decrease in ‘g’ at small heights is more than the decrease in ‘g’ at small depths.
b) At large heights and large depths :
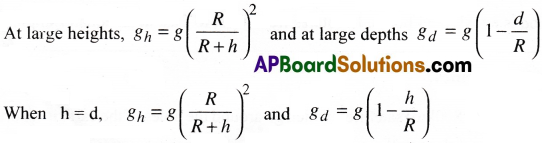
At large heights decrease in ‘g’ is less than the decrease in ‘g’ at large depths.
Question 4.
What is orbital velocity? Obtain an expression tor it. [IPE’ 10, 14; AP 17,18]
Answer:
Orbital Velocity :
The horizontal velocity required for an object to revolve around a planet in a circular orbit is called orbital velocity.
Expression :
Consider an object of mass m revolving around a planet of mass M and radius R. Let ‘h’ be the distance of centre of mass of the object from the surface of the planet.
Let v0 be the horizontal speed of the object when it revolves around the planet in circular orbit. Centripetal force on the object = Gravitational force of attraction of the planet on the object.
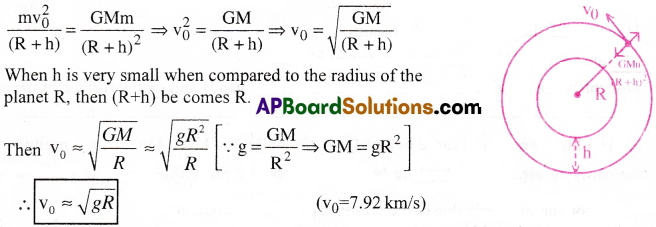
Question 5.
What is escape velocity? Obtain an expression for it. [TS 16, 19, 22] [AP 15, 16, 18, 19]
Answer:
Escape Velocity :
The minimum velocity required for an object to escape from the gravitational influence of a planet is known as escape velocity.
Expression :
Consider an object of mass ‘m’ at rest on the surface of a planet of mass M and radius R.
The gravitational potential on the surface of a planet = \(\frac{-GM}{R}\) —– (1)
The gravitational potential energy of the system = gravitational potential x mass of the object = \((\frac{-GM}{R})m\) —– (2)
The object can be made to escape from the gravitational field of the planet by imparting certain minimum speed to the object.
This minimum speed to be imparted to the bound object at rest is escape velocity ve.
The kinetic energy imparted to the object must be equal and opposite to the potential energy of the system so that the total energy is equal to zero.
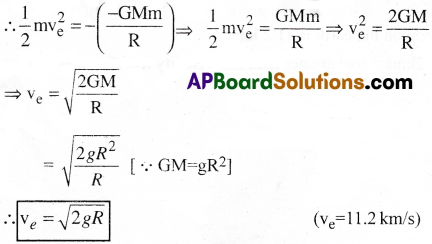
![]()
Question 6.
What is a geostationary satellite? State its uses. [TS 18, 22; AP,TS 15, 16, 20, 22]
Answer:
Geostationary satellite :
If the period of revolution of an artificial satellite is equal to the period of rotation of the earth then such a satellite is called geostationary satellite.
Uses :
Geostationary satellites can be used to
- Study the upper layers of the atmosphere.
- Forecast the changes in the atmosphere.
3) Know the shape and size of the earth. - Transmit the T.V programmes to distant places.
- Identify the minerals and natural resources present inside and on the surface of the earth.
Question 7.
If two places are at the same height from the mean sea level; One is on a mountain and the other in air. At which place ‘g’ will be greater? State the reason for your answer.
Answer:
‘g’ is more on mountain due to the presence of mass of mountain.
Question 8.
The weight of an object is more at the poles than at the equator. At which of these places we can get more sugar for the same weight? State the reason for your answer.
Answer:
Weight W = mg
For same weight at two different places, m ∝ \(\frac{1}{g}\)
But acceleration due to gravity at poles is greater than that at equator.
Hence more sugar is obtained at equator for same weight.
Question 9.
If a nut becomes loose and gets detached from a satellite revolving around the earth, will it fall down to earth or will it revolve around earth? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
It revolves in the same orbit due to inertia of motion.
Question 10.
An object projected with a velocity greater than or equal to 11.2 kms-1 will not come to the earth. Explain.
Answer:
The escape velocity of the body on the earth is 11.2 kms-1.
If a body is projected with 11.2kms-1 (or) greater than this velocity it will not come back to the earth.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define gravitational potential energy and derive an expression for it associated with two particles of masses m1 and m2.
Answer:
Gravitational potential energy of a body at a point is defined as the amount of work done in bringing the given body from infinite to that point against the gravitational force.
For two particle system gravitational potential energy U = \(\frac{Gm_1m_2}{r}\)
Expression for Gravitational Potential Energy associated with two particles :
Consider a body of mass m2 is placed at P in the gravitational field of a body of mass m1.
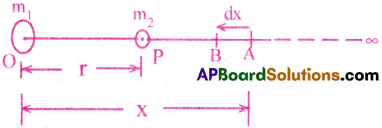
Let ‘r’ be the distance of separation between two particles.
In order to determine the gravitational potential energy of this system of two particles, let us calculate the work done in moving mass m2 from infinity to P. When the mass m2 is at A, the gravitational force of attraction on it due to mass m1 is given by
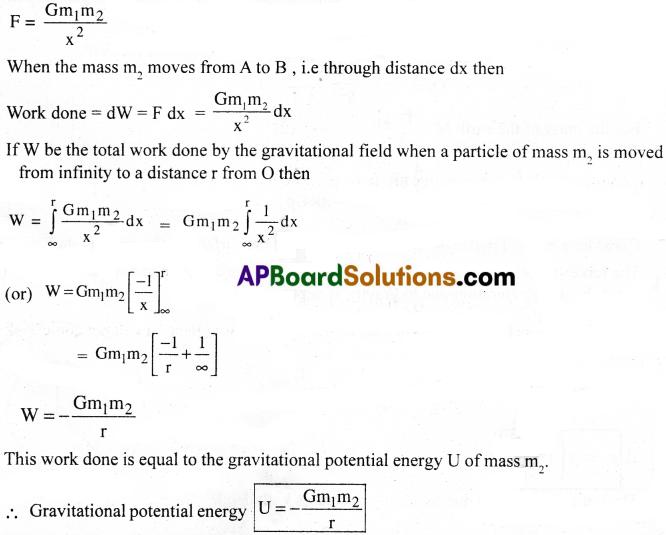
![]()
Question 2.
Derive an expression for the variation of acceleration due to gravity (a) above and (b) below the surface of the Earth. [lmp. Q]
Answer:
(a) Variation of ‘g’ with height :
Consider a body of mass ‘m’ at a height ‘h’ from the surface of the earth of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’.
According to Newton’s law of gravitation, the gravitational force of attraction of the earth on
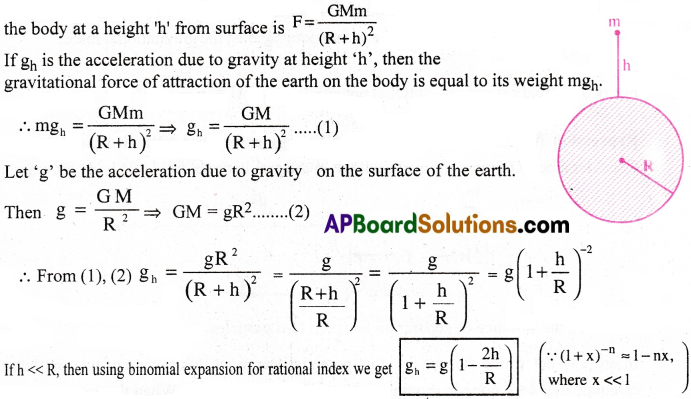
Thus the acceleration due to gravity decreases with height.
(b) V ariation of g with depth :
Let us assume that the earth to be a homogeneous uniform sphere of radius ‘R’, density ‘ρ’ and mass ‘M’.
Let g be the acceleration due to gravity at a place on the surface of the earth.
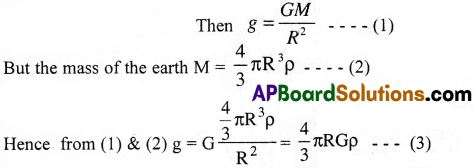
Consider a body of mass ‘m’ is at a depth ‘d’ from the surface of the earth as shown in figure. The force on the body will be due to the mass of the earth confined in a sphere of radius (R-d). Let gd be the acceleration due to gravity at depth d.

Thus, the acceleration due to gravity decreases with depth.
Question 3.
State Newton’s Universal law of Gravitation. Explain how the value of the Gravitational constant (G) can be determined by Cavendish method.
Answer:
Universal Law of Gravitation :
“Every body in the universe attracts every other body with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them”. Funiversal = \(\frac{Gm_1m_2}{r^2}\)
Determination of Universal Gravitational constant(G):
The experimental arrangement used by Cavendish to determine the Universal Gravitational constant is shown in figure.
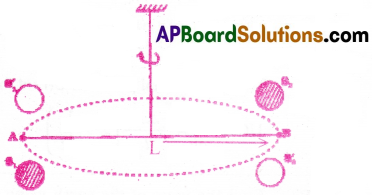
A bar AB is suspended from a rigid support by a fine wire. Two small lead spheres are attached at the ends of bar. When two big lead spheres are brought close to the small spheres on opposite sides then a torque acts on the bar. Due to this torque, the suspended wire gets twisted till the restoring torque of the wire equals to the gravitational torque.
Let θ be the angle of twist of the suspended wire.
The restoring torque = τθ where τ is the restoring couple per unit angle of twist.
If r is the separation between the centres of the big and small spheres then the gravitational force between them is
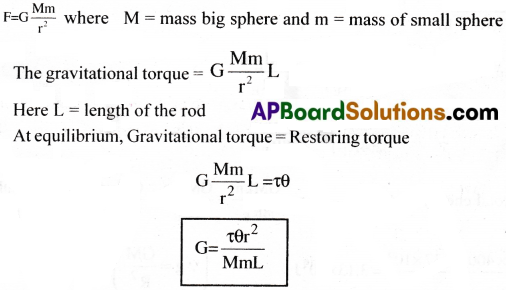
G can be calculated by Substituting different values in the above equation.
Solved Problems
Question 1.
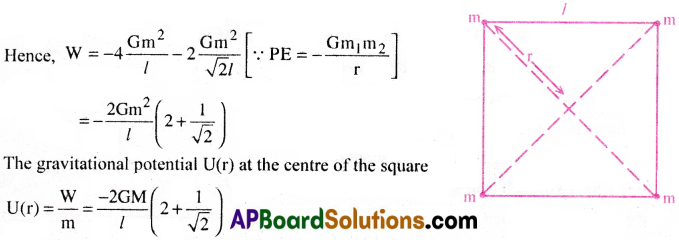
Find the potential energy of a system of four particles placed at the vertices of a square of side /. Also obtain the potential at the centre of the square.
Answer:
Consider four masses each of mass m at the comers of a square of side l;
We have four mass pairs at distance l and two diagonal pairs at distance √2l
∴ Work done to form the given configuration is
Question 2.
Find the mass of the earth using the following data:
g = 9.81 ms-2, RE = 6.37 × 106 m, the distance to the moon R = 3.84 × 108 m and the time period of the moon’s revolution is 27.3 days.
Answer:
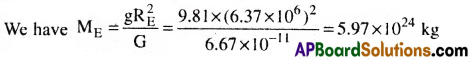
![]()
Question 3.
A 400kg satellite is in a circular orbit of radius 2RE about the Earth. How much energy is required to transfer it to a circular orbit of radius 4RE? What are the changes in the kinetic and potential energies?
Answer:
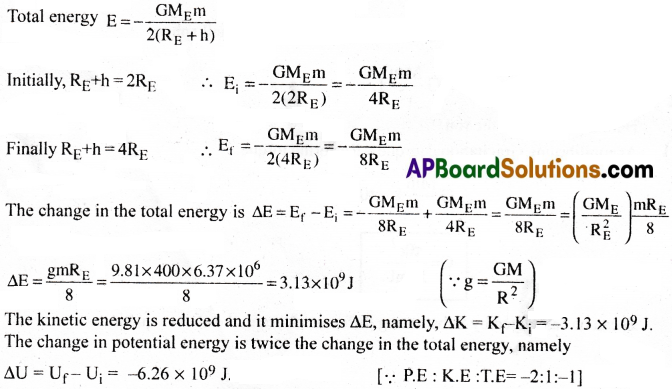
Exercise Problems
Question 1.
Two spherical balls each of mass I kg are placed 1 cm apart. Find the gravitational force of attraction between ‘them.
Solution:
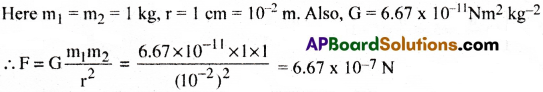
Question 2.
The mass of a bail is four times the mass of another bail. When these balls are separated by a distance of 10 cm the force of gravitation between them is 6.67 × 10-7 N. Find the masses of the two bails.
Solution:

Question 3.
Three spherical balls of mass 1kg, 2kg and 3kg are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side lm. Find the magnitude of gravitational force exerted by the 2kg and 3kg masses on the 1kg mass.
Solution:
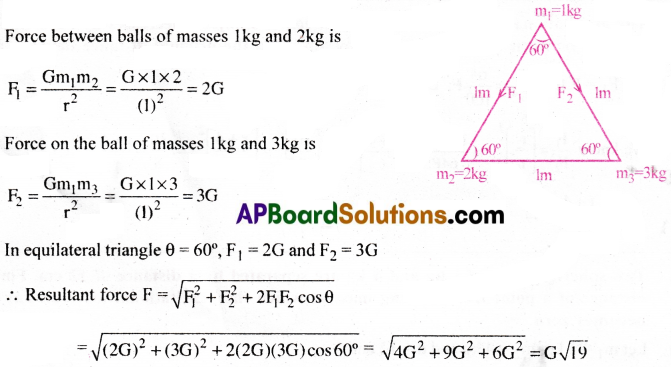
Question 4.
At a certain height above the earth’s surface, the acceleration due to gravity is 4% of its value at the surface of earth. Determine the height.
Solution:
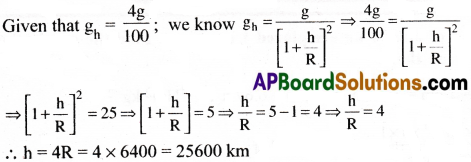
Question 5.
A satellite is orbiting the earth at a height of 1000 km. Find its orbital speed.
Solution:
Given that h = 1000km, R = 6400km. Also, G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm²/kg², ME = 6 × 1024kg
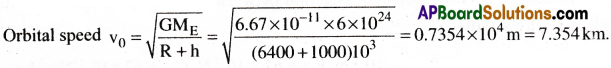
![]()
Question 6.
A satellite orbits the earth at a height equal to the radius of earth. Find it’s
i) orbital speed and
ii) period of revolution.
Solution:
Given that h = R = 6.4 × 106m. Also, G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm²/kg²; ME = 6 × 1024kg
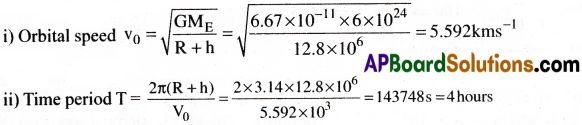
Question 7.
The gravitational force of attraction between two objects decreases by 36% when the distance between them is increased by 4m. Find the original distance between them.
Solution:

Question 8.
Two spherical balls of l kg and 4 kg are separated by a distance of 12 cm. Find the distance of a point from the 1 kg mass at which the gravitational force on any mass becomes zero.
Solution:
Let mj = l kg; m2 = 4 kg and d = 12 cm

Question 9.
For identical masses of m are kept at the corners of a square of side a. Find the gravitational force exerted on one of the masses by the other masses.
Solution:
We take m1 = m2 = m3 = m4 = m
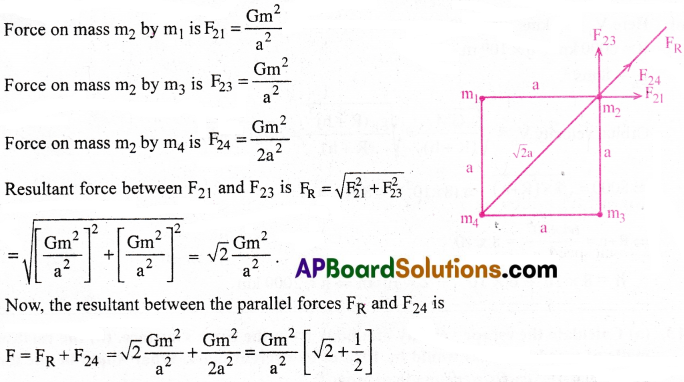
Question 10.
Three uniform spheres each of mass m and radius R are kept in such a way that each touches the other two. Find the magnitude of the gravitational force on any one of the spheres due to the other two. .
Solution:
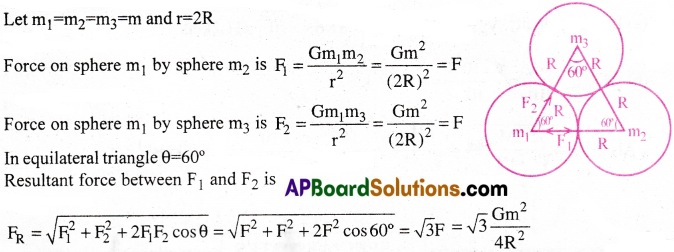
Question 11.
Two satellites are revolving round the earth at different heights. The ratio of their orbital speeds is 2:1. If one of them is at a height of 100km. What is the height of the other satellite?
Solution:
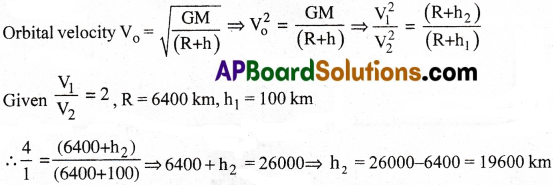
Question 12.
A satellite is revolving round in a circular orbit with a speed of 8 kms-1 at a height where the value of acceleration due to gravity is 8 ms-2. How high is the satellite from the Earth’s surface? (Radius of planet = 6000 km)
Solution:
Here V0 = 8 kms-1 = 8000 m/s,
R = 6000km = 6 × 106m,
gh = 8 ms-2.
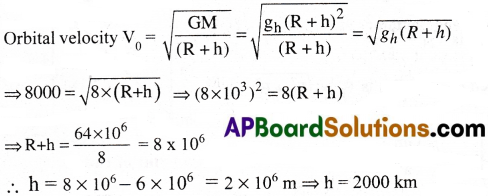
![]()
Question 13.
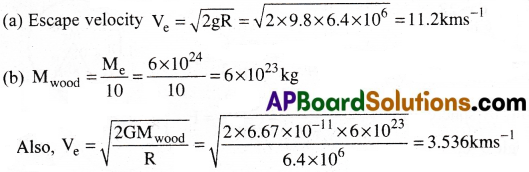
(a) Calculate the escape velocity of a body from the earth’s surface, (b) the earth were made of wood, its mass would be 10% of its current mass. What would be the escape velocity, if the earth were made of wood?
Solution:
We know mass of earth M = 6 × 1024 kg;
g = 9.8 ms-2;
radius R = 6400 km = 6.4 × 106 m
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
When a body is taken from equator to the poles, its weight
1) Remains the same
2) Increases
3) Decreases
4) Increases at north pole and decreases at south pole.
Answer:
2) Increases
Question 2.
With increase in height and depth, the acceleration due to gravity
1) Increases
2) May increase or decrease
3) Decreases
4) Does not change
Answer:
3) Decreases
Question 3.
The escape velocity on earth is I1.2kms The escape velocity on a planet of mass M/4 and radius R/2 is (M and R are the mass of earth and its radius)
1) 11.2 kms-1
2) 8 kms-1
3) 4 kms-1
4) zero
Answer:
2) 8 kms-1
Question 4.
The orbital period of a geo stationary satellite is
1) 2 hr
2) 6 hr
3) 24 hr
4) 12 hr
Answer:
3) 24 hr
Question 5.
The escape velocity of an object on a planet who radius is 4 times that of the earth and acceleration due to gravity 9 times that on the earth is
1) 67.2 kms-1
2) 37.4 kms-1
3) 111.2 kms-1
4) 25.2 kms-1
Answer:
1) 67.2 kms-1
![]()
Question 6.
A satellite is revolving near the earth’s surface. Its orbital velocity is
1) 5.8 kms-1
2) 18.4 kms-1
3) 11.4 kms-1
4) 8 kms-1
Answer:
4) 8 kms-1
Question 7.
If A is the areal velocity of a planet of mass ‘M’, its angular momentum is
1) M/A
2) 2MA
3) A²M
4) AM²
Answer:
2) 2MA
Question 8.
The angular velocity of rotation of a star (of mass M and radius R) at which the matter will start escaping from its equator is

Answer:
2
Question 9.
Energy required to move a body of mass ‘M’ from an orbit of radius 2R to 3R is

Answer:
4
Question 10.
The escape velocity on earth is 11.2kms-1. Its value for a planet having double the radius and 8 times mass of the earth is
1) 11.2 kms-1
2) 22.4 kms-1
3) 5.6 kms-1
4) 8 kms-1
Answer:
2) 22.4 kms-1
Question 11.
What will be the formula of mass of the earth in terms of g, R and G?
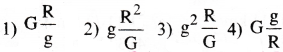
Answer:
2
Question 12.
Two spheres of masses m and M are situated in air and the gravitational force between them is F. The space around the masses is now filled with a liquid of specific gravity 3. The gravitational force will now be
1) 3 F
2) F
3) F/3
4) F/9
Answer:
2) F
![]()
Question 13.
A body of weight 72 N moves from the surface of earth at a height half of the radius of earth, then gravitational force exerfed on it will be
1) 36 N
2) 32 N
3) 144 N
4) 50 N
Answer:
2) 32 N
Question 14.
Gravitational force is required for
1) stirring of liquid
2) convection
3) conduction
4) radiation
Answer:
2) convection
Question 15.
If ve is escape velocity and v0 is orbital velocity of a satellite for orbit close to the earth’s surface, then these are related by

Answer:
4
Question 16.
For a planet having mass equal to mass of the earth but radius is one fourth of radius of the earth. The escape velocity for this planet will be
1) 11.2 km/s
2) 22.4 km/s
3) 5.6 km/s
4) 44.8 km/s
Answer:
2) 22.4 km/s
Question 17.
The escape velocity of a sphere of mass m is given by (G = Universal gravitational constant; Me = Mass of the earth and Re = Radius of the earth)

Answer:
2
Question 18.
For a satellite escape velocity is 11 km/s. If the satellite is launched at an angle of 60° with the vertical, then escape velocity will be
1) 11 km/s
2) 11√3 km/s
3) 11/√3 km/s
4) 33 km/s
Answer:
1) 11 km/s
![]()
Question 19.
The ratio of escape velocity at earth (ve) to the escape velocity at a planet (vp) whose radius and mean density are twice as that of earth is
1) 1 : 4
2) 1 : √2
3) 1: 2
4) 1 : 2√2
Answer:
4) 1 : 2√2
Question 20.
The acceleration due to gravity at a height 1 km above the earth is the same as at a depth d below the surface of earth. ’Then
1) d = 1 km
2) d = 3/2 km
3) d = 2km
4) d = 1/2 km
Answer:
3) d = 2km
Question 21.
A body weighs 200 N on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh half way down to the centre of the earth?
1) 100 M
2) 150 N
3) 200 N
4)250 N
Answer:
1) 100 M
Question 22.
The acceleration due to gravity g and mean density of the earth p are related by which of the following relations? (where G is the gravitational constant and R is the radius of the earth.)

Answer:
1
Question 23.
A body weighs 72 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it, at a height equal to half the radius of the earth?
1) 48 N
2) 32 N
3) 30 N
4) 24 N
Answer:
2) 32 N
Question 24.
A satellite A of mass m is at a distance of r from the centre of the earth. Another satellite B of mass 2m is at a distance of 2r from the earth’s centre. Their time periods are in the ratio of
1) 1 : 2
2) 1 : 16
3) 1 : 32
4) 1 : √2
Answer:
4) 1 : √2
![]()
Question 25.
The distance of two planets from the sun are 1013 m and 1012 m respectively. The ratio of time per the planets is
1) √10
2) 10√10
3) 10
4) 1/√10
Answer:
2) 10√10
Question 26.
The period of revolution of planet A around the sun is 8 times that of B. The distance of A from the sun is how many times greater than that of B from the sun?
1) 4
2) 5
3) 2
4) 3
Answer:
1) 4
Question 27.
A planet moving along an elliptical orbit is closest to the sun at a distance r1 and farthest away at a distance of r2. If v1 and v2 are the linear velocities at these points respectively, then the ratio v1/v2 is
1) (r1/r2)²
2) r2/r1
3) (r2/r1)²
4) r1/r2.
Answer:
2) r2/r1
Question 28.
The kinetic energies of a planet in an elliptical orbit about the Sun, at positions A, B and C are KA, KB and KC respectively, is the major perpendicular to AC at the position of the Sun S as shown in the figure. Then
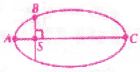
1) KA < KB < KC
2) KA > KB > KC
3) KB < KA < KC
4) KB > KA > KC
Answer:
2) KA > KB > KC
Question 29.
Two astronauts are floating in gravitational free space after having lost contact with their spaceship. The two will
1) move towards each other
2) move away from each other
3) will become stationary
4) keep floating at the same distance between them
Answer:
1) move towards each other
![]()
Question 30.
The work done to raise a mass m from the surface of the earth to a height h, which is equal to the radius of the earth, is
1) 3/2 mgR
2) mgR
3) 2mgR
4) 1/2 mgR
Answer:
4) 1/2 mgR
Question 31.
A particle of mass M is situated at the centre of a spherical shell of same mass and radius a. The magnitude of the gravitational potential at a point situated at a/2 distance from the centre, will be
1) GM/a
2) 2GM/a
3) 3GM/a
4) 4GM/a
Answer:
3) 3GM/a
Question 32.
The additional kinetic energy to be provided to a satellite of mass m revolving around a planet of mass M, to transfer it from a circular orbit of radius
R1, to another of radius R2 (R2 > R1) is

Answer:
4
Question 33.
Which one of the following plots represents the variation of gravitational field on a particle w ith distance r due to a thin spherical shell of radius R? (r is measured from the centre of the spherical shell)
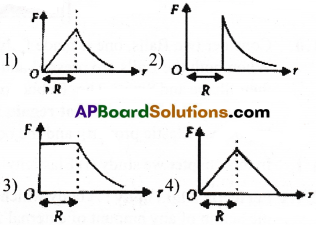
Answer:
2
Question 34.
The dependence of acceleration due to gravity g on the distance r from the centre of the earth, assumed to be a sphere of radius R and of uniform density is as shown in figures.
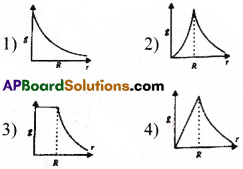
The correct figure is
Answer:
1
![]()
Question 35.
A particle of mass m is thrown upwards from the surface of the earth, with a velocity u. The mass and the radius of the earth are, respectively, M and R. G is gravitational constant and g is acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth. The minimum value of u to that the particle does not return back to earth, is
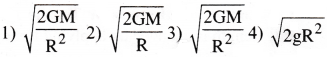
Answer:
2