Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 5th Lesson Partnership Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 5th Lesson Partnership
Essay Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Partnership. Discuss its merits and limitations. [Mar. 2019; May 17 – T.S. M Mar. 15 – A.P. & T.S.]
Answer:
Partnership is an association of two or more persons who pool their financial and managerial resources and agree to carry on a business with profit motive. The persons who are enter into partnership individually called ‘Partners’ and collectively known as ‘Firm’.
Partnership – Definition :
Partnership is “the relation between two or more persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all” – Section 4 of the Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
Merits:
1) Easy to form :
A partnership can be formed easily without many legal formalities. Since it is not compulsory to get the firm registered, a simple agreement, either in oral, writing or implied is sufficient to create a partnership firm.
2) Availability of larger resources :
A partnership firm consists of more than one person, it may be to pool more resources as compared to sole proprietorship.
3) Better decisions :
In partnership firm each partner has a right to take part in the management of the business. All important decisions are taken in consultation with and with the consent of all partners. Thus, collective wisdom prevails and there is less scope for reckless and hasty decisions.
4) Flexibility:
The partnership firm is a flexible organisation. Changes in the business can be adopted easily. At any time the partners can change the size or nature of business or area of its operation after taking the necessary consent of all the partners.
5) Sharing of risks:
The losses of the firm are shared by all the partners equally or as per the agreed ratio.
6) Protection of interest:
In partnership form of business organisation, the rights of each partner and his/her interests are fully protected. If a partner is dissatisfied with any decision, he can ask for dissolution of the firm or can withdraw from the partnership.
7) Secrecy :
Business secrets of the firm are known to the partners only. It is not required to disclose any information to the outsiders. It is also not mandatory to publish the annual accounts of the Partnership firm.
Limitations:
1) Unlimited liability :
The partners liability is unlimited. This is the most important drawback of partnership. The partners are personally liable for the debts and obligations of the firm. In other words, their personal property can also be utilised for payment of firm’s liabilities.
2) Limited capital:
Since the total number of partners cannot exceed 20, the capacity to raise funds remains limited as compared to a joint stock company where there is no limit on the number of share holders.
3) Non-transferability of share :
In partnership firm, the partners cannot transfer his share of interest to other without consent of remaining partners.
4) Possibility of conflicts:
Differences and disputes among the partners are common. These conflicts harm to the firm. Difference of opinion may give rise to quarrels and lead to dissolution of the firm.
Question 2.
Is registration of Partnership compulsory under the Partnership Act, 1932? Explain the procedure required for registration of a firm.
Answer:
Partnership is an association of two or more persons who pool their financial and managerial resources and agree to carry on a business, and share its profits or losses. The persons who form a partnership are individually known as ‘Partners’ and collectively a firm or partnership firm.
The Indian Partnership Act, 1932 does not make it compulsory for a firm to be registered; but there are certain disabilities which attach to an unregistered firm. These disabilities make its virtually compulsory for a firm to be registered. Registration can take place at any time.
The procedure for registration of a firm is as follows:
- The firm will have to apply to the Registrar of Firms of the state concerned in the prescribed form.
- The firm will have to apply to the Registrar of firms of the state concerned in the prescribed form. For this, a form containing the following particulars, accompanied by a fee of ₹3/- has to be sent to the Registrar of Firms.
a) The name of the firm
b) Location of the firm
c) Names of other places where the firm carries on business
d) The name in full and addresses of the partners
e) The date on which various partners joined the firm.
f) The duration of the firm - The duly filled in form must be signed by all the partners. The filled in form along with prescribed registration fee must be deposited in the office of the Registrar of Firms.
- The Registrar will scrutinise the application, and if he is satisfied that all formalities relating to registration have been duly complied with, he will put the name of the firm in his register and issue the Certificate of Registration.
![]()
Question 3.
Discuss different types of Partners. [Mar. 2019; May 17 – A.P. Mar. 17 – T.S.]
Answer:
A Partnership firm can have different types of partners with different roles and liabilities. Some of them may take part in the management while other may contribute capital.
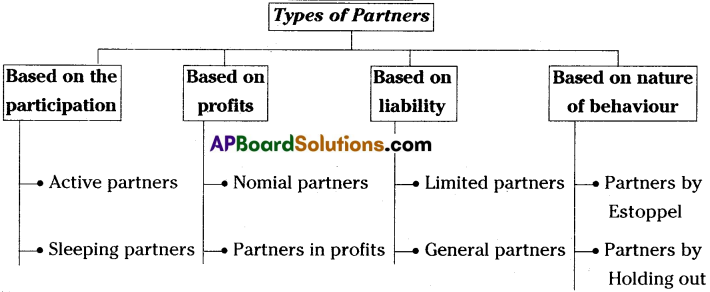
1) Active Partners or Working Partners:
The partners who actively participate in the day-to-day operations of the business are known as active partners or working partners.
2) Sleeping Partners :
The partners, who simply provide capital and do not participate in the management activities of the firm are called sleeping partners.
3) Nominal Partners :
Nominal partners allow the firm to use their name as partner. They neither invest any capital nor participate in the day-to-day operations. They are not entitled to share the profits of the firm. However they are liable to third parties for all the acts of the firm.
4) Partners in Profits :
A person who shares the profits of the business without being liable for the losses is known as partner in profits. This is applicable only to the minors who are admitted to the benefits of the firm and their liability is limited to their capital contribution.
5) Limited Partners :
The partners whose liability is limitied in a firm are called limited partners. They are also known as special partners.
6) General Partners :
The partners having unlimited liability are called general – partners. According to Indian Partnership Act, 1932 the liability of the partner is unlimited. So they are general partners (excpet minor partner).
7) Partner by Estoppel:
A person, who behaves in the public is such a way as to give an impression that he/she is a partner of the firm, is called partner by Estoppel. Such partners are not entitled to share the profits of the firm, but are, fully liable if somebody suffers because of his/her false representation.
8) Partner by Holding out:
Sometimes, the firm may use the name of a person in its activities, creating a sense in the public that he is also a partner. If that person accepts the same, he becomes automatically responsible to the third parties. Such person is known as “Partner by Holding out”.
4. What is Partnership Deed? And also explain its contents. [Mar. 2018 – T.S.]
Answer:
Partnership is an association of two or more persons who pool their financial and managerial resources and agree to carry on a business, and share its profits or losses. Partnership was established among partners through an agreement. Such agreement may be in the form of oral or written. If partnership agreement is in registration it is known as Partnership Deed.
Partnership Deed is a document containing the terms and conditions of a partnership. It is an agreement in writing signed by the partners duly stamped and registered. The Partnership deed defines certain rights, duties and obligations of partners and governs relations among them in the conduct of business affairs of the firm.
The Partnership deed must not contain any term which is contrary to the provisions of the Partnership Act. Each partner should have a copy of the deed.
The following points are generally included in the deed.
Partnership Deed – Contents
- Name of the firm
- Nature of the business
- Names and addresses of partners
- Location of business
- Duration of partnership, if decided
- Amount of capital to be contributed by each partner
- Profit and loss sharing ratio
- Duties, powers and obligations of partners
- Salaries and withdrawals of the partners
- Preparation of accounts and their auditing
- Procedure for dissolution of the firm
- Procedure for settlement of disputes
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Partnership and state its important features. [Mar. 17 – A.P.]
Answer:
Partnership is an agreement between two or more persons to carry on business with profit motive, carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.
Partnership – Definition :
“Partnership is the relation existing between persons competent to make contract, who agree to carry on a lawful business in common with a view to private gain.” – L.H. Haney
“The relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all of them acting for all.” – Indian Partnership Act, 1932, Section 4
Partnership Firm – Features:
The following are the important features of partnership organisation.
- Formation
- Unlimited liability
- Existence of lawful business
- Principal agent relationship
- Voluntary registration
1) Formation :
The partnership form of business organisation is governed by the provision of Indian Partnership Act, 1932. It comes into existence through a legal agreement where in the terms and conditions governing the relationship among partners. Partnership formation is very easy.
2) Unlimited Liability :
The liability of partner is unlimited, joint and several. Personal assets may be used for repaying debts in cases the business assets are insufficient. All the partners are responsible for the debts and they contribute in proportion to their share in business and as such are Habile to that extent.
3) Existence of lawful business:
The business to be carried on by a partnership must always be lawful. Any agreement to indugle in sumuggling, black marketing, etc. cannot be called partnership business in the eyes of law.
4) Principal agent relationship :
Each partner is an agent of the firm. He can act on behalf of the firm. He is responsible for his own acts and also the acts on behalf of the other partners. There must be an agency relationship between the partners.
5) Voluntary registration :
The registration of a partnership firm is not compulsory. But an unregistered firm suffers from some limitations which make it virtually compulsory to be registered.
Question 2.
Discuss the registration procedure of partnership.
Answer:
The Indian Partnership Act, 1932 does not make it compulsory for a firm to be registered; but there are certain disabilities which attach to an unregistered firm. These disabilities make it virtually compulsory for a firm to be registered. Registration can take place at any time. The procedure for registration of a firm is as follows:
- The firm will have to apply to the Rigistrar of Firms of the state concerned in the prescribed form.
- The firm will have to apply to the Registrar of Firms of the state concerned in the prescribed form. For this, a form containing the following particulars, accompanied by a fee of Rs. 3/- has to be sent to the Registrar of Firms.
a) The name of the firm
b) Location of the firm
c) Names of other places where the firm carries on business
d) The name in full and addresses of the partners
e) The date on which various partners joined the firm
f) The duration of the firm - The duly filled in form must be signed by all the partners. The filled in form along with prescribed registration fee must be deposited in the office of the Registrar of Firms.
- The Registrar will scrutinise the application, and if he is satisfied that all formalities relating to registration have been duly complied with, he will put the name of the firm in his register and issue the Certificate of Registration.
![]()
Question 3.
Briefly explain the rights of partners.
Answer:
The rights and duties of the partners of a firm are usually governed by the partnership agreement among the partners. In case the Partnership Deed does not specify them, then the partners will have rights and duties as laid down in the Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
Rights of Partners :
- Every partner has a right to take part in the management of the business.
- Right to be consulted and expressed his opinion on any matter related to the firm.
- Partner has a right to inspect the books of accounts or to copy them.
- Right to have an equal share in the profits or losses of the firm, unless and otherwise agreed by the partners.
- Right to receive interest on loan and advances made by partner to the firm.
- Right to the partnership property unless and otherwise mentioned in the partnership deed.
- Every partner has power or authority, in an emergency, to do any such acts, for the purpose of protecting the firm from losses.
- Right to prevent the introduction of a new partner without consent of other partners.
- Right to act an agent of the partnership firm in the ordinary course of business.
- Right to be indemnified for the expenses incurred and losses sustained by partner to the firm.
Question 4.
Briefly explain the duties of partners.
Answer:
Generally, the Partnership Deed contains rights and duties of the partners. If deed is not prepared, the provisions of the Partnership Act will apply. Also when deed is in silent on any point, the relevant provisions of the act will apply.
Duties of Partners
- Every partner has to attend diligently to his duties in the conduct of the business.
- Should act in a just and faithful manner towards other partner and partners.
- Should bound to share the losses of the firm equally unless and otherwise agreed upon by all partners.
- No partner shall carry on any business competing with the firm. If he does so, he has to render to the firm any profits arising out of such business.
- Must maintain true and correct accounts relating to the firm’s business.
- No partner should make secret profits by way of commission or otherwise from the firm’s business.
- Every partner is bound to keep and render true and proper accounts of the firm to his copartners.
- No partner is allowed to assign or transfer his rights and interest in the firm to an ‘ outsider without the consent of other partners.
Question 5.
Explain the ways of dissolution of a Partnership Firm.
Answer:
The partnership is established through an agreement among partners. The partnership firm is established through partnership. A distinction should be made between the “Dissolution of partnership” and “Dissolution of firm”.
Dissolution of Partnership:
Dissolution of partnership implies the termination of the original partnership agreement or change in contractual relationship among partners. A partnership is dissolved by the insolvency, retirement, incapacity, death, expulsion, etc. of a partner or on the expiry/ completion of the term of partnership.
A partnership can be dissolved without dissolving the firm.
In dissolution of partnership, the business of the firm does not come to an end. The remaining partners continue the business by entering into a new agreement. On the Other hand, dissolution of firm implies dissolution between all the partners. Thus, business of the partnership firm comes to an end. The remaining partners continue the business by entering into a new agreement.
Dissolution of Firm:
Dissolution of firm implies dissolution between all the partners. The business of the partnership firm comes to an end. Its assets are realised and the creditors are paid off. Thus, dissolution of firm always involves dissolution of partnership but the dissolution of partnership does not necessarily mean dissolution of the firm.
Dissolution of the firm takes place under certain circumstances.
1) Dissolution by agreement:
A partnership firm may be dissolved with the mutual consent of all the partners or in accordance with the terms of the agreement.
2) Dissolution by notice :
In case partnership-at-will, a firm may be dissolved, if any partner gives a notice in writing to other partners indicating his intention to dissolve the firm.
3) Contingent dissolution :
A firm may be dissolved on the expiry of the firm, completion of the venture, death of a partner, adjudication of a partner as insolvent.
4) Compulsory dissolution:
A firm stands automatically dissolved if all partners or all but one partner are declared insolvent, or business becomes unlawful.
5) Dissolution through Court:
Court may order the dissolution of a firm, when any partner becomes members unsound, permanently incapable of performing his duties, guilty of misconduct, wilfully and persistently commits breach of the partnership agreement, unauthorised transfers the whole of his interest or share in the firm to a third person.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Partnership Firm
Answer:
Partnership is an association of two or more persons who pool their financial and managerial resources and agree to carry on a business, and share its profits or losses. Partnership was established among partners through an agreement. Such agreement may be in the form of oral or written. If partnership agreement is in registration, it is known as partnership deed.
Question 2.
Partnership Deed [May 17 -A.P.]
Answer:
Partnership Deed is a document containing the terms and conditions of a partnership. It is an agreement in writing signed by the partners duly stamped and registered. The partnership deed defines certain rights, duties and obligations of partners and gov- erj^s relations among them in the conduct of business affairs of the firm.
Question 3.
Active Partner [Mar. 2018, -A.P. & T.S.]
Answer:
The partners who actively participate in the day-to-day operations of the business are knovyn as active partners or working partners.
Question 4.
Sleeping Partner
Answer:
The partners, who simply provide capital and do not participate in the management activities of the firm are called sleeping partners.
Question 5.
Partner by Estoppel
Answer:
A person who behaves in the public in such a way as to give an impression that he/she is a partner of the firm is called partner by estoppel. Such partners are not entitled to share the profits of the firm, but are fully liable if somebody suffers because of his/her false representation.
![]()
Question 6.
Prartner by Holding out
Answer:
Sometimes, the firm may use the name of a person in its activities, creating a sense in the public that he is also a partner. If that person accepts the same, he becomes automatically responsible to the third parties. Such person is known as “Partner by Holding Out”.
