Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Important Questions 9th Lesson The s-Block Elements which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Important Questions 9th Lesson The s-Block Elements
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give reasons for the diagonal relationship observed in the periodic table.
Answer:
The diagonal relationship is due to nearly equal
a) Ionic or atomic sizes.
b) Electronegative values.
c) Polarising powers.
Question 2.
Write completely’ the electronic configuration of K and Rb.
Answer:
The E.C of ‘K’ with atomic number Z = 19 is
1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p6 4s¹
The E.C of ‘Rb’ with atomic number Z = 37 is
1s² 2s² 2p6 3s² 3p6 4s² 3d10 4p6 5s¹
Question 3.
Lithium salts are mostly hydrated. Why? [TS 15, 22]
Answer:
Lithium is the smallest in size among the alkali metals. Hence, Li+ ion can polarize water molecules more easily than other alkali metals.
As a result, Li+ has maximum degree of hydration and lithium salts are mostly hydrated.
Ex: LiCl.2H2O
Question 4.
Which of the alkali metals shows abnormal density? What is the order of the variation of density among the IA group elements? [AP 18]
Answer:
a) In the alkali metals, Potassium(K) shows abnormal density due to
i) abnormal increase in its atomic size.
ii) Presence of vacant 3d orbitals
iii) Empty space in its crystal lattice.
b) Order of density of IA group elements is Li < Na > K < Rb < Cs.
Question 5.
Lithium reacts with water less vigorously than sodium. Give your reasons. [TS 18]
Answer:
Lithium reacts with water less vigorously than Sodium, because Lithium has small size and very high hydration energy than Sodium.
![]()
Question 6.
Lithium iodide is the most covalent among the alkali metal halides. Give the reasons.
Answer:
Reasons:
- Li+ ion has very small size and I– ion has large size.
- The polarising power of lithium ion is high.
- Li+ ion has high tendency to distort electron cloud around the iodide ion.
- So Lithium iodide is the most covalent among the alkali metal halides.
Question 7.
In what respects, lithium hydrogen carbonate differs from other alkali metal hydrogen carbonates?
Answer:
Except Lithium hydrogen carbonate, other alkali metal hydrogen carbonates are solids. Lithium does not exist in solid state due to its less electropositive nature.
Except Lithium hydrogen carbonate, other alkali metal hydrogen carbonates are decomposed on heating.
Question 8.
Write the complete electronic configurations of any two alkaline earth metals.
Answer:
The E.C. of Be with atomic number Z = 4 is 1s² 2s²
The E.C. of Mg with atomic number Z = 12 is 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s²
Question 9.
Tell about the variation of melting points and boiling points among the alkaline earth metals.
Answer:
Due to low I.P. values and different crystalline structures, the variation of melting points and boiling points among alkaline earth metals is irregular.
Variation of M.P:
Be>MgSr>Ba>Ra (Be>Ca>Sr>Ba>Ra>Mg)
Variation of B.P:
Be>MgSrRa (Be>Ba>Ca>Sr>Mg)
Question 10.
What are the characteristic colours imparted by the IIA elements? [TS 22]
Answer:
Be and Mg do not produce any colour in bunsen flame. But other metals produce the following colours.
Calcium – Brick red
Strontium – Crimson red
Barium – Apple green
![]()
Question 11.
What happens when magnesium metal is burnt in air? [TS 15, 18, 19]
Answer:
When Magnesium is burnt in air, it bums with dazzling brilliance and gives MgO and Mg3N2.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
Question 12.
Lithium carbonate is not so stable to heat as the other alkali metal carbonates. Explain.
Answer:
Lithium ion being very small in size and polarises the bigger carbonate ion and distort its electron cloud. So it dissociates forming stable Li2O.
Li2CO3 → Li2O + CO2
Question 13.
Write a balanced equation for the formation of ammoniated group IIA metal ions from the metals in liquid ammonia.
Answer:
Alkaline earth metals dissolve in liquid ammonia and give deep blue black solutions . forming ammoniated ions.
M + (x + 2y)NH3 → MM(NH3)x]+2 + 2[e(NH3)y]–
Question 14.
The fluorides of alkaline earth metals are relatively less soluble than their respective chlorides in water. Why?
Answer:
The fluorides of alkaline earth metals are relatively less soluble in water than the chlorides due to their high lattice energies.
Question 15.
What happens when hydrated Mg(NO3)2 is heated? Give the balanced equation. [AP 22]
Answer:
When hydrated Mg(NO3)2 is heated it decomposes and gives MgO.
2Mg(NO3)2 → 2MgO + 4NO2 + O2
Question 16.
Why does the solubility of alkaline earth metal hydroxides in water increases down the group? [AP 20]
Answer:
The lattice enthalpy decreases much more than the hydration enthalpy, with increasing ionic size down the group. So the solubility increases as we go down the group.
![]()
Question 17.
Why does the solubility of alkaline earth metal carbonates and sulphates in water decrease down the group?
Answer:
Down the group, with increase atomic size the lattice enthalpies and hydration enthalpies of carbonates and sulphates decrease. But the decrease in hydration enthalpies is rapid than lattice enthalpies. So the solubilities of carbonates and sulphates decrease down the group.
Question 18.
Write the average compositiqn of Portland cement.
Answer:
Average composition of portland cement:
CaO : 50%-60%
SiO2 : 20% – 25%’ :
Al2O3 : 5 % -10%
MgO : 2% – 3%
SO3 : 1% – 2%
Fe2O3 : 1% – 2%
Question 19.
Why is gypsum added to cement? [TS 15, 19]
Answer:
Gypsum (Calcium sulphate dihydrate) is added to cement to slow down the setting time. Hence hardness of cement increases.
Question 20.
Why are alkali metals not found in the free state in nature? [Mar 13][ AP 17]
Answer:
Alkali metals are highly reactive. Hence they do not found in the free state in nature.
Reason :
All alkali metals have one valance electron, ns¹. The loosly held s-electron in the outermost valence shell of these elements makes them the most electropositive metals. They readily lose electron to give monovalent M+ ions.
Question 21.
Potassium carbonate cannot be prepared by Solvay process. Why? [AP 19]
Answer:
The Solvay process cannot be extended for the manufacture of K2CO3, because KHCO3 is more soluble in water unlike NaHCO3. So it cannot be isolated.
![]()
Question 22.
Describe the important uses of Caustic Soda (or) sodium hydroxide. [TS 18, 19][AP 15, 16, 18]
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is used
- in the manufacture of Soaps, paper industries.
- in ‘petroleum refining’.
- in ‘textile finishing’.
- as a ‘laboratory reagent’.
Question 23.
Describe the important uses of sodium carbonate. [AP 20]
Answer:
Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3) is used
- to remove hardness of water.
- in the preparation of glass, caustic soda.
- in laundries as washing soda.
- in paper, paints and petroleum industries.
Question 24.
Describe the important uses of quick lime [AP 19]
Answer:
Quick lime(CaO) is used:
- as a primary material for manufacturing cement.
- in the manufacture of Na2CO3 from caustic soda.
- in the purification of sugar and dye stuffs.
Question 25.
Draw the structures of i) BeCl2 (vapour) and ii) BeCl2 (solid).
Answer:
a) Structure of BeCl2 (vapour) :
BeCl2 exists as a dimer in vapour state.

b) Structure of BeCl2 (solid):
BeCl2 exists as a polymer in solid state.

Question 26.
Describe the importance of Plaster of Paris.
Answer:
Plaster of paris is used in
- Surgical bandages for bone fracture
- making white chalks.
- making casts for statues, roofs, toys etc.
Question 27.
Which of the alkaline earth metal carbonates is thermally the most stable? Why?
Answer:
BaCO3 is thermally most stable among Alkaline earth metal carbonates
Reason:
The bigger cation Ba2+ having less polarising power, cannot distort the carbonate ion. So its stability is more.
![]()
Question 28.
Write balanced equations for the reactions between
(i) Na2O2 and water (ii) K2O and water.
Answer:
i) Na2O2 + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2O2
(ii) K2O + H2O → 2KOH
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Alkali metals and their salts impart characteristic colours to an oxidizing flame. Explain the rea$onizing flame. Explain the reason.
Answer:
Alkali metals and their salts impart characteristic colours to oxidising flame. Reason: The heat from the flame excites the outer most electron to a higher energy level. When excited electrons come back to the ground state, they emit the absorbed energy in the form of light in visible region.
Lithium – Crimson red
Sodium – Yellow
Potassium – Lilac or pale violet
Rubidium – Red violet
Caesium – Blue violet
Question 2.
What makes caesium and potassium useful as electrodes in photoelectric cells?
Answer:
Potassium(K) and Caesium(Cs) have low- ionisation energy and can easily lose electrons.
Alkali metals when irradiated with light, the light energy absorbed is just sufficient to make an atom lose electron.
This makes caesium and potassium useful as electrodes in photo electric cells.
Question 3.
Write a short note on the reactivity of alkali metals towards air.
Answer:
Reactivity of alkali metals towards air: The alkali metals tarnish in dry air due to formation of their oxides, which in turn react with moisture to form hydroxides. They bum vigorously in oxygen and form oxides. Lithium forms only monoxide.
4Li + O2 → 2Li2O
Sodium forms monoxide in limited supply of air but forms peroxide in excess of oxygen.
4Na + O2 → 2Na2O
2Na + O2 → Na2O2
Other alkali metals form superoxides.
M + O2 (excess) → MO2 (M = K, Rb, Cs)
Question 4.
Give any two uses for each of the following metals, i) Lithium ii) Sodium
Answer:
i) Lithium is used
- in making electrochemical cells.
- in thermo nuclear reactions.
- in the preparation of alloys.
Ex: White metal is an alloy of lithium and lead used in making bearings for motor engines. The alloy of lithium-magnesium is used to make armour plates.
ii) Uses of Sodium ;
- Sodium-lead alloy is used in making tetraethyl lead, an anti knocking agent in petrol.
- Liquid sodium metal is used as coolant in nuclear reactors.
Question 5.
Give an account of properties of Washing soda?
Answer:
Properties of Washing soda:
- Na2CO3 is a white crystalline solid.
- Na2CO3 exists as a decahydrate ,(NaCO3.10H2O).
This is called washing soda - Na2CO3 is readily soluble in water
- On heating it loses water of crystallization and froms monohydrate.
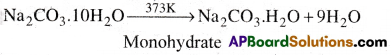
- Above 373K, the monohydrate becomes completely anhydrous and changes to a white powder called soda ash.
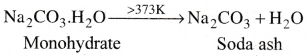
- Carbonate part of sodium carbonate gets hydrolysed by water to fomi an alkaline solution.
CO2-4 + H2O → HCO–3 + OH–
![]()
Question 6.
Mention r some uses of Sodium carbonate.
Answer:
Sodium earbonate(Washing soda) is used
- in water softening, cleaning and laundries.
- in the manufacture of glass, water glass, caustic soda, paper dyes.
- in paper, paints and textile industries. ,
- as a reagent in the laboratory in qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Question 7.
How do you obtain pure sodium chloride from a crude sample?
Answer:
- Crude sodium chloride, contains sodiumsulphate, calcium sulphate, calcium chloride and magnesium chloride as impurities.
- First the crude sodium chloride is dissolved in minimum amount of water and filtered to remove insoluble impurities.
- Now hydrogen chloride gas is passed into the saturated solution of sodium chloride.
- Then pure sodium chloride crystallises out.
Question 8.
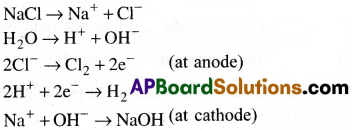
What do you know about Castner-Kellner process? Write the principle involved in it.
Answer:
- Castner-Kellner process is a commercial method used for the preparation of sodium hydroxide.
- In this process sodium hydroxide is prepared by the electrolysis of sodium chloride,
- Brine solutiont (NaCl solution) is electrolysed using a mercury cathode and a carbon anode.
- Sodium metal is formed at cathode and it combine with mercury to form sodium amalgam.
- Chlorine gas is evolved at anode.
- The amalgam is treated with water to form sodium hydroxide.
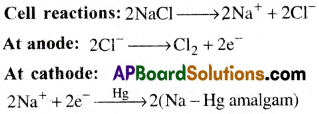
This amalgam is treated with water to give sodmmhydroxide and hydrogen gas.
2(Na – Hg) + 2H2O → 2NaOH + 2Hg + H2
This process is also called as mercury cathode process.
Question 9.
Write a few’ applications of caustic soda. [May’ 13][AP 15]
Answer:
Caustic Soda (NaOH) is used
- in the manufacture of Soaps, paper- industries.
- in ‘petroleumrefining’.
- in ‘textile finishing’.
- as a ‘laboratory reagent’.
Question 10.
Give an account of biological importance of Na+ and K+ ions. [AP 18][TS 17]
Answer:
Sodium(Na):
- Sodium ions are found primarily in the blood plasma.
- They are also found in the interstitial fluids surrounding cells.
- Sodium ions help in the transmission of nerve signals.
- They help in regulating the flow of water across the cell membranes.
- They also help in transporting sugars and aminoacids into the cells.
Potassium (K):
- Potassium ions are found in the highest quantity within the cell fluids.
- K+ ions help in activating many enzymes.
- They also participate in oxidising glucose to produce ATP.
- They also help in transmitting nerve signals.
![]()
Question 11.
Mention the important uses of Mg metal. [TS 19]
Answer:
Uses of Magnesium:
- Mg forms alloys with Al, Zn, Mn and Sn.
- Mg is used in flash powders and bulbs, incendiary bombs and signals.
- A suspension of Mg(OH)2 in water is known as Milk of magnesia. It is used as antacid and laxative in medicine.
- MgCO3 is an ingredient of toothpaste.
Question 12.
Show that Be(OH)2 is amphoteric in nature.
Answer:
Beryllium hydroxide is amphoteric in nature as it reacts with both acids and bases.
1) Reaction with Acid:
Be(OH)2 + 2HCl → BeCl2 + 2H2O
The reaction of Be(OH)2 with hydrochloric acid shows its basic nature.
2) Reaction with Base:
Be(OH)2 + 2NaOH → Na2BeO2 + 2H2O
The reaction with sodium hydroxide shows its acidic nature.
So Be(OH)2 is amphoteric.
Question 13.
Write a note on the anomalous behaviour of Beryllium.
Answer:
Anomalous characters of Beryllium:
- Compounds of Be are predominantly covalent.
- Be is not easily affected by air and does not decompose water at ordinary temperature.
- Be is an amphoteric metal. It dissolves in alkali solutions forming beryllates.
- BeSO4 is soluble in water whereas the sulphates of Ca, Sr and Ba are insoluble.
- Be and its salts do not respond to flame test while Ca,Sr and Ba give characteristic flame colours.
- Be forms many complexes, while heavier elements do not form complexes easily.
- Be has a maximum covalency of 4, while others have a maximum covalency of 6.
Question 14.
Be shows diagonal relationship with Al. Discuss.
Answer:
Beryllium shows a diagonal relationship with aluminium in the following respects.
- Both Be and Al have the same EN value (1.50)
- Both the compounds ofBe and Alundergo hydrolysis.
BeCl2 + 2H2O → Be (OH)2 + 2HCl
AlCl3 + 3H2O → Al (OH)3 + 3HCl - Be and Al are rendered passive by cone HNO3.
- Both Be and Al form complexes.
- Both Be and Al are amphoteric metals. They dissolve in alkali and form beryllates and aluminates respectively.
Be + 2 NaOH → Na2BeO2 + H2
2Al + 2NaOH + 2H2O → 2NaAlO2 + 3H2 - The carbides of Be and Al liberate CH4 gas on treatment with water.
Be2C + 4 H2O → 2Be(OH)2 + CH4
Al4Cl3 + 12 H2O → 4Al(OH)3 + 3CH4
Question 15.
What is Plaster of Paris? Write a short note on it. [AP 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 22][TS 16, 17]
Answer:
1) Plaster of Paris:
Hemih.ydrate of calcium sulphate (CaSO4 \(\frac{1}{2}\) H2O) is called plaster of paris.
2) It is obtained when gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O) is heated to 393K .
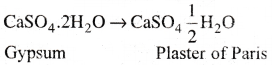
3) Above 393K, it loses water molecules to form anhydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO4). This is known as ‘dead burnt plaster’.
4) It has remarkable property of setting with water on mixing with an adequate quantity of water. It forms a plastic mass that gets into a hard solid in 5 to 15 minutes.
5) Plaster of paris is used
(i) in making casts for statues, toys etc,
(ii) in surgical bandages for bone fracture
(iii) in making white chalks.
Question 16.
In what ways lithium shows similarities to magnesium in its chemical behavior?
Answer:
Li shows similarity with Mg in the following respects.
- Li & Mg have diagonal relationship.
- Both Lithium and Magnesium are harder and lighter than other elements in the respective groups.
- Both Lithium and Magnesium give monoxides only.
- Lithium and Magnesium react slowly with water.
- LiCl deliquescent ( absorbs water from atmosphere) like MgCl2.
- Halides of Lithium and Magnesium are soluble in ethanol
- Both Li+ and Mg+2 ions are highly hydrated.
- The carbonates, phosphates and fluorides of both Lithium and Magnesium are sparingly soluble in water.
- Alkyl Lithium is chemically similar to Grignard reagents(R-Mg-X) in organic synthesis.
![]()
Question 17.
When an alkali metal dissolves in liquid ammonia, the solution can acquire different colours. Explain the reasons for this type of colour change.
Answer:
- The Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia and they give deep blue solutions. They are conducting in nature.
M + (x + y)NH3 → MM(NH3)x]+ + [e(NH3)y]– - The blue colour of the solution is due to the ammoniated electrons which absorb energy in the visible region of light and thus impart blue colour to the solution.
- The solutions are paramagnetic and on standing slowly liberate hydrogen resulting in the formation of amide.
M+ + e– +NH3 → MNH2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)H2 - In concentrated solution, on warming, the blue colour changes to bronze colour and becomes diamagnetic.
Question 18.
What happens when (i) Sodium metal is dropped in water? (ii) Sodium metal is heated in a free supply of air? (iii) Sodium peroxide dissolves in water?
Answer:
- When Sodium metal is dropped in water, it reacts with water vigorously and liberates H2 gas.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 - When Sodium metal is heated in free supply of air it forms Sodium peroxide.
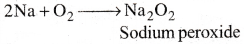
- When Sodium peroxide is dissolved in water it forms NaOH and Hydrogen peroxide.
Na2O2 + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2O2
Question 19.
State as to why i) An aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 is alkaline. ii)Alkali metals are prepared by the electrolysis of their fused chlorides?
Answer:
i) When Sodium carbonate is added to water, it undergoes anionic hydrolysis to give weak carbonic acid (H2CO3) and strong base sodium hydroxide (NaOH). NaOH being strong electrolyte ionises completely but H2CO3 does not ionise. So the solution is alkaline.
Na2CO3 + 2H2O ⇌ 2Na+ + 2OH– + H2CO3
ii) Alkali metals themselves are strong reducing agents. Any reducing agent stronger than alkali metal is no where available. Hence they cannot be extracted by chemical reduction methods.
When aqueous solutions of alkali metal salts are electrolysed, hydrogen gas will be liberated at cathode instead of alkali metal. This is because, the discharge potential of H+ is less than Na+.
Hence alkali metals are prepared by the electrolysis fused chlorides. To decrease the melting points of the alkali metal halides, they are mixed with some other compounds.
Question 20.
How would you explain the following observations?
i) BcO is almost insoluble but BeSO4 is soluble in water?
ii) BaO is soluble but BaSO4 is insoluble in water?
Answer:
i) BeO is almost insoluble due to its high degree of covalency.
But, BeSO4 is soluble in water due to high hydration energy of Be+2 ion.
ii) BaO is soluble in water due to its high ionic nature.
But. BaSO4 is insoluble in water due to low heat of hydration of Ba+2
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Justify the inclusion of alkali metals in the same group of the periodic table with reference to the following, i) Electronic configuration ii) Reducing nature iii) Oxides and hydroxides.
Answer:
i) The electronic configurations of alkali metals are as follows.
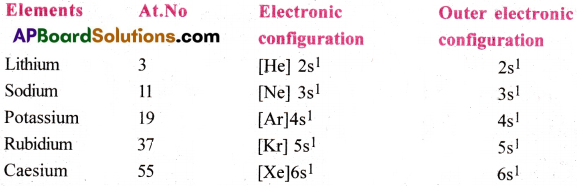
All the alkali metals have one valence electron (ns¹). Because of this similarity in electronic configuration, they are placed in the same group and hence they resemble in their physical and chemical properties.
ii) Reducing nature:
All the Alkali metals have bigger atomic sizes and have low I.P values. So they have a tendency to lose electron and thus they act as strong reducing agents. The large hydration energy of small Li+ ion makes the Lithium, the strongest reducing agent. The order of reducing powers of alkali metals: Li>Cs>Rb>K>Na
iii) Oxides and Hydroxides:
Alkali metals when heated with oxygen form three types of oxides, namely oxides, peroxides and superoxides depending up on the activity of the metal. The oxides and hydroxides of all the alkali metals are strongly alkaline. Because of High electropositive character of alkali metals, their oxides and hydroxides are strongly basic.
The basic character of alkali metals hydroxides increases down the group:
LiOH<NaOH<KOH<RbOH<CsOH.
Thus there is a gradual change in the properties with the increase of their atomic number. This justifies their inclusion in the same group of the periodic table.
![]()
Question 2.
Write an essay on the differences between lithium and other alkali metals.
Answer:
- The anomalous behaviour of Lithium is due to its exceptionally small size and high polarising power
- Lithium is a much harder metal while other alkali metals are soft.
- Lithium is least reactive but the strongest reducing agent among all the alkali metals.
- When Lithium is burnt in air, it forms Li2O and Li3N. But remaining alkali elements form only oxides.
4Li + O2 → 2 Li2O; 6Li + N2 → 2 Li3N - Li Cl is deliquescent (absorbs water form atmosphere) and crystallises as a hydrate, LiCl.2H2O whereas other alkali metal chlorides do not form hydrates.
- Lithium hydrogen carbonate is not obtained in the solid form while all other elements form solid hydrogen carbonates.
- Lithium does not react with acetylene, but remaining elements react with acetylene.
- Lithium nitrate when heated gives Lithium oxide Li2O, whereas other alkali metal nitrates decompose to give the corresponding nitrite.
4LiNO3 → 2LiO + 4NO2 + O2
2NaNO3 → 2NaNO2 + O2 - Lithium compounds (LiF, Li2O) are less soluble in water, than the corresponding compounds of other alkali metals.
Among the carbonates of IA group only Li2CO3 is decomposable remaining are stable.
Li2CO3 → Li2O + CO2
Question 3.
Discuss the preparation and properties of sodium carbonate.
Answer:
1) Preparation:
SodtUm carbonate is prepared by Solvay process.
2) The required raw materials:
1) Brine solution 2) Ammonia 3)Lime Stone.
3) Principle:
Brine solution is saturated with Ammonia and C02 gas is passed through it. Then sodium bicarbonate is formed.
NH3 + H2O + CO2 → NH4HCO3
NH4HCO3 + NaCl → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
The sodium bicarbonate thus formed on heating decomposes to give sodium carbonate.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
Process:
Step 1 :
When carbondioxide is passed through a concentrated brine solution saturated with ammonia, it results in the formation of ammonium bicarbonate.
2NH3 + H2O + CO2 → (NH4)2CO3
(NH4)2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NH4HCO3
Step 2 :
The ammonium bicarbonate then reacts with common salt forming sodiumbicarbonate.
NH4HCO3 + NaCl → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
The solution containing crystals of NaHCO3 is fdtered to obtain NaHCO3.
Step 3 :
Fusion of sodium bicarbonate: NaHC03 is heated to high temperatures to convert it into Na2CO3.
![]()
Note: Recovery of Ammonia:
The filtrate NH4Cl obtained in step 2, is mixed with Ca(OH)2 and heated with steam. Then NH3 gas is liberated which is sent back to saturation tower. In this process CaCl2 is obtained as a by-product.
Ca(OH)2 + 2NH4Cl → 2NH3 + 2H2O + CaCl2
The overall reaction taking place in Solvay process is
2NaCl + CaCO3 → Na2CO3 + CaCl2
Chemical properties of Na2CO3:
1) Na2CO3 is a white crystalline solid.
2) Na2CO3 exists as a decahydrate Na2CO3.10H2O which is called washing soda.
3) Na2CO3 is readily soluble in water.
4) Aqueous Na2CO3 solution is basic in nature. So methyl orange produces yellow colour in that solution.
5) Action with acids:
When Na2CO3 is treated with HCl then CO2 gas is liberated.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
6) Action with non-metals and their oxides:
When Sodium carbonate reacts with a mixture of S and S02, Hypo (Sodium thiosulphate) is formed.
Na2CO3 + SO2 + S → Na2S2O3 + CO2
7) Action with CO2 :
An aq. solution of sodium carbonate when saturated with CO2 gives ppt. of sodium bicarbonate.
Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NaHCO3
8) Action with silica :
When Na2CO3 is fused with SiO2., water glass is formed.
Na2CO3 + SiO2 → Na2SiO3 + CO2
Question 4.
Discuss the similarities between alkaline earth metals and gradation in the following aspects:
i) Electronic configuration ii)Hydration enthalpies iii) Nature of the oxides and hydrides,
Answer:
i) Electronic configuration of alkaline earth metals:

All the alkaline earth metals have same outer electrons (ns²). But, the atomic size increases gradually due to increase in the number of orbits.
ii) Hydration enthalpies: Alkali metal ions (M2+) have more charge and small size. So they have high hydration enthalpies. But with the increase in ionic size, the attraction towards water molecules decreases. So hydration enthalpies of alkaline earth metal ions decreases gradually down the group.
Be2+ > Mg2+ > Ca2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+
iii) Nature of oxides and hydroxides :
The oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals are strongly alkaline in nature. BeO and Be(OH)2 are amphoteric. The oxides of other elements are ionic and basic in nature. The oxides react with water forming hydroxides.
MO + H2O → M(OH)2
The solubility thermal stability and the basic character of these oxides and hydroxides increase with increasing atomic number.
![]()
Question 5.
Discuss on: i) Carbonates ii) Sulphates and iii) Nitrates of alkaline earth metals.
Answer:
i) Carbonates:
Carbonates of alkaline earth metals are insoluble in water. The solubility of these carbonates decreases down the group. Thermal stability of these carbonates increases down the group with increasing cationic size. So their decomposition temperatures increase down the group, These are prepared by the addition of sodium or ammonium carbonate solution to the solutions of soluble compounds of these metals.
ii) Sulphates :
Sulphates are white solids. Their solubility decreases down the group. Thermal stability increases down the group. BeSO4 and MgSO4 are soluble. The greater hydration enthalpies of Be2+ and Mg2+ ions overcome the lattice enthalpy factor and therefore their sulphates are soluble.
iii) Nitrates :
They exist as hydrated salts. These can be prepared by dissolving their carbonates in dilute nitricacid. Barrium nitrate crystallise as anhydrous salt. This is because of the decrease in the hydration enthalpies. All these nitrates decompose on heating.
2M(NO3)2 → 2MO + 4NO2 + O2, (M = Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba)
Question 6.
What are the common physical and chemical features of alkali metals?
Answer:
Physical properties:
- All the alkali metals are soft metals with low melting points and boiling points.
- In each period the alkali metals have large atomic sizes.
- All the alkali metals exhibit only one oxidation state +1.
- All the alkali metals exhibit flame colours.
- Alkali metals have low IP and have tendency to lose electrons. So they act as strong reducing agents.
Chemical properties:
- All the alkali metals react with oxygen in air forming oxides.
Ex: 4Li + O2 → 2Li2O - All the alkali metals react with water liberating hydrogen.
Ex: 2M + 2H2O → 2MOH + H2 - All the alkali metals react with hydrogen forming ionic hydrides.
- All the alkali metals react with halogen forming similar halides of the type MX.
- The oxides and hydroxides of the alkali metals are strongly alkaline.
- All the alkali metals dissolve in ammonia forming blue coloured solution due to the presence of ammoniated electrons. These solutions are good reducing agents, good conductors of electricity and are paramagnetic. In concentrated solution, the blue colour changes to bronze colour on warming and becomes diamagnetic.
Question 7.
Discuss the general characteristics and gradation in properties of alkaline earth metals.
Answer:
- The general electronic configuration of alkaline earth metals is ns².
- Atomics Size increases from top to bottom in the group due to increase in the number of orbits.
- Density increases from top to bottom in the group but Ca is less denser than Mg.
- Melting points and boiling points do not vary regularly.
- Ionisation enthalpies decrease from top to bottom.
- Hydration enthalpies decrease from top to bottom in the group.
- All these elements react with halogens forming halides.
- All these elements except beryllium react with hydrogen directly forming ionic hydrides.
- These elements readily react with acids liberating hydrogen.
- Alkaline earth metals are good reducing agents and their reduction power increases from top to bottom.
- Reactivity towards air and water increases from top to bottom in the group. All these elements bum in air forming metal oxides and metal nitrides. Be and Mg do not react with water but other elements react with water and the reactivity increases from Ca to Ba.
Question 8.
Discuss the various reactions that occur in the Solvay process. [AP 16]
Answer:
Various reactions that occur in the Solvay process:
Reaction 1:
When carbondioxide is passed through a concentrated brine solution saturated with ammonia, it results in the formation of ammonium bicarbonate.
2NH3 + H2P + CO2 → (NH4)2CO3
(NH4)2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NH4HCO3
Reaction 2:
The ammonium bicarbonate then reacts with common salt forming sodium bicarbonate.
NH4HCO3 + NaCl → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
Reaction 3:
NaHCO3 is heated to high temperatures to convert it into Na2CO3.
![]()
The overall reaction taking place in Solvay process is
2NaCl + CaCO3 → Na2CO3 + CaCl2
Question 9.
Starting with sodium chloride how would you proceed to prepare
i) Sodium metal;
ii) Sodium hydroxide
iii) Sodium peroxide
iv) Sodium carbonate.
Answer:
i) Sodium nictal :
When molten sodium chloride is electrolysed sodium metal is formed. To decrease the melting point of sodium chloride it is mixed with KCl and CaCl2.

ii) Sodium hydroxide:
Electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride either in Nelson’s cell or in Castner-Kellner cell gives sodium hydroxide.
iii) Sodium peroxide :
First sodium metal is prepared from sodium chloride as above.
Then it is burnt in excess of O2 to produce sodium peroxide.
2Na + O2 → Na2O2
iv) Sodium carbonate :
Brine is saturated with ammonia. Then CO2 is passed into the solution. Then Sodium bicarbonate is formed due to the following reactions.
NH3 + H2O + CO2 → NH4HCO3
NaCl + NH4HCO3 → NaHCO3 + NH4Cl
This sodium bicarbonate on calcination gives sodium carbonate.
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
![]()
Question 10.
What happens when (i) Magnesium is burnt in air?
(ii) Quick lime is heated with silica?
(iii)Chlorinc reacts with slaked lime?
(iv) Calcium nitrate is strongly heated?
Answer:
i) When magnesium is burnt in air, it bums with brilliant white light to form MgO and Mg3N2.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
ii) When quick lime is heated with silica, calcium silicate is formed.
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
iii) When Cl2 reacts with slaked lime, bleaching powder(CaOCl2) is formed.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + HCl
iv) When calcium nitrate is heated strongly, calcium oxide is formed with the liberation of NO2 and O2 gases.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain the significance of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium in biological fluids. [TS 16,20]
Answer:
Significance of Na, K in biological fluids:
- Na+ ions participate in the transmission of nerve signals.
- Na’ ions regulate the flow of water across cel! membranes.
- Na+ ions responsible for transport of sugars and amino acids into cells.
- K+ ions are useful in activating enzymes.
- K+ ions participate in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP.
- K+ along with Na+ responsible for the transmission of nerve signals.
Biological importance of Mg and Ca: [TS 18]
Significance of Mg2+ :
- Mg2+ ions are concentrated in animal cells.
- Enzymes like ‘phosphohydrolases’ and ‘Phospho transferases’ contain Mg2+ ions.
These enzymes participate in ATP reactions and release energy in the process. Mg2+ forms a complex with ATP. - Mg2+ is a constituent of chlorophyll, the green component of plants.
Significance of Ca2+:
- About 99% of body calcium is present in bones and teeth. It plays important roles in neuro muscular function, intemeuronal transmission, cell membrane integrity and blood coagualation.
- The calcium concentration in plasma is regulated at about 100 mg/Lit. It is maintained by two hormones, calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. Ca2+ ion are necessary for muscle contraction.
Question 12.
Write a few lines about cement.
Answer:
Cement :
Cement is an important building material. It is also called portland cement. It is the product obtained by combining materials rich in lime (CaO) wdth other material such as clay which contains silica (SiO2) along with oxides of Al, Fe and Mg.
Raw material :
The raw materials used for manufacture of cement are
i) Limestone ii) Clay iii) Gypsum
When clay and lime are heated strongly together, they fuse and react to form cement clinker. This clinker is mixed with 2 to 3% by weight of gypsum to form cement. The important ingredients present in portland cement are dicalcium silicate (Ca2SiO4 : 26%) tricalcium silicate (Ca3SiO4 :51%) and tricalcium aluminate (Ca3Al2O6 : 11%).
Setting of Cement:
When cement is mixed with water, the setting of cement takes place to give a hard mass. This is due to hydration of the molecules of the constituents and their rearrangement. The purpose of adding gypsum is only to slow’ down the process of setting time so that it gets sufficiently hardened.
Uses: Cement is used
- in concrete and reinforced concrete.
- in plastering
- in the construction of buildings, dams and bridges.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The formula of soda ash is
1) Na2CO3.10H2O
2) Na2CO3.2H2O
3) Na2CO3.H2O
4) Na2CO3
Answer:
4) Na2CO3
Question 2.
Suspension of slaked lime in. water is known as
1) lime water
2) quick lime
3) milk of lime
4) aqueous solution of slaked lime
Answer:
3) milk of lime
![]()
Question 3.
By adding gypsum to cement
1) setting time of cement becomes less.
2) setting time of cement increases.
3) colour of cement becomes light.
4) shining surface is obtained.
Answer:
2) setting time of cement increases.
Question 4.
The alkali metals are low melting. Which of the following alkali metal is expected to melt if the room temperature rises to 30°C?
1) Na
2) K
3) Rb
4) Cs
Answer:
4) Cs
Question 5.
The order of decreasing ionisation enthalpy in alkali metals is
1) Na > Li > K > Rb
2) Rb < Na < K < Li
3) Li > Na > K > Rb
4) K < Li < Na < Rb
Answer:
3) Li > Na > K > Rb
Question 6.
When sodium is dissolved in liquid ammonia, a solution of deep blue colour is obtained. The colour of the solution is due to
1) ammoniated electron
2) sodium ion
3) sodium amide
4) ammoniated sodium ion
Answer:
1) ammoniated electron
![]()
Question 7.
The reducing power of a metal depends on various factors. Suggest the factor which makes Li, the strongest reducing agent in aqueous solution.
1) Sublimation enthalpy
2) Ionisation enthalpy
3) Hydration enthalpy
4) Electron-gain enthalpy
Answer:
3) Hydration enthalpy
Question 8.
Alkali metals react with water vigorously to form hydroxides and dihydrogen. Which of the following alkali metals reacts with water least vigorously?
1) Li
2) Na
3) K
4) Cs
Answer:
1) Li
Question 9.
Amongst fluorides of alkali metals, the lowest solubility of LiF in water is due to
1) Ionic nature of lithium fluoride
2) High lattice enthalpy
3) High hydration enthalpy for lithium ion.
4) Low ionisation enthalpy of lithium atom
Answer:
2) High lattice enthalpy
Question 10.
Ionic mobility of which of the following alkali metal ions is lowest when aqueous solution of their salts are put under an electric field?
1) K
2) Rb
3) Li
4) Na
Answer:
3) Li
Question 11.
Which of the alkali metal chloride (MCl) forms its dihydrate salt (MCl.2H2O) easily?
1) LiCl
2) CsCl
3) RbCl
4) KCl
Answer:
1) LiCl
Question 12.
HCl was passed through a solution of CaCl2, MgCl2 and NaCl. which of the following compounds crystallises?
1) Both MgCl2 and CaCl2
2) Only NaCl
3) Only MgCl2
4) NaCl, MgCl2 and CaCl2
Answer:
2) Only NaCl
Question 13.
Crude sodium chloride obtained by crystallisation of brine solution does not contain
1) MgSO4
2) Na2SO4
3) MgCl2
4) CaSO4
Answer:
1) MgSO4
![]()
Questionn 14.
In the synthesis of sodium carbonate, the recovery of ammonia is done by treating NH4CI with Ca(OH)2. The by-product obtained in this process is
1) CaCl2
2) NaCl
3) NaOH
4) NaHCO3
Answer:
1) CaCl2
Question 15.
A substance which gives brick red flame and breaks down on heating to give oxygen and a brown gas is
1) Magnesium nitrate
2) Calcium nitrate
3) Barium nitrate
4) Strontium nitrate
Answer:
2) Calcium nitrate
Question 16.
The following metal ion activates many enzymes, participates in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP and w ith Na, is responsible for the transmission of nerve signals.
1) Iron
2) Copper
3) Calcium
4) Potassium
Answer:
4) Potassium
Question 17.
Which of the following elements does not form hydride by direct heating with dihydrogen?
1) Be
2) Mg
3) Sr
4) Ba
Answer:
1) Be
Question 18.
Among CaH2, BeH2, BaH2 the order of ionic character is
1) BeH2 < CaH2 < BaH2
2) CaH2 < BeH2 < BaH2
3) BeH2 < BaH2 < CaH2
4) BaH2 < BeH2 < CaH2
Answer:
1) BeH2 < CaH2 < BaH2
Question 19.
Which of the following is an amphoteric hydroxide?
1) Be(OH)2
2) Sr(OH)2
3) Ca(OH)2
4) Mg(OH)2
Answer:
1) Be(OH)2
Question 20.
The structures of beryllium chloride in solid state and vapour phase are
1) chain in both
2) chain and dimer respectively
3) linear in both
4) dimer and linear, respectively.
Answer:
2) chain and dimer respectively
![]()
Question 21.
Among the following alkaline earth metal halides one which is covalent and soluble in organic solvents is
1) beryllium chloride
2) calcium chloride
3) strontium chloride
4) magnesium chloride
Answer:
1) beryllium chloride
Question 22.
Which of the follow ing statements is true about Ca(OH)2?
1) It is used in the preparation ofbleaching powder
2) It is a light blue solid
3) It does not possess disinfectant property.
4) It is used in the manufacture of cement.
Answer:
1) It is used in the preparation ofbleaching powder
Question 23.
Some of the Group 2 metal halides are covalent and soluble in organic solvents. Among the following metal halides, the one which is soluble in ethanol is
1) BeCl2
2) MgCl2
3) CaCl2
4) SrCl2
Answer:
1) BeCl2
Question 24.
Magnesium reacts with an element (X) to form an ionic compound. If the ground state electronic configuration of (X) is 1s²2s²2p³, the simplest formula for this compound is
1) Mg2X3
2) MgX2
3) Mg2X
4) Mg3X2
Answer:
4) Mg3X2
Question 25.
Metals form basic hydroxides. Which of the following metal hydroxide is the least basic?
1) Mg(OH)2
2) Ca(OH)2
3) Sr(OH)2
4) Ba(OH)2
Answer:
1) Mg(OH)2
Question 26.
Which of the carbonates given below is unstable in air and is kept in C02 atmosphere to avoid decomposition.
1) BeCO3
2) MgCO3
3) CaCO3
4) BaCO3
Answer:
1) BeCO3
Question 27.
Metal carbonates decompose on heating to give metal oxide and carbon dioxide. Which of the metal carbonates is most stable thermally?
1) MgCO3
2) CaCO3
3) SrCO3
4) BaCO3
Answer:
4) BaCO3
![]()
Question 28.
Dead burnt plaster is
1) CaSO4
2) CaSO4½H2O
3) CaSO4.H2O
4) CaSO4.2H2O
Answer:
1) CaSO4