These AP 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Physical Science 4th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
8th Class Physical Science 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is polymer?
Answer:
Many small identical units combine to form a large unit is called polymer. The small units are called monomers.
Question 2.
What are synthetic fibres?
Answer:
The fibres obtained from petrochemicals when they are subjected to chemical processes are called synthetic fibres.
Have you ever heard a cracking sound when you take off certain type of clothes? or did you see sparks in them when it is dark?
![]()
Question 3.
What is the reason?
Answer:
This is static electricity developed by artificial fibres due to friction.
Question 4.
Why does wearing nylon clothes are not preferable while cooking or working near a fire?
Answer:
Nylon fibre easily catches fire. So it is not preferable to wear it while cooking, welding, working near a fire.
Question 5.
What is blending and what is the advantage of blending?
Answer:
Any synthetic fibre can be combined with two or more other fibres is called blending.
When two fibres are blended the resultant blended fibre possess the best qualities of both.
Question 6.
What are the uses of plastics?
Answer:
Plastics are used in milk and oil pouches, containers to store pickles and rice, buckets to store water, chairs, water pipes, electrical appliances, television, radio and comput¬ers and mobile phones.
Question 7.
What material is used to make handles of utensils?
Answer:
Bakelite is used for making handles of various utensils due to its poor conductivity of heat and electricity.
![]()
Question 8.
How do you appreciate 4R principle?
Answer:
4R principle is useful in developing ecofriendly environment and bright future for next generation of people.
8th Class Physical Science 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How is nylon made? What are the advantages of nylon as fibre?
Answer:
Nylon is a polymer made of chemical units called polyamides.
Advantages of nylon as fibre:
- Nylon fibre is strong, elastic and light weight.
- Cloth made of nylon are lustrous and easy to wash.
- Nylon does not absorb water.
Question 2.
Where does we use nylon?
Answer:
Nylon can be used in tooth brush bristles, ropes, fishing nets, tents, sarees, stockings and socks, car seat belts, sleeping bags, curtains, carpets and also used in making parachutes.
Rock climbers use nylon ropes to climb mountains. It is also used in making of swim suits, sheer hosiery, sails, umbrella cloth, dress materials, car tyres, etc.
Question 3.
How would you prepare rayon?
Answer:
The cellulose that was collected from wood or bamboo pulp is treated with sodium hydroxide and then carbon disulphide. It forms a syrup called viscose. Viscose is forced through a spinneret into a solution of dilute sulphuric acid. This gives us silk like threads. This new fibre is called rayon which is an artificial silk.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the uses of rayon?
Answer:
- Rayon is cheaper than silk and can be woven like silk fibre.
- Rayon is mixed with cotton to make bed sheets.
- Rayon is mixed with wool in making of carpets.
- Rayon is often used in fashion and home furnishings.
- Rayon is also found in sanitary products, diapers and bandages and lints for dressing wounds.
Question 5.
What is acrylic ? Where do we use acrylic?
Answer:
Acrylic is a synthetic fibre made from the combination of coal, air, water and lime¬stone. It looks like natural wool. If can be considered as artificial wool.
It is used in knitted apparels such as fleece, socks, sportswear and sweaters. It is also used in craft yarns, upholstery fabric, carpets, luggage yawning and vehicle covers.
Question 6.
What are the advantages of natural fibre over artificial fibres?
Answer:
When natural fibres, contribute to a fabric it allows the skin to breathe easily. Also natural fibres are generally free from irritating chemicals. Whenever fire accidents takes place they does not stick to the body.
Question 7.
How do you prepare polyester? What are the advantages of polyester as fabric?
Answer: Polyester is made by reacting dicarboxylic acid with dihydric alcohol.
Advantages :
- Polyester can be melted and spun. This property allows the fibre to convert into different sizes and shapes.
- They are altra thin, microfiber which gives them a smoothen and soft feel.
- They does not get wrinkled easily.
- It remains crisp and easily washable.
Question 8.
Give example for popular polyester and what are its advantages?
Answer:
The popular polyester is terylene.
- It can be drawn into very fire fabric fibres.
- Terylene is after mixed with cotton to form terricot with wool to give terriwool. Which has best qualities of both blunded fibres.
Question 9.
What are plastics? How many types of plastics are there? Explain them with examples.
Answer:
Organic polymers are called plastics. Plastics are two types :
- Thermoplastics: The plastics which get deformed easily on heating and can be bent are called thermoplastics, e.g.: Polyethene, PVC.
- Thermosetting plastics: The plastics which molded once cannot be softened on heating are called thermosetting plastics, e.g.: Bakelite, melamine.
![]()
Question 10.
Where do we use bakelite?
Answer:
- Bakelite is used for making handles of various utensils.
- It is used for making electrical appliances including switch boards.
- It is an alternative for pearl and jade.
- In manufacture of telephone.
Question 11.
Where do we use melamine?
Answer:
- Melamine is used in making of utensils and other grocery of kitchen.
- It is used for making of floor and dress material (firemen dress) for their nature of fire resistance.
- Computer and T.V. cabinets are made by melamine.
Question 12.
Ramu observing his grandmother keeping pickles in plastic bottles. What are the questions raised in his mind by seeing this?
Answer:
The questions raised in Ramu’s mind
- Whether plastic is cheap when compare with metal?
- Why does she not put the pickles in metal containers?
- Whether metal containers react with pickles? If so they form harmful substances?
Question 13.
What do you know about creator of first man made plastic? How he prepare the plastic?
Answer:
The creator of first man made plastic is Alexander Parkes the name of the plastic is parkesine.
To prepare this material Parkes heated nitrated cotton which previously soaked in sulphuric acid and made fabric soft and elastic with oil and camphor. The end product was an ivory – coloured material that became distorted when subjected to heat. This is named as Parkesine.
Question 14.
What do you know about father of plastic industry? What are his major inventions and discoveries?
Answer:
Dr. Baekeland is considered as the father of present plastic industry. He was respon¬sible for the invention of bakelite. He accidently discovered the compound of carbolic acid and formaldehyde. When he tried to reheat the solidified compound he discovered it would not melt, no matter how high the temperature would be.
![]()
Question 15.
List out the objects made up of Acrylic.
Answer:
- It is used in knitted apparels such as fleece, socks, sports wear and sweaters.
- It is also used in craft yarns, upholstery fabric, carpets, lugguage awnings and vehicle covers.
Question 16.
Draw and explain the diagram of Universal recycling symbol.
Answer:
When the number is omitted from recycling icon then it is known as Universal recycling symbol.

Question 17.
What are thermosetting plastics? Give two examples.
Answer:
Thermosetting plastics are synthetic materials which gain strength during moulding by heating, but cannot be remoulded or reheated after their initial heat, moulding.
Ex : Bakelite and melamine.
Question 18.
What made the human beings to search for the alternative for natural fibres?
Answer:
Human being is always going in search of new things which can make his life more comfortable and durable. As the natural fibres are not durable, elastic or light weight or lustrous or easy to wash, he needed an alternative to fulfill his expectations. The solution to his expectations is synthetic fibre.
Question 19.
Imagine what would happen if we do not discover plastics.
Answer:
Nowadays every object used in our day to day life is made of plastic. For example milk and oil pouches, containers to store pickles and rice, buckets to store water, chains, water pipes, electrical appliances, television, radio and computers, mobile phones.
So plastics has taken over the place occupied by metal wood and glass items due to its special properties. So we cannot imagine our life without plastics because it is part of each and every aspect of life.
Question 20.
What is the most common material used in making the household articles ? Give some examples.
Answer:
Mostly household articles are made up of plastics.
Milk and oil pouches, containers to store pickles and rice, buckets to store water, chairs, water pipes, electric appliances, television, radio and computers, mobile phones, etc. are made of plastic.
Question 21.
What are the properties of thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics ?
Answer:
Thermoplastic will soften when heated and harden when cooled. It is a polymer that turns into a liquid when heated and freezes to a very glassy state when cooled sufficiently. Thermosetting plastics are not remouldable or reheatable. They are poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are fire resistants.
![]()
Question 22.
Why polyster is quite suitable for making dress materials ? Name any two types of polyesters and their uses.
Answer:
a) Fabric made from polyester does not wrinkled easily.
b) If remains crisp and it is easy to wash.
c) Terylene is a type of popular polyester.
d) It can be drawn into very fine fibres that can be woven like any other yarn.
e) PET is very familiar form of polyester. It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires and many other useful products.
Question 23.
Write some disadvantages of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
a) Synthetic fibres cannot absorb moisture, thus they cannot be used as dress materials during summer.
b) They are dangerous to be worn near fire or heat as they catch fire easily.
c) They cannot be easily ironed.
Question 24.
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer:
Three main advantages of using plastic containers for storing food are :
a) They do not react with food items
b) They do not get rusted
c) They are light, strong and durable
![]()
Question 25.
Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics,
a) saucepan handles
b) electric plugs/switches.
Answer:
Above things are made up of bakelite (thermosetting plastic) because it is
a) bad conductor of heat
b) poor conductor of electricity.
8th Class Physical Science 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain 4R principle for creating ecofriendly environment.
Answer:
The 4R principle involves 1) Reduce 2) Reuse 3) Recycle 4) Recover.
- Reduce: Reduce the usage of plastic to avoid its negative consequence on environment. Land filling or plastics and burning of plastics in incinerators in the way of disposal of plastics. These have negative consequence on environment. So reduce the usage of plastic whenever it is possible.
- Reuse: Articles made of plastic is used again and again for its optimum utilization. There by we can decrease the usage of plastics.
- Recycle: We can recycle the plastic material from broken plastic material that will decrease the production of excess of plastic.
- Recover: The principle of recover plays major role in plastic waste management. The solid waste should be converted into resources such as electricity, heat, compost and fuel through thermal and biological means.
(OR)
- Reduce: Try to use less plastic material in our daily life.
- Reuse: Whenever we need to use plastic material, use the same material again and again don’t go for new one every time.
- Recycle: Instead of throw away the waste plastic material try to give it the vendor.
- Recover: Aware the people about establishing “garbage to energy” plant in your area.
Question 2.
Is there any such effort for solid waste management taking place in your village/ town ? How do you appreciate 4R principle?
Answer:
4R Principle is for creating an eco friendly environment.
4R = Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
Reduce: Reducing the usage of plastics by reusing them helps the negative conse-quences on environment.
Reuse: When some things made of plastics are not in use to us, we can give them to others who need them. This helps the negative consequence or environment. This is eco friendly.
Recycle: In this process, we can obtain a new substance from the old plastics. Recycling can be used to obtain materials from which the original products were made.
Recover: The solid wastes in which plastics are major should be converted into resources such as electricity, heat, compost and fuel through thermal and biological means.
In these ways 4R principle is eco-friendly.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the differences between the thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics with help of a diagram explaining in terms of arrangements of monomers.
Answer:
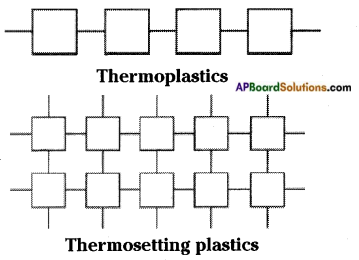
| Thermoplastics | Thermosetting plastics |
| Plastics which get deformed easily on heating and can be bent are known as thermoplastics. Ex: PVC, polythene bags, toys, combs, etc. |
Plastics which moulded once can’t be softened by heating are called thermosetting plastics. Ex : Bakelite and melamine. |
Explanation:
- Thermoplastics have linear arrangement of monomers.
- But thermosetting plastics have cross linked arrangement.
- The difference in the arrangement of monomers bring the difference in their properties.
Question 4.
Do you know how various synthetic fibres are obtained ?
Answer:
Nylon:
Nylon is a polymer made of chemical units called polyamides which contain carbon, oxygen and nitrogen. Polyamides are melted and forced through a heated spinneret which has very, very tiny holes. The size and shape of the holes changes, the characteristics of the resulting fibre. The fibre solidifies as it cool and can be spun or woven.
Rayon:
The cellulose that was collected from wood or bamboo pulp, is treated with several chemicals.
First sodium hydroxide is added and then carbon disulphide to the cellulose.
The cellulose dissolves in chemicals add to it and gives a syrup called viscose. Viscose is forced through a spinneret, into a solution of dilute sulphuric acid. This gives us silk like threads. The threads are cleaned with soap and dried. This new fibre is called rayon.
Acrylic:
It is made from the combination of coal, air, water, oil and limestone. It is spun by either dry spinning or wet spinning.
In dry spinning the dissolved polymers are extruded into warm air. The fibres solidify by evaporation. In wet spinning the polymers are dissolved and extruded into a bath and then dried.
![]()
Question 5.
Can you name the few things made up of i) nylon ii) rayon (iii) acrylic and (iv) polyesters ?
Answer:
The things made from nylon:
Tooth brush bristles, ropes, fishing nets, tents, sarees, stockings and socks, car seat belts, sleeping bags, curtains, etc. are made up of nylon. The things made from rayon: Bed sheets, carpets, home furnishings, sanitary products, diapers and bandages and lints for dressing wounds.
The things made from acrylic: Socks, sportswear and sweaters, craft yarns, upholstery fabrics, carpets, luggage, awnings and vehicle covers.
The things made from Polyester: PET bottles, utensils, films, wires, etc.
Question 6.
Why it is advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working in a laboratory or working with fire in the kitchen ?
Answer:
- The synthetic fibres melt on heating.
- This is actually a disadvantage with synthetic fibres.
- If the cloth catches fire it can be very disastrous.
- The fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it.
- It is therefore advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working in a laboratory or working with fire in the kitchen.
Question 7.
Classify the material as biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
- paper
- wood
- metals
- cotton cloth
- plastic container
- woolen sweater
- peels of vegetable and fruit
Answer:
| Material | Biodegradable/non-biodegradable |
| 1. paper | Biodegradable |
| 2. wood | Biodegradable |
| 3. metals | Non-biodegradable |
| 4. cotton cloth | Biodegradable |
| 5. plastic container | Non-biodegradable |
| 6. woolen sweater | Biodegradable |
| 7. peels of vegetable and fruit | Biodegradable |
![]()
Question 8.
Write short notes on the following.
a) Plastic and health care industry b) Plastic cookware c) Teflon d) Fire proof plastic.
Answer:
a) Plastic and health care industry : Plastics find extensive use in the health care industry. Some examples of their use in health care are the packing of tablets, threads used for stitching wounds, syringes, doctor’s gloves, a number of medical instruments, etc.
b) Plastic cookware: Plastic cookware is used in microwave ovens for cooking food. The heating process is different in microwave ovens. The heat cooks the food but does not affect the plastic vessel.
c) Teflon: Teflon is a non-stick plastic used as non-stick coating in cookwares. It is also used as tape for sealing purpose.
d) Fire proof plastics: Although synthetic fibres catches fire easily, it is interesting to know that the fire proof material is made from synthetic plastics.
8th Class Physical Science 4th Lesson Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
State government decided to avoid Flexi Banners. Predict the effect of Flexi banners
on environment.
Answer:
- PVC flexi banners can take several years to decompose in land fills.
- These flexi banners contain dangerous chemical additives like lead, cadmium which can be toxic to our health as well as animals health.
Question 2.
Write two slogans on solid waste management.
Answer:
- Convert waste to wealth
Don’t convert wealth to waste. - Recycle waste solid today
for a better solid future. - Reuse, Reduce, Recycle
The good, The bettel, the best
Question 3.
Draw and explain the diagram of Universal redyeing symbol.
(OR)
Draw “Universal Recycling Symbol”.
Answer:
When the number is omitted from recycling icon then it is known as Universal recycling symbol.

![]()
Question 4.
Nylon is a synthetic fibre. Write the advantages and disadvantages of it.
Answer:
Advantages of nylon as fibre:
- Nylon fibre is strong, elastic and light weight.
- Cloth made of nylon are lustrous and easy to wash.
- Nylon does not absorb water.
Disadvantages of nylon as fibre:
- Synthetic fibres cannot absorb moisture, thus they cannot be used as dress materials during summer.
- They are dangerous to be worn near fire or heat as they catch fire easily.
- They cannot be easily ironed.
Question 5.
Though there are so many harmful effects of plastic, we still prefer to use it. What could be its major advantages?
Answer:
Plastics are used in milk and oil pouches, containers to store pickles and rice, buckets to store water, chairs, water pipes, electrical, appliances, television, radio and computers and mobile phones.
Bakelite is used for making handles of various utensils due to its poor conductivity of heat and electricity.
Question 6.
Using an experiment explain how synthetic fibres are stronger than cotton fibres.
Answer:
- Take an iron stand with a clamp.
- Take cotton thread and synthetic threads like nylon about 50 cm in length.
- Tie the cotton thread to the stand, so that it hangs freely from it.
- At the free and attach a pan, so that a weight can be placed on it.
- Add weight starting from 10 grams one by one, till the thread breaks down.
- Note the total weight required to break the thread.
- Repeat the same activity with synthetic thread also.
- We can observe that more weights are required to break the synthetic thread than cotton thread.
- Conclusion: Synthetic threads are stronger than cotton threads.
Question 7.
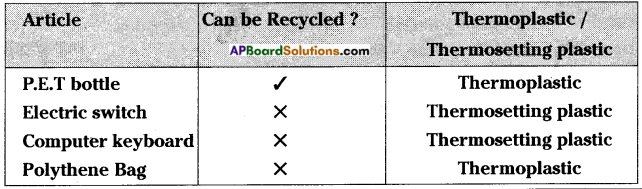
Answer the following questions.
i) Name the recyclabel material / materials.
ii) Name the thermosetting plastic articles.
iii) Which are thermoplastics but not to be recycled?
iv) Which are recycled but not thermosetting plastics?
Answer:
i) P.E.T bottles
ii) Electric switch, computer keyboard
iii) Polythene bag
iv) P.E.T bottle
![]()
Question 8.
Observe the following table.

Answer the following questions.
i. P.E.T is not used in the manufacture of cooker handles. Why?
ii. Which substance is used to manufacture electric switches? Why?
iii. Which is thermo plastic that can not be recycled?
iv. Why we have to ban the polythene covers?
Answer:
i) P.E.T is not used in the manufacture of cooker handles, because it is not a thermosetting plastic.
ii) Bakelite is used to manufacture electric switches, because it is thermosetting plastic.
iii) Polythene and PVC are thermoplastics that cannot be recycled.
iv) Polythene covers cannot be recycled. So, we have to ban the polythene covers.
Question 9.
Based on the smell given in the table identify the fibre and complete the table.
| Smell on burning | Name of the fibre |
| If it smells like burning hair | |
| If it smells like burning paper | |
| If the yarn melts |
Answer:
| Smell on burning | Name of the fibre |
| If it smells like burning hair | Wool (or) Silk |
| If it smells like burning paper | Cotton |
| If the yarn melts | Polyester (or) nylon |
![]()
Question 10.
Explain biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials with examples. Include their impact on environment.
Answer:
- A material which is easily decomposed by natural process is called bio degradable, eg : Peels of fruits, papers, wood, cotton bags, etc.
- A material which is not decomposed by natural process is called non-bio degradable, eg: Plastic
- Impact on environment: Slow decomposition causes environmental pollution. The burning process of synthetic materials is also pollute the environment. This pollution causes health problems to the living things.
