These AP 10th Class Maths Chapter Wise Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Trigonometry will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Maths 12th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Applications of Trigonometry
Question 1.
A boy observed the top of an electric pole at an angle of elevation of 30°, when the observation point is 10 meters away from the foot of the pole. Draw suitable diagram for the above situation.
Solution:
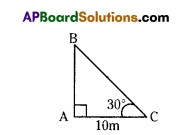
AB = Height of the Electric Pole
AC = Distance between the foot of the pole to the observer = 10 m
Angle of Elevation = 30°
Question 2.
Draw a diagram to find the height of the kite in the situation given below. “A person is flying a kite at an angle of elevation ‘a’ and the length of thread from his hand to kite is ‘l'”.
Solution:
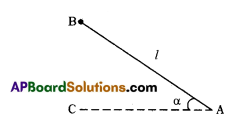
B is position of kite.
AB = Length of thread = ‘l’
Persons hand is at ‘A’.
∠BAC – α – Angle of elevation.
![]()
Question 3.
A flag pole 4 m tall casts a 6 in shadow. At the same time, a nearby building casts a shadow of 24. m. How tall is the building?
Solution:
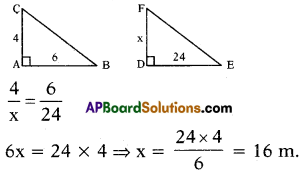
∴ The height of the building = 16 cm.
Question 4.
A tower is 100√3 m high.Find the angle of elevation of its top when observed from a point 100 m away from the foot of the tower.
Solution:
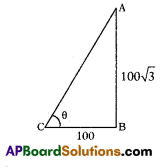
Height of a tower
(AB) = 100√3 m.
Distance between foot of tower and observer point (BC) = 100m
InΔABCTan θ = \(\frac{100 \sqrt{3}}{100}\)= √3 = tan 60°
∴ θ = 60°
Question 5.
Rehman observed the top of a temple at an angle of elevation of 30°, when the observation point is 24 m. away from the foot of the temple. Find the height of the temple.
Solution:
InΔABC,
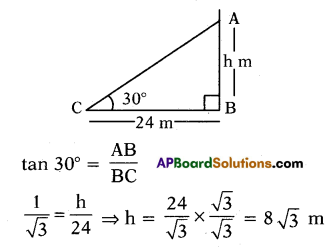
Question 6.
A flag pole 7 m tall, casts a 8 m shadow. At the same time, a nearby building casts a shadow of 32 mts. How tall is the building?
Solution:
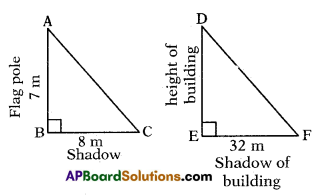
ΔABC ~ ΔDEF;
\(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{EF}}\) ⇒ \(\frac{7}{\mathrm{DE}}=\frac{8}{32}\)
∴ DE = 28 m
Question 7.
An observer of height 1.8 m is 13.2 in away from a palm tree. The angle of elevation of the top of tree from his eyes is 45°. What is the height of the palm tree?
Solution:
Height of observer = 1.8 m = AB
Distance from palm tree = 13.2 m = AE = BD
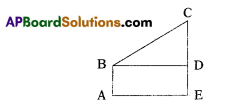
Angle of elevation = ∠CBD = 45°
In Δ BCD = tan 45° = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{BD}}\)
⇒ 1 = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{13.2}\) ⇒ CD = 13.2 m
∴ Height of palm tree = CE
= CD + DE
= 13.2 m + 1.8 = 15 m.
Question 8.
Two poles of heights 6 m. and 11m. stand on a plane ground. If the dis¬tance between the feet of the poles is 12 m. find the distance between their tops.
Solution:
Given,
Height of first pole = AB = 6 m.
Height of second pole = CD = 11 m
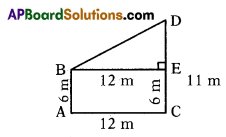
Distance between feet of poles = AC = 12 m
Distance between the tops of the pole,
i.e., BD
So, BE = AC = 12 m ’
Similarly, AB EC 6m.
Now, DE = DC – EC = 11 – 6 – 5 m
BD2 = DE2 + BE2
= 52 + 122 = 25 + 144 – 169
∴ BD = 13 m
![]()
Question 9.
An observer flying in an aeroplane at an altitude of 900 m observes two ships in front of him, which are in the same direction at an angles of depression of 60° and 30° respectively. Find the distance between the two ships.
Solution:
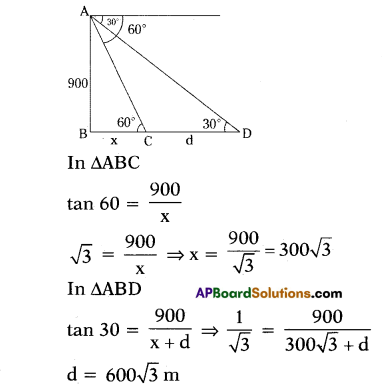
Question 10.
A wire of length 24 m had been tied with electric pole at an angle of elevation 30° with the ground. As it is covering a long distance, it was cut and tied at angle of elevation 60° with the ground. How much length of the wire was cut?
Solution:
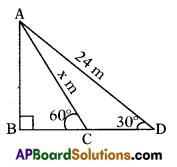
Let AD be length of wire before cut = 24 m
Let AC be length of wire after cut (AC) = x m
Height of the electric pole = AB
Angle of elevation
∠BDA = 30°
∠BCA = 60°
In right Δle ABD
sin 30° = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AD}}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{24}\) ⇒ 2AB = 24 ⇒ AB = 12m
In right Δle ABC
sin 60° = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AC}}\) ⇒ \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\frac{12}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
= √3 AC = 24 ⇒ AC = \(\frac{24}{\sqrt{3}}\)
= 8√3m = 8 × 1.732 = 13.856 m
Length of the wire was cut
= 24 – 13.856 = 10.144 m
Question 11.
A man on the top of vertical tower observes a car moving at a uniform speed coming direcdy towards it. If it takes 12 seconds to change the angle of depression from 30° to 60°, then how long will the car take to reach the tower from that point.
Solution:
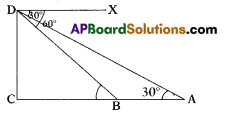
Position of observer = ‘D’
Initial position of car = ‘A’
then angle of depression
= ∠DA = 30°
∴ In ΔACD, ∠C = 30°
⇒ tan 30 = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{AC}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
⇒ CD = \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\sqrt{3}}\) ……………..(1)
and after 12 seconds of time, position of car = ’B’
then angle of depression
= ∠XDB = 60° = ∠DBC
∴ In ΔBCD, ∠B = 60°
⇒ tan 60° = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{BC}}\) = √3
⇒ CD = BC√3 ……………… (2)
∴ (1) = (2)
⇒ CD = \(\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = BC √3 ⇒ AC = 3BC
Now from the figure
AC = AB + BC
⇒ 3BC = AB + BC ( ∵ AC = 3BC)
⇒ AB = 2BC
So the time taken to cover the distance
\(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) or the distance 2\(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\) =12 seconds
∴ Time taken to cover \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\) distance
= 6 sec (∵ \(\frac{12}{2}\))
Then the time taken to approach the tower = time taken to cover the distance
\(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}\) = 3\(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\) = 3(6) = 18 seconds that means it takes 6 more seconds (18 – 12) to reach tower.
Question 12.
Two boys on either side of a temple of 60 m height observe its top at the angles of elevation 60° and 30°. Find the distance between the two boys.
Solution:
Height of the temple BD = 60 metres.
Angle of elevation of one person ∠BAD = 60° .
Angle of elevation of another person ∠BCD = 30°
Let the distance between the first person and the temple, AD = x and distance between the second person and the temple, CD = d
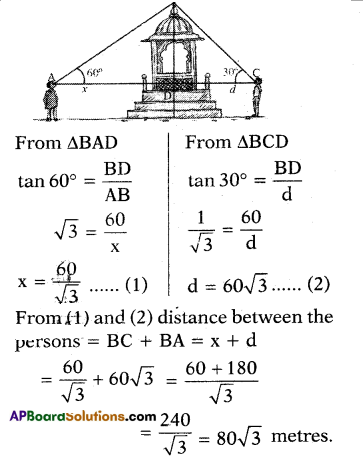
Question 13.
A pole is arranged from a height of 30m from the ground, making 60° angle with earth. Then what is its length?
Solution:
Height from the earth = AB = 30m
Length of pole = BC = ?
∠ACB = 60°
Then in ΔABC AB BC
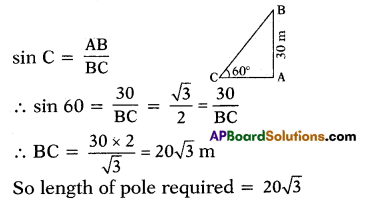
![]()
Question 14.
A long pole is broken in a storm. Top end of the broken pole touched the head of a man at a distance of ‘d\ Then find the angle between the man and the pole that before storm.
Solution:
AB – height of pole
AC – distance = d
CD = man
‘D’ is head of man
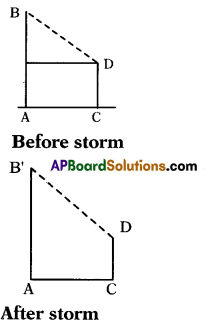
After storm
B’ – broken point
‘D’= ‘B’ (∵ they coincides after storm because D’ i.e., head of man which is touched by end of tree = B’)
∴ AngIe between these two points = zero.
Question 15.
A kite is flown from a building with a height (h) m with a long rope. Now the kite and the person having it are observed with angles of elevation α and β respectively by a boy. The distance between boy and building is ‘x’ m. So draw a diagram for this data.
Solution:
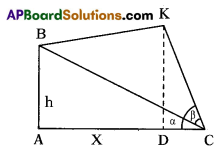
AB is building height = h
K is kites position.
‘C’ is position of boy.
AC = Distance between boy and building AB = X
∠DCK = Elevation angle to kite = ∝
∠BCK Elevation angle to building top = β
Question 16.
A person observes tops of two buildings with an angle of elevations 35° and 46° from the mid point in between them. So which building is higher ? Why?
Solution:
Let ‘E’ is mid point between two buildings AB and CD.
In ΔAEB let ∠E = 35°
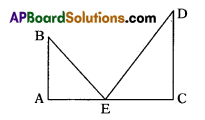
tan 35 = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AE}}\)
∴ Height of building (AB)
= (AE) tan 35° ……………… (1)
In ΔECD let ∠E – 46°
∴ tan 46 = \(\frac{\mathrm{CD}}{\mathrm{EC}}\)
∴ Height of building (CD)
= EC tan 46° ……………. (2)
In (1) and (2) AE = EC
( ∵ E is mid point)
Then value of tan 35 is less than tan 46°. So, height of CD (= EC tan 46) is higher than height of AB (= EC tan 35)
(∵ tan 46 > tan 35)
(∵ values of tan increases from 0 to 90)
Question 17.
A 15m long pole forms 53 m long shadow at 8 AM in the morning. Then find the angle made by sun rays with earth.
Solution:
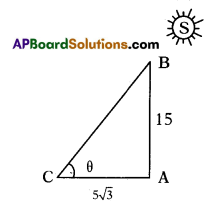
As shown in figure
Height of pole (AB) = 15m
Length of shadow (BC) = 5√3
∠ACB = θ
∴ In ΔABC tan θ = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AC}}=\frac{15}{5 \sqrt{3}}\) = √3
∴ tan θ = √3 ⇒ θ = 60°
∴ The sun rays made 60° angle on the earth at that time.
![]()
Question 18.
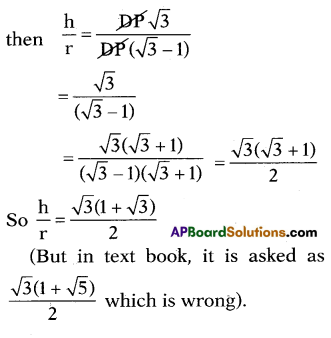
A right circular cylindrical tower, height ‘h’ and radius ‘r’ stands on the ground. Let ‘P’ be a point in the horizontal plane ground and ABC be the semi-circular edge of the top of the tower such that B is the point in it nearest to P. The angles of elevation of the points A and B are 45° and 60°
respectively. Show that \(\frac{\mathbf{h}}{\mathbf{r}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}(1+\sqrt{5})}{2}\)
Solution:
As shown in the figure
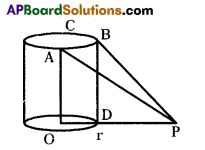
OA = BD = h (height of cylinder)
OD = r (radius of cylinder) .
‘O’ is the centre.
ABC is the edge of semicircle (in the top of cylinder).
B is nearer to the point P. So B should be at the outer edge of diameter. That means just above ‘D’.
∠DPB = 60°, ∠OPA = 45° (given)
In ΔBDP tan P = \(\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{DP}}\) (P = 60°, BD = h)
⇒ √3 = \(\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{DP}}\) ⇒ h = DP√3 …………….(1)
In ΔAB tan P = \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OP}}\)
(here P = 45°, OA = h)
⇒ tan 45° = \(\frac{\mathrm{OA}}{\mathrm{OP}}\) = 1
⇒ OA = OP
So OA = h = OP = OD + DP = r + DP
So h = r + DP …………….. (2)
From the equation (1) & (2)
h = DP√3 , h = r + DP
∴ DP√3 = r + DP
So r = DP√3 – DP
r = DP (√3 – 1) ……………. (3)