Students must practice these AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Important Questions 2nd Lesson Population and Human Resources Development to boost their exam preparation.
AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Important Questions 2nd Lesson Population and Human Resources Development
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the theory of Demographic Transition.
Answer:
It is an important theory that studies the relationship between size of the population, birth rates, death rates and Economic Development. According to this theory in development process, every country passes through 3 stages of population growth. They are:
1st stage: According to the first stage, the country happens to be a underdeveloped and backward country with more importance to the agricultural sector. In this stage, due * to the agrarian nature and general backwardness of the economy birth rates are very high. High birth rates are basically due to traditional social beliefs, high rate of illiteracy, lack of education, ignorance and social beliefs of the ‘society that large number of children in the family mean higher earnings to the family etc. Along with high birth rates, death rates are also very high in this stage due to factors like poor diet malnutrition lack of sanitation, lack of or inadequate health and medical facilities, etc. With high birth rates, more or less equal to high death rates, there will be stable population and no population control problem. Upto 1921, India was in this first stage of Demographic Transition.
2nd Stage: In this stage, the Country/Economy becomes more developed economically. Due to that slight development, there will be sharp decrease in the death rate due to reasons like more availability of food, control of diseases and epidemics, availability of better health and medical services, etc.
However, birth rate continues to be high since there is not much development and the Economy/society still continues to be agrarian in nature. With high birth rate and sharp declining death rate there will be a very rapid increase in the population. In other words, the 2nd stage is the stage of population explosion. At present, India is passing through 2nd stage of population explosion.
3rd Stage: In this stage, the Economy achieves still more Economic Development with such higher level of development, people get better educated and more enlighted. With such better education and enlightenment, people know the importance of small family. Due to the importance given to small families, first in Urban areas and later in the rural areas of the Economy there will be sharp decrease in the birth rates. With decreased birth rate and with the already decreased death rate of 2nd stage, the economy witnesses both low birth rates and low death rates. This again results in population stability. At present all the developed countries are in the 3rd stage of Demographic transition.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the causes of high birth rate and low death rate in India? [Mar ’19 (AP)]
Answer:
As a developing Economy, India, in present 2nd stage of Demographic transition is experiencing high birth rate along low death rate and the problem of population explosion.
Causes of high birth rates:
The causes of high birth rates in India are classified as:
1) Economic factors: They are divided into
a) Predominance of Agriculture: India is predominantly an agrarian Economy. The people living in rural areas feel that children are not a burden on the family. On the other hand they think that more children in family is an asset as the children help in agricultural activities.
b) Slow Urbanisation and Predominance of agriculture: Urbanisation and birth rates are inversely related. In a country where there is a rapid industrialisation and Urbanisation, birth rate decreases rapidly. But in India Urbanisation is very slow and as such birth rate is still high.
c) High Incidence of poverty: An important consequence of poverty is high birth rates. Poor people with low incomes generally think that every child is an earning hand and an asset of generating additional income to the family.
2) Social Factors: They are divided into:
a) Compulsory Marriage: In India, marriage is social and religious obligation and necessity. It is observed that in India only 5 out of 1000 women remain unmarried at the age of 50. Such social obligation of marriage is also responsible for high birth rates in India.
b) Early Marriages: In India, marriage is not only social and religious compulsion but also take place at very early age. With such early marriages at very young age and longer child bearing age of women, birth rate is higher in India.
c) Religious and Social beliefs: Superstitions and religious beliefs among the people, that child is a gift of god which they should not decline is yet another reason for high birth rates in India.
d) Joint family system: The existence of joint family system in some villages, with elders taking care of the infants, is also one factor that is responsible for high birth rates in India.
3) Illiteracy: Illiteracy and low education among women in India by contributing to irrational attitudes and thinking are also responsible for high birth rates in India. Causes of low death rate:
The important causes of low death are:
a) Control of famines: During the British death rate was higher due to frequent and wide spread famines. The control of famines by Indian Government after independence is an important cause of low birth rate in India.
b) Control of Epidemics: The progress achieved in health sector and control of epidemics like Cholera, small pox through powerful vaccinations is another factor that is responsible for low death rates in India.
c) Other factors: The other factors that contributed to low death rates in India are:
- Development of education and spread of literacy among Indians.
- Development of health sector and expansion and availability of better health care % and medical facilities.
- The availability and supply safe and protected drinking water.
- Improvement in Nutritional level and supply of nutritional food to the members of poor families.
- Improvement in sanitation and public health care.
- An increase in the availability of food grains in India at lower prices, due to the agricultural development through HYVP.
Question 3.
What are the measures to control population explosion?
Answer:
India as a developing Economy is facing an important problem in the form of population explosion. The problem of population explosion can be solved/controlled by the following measures.
1) Economic of Measures: The Economic measures that can control population explosion are sub-divided into:
a) Expansion of Industrial Sector: Rapid industrialisation, though difficult, is an effective remedy/solution to the problem of population explosion. In rural areas, low-educated people think that children are a source of income. But, in urban areas with higher literacy, difficult working conditions and high cost of living, the people employed in the industrial sector are compelled to limit the number of children.
b) Creation of more employment opportunities in Urban areas: The creation of more employment opportunities in Urban areas through the development Urban areas and migration of unemployed people to Urban areas can solve the problem of population explosion. Urban-related problems like high cost of living, housing scarcity, difficult living conditions and busy work schedules, etc. prompt them to limit the children.
c) Equitable Distribution of Income and Removal of poverty: As long as poverty persists, high birth rates continue in the Economy. This is because of the feeling of the poor people that they are covered and supported by government welfare programmes. Implementation of various poverty eradication measures and measures that ensure equitable distribution of Income in the society can lead to a reduction in the birth rates.
2) Social Measures: High birth rates and population explosion being an important socio-economic problems can be controlled/reduced with the following social measures.
a) Education: The spread of education development of education facilities and institutions and providing women with education can reduce birth rates education among women results in economic independence, late marriages, lesser child bearing age, better wisdom in women and ultimately to lower birth rates.
b) Improving the status of women: Even though the constitution of India has provided equality of status for men and women, women enjoy a lower status in society. In India, women will not have freedom in deciding the choice relating to the number of children in the family due to their low status. By improving the status women in India through higher education and employment opportunities birth rates can be reduced.
c) Raising the minimum age of marriage: Birth rate generally depends upon the age of the women at the time of the marriage. Fertility rate among women in India can be reduced by strictly forcing the provisions of child marriage restraint act.
3) The family planning programme: The control of population and birth rates is possible through proper implementation of family planning programme. Through the adoption of one child norm, China has achieved a lot of success in bringing down birth rate to 21.6 per thousand in 2012. Family planning programme can be popularised by:
a) Public Information programme, in which wide publicity is given to couples in reproductive age about the importance of family planning.
b) Incentives and Disincentives: Incentives to those who go for sterilisation like cash prizes, special and additional increments to employees can reduce birth rates. Similarly those who do not adopt small family norm and reject family planning are denied certain facilities can also help in the control of birth rates in India.
c) Family Planning Centres: The establishment of family planning centres in large number in rural areas with the required facilities and qualified health and medical personnel to popularise family planning programme can help in reducing birth rates inlndia.
d) Research: It is possible to control birth rates in India if government spends more money towards advance research in the field of demography, reproductive biology, fertility control.
Question 4.
Bring out the main elements of population policy, 2000.
Answer:
The National population policy 2000 was formulated with the important long term objective of stabilising the population of India by 2045. Its important elements are:
- Reducing maternal mortality rate to below 100 per 1 lakh live births..
- Reducing infant mortality rate to below 30 per one thousand live births.
- Achieving immunisation to all children against all vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Achieving 100 per cent deliveries in hospitals and dispensaries.
- Prevention and control of communicable diseases.
- Achieving/providing Universal access to information and counselling and services – relating to fertility regulation and contraception.
- Increasing facilities for safe abortions.
- Promoting and popularising delayed marriages among girls preferably above the age of 20 years.
- Promoting small family norm to achieve replacement level of total fertility rate.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the occupational distribution of the population in India.
Answer:
The term occupational distribution of population refers to the division or distribution of population of the country based on the occupation which they take up to earn their income.
The 3 important occupations in India are:
- Primary occupational
- Secondary occupations
- Tertiary occupations
It is observed that there is a close relationship between development of Economy and percentage of people/population employed in various sectors/occupations.
Prof. Simon Kuznets observes that “when the development of a country takes place the percentage of population engaged in primary sector shifts to industry and service sectors.
Occupational changes in distribution of population in India:
1) The percentage of work force employed in primary sector in India has decreased from 72.1% in 1951 to 48.9% in 2011.
2) Inspite of rapid industrialisation in the country the percentage of work force employed in the secondary/industrial sector has increased from 10.7% in 1951 to 24.3% in 2011.
3) The percentage of labour force/work force employed in service/tertiary sector has increased from 17.2% in 1951 to 26.8% by 2011.
Question 6.
Define Human Resource Development. How do you improve it ?
Answer:
Along with other resources, the Economic Progress and Economic Development of a country depend upon the availability of man power or Human Resources in the country.
The term Human Resource Development refers to the “Process of acquiring and increasing the number of persons who have the skills, education and experience which are critical for the Economic and political development of a country. In other words, Human Resource Development is associated with investment in man and his development as creative and productive resource.
According to Prof. Schultz, Human Resource Development is possible in 5 ways.
a) Enhancing Expenditure towards the improvement of health and medical services in the country which have the effect of increasing life expectancy, strength, stamina, vigor and vitality of the people.
b) Arranging / providing on-the-job training and apprenticeship programmes to employees/ workers to improve their job-related skills/efficiency and productivity.
c) Organising formal education at primary, secondary and higher levels.
d) Conducting and organising Non-formal adult education programmes in rural areas to village farmers through agricultural extension programmes/services.
e) Encouraging rural-urban migration of individuals and families to adjust to changing job opportunities.
In other words, the enhancement of Human Capital like increasing the expenditure on education, health, training and social services contributes to the development of Human Resources.
Question 7.
Explain the role of education in Economic Development.
Answer:
The rate of Economic Growth and pace of Economic Development of any country mainly depends upon the rate of literacy and the level of education in that society.
Profs. Todaro and Smith feel that education contributes to Economic development in the following ways.
1) By enhancing and improving job-related knowledge and skills among workers education enhances the productivity of workers in society.
2) Through the opening of new schools, colleges and higher education institutions, education results in the creation of new employment opportunities to educated youth in the country.
3) It helps in the creation of new educated leaders to fill in and replace the vacancies created by retiring government officials and corporate professionals.
4) Education helps in the provision of basic skills and make people modern and progressive.
5) Education helps in the reduction of income and wealth inequalities in the society.
6) By improving the skills and capabilities of rural people, education contributes to an increase in rural employment, enhancement of rural incomes reducing of rural poverty and integrated rural development.
7) Education by modernising society and thinking of the young generation contributes to small family norm and decrease birth rates and the population of the country.
8) Education contributes to the discovery of new talents and the grooming of potential v talent in the society.
9) Education in a society contributes to and encourages advanced research studies in the area of science and technology.
10) Education in a society makes citizens law-abiding and makes them participate actively and voluntarily in welfare and development programmes.
11) Education, by getting educated and elite electorate, contributes to elite society and political stability in the country.
12) By transforming society into elite and intellectual society, education enhances people’s choice and makes them enjoy more leisure and better quality of life.
Question 8.
Explain the importance of health in Economic Development.
Answer:
The Economic Progress and Economic Development of a country to a large extent depends upon the efficiency and health of workers in the country. It is true that healthy society is also a wealthy society.
Contribution of Health to Economic Development:
a) By reducing absenteeism arising out of ill health, good health contributes to Economic development by reducing production losses.
b) Good health results in or makes possible the optimum utilisation of available natural resources in the economy.
c) Good health in a society contributes to higher enrollment of children in primary and secondary educational institutions and enables them to learn better.
d) In a society with good health, the resources that would have been spent on the treatment of sick people and illness can be freed and used for development programmes in the country.
e) Good health in a society is mainly beneficial to poor and economically and socially handicapped sections in the society. Because they are people that are likely to be more benefitted with the use of under utilised natural resources.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the different indexes to measure Human Development?
Answer:
The term human development refers to the process of acquiring an increase in the number of persons who have the skills, education and experience which are critical for Economic and political development of a country.
To calculate the extent of human development in a society United Nations Development Programme in its report has developed. Human Development Index (HDI) as an alternative to GNP Human Development Index measures the average achievement in three basic dimensions of human development. They are:
- The longevity of life as measured in terms of life expectancy at birth.
- Knowledge as measured in terms of education.
- Standard of living as measured in terms of GDP per capita (PPP US $)
Human Development Index, measures the average achievement in the above three basic dimensions of Human Development. Performance of each of the above three dimensions is expressed as a value between 0 and 1 in the scale.
Basing on the reading in the scale, in 2014.
- Countries with a HDI value of 0.8 and above are grouped as “Very High Development Countries”.
- Countries with a HDI value of ranging 0.7 and 0.8 are grouped as “High Human Development Countries”.
- Countries with HDI value ranging between 0.5 and 0.7 are grouped as “Medium Human Development Countries”.
- Countries with HDI value of less them 0.5 are considered as “Low Human Development Countries” by Human Development Report of 2014.
Question 10.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of population?
Answer:
The Economic Development and Economic progress of a country among other things depend upon the Quantity and Quality of human resources available in that Economy.
Recognising this basic fact, the various countries of the world nowadays, are attaching a lot of importance towards the development of Human resources. Human Resources or the Size of Population of a country is both an asset as well as a liability to Economy. Population, as an important resource, has the following advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Population provides the necessary work force to produce goods and services in the Economy and acts as important contributor to Economic activity.
- In addition to providing the work force for the production of goods and services, the population provides the needed demand and markets for the produced goods.
- Blessed with (wise) brain to think among all living things, the population contributes to the development and promotion innovative ideas in the society.
- Sizable and adequate population of a country makes possible division of labour, specialisation and large scale production in the Economy.
Disadvantages:
- Population of a country if more than optimum puts pressure on the means of subsistence.
- If there is no desired development in the Economy and if the economy could not generate adequate employment/job opportunities population on the negative side leads to unemployment in the economy.
- An Economy, with more than the optimum population, always experiences or faces unduly heavy pressure on social overheads like hospitals, roads, schools, etc.
- An Economy with heavy population or with more than optimum population experiences problems like excessive (Increased) consumption and low rate of savings and capital formation.
- An Economy with heavy population faces the problem of excessive increased dependency on foreign countries.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Trends of world population
Answer:
Due to the high birth rates and rapid growth of the population in developing countries at present world’s population is increasing very rapidly.
After millions of years the population of world reached 100 crores in 1830. In another 100 years, that is by 1930, the population of world has doubled to 200 crores. In a span of 30 years it has further increased to 300 crores in 1960. Due to the impact of population explosion in developing Economies, it has become 400 crores by 1974. In next 13 years, between 1974 and 1987 it has increased from 400 crores to 500 crores. In the next 12 years, by 1999 the population of the world has further increased to 600 crores. It has further increased to 700 crores by 2011 and estimated population of the world in 2015 is 732.50 crores.
With around 98% of world’s population growth taking place in developing economies, by 2050, the population of the world is likely to reach 9.2 billions or 920 crores.
![]()
Question 2.
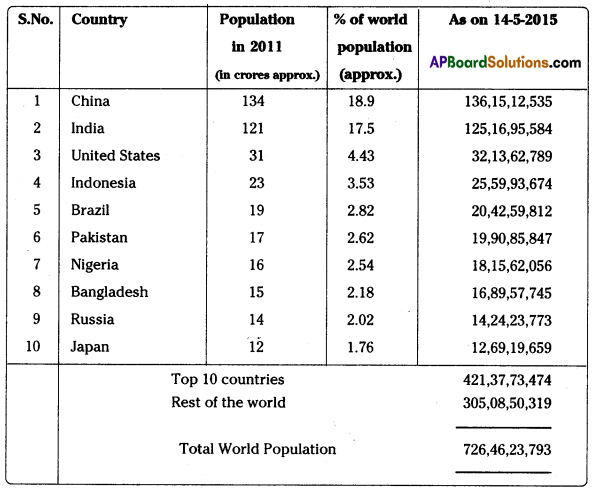
Top 10 populous countries in the world.
Answer:
Due to high birth rates of developing economies of South Asia, the population of the world is increasing rapidly. As per the latest data (as on 14-5-2015) the top 10 populous countries in the world are as below.
Question 3.
Causes of high birth rate in India. [Mar ’19 (AP); May ’18]
Answer:
India, as a developing Economy is facing the problem of heavy population and high birth rates. Even though birth rates have decreased sharply in recent decades birth rates are still high. The various causes of high birth rates in India are:
1) Economic causes/factors, consisting of a) predominance of agriculture b) Slow Urbanisation and predominance of villages c) High incidence of poverty.
2) Social factors/causes, consisting of a) Compulsory marriage b) Early marriages and child marriages in Indian society c) Religious beliefs and superstitions d) Existence of joint family system and e) High rate of illiteracy, etc.
Question 4.
What are the family planning programmes in India? [March 2017]
Answer:
As birth rate in India is still high at 26 per 1000 (in 2012) the Government of India is giving a lot of importance to popularise and implementing family planning programme. Some of the important family planning programmes in India are:
a) Public Information Programmes: In which a wide publicity is given in various media, like cinema, television and other electronic media about the importance of family planning.
b) Incentives and Disincentives: Since family planning is purely voluntary in India incentives like cash prizes and special increments to employees who opt for sterilisation are given. Similarly, disincentives like disqualifying young couples from contesting and holding public positions, denying certain benefits to people who do not adopt family planning and small family norms are followed in India as a part of family planning programme.
c) Family planning Centres: As a part of family planning programme in India family planning centres with health personnel and equipment facilities to conduct sterilisation operations are opened in rural areas in large numbers. In addition to clinical centres, contraceptives are distributed by government agencies in rural areas to young couples in their reproductive age.
d) Research: In recent years, in India the government is an encouraging and promoting advance research studies in demography reproductive biology and fertility control to popularise family planning programme.
Question 5.
Importance of Human Resource Development. [May 2017]
Answer:
Recognising the importance of Human resources, a number of countries of the world are giving importance to the development of Human resources.
Importance of Human resource Development:
The significance and importance of Human Resources development for a country can be stated as below.
1) The development of human resources in a country contributes to the productive utilisation of physical resources in the country.
2) It results in an overall increase in the productive efficiency of the country.
3) Human resource development contributes to a high rate of Economic Growth and rapid Economic Development in the country.
4) It makes possible the implementation of various programmes at National Level to promote social welfare and to increase in national wealth.
5) By promoting the health and literacy level in the society, human resources development contributes to reduction of unemployment, poverty and in equalities in the society.
6) It makes possible the development of scientific abilities and technical capabilities in the economy.
7) Well designed and properly implemented Human resource development programmes enhance the image of a country at international level.
Question 6.
What is the role of education in rural development? [March 2018]
Answer:
Education plays an important role in the development of any society. In all developing economies where agricultural sector and rural areas are important education, through rural development makes an important contribution to the overall progress of such Economies.
Education and Rural Development: Education contributes to rural development in the following ways.
1) It removes the ignorance and superstitions among rural people. By increasing their literacy and by widening their knowledge, it makes rural people more progressive, broad minded and dynamic.
2) It enables the rural people to adopt new new techniques and methods in agriculture.
3) By improving the skills of rural people, education in rural areas enhances/increases the incomes of rural people and results in better health and nutrition. It makes rural people to adopt small family norm and results in better quality of life.
4) It encourages the rural people to start cottage and rural industries and reduces seasoned and disguised Unemployment in rural areas.
5) Education in rural areas results in clean environment and conservation of valuable natural resources.
6) Rural education, by reducing unemployment and poverty in rural areas ultimately results in a higher growth rate in the Economy.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the education system in India.
Answer:
By contributing to the development of human resources in the country, education system is an important system that contributes to rapid economic development. However, in India educational system is not well developed since expenditure on education is not considered as an investment in Human resources. In terms of public expenditure on education, India ranks 86 among 106 countries.
In recent years recognising the importance of education in the 11th Five Year Plan public expenditure on education was increased considerably. In 2011-12, it is 4% of GDP. About 43% of public expenditure on education was incurred on elementary education 25% on secondary education and the balance 32% on higher education.
The ministry of HRD has indicated that in the 12th Five Year Plan, the gross budgetary support for education would be around Rs. 453, 728 crores. To provide universal free elementary education to children between in the age group of 6-14, Sarva Siksha Abhiyan (SSA) was introduced. Similarly to achieve gender equality, National programmes for education of girls at primary level (NPEGEL) was made an important component of SSA. Inspite of some progress achieved through SSA (with Gross Enrollment Ratio increasing from 32.1 in 1950-51 to 115 in 2011) India’s educational system still remains to be backward.
Question 8.
Health programmes in India
Answer:
In order to improve the health standards in India and to provide better and advanced health facilities to the people the Government of India in recent years launched the following health programmes in India.
Health programmes in India:
- National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was started in 2005 to provide affordable, accessible, and quality health services in rural areas.
- In 2013, National Health Mission was started by renaming NRHM and NUHM (National Urban Health Mission, started for providing health services in Urban areas)
- Janani Suraksha Yojana started for bringing down maternal mortality rate.
- Pradhan Mantri Swasthiya Yojana (PMSY) to correct regional imbalances in the availability of reliable health care services.
- Rogi Kalyan Samithis
- Village health and Sanitation committees.
- Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) have been selected and trained in health care for various villages.
- Mobile Medical Units.
- Ayurveda Yunani Siddha Homeo (AYUSH) services.
- Janani Sishu Suraksha Karyakramam to provide child and mother care.
- 12th Five Year Plan aims at providing easy access to Quality health services at affordable prices to all people of India.
Question 9.
Physical Quality of Life Index (PQU). [Mar ’19 (TS)]
Answer:
Physical Quality of Life Index is an attempt to measure the quality of life or well being of the people of a country. It is a new index that measures the quality of life of the people in a country replacing GNP as an indicator of development in a country.
Developed in mid 1970s by Morris David Morris, it is the average of three statistics-
a) the basic literacy rate b) infant mortality rate and c) life expectancy at the age of 1 year – all weighed on a scale between scale ranging between 0 and 100. Even though PQLI is considered to be an improvement over GNP as a measure of well being and quality of life of the people in the society, it suffers with the draw back that there is considerable overlap between infant mortality and life expectancy. Hence, at present the UN Human Development Index is a more widely used means of measuring well being in the world.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Population explosion
Answer:
The term population explosion refers to a steep or uncontrolled rise in the population of a country. It is an important feature of all developing countries. An important cause of population explosion is birth rates being higher than death rates.
Question 2.
Great dividing year of population
Answer:
The year 1921 was considered as Great dividing year of population in India as the population of India started rising very rapidly since 1921.
Question 3.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
Answer:
The term infant mortality rate refers to the ratio of the number of deaths among 1000 born children in a year. It is an important health indicator that focusses on the health care of infants in the society.
![]()
Question 4.
Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR)
Answer:
Maternal Mortality rate is a rate calculated as a ratio of (the rate of) the number of . delivery deaths among 1 lakh women year in a year. It is an important indicator that focusses on the health and medical care of pregnant women during pregnancy and the time of child birth. It indicates the extent of pre-natal and post-natal medical care given to women in the society.
Question 5.
Birth Rate
Answer:
The term birth rate refers to the number of births per 1000 of population in the society. It is an important indicator of health status in the society. It is an determinant of population growth in the society.
Question 6.
Death rate [May 2017]
Answer:
The term death rate refers to the number of deaths per 1000 (thousand) of population in the society. It is an important determinant of population growth rate and health status in the society. A lower death rate and lower birth rate in the society implies rapid development in the society.
Question 7.
Urbanisation [May 2018]
Answer:
The conversion and gradual transformation of rural and semi-urban areas into urban areas and cities is called as urbanisation. It is an important indicator of economic development in the society.
Question 8.
Joint Family System
Answer:
It is a system of family in which the members of a family belonging to successive/ different generations live together. It is still prevalent in some of the Indian villages and one of the causes of high birth rates in India.
Question 9.
Occupational Distribution of Population
Answer:
The term occupational distribution of population refers to the division or distribution of population of the country basing on the occupations which they take up or select to earn their income or livelihood.
Question 10.
Primary Sector
Answer:
The term primary sector refers to that sector of the economy which supplies/provides basic and essential requirement of living like food, clothing and other agricultural products. It includes agriculture and agricultural related activities like dairying, poultry, fishing, forestry, flori culture, horti culture, etc.
Question 11.
Tertiary Sector [May, March 2018]
Answer:
The term tertiary refers to that sector of the Economy that provides the required services and facilities that are necessary for the development of primary sector and secondary sector. It provides services needed for the society like transport communications Banking, Finance, Insurance, trade and commerce, etc.
Question 12.
Human Resource Development
Answer:
The term human resources development refers to process of developing and improving the skills, talents, abilities and capabilities of human beings. It refers to the process of acquiring and increasing the number of persons who have skills, education and experience which are critical for economic and political development of a country.
Question 13.
Literacy Rate
Answer:
The literacy rate (ratio) refers to the percentage of literate people above the age of 7 years, in the total population of the country. It is an important indicator of Economic and Social development in the society.
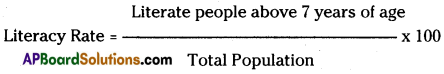
Question 14.
Sarva Siksha Abhiyan [Mar ’19 (AP); Mar ’18, ’17; May ’18]
Answer:
Sarva Siksha Abhiyan was introduced in 2001-02 with the objective of providing Universal elementary education to all children in the age group of 6 -14 years by 2010. It aims to bridge social, regional and gender gaps through the active participation of community in the management of schools.
![]()
Question 15.
Janani Suraksha Yojana [Mar ’19 (AP&TS); May ’17]
Answer:
Janani Suraksha Yojana was started in the year 2005-06 with the objective of providing safety to pregnant women at the time of child birth. It aims at encouraging pregnant women to have child delivery i.e., health institutions (Private or Public) and there by reducing Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) and Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) in the country.
Question 16.
Human Development Index
Answer:
The concept of Human Development was introduced in 1990. It is an important index or indicator that measures the extent of development of Human resources in a country. It is the average of achievement in 3 areas of Human development / Human life namely
- a long and healthy life
- knowledge
- decent standard of living.
Question 17.
Gender-Related Index [March 2017]
Answer:
Gender-Related Index is an important index or indicator that indicates or measures the extent of inequalities between man and woman in the society. It is calculated basing on 3 important components namely:
- Female life expectancy
- Female adult literacy rate and gross enrollment ratio and
- Female per capita Income.
Question 18.
Gender Empowerment Measure.
Answer:
Gender Empowerment Measure was introduced in 1995. It is an important indicator that measures the extent active participation of women in Economic and political life in the society. It is calculated or measured basing on
- Women participation in Economic and political activities.
- Gender Inequality in Economic and political participation.
- Female Empowerment
Question 19.
Human Poverty Index
Answer:
It was introduced in 1997 and is an important indicator or measure of poverty and the extent of deprivation of basic facilities to poor people in the society. It is calculated basing on deprivation in three important essential elements of human life, namely:
- longevity of life
- knowledge and
- a decent standard of living
Question 20.
Total Fertility Rate
Answer:
The term total fertility rate refers to the number of live births which a woman gives during her entire reproductive period or child bearing age. A high total fertility rate is not desirable in the society as it results in a rapid growth of population.
![]()
Question 21.
Secondary Sector
Answer:
Secondary Sector also known as Industrial or manufacturing sector that includes activities like mining, quarrying, manufacturing, construction, large scale and small scale industries, electricity, gas, water supply, etc. It is the important sector which converts raw materials into finished goods, etc.