TS Board Telangana SCERT Class 8 Biology Solutions 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems Textbook Questions and Answers.
TS 8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Questions and Answers Telangana – Different Ecosystems
Question 1.
Define an ecosystem. Explain it with a suitable example.
Answer:
An ecosystem can be defined as a functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment.
Forest Ecosystem: All the habitats can be considered eco system. It is the basic unit of biosphere. It consists of biotic and abiotic components which interact with each other and influence each other.
Mangrove Ecosystem – Coringa : Mangroves are one of the most productive ecosystems on earth deriving from terrestrial fresh water and tidal salt water. Biotic and abiotic components of caring ecosystem.
![]()
Biotic components :
- Producers: Mangrove, spirogyra, euglena, oscillatoria, blue green algae, ulothrix etc.
- Consumers : Shrimp, crab, hydra, protozoans, mussel, snails, turtle, daphnia, brittle worm, tube worm etc.
- Decom posers: Detritus feeding bacteria etc.
- Abiotic coin ponents: Salt and fresh water, air, temperature, soil etc.
Question 2.
Explain how diversity of living organisms helps in enriching any ecosystem.
Answer:
Organisms obtain food from its surroundings. Plants are naturally described as autotrophs. They synthesize their food by photosynthesis. Remaining creatures are determined as heterotrophs. Some of them depend on plants and some depend on other animals. Heterotrophs are divided into herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
Herbivores obtain food from plants. These are primary consumers in an ecosystem. Eg : Cattle, rabbit, deer, zoo planktons in water. The organisms which feed on herbivores are called carnivores. Eg: Wolf, frog, lizard etc. These are secondary consumers.
The organisms which feed on secondary consumers are tertiary consumers.
Eg : Snakes (feeds n frog), frog eating birds. Man is the omnivore. He obtains food both from plants and animals.
Existence of organisms in different ecosystems facilitates survival of all the organisms directly or indirectly. Therefore every ecosystem saves the life on this planet. Ecosystems show bio diversity by utilising biotic and abiotic components. Organisms depend on one another for what each offers such as food, shelter, oxygen and soil enrichment.
Question 3.
What happens when two animals having similar habits share one ecosystem? How could you conserve this type of bio-diversity?
Answer:
Competition takes place between two animals having similar habits sharing one ecosystem. The competition between two animals of the same species for food, shelter and mates in a habitat is known as intra-specific interaction. This interaction results in the selection and survival of stronger and better-equipped members of the species.
The surviving members pass on these characters to their offsprings. Hence the dominated animal survives. On the other hand the other animal may leave or is removed from the habitat. This is called ‘Survival of the fittest’.
Question 4.
What is the difference between habitat and ecosystem?
Answer:
| Habitat | Ecosystem |
| 1. Natural living place of an organism is habitat. | 1. Inter relation between biotic and abiotic factors is called an ecosystem. |
| 2. This is the part of ecosystem. | 2. Ecosystem leads to the existence of different habitats. |
| 3. Only few different species live in the habitat. | 3. Variety of habitats, biotic and abiotic things are seen. |
Question 5.
Who am I?
a. I am the base of food chain ………….
b. I depend on plants for food ………….
c. I break down the remains of dead plants and animals ………….
Answer:
a. producers.
b. primary consumers.
c. decomposers.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following is producer? And why ?
a. fox
b. fungus
c. chicken
d. grass
Answer:
Grass is the producer as they use sunlight to make food of their own.
Question 7.
What do you understand by food web?
Describe your own food web with the help of a diagrammatic representation.
Answer:
A food web is a diagram, of some sort, that links at least two food chains together.
Food webs:
In nature, the food relationships are not so simple and cannot be explained by a single food chain. For example, rats and insects eat seeds and other plant parts as their food. Insects are eaten by frogs and lizards. Rats and frogs are eaten by snakes. Lizards and snakes are eaten by birds. Thus, a single plant or an animal may become food for more than one animal. Similarly, an animal may consume more than one type of food or more than one type of food depending on its taste and availability of a particular type of food in the ecosystem.
Thus, each organism in an ecosystem may be a member of more than one food chain. When we look at these relationships between various organisms for food in the ecosystem, it appears that several food chains are interlinked with one another forming a food web. A food web consists of several interlinked food chains and each organism in a food web will be a member of more than one food chain.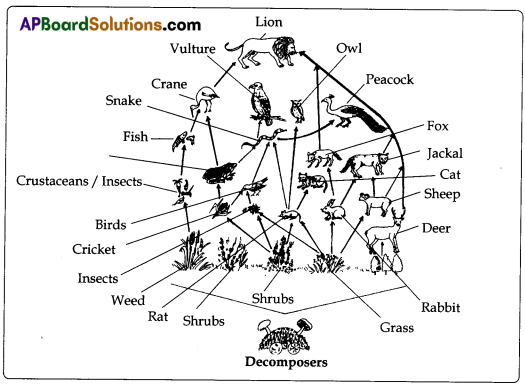
Question 8.
An ecosystem has mice. What happens if more cats are added to it?
Answer:
Soon the population of mice will be disappeared and then cat population will show declining trend due to the nonavailability of food. Very few cats will be left in the eco system. This increases the chances of survival of remaining cats, hence their number gradually increases. Slowly the remaining mice population too increases. In other words, a balance is reached between the size of predator and prey population.
The ecosystem has many cats and few mice. Then the competition for food will be very severe among cats as less amount of food will be available for them. As a result, some of the cats may not get enough food and die due to starvation. This reduces the population of cats and very few cats will be left in the ecosystem. This increases the chances of survival of cats hence their number increases. This increases the availability of food for cats. In other words, a balance is reached between the size of predator and prey population.
![]()
Question 9.
List out Producers (Plants, Bushes, Trees), Consumers (herbivores, carnivores) and Decomposers that you observed in your agriculture field or school garden.
Answer:
Ecosystem : Paddy field
Producers : Paddy, weed plants like Digitaria, Scirpus, Cyperus, Alternanthera, Phyllanthus, Parthemum etc., algae and mosses.
Consumers :
- Herbivores : Rats, insects, spider, wasps, bees, grasshoppers.
- Carnivores : Microcrustaceans, insect larvae, gastropods, carnivorous insects and fishes.
- Decomposers : These include wide variety of microorganisms those feed on dead bodies of flora and fauna including fungi and bacteria.
Question 10.
In grassland ecosystem, rabbit eats only plants. They eat plants faster than the plants can grow back. What must happen to bring the ecosystem into balance?
Answer:
A delicate balance is seen in nature among members of different species. Any disturbance in this balance effects more than one type of organism in the habitat and may even have a catastrophic effect. Rabbit eats only plants. If they eat plants faster than the plants can grow back, there will be a tough competition among rabbits.
As a result, some of the rabbits may not get enough food and die due to food scarcity. This reduces the rabbit population. This increases the chances of growth of grass plants. This increases the availability of grass for rabbits. Very soon a balance will be established among the rabbits and plants.
Question 11.
plant, tiger, rabbit, fox, eagle
Did you find any connection among the above list of things. if we remove Rabbit from the list what will happen?
Answer:
Yes, there exists a feeding relationship between them.
plant, tiger, rabbit, fox, eagle
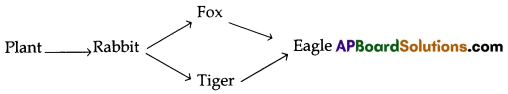
If we remove rabbit, the above food chain will collapse totally.
![]()
Question 12.
What do you understand by inter-dependency of animals and plants? How do you appreciate?
Answer:
The two principal groups of living organisms are plants and animals. From the very early phase of evolution both the communities have lived together side by side in an intimate association to form the biotic environment or biosphere.
In a stable ecosystem the plants and animals form a delicate nutritional interdependence with which minor fluctuations and is rebalanced fairly rapidly. In addition to their nutritional interdependence biotic population of an ecosystem have various other types of interdependence like reproduction, protection etc.
TS 8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems Activities
Structure of the ecosystem :
From the discussion related to Venktesh and Gaythri’s doubt, we can conclude that there are several ecosystems around us. A field, a pond or your school garden all are examples of the same. (Or)
Write the apparatus and procedure of the experiment to study an ecosystem in your school.
Answer:
Aim: To study an Ecosystem at your school/home garden to understand its structure. For this you require the following material.
Material required: Measuring tape string, small sticks, hand lens, hand towel.
Procedure : To know about structure of the ecosystem you have to follow the following procedure.
- Use tape to measure a square area that is one meter long and one meter wide. It can he on grass, bare dirt or side walk.
- Mark the edges of the square with the help of string chalk as shown in figure.
- Observe the study area (that has been marked). Look for plants and animals that live there. Else the hand lens.
- Record all the living organisms you see. You can even dig to go deeper to find out other living organisms that may be present there.
Observations/ Findings: (Note your Observations below)
- Grass, small plants.
- Insects like ants, cricket.
- Lizard, Earthworms, etc are seen.
- Some insect hugs, the larval forms of insects (soft white body animals and many Legged insects are also seen.
Discussion
a. What living things did you find in your study area? Try to count them if possible.
Answer:
Plants and animals like earthworms, lizards, frogs, insects.
b. Which kind of living thing was most common in your study area?
Answer:
Plants.
![]()
c. How was your study area different from those of other student groups?
Answer:
I preferred garden at my home as study area to collect the data. Some of my friends collected data from paddy fields and ponds.
d. Other than the living organisms what other things can you record for your study area?
Answer:
Litter, light, soil, temperature, humidity.
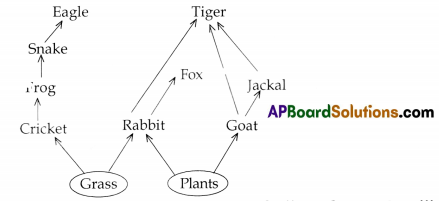
Interdependence hetien the biotic components:
a. What do the arrows in the figure indicate?
Answer:
Feeding relationships
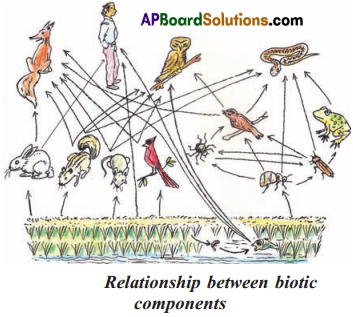
b. Trace the path from grass to tiger. You may trace out other paths as well.
Answer:

c. On how many organisms is rabbit dependent? Write their names.
Answer:
Rabbit is depends on only one organism — Plants.
d. How many organisms depend on rabbit? Write their names.
Answer:
Four organisms are depending on the Rabbit, They are Snake, Owl,Fox, and Tiger.
e. From where does plants get their food from?
Answer:
Plants use light energy from Sun and prepare food of their own through the process called photosynthesis.
![]()
f. What other things do animals need for their survival?
Answer:
Along with food we can see an interdependence between plants and animals for space, reproduction, shelter etc. as well.
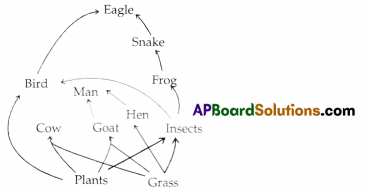
Activity – 2 :
Observe the food web given in figure and answer the following questions.
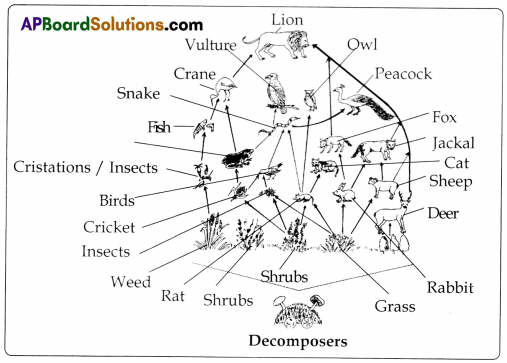
a. Which are the producers in the food web?
Answer: Plants.
b. Which are consumers?
Answer: Animals.
c. Where does the food web start from?
Answer: Producers.
d. Name the organisms where the food web ends.
Answer: Lion.
![]()
e. What happens when plants and animals die in a food web?
Answer: That food web will collapse totally.
Activity – 3 :
Collect the information on forest of Andhra Pradesh and write the flora and fauna and fill the following table.
| Flora | Fauna | ||
| Trees | Herbivores | ||
| Shrubs | Carnivores | ||
| Creepers | Rodents | ||
| Moss and fungi | Birds | ||
| Add other plants | Insects |
Answer:
Name of the forest : Tropical semi-evergreen forests
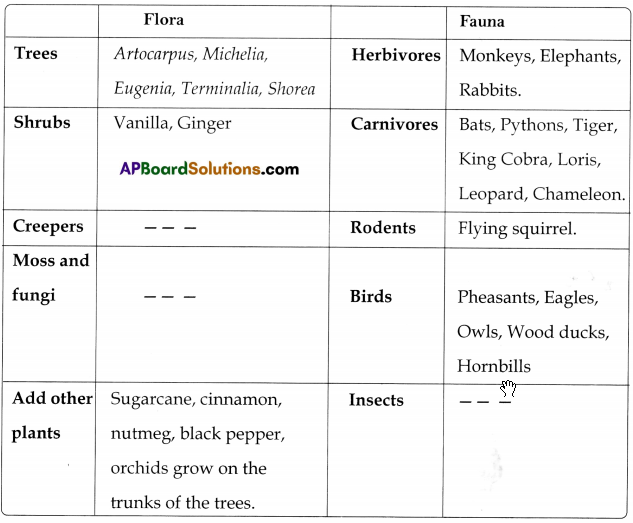
Name of the forest: Tropical moist deciduous forests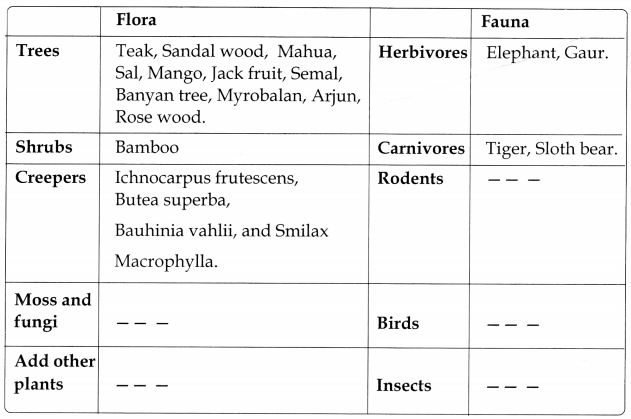
Name of the forest: Tropical dry deciduous forests
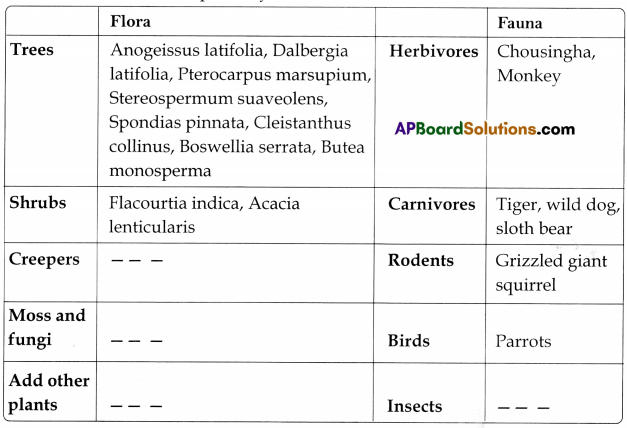
Name of the forest: Mangrove forests
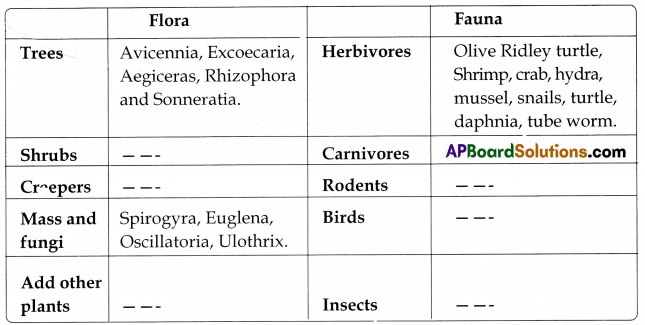
a. Do all the forests have saisie type of vegetation?
Answer: No.
b. Are producers of forest ecosystem greater than its consumers?
Answer: Yes.
![]()
c. Do all the forests have same type of animals?
Answer: No.
TS 8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems Important Questions
Question 1.
Draw a flow chart with grass, plant, cricket, frog, snake, eagle, goat, lion, jackal, rabbit that are interdependence of food?
Answer:
Question 2.
Desert animals their living conditions – Collect from your library and write a note.
(Collect information from your school library and write a note or desert animals their living conditions according to their climate.
Answer:
Adiptations in animals:
Animals living in areas with limited amount of water supply also show suitable adaptations. Usually these animals live in burrows where it is cool and moist. They are generally nocturnal – active during night thereby avoid the day time when it is hot and dry. These animals absorb more water from food materials.
They eat food with high water content or fats. Fats, web oxidised, produce more water than carbohydrates and the animals completely absorb this water. The also absorb water from their urine and excrete urine in a more concentrated form or in the form of a semi solid.
Some of the animals living in extreme conditions of water scarcity, do not excrete any nitrogenous wastes in their life time. Animals living in conditions of seasonal water scarcity burrow into deeper layers of mud during summer months and reduce their metabolic rate. These animals do not come out (even food) till water becomes available.
Question 3.
Make a list of producers and consumers that you have observed in your surroundings. Prepare a food web using them.
Answer:
Producers – Plants, grass etc.
Consumers – goat, man, insects, snake, hen, rat, cow, frog, eagle, bird.
One mark answer questions
Question 1.
What is the functional unit of nature?
Answer:
Ecosystem.
Question 2.
What is meant by the term ‘habitat’?
Answer:
Habitat is the dwelling place for living organisms.
Question 3.
List some abiotic (non-living) components of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Light, temperature, humidity, soil, water.
Question 4.
The ultimate source of energy for all living organisms on the earth is ?
Answer:
Sun.
![]()
Question 5.
Organisms that are able to make their food by using sunlight are called?
Answer:
Producers
Question 6.
‘Coringa’ is an example for which type of ecosystem?
Answer:
Mangrove ecosystem.
Question 7.
List some consumers in the mangrove ecosystem.
Answer:
Shrimp, crab, hydra, protozoa, mussel, snail, turtle, daphnia, brittle worm, tube worm etc.
Question 8.
Decomposers are a few in which ecosystem?
Answer:
Desert ecosystem
Question 9.
A food chain consists of four-steps. What are they?
Answer:
Producers, Primary consumers, Secondary consumers and Tertiary consumers.
Question 10.
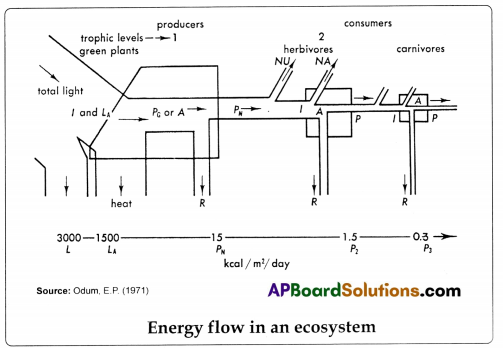
The total energy produced during photosynthesis in an ecosystem is called?
Answer:
Gross Primary Production.
Diagram:
Questions based on DO YOU KNOW?
Question 1.
What do we study in an Ecosystem?
Answer:
- In Ecosystem we study about the changes occurring in the habitat like organisms moving away from the habitat or entering the habitat.
- It is easily understood about food habits, food chains and food web in a specific Ecosystem.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about some amazing facts of oceanic species.
Answer:
- It is said that there are more micro organisms in the sea than there are stars in the universe.
- There are 32 of the 34 known phyla on earth and in ocean between 5,00,000 and 10 million marine species.
- Species diversity is as high as 1000 per square metre in the Indo-Pacific Ocean and new oceanic species are continuously being discovered.
Choose the correct answers :
Conceptual Understanding
Question 1.
The word ‘ecosystem’ was coined by ( )
A) Reiter
B) Tansley
C) Odum
D) None of the above
Answer:
B) Tansley
Question 2.
Which organisms form the base for most of the ecosystems? ( )
A) Producers
B) Consumers
C) Decomposers
D) Any one of the above
Answer:
A) Producers
Question 3.
Rabbit is a ( )
A) Primary consumer
B) Secondary consumer
C) Tertiary consumer
D) Decomposer
Answer:
A) Primary consumer
Question 4.
Which one of the following is the most productive ecosystem? ( )
A) Desert ecosystem
B) Pond ecosystem
C) Mangrove ecosystem
D) All the above are equally productive
Answer:
C) Mangrove ecosystem
![]()
Question 5.
Which one of the following is not a decomposer? ( )
A) Bacteria
B) Fungi
C) Insect larvae
D) None of the above
Answer:
C) Insect larvae
Question 6.
Energy lost after respiration and stored as organic matter in the producers is called ( )
A) Gross Primary Production
B) Net Primary Production
C) Gross Secondary Production
D) Net Secondary Production
Answer:
B) Net Primary Production
Question 7.
Food chain starts with ( )
A) bacteria
B) animals
C) plants
D) microorganisms
Answer:
C) plants
Question 8.
The factor mostly useful for synthesis of food by plants: ( )
A) soil
B) heat
C) light
D) water
Answer:
C) light
Question 9.
Find out the producers ( )
A) Fox
B) Plants
C) Bacteria
D) Fungi
Answer:
B) Plants
Question 10.
The amount of energy that is absorbed into atmosphere: ( )
A) 37%
B) 57%
C) 47%
D) 67%
Answer:
B) 57%
Question 11.
The energy in an ecosystem flows in the form of ( )
A) Solar energy
B) Kinetic energy
C) Mechanical energy
D) Potential energy
Answer:
D) Potential energy
Question 12.
The basic unit of nature is ( )
A) Ecosystem
B) Geosytem
C) Biome
D) Biosphere
Answer:
A) Ecosystem
Question 13.
Food chains have levels ( )
A) 2
B) 4
C) 3
D) 5
Answer:
B) 4
![]()
Question 14.
List-I — List-II
1) Ecosystem — A) Man made
2) Aquarium — B) A.G. Tansley
3) Largest ecosystem — C) Forest
A) 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c
B) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
C) 1 – a, 2 – c, 3 – b
D) 1 – b, 2 – c, 3 – a
Answer:
A) 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c
Question 15.
Mangrove situated in Kakinada bay ( )
A) Kalinga
B) Koringa
C) Polavaram
D) Milavaram
Answer:
B) Koringa
Question 16.
Larger ecosystem is ( )
A) Biome
B) Habitat
C) Food chain
D) Food web
Answer:
A) Biome
Question 17.
The biotic factor of an ecosystem is ( )
A) Microbes
B) Soil
C) Bacteria
D) Plant
Answer:
B) Soil
Question 18.
Habitat is a part of ( )
A) Food chain
B) Food web
C) Niche
D) Biome
Answer:
C) Niche
Question 19.
List-I —- List-Il
1) Goat — A) Producer
2) Tiger — B) Primary Consumer
3) Diatoms — C) Secondary Consumer
A) 1 – b, 2 – c, 3 – a
B) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
C) 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c
D) 1 – a, 2 – c, 3 – b
Answer:
B) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
![]()
Question 20.
Several food chains interlinked themselves to form a … ( )
A) Niche
B) Biome
C) Ecosystem
D) Food Web
Answer:
D) Food Web
II. Information skills and projects
Question 21.
The box ‘3’ denotes ( )
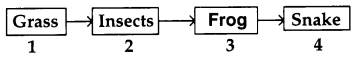
A) Producer
B) Primary consumer
C) Secondary consumer
D) Microbes
Answer:
C) Secondary consumer
Question 22.
Choose the correct matching.
1. Tiger ( ) — A) Snake
2. Peacock ( ) — B) Nectar
3. Butterfly ( ) — C) Goat
A) 1 – a, 2 – c, 3 – b
B) 1 – c, 2 – b, 3 – a
C) 1 – b, 2 – c, 3 – a
D) 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – b
Answer:
D) 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – b
![]()
Question 23.
Which animal is called as desert ship? ( )
A) Elephant
B) Camel
C) Ostrich
D) Zebra
Answer:
B) Camel
Question 24.
1) Grass species is an example for producers
2) Hawk is an example for consumers ( )
A) 1, 2 are wrong
B) 1 is right 2 is wrong
C) 1, 2 are right
D) 1 is wrong 2 is right
Answer:
C) 1, 2 are right