Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 1(a) Digestion and Absorption which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 1(a) Digestion and Absorption
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give the dental formula of adult human beings.
Answer:
- The dental formula of adult human beings is \(\frac{2123}{2123}\)
- This formula denotes the arrangement of teeth in each half of both the jaws.
- They are: Incisors(I) = \(\frac{2}{2}\); Canines (C) = \(\frac{1}{1}\); Premolars (PM) = \(\frac{2}{2}\) ; Molars (M) = \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Question 2.
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. How? [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
- Bile juice does not contain digestive enzymes, but it contains bile salt.
These bile salts emulsify fats into very small micelles (Emulsified fats). - Bile also activates lipase. This lipase converts emulsified fats into fatty acids and glycerols. In this way, bile juice helps in the digestion of fats.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the role of chymotrypsin. Name two other digestive enzymes of the same category and secreted by the same gland.
Answer:
- Chymotrypsin of pancreas plays an important role in the digestion (conversion) of proteins, proteoses, peptones into ‘Tripeptides’ and ‘Dipeptides’.
- The other two enzymes from the same gland pancreas are ‘Trypsinogen’ and ‘Carboxypeptidase’.
Question 4.
What would happen if, HCl were not secreted in the stomach?
Answer:
If HCl were not secreted in the stomach then
- Acidic pH (1.8) could not be maintained –
- Pepsinogen would not be activated.
- Protein digestion and milk digestion does not begin.
- The micro-Organisms that are taken along with the food are not killed.
Question 5.
Explain the terms thecodont and diphyodont dentitions.
Answer:
- Thecodont: The dentition in which the teeth embedded in the sockets of jaw bones is called the thecodont.
Ex: Human beings. - Diphyodont: The formation of two sets of teeth during a life time is called diphyodont. Here, the first set of temporary / milk teeth is replaced by the second set of permanent teeth. Ex: Most of the mammals including human beings.
Question 6.
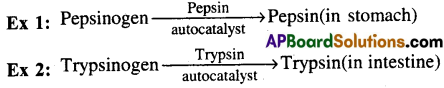
What is auto catalysis? Give two examples.
Answer:
- Auto catalysistThe catalysis reaction in which, catalyst itself is one of the products of the reaction is called autocatalysis, (or)
When the same enzyme is used as catalyst for the activation of its proenzyme, the phenomenon is called autocatalysis. - Ex: Pepsin, Trypsin
Question 7.
What is chyme? [TS MAR-19] [TS MAR, MAY-17] [AP MAR-15,17]
Answer:
- Chyme: It is the acidic semi digested fluid food formed in the stomach.
- It is formed by the churning movements of the stomach muscles.
Question 8.
Name the different types of salivary glands of man and their locations in the human body? [AP MAR-20]
Answer:
There are 3 pairs of salivary glands in man.
- ‘Parotid glands’: These are located below the pinnae (ear lobe)
- ‘Submaxillary’ or ‘submandibular’ glands: These are located in the comer of lower jaw.
- ‘Sub lingual’ glands: These are located below the tongue.
Question 9.
Name different types of papillae present on the tongue of man? [AP MAR-19]
Answer:
There are 3 types of papillae (small projections on the upper surface of the tongue)
- ‘Fungiform’ papillae: These are located at the margin and tip of the tongue.
- ’Filiform’ papillae: These are located on the upper surface of the tongue.
- ‘Circumvallate’ papillae: These are located at the base of the tongue.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the hardest substance in the human body? What is its origin?
Answer:
- The hardest substance in human body is enamel (which forms the crown of the tooth).
- It is secreted by ameloblasts of ectodermal origin.
Question 11.
Name the structure of gut which is vestigial in human beings, but well-developed in the herbivores. And mention the type of tissue with which it is mostly formed.
Answer:
- Vermiform Appendix is the vestigial part in human beings. It is well developed and useful in
the digestion process in the herbivores. - Appendix is mostly formed with lymphoid tissue.
Question 12.
Distinguish between deglutition and mastication.
Answer:
| Deglutition | Mastication |
| 1) Here food bolus is swallowed into Pharynx and Oesophagus with the help of saliva & mucus. | 1) Here food is chewed and crushed by the teeth with the help of tongue & saliva. |
| 2) During this process the food is not mixed with any enzyme. | 2) In Mastication, the food is mixed with salivary enzymes. |
Question 13.
Distinguish between diarrhoea and constipation.
Answer:
| Diarrhoea | Constipation |
| 1) Diarrhoea occurs when the undigested liquid food that enter the large intestine is sent out by abnormal frequency of bowel movement. 2) Loss of water (dehydration) occurs. |
1) Constipation occurs when faeces are retained within the rectum due to the low content of water and irregular movement of bowel. 2) Faeces formed is hard. |
Question 14.
Name two hormones secreted by the duodenal mucosa.
Answer:
The hormones secreted by duodenal mucosa are
- Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
- Secretin
- Cholecysotokinin(CCK)
Question 15.
Distinguish between absorption and assimilation.
Answer:
| Absorption | Assimilation |
| 1) The movement of digested food from the digestive system into blood system is called Absorption. 2) It occurs in small intestine. |
1) After absorption, the uptake of nutrients into cells and tissues is called assimilation. 2) It occurs in every cell of the body. |
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
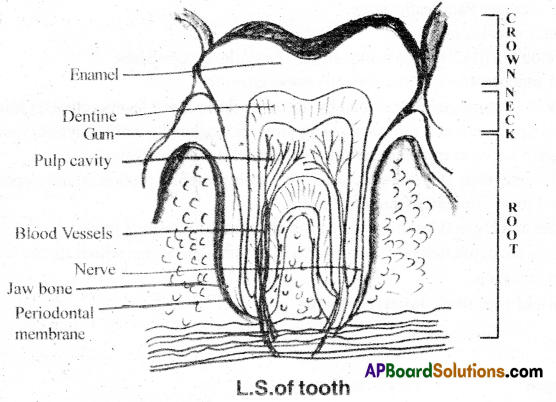
Draw a neat labelled diagram of L.S. of a tooth. [TS MAR, MAY-17] [AP MAR-16,17,19,20]
Answer:
Question 2.
Describe the process of digestion of proteins in the stomach. [TS MAR-19] [ AP MAR-15]
Answer:
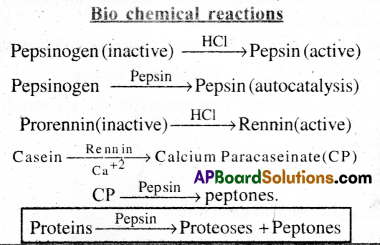
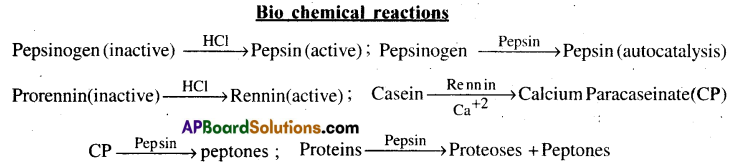
Digestion process of proteins:
- The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach and ends in the small intestine.
- When the food enters into the stomach, a digestive acidic juice called gastric juice is secreted.
- Food mixed with gastric juice forms a semi fluid mass called Chyme.
- This gastric juice contains HCl, pepsinogen, rennin and mucus.
- HCl provides the optimal pH (1.8) for the action of Pepsin.
- Pepsin is a protein digesting enzyme
- HCl converts inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin.
- The activated pepsin converts proteins into proteoses and peptones.
- In infants, HCl activates the inactive prorennin into active enzyme rennin.
- Rertnin acts on casein (milk protein) in the presence of Calcium ions and converts it into Calcium Paracaseionate (CP).
- Then pepsin acts on CP and converts it into peptones.
- The entire process takes about 4 to 5 hours in the stomach.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the role of pancreatic Juice in the digestion of proteins.
Answer:
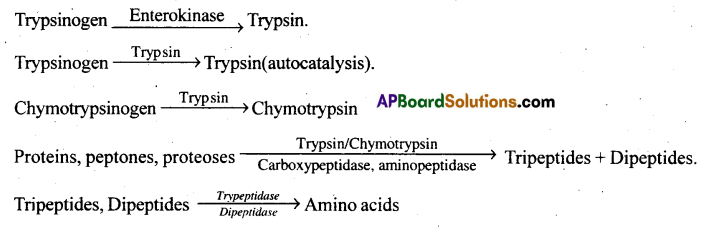
Pancreatic Juice and protein digestion:
- Pancreas secretes Pancreatic juice.
- It contains 3 inactive enzymes:
(i) Trypsinogen (ii) Chymotrypsinogen (iii) Procarboxypeptidases. - Intestinal mucosa secretes the enterokinase enzyme.
- The inactive trypsinogen is activated by this enterokinase and forms active trypsin.
- This trypsin now activates the inactive Chymotrypsinogen into active chymotrypsin.
- Also, trypsin activates trypsinogen into trypsin itself (Autocatalysis).
- Proteolytic enzymes of pancreatic juice act upon proteins, proteoses and peptones in the chyme and form Tripeptides and Dipeptides.
- Tripeptides and Dipeptides are acted by the enzymes of intestinal juice.
- Finally they are converted into amino acids in the small intestine, which are the end products of protein digestion.
Question 4.
How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested?
Answer:
Digestion of Polysaccharides and disaccharides (carbohydrates) takes place in mouth and small intestine. But Carbohydrate digestion does not take place in stomach because of HCl.
(a) Digestion in mouth:
- The saliva released in the mouth contains carbohydrates splitting enzyme called salivary amylase.
- This enzyme hydrolyses a part of carbohydrate (30% of starch) into maltose (disaccharides)
(b) Digestion in small intestine:
- Further digestion of carbohydrates takes place in the small intestine by the amylase of pancreatic juice and disaCcharidases of intestinal juice.
- Here, Carbohydrates are converted to maltose, sucrose and lactose by amylase.
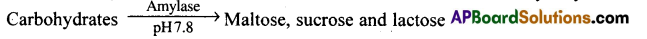
- These disaccharides are converted to monosaccharides (Glucose) by disaccharidases

Question 5.
If, you take butter in your food, how does it get digested and absorbed in the body? Explain. [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
Digestion of Butter (Fat):
- Butter is a fat (lipid)
- It is digested only in the small intestine.
- Bile juice contains Bile salts. They emulsify fats into very small micelles.
- Bile also activates lipase. This lipase converts emulsified fats into fatty acids and glycerols.
Absorption of butter:
- ‘Fatty acids and glycerol’, being insoluble in water cannot be absorbed into the blood directly.
- They are first modified into small micelles, which move into intestinal mucosal cells.
- They are reformed into very small protein coated fat globules called chylomicrons.
- Chylomicrons are transported into the lymph capillaries.
- The lymph vessels ultimately release the absorbed substances into the blood stream.
- The chylomicrons(triglycerides) are broken down to fatty acids and glycerol by the action of the enzyme ‘lipoprotein lipase’.
- They diffuse into the adipocytes of the adipose tissue and liver for storage.
Question 6.
What are the functions of liver? [TS MAR-15]
Answer:
Functions of liver :
- Liver is the largest gland of the body weighing about 1.2 kg to 1.5 kg in an adult human.
- Liver perfQrms many functions such as synthesis, storage and secretions.
- Liver secretes bile juice. Bile juice helps in the emulsification and digestion of fats.
- Liver is the chief organ of detoxification. It removes toxic substances that enter the gut along with food.
- Liver acts as a thermo regulatory organ.
- Liver plays the’key role in carbohydrate metabolism.
- Liver also plays a role in lipid metabolism (synthesis of cholesterol and triglycerides).
- Deamination and formation of urea via ornithine cycle is done in liver.
- Liver is a haemopoietic organ in foetus and erythroclastic organ in adult (destruction of aged RBC)
- Liver synthesizes plasma proteins like albumin and globulin, blood clottjng factors like fibrinogen, prothrombin and anticoagulant heparin.
- Kupffercells present in sinusoids of liver remove unwanted substances and microbes.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe the physiology of digestion of various types of food in the human digestive system.
Answer:
Digestion in human beings: Digestion is the process of conversion of complex and non diffusible food substances into simple diffusible compounds.
- Digestion involves mechanical and chemical processes.
The physiology of digestion is described under the following headings.
A. Digestion at various parts
B. Digestion of various types of food
![]()
A) Digestion at various parts:
1) Digestion in the Buqcal Cavity: Buccal cavity performs Mastication and deglutition.
- Teeth are used to masticate (Chew) the food.
- Tongue helps in the movement of the food.
- The food is mixed with saliva and made into a bolus.
- The bolus is swallowed with the help of mucus in saliva.
- About 30 percent of starch is hydrolyzed here into a disaccharide called maltose by the enzyme ptyalin.
- Lysozyme present in the saliva acts as an antibacterial agent that prevents infections.
2) Digestion in the Stomach:
- When the food enters into the stomach, a digestive acidic juice called gastric juice is secreted.
- Food mixed with gastric juice forms a semi fluid mass called Chyme.
- This gastric juice contains HCl, pepsinogen, rennin and mucus.
- HCl provides the optimal pH (1.8) for the action of Pepsin.
- Pepsin is a protein digesting enzyme.
- HCl converts inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin.
- The activated pepsin converts proteins into proteoses and peptones.
- The entire process takes about 4 to 5 hours in the stomach.
3) Digestion in small intestine:Various types of movements are generated by the muscularis
externa layer of the smallintestine.
- These movements help in thorough mixing up of the food with bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice in the intestine and thereby facilitate digestion.
- The mucus along with the bicarbonates from pancreas protects the intestinal mucosa from the acidic medium and provides an alkaline medium (pH 7.8) for enzymatic activities.
- All the enzymes of the pancreatic juice and succus entericus act only in alkaline medium.
B) Digestion of various components of food;
1) Digestion of Proteins:
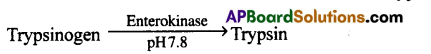
- Pancreatic juice contains proenzymes trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and procarboxypeptidase.
- Enterokinase from the intestinal mucosa converts trypsinogen to trypsin.
- Trypsin acts as an autocatalyst and converts more trypsinogen to trypsin.
- Chymotrypsinogen is converted to chymotrypsin by trypsin.
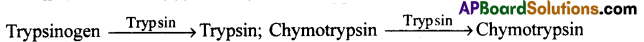
- There are proteins, proteoses and peptones in chyme. They are converted to tripeptides and dipeptides.

- Enzymes from intestinal juice tripeptidase and dipeptidase convert the tripeptides and dipeptides into amino acids.

- Amino acids are the end products of protein digestion. They are absorbed into blood.
2) Digestion of Fats: Bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice are the chief digesting juices.
- Bile does not contain enzyme. The bile salts emulsify the fats.
- Pancreatic lipase and intestinal lipase act on emulsified fats to produce glycerol and fatty acids.
- The glycerol and fatty acids are absorbed into lacteals.

- Diglycerides and monoglycerides are intermediate steps in fat digestion.
3) Digestion of Carbohydrates :
- Pancreatic amylase converts carbohydrates, into maltose, sucrose and lactose.
- Intestinal disaccharidase convert these disaccharides into glucose, fructose and galactose.

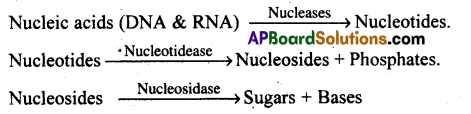
4) Digestion of Nucleic acids:
- Nucleases of pancreatic juice act on nucleic acids to convert them to nucleotides and nucleosides.
- Nucleotidases convert the nucleotides to nucleosides and phosphates.
- The nucleosidases convert the nucleosides into sugars and bases.
Question 2.
Explain the digestive system of man with neat labelled diagrams.
Answer:
![]()
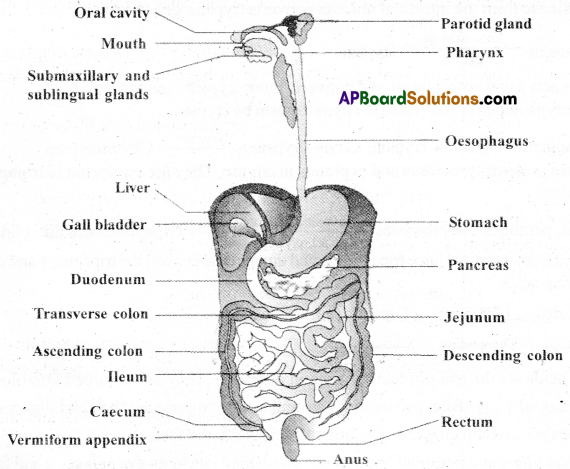
The digestive system consists of A) Alimentary canal, and B) the Associated glands.
A) Alimentary canal (gut): It is a coiled tube with mouth at the anterior end and anus at the posterior. The parts of alimentary canal are
- Buccal cavity
- Pharynx
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
1) Buccal cavity (oral cavity):
- Mouth is bordered by upper and lower lips. It leads into buccal cavity.
- A palate divides the cavity into upper respiratory passage and lower food passage.
- The palate has anterior hard palate with transverse rugae (ridges).
- Posterior soft palate ends in hanging uvula.
(a) Teeth: The dentition is thecodont, heterodont and diphyodont.
- The four types of teeth are incisors, canines, premolars and molars, hence heterodont.
- The teeth are fixed in sockets of jawbones, hence thecodont .
- There are two sets of teeth in life time, the milk teeth and adult teeth, hence diphyodont.
- Dental formula of adult is

(b) Tongue: It is freely, movable, muscular, sense organ of taste, helps in mastication and bolus formation deglutition and speech. It is attached to the floor of buccal cavity by frenulum.
- The upper surface of the tongue has small projections called papillae namely fungi form, filiform and circumvallate papillae.
- The tongue acts as ‘universal tooth brush’.
2) Pharynx: It is a common passage for food and air. It is divided into nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. Eustachian tubes from middle ear open into nasopharynx.
- At the base of laryngopharynx epiglottis is present.
- There are a pair adenoids (pharyngeal tonsils) a pair palatine tonsils and a pair of lingual tonsils which are lymphoid tissues.
3) Oesophagus: It is a narrow tube which passes through thoracic box and diaphragm to open into stomach.
- There is an oesophageal sphincter at the beginning of oesophagus and a cardiac sphincter at its opening into stomach.
4) Stomach: It is a wide distensible muscular sac present on left side of abdomen below the diaphragm. It has cardiac, fundic and pyloric parts.
- There is a pyloric sphincter at the junction of stomach and duodenum.
5) Small Intestine: The small intestine’ is the longest part of alimentary canal.
It consists of three regions i) duodenum ii) jejunum and iii) ileum.
- Hepato pancreatic duct opens into duodenum.
- There is ilio-caecal valve at the junction of ileum and colon.
6) Large intestine: It consists of caecum, colon and rectum.
- Caecum is a small blind sac containing Symbiotic organisms.
- A narrow finger-like tubular projection called vermiform apendix arises from the caecum.
- Colon has ascending, transverse and descending parts? It is produced into pouches called haustra
- Taenia coli are three longitudinal muscle folds inside colon.
- Rectum is a small dilated sac open to outside through small anal canal and anus.
![]()
B) Digestive glands: There are five types of digestive glands.
They are salivary glands, gastric glands intestinal glands, liver and pancreas.
1) Salivary glands: There are 3 pairs of salivary glands opening into buccal cavity.
- A pair of parotid glands are located below pinnae.
- A pair of sub maxillary glands at the angles of lower jaws.
- A pair of sublingual glands below the tongue.
- Serous cells secrete ptyalin and mucus cells secrete mucus.
2) Gastric glands: These are located in the wall of the stomach beneath the surface epithelium. Gastric glands are of three types.
- Cardiac glands (secrete mucus for protection)
- Pyloric glands (secrete mucus and gastrin),
- Fundic or cystic glands. It contains three types of cells.
a) Mucus secreting neck cells
b) Peptic or chief cells secreting proenzymes pepsinogen, prorennin and gastric lipase.
c) Oxyntic or parietal cells secreting HCl and castle’s intrinsic factor.
- pH of gastric juice: 0.9 to 1.8.
3. Intestinal glands: They are present in mucosa.
They are of two types i) Brunner’s glands ii) Crypts of Lieberkuhn
4. Liver: It is the largest gland in human beings. Liver secretes bile juice which contains bile salts. These bile salts play an important role in lipid digestion. A gall bladder is present between the two lobes. It stores bile secreted by hepatic cells.
5. Pancreas: It is the second largest gland. It is a mixed gland and a diffused gland.
- It is present in between two limbs of duodenum.
- The exocrine part has acini which secrete alkaline pancreatic juice(pH 8.4)
- There are groups of cells called islets of Langerhans (is the endocrine part) which secrete insulin and glucagon.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
human teeth are
1. Endo-mesodermal
2. Ectodermal only
3. Eeto-mesodermal
4. Endodermal only
Answer:
3. Eeto-mesodermal
Question 2.
Enamel of the teeth is secreted by
1. Odontoblasts
2. Amelob lasts
3. Parotid glands
4. Lingual glands
Answer:
2. Amelob lasts
Question 3.
Dentition of the human is described as
1. Diphyodont, lieterodont, Thecodont
2. 1-lomodont, Acrodont, Thecodont
3. Heterodont. Thecodont, Pleurodont
4. Acrodont, Diphydont, Heterodont
Answer:
1. Diphyodont, lieterodont, Thecodont
Question 4.
Total number of canines in permanent dental set of humans Is
1.6
2. 4
3. 8
4. 12
Answer:
2. 4
Question 5.
The dental formula of a human baby is
1. \(\frac{2112}{2112}\)
2. \(\frac{2122}{2122}\)
3. \(\frac{2102}{2102}\)
4. \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
3. \(\frac{2102}{2102}\)
Question 6.
Liver is able to produce vitamin
1. A
2. B
3. K
4. D
Answer:
1. A
![]()
Question 7.
Tonsils present in the pharynx are formed of
1. Pharyngeal tissue
2. Lymphoid tissue
3. Cuboidal tissue
4. Palatine tissue
Answer:
2. Lymphoid tissue
Question 8.
Glottis is the passage which opens trachea into
1. Oropharynx
2. Nasopharynx
3. Epiglottis
4. Laryngopharynx
Answer:
4. Laryngopharynx
Question 9.
The lengthy region of alimentary canal in man is
1. Large Intestine
2. Jejunum
3. Ileum
4. Oesophagus
Answer:
3. Ileum
Question 10.
The common duct of liver and pancreas of a human being opens into the lumen of
1. Stomach
2. Jejunum
3. Ileum
4. Duodenum
Answer:
4. Duodenum
Question 11.
In man, the large intestine secretes
1. Water
2. Mucus
3. Cellulase
4. Undigested food
Answer:
2. Mucus
Question 12.
The ‘J’ shaped muscular bag of the human alimentary canal is
1. Duddenum
2. Large intestine
3. Rectum
4. Stomach
Answer:
4. Stomach
Question 13.
Which one of the salivary content kills bacteria?
1. Ptyalin
2. Mucin
3. Lysozyme
4. Salivary amylase
Answer:
3. Lysozyme
Question 14.
The hormone ‘gastrin’ secrets by
1. Parotid glands
2. Pyloric glands
3. Cardiac glands
4. Oxyntic glands
Answer:
2. Pyloric glands
Question 15.
Pepsinogen and prorennin are secreted by
1. Oxyntic cells
2. Neck cells
3. Peptic cells
4. Serous cells
Answer:
3. Peptic cells
Question 16.
The largest gland of human body is
1. Pituitary gland
2. Thyroid gland
3. Liver
4. Pancreas
Answer:
3. Liver
![]()
Question 17.
The second largest gland in human body is
1. Liver
2. Pancreas
3. Spleen
4. Thyroid
Answer:
2. Pancreas
Question 18.
The weight of an adult human liver ranges from
1.0.9 to 1.8 Kg
2. 1.5 to 1.8 Kg
3. 1.2 to 2.5 Kg
4. 1.2 to 1.5 Kg
Answer:
4. 1.2 to 1.5 Kg
Question 19.
The structural and functional units of liver are
1. Hepatic lobules
2. Hepatic cords
3. Kupffer’s cells
4. Bilepigments
Answer:
1. Hepatic lobules
Question 20.
The HCl is secreted by the gastric cells called
1. Parietal cells
2. Peptic cells
3. Neck cells
4. Goblet ceils
Answer:
1. Parietal cells
Question 21.
Glycogenesis and gluconeogenesis are the metabolic processes of
1. Fats
2. Proteins
3. Carbohydrates
4. Minerals
Answer:
3. Carbohydrates
Question 22.
The liver plays a key role in
1. Detoxification of minerals
2. Detoxification of drugs
3. Detoxification of vitamins
4. Elimination of urea
Answer:
2. Detoxification of drugs
Question 23.
Urea is synthesized in
1. Cori cycle
2. Krebs cycle
3. Kelvin cycle
4. Ornithine cycle
Answer:
4. Ornithine cycle
Question 24.
The haemopoietic organ in the foetus is
1. Pancreas
2. Muscle
3. Yellow bone marrow
4. Liver
Answer:
4. Liver
Question 25.
Gastric juice has a pH of about
1. 1
2. 1.8
3. 5
4. 6
Answer:
2. 1.8
Question 26.
The pH level of pancreatic juice is –
1. 7.8
2. 2.5.
3. 8.4
4. 10.0
Answer:
3. 8.4
![]()
Question 27.
After mixing with acidic gastric juice, the food turns into
1. Chyme
2. Bolus
3. Liquid gelatinous form
4. Maltose
Answer:
1. Chyme
Question 28.
In the presence of calcium ions, casein is converted to
1. Peptones
2. Calcium paracaseinate
3. Paracasein
4. Amino acids
Answer:
2. Calcium paracaseinate
Question 29.
In the duodenum, the acidic food is neutralized by
1. Mucus
2. Bicarbonates
3. Trypsin
4. Pepsin
Answer:
2. Bicarbonates
Question 30.
The acidic chyme is neutralized in
1. Liver
2. Pancreas
3. Duodenum
4. Stomach
Answer:
3. Duodenum
Question 31.
The end products of protein digestion are
1. Amino acids
2. Fatty acids
3. Dipeptides
4. Glucose
Answer:
1. Amino acids
Question 32.
The emulsification of fats is facilitated by
1. Lipases
2. Bile pigments
3. Bile salts
4. Water
Answer:
3. Bile salts
Question 33.
The milk protein ‘Casein’ is converted to Calcium paracaseinate by
1. Pepsin
2. Prorennin
3. Try sin
4. Rennin
Answer:
4. Rennin
![]()
Question 34.
Amino acids are absorbed in
1. Blood capillaries of villi
2. Wall of rectum
3. Lacteals and blood capillaries of villi
4. Lacteals of villi
Answer:
1. Blood capillaries of villi
Question 35.
Bile is secreted by
1. liver
2. gall bladder
3. pancreas
4. duodenal wall
Answer:
1. liver
Question 36.
Chisel shaped teeth are
1. premolars
2. molars
3. canines
4. incisors
Answer:
4. incisors
Question 37.
Distal part of the stomach that opens into duodenum is called
1. fundus
2. pylorus
3. eardiac
4. jejunum
Answer:
2. pylorus
Question 38.
Enzyme showing greatest substrate specificity is .
1. Nuclease
2. Trypsin
3. Sucrase
4. Pepsin
Answer:
3. Sucrase
Question 39.
Food bolus after passing through alkaline medium is
1. chyle
2. chyme
3. chylomicron
4. fat body
Answer:
1. chyle
Question 40.
Glisson’s capsules are present in
1. Liver
2. Lung
3. Kidney
4. Stomach
Answer:
1. Liver
Question 41.
Herbivorous animals can digest cellulose because .
1. their molar and premolar teeth can crunch and grind the food
2. Bacteria present in their caecum help in digestion of cellulose
3. Gastric Juice has digestive enzyme for cellulose digestion
4. Alimentary Canal is very long
Answer:
2. Bacteria present in their caecum help in digestion of cellulose
Question 42.
Alimentary canal of herbivorous differ4rom carnivorous in having
1. short alimentary canal
2. long alimentary canal
3. wide alimentary canal
4. thin alimentary canal
Answer:
2. long alimentary canal
![]()
Question 43.
Villi present in intenstine helps in
1. secreting enzymes
2. increasing surface area for absorption
3. protection
4. None
Answer:
2. increasing surface area for absorption
Question 44.
Brunner’s glands arc found in
1. liver
2. oesophageal wall
3. surface epithelium of stomach
4. surface epithelium of intenstine
Answer:
4. surface epithelium of intenstine
Question 45.
In vertebrates, lacteals are found in
1. oesophagus
2. ear
3. ileum
4. ischium
Answer:
3. ileum
Question 46.
Oxyntic cells secrete
1. HCl
2. NaOH
3. pepsin
4. trypsin
Answer:
1. HCl
Question 47.
Ptyalin cannot work in stomach, because it becomes
1. Inactive due to HCl
2. Active due to Renin
3. Inactive due to Pepsin
4. Active due to Pepsin
Answer:
1. Inactive due to HCl
Question 48.
Vitamin B12 is actively reabsorbed by
1. Chymotrypsin
2. trypsin
3. pepsinogen
4. Castle’s Intrinsic factor
Answer:
4. Castle’s Intrinsic factor
Question 49.
The common passage for bile and pancreatic duct is
1. ductus choledochus
2. ampulla of vater
3. duct of Wirsung
4. duct of Santorini
Answer:
2. ampulla of vater
Question 50.
Succus entericus is secreted by
1. Auerbach’s plexus
2. Brunner’s gland
3. Peyers patches
4. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
Answer:
4. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
![]()
Question 51.
The wall of the stomach is protected against the action of HCl by
1. epidermal layer
2. mesodermal layer
3. mucous layer
4. muscular layers
Answer:
3. mucous layer
Question 52.
The sphincter of Oddi found in man, guards the
1. Pancreatic duct
2. hepatopancreatic duct
3. bile duct
4. cystic duct
Answer:
2. hepatopancreatic duct
Question 53.
Pepsinogen is activated by
1. trypsin
2. chymotrypsin
3. hydrochloric acid
4. Rennin
Answer:
3. hydrochloric acid
Question 54.
Identify the correct set which shows the name of the enzymes from where it is secreted and substrate upon which is acts
1. Pepsin – Stomach wall – protein
2. Ptyalin – Intestine – Maltose
3. Chymotrypsin – Salivary gland – Lactose
4. Ptyalin – Pancreas – Lipid
Answer:
1. Pepsin – Stomach wall – protein
Question 55.
Secretin hormone is produced in
1. Stomach and stimulates gastric glands
2. Intestine and stimulates Pancreatic glands
3. Liver and stimulates gall bladder
4. Intestine and stimulates crypts of lieberkuhn
Answer:
2. Intestine and stimulates Pancreatic glands
Question 56.
The three secretions meeting the food in small intestine are
1. Bile juice, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice
2. Pancreatic, intestinal and gastric juice
3. Bile, Pancreatic and gastric juice
4. Bile, gastric juice and Saliva
Answer:
1. Bile juice, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice
Question 57.
Bow-Shaped legs in children are due to deficiency of Vitamin
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Answer:
4. D
Question 58.
The Hormone which causes the contraction of the gall bladder is
1. Secretion
2. Gastrin
3. Villikinin
4. Gholecysotkinin
Answer:
4. Gholecysotkinin
![]()
Question 59.
The end products of fat digestion are
1. Amino acids
2. Fatty acids and glycerol
3. Diglycerides
4. Monosaccharides
Answer:
2. Fatty acids and glycerol
Question 60.
carbohydrate digestion does not take place in
1. Stomach
2. Duodenum
3. Buccal cavity
4. Both (2) and (3)
Answer:
1. Stomach